Image false matching detection method based on augmented homogeneous coordinate matrix
A homogeneous coordinate and wrong matching technology, applied in image analysis, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of sensitivity to matching number and noise interference, algorithm performance degradation, poor detection effect, etc. Fast, adaptable effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
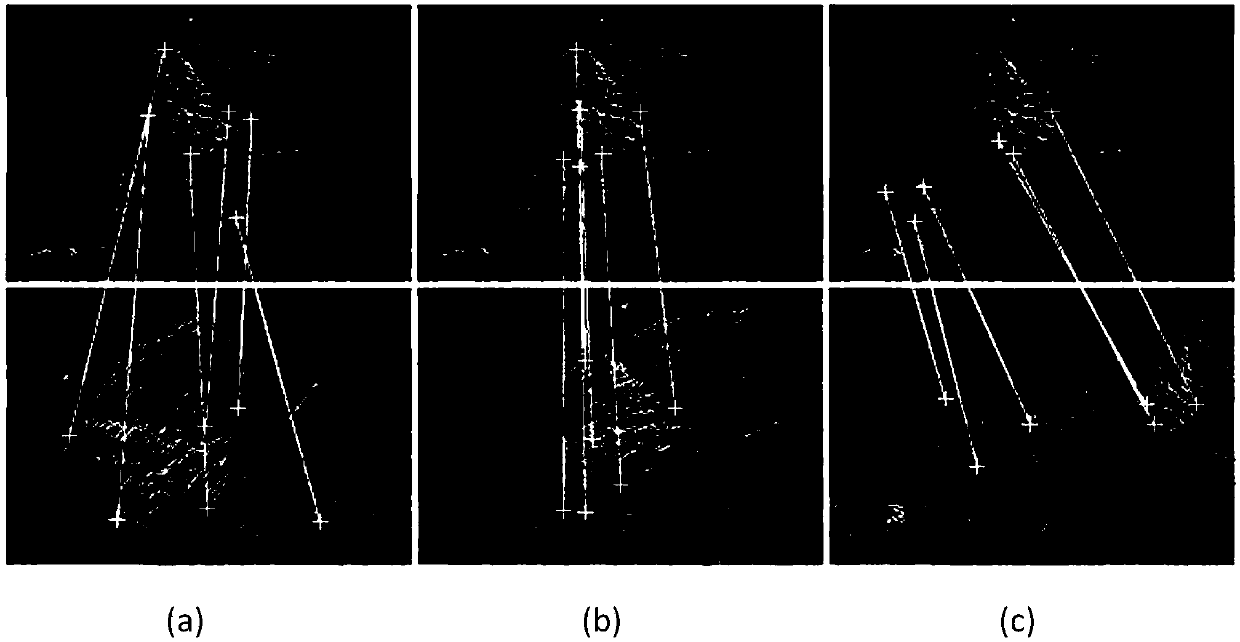
[0120] Dataset: The typical Mikolajczyk and Schmid (document [19]) dataset is used as the retrieved dataset. The data set has 8 groups of pictures, and each group of pictures contains 6 pictures. There are similarities, affine or projective transformation relationships and lighting effects between the 2nd to 6th pictures and the 1st picture. This image set provides the transformation matrix between each group of images to test the reliability of different algorithms.
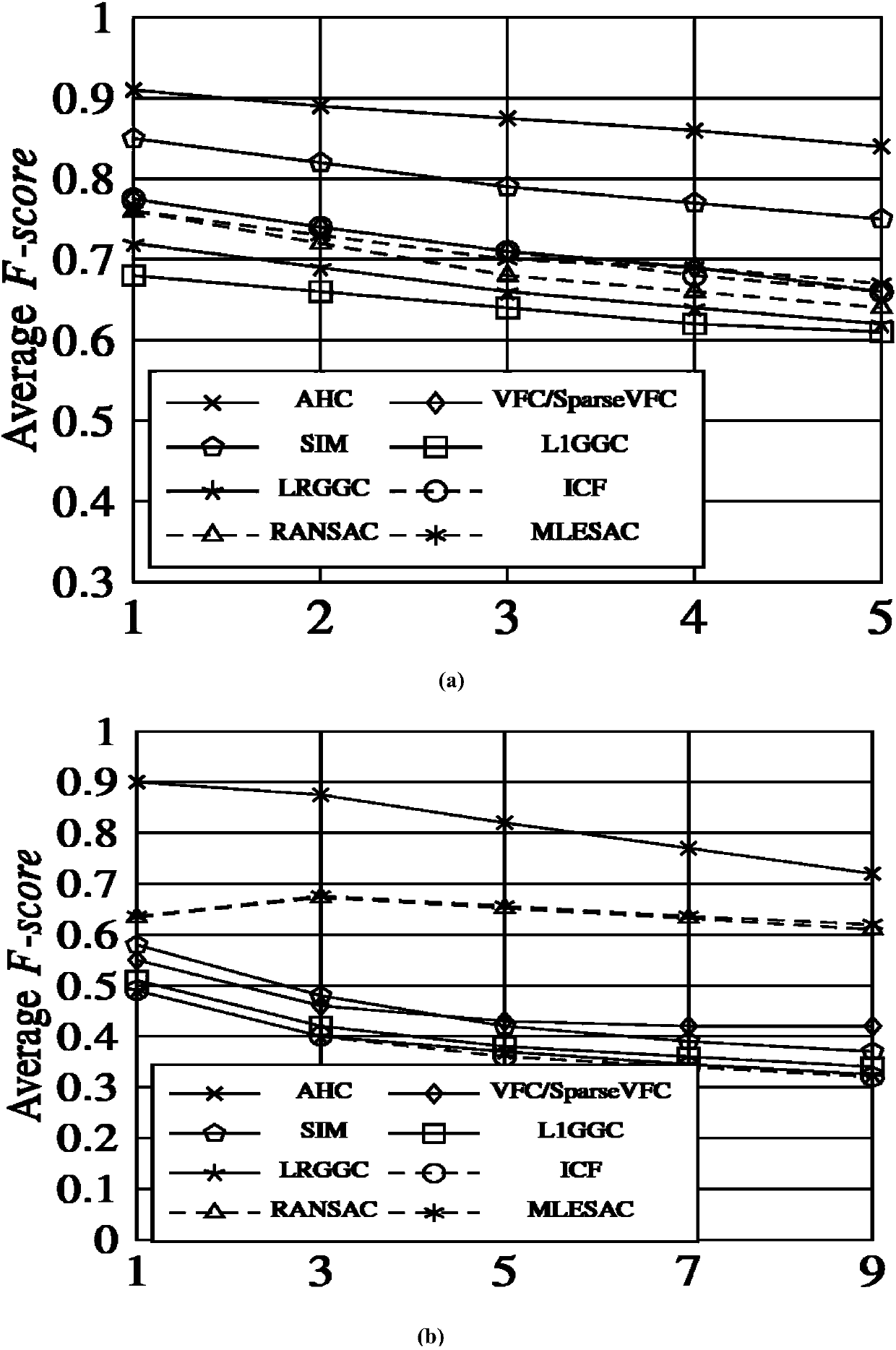
[0121] Evaluation indicators: This embodiment uses average F-score and average retrieval time to compare with other best methods in the industry. Average F-score is a comprehensive evaluation of recall rate (Recall) and precision rate (Precision), wherein recall rate (Recall )=retrieved matching images / total number of all images, precision (Precision)=retrieved matching images / all matching images.
[0122]F-score=2*Precision*Recall / (Precision+Recall).
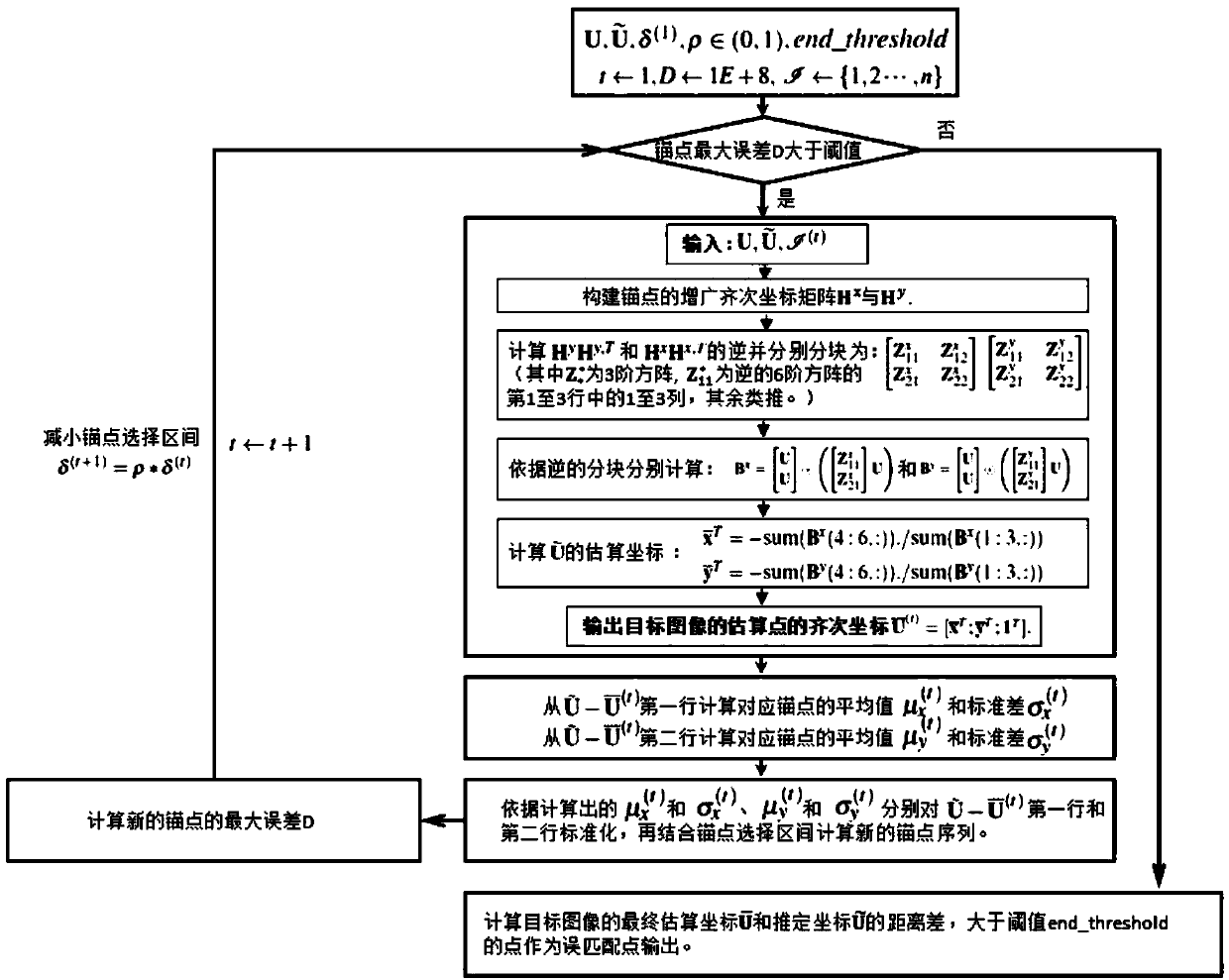
[0123] Implementation steps:
[0124] We use ASIFT as a ...
Embodiment 2
[0130] Datasets: Popular datasets are used as the retrieved datasets, namely Holiday[7], GCDup[20] and Oxford5k[21] datasets. Among them, Holiday is a data set with a total of 500 groups of approximately repeated pictures containing 1491 images; GCDup is a data set with a total of 33 groups containing 1104 partially repeated pictures; Oxford5k is a data set with a total of 55 groups containing 5062 high-resolution photos and partially repeated data set. In order to make the example more realistic, this embodiment also downloaded the MIRflickr1M [22] data set from the Flickr website as an interference data set. The MIRflickr1M data set contains one million mutually irrelevant pictures.
[0131] In this embodiment, the first five images of each group in the three benchmark datasets are set as query images. Then, the remaining images in the same group were mixed into different numbers of MIRflickr1M datasets, and finally the retrieval results were checked by observing whether th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com