Node cache replacement method in information center wireless network virtualization network
A virtualized network and wireless network technology, applied in the field of node data cache replacement, can solve the problems of unfavorable data cache overall transmission efficiency, low frequency of use, memory space occupation, etc., to improve transmission performance, utilization rate, and transmission efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
[0061] This embodiment is a preferred implementation manner of the node cache replacement method in the information center wireless network virtualization network of the present invention.
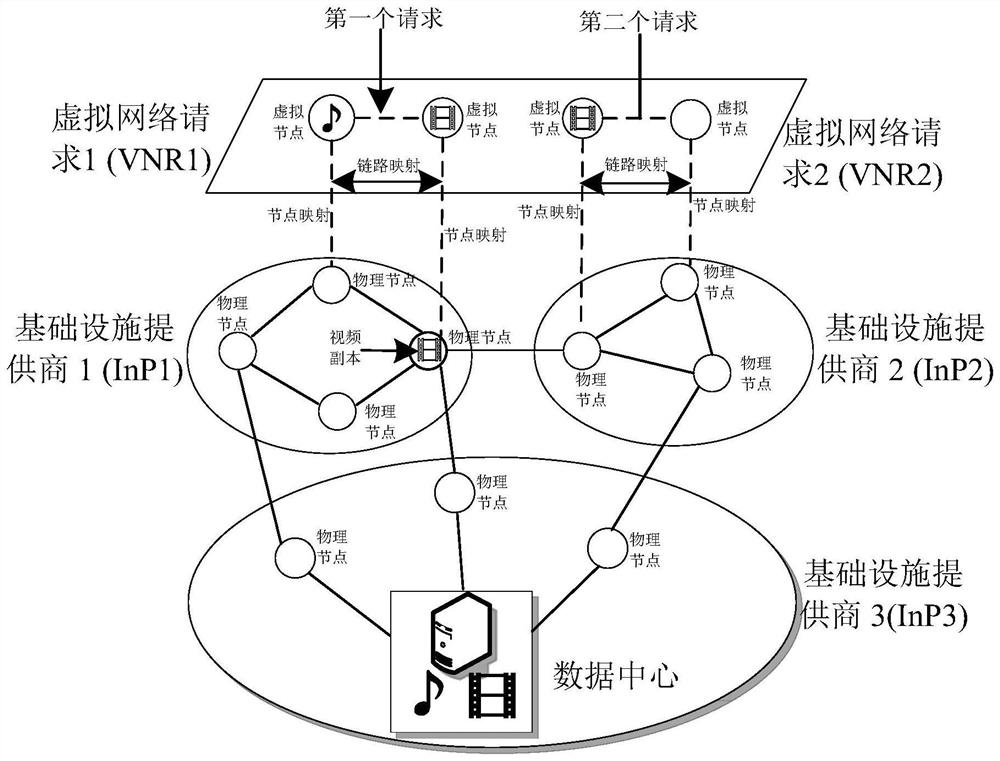
[0062] In the ICWNV network of this specific embodiment, the set of network nodes is, V=(v 1 ,v 2 ,...,v i ,...,v I ), where i is the node number, v I is the data center; the set of data packets in the network is C=(c 1 ,c 2 ,...,c k ,...,c K ), where k is the serial number of the data packet, k=1,2...K. node v i The maximum number of data packets that can be stored is J,
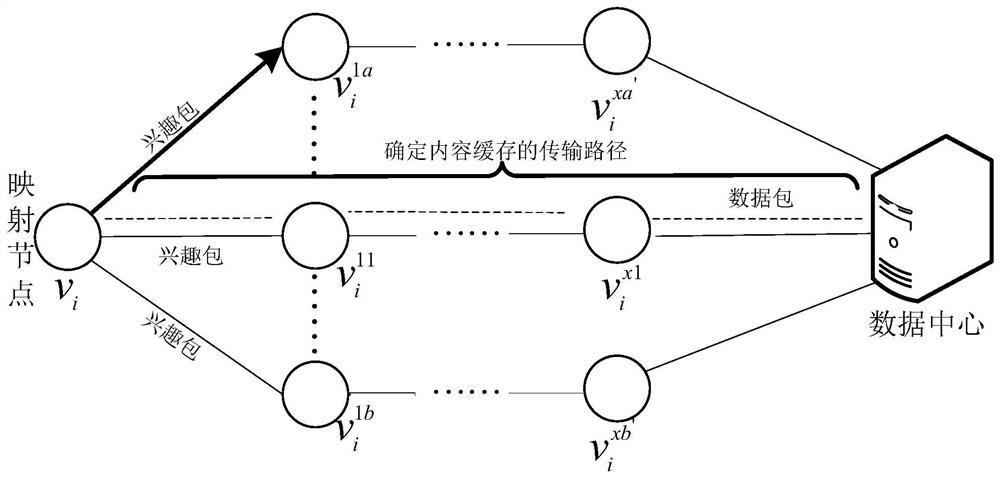
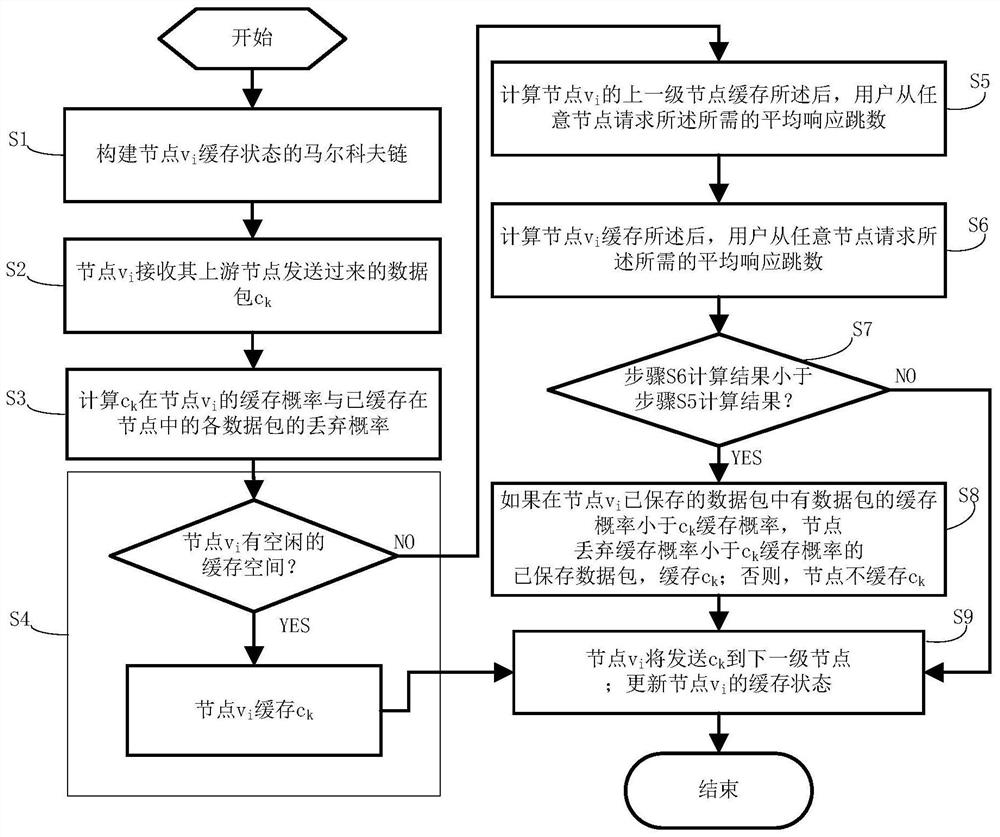
[0063] see image 3 , the flow of the node data cache replacement method in this embodiment is as follows image 3 shown, including:
[0064] S1. Build node v i Markov chain of cache state;
[0065] node v i The number of data packets currently stored j represents the node v i Current cache state, node v i The cache state is a Markov chain; when the node's cache state is in state j, v i Caching a data ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com