Turing machine insolubility discrimination method and system for big data
A discriminant method and Turing machine technology, applied in the field of Turing machines, can solve problems such as high communication overhead, communication paralysis, and low value density of big data, and achieve the effect of improving computing efficiency and reducing the probability of doing useless work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
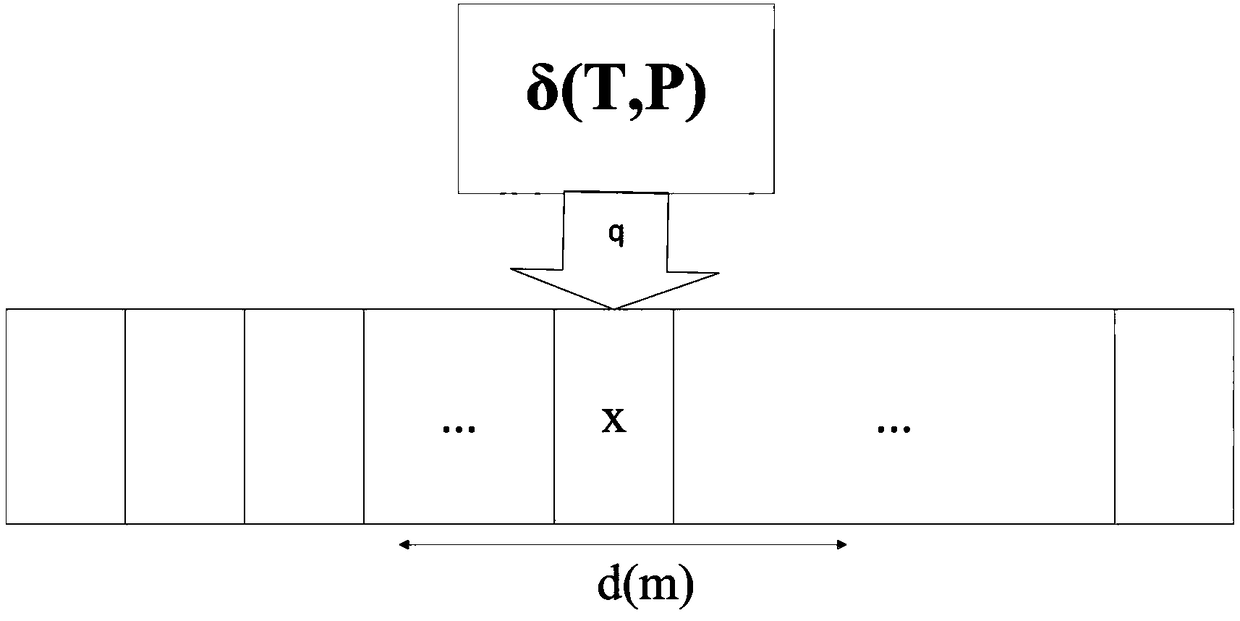
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, there are four unsolvable cases of big data Turing machines as follows:
[0032] The first case is unsolvable beyond the time limit, which is called overtime unsolvable.
[0033] Define Turing machine M=(Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q0, qaccept, qreject, m, P, T), wherein: Q is a state set, Σ is an input character set, Γ is a storage band character set, Γ=Σ ∪{□}, δ is the transfer function, δ: Q×Γ→Q×Γ×{L,R}; q0 is the initial state, qaccept is the acceptance state, and qreject is the rejection state.
[0034] The number of transfers of the transfer function δ is limited, instead of being transferred endlessly, once the running time exceeds T, it will end in the qreject state, which is called timeout unsolvable. Unsolvable over time does not mean that the big data application is really unsolvable. It only means that the processing program design of the big data application is unreasonable and does not take into account the real-time nature of the processing. ...
Embodiment 2
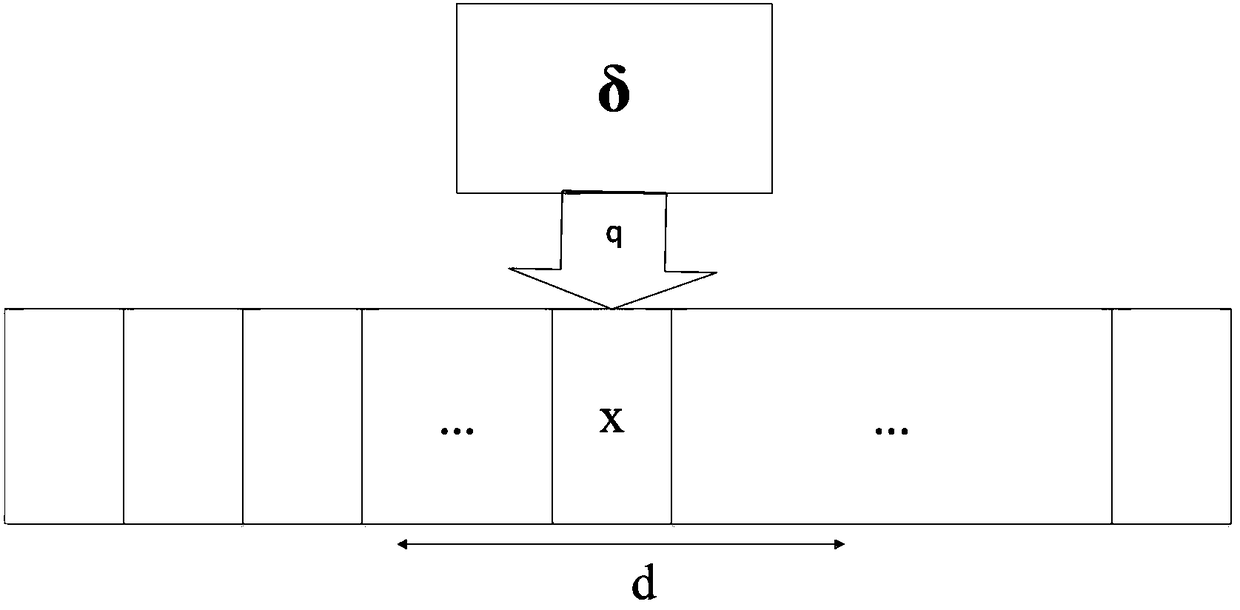
[0046] There are four solvable cases of big data Turing machines:
[0047] The first type is solvable within the time limit, which is called time-solvable.
[0048] Define Turing machine M=(Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q0, qaccept, qreject, k, m, P, T), wherein: Q is a state set, Σ is an input character set, Γ is a storage band character set, Γ =Σ∪{□}, δ is the transfer function, δ: Q×Γ→Q×Γ×{L,R}; q0 is the initial state, qaccept is the acceptance state, and qreject is the rejection state.
[0049] Among them, both m and P are set to be empty, and only the limit of the end condition of T is imposed. The number of transfers of the transfer function is limited, instead of being able to transfer endlessly. Once the running time does not exceed T and ends in the qaccept state, it is called Solvable in time. Time-solvable means that this big data application is really solvable, and it can also show that the processing program of this big data application is designed reasonably, taking into accoun...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com