A method for visitor's exhibition garden subdivision selection behavior preference when visiting an exhibition
A tourist and behavioral technology, applied in the field of big data, can solve problems such as preference understanding and behavior prediction bias, negative industry decision-making, single model is difficult to grasp, etc., and achieve good scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
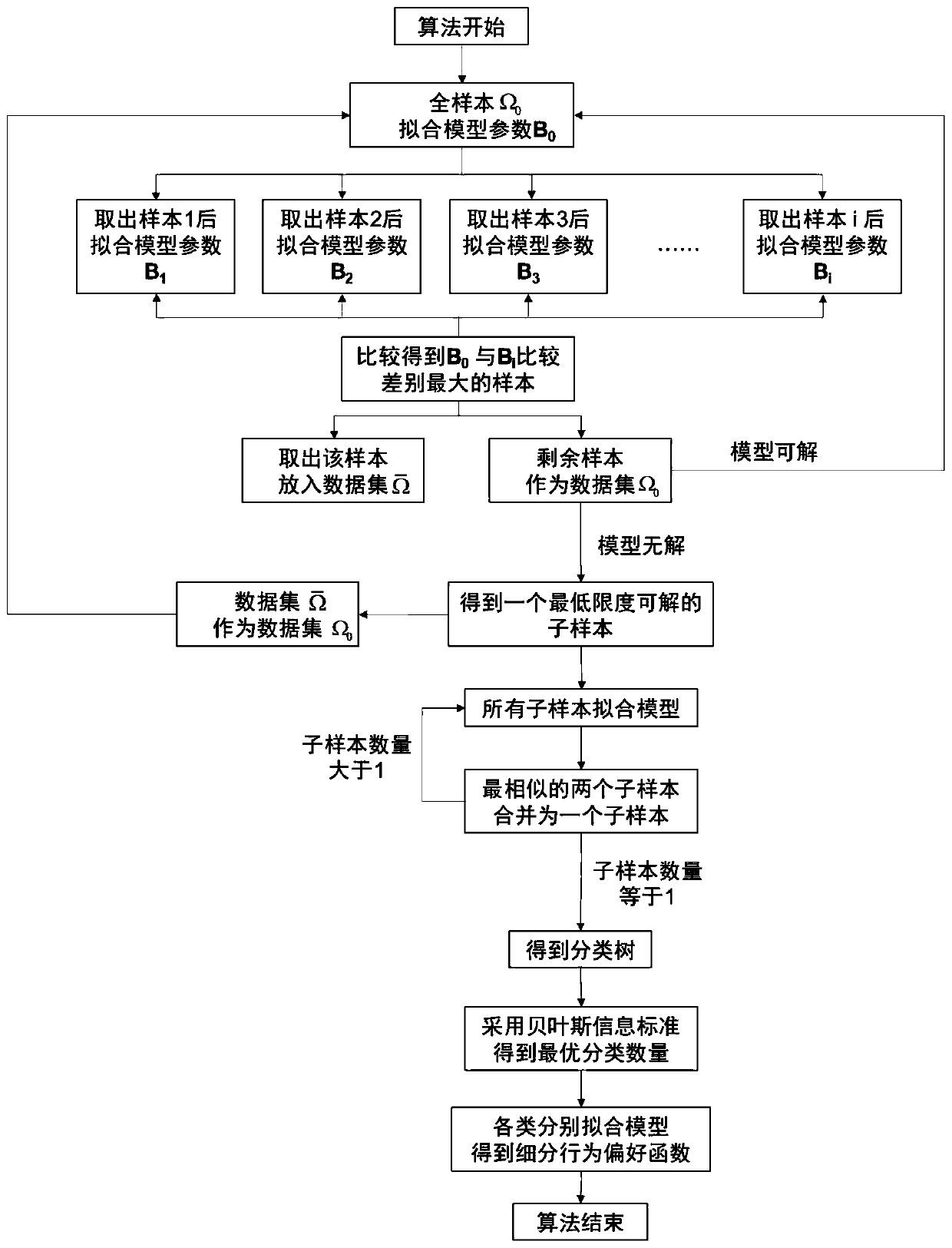
[0030] The present invention estimates model parameters based on selection behavior data and multi-logic special models as a representation of selection behavior preferences, and adopts a hierarchical clustering algorithm according to the similarity of model parameters to obtain subdivided selection behavior preference types. The algorithm of the present invention mines the heterogeneity in the selection behavior data, and can obtain more accurate selection behavior preference models of different types of individuals or organizations.
[0031] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific example, and this example selects the stop destination for the tourist.
[0032] As shown in the attached figure, the algorithm steps are as follows:
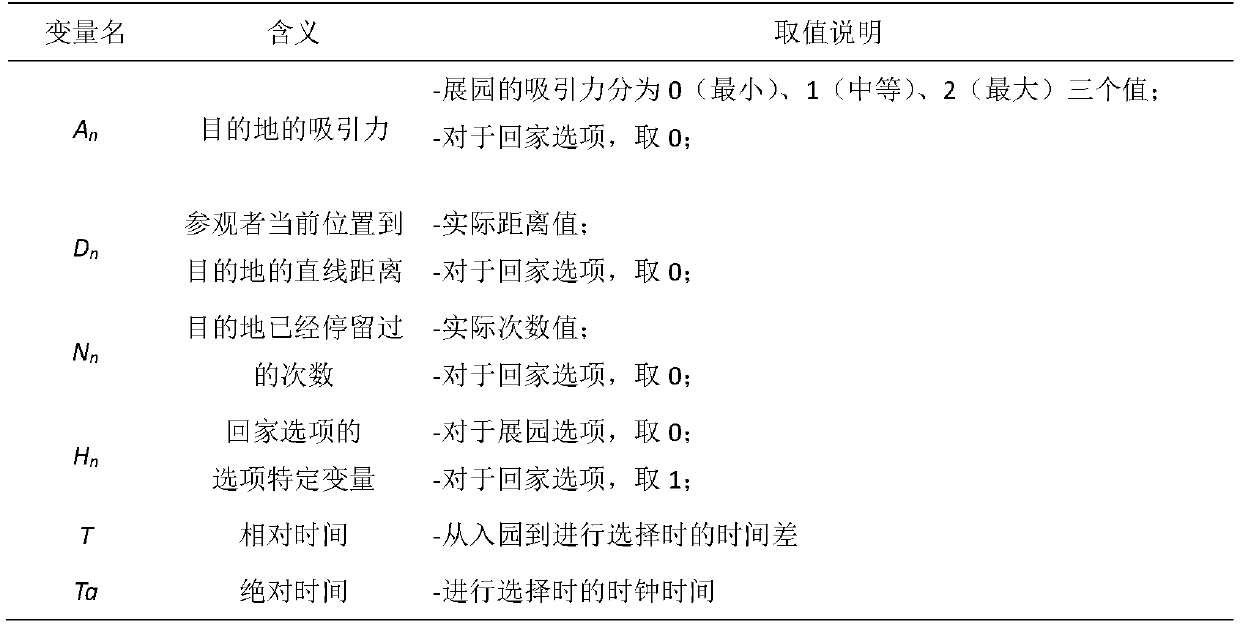
[0033] First, collect the exhibition park selection behavior data of tourists when visiting the exhibition, and build a number of logistic models as follows:
[0034] V n =(λ A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com