Preparation method of glimepiride impurity
A technology for glimepiride and impurities, which is applied in the field of preparation of glimepiride impurities, can solve problems such as inseparability, and achieve the effects of mild reaction, controllable process parameters and high purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
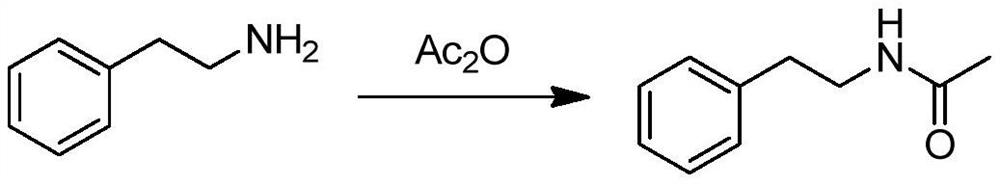
[0038] (1) Preparation of N-acetylphenethylamine
[0039] Add 24.2 g of 2-phenylethylamine and 50 ml of dichloromethane into a four-necked flask, and stir to lower the temperature to below 10°C. 21.4 g of acetic anhydride was added dropwise while keeping the temperature below 10°C. After the addition, keep the reaction for 10 minutes, and add 200ml of purified water dropwise. After standing still, the organic layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted once more with 25ml of dichloromethane. The organic layers were combined, washed twice with 25ml×2 saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, and then washed twice with 25ml×2 purified water. The organic layer was dried over an appropriate amount of anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure at 45°C to obtain 32.5 g of crude N-acetylphenethylamine, which was directly used in the next step without purification.
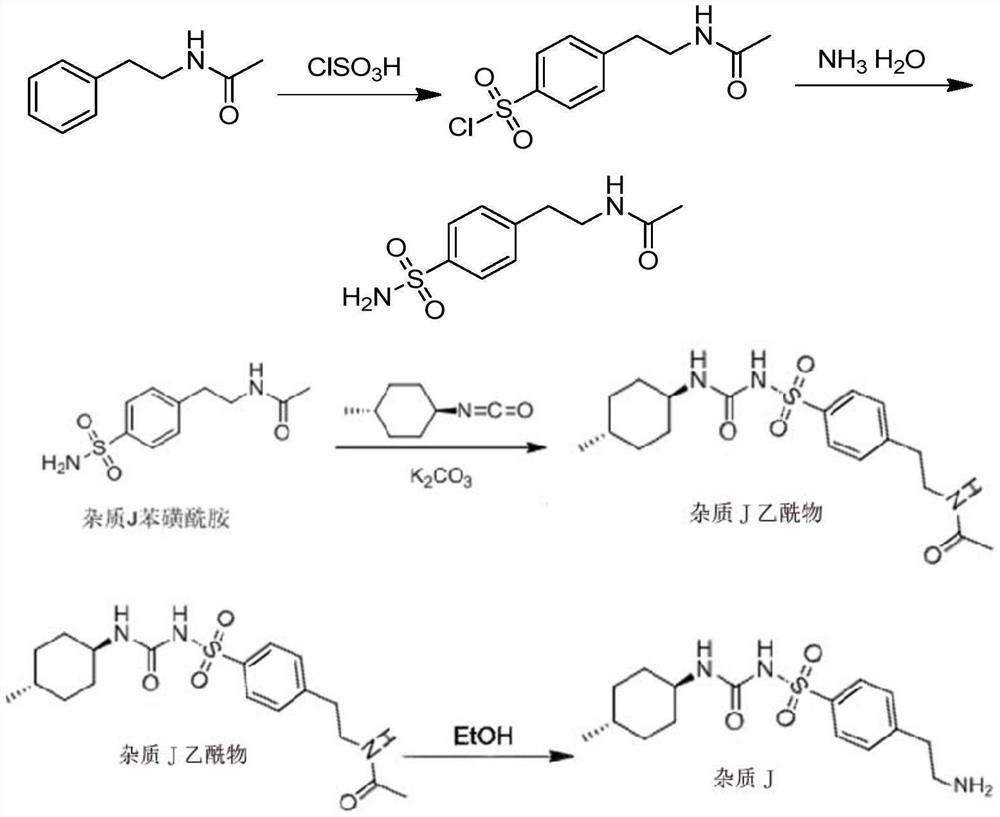
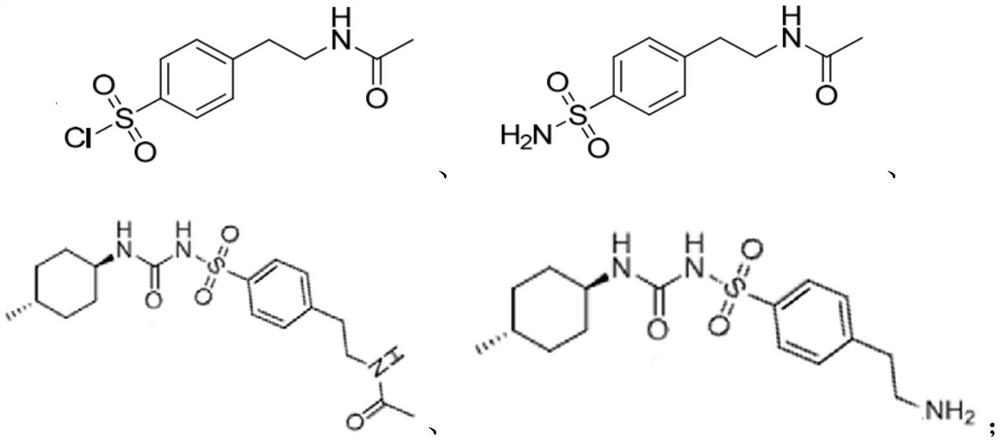
[0040] (2) Preparation of impurity J benzenesulfonamide (chemical ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] (1) Preparation of N-acetylphenethylamine
[0050]Add 24.2 g of 2-phenylethylamine and 50 ml of ethyl acetate into a four-necked flask, and stir to lower the temperature to below 10°C. 21.4 g of acetic anhydride was added dropwise while keeping the temperature below 10°C. After the addition, keep the reaction for 10 minutes, and add 200ml of purified water dropwise. After standing still, the organic layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted once more with 25 ml of ethyl acetate. The organic layers were combined, washed twice with 25ml×2 saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, and then washed twice with 25ml×2 purified water. The organic layer was dried over an appropriate amount of anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure at 50°C to obtain 30.7 g of crude N-acetylphenethylamine. It was directly used in the next step without refining.
[0051] (2) Preparation of impurity J benzenesulfonamide (chemical name: 4-(N...
Embodiment 3
[0060] (1) Preparation of N-acetylphenethylamine
[0061] Add 24.2 g of 2-phenylethylamine and 50 ml of dichloromethane into a four-necked flask, and stir to lower the temperature to below 15°C. 21.4 g of acetic anhydride was added dropwise while keeping the temperature below 15°C. After the addition, keep the reaction for 10 minutes, and add 200ml of purified water dropwise. After standing still, the organic layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted once more with 25ml of dichloromethane. The combined base layer was first washed twice with 25ml×2 saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, and then washed twice with 25ml×2 purified water. The organic layer was dried over an appropriate amount of anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure at 45°C to obtain 31.7 g of crude N-acetylphenethylamine. It was directly used in the next step without refining.
[0062] (2) Preparation of impurity J benzenesulfonamide (chemical name: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com