A kind of breeding method of using ethyl methanesulfonate to induce in vitro mutagenesis of Ciba japonica
A kind of ethyl methanesulfonate, consistent technology, applied in the breeding field of using ethyl methanesulfonate to induce in vitro mutagenesis of Cizhu liangshanensis, can solve the problems such as unseen mutation breeding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Embodiment 1, preparation bamboo callus
[0069] 1. Preparation of explants
[0070] 1. Take the young side branches of Cizhu liangshan, remove the leaf sheaths, and then carry out the following disinfection steps in sequence: wash with 70% ethanol aqueous solution, then rinse with running water, then soak for 30 sec with 70% ethanol aqueous solution, then fully clean with sterile water, Then with 0.1% HgCl 2 The aqueous solution was disinfected for 10 minutes, and then fully rinsed with sterile water.
[0071] 2. After completing step 1, take side branches and cut them into stem segments with a length of 1±0.2cm (each stem segment has at least one node).
[0072] 2. Preparation of callus (the culture temperature in the whole process is 25±2°C)
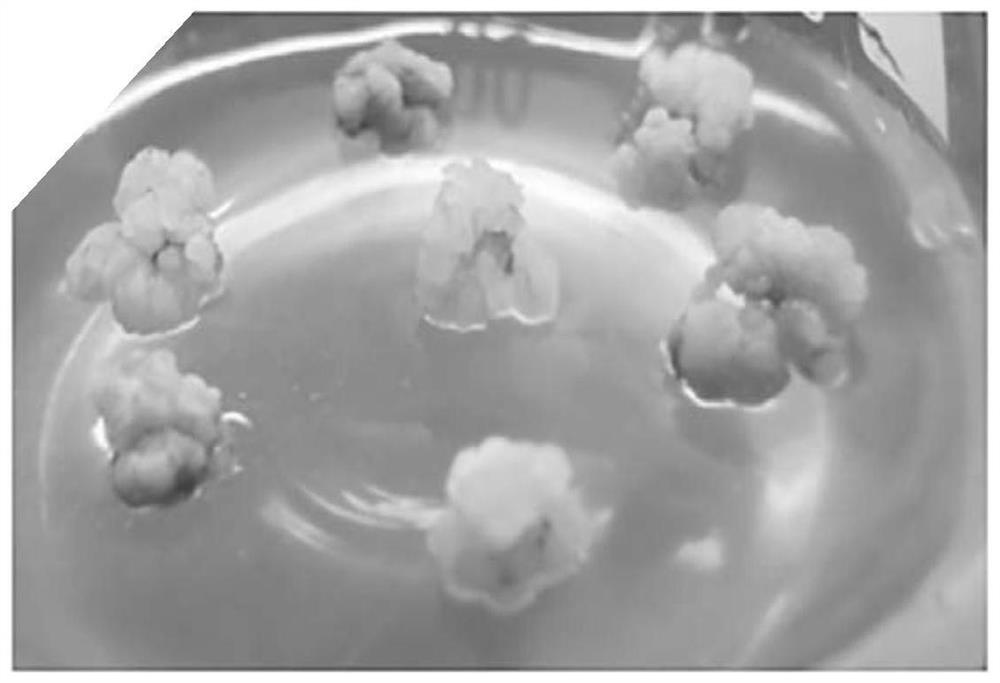
[0073] 1. Take the stem segment obtained in step 1, inoculate it on the callus induction medium, cultivate it for 2 weeks (dark culture), and then cultivate it for 6-8 weeks (16 hours of light per day) to obtain callus.
[...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Embodiment 2, utilization of ethyl methanesulfonate in vitro mutagenesis of Cizhu liangshan
[0080] 1. Prepare pH 4.8, 0.01M phosphate buffer, autoclave and cool to room temperature.
[0081] 2. Take ethyl methanesulfonate, filter and sterilize with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane.
[0082] 3. Take the ethyl methanesulfonate obtained in step 2 and dilute it with the phosphate buffer obtained in step 1 to obtain an ethyl methanesulfonate solution.
[0083] In the ethyl methanesulfonate solution, the volume percent content of ethyl methanesulfonate is 0.6%, 0.8% or 1.0%, respectively.
[0084] 4. Take the callus obtained in Example 1 (the number is n1), place it in ethyl methanesulfonate solution, and shake it for 30 minutes.
[0085] 5. After completing step 4, take the callus and rinse it with sterile water.
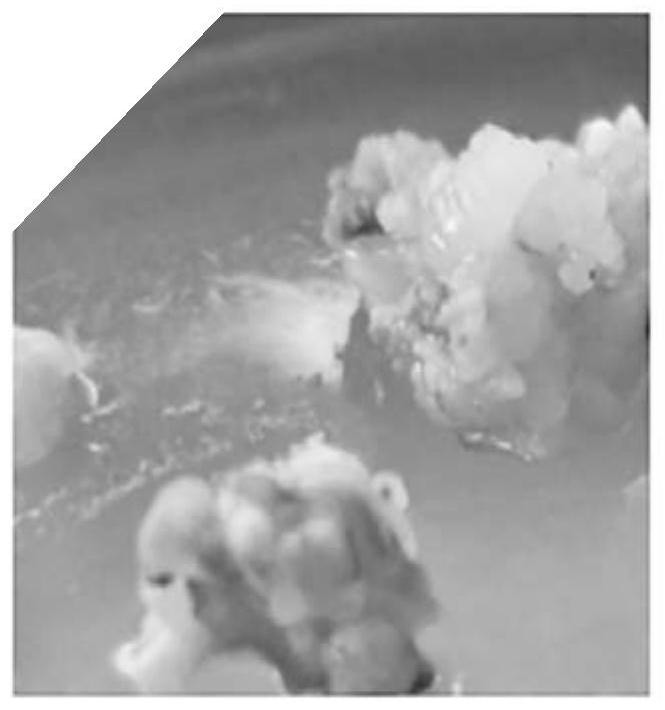
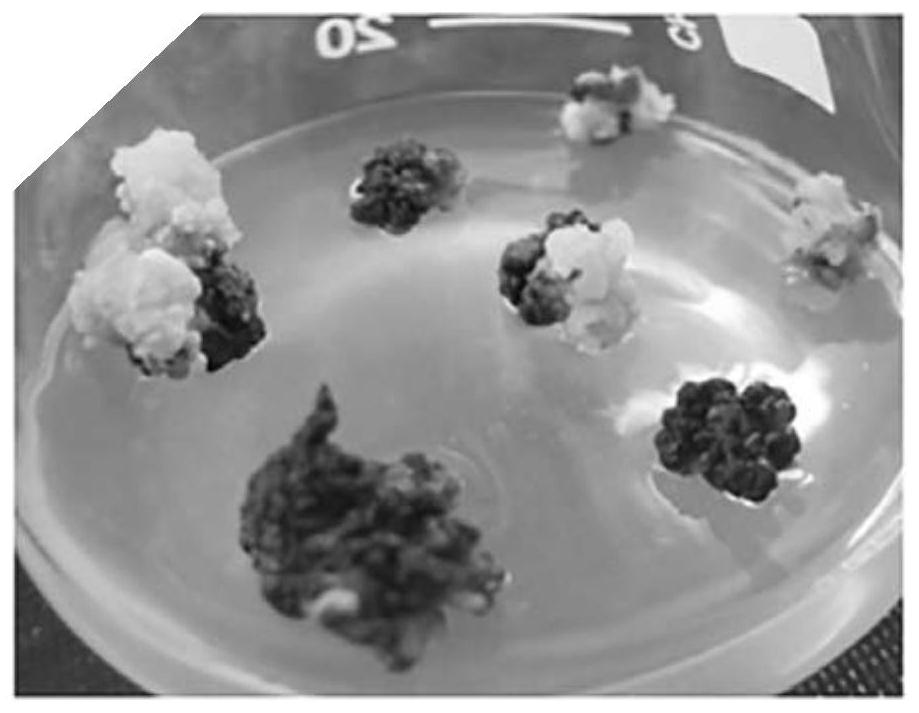
[0086] 6. After step 5 is completed, the callus is taken, inoculated into the cluster bud differentiation medium, and cultured until the cluster shoots grow ou...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Example 3. Analysis of Mutagenized Progeny Using ISSR Molecular Marker Technology
[0105] From the 96 regenerated plants obtained after mutagenesis with 0.6% ethyl methanesulfonate solution in Example 2, 47 were randomly selected as candidate mutants.
[0106] Each candidate mutant strain and control strain were analyzed by ISSR molecular marker technology.
[0107] 1. Take leaves and extract genomic DNA.
[0108] 2. Using the genomic DNA obtained in step 1 as a template, carry out ISSR-PCR amplification with ISSR primers.
[0109] The 14 ISSR primers in Table 2 were used respectively. In Table 2, Y stands for C or T, R stands for A or G, B stands for C or G or T, D stands for A or G or T, and S stands for G or C.
[0110] Table 2
[0111] Primer name Primer sequence (5'-3') ISSR-A AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGYA ISSR-B GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAYC ISSR-C (Sequence 1 of the Sequence Listing) CTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTRC ISSR-D (Sequence 2 of the Sequence Lis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com