Method for biologically drying sludge by using rice hull as additive
A technology of biological drying and additives, applied in biological sludge treatment and other directions, to achieve the effect of uniform mixing, stable operation and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Rice husk is used as a co-matrix auxiliary material to participate in the evaluation of the biological drying effect.
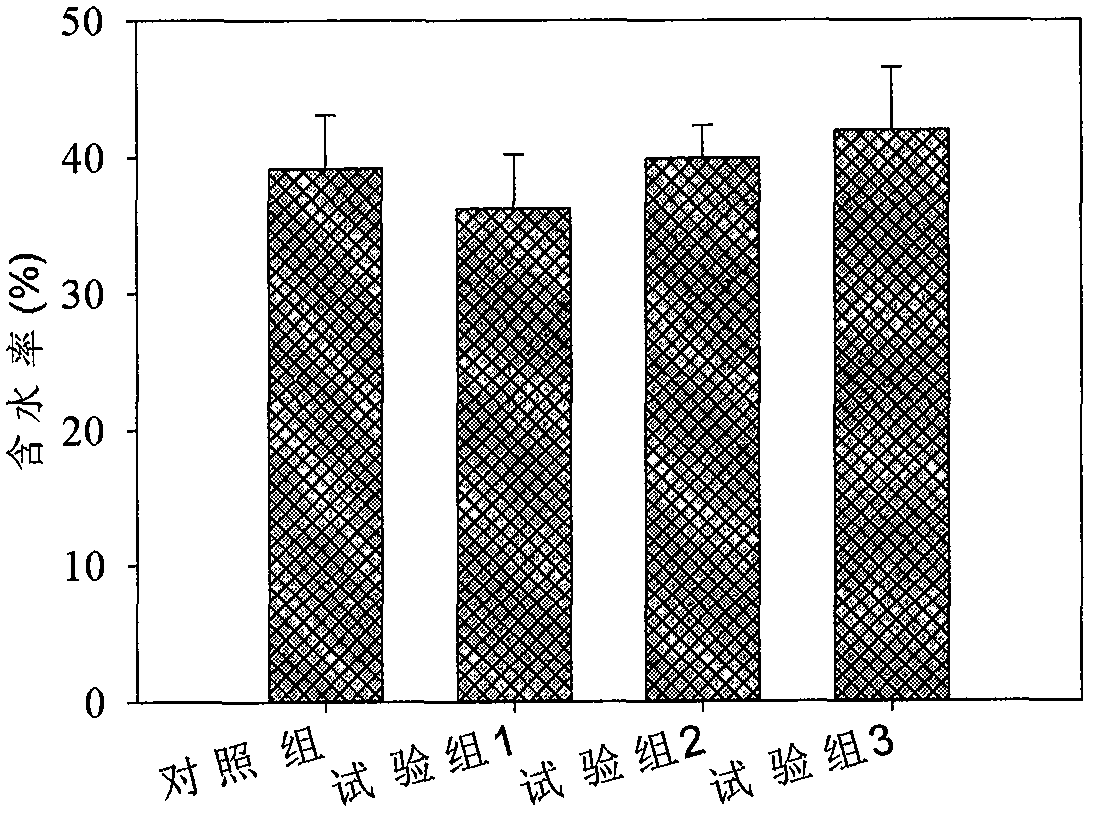
[0029] This experiment was divided into three groups, the first group was corn stalk as co-substrate; the second group was corn stalk + rice husk as co-substrate, the mass ratio was 1:1; the third group was rice husk as co-substrate. The material ratio (sludge: co-substrate: backmixing material) is 1:0.01:1.2, and the aeration control parameters are 2min / h for section A; 5min / h for section B; 15min / h for section C; 15min / h for section D; E section 15min / h; F section 10min / h. Record the initial moisture content, and ferment for 22 days after fully mixing, record the discharge moisture content, the results are shown in Table 1:
[0030]
[0031] The experimental results in Table 1 show that the average moisture content of the sludge in the third group when the rice husk is used as the co-matrix is 47.47 ± 6.07%, which is slightly ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Evaluation of the effect of different material ratios on biological drying.
[0033] This experiment was divided into 5 groups, and the ratio of sludge, rice husk, and back-mixed materials from the first group to the fifth group was set as 1: 0.048: 0.89, 1: 0.048: 1.1, 1: 0.09: 1.93, 1:0.12:0.88, 1:0.15:0.65, the initial moisture content of the mixture from the first group to the fifth group was 56.76%, 57.14%, 64.37%, 59.95%, 55.84%, the exposure of the six fermentation stages Gas control parameters are 2min / h for section A; 5min / h for section B; 5min / h for section C; 15min / h for section D; 15min / h for section E; 10min / h for section F.
[0034] The experimental results show that further reducing the addition of rice husk (1:0.048) is not conducive to the fermentation process, and the moisture content is 39.15±2.5 and 39.28±1.6 respectively. When it reaches 1:0.88~1:0.65, the fermentation effect is ideal, the average moisture content is about 36%, and the c...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3: Evaluation of the effect of aeration parameter control on sludge biological drying.
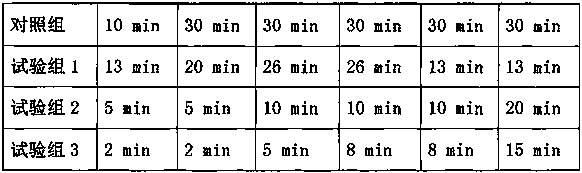
[0036] Control the ratio of sludge, rice husk, and back-mixed materials to 1:0.15:0.6, and turn over once a day. The first group is the aeration parameters before optimization, and the second group is the aeration parameters after optimization. The aeration parameters are set as shown in Table 2:
[0037] Aeration time
[0038]By measuring the moisture content (%) of the output material, the results show that the moisture content of the output material is 34.37 ± 1.84% with optimized aeration parameters, which is significantly lower than the 39.97 ± 2.24% of the aeration parameters before optimization. Therefore, the optimized aeration parameters have It is beneficial to the rapid progress of the biological drying process. Compared with the parameters before optimization, the microbial activity in the heating stage of section A is higher. At this stage, oxygen sup...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com