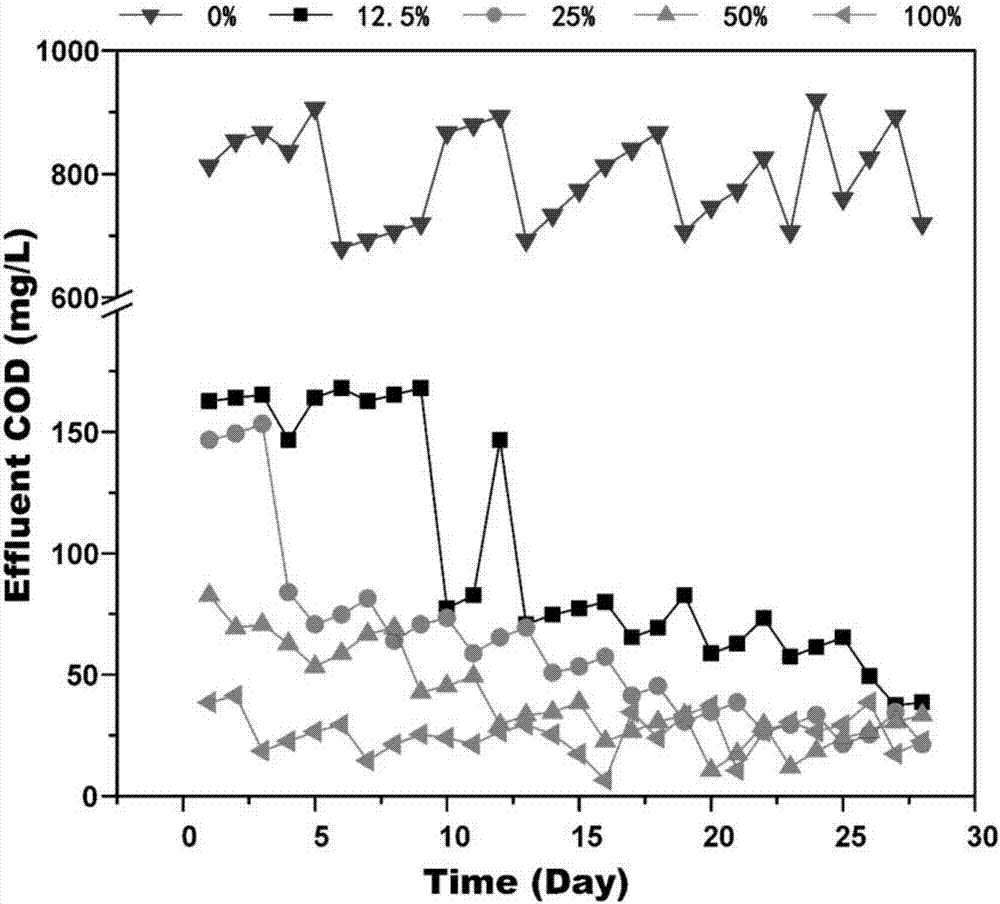
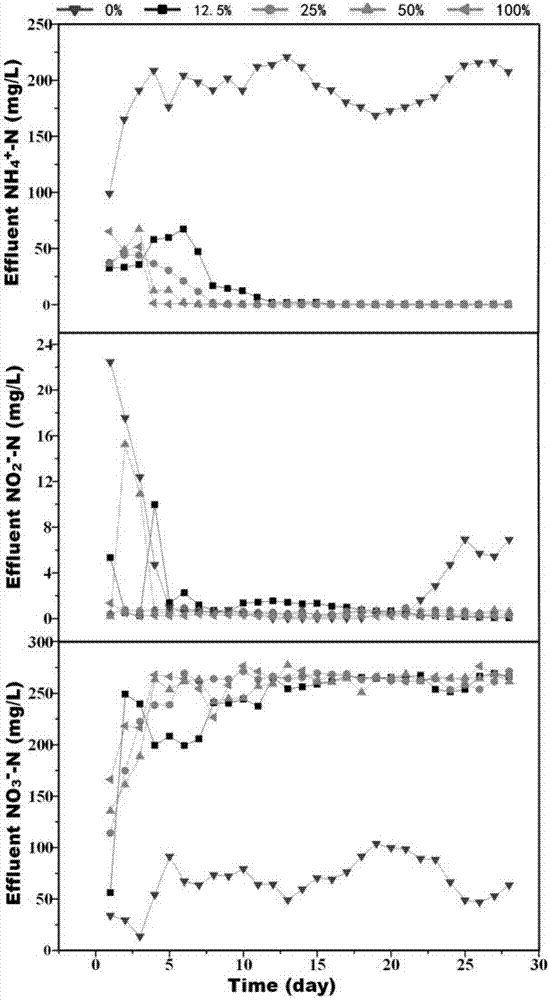
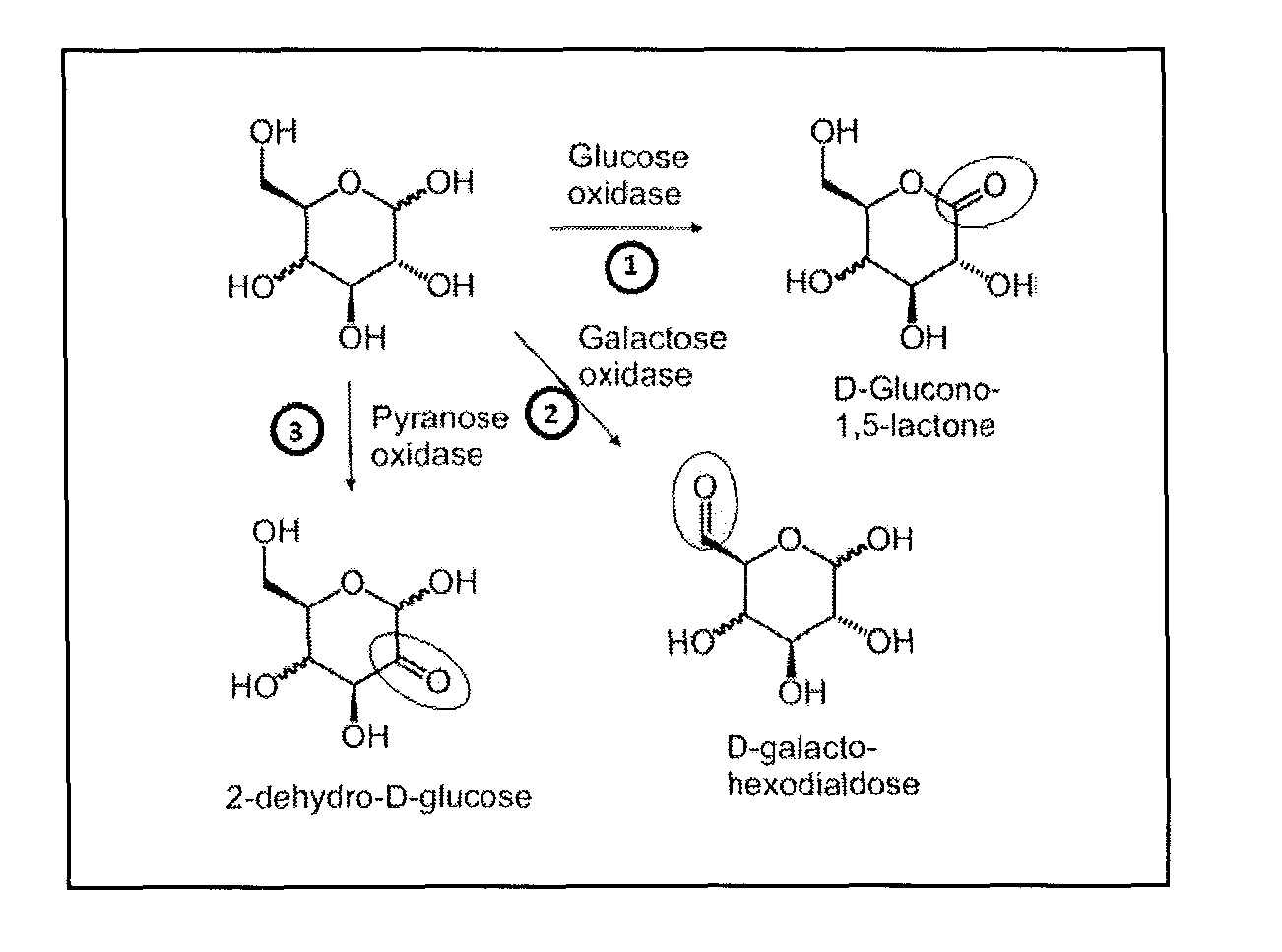
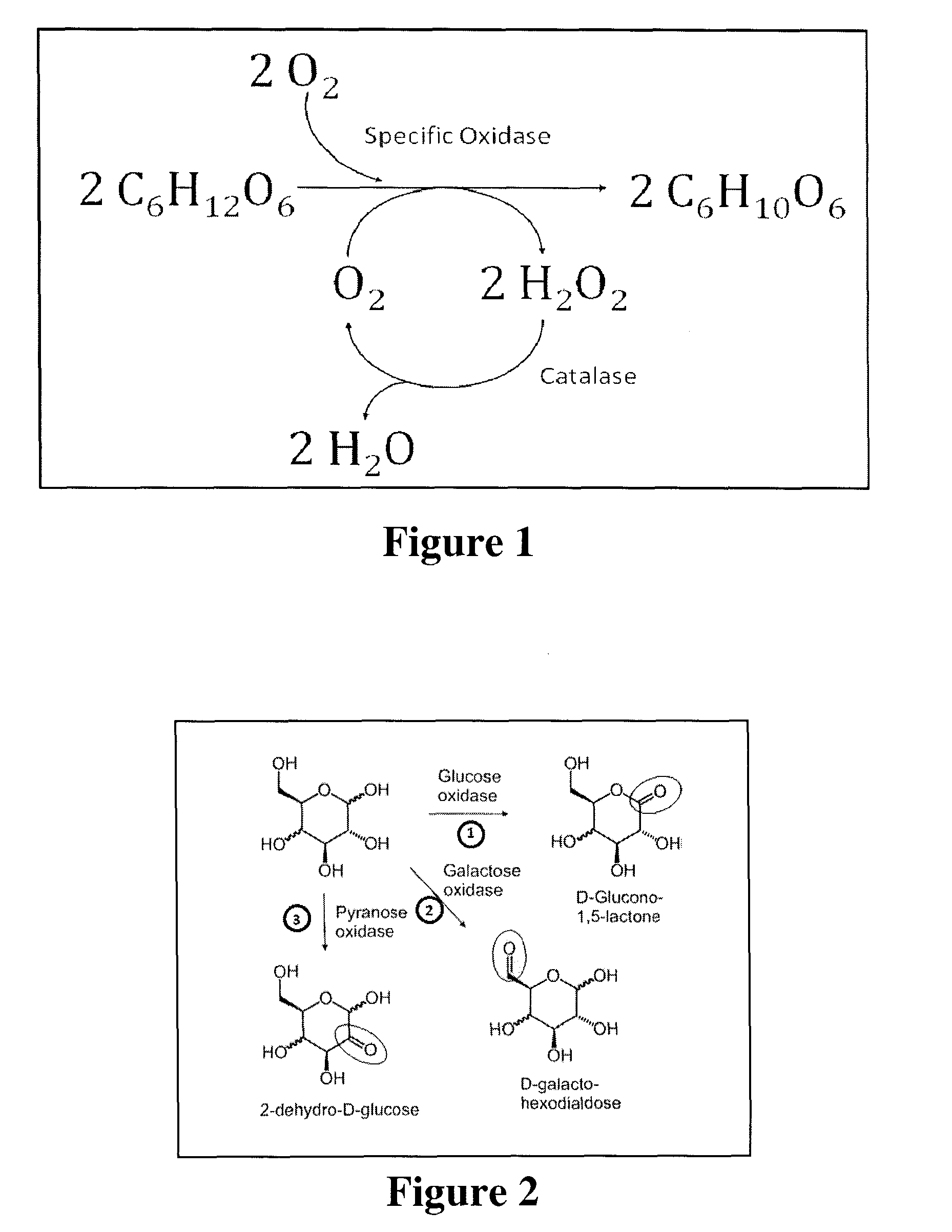
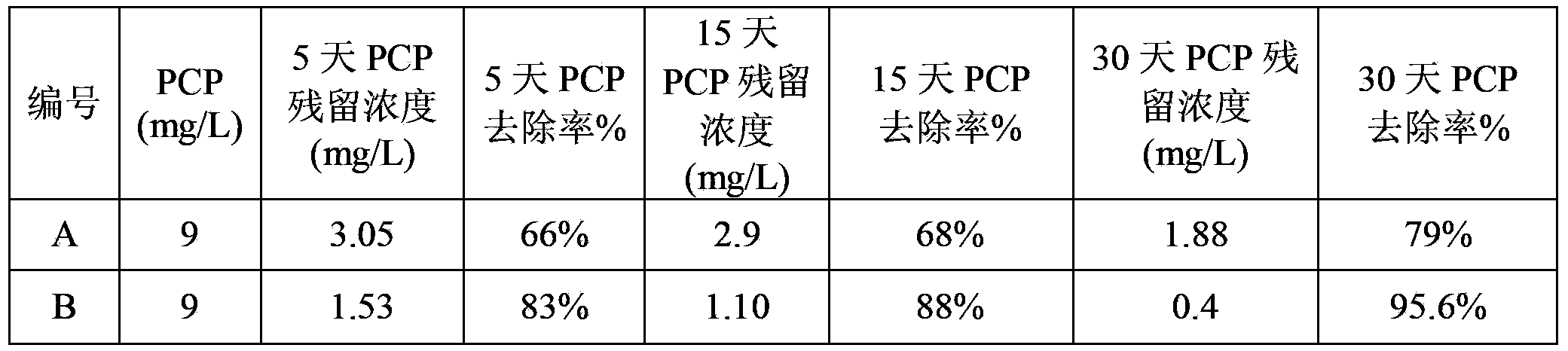
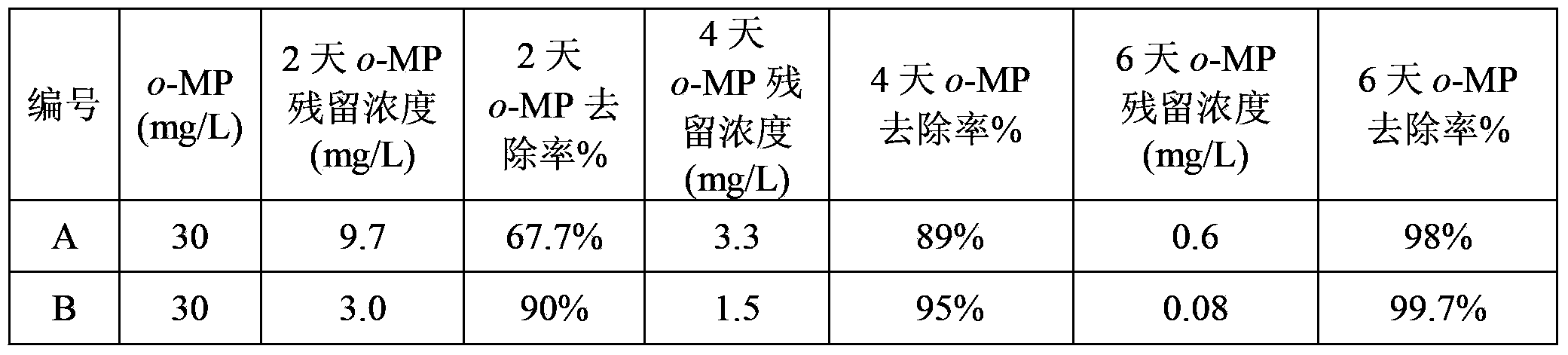
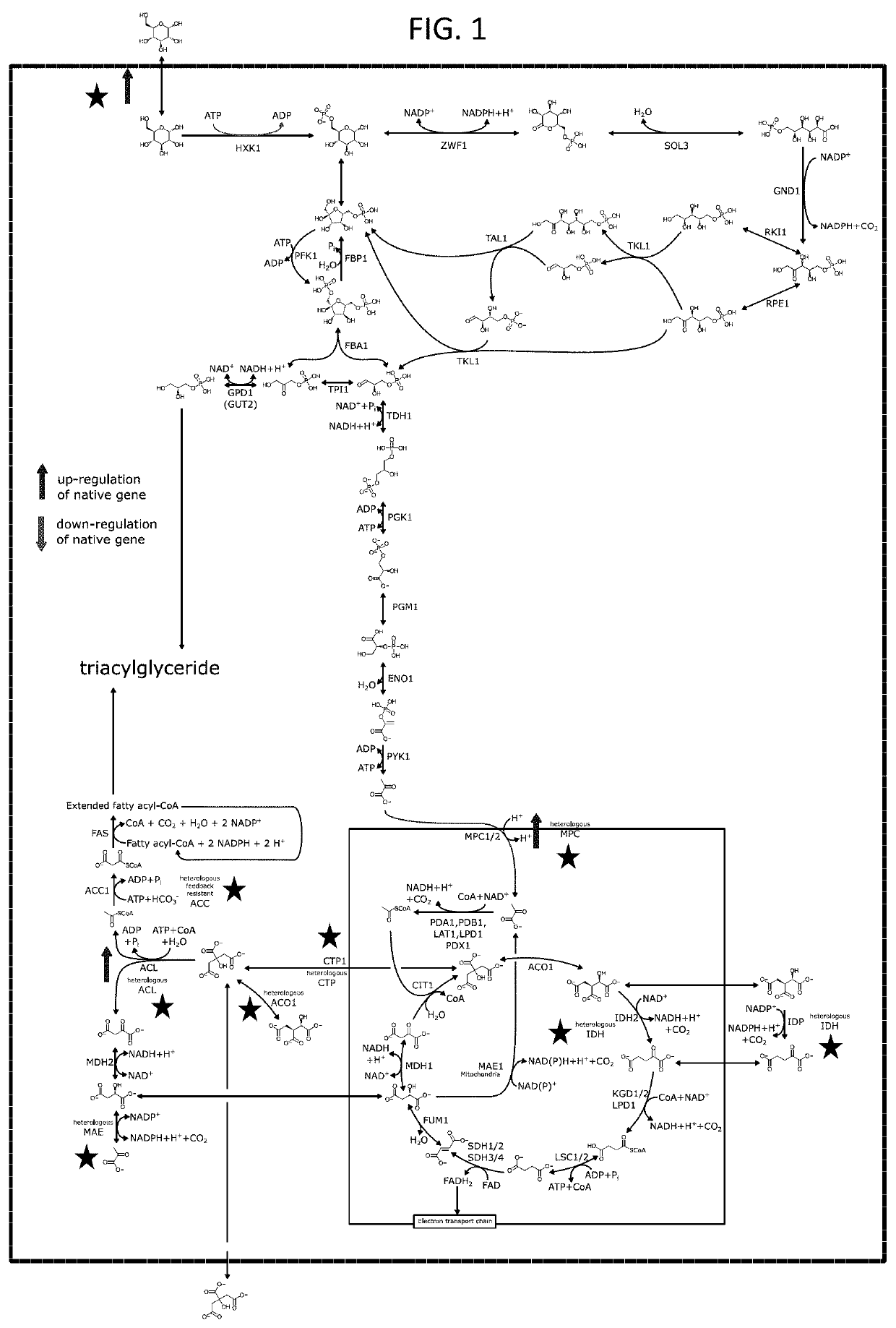
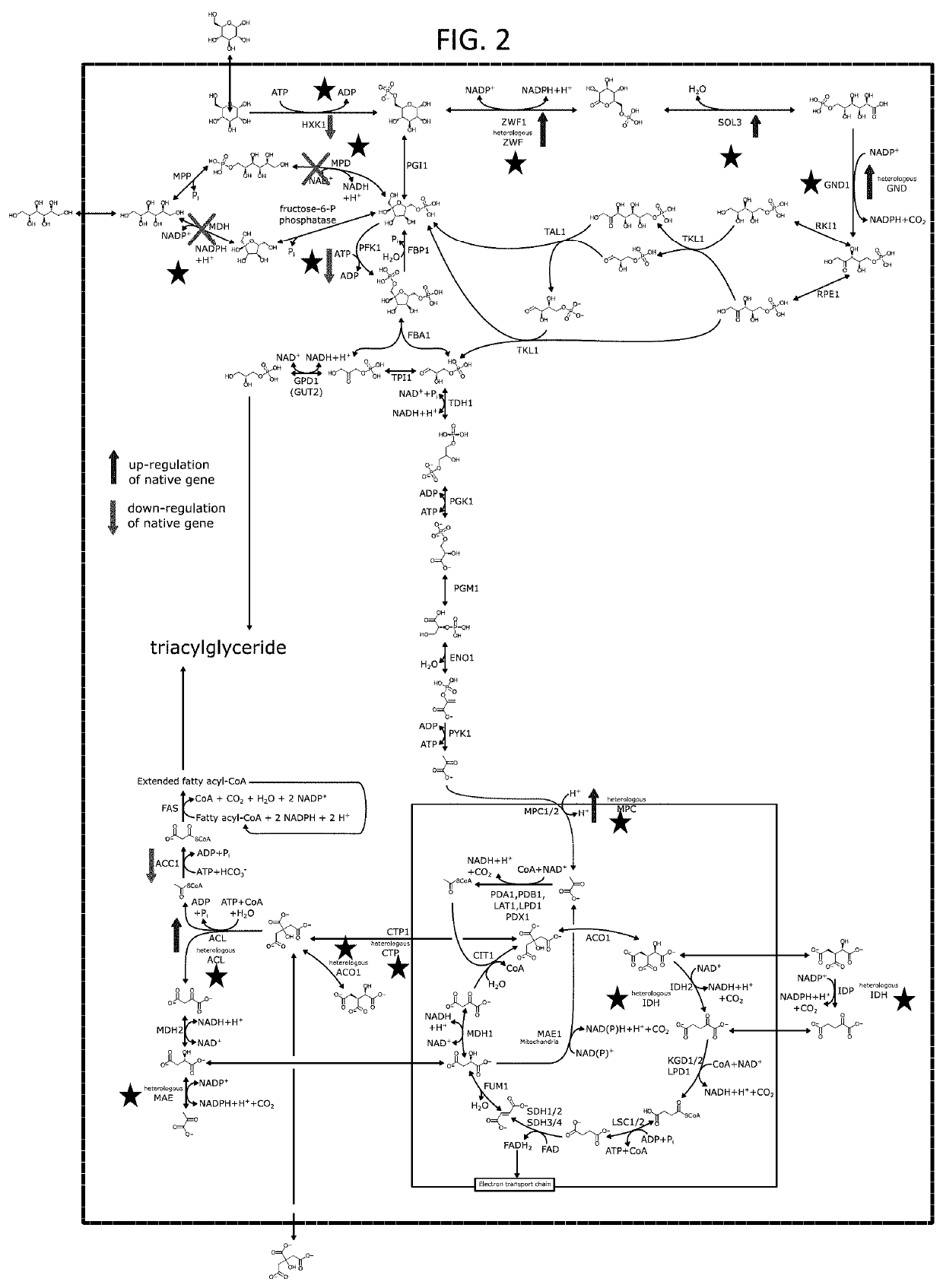
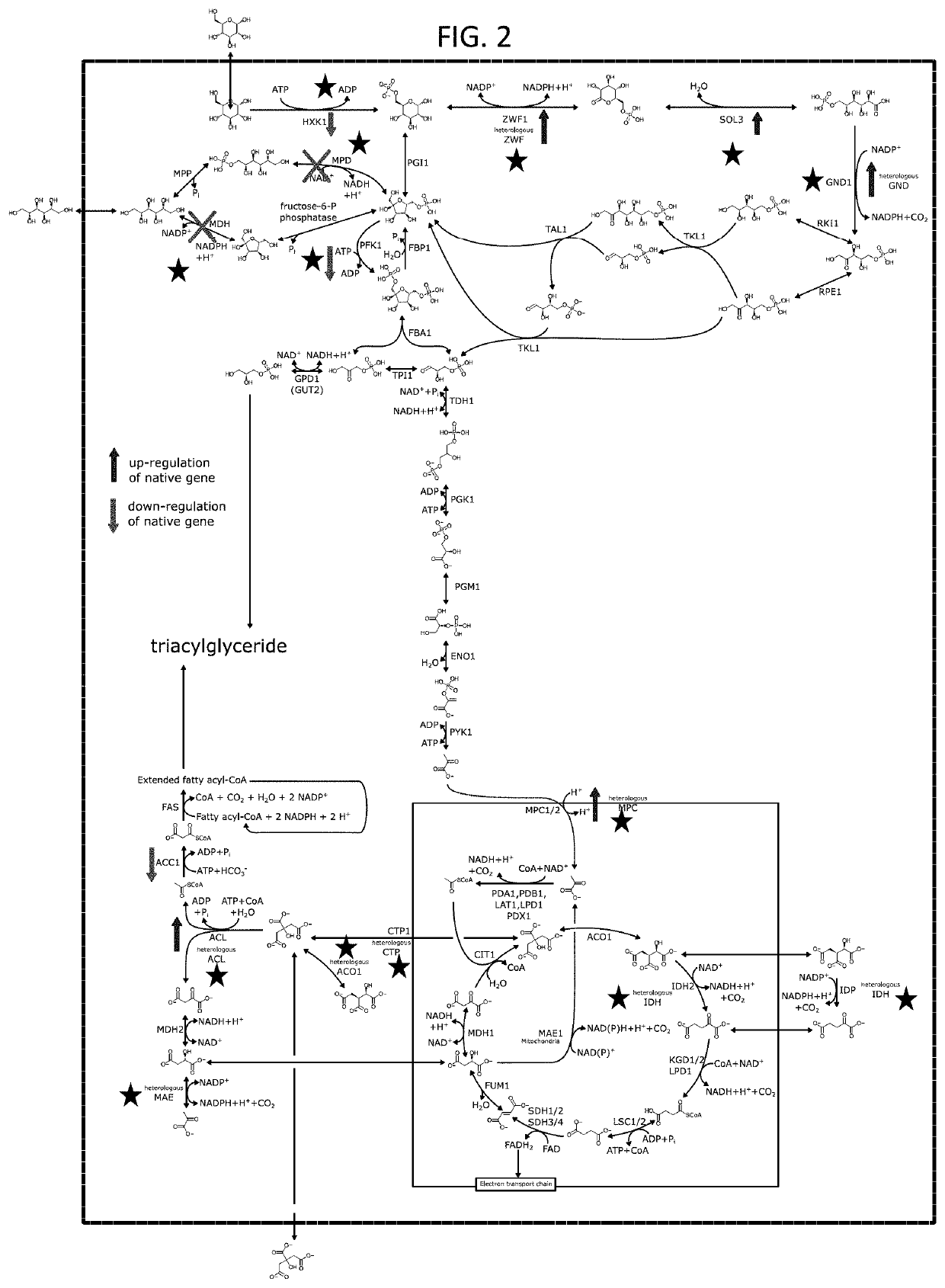
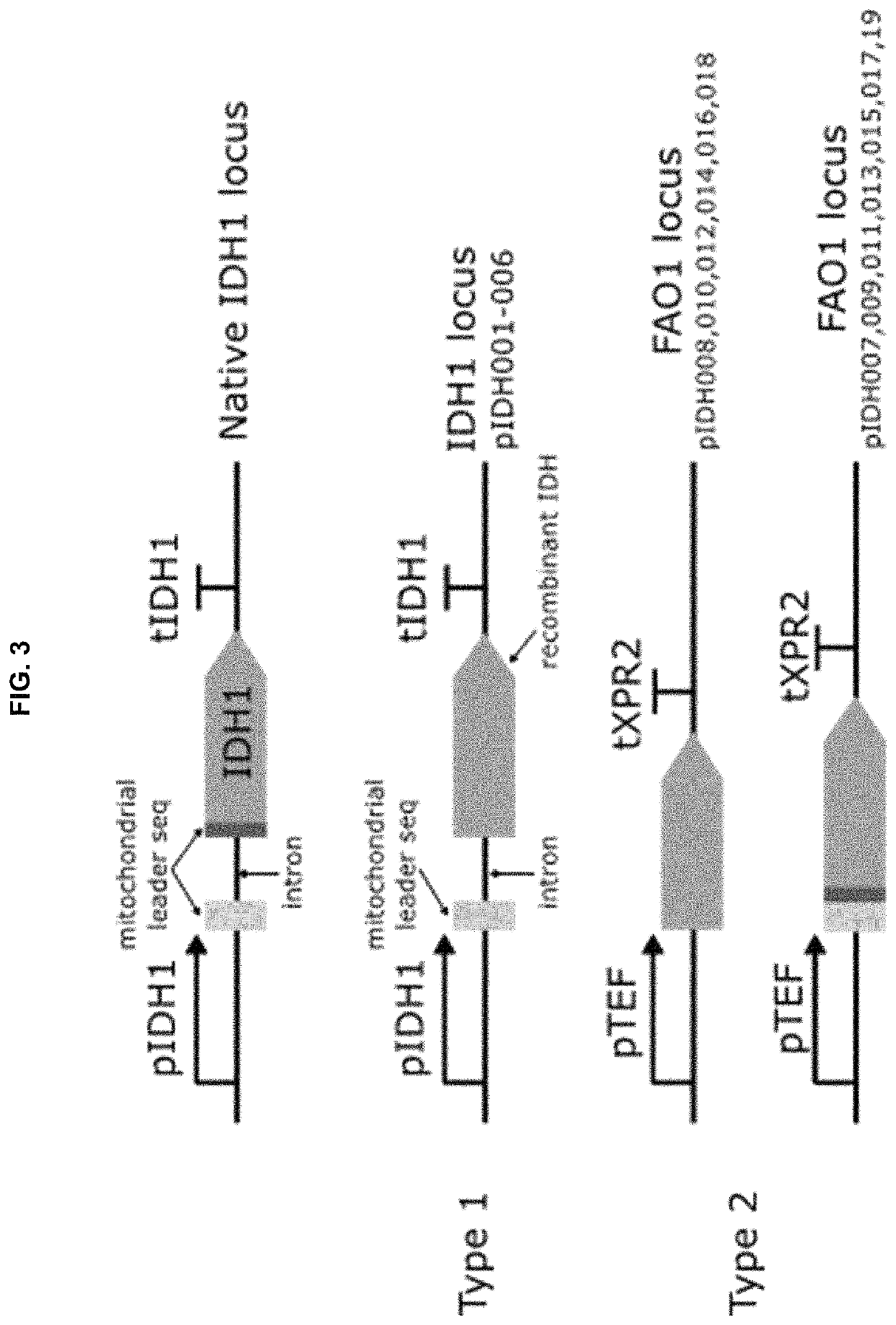
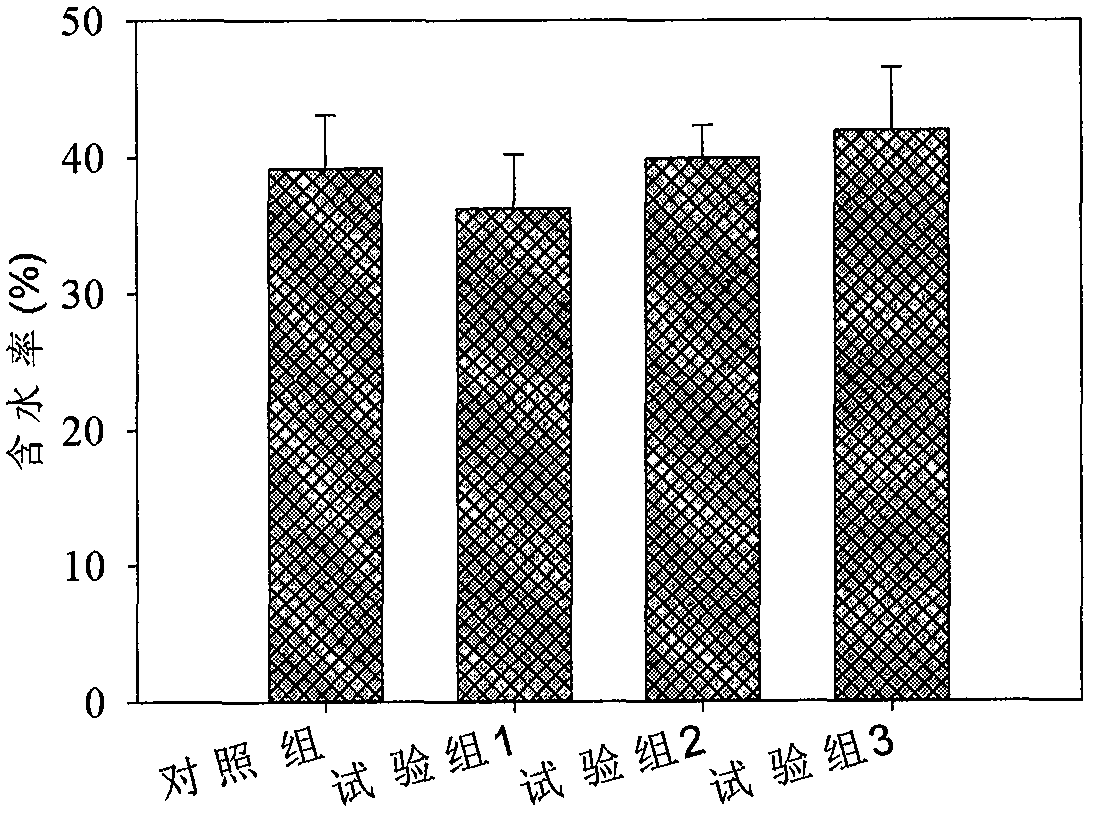
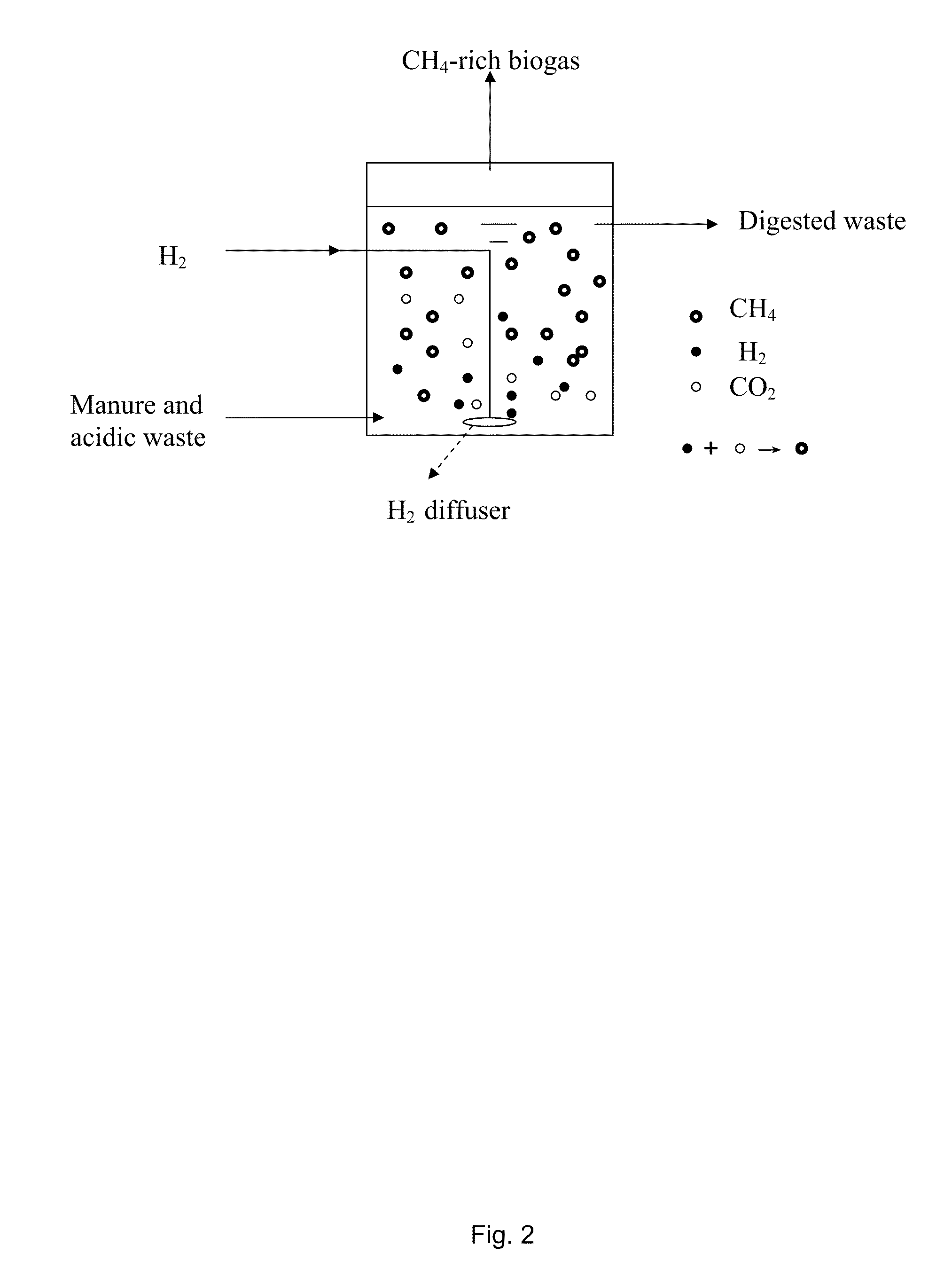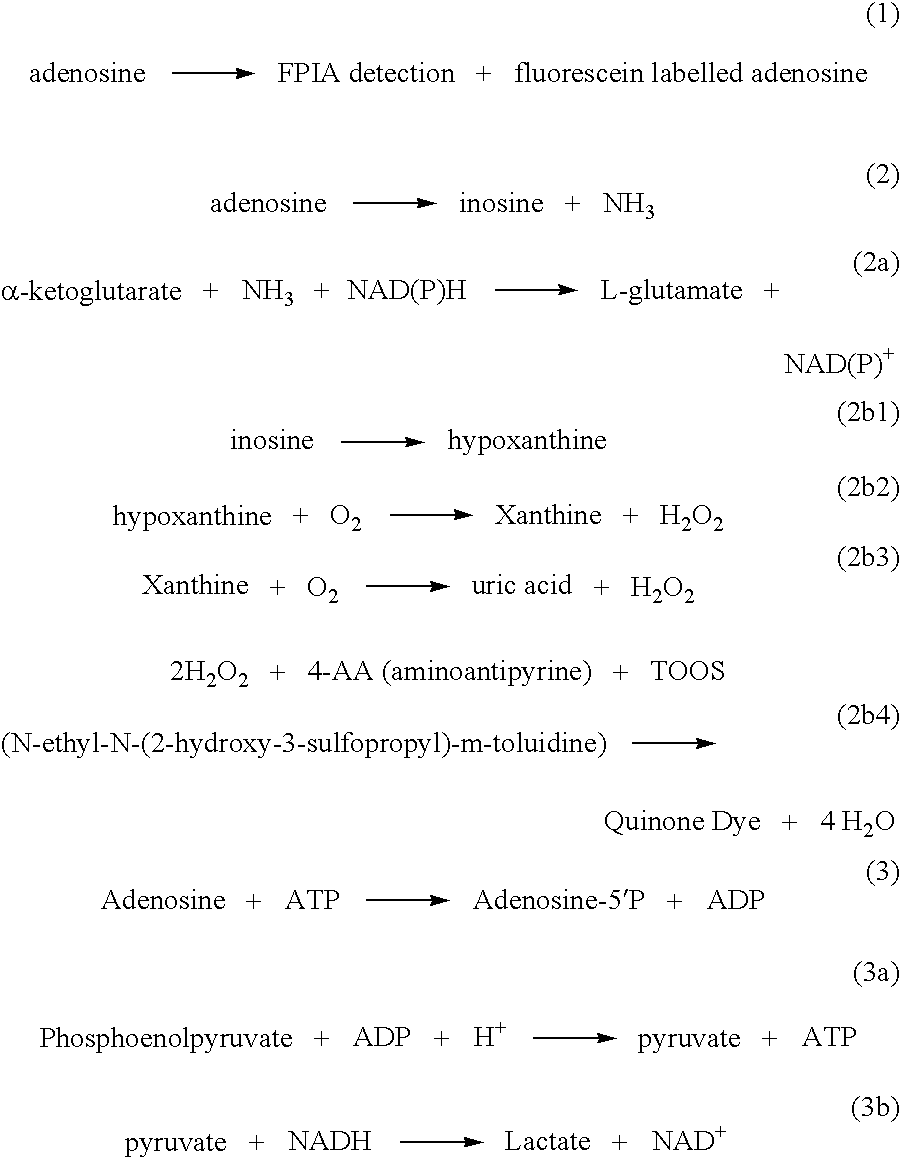Patents
Literature
72 results about "Co substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An organic substance that reversibly combines with a specific protein, the apoenzyme, and with a substrate to form an active enzyme system. co′en·zy·mat′ic (-zə-măt′ĭk) adj. co·en′zy·mat′i·cal·ly adv. co•en`zy•mat′ic (-zaɪˈmæt ɪk, -zɪ-) adj. co•en`zy•mat′i•cal•ly, adv.
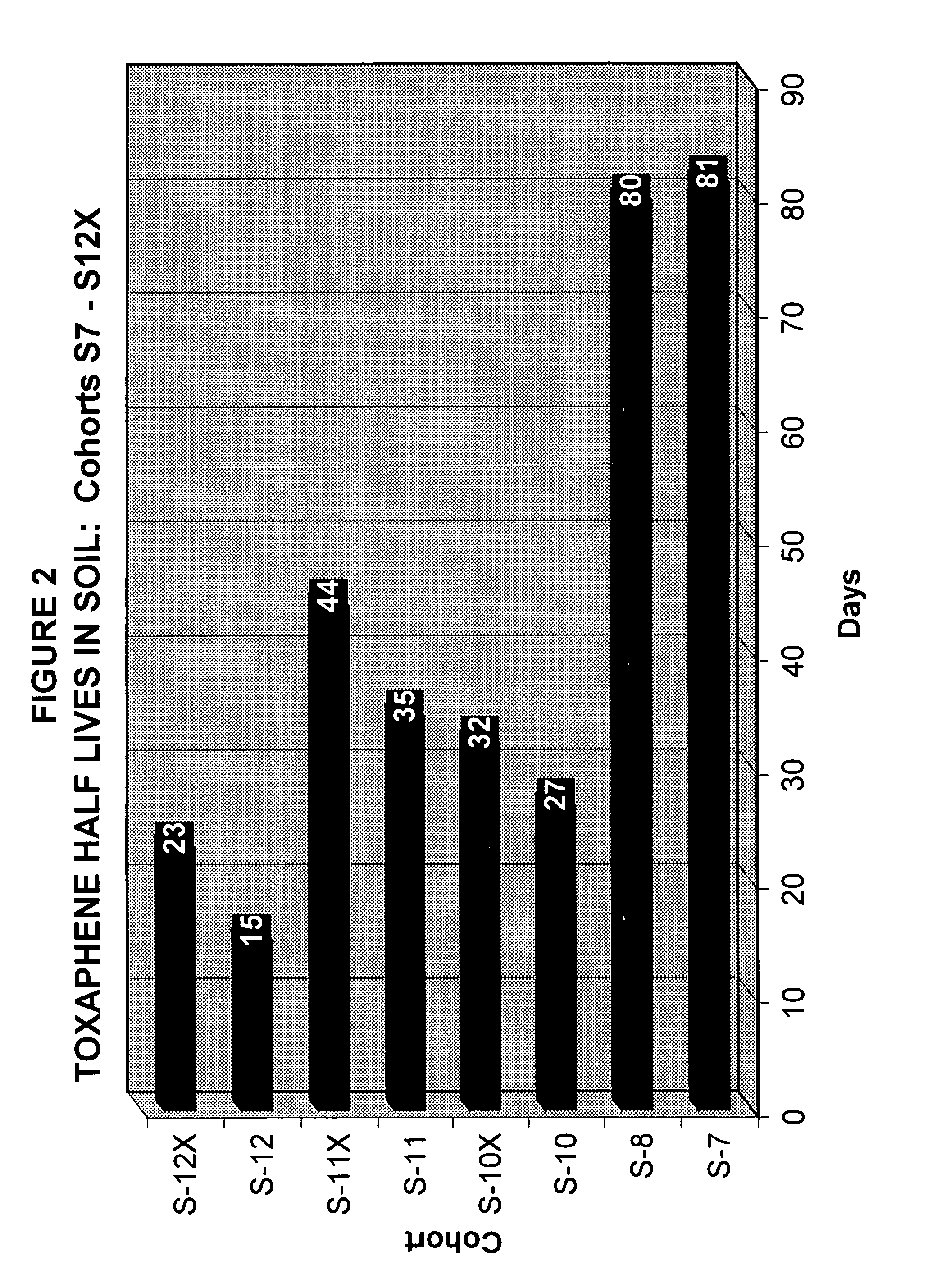
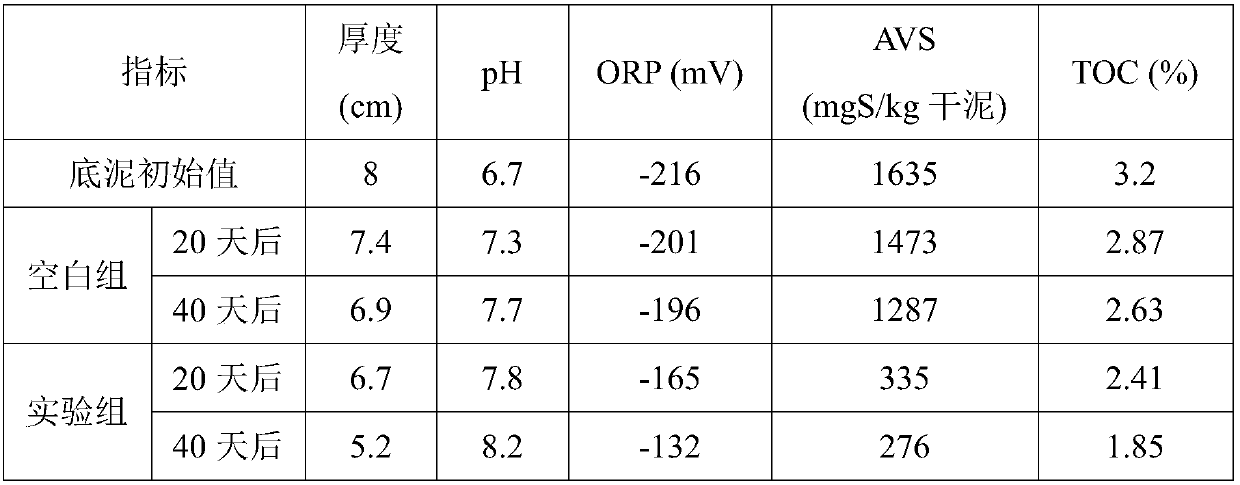
Method for the enhanced anaerobic bioremediation of contaminants in aqueous sediments and other difficult environments
InactiveUS6403364B1Easy to handleEasy to storeSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationBioremediationElectron
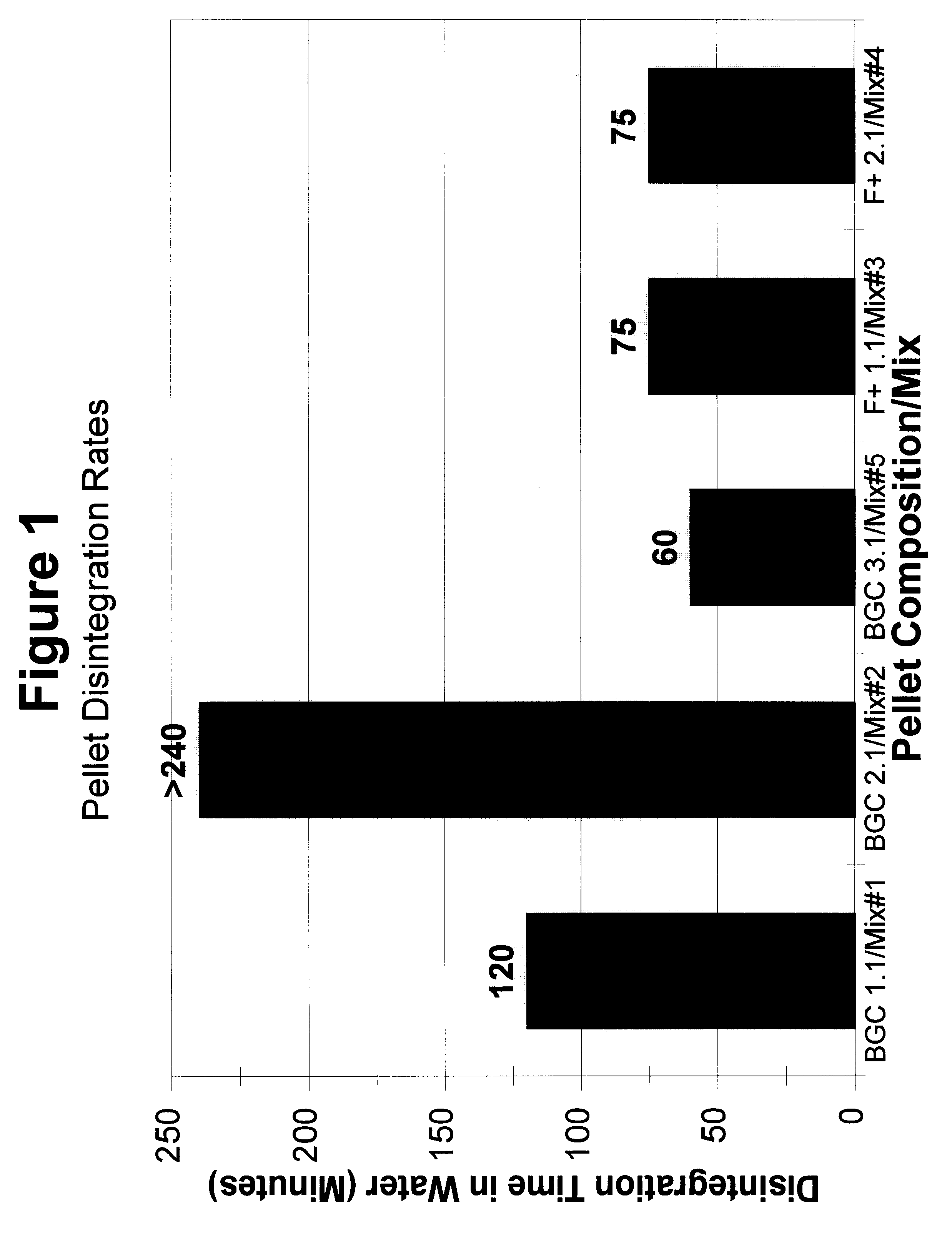
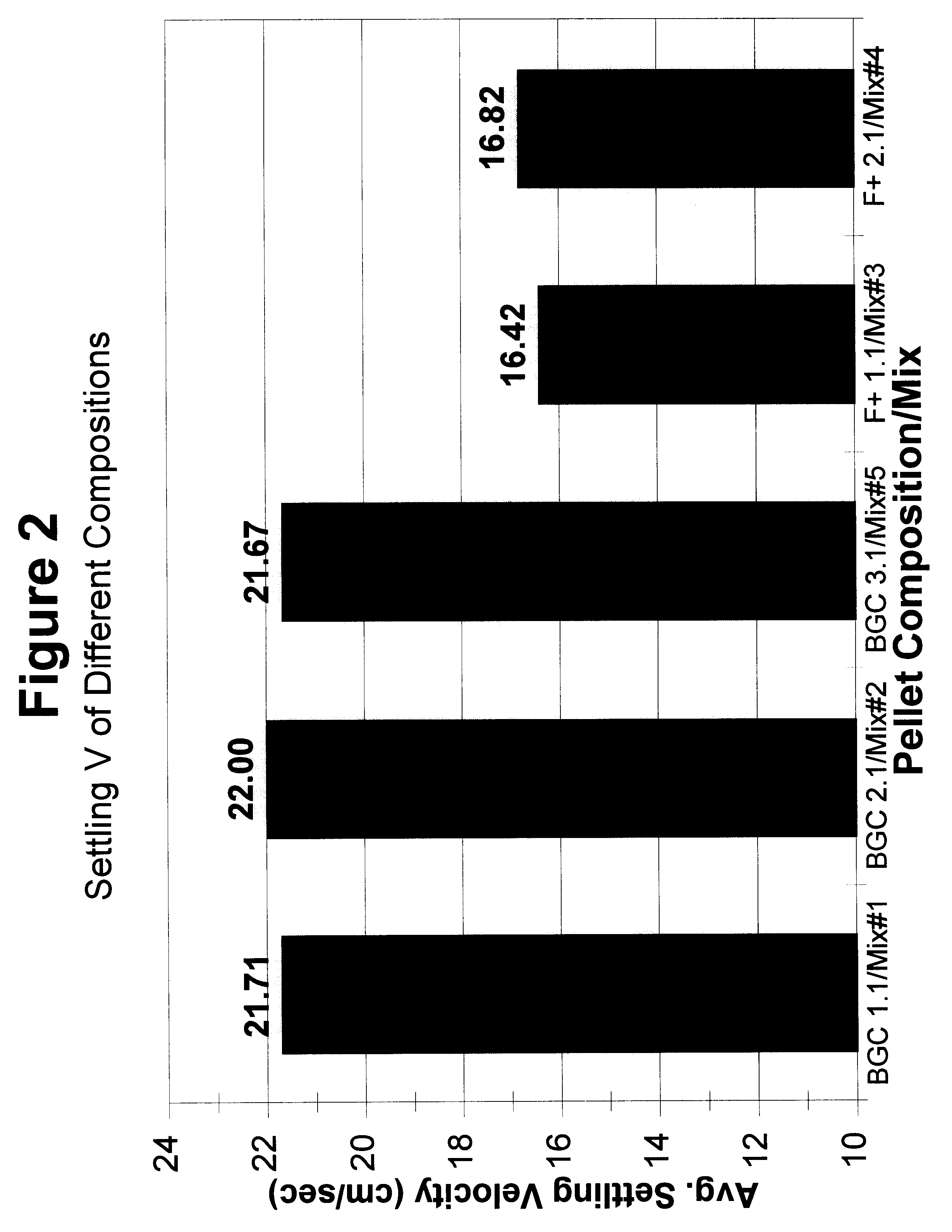
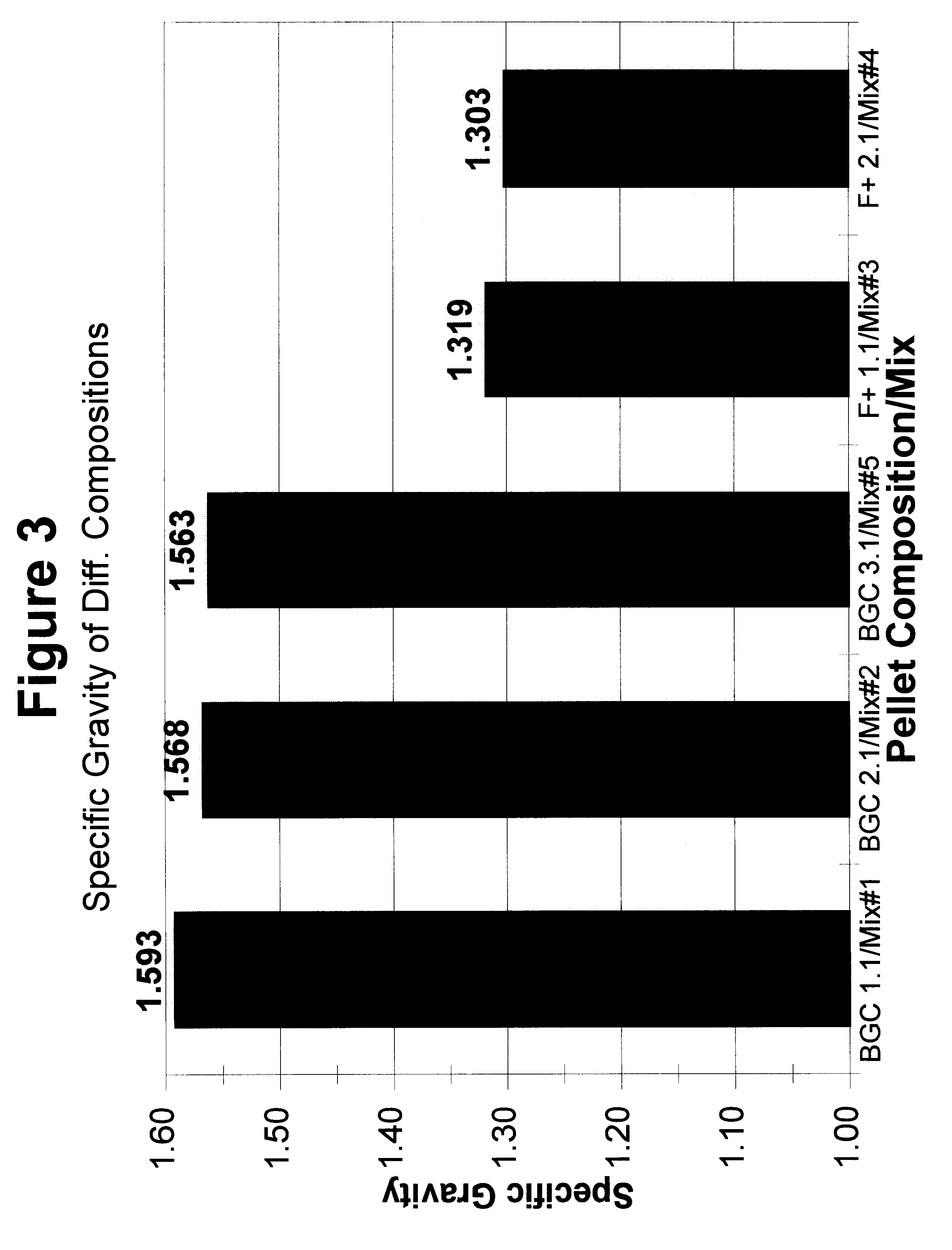
The present invention discloses the formulation and use of advanced solid-media chemical compositions in the preferred forms of pellets, tablets, capsules, or other similar forms which are designed and intended to enhance the removal of a broad range of recalcitrant organic and inorganic contaminants from a variety of difficult-to-treat environments, in particular, sediments beneath water bodies, by providing an improved means of promoting the anaerobic, biologically mediated degradation, transformation, and / or detoxification of the contaminants. Specific properties of the pellet, tablets, capsules, or other similar forms of the compositions are disclosed which enable the variation in the settling velocity of the compositions and hence the depth to which the compositions will penetrate the underlying contaminated sediments. The compositions comprise carbonaceous co-substrates, inorganic and organic anaerobic electron acceptors, organic and inorganic nutrients to promote the growth of contaminant-degrading microorganisms, and inoculum of naturally occurring microorganisms which act to promote the biodegradation of contaminants.
Owner:HINCE ERIC CHRISTIAN MR
Plant-fiber containing composition for anaerobic bioremediation
The present invention discloses the formulation and use of an advanced organic solid-media chemical composition designed and intended to enhance the removal of a broad range of contaminants in the environment by provided an improved means of promoting the anaerobic, biologically mediated degradation, transformation, and / or detoxification of the contaminants which may be present in solid and liquid wastes, soils, sediments, and water bodies. The invention provides for improved means of (i) promoting the solid-phase extraction and absorption of recalcitrant contaminants from contaminated media, (ii) creating, enhancing, and maintaining anaerobic conditions (i.e., negative Eh values), (iii) providing a source of carbonaceous co-substrates, anaerobic electron acceptors, and nutrient to promote the growth of contaminant-degrading microorganisms, and (iv) providing sources of inoculum of naturally occurring microorganisms which act to promote the biodegradation of contaminants.
Owner:HINCE ERIC CHRISTIAN MR
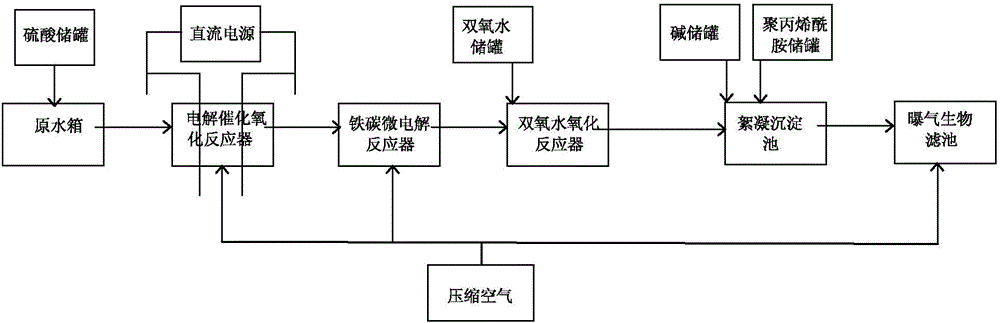
Treatment method for reverse osmosis concentrated water
ActiveCN104556533AImprove oxidation efficiencyLarge specific surface areaTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentElectrolysisReverse osmosis
The invention relates to a treatment method for reverse osmosis concentrated water, in particular to a standard treatment method for the reverse osmosis concentrated water which is produced during sewage reusing. The treatment method comprises the following steps: the pH value of the reverse osmosis concentrated water is regulated to be 2.0-4.0, and electrolytic catalysis oxidation is carried out; water produced from the electrolytic catalysis oxidation is subjected to redox reaction in an electrolytic reactor, which is filled with iron-carbon fillers obtained through sintering of iron and carbon; hydrogen peroxide is then added, so that oxygenolysis is further achieved; the pH value is regulated to be 6.0-8.0, and a flocculant is added for flocculent settling; a supernate obtained from the flocculent settling enters an aeration biological tank, and a co-substrate is added for biological degradation. The COD of the reverse osmosis concentrated water with lower biodegradability, which is obtained through reverse osmosis reusing treatment after standard biochemical treatment, is reduced from 70-200 milligrams per liter to below 50 milligrams per liter, so that the strictest local emission standards can be met.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
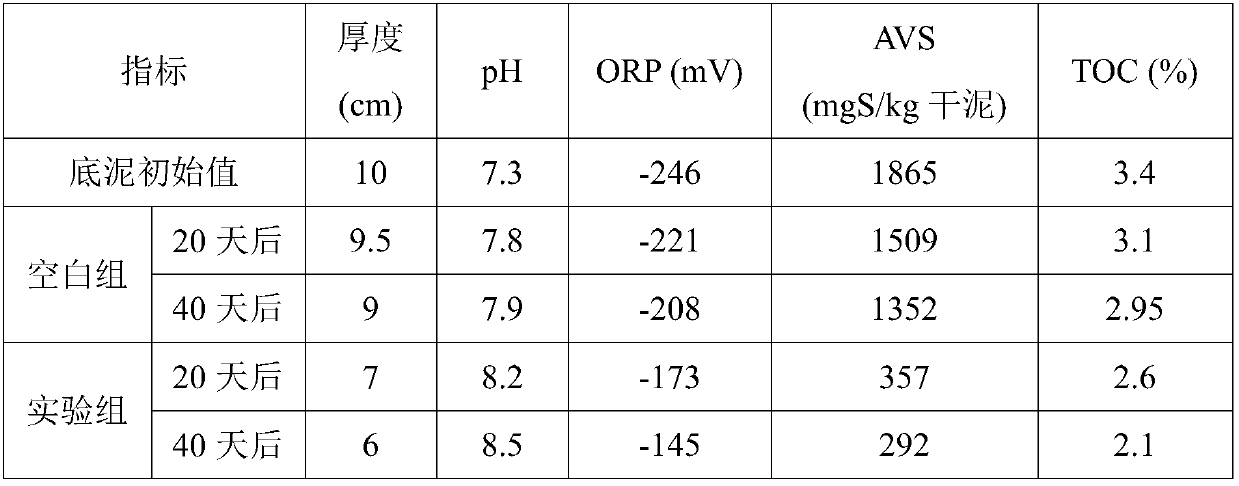
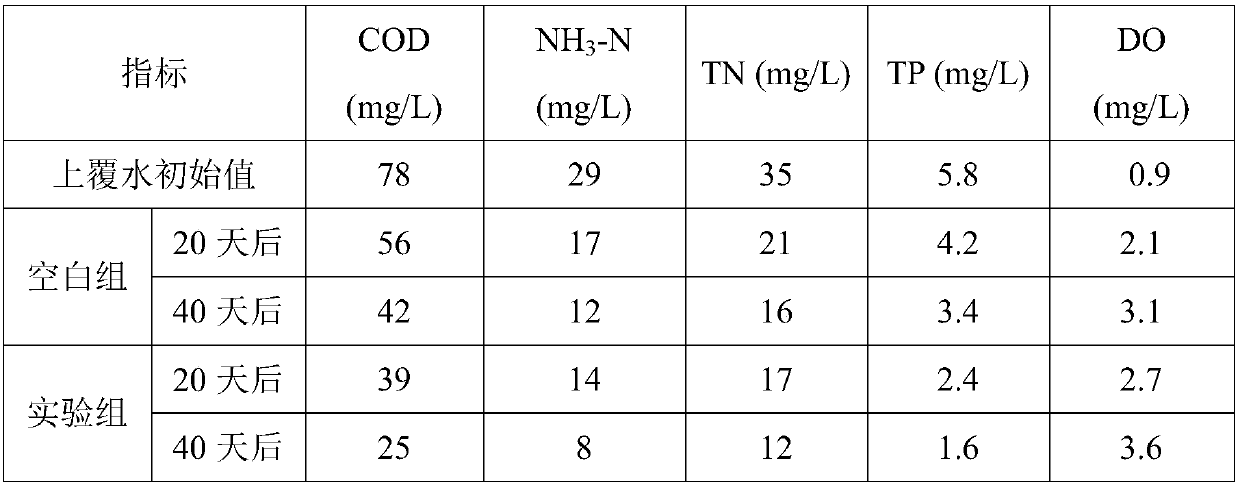
In-situ biochemical repairing agent for bottom mud of black and odorous water body, preparation method and repairing method
InactiveCN107651821AReduce pollutionPollution reduction effect The reduction effect is obviousWater treatment parameter controlSludge treatment by oxidationChemical treatmentBiology
The invention relates to an in-situ biochemical repairing agent for bottom mud of a black and odorous water body. The in-situ biochemical repairing agent is prepared from the following raw-material constituents in parts by weight: 30 to 40 parts of modified biological charcoal powder, 20 to 60 parts of aggregate, 15 to 20 parts of microbial bacterial agent and 10 to 15 parts of co-substrate. The biochemical repairing agent provided by the invention is combined with physical absorption, chemical treatment and biological treatment; all components have mutual synergistic effects; the effect of reducing the pollution by the bottom mud is obvious, wherein modified biological charcoal can be used for effectively adsorbing a heavy metal and part of organic matters, which are released by the bottom mud; diatomite and montmorillonite, which serve as the aggregate, on one hand, can be used for effectively adsorbing part of pollutants, and on the other hand, can be used for providing an attachment carrier for the growth of a microbe together with the modified biological charcoal at the same time; the co-substrate can be used for promoting the growth of the microbe and activating the activityof the microbial bacterial agent; the repairing agent for the bottom mud is spherical, is difficult to flow away along with water, and can sufficiently exert an effect, and in addition, the in-situ biochemical repairing agent for bottom mud, which is provided by the invention, is wide in material source and low in cost and has practical popularization and application conditions.
Owner:HUNAN YONKER ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION RES INST +1
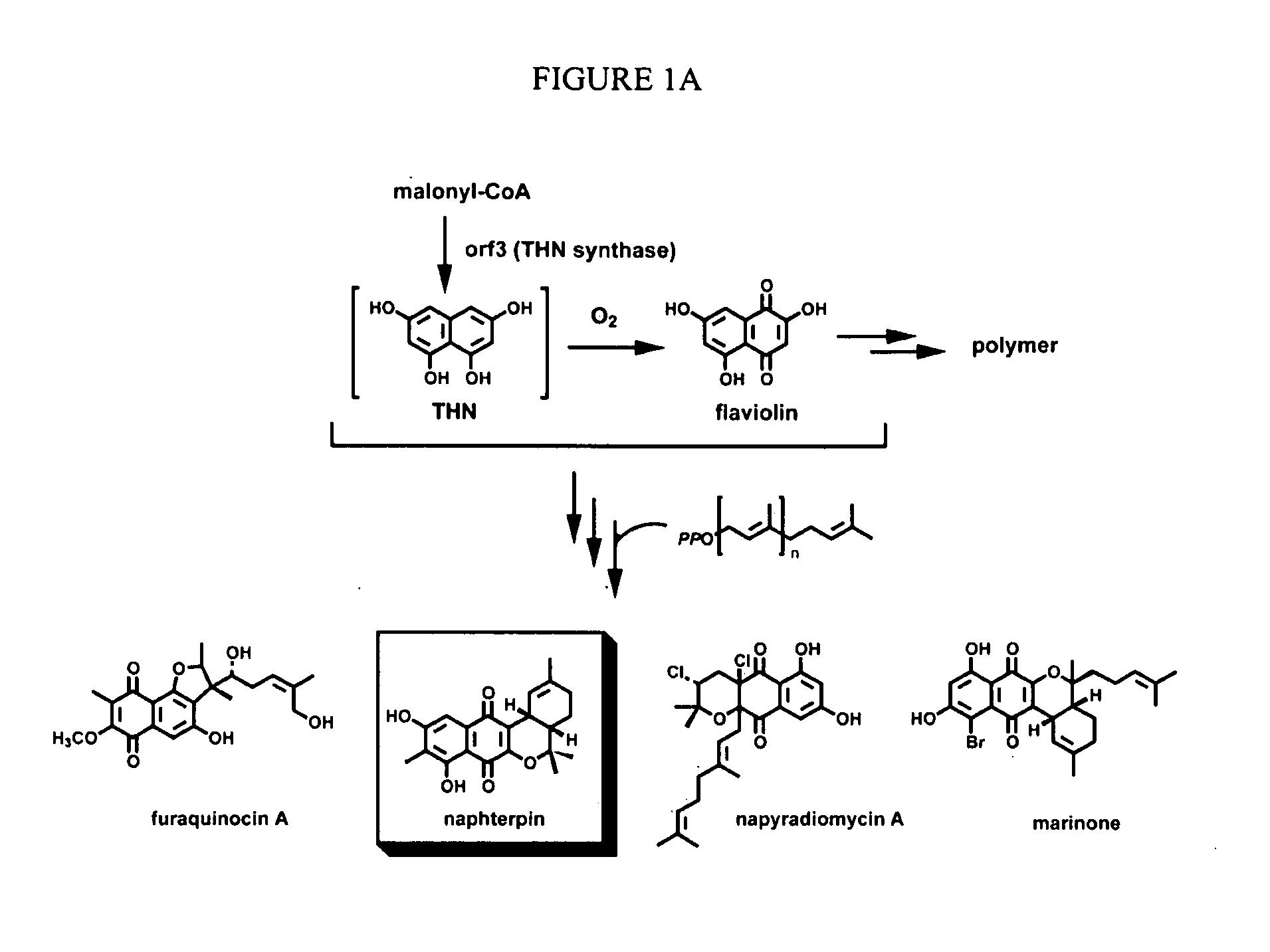
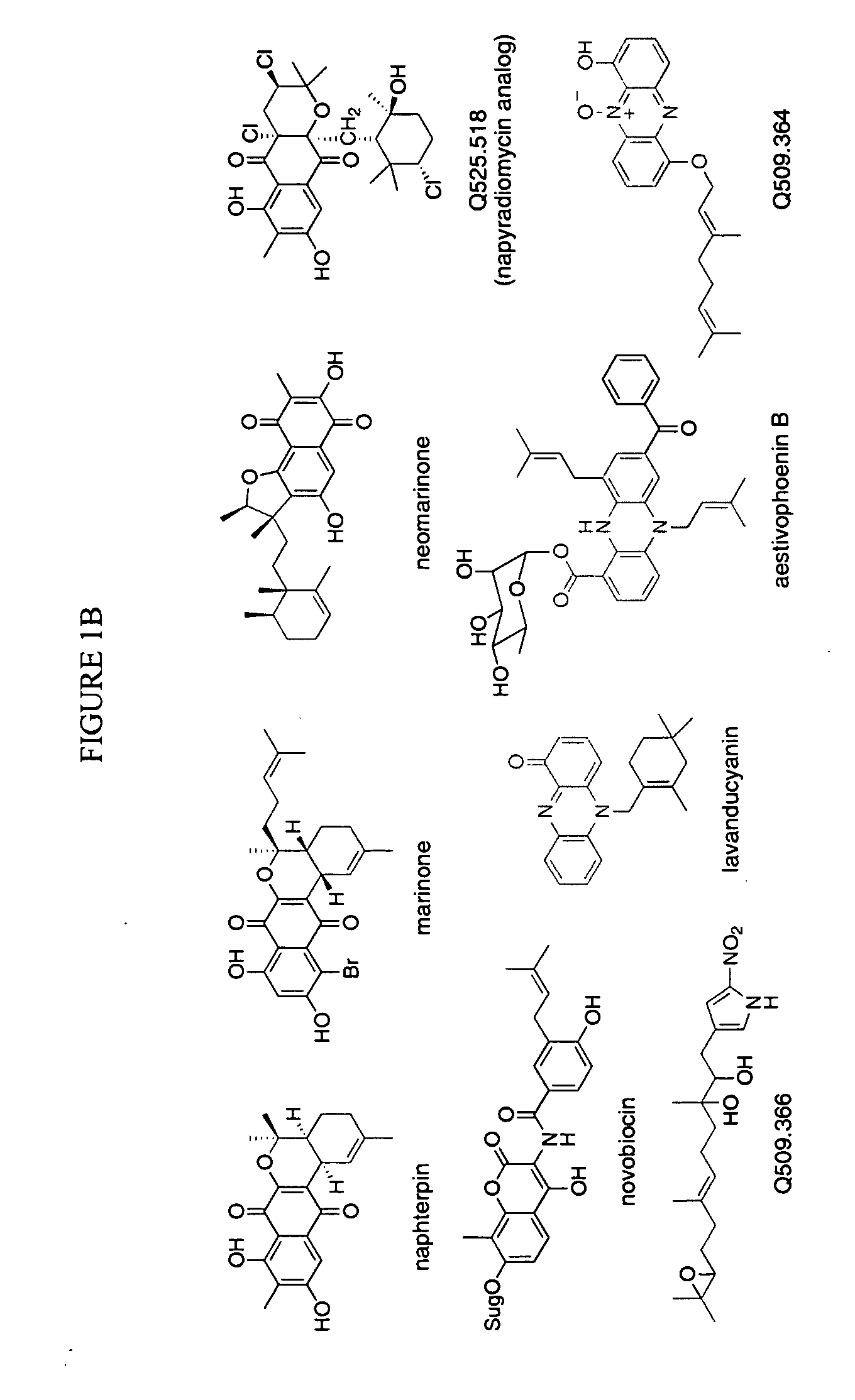
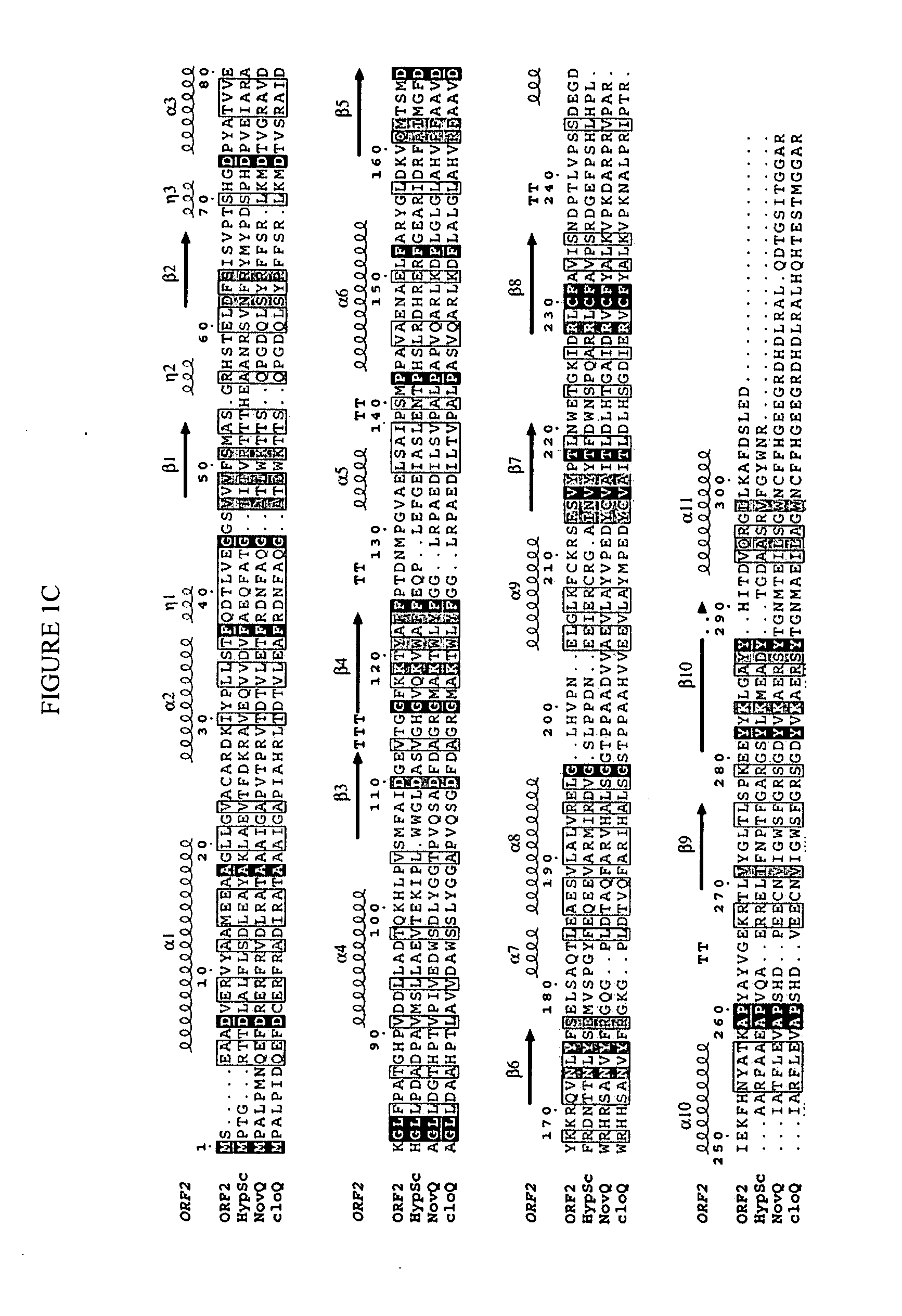
Novel aromatic prenyltransferases, nucleic acids encoding same and uses therefor
ActiveUS20060183211A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPrenyltransferase activityIsoprene
In accordance with the present invention, a novel aromatic prenyltransferase, Orf2 from Streptomyces sp. strain CL190, involved in naphterpin biosynthesis has been identified and the structure thereof elucidated. This prenyltransferase catalyzes the formation of a C—C bond between a prenyl group and a compound containing an aromatic nucleus, and also displays C—O bond formation activity. Numerous crystallographic structures of the prenyltransferase have been solved and refined, e.g., (1) prenyltransferase complexed with a buffer molecule (TAPS), (2) prenyltransferase as a binary complex with geranyl diphosphate (GPP) and Mg2+, and prenyltransferase as ternary complexes with a non-hydrolyzable substrate analogue, geranyl S-thiolodiphosphate (GSPP) and either (3) 1,6-dihydroxynaphthalene (1,6-DHN), or (4) flaviolin (i.e., 2,5,7-trihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, which is the oxidized product of 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene (THN)). These structures have been solved and refined to 1.5 Å, 2.25 Å, 1.95 Å and 2.02 Å, respectively. This first structure of an aromatic prenyltransferase displays an unexpected and non-canonical (β / α)-barrel architecture. The complexes with both aromatic substrates and prenyl containing substrates and analogs delineate the active site and are consistent with a proposed electrophilic mechanism of prenyl group transfer. These structures also provide a mechanistic basis for understanding prenyl chain length determination and aromatic co-substrate recognition in this structurally unique family of aromatic prenyltransferases. This structural information is useful for predicting the aromatic prenyltransferase activity of proteins.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Methods and Apparatus for Hydrogen Based Biogas Upgrading
ActiveUS20140342426A1Raise the pHSustained and high-performing processBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberHollow fibre membrane
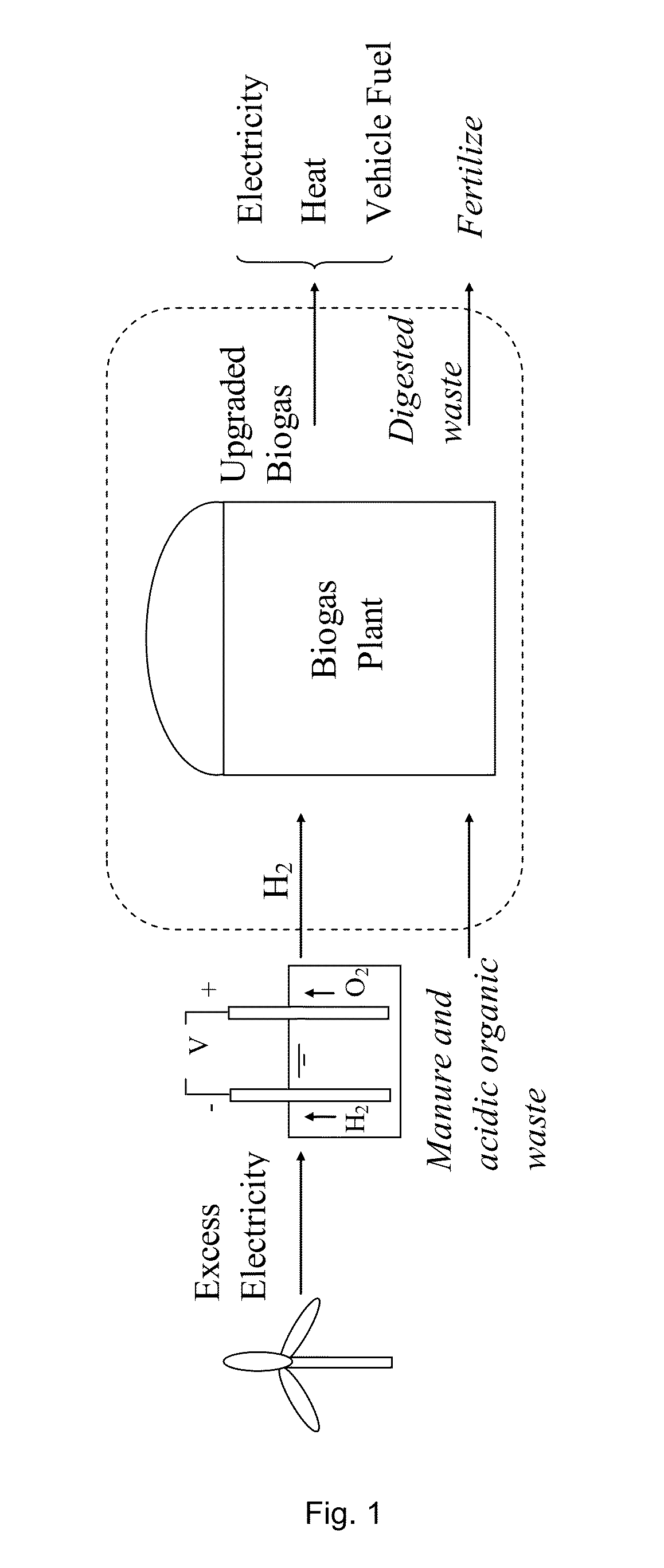
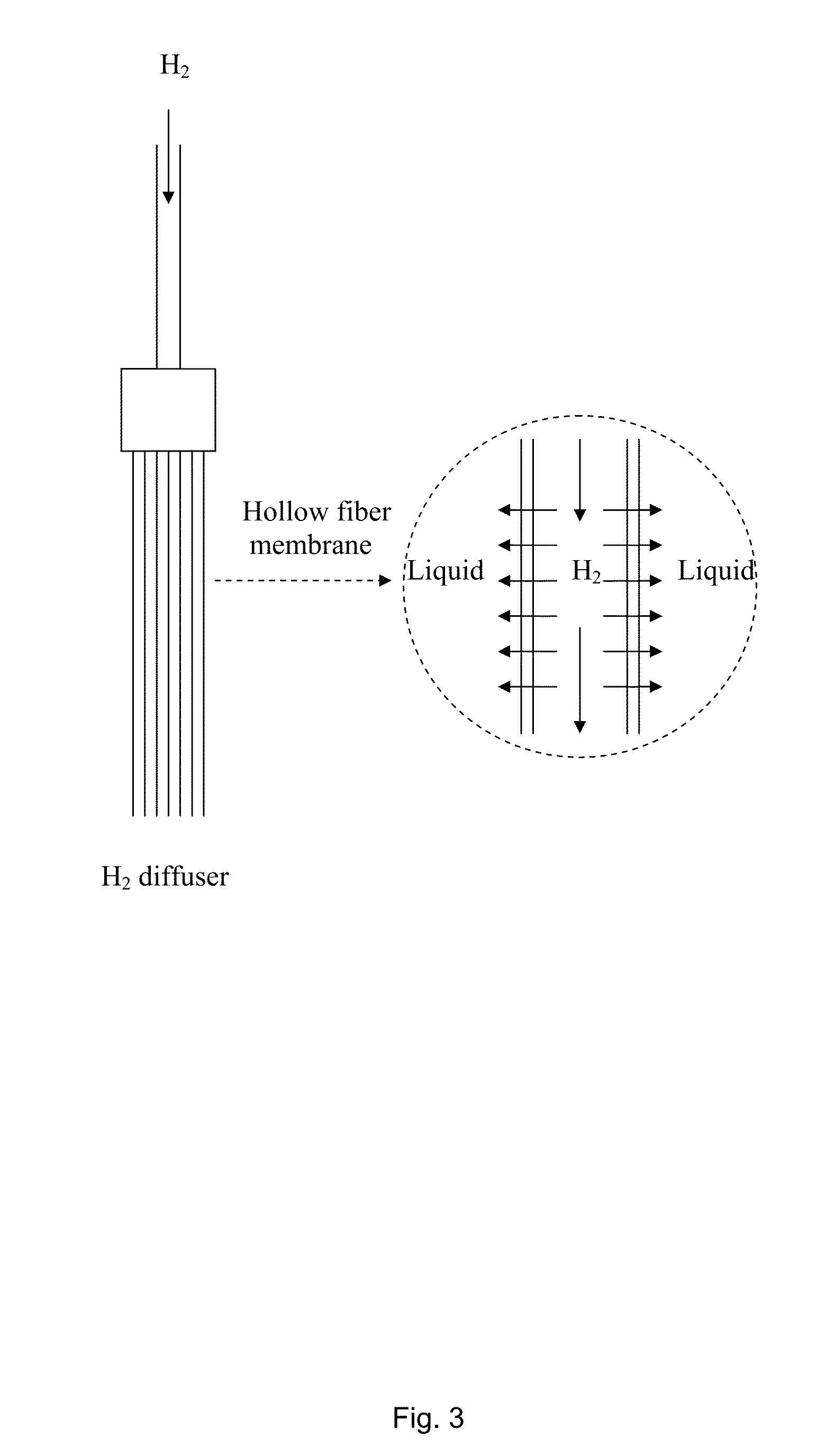
The present invention relates to an anaerobic process for biogas upgrading and hydrogen utilization comprising the use of acidic waste as co-substrate. In this process, H2 and CO2 will be converted to CH4, which will result in lower CO2 content in the biogas. The invention relates to both in situ and ex situ methods of biogas upgrading. The invention further relates to a bioreactor comprising hollow fibre membranes.
Owner:VESTFORSYNING +1
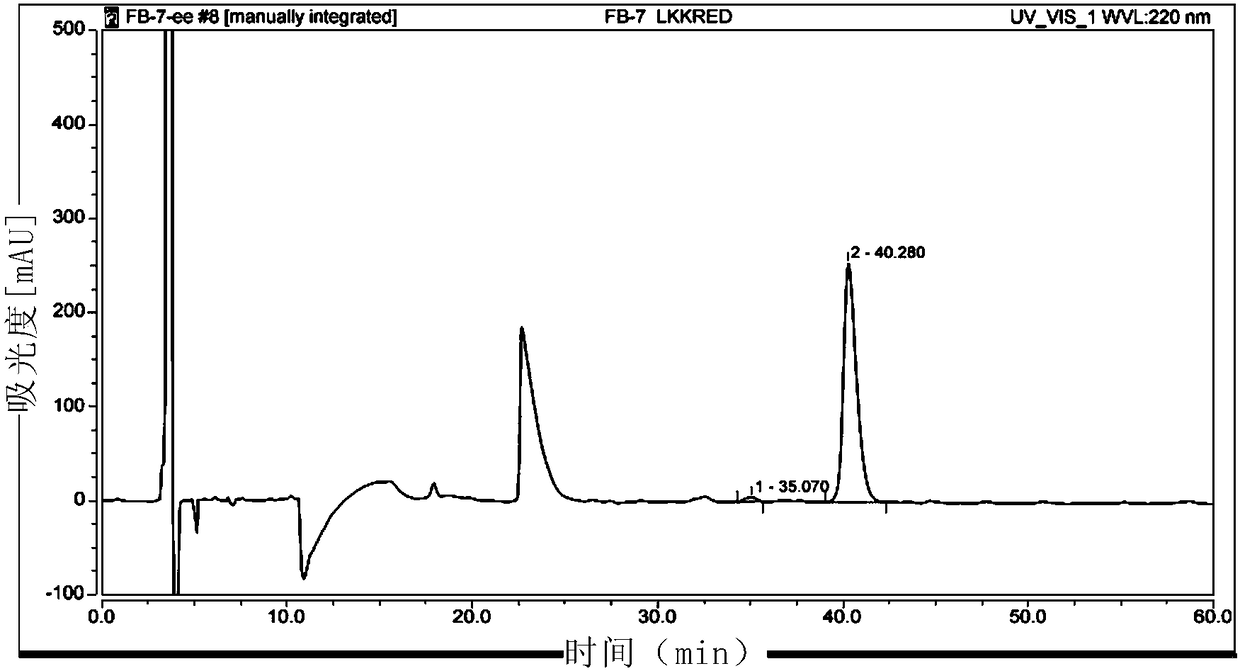
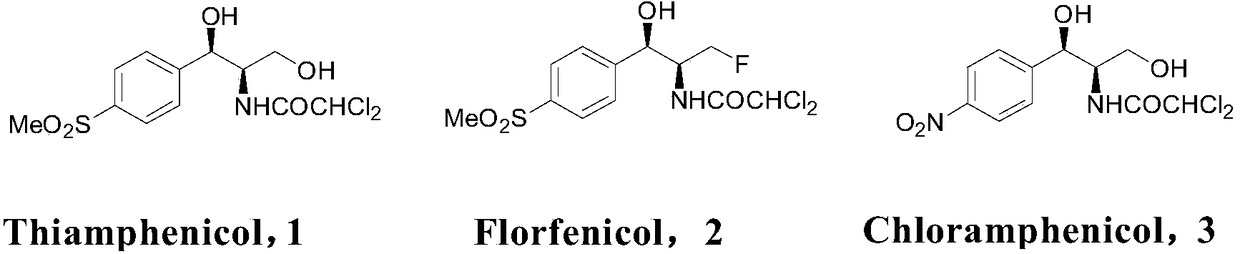
Biological preparation of key intermediate of thiamphenicol and florfenicol
The invention provides a biological preparation method of a key intermediate of thiamphenicol and florfenicol. Specifically, the method of the present invention comprises the following steps: (a) in aliquid reaction system, a reaction represented by formula A is carried out in the presence of a coenzyme and catalyzed by a carbonyl reductase, using compound X as a substrate, thereby forming compound Y; and (b) optionally separating the compound Y from the reaction system after the reaction of the previous step. The invention also provides a reaction system comprising: (i) an aqueous solvent; (ii) a substrate, said substrate being the compound X; (iii) coenzyme; (iv) carbonyl reductase; (v) a co-substrates; and (vi) enzymes for coenzyme regeneration.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
Method for the enzymatic production of chiral alcohols
A method of producing a chiral secondary alcohol in which a biotransformation composition containing a ketone of the formula (I),R1 and R2 being different and each being an organic radical, an oxidoreductase and a co-substrate is reacted to form a chiral secondary alcohol with the adsorbent being associated with the oxidoreductase. The adsorbent associated with the oxidorecutase is separated off from the biotransformation composition after completion of the reaction.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
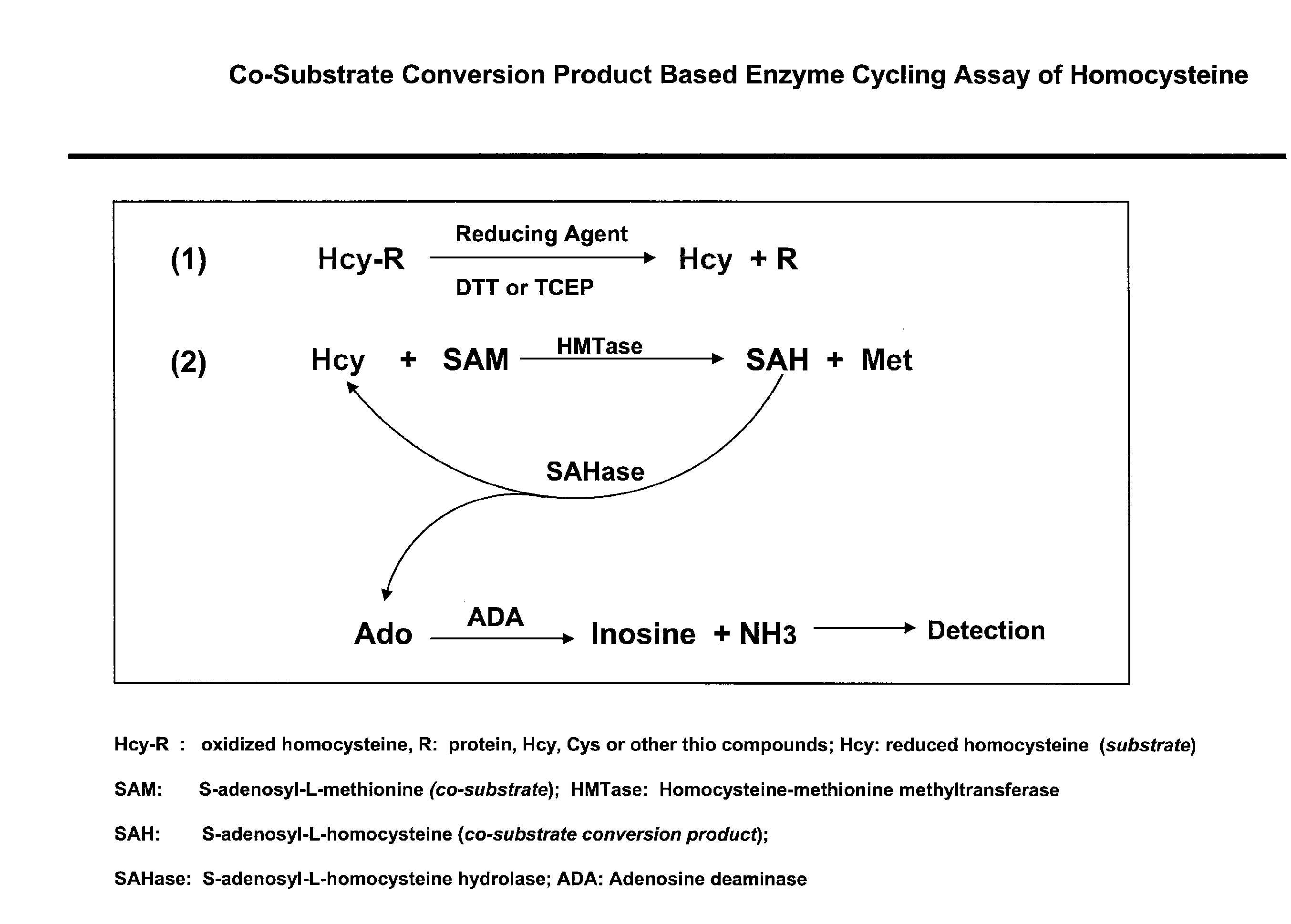
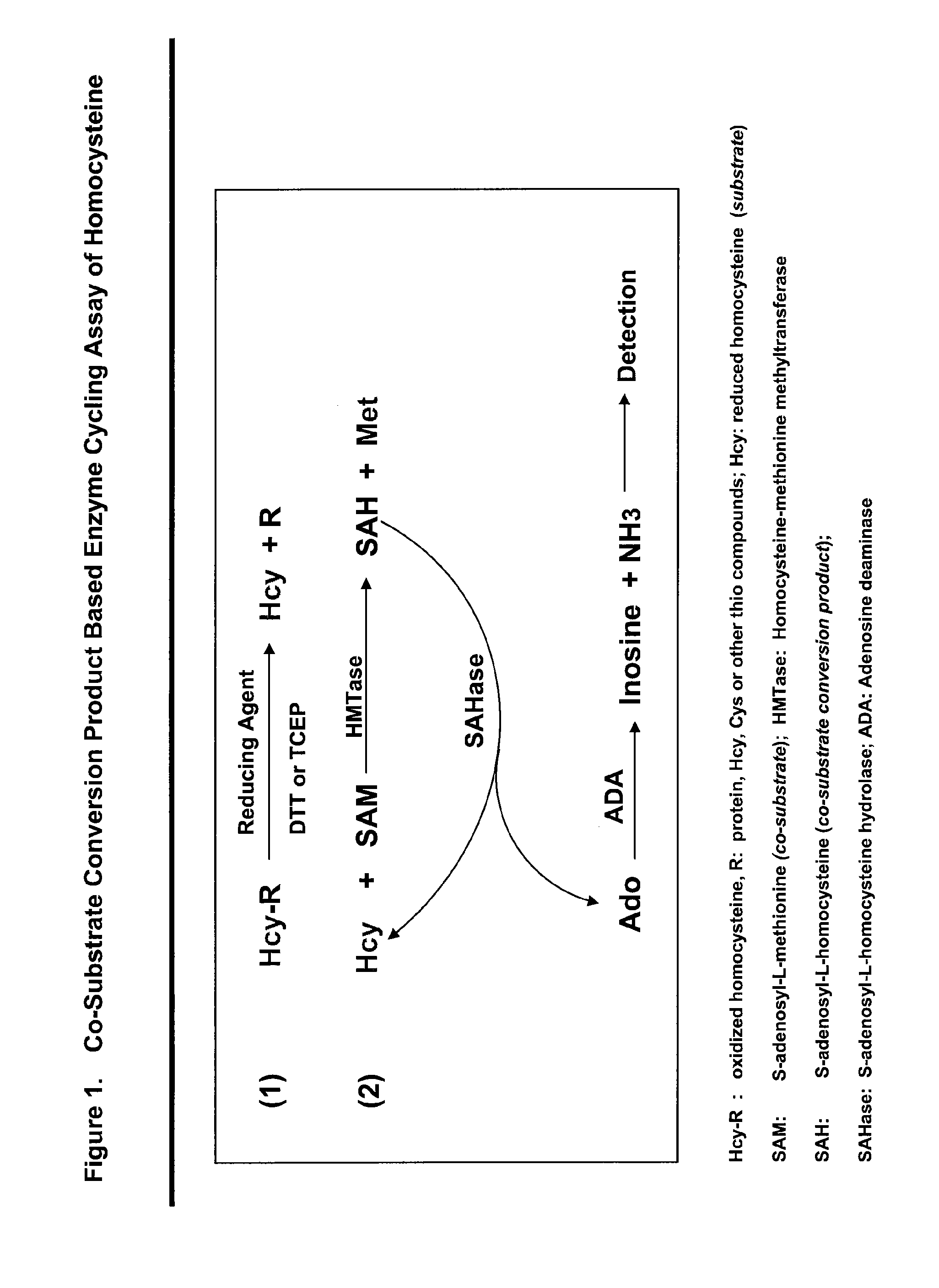
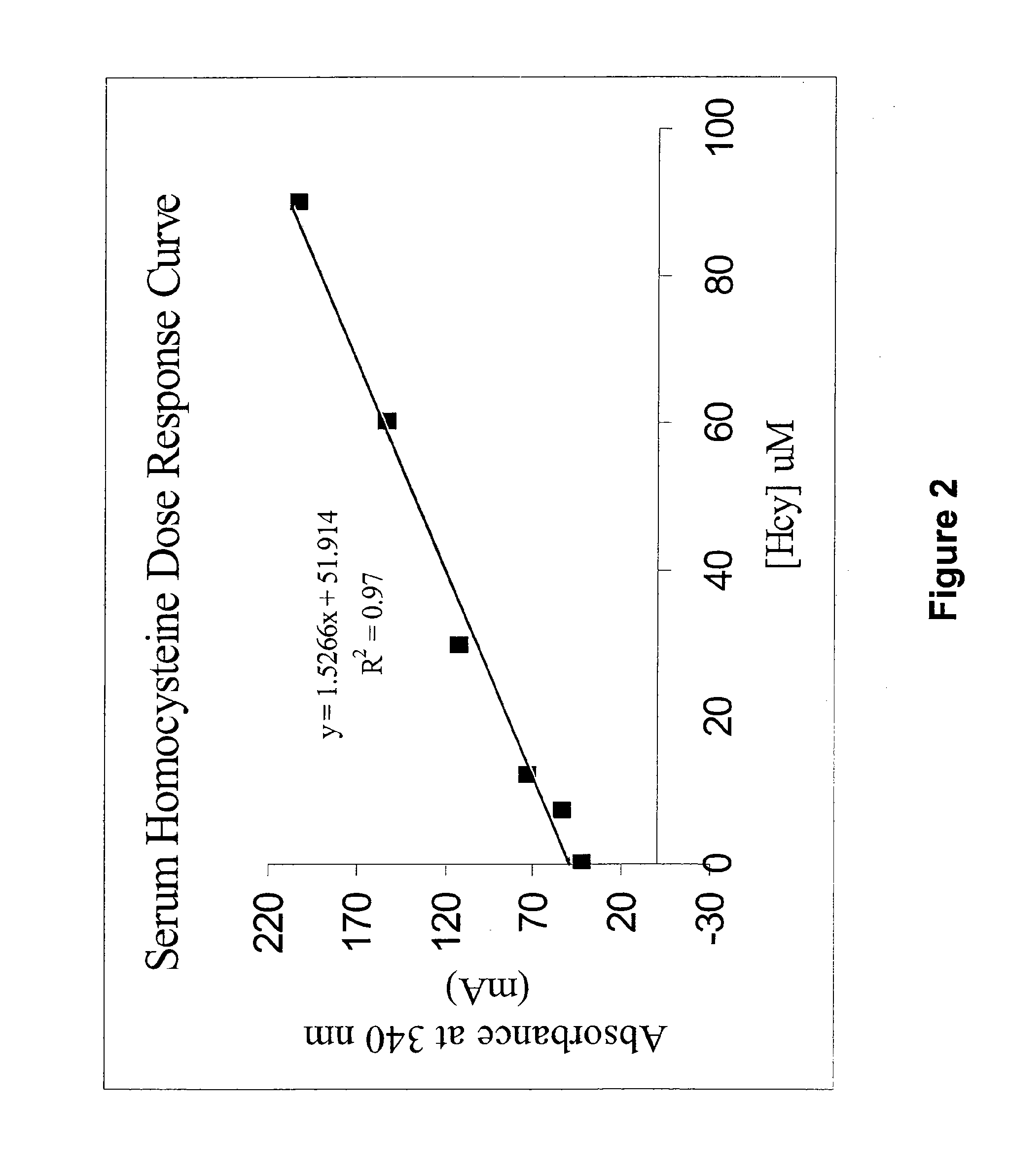
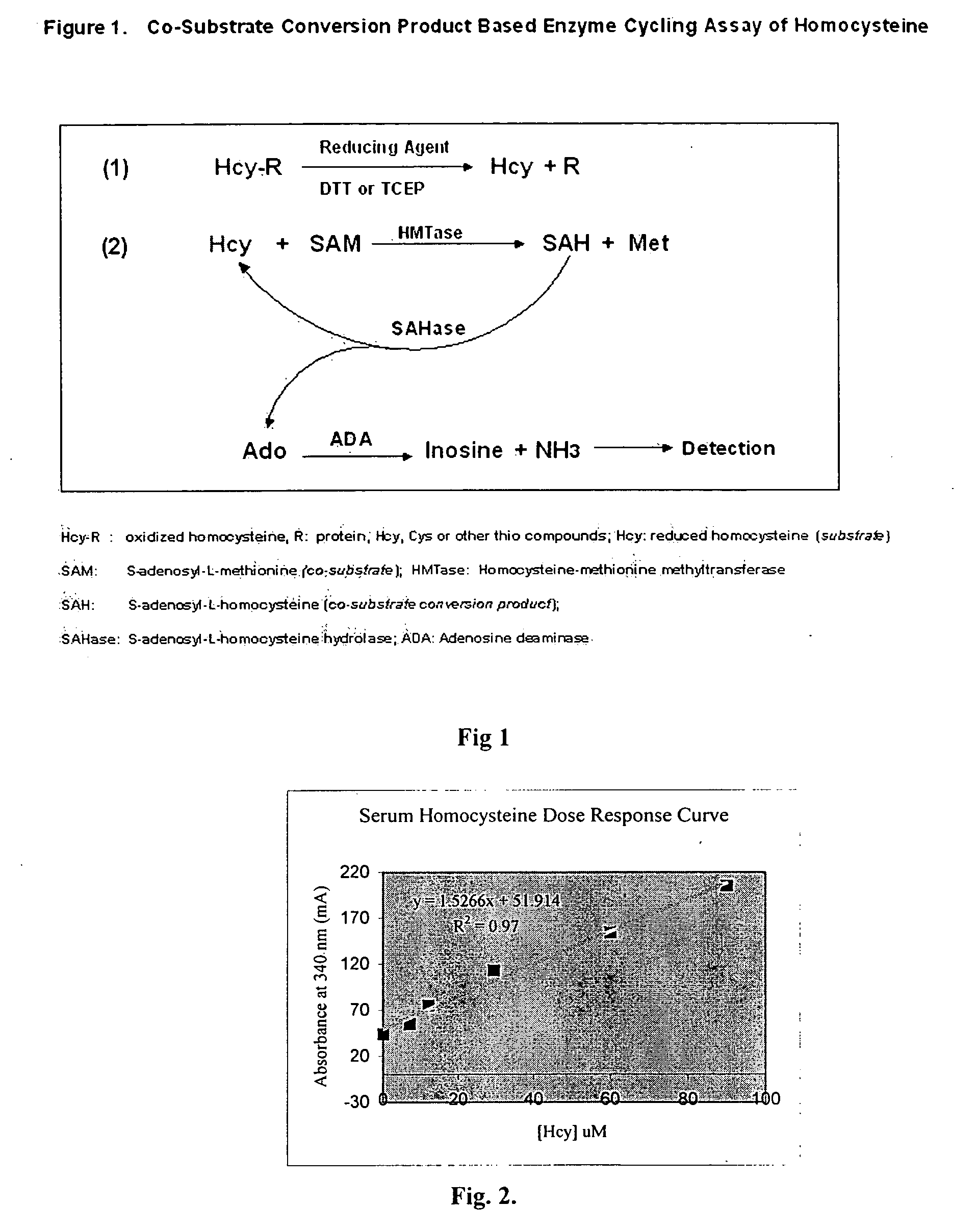
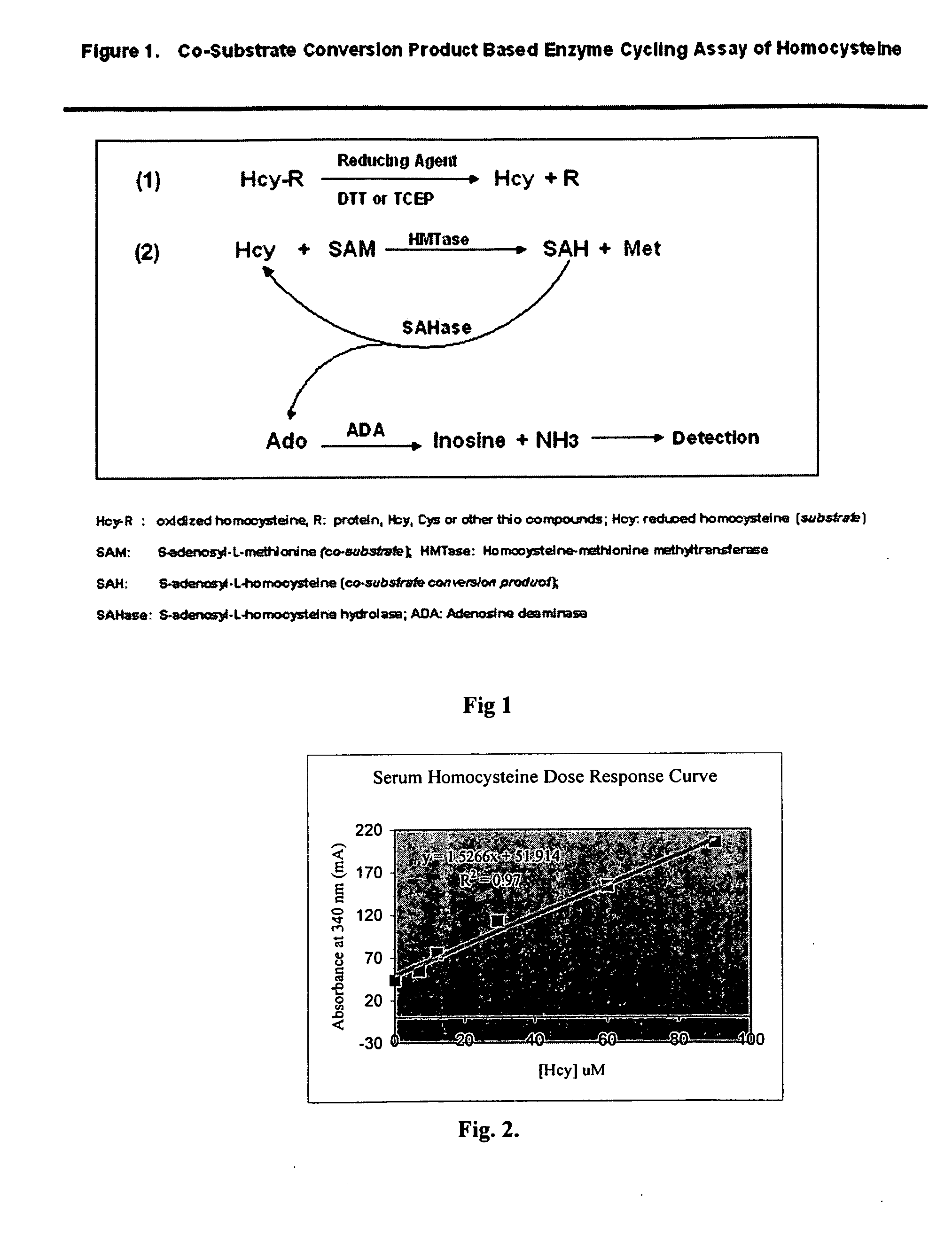
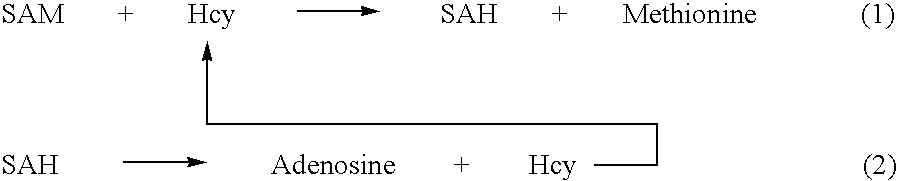
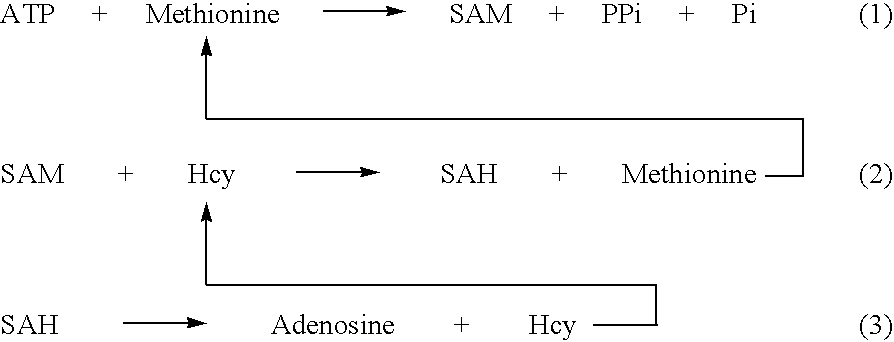
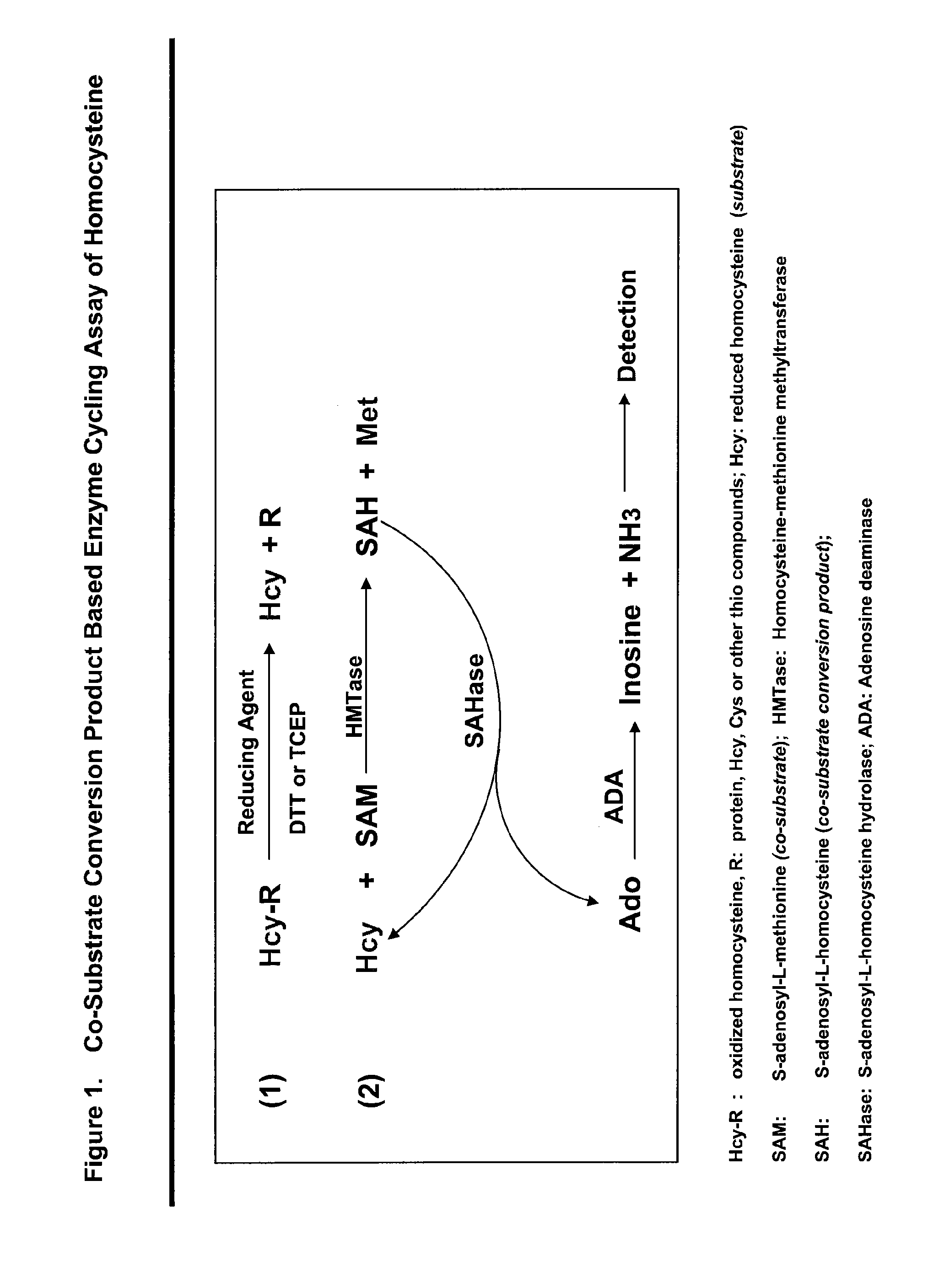
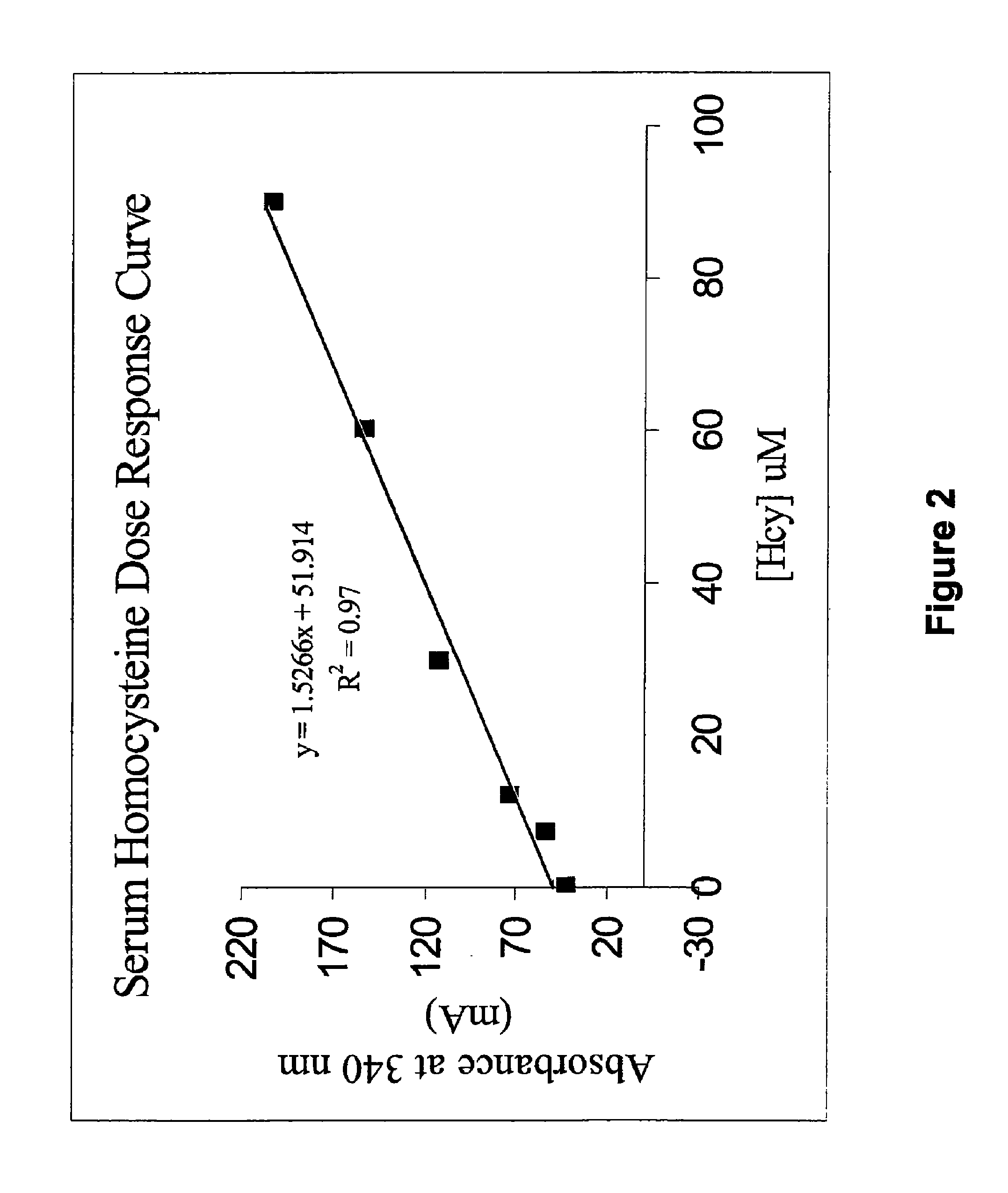
Methods and compositions for assaying homocysteine
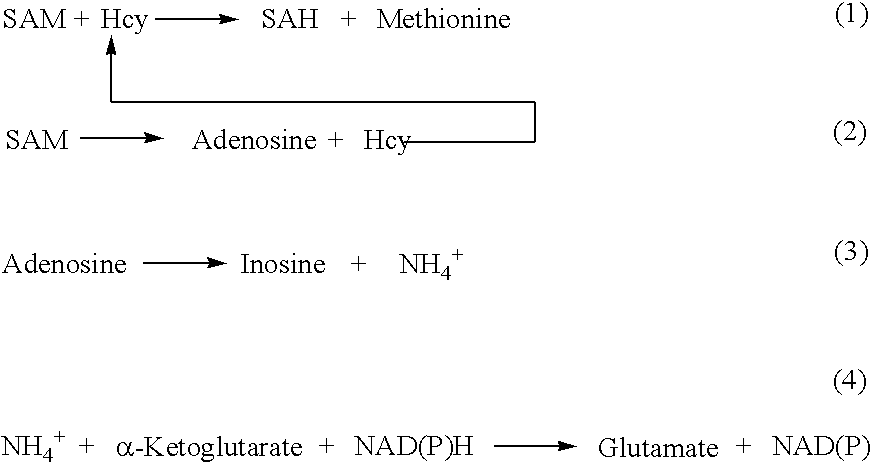
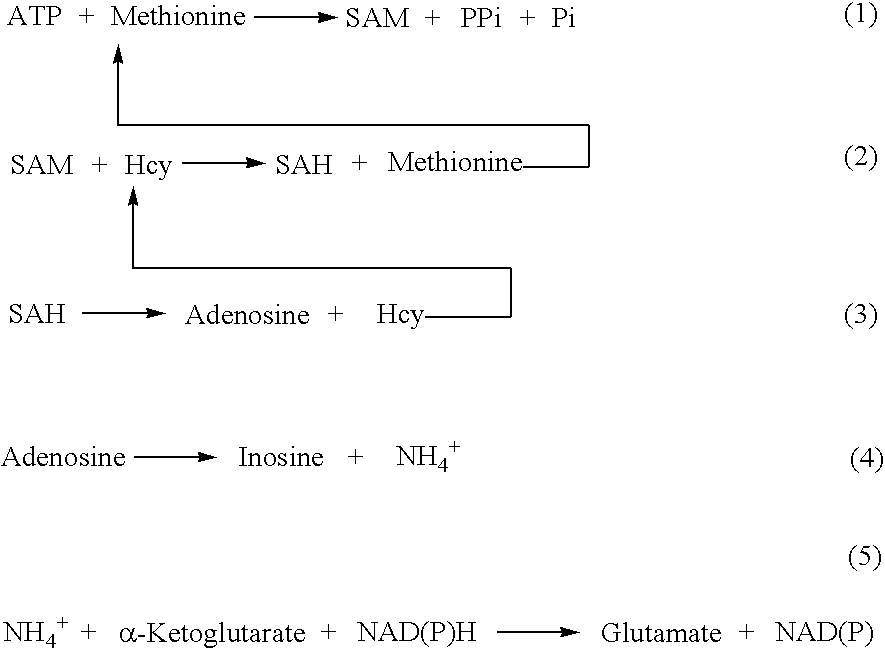
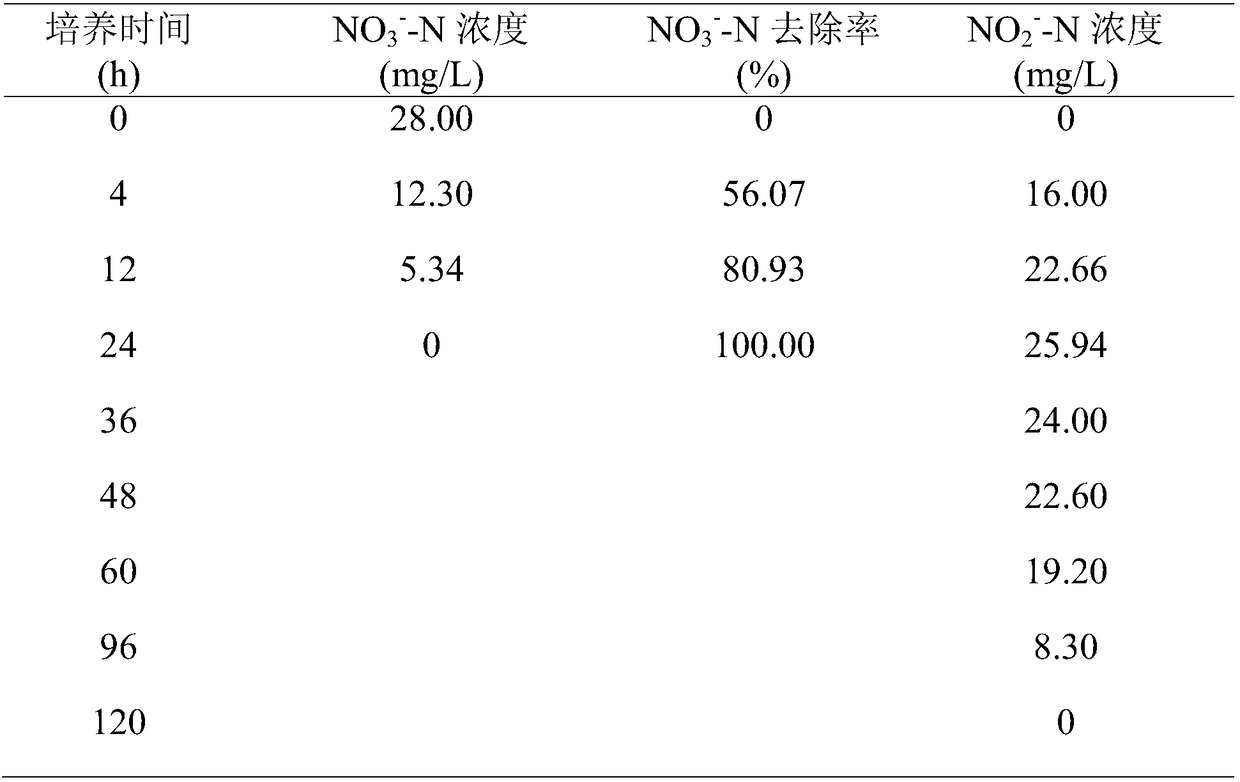
ActiveUS20080305507A1Improve automationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCo substrateHomocysteine
This invention relates generally to the field of homocysteine detection. In particular, the invention provides a method for determining homocysteine presence or concentration in samples, which method comprises: contacting a sample containing or suspected of containing Hcy with a Hcy co-substrate and a Hcy converting enzyme in a Hcy conversion reaction to form a Hcy conversion product and a Hcy co-substrate conversion product; and assessing the Hcy co-substrate conversion product to determine the presence, absence and / or amount of the Hcy in the sample. The Hcy co-substrate conversion product may be assessed directly, or it may be assessed by further conversion of the Hcy co-substrate conversion product into another material by the action of one or more additional enzymes. A kit for assaying homocysteine based on the same principle is also provided.
Owner:DIAZYME LAB INC
White rot fungus biological microsphere and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106011124AStrong ReusabilityHigh reuse rateMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierTextile printerBiotechnology
The invention relates to a white rot fungus biological microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a plant straw powder and white rot fungus co-substrate body, preparing a white rot fungus biological microsphere, and embedding the plant straw powder and white rot fungus co-substrate body in the white rot fungus biological microsphere. The biological microsphere prepared in the invention solves the problems of low wastewater treatment stability of white rot fungi and consumption of a nutrient matrix source by immobilized white rot fungi, can be used to great wastewater generated in the leather making industry, the fur industry and the textile printing and dyeing industry, and has the advantages of no need of an applied nutrient source, strong environment adaptability, strong degradation ability, non-toxicity and no hidden safety troubles.
Owner:山东济清科技服务有限公司
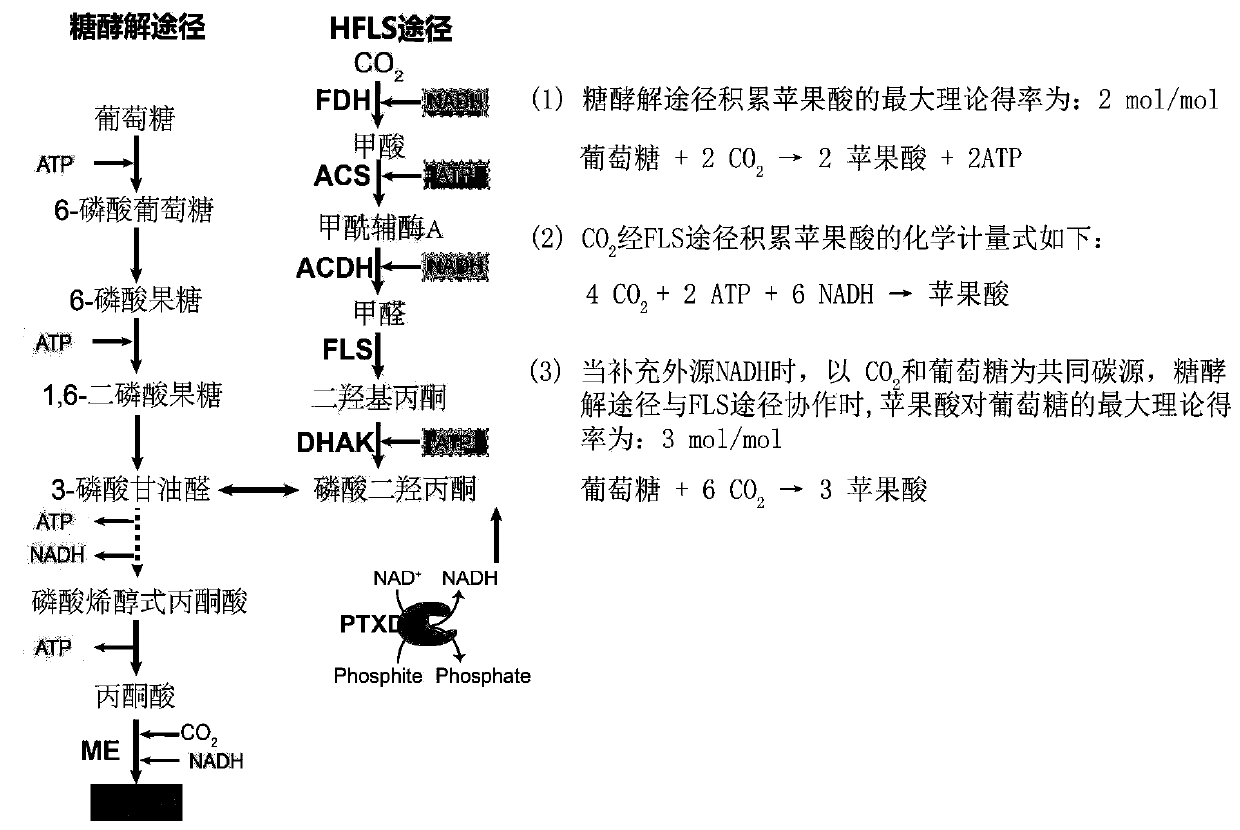
Construction and application of Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for immobilizing CO2 and producing malic acid
ActiveCN110951660APromote accumulationIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliPhosphorous acid
The invention discloses construction and application of Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for immobilizing CO2 and producing malic acid, and belongs to the field of fermentation. The engineeringbacterium is a strain obtained by carrying out gene engineering modification on Escherichia coli MG1655. The genetic engineering transformation is as follows: 1, knocking out a fumarate reductase gene, a fumarase gene, a lactic dehydrogenase gene and an ethanol dehydrogenase gene, and carrying out free over-expression on formate dehydrogenase, acetyl coenzyme A synthetase, acylated acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, formaldehyde lyase, dihydroxyacetone kinase, malic enzyme and phosphorous acid oxidordeuctase so as to obtain a strain GH0407. The strain is used for fermentation production of malic acid, CO2 and glucose are used as co-substrates for anaerobic fermentation for 72 h, the malic acid yield reaches 39 g / L, the yield is 1.53 mol / mol, and malic acid is not accumulated in an original starting strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Methods and compositions for assaying homocysteine
This invention relates generally to the field of homocysteine detection. In particular, the invention provides a method for determining homocysteine presence or concentration in samples, which method comprises: contacting a sample containing or suspected of containing Hcy with a Hcy co-substrate and a Hcy converting enzyme in a Hcy conversion reaction to form a Hcy conversion product and a Hcy co-substrate conversion product; and assessing the Hcy co-substrate conversion product to determine the presence, absence and / or amount of the Hcy in the sample. A kit for assaying homocysteine based on the same principle is also provided.
Owner:DIAZYME LAB INC
Bio-preparation method for (R)-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl) phenyl ethanol
The invention provides a bio-preparation method for (R)-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl) phenyl ethanol (I). The method specifically comprises the following steps: (a) an asymmetric reduction reaction is performed in a liquid reaction system with a compound shown in the formula II as a substrate in presence of a coenzyme under catalysis of carbonyl reductase, and a compound shown in the formula I is prepared, wherein in the reaction system, the concentration of the compound shown in the formula II is 50-1,000 g / L; (b) the compound shown in the formula I is optionally separated from the reaction system subjected to the reaction in the step (a). The invention further provides the reaction system. The reaction system comprises (i) a waterborne solution, (ii) the substrate which is the compound shown in the formula II, (iii) the coenzyme, (iv) carbonyl reductase, (v) a co-substrate and (vi) an enzyme for regenerating the coenzyme.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
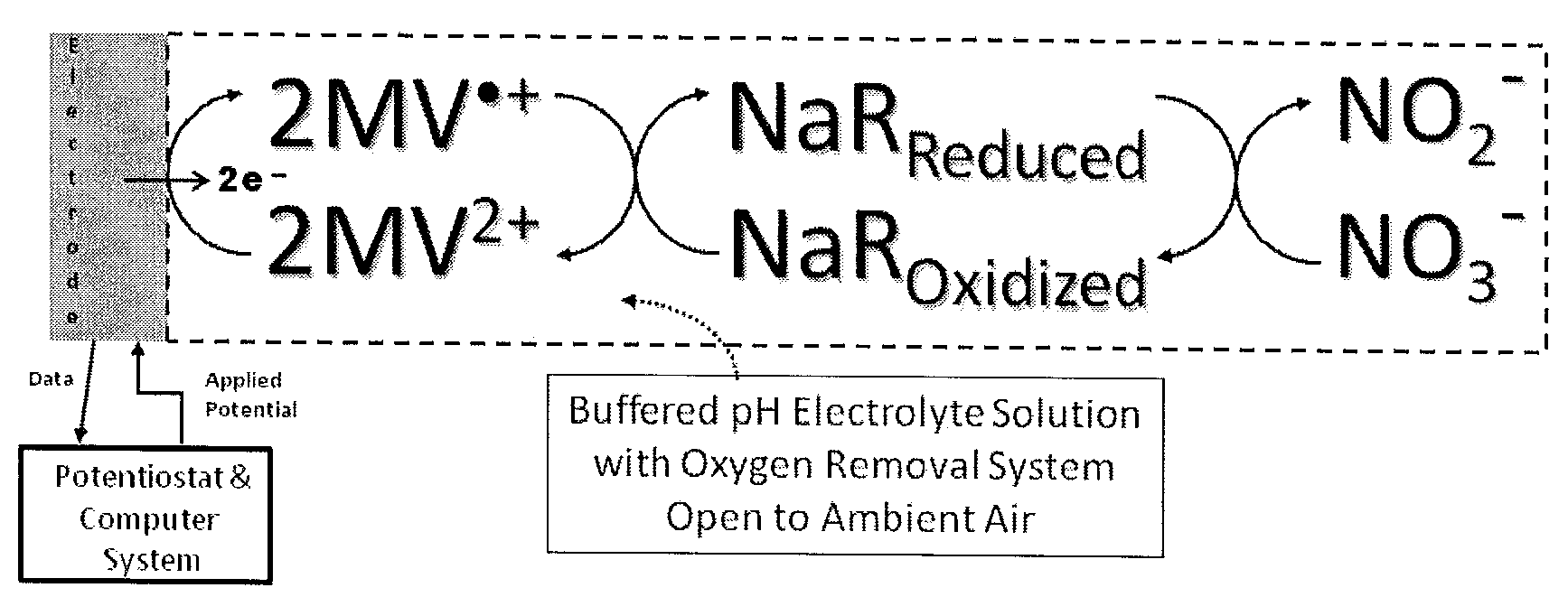
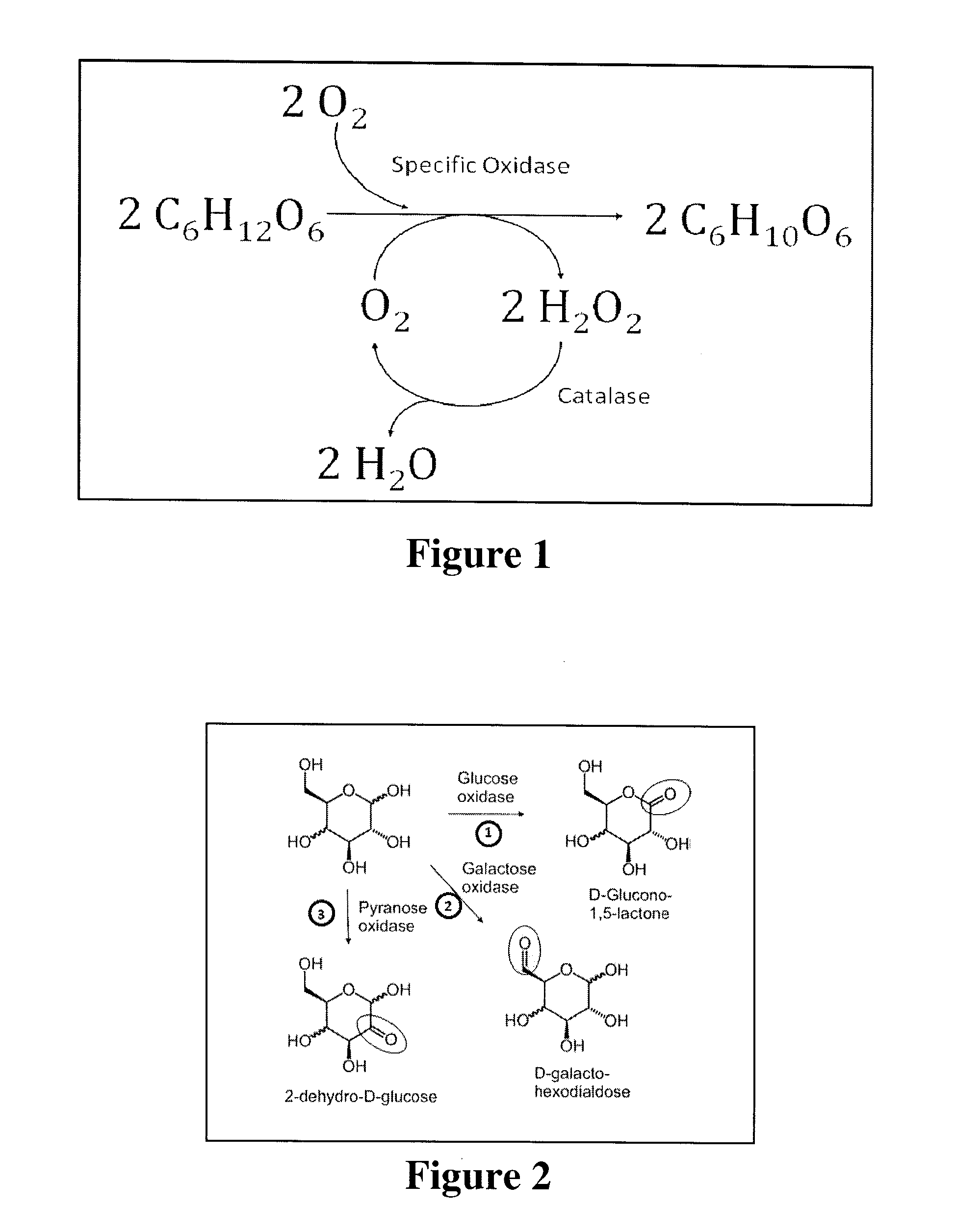
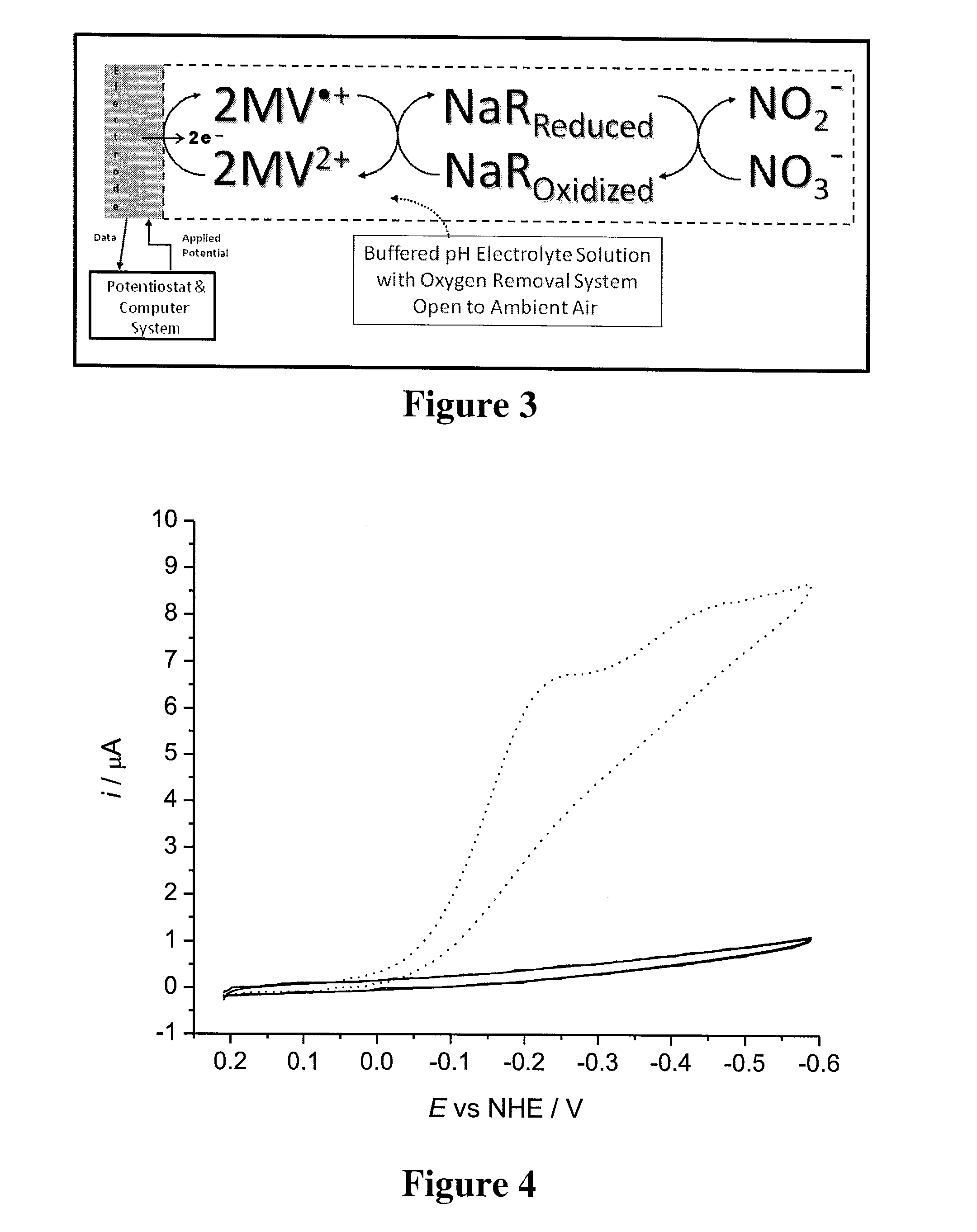
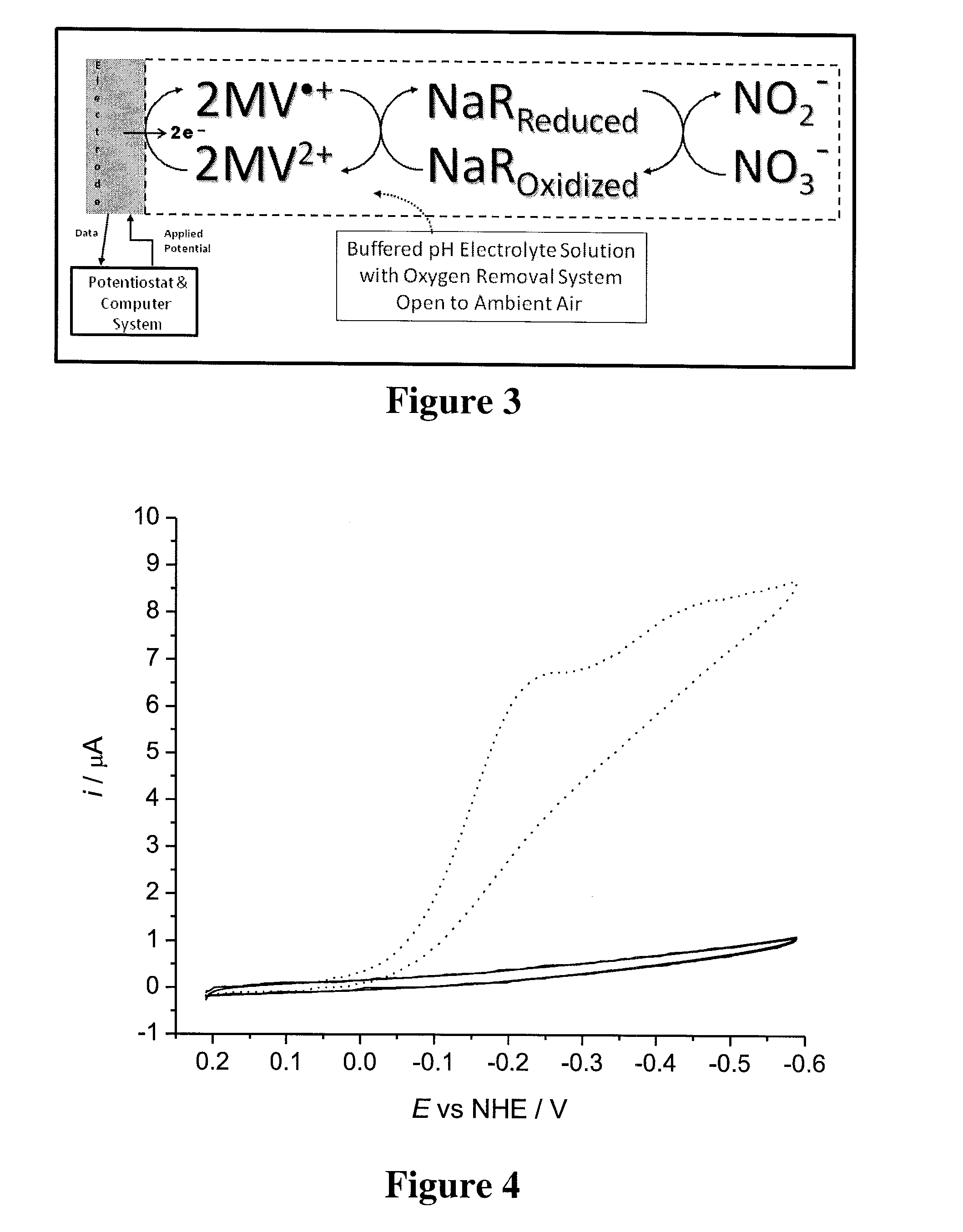
Systems and Methods for Enzymatic Oxygen Removal
ActiveUS20120211372A1Microbiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementElectrochemical responseOxidative enzyme
Systems and methods for oxygen removal from aqueous solutions are presented in which a bi-enzymatic reaction sequence recycles and depletes oxygen to extinction, preferably using an oxidase and a catalase as biocatalysts and a carbohydrate as co-substrate. Contemplated systems and methods are particularly advantageous in conjunction with electrochemical reaction systems in which oxygen would adversely interfere with the reaction system.
Owner:SILVER BEAR INC
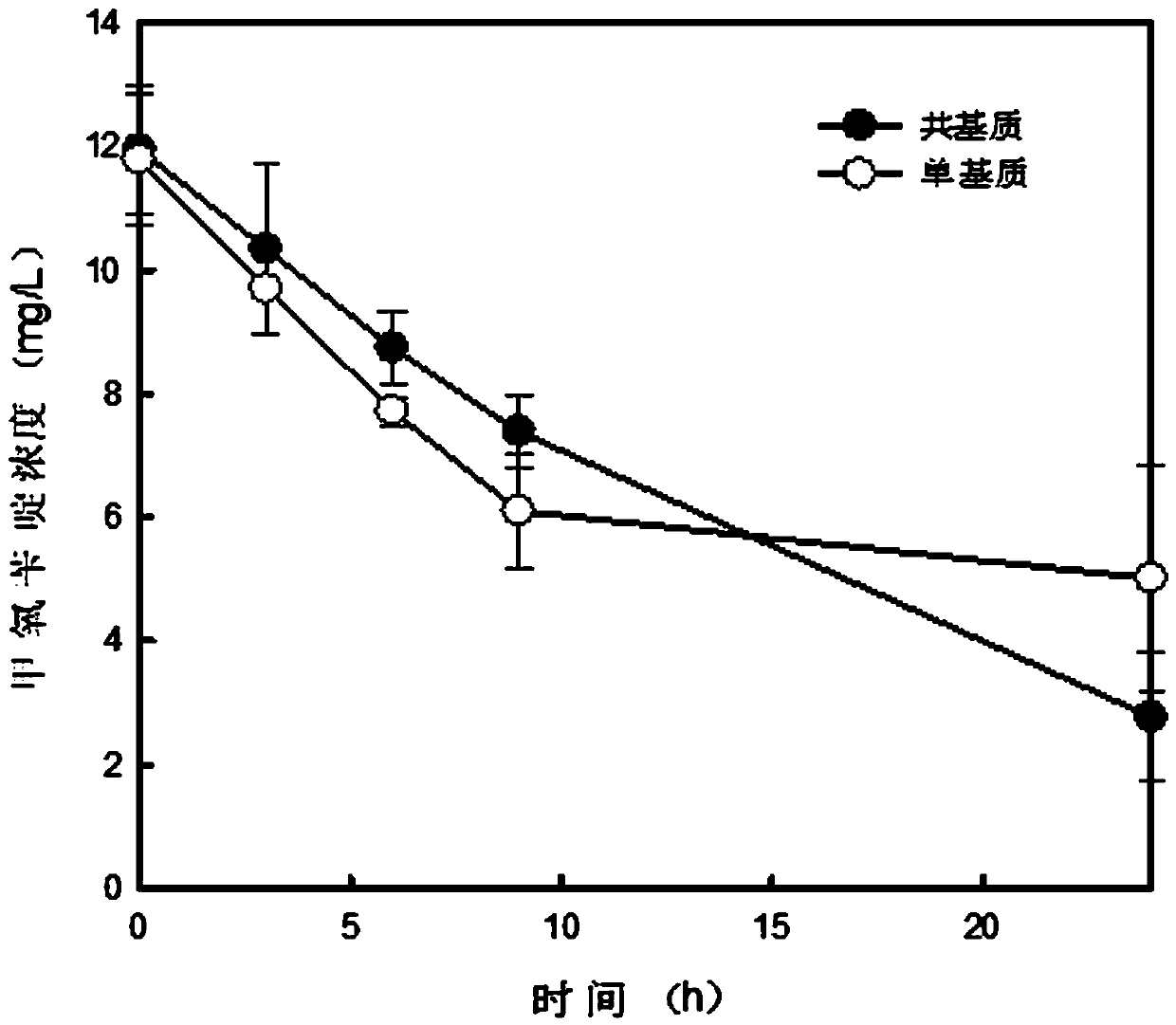
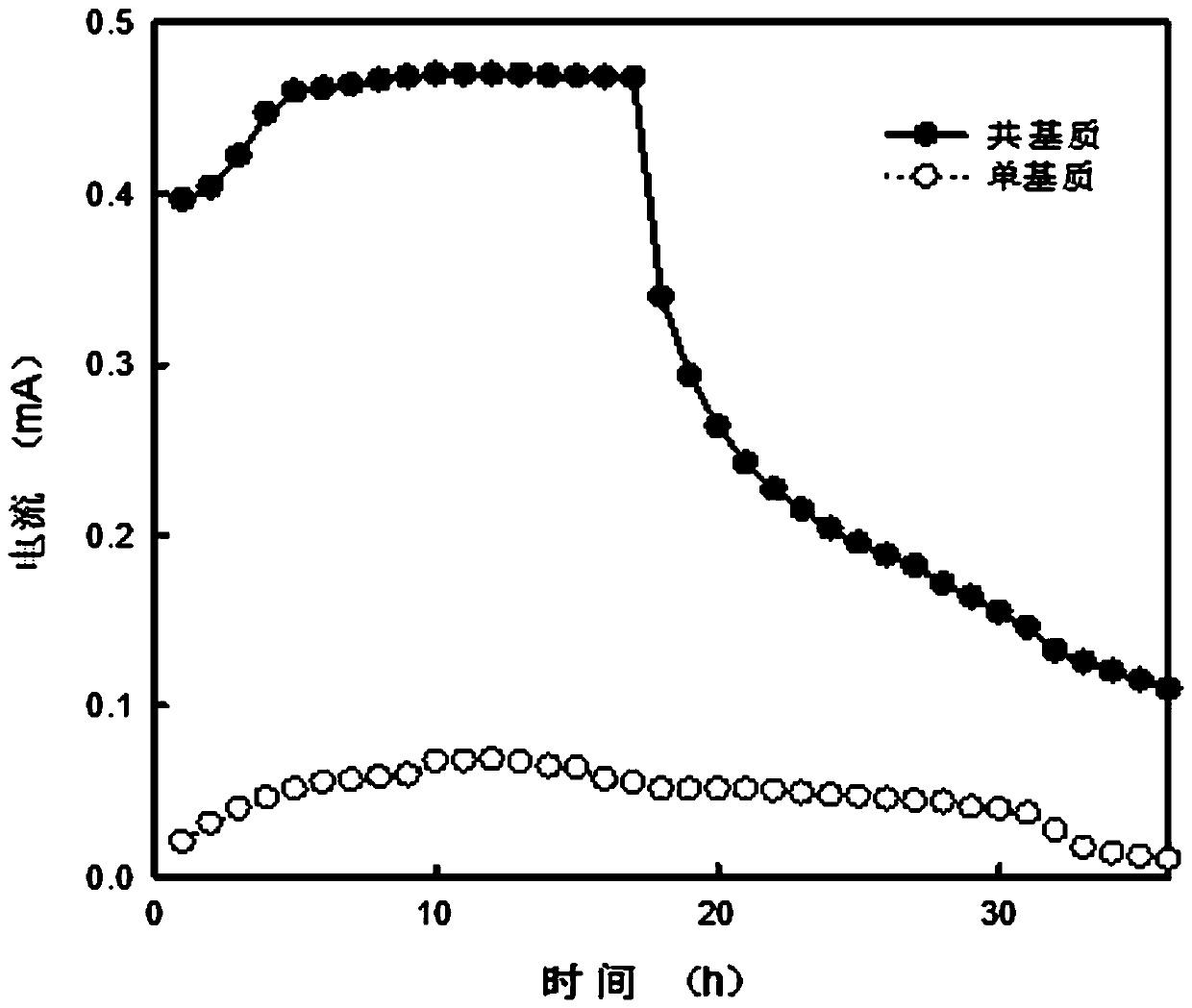
Method for degrading trimethoprim by adopting microbial fuel cell
ActiveCN107601677AStable degradationEfficient degradationWater contaminantsBiochemical fuel cellsTrimethoprimInoculation
The invention relates to the field of sewage treatment, and discloses a method for degrading trimethoprim by adopting a microbial fuel cell (MFC). The invention aims to solve prominent problems that biological degradation difficulty is large, a residual amount in environments is high, biological toxicity is strong and the like existing in a current antibiotic treatment method, and aims to degradethe trimethoprim by adopting the microbial fuel cell and synchronously generate energy. The microbial fuel cell provides a novel way for production of renewable energy and treatment of the difficultly-degraded antibiotic trimethoprim. The method comprises the following steps: 1, assembling and connecting a data recorder; 2, pre-treating a carbon brush electrode and a cation exchange membrane; 3, assembling a reactor; 4, performing inoculation starting of the MFC and performing domestication of functional microorganisms; and 5, performing single substrate and co-substrate trixmethoprim anode degradation and producing electric energy. The method can be successfully applied to treatment of antibiotic wastewater, and is a fast and high-efficiency method; and as a catalyst, the microorganisms can directly converte chemical energy of the trixmethoprim into electric energy while degrading and utilizing the trixmethoprim.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
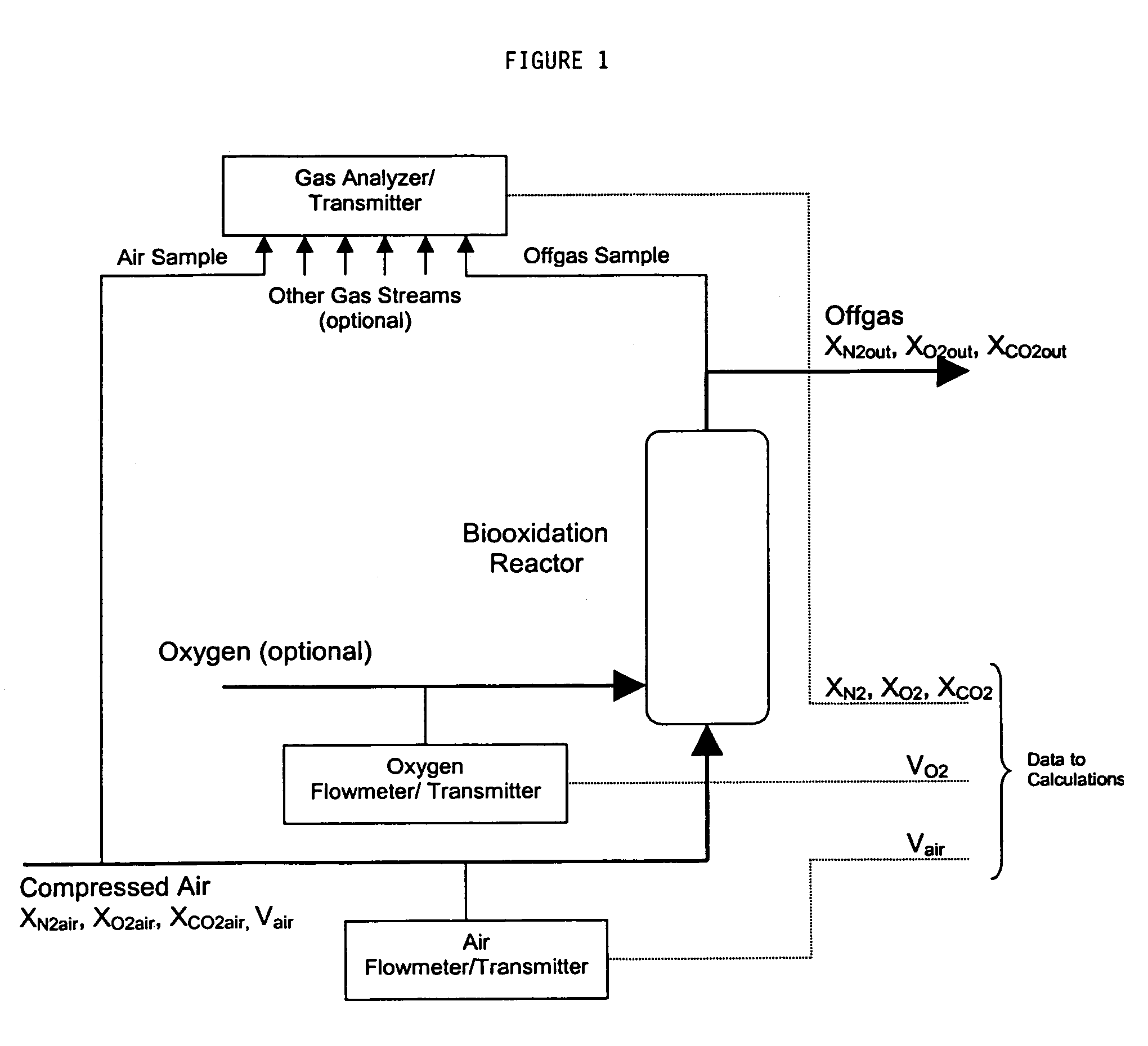
Method for controlling biooxidation reactions
InactiveUS7270947B2Speed maximizationMinimizing rateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCombustionCo substrate
Biooxidation reactions can be controlled by a method which comprises the steps of: (1) independently adding a substrate and a co-substrate at predetermined rates to a bioxidation reaction mixture comprised of a biocatalyst; (2) measuring the oxygen consumption rate and carbon dioxide evolution rate from the reaction mixture; (3) determining the instantaneous rates of substrate and cosubstrate consumption by solving simultaneous equations relating carbon dioxide evolution rate and oxygen consumption rate to the substrate oxidation stoichiometry, the cosubstrate combustion stoichiometry, and optionally the biomass formation stoichiometry; (4) simultaneously adjusting the substrate and cosubstrate addition rates to the rates of substrate oxidation and cosubstrate consumption in order to maximize the rate of product formation while simultaneously minimizing the rate of cosubstrate usage. The method provides a rapid means of controlling fed-batch biooxidation reactions which can employ in-line techniques and is broadly applicable for diverse oxidation reactions.
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
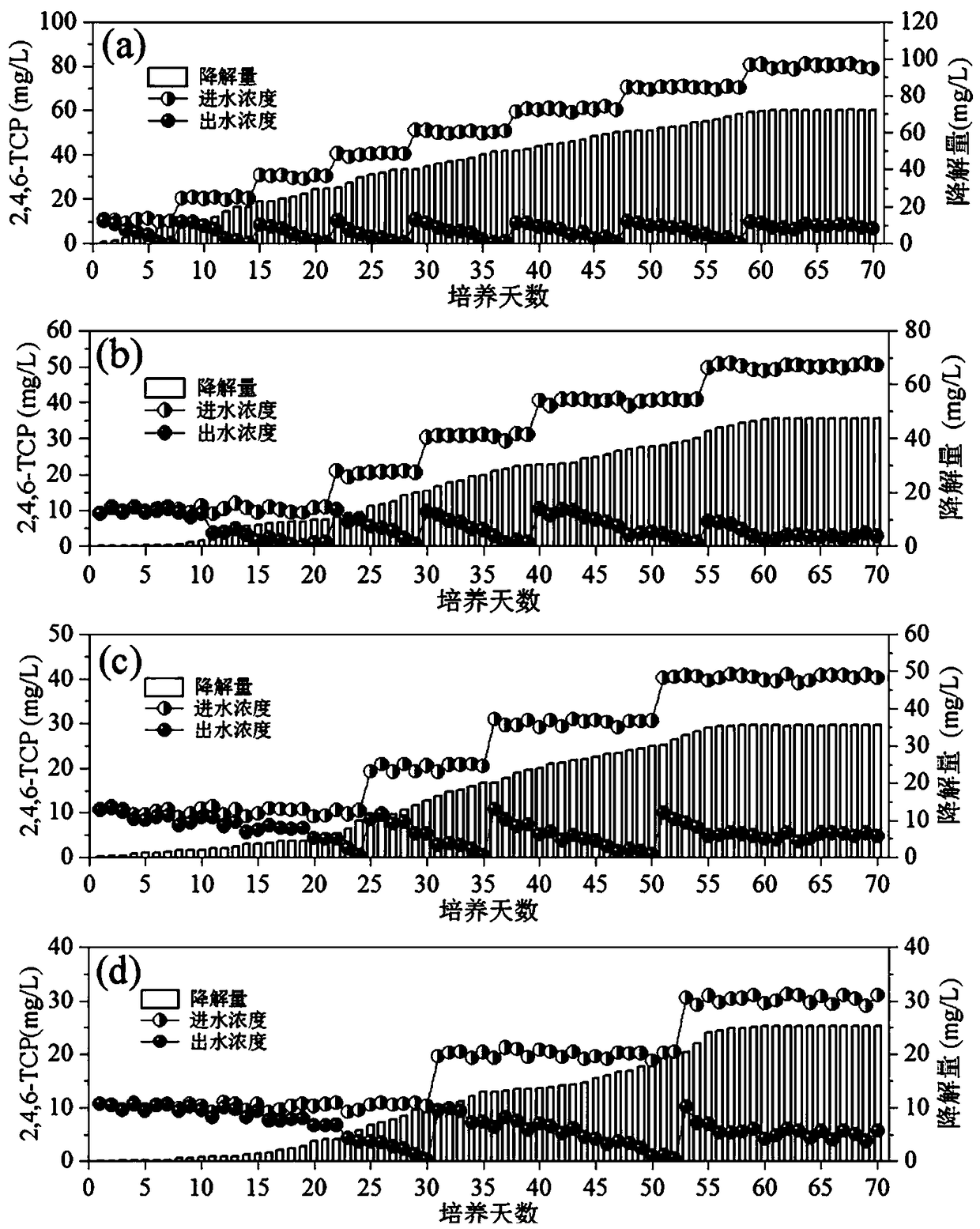
Method for quickly acclimating microorganism capable of degrading 2,4,6-trichlorophenol
ActiveCN109502745AEliminate distractionsShorten the aeration reaction timeWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
The invention discloses a method for quickly acclimating microorganism capable of degrading 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, and belongs to the technical field of biological sewage treatment. The method is characterized by taking an SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) as a main reaction device, inoculating activated sludge of a secondary settling pond of a municipal sewage treatment plant, and acclimating by adopting two stages, i.e., firstly introducing sewage containing the 2,4,6-trichlorophenol to enter the SBR for aeration acclimating, thus obtaining the activated sludge having certain degradation ability; then taking saccharose as a co-substrate organic carbon source, and introducing the saccharose into the SBR for aeration acclimating, thus finally obtaining aerobiotic activated sludge with higherability of degrading the 2,4,6-trichlorophenol. Through a two-stage acclimating method adopted by the invention, not only the microorganism with the higher ability of degrading the 2,4,6-trichlorophenol is enabled to be obtained within a shorter time, but also energy consumption is reduced, and a guiding significance in treating phenolic wastewater is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
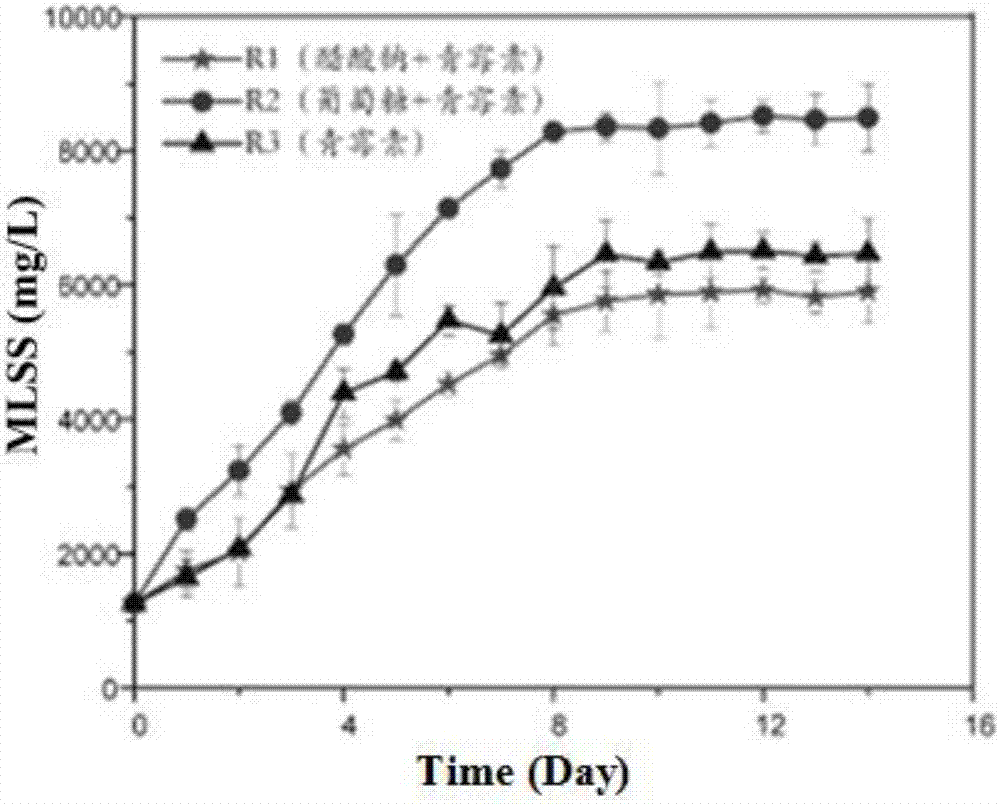
Method for domesticating and culturing activated sludge for degrading penicillin by using glucose as co-substrate
ActiveCN107162175AIncrease varietyEliminate the screening stepWater treatment compoundsNature of treatment waterActivated sludgeMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for domesticating and culturing activated sludge for degrading penicillin by using glucose as a co-substrate. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining the reflux sludge from a secondary settling tank of a domestic sludge treatment plant as seed sludge, using the glucose as the co-substrate of penicillin to provide a carbon source for the system, operating a membrane biological reactor to perform aerobic treatment on the penicillin wastewater, and gradually increasing the load of the reactor; after stably running, continuously increasing the concentration of the penicillin in the intake water by gradients, and reducing the concentration of glucose in the intake water, until the carbon source is completely replaced into the penicillin; in the process, enabling a bacterial flora in the membrane biological reactor to continuously adapt to the stress of the penicillin, so as to form novel microorganism ecology. The domesticating method has the advantages that the troublesome bacteria screening step is not needed, the operation is simple and flexible, and the existing functional microorganism which is difficult in separating and culturing can be furthest utilized; by using the degradable glucose as the co-substrate, the bacterial flora with degrading function can be quickly screened from the penicillin, so as to apply to the high-efficiency treatment of the penicillin wastewater.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Systems and methods for enzymatic oxygen removal
ActiveUS9187779B2Microbiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementElectrochemical responseCo substrate
Systems and methods for oxygen removal from aqueous solutions are presented in which a bi-enzymatic reaction sequence recycles and depletes oxygen to extinction, preferably using an oxidase and a catalase as biocatalysts and a carbohydrate as co-substrate. Contemplated systems and methods are particularly advantageous in conjunction with electrochemical reaction systems in which oxygen would adversely interfere with the reaction system.
Owner:SILVER BEAR INC
Methods and compositions for assaying homocysteine
InactiveUS20060172362A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingCo substrateHomocysteine
This invention relates generally to the field of homocysteine detection. In particular, the invention provides a method for determining homocysteine presence or concentration in samples, which method comprises: contacting a sample containing or suspected of containing Hcy with a Hcy co-substrate and a Hcy converting enzyme in a Hcy conversion reaction to form a Hcy conversion product and a Hcy co-substrate conversion product; and assessing the Hcy co-substrate conversion product to determine the presence, absence and / or amount of the Hcy in the sample. A kit for assaying homocysteine based on the same principle is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Method for intermittent co-substrate-controlled co-metabolism decomposition of difficultly degraded phenol pollutants
ActiveCN103395894AImprove effective utilizationReduce consumptionWater contaminantsBiological water/sewage treatmentCo substrateTreatment effect
The invention discloses a method for intermittent co-substrate-controlled co-metabolism decomposition of difficultly degraded phenol pollutants. The method is characterized in that co-substrate solutions are intermittently added into water containing phenol pollutants in a concentration decreasing way, wherein a weight ratio of co-substrates in the first added co-substrate solution to the phenol pollutants in the water containing the phenol pollutants is 10-500: 1, a time pace of the co-substrate solution filling comprises 1-7 days, a weight ratio of the second added co-substrate solution to the first added co-substrate solution is 1 / 10-9 / 10, a weight ratio of the third added co-substrate solution to the second added co-substrate solution is 1 / 10-9 / 10 and the rest can be done in the same manner until the concentration of the phenol pollutants in the water is reduced in an allowable scope. The method has the advantages of flexible operation, wide application range, low operation cost, good treatment effects and large application prospect.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Multi-substrate metabolism for improving biomass and lipid production
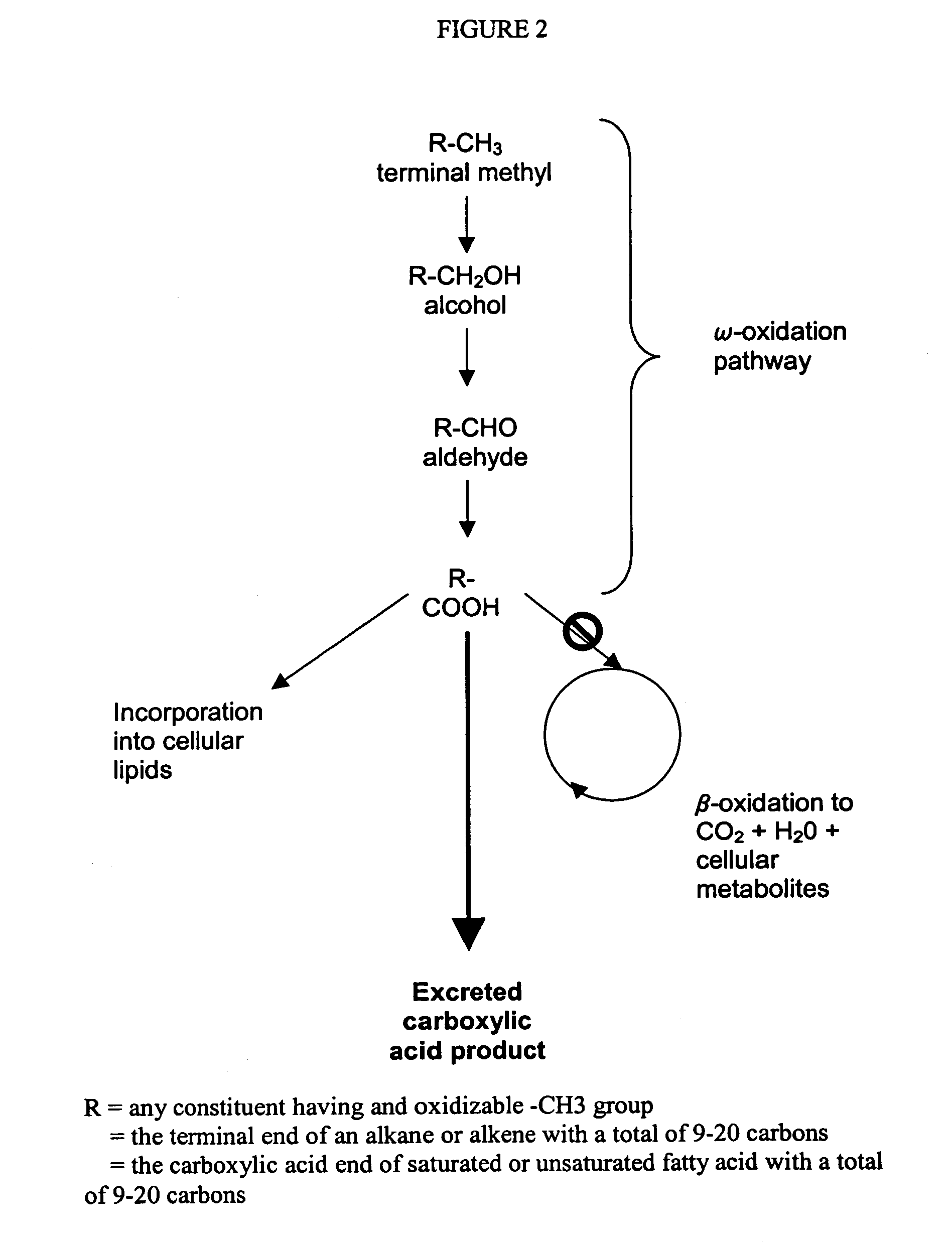
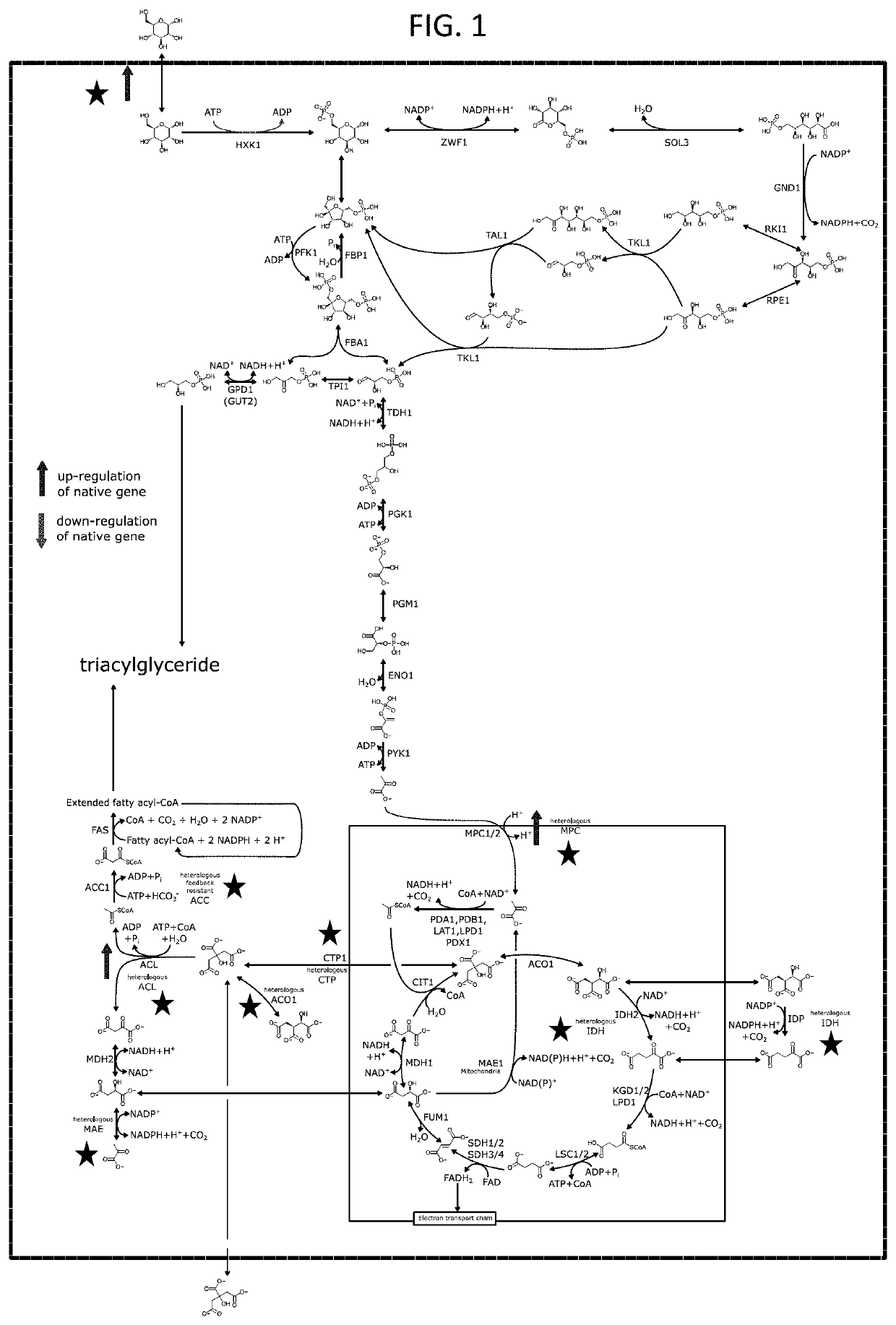
ActiveUS20190338295A1Increased biomass productionMore productiveHydrolasesOxidoreductasesFlavorMicroorganism
The present application relates to methods to improve biomass or lipid production in a microorganism from one or more fatty acid and one or more simple carbon co-substrates. Produced lipids may include unsaturated C6-C24 fatty acids, alcohols, aldehydes, and acetates which may be useful as final products or precursors to insect pheromones, fragrances, flavors, and polymer intermediates. The application further relates to recombinant microorganisms modified for improved production of biomass or lipid, or improved lipid selectivity. Also provided are methods of producing one or more lipid using the recombinant microorganisms, as well as compositions comprising the recombinant microorganisms and / or optionally one or more of the product lipid.
Owner:PROVIVI
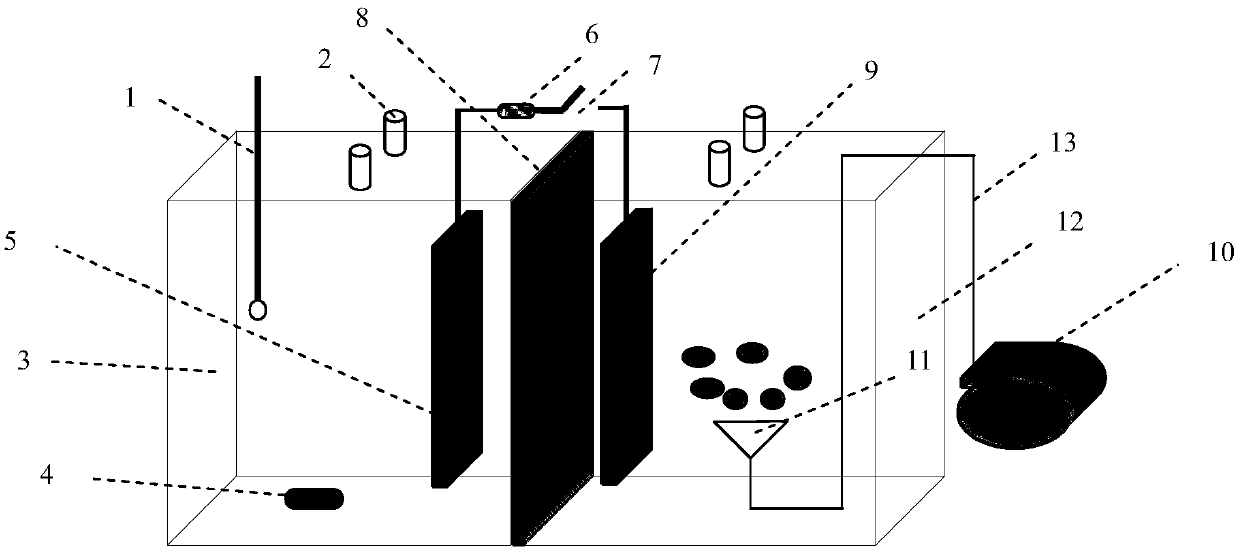
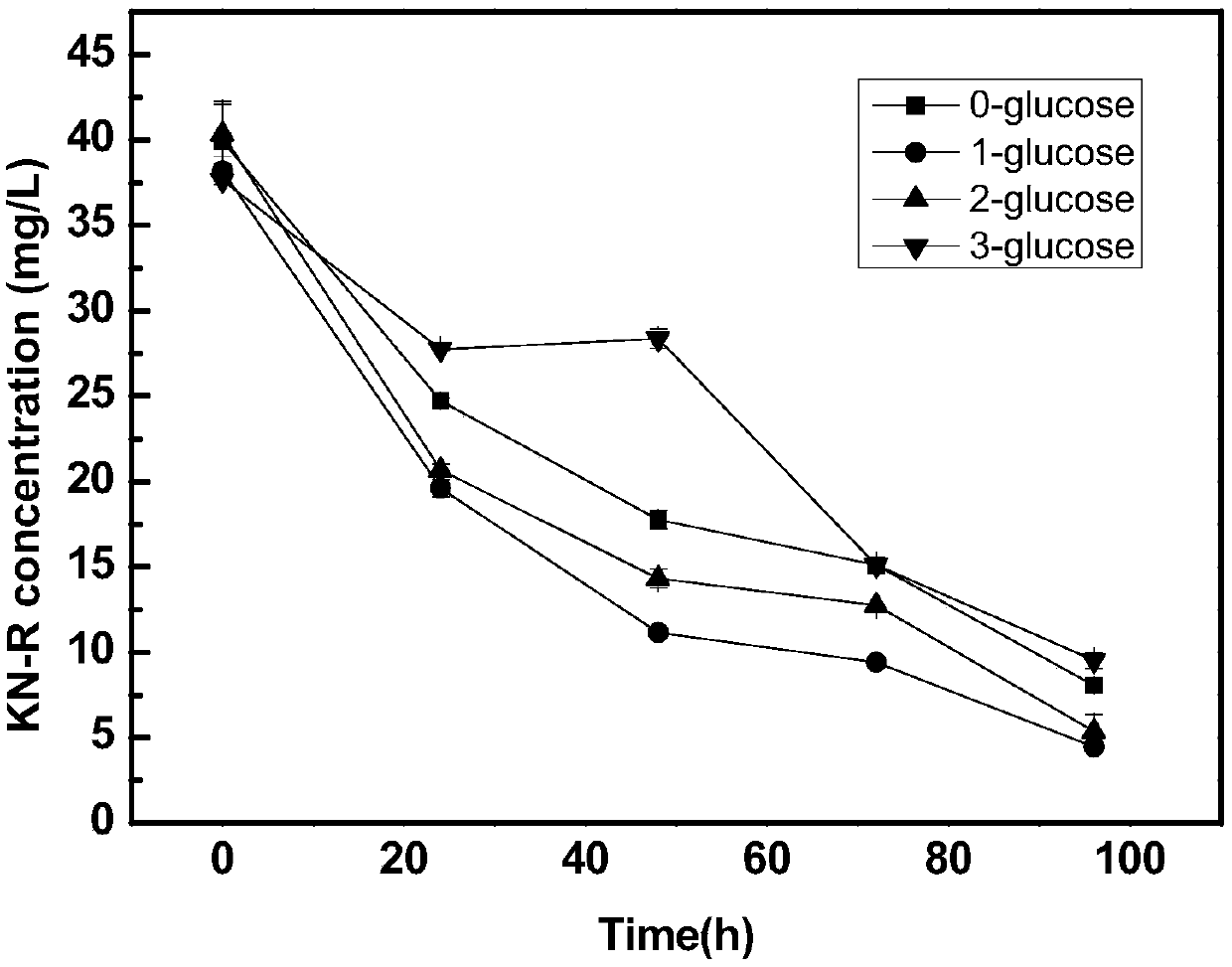
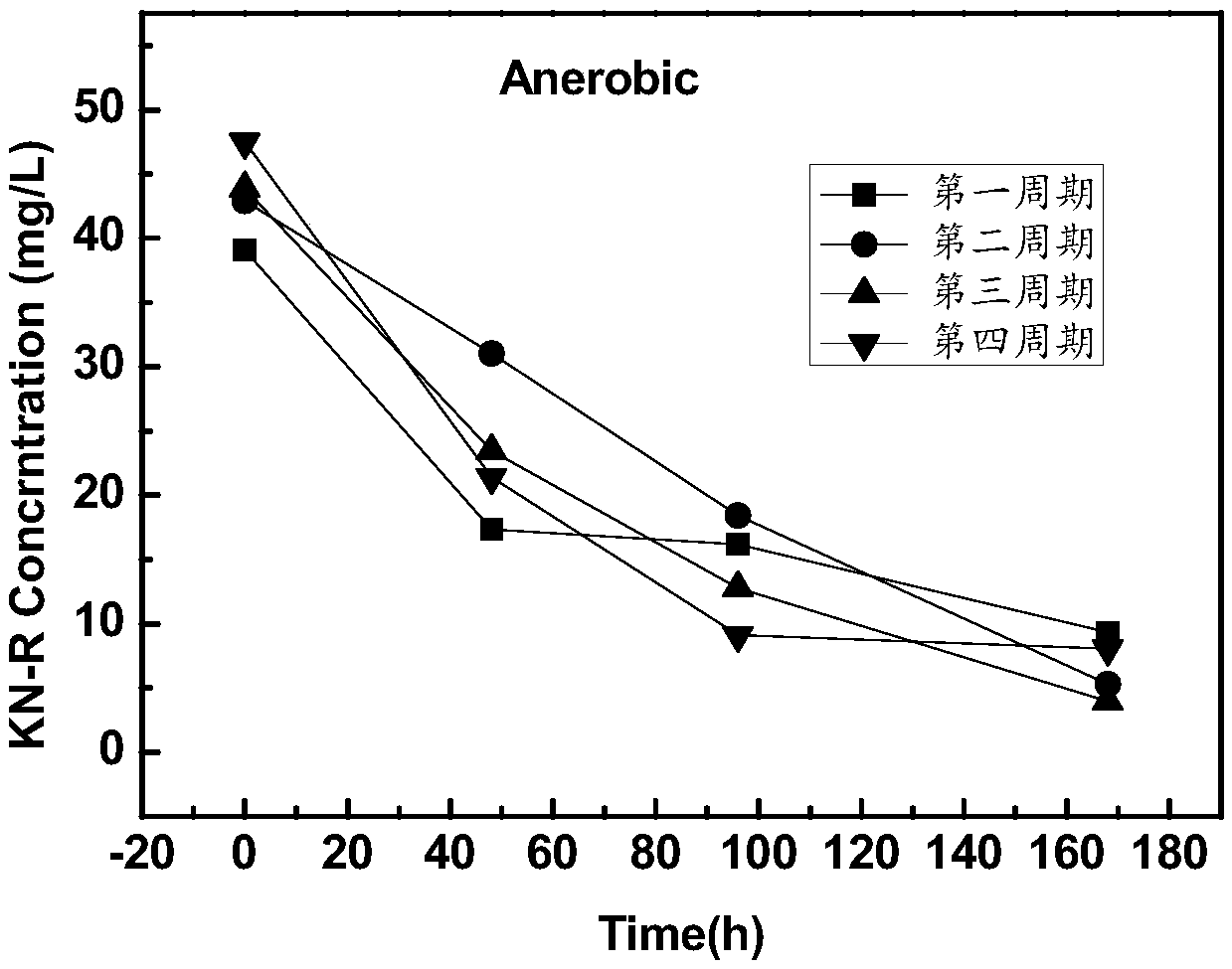
Device and method for promoting rapid anthraquinone dye decolorization based on microbial fuel cell technology
ActiveCN108675444AFast decolorizationRealize resourcesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsCulture fluidTherapeutic effect
Belonging to the technical field of sewage treatment, the invention discloses a device and method for promoting rapid anthraquinone dye decolorization based on microbial fuel cell technology. The method is based on the combination of anaerobic sludge decolorization and bioelectrochemical treatment technology, a two-chamber microbial fuel cell system is constructed, electrogenesis bacteria and anaerobic sludge with decolorization function are added to the positive electrode, also glucose is added as a co-substrate to coordinate decolorization of the anthraquinone dye reactive brilliant blue KN-R, at the same time a culture solution is added as the nutrient to ensure the anaerobic environment of the positive electrode, air is introduced to the negative electrode to serve as the electron acceptor of the system, and the positive electrode and negative electrode are externally connected to a resistor to compose a loop. The device and method for rapid decolorization of anthraquinone dye provided by the invention have good effect, and have the advantages of small floor area, wide application range, simple equipment, easy operation, good treatment effect, energy recovery and the like, andcan be wide applied to biological treatment of sewage in the printing and dyeing industry and recovery of part electric energy, thus having good economic and environmental protection benefits.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Carbonyl reductase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111996176AHigh stereoselectivityGood energyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCo substrateCarbonyl Reductase
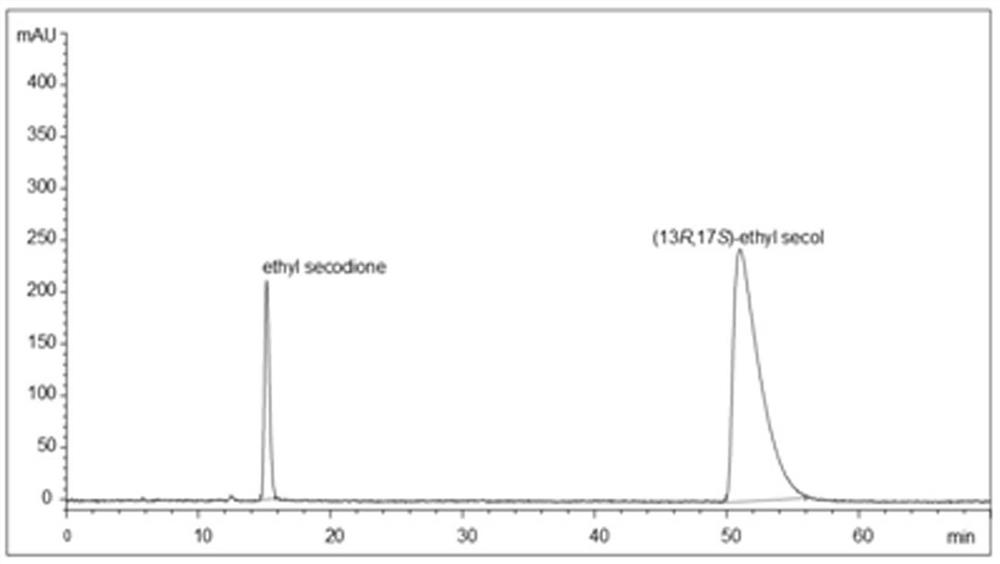
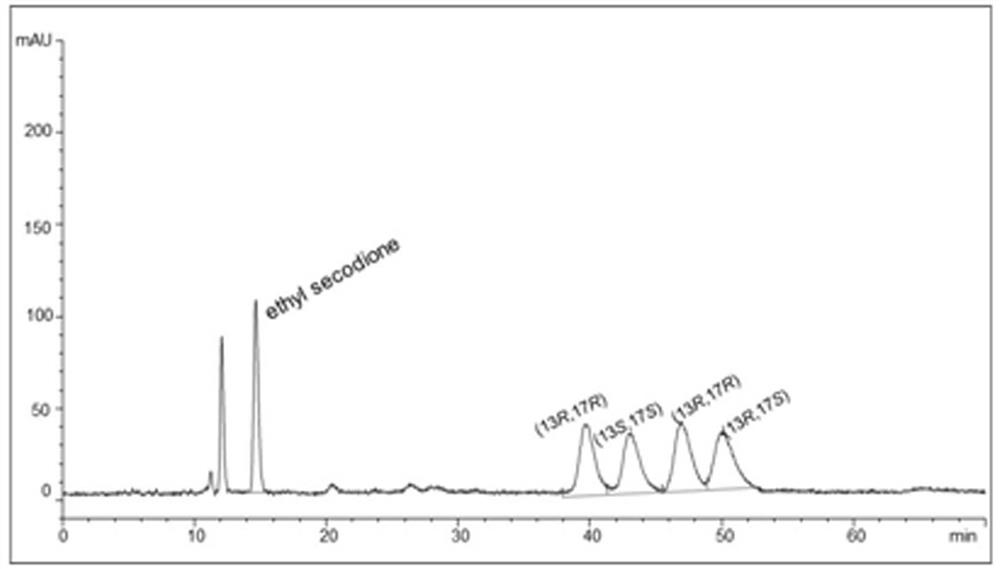
The invention provides a carbonyl reductase mutant and application thereof in (13R, 17S)-ethyl secol synthesis. Specifically, ethyl condensate ethyl secodione and isopropanol are taken as substrates for directed evolution to obtain the carbonyl reductase mutant, glucose / glucose dehydrogenase or sodium formate / formate dehydrogenase is prevented from being used as coenzyme for regeneration, only isopropanol is used as a co-substrate and a cosolvent, and carbonyl is reduced to prepare (13R, 17S)-ethyl secol with high chiral purity.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
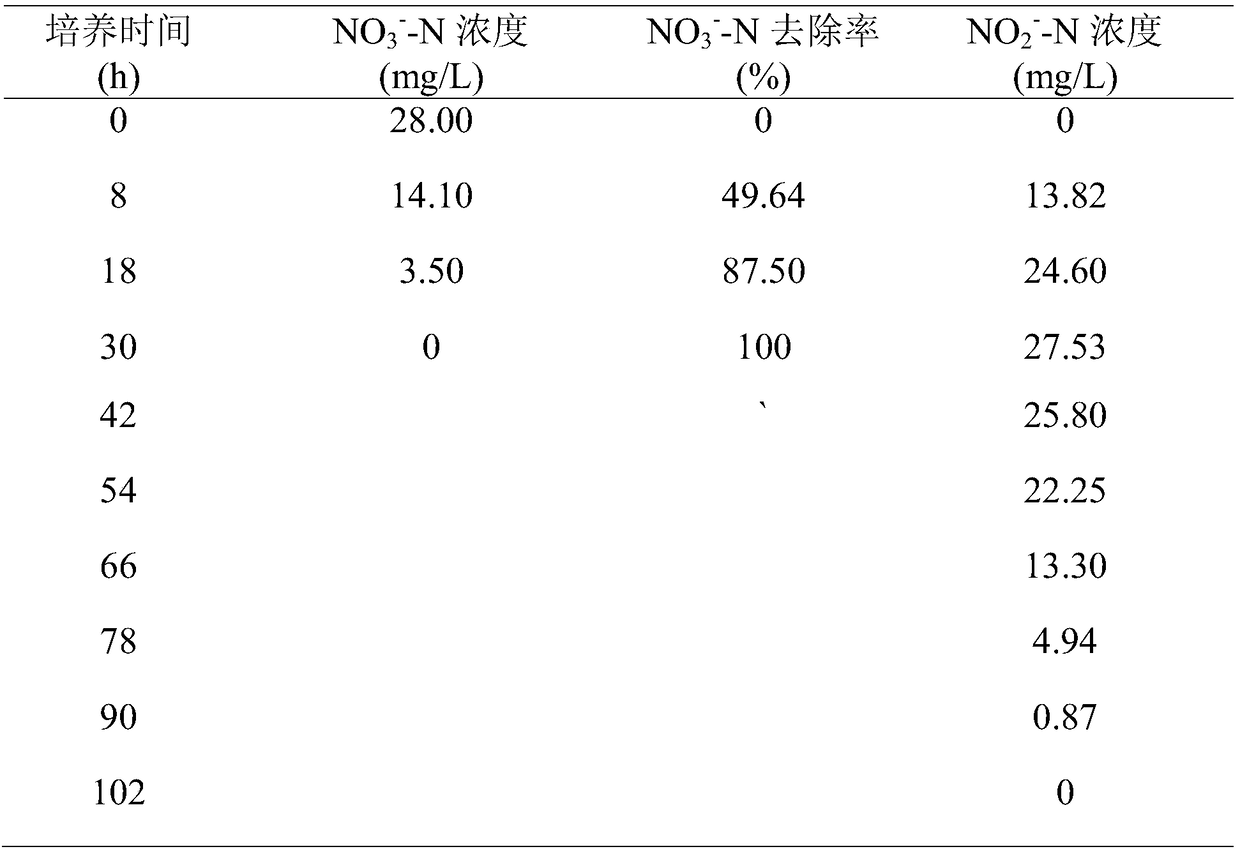
Paracoccus denitrificans strain with sulfur and ferrum co-substrate autotrophic denitrification function and culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN108823117AReduce energy consumptionLow costBacteriaWater contaminantsAutotrophic ProcessesElectron donor
The invention belongs to the environmental biotechnical field and relates to a paracoccus denitrificans strain with a sulfur and ferrum co-substrate autotrophic denitrification function and a culturemethod and application thereof. The bacterium is Paracoccus denitrificans ZGL1. Under an anaerobic condition, nitrate or nitrite in waste water is reduced to nitrogen by taking iron pyrite or ferroussulfide as an electron donor. The bacterium is used for waste water denitrification through an autotrophic process of the sulfur and ferrum co-substrate. The energy consumption is low, the process issimple and the amount of sludge is small. The paracoccus denitrificans strain has a relatively good application potential in the field of waste water denitrification.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Methods and compositions for assaying homocysteine
ActiveUS8476034B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCo substrateHomocysteine
This invention relates generally to the field of homocysteine detection. In particular, the invention provides a method for determining homocysteine presence or concentration in samples, which method comprises: contacting a sample containing or suspected of containing Hcy with a Hcy co-substrate and a Hcy converting enzyme in a Hcy conversion reaction to form a Hcy conversion product and a Hcy co-substrate conversion product; and assessing the Hcy co-substrate conversion product to determine the presence, absence and / or amount of the Hcy in the sample. The Hcy co-substrate conversion product may be assessed directly, or it may be assessed by further conversion of the Hcy co-substrate conversion product into another material by the action of one or more additional enzymes. A kit for assaying homocysteine based on the same principle is also provided.
Owner:DIAZYME LAB INC
Method for catalyzing synthesis of atazanavir intermediate by carbonyl reductase CLEAs
InactiveCN109988789ASimple reaction systemEasy to purifyOrganic chemistryOxidoreductasesCarbamateReaction temperature
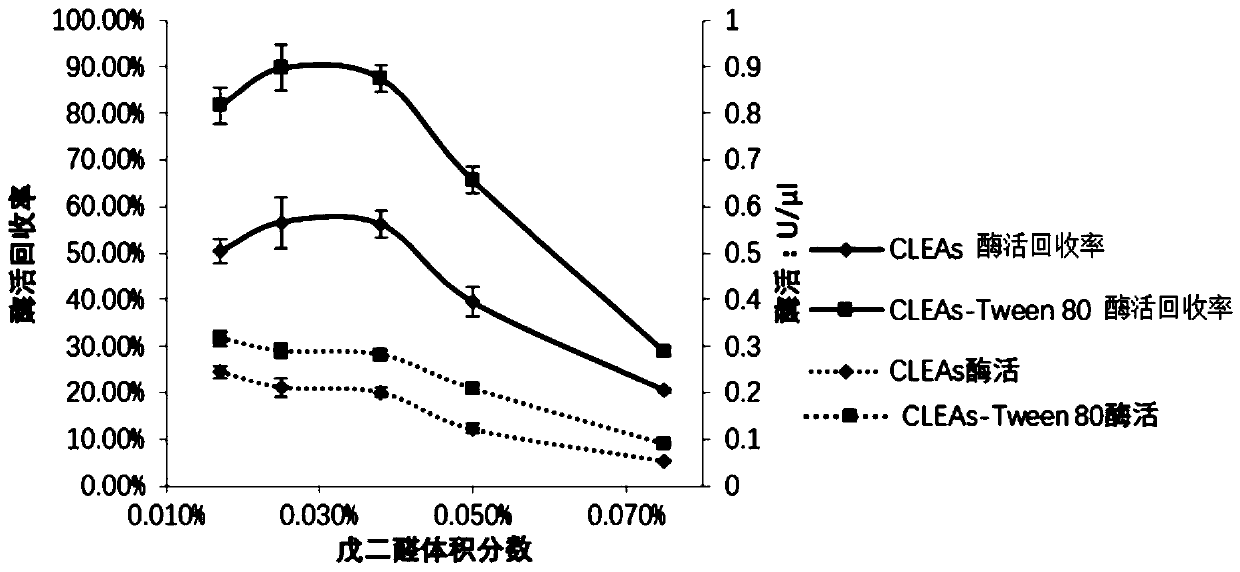
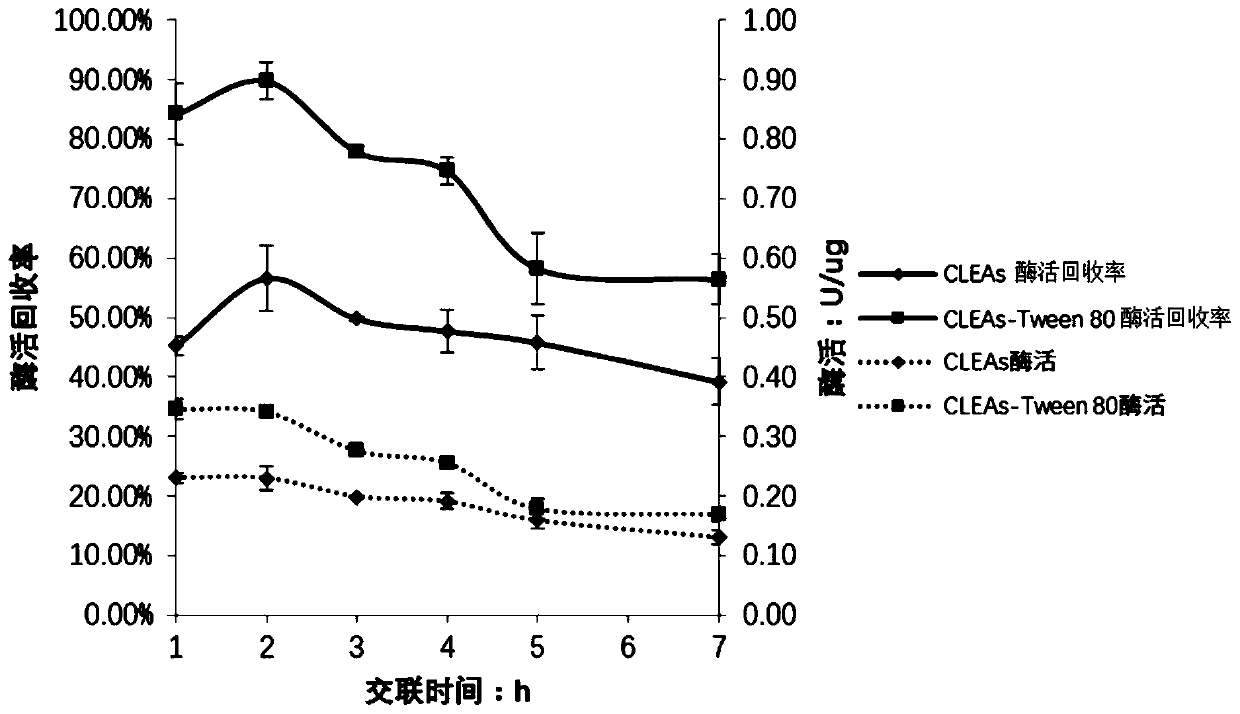
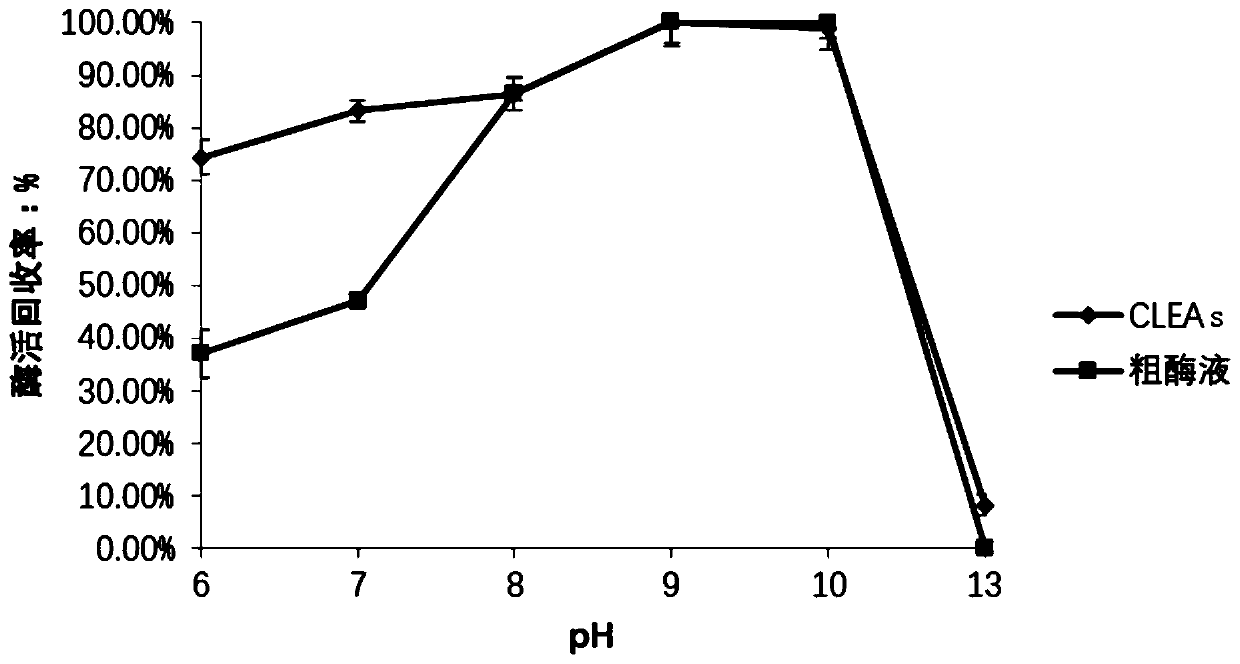
The invention relates to the field of medicine, in particular to a method for catalyzing synthesis of an atazanavir intermediate by a carbonyl reductase CLEAs. The method uses (S)-tert-butyl (4-chloro-3-carbonyl-1-phenylbutyl-2-yl) carbamate as a substrate and a carbonyl reductase NaSDR crosslinked aggregate as a catalyst, and the catalyzing synthesis of tert-butyl ((2S, 3R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutyl-2-yl)) carbamate is carried out in a system in which a co-substrate, a co-solvent and a buffer solution are present. By the adoption of the method for the catalyzing synthesis of the atazanavir intermediate by the carbonyl reductase CLEAs, a reaction system is simpler, additional expensive coenzymes are not necessary, and glucose is not required to participate in a coenzyme cycle; in addition, the reaction temperature is closer to room temperature; the carbonyl reductase NaSDR crosslinked aggregate as a biocatalyst has better temperature stability and pH stability and can be reusedin 6 batches, so that the method is more energy-saving and environmentally friendly, and cost is further reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF MEDICINE & HEALTH SCI
System and method for purifying organic pollutants in lake sediment and lake water
ActiveCN110606543AImprove degradation efficiencyInhibitory activityTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsElectronUnevaluable
The invention discloses a system and method for purifying organic pollutants in lake sediment and lake water. The system is composed of a sediment microbial fuel cell (SMFC) unit and a biofilm electrode (BER) unit. According to the method, degradation-resistant organic pollutants in lake sediment and lake sediment are degraded and removed through the SMFC unit, and degradation-resistant organic pollutants in lake water are degraded and removed through the BER unit. According to the method, a large amount of humic acid existing in the lake bottom mud is fully utilized as a co-substrate to promote the degradation capacity of the SMFC anode on refractory organic pollutants in the bottom mud; meanwhile, electrons generated by the SMFC unit are utilized by BER, and the degradation effect of theBER unit on the refractory organic pollutants in the lake water body is enhanced. In the invention, the effective way is provided for relieving the current energy crisis and solving the environmentalproblem, so that the system and method have immeasurable application and development potentials.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for biologically drying sludge by using rice hull as additive
Owner:SHENYANG ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com