Method for catalyzing synthesis of atazanavir intermediate by carbonyl reductase CLEAs
A carbonyl reductase and atazanavir technology, which is applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of unreusable carbonyl reductase, high requirements on reaction conditions, low reaction efficiency, etc., and achieves low cost, good temperature stability, and simple reaction system. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] This example discloses a method for catalytically synthesizing an atazanavir intermediate, using (S)-tert-butyl (4-chloro-3-carbonyl-1-phenylbutyl-2-yl) carbamate as Substrate, using carbonyl reductase NaSDR cross-linked aggregates as a catalyst, catalyzes the synthesis of tert-butyl ((2S,3R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyl-1 -phenylbutyl-2-yl)carbamate.
[0051] Wherein, the method for generating the cross-linked aggregate of the carbonyl reductase NaSDR comprises the following steps:
[0052] S1: obtaining the crude enzyme solution of carbonyl reductase NaSDR;
[0053] S2: using a precipitating agent to precipitate the crude enzyme solution of carbonyl reductase NaSDR;
[0054] S3: adding a cross-linking agent and an additive at the same time to carry out a cross-linking reaction to obtain a cross-linked aggregate of carbonyl reductase NaSDR.
[0055] The precipitating agent is tert-butanol, and the crosslinking agent is pentylene glycol.
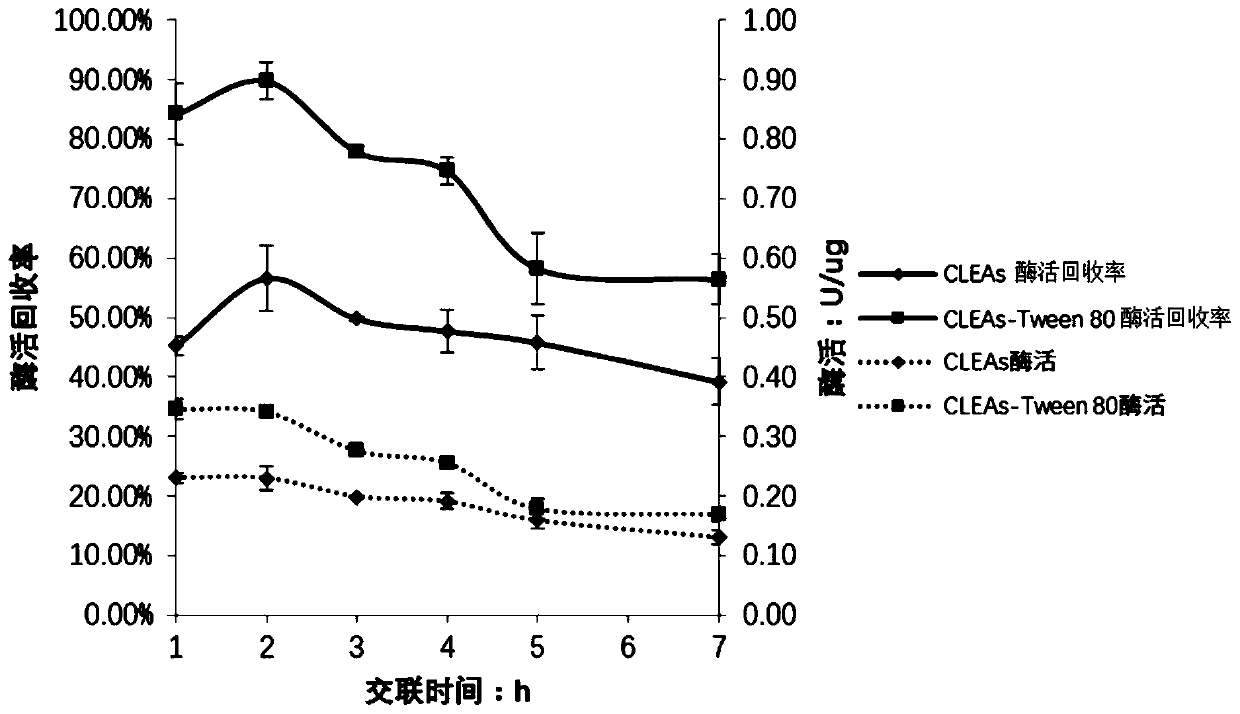
[0056] In S3, the crosslinking time...
Embodiment 2
[0062] This embodiment discloses a method for preparing carbonyl reductase NaSDR crude enzyme liquid, comprising the following steps:
[0063] 1. Activation of E.coli-NaSDR bacteria
[0064] On the LB solid plate containing kanamycin (50μg / ml), the bacterial solution was coated by the method of partitioning or dilution. After culturing at 37°C for 20 hours, a single colony of activated E.coli-NaSDR was obtained.
[0065] 2. Fermentation and cultivation of E.coli-NaSDR bacteria
[0066] (1) Inoculate a single colony of E.coli-NaSDR bacteria into 5ml primary seed medium, and cultivate it at 37°C and 220rpm for 11 hours, and the OD600 reaches 0.9-1.2, which is the primary seed solution.
[0067] (2) Inoculate 5 ml of the primary seed solution into the fermentation medium (2.5% inoculum size), and cultivate at 37° C. and 220 rpm for 2-3 hours. When the OD600 of the fermentation medium reaches 0.9-1.2, add 400 μL of IPTG (isopropylthiogalactopyranoside, concentration 100 mmol / L)...
Embodiment 3
[0073] This embodiment discloses the method for preparing CLEAs:
[0074] 1. Screen the most suitable precipitation conditions
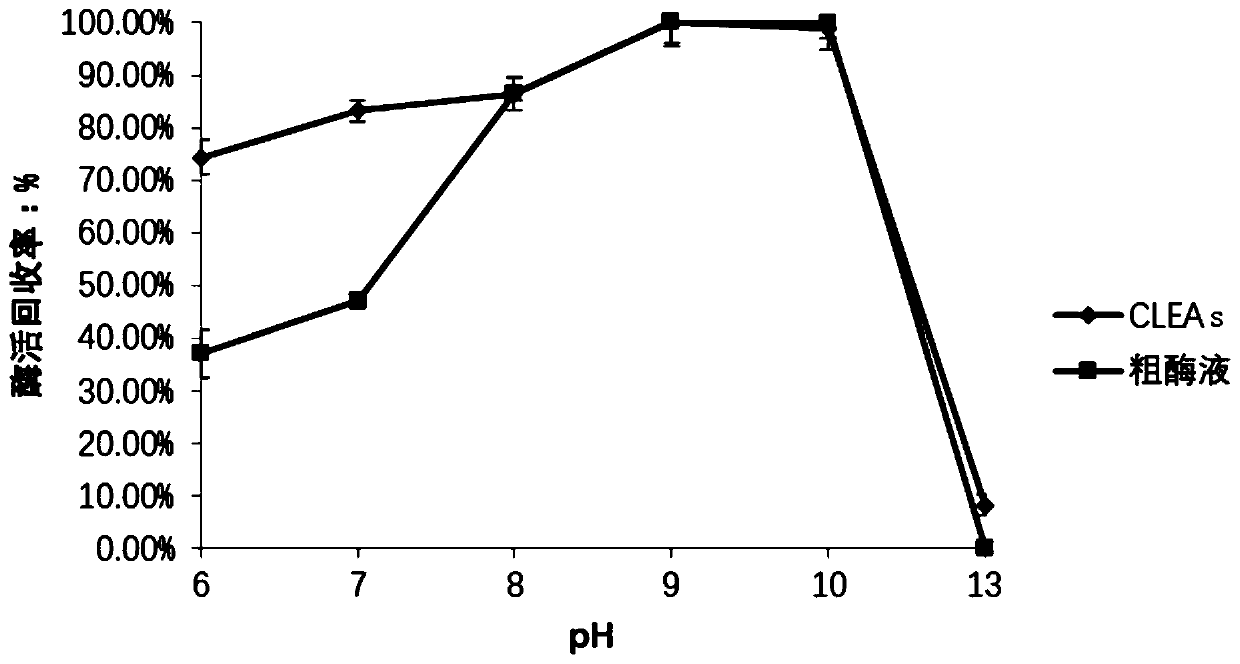
[0075] The inventor screened a variety of precipitants, including acetone, ammonium sulfate saturated solution, tert-butanol and PEG600. 4ml precipitation system: including 400 μL of crude enzyme solution, the final volume fractions were 30%, 40%, 50%, 60% , 70%, 80% and 90% of the precipitant, and supplement the TEA-HCL buffer solution to 4ml. After stirring slowly for 1 h in an ice-water bath, the mixed solution was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 2 min, and the supernatant was discarded, then resuspended with 2 mL of buffer, and the enzyme activity of the precipitate was determined. The results showed that the recovery rate of enzyme activity was the highest when the volume fraction of tert-butanol was 60%.
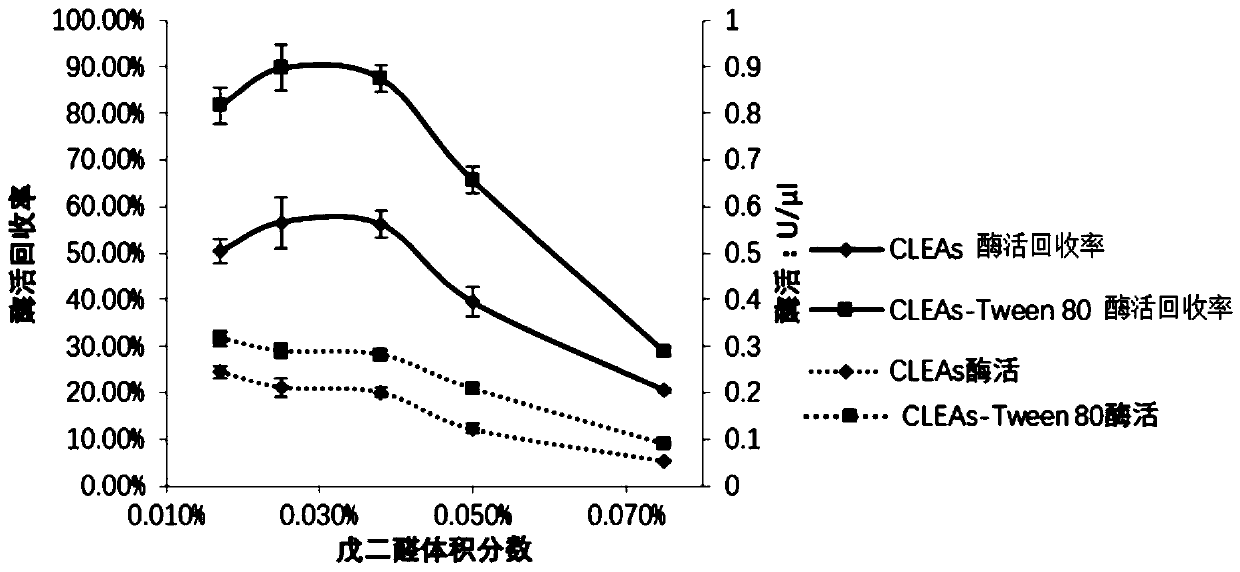
[0076] 2. Screen the optimal concentration of cross-linking agent
[0077] This step studies the optimum concentration of glutaraldehyde, whi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com