Multi-Average Artifact Mitigation Method for Fast Spin Echo
A spin-echo and averaging technology, applied in the direction of magnetic variable measurement, nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system for measurement, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of low signal strength and large difference in signal strength, etc., and achieve good contrast and reduced artifacts , the effect of reducing artifacts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
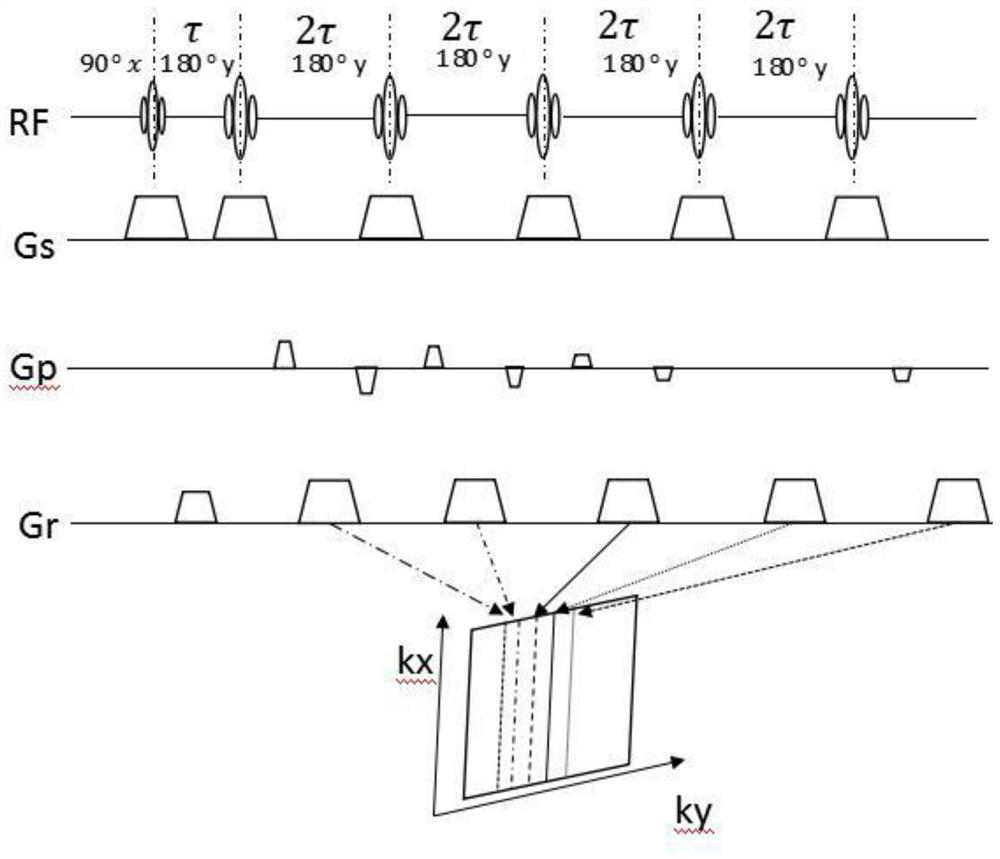
[0023] combine Figure 3 to Figure 6 Shown is a specific implementation of a method for multiple averaging of fast spin echoes to reduce artifacts according to the present invention. First, it mainly includes the following steps:
[0024] Step 1): Use two FSE sequences to excite the target scanning part to obtain K-space data;
[0025] Step 2): Use the alternate K-space filling method to scan and collect to obtain the first K-space data, and the T2 weighting function of the corresponding signal changes smoothly in the entire K-space;
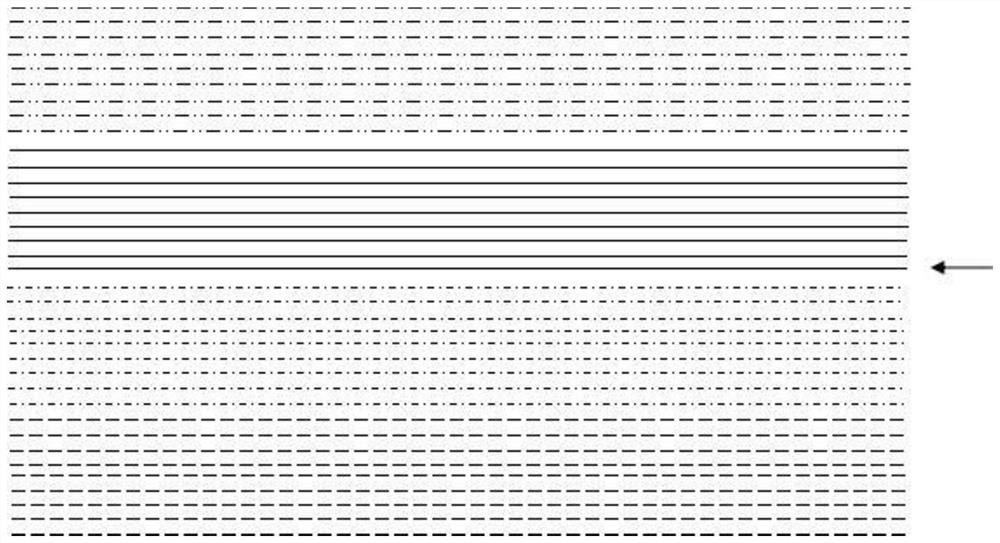
[0026] Such as image 3 As shown, the alternate K-space filling method includes dividing the K-space into 9 filling areas, and the 9 echo chains after each shot are respectively assigned to different filling areas. It can be seen from the figure that a line represents a shot The arrow points to the center of K space, there are 4 shot excitations, and the echoes after each shot include 9 echo chains, that is, ETL=9, PE=36, the fifth echo after ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com