Adaptive iterative learning control method based on non-strict repetition
An adaptive iterative and learning control technology, applied in the field of iterative learning control systems, can solve problems such as limited research, achieve rapid convergence, reduce the range of jitter, and solve the effects of poor anti-interference ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
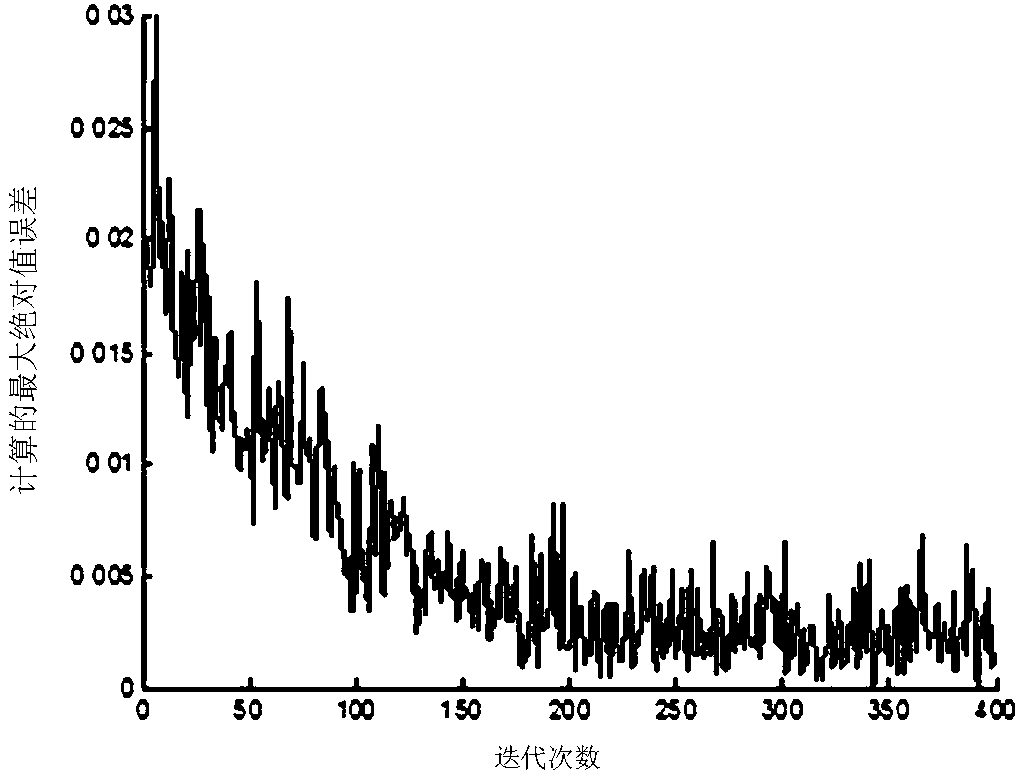
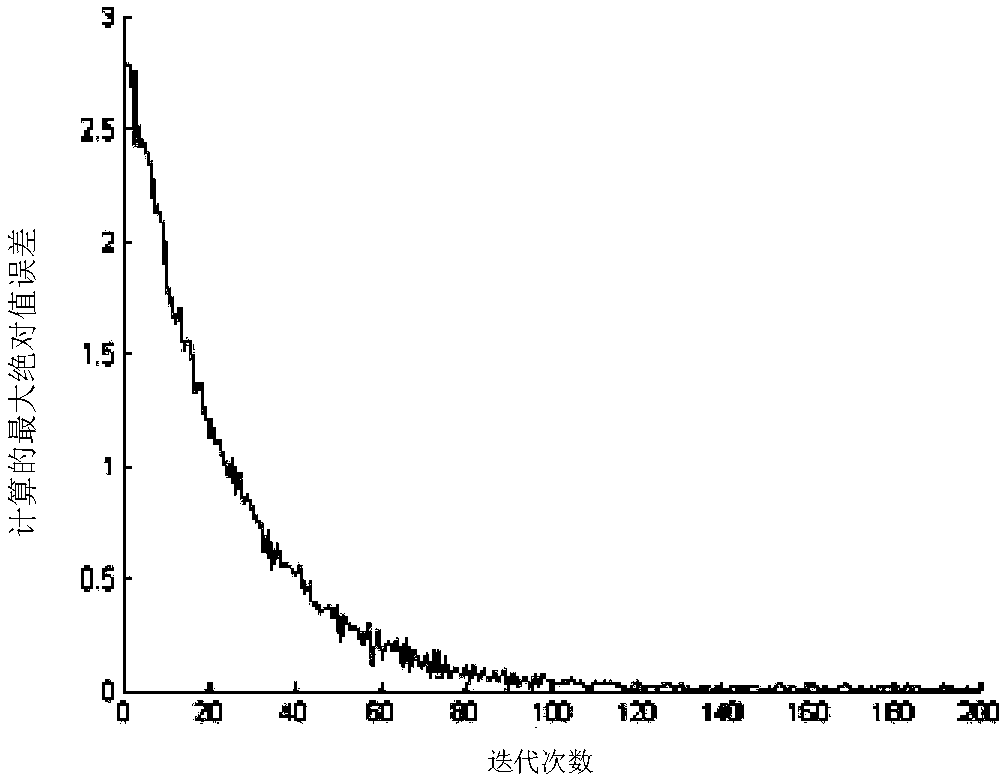
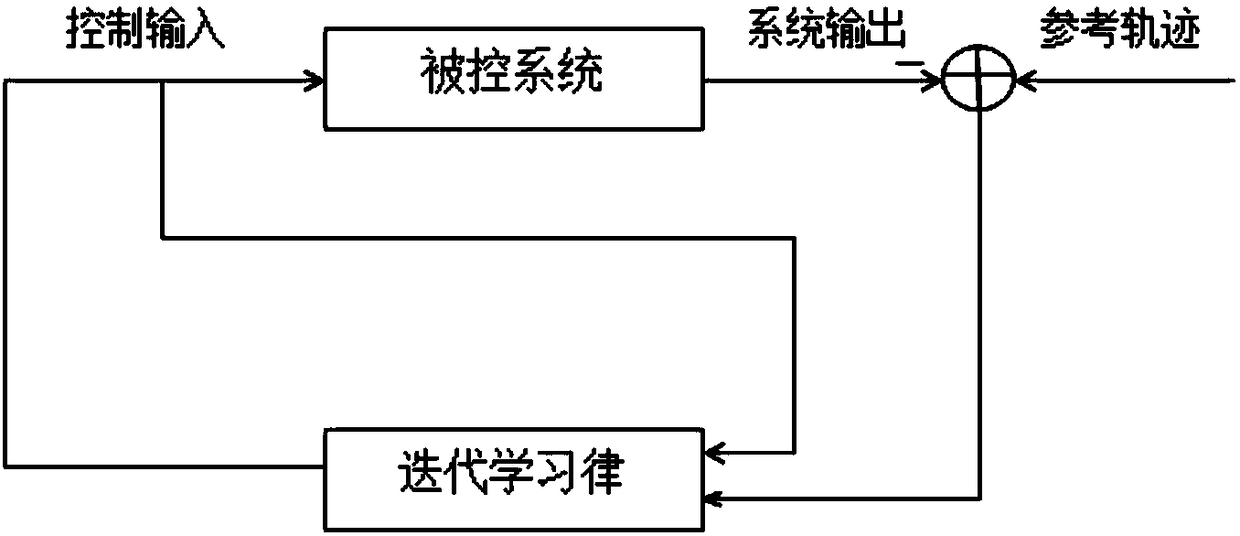
[0049] Embodiment 1: In order to solve the problems in the traditional iterative learning control method, when the controlled system is not strictly repeated, the initial state of the system is not strictly positioned, and the tracking trajectory is not strictly repeated, the tracking accuracy is low, the number of iterations is large, and the tracking error vibration range is large By establishing a variety of non-strict repetition constraint models, introducing state-space matrix vectors, and combining the adaptive energy function mechanism, the non-strict repetition is learned, and an adaptive iterative learning control method based on non-strict repetition is invented. The setting function that makes the trajectory automatically track the change has high trajectory tracking accuracy, and the control algorithm has strong robustness at the same time.
[0050] The self-adaptive iterative learning control method based on non-strict repetition of the present invention is general...
Embodiment 2
[0125] Example 2: A more general non-strictly repeatable nonlinear system is as follows:
[0126] x k (t+1)=θ k (t)ξ(x k (t),t)+b(t)u k (t)+d(t)
[0127] Among them, the known function ξ(x k (t),t)=0.1sin(x k (t)); unknown time-varying control gain b(t)=1+sin(0.5t); external disturbance d(t) changes randomly on the interval [0,0.1]; unknown parameter variable θ k (t) The repetition law of the iterative domain can be checked.
[0128] θ k The iterative changes of (t) are as follows:
[0129] θ k (t)=-2cos0.4θ k-1 (t)-θ k-2 (t)
[0130] Among them, the unknown initial state functions are θ -1 (t) = 1.4sin(0.02πt) and θ 0 (t)=0.4cos(0.02πt).
[0131] The initial state of the system x k (0) is a bounded random signal, which changes randomly in the interval (0,1].
[0132] The reference trajectory of system state tracking iterative changes is shown in the following formula:
[0133]
[0134] Among them, r k ∈(0,1], change randomly on the interval (0,1].
[01...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com