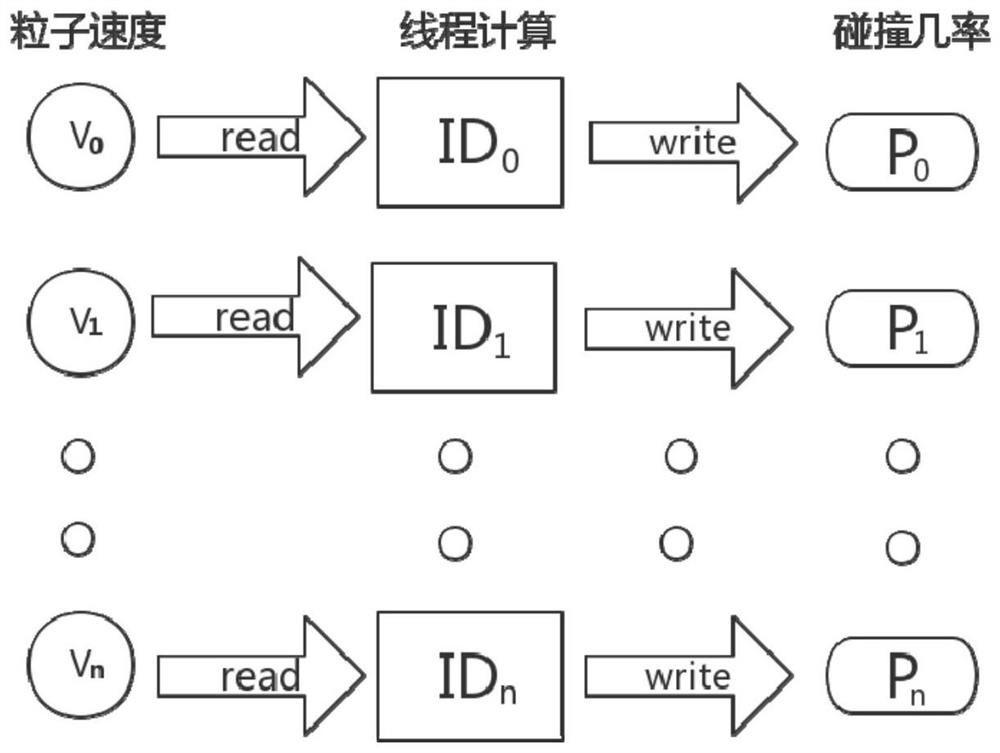
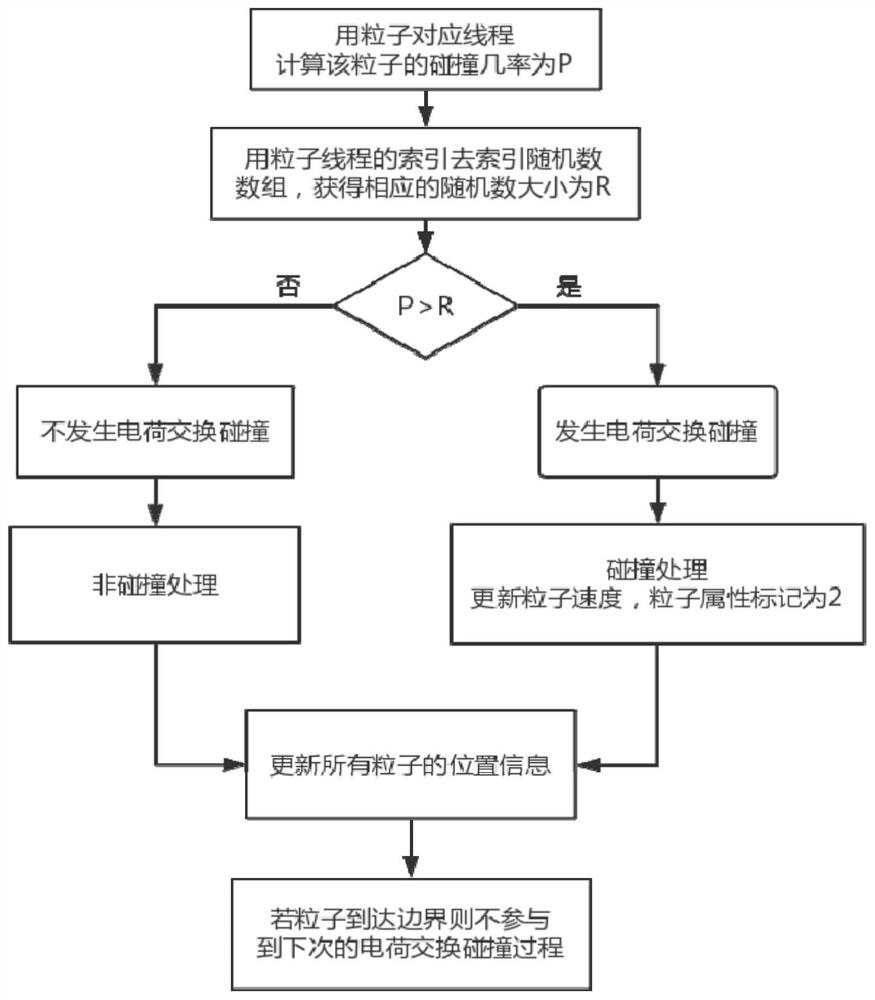
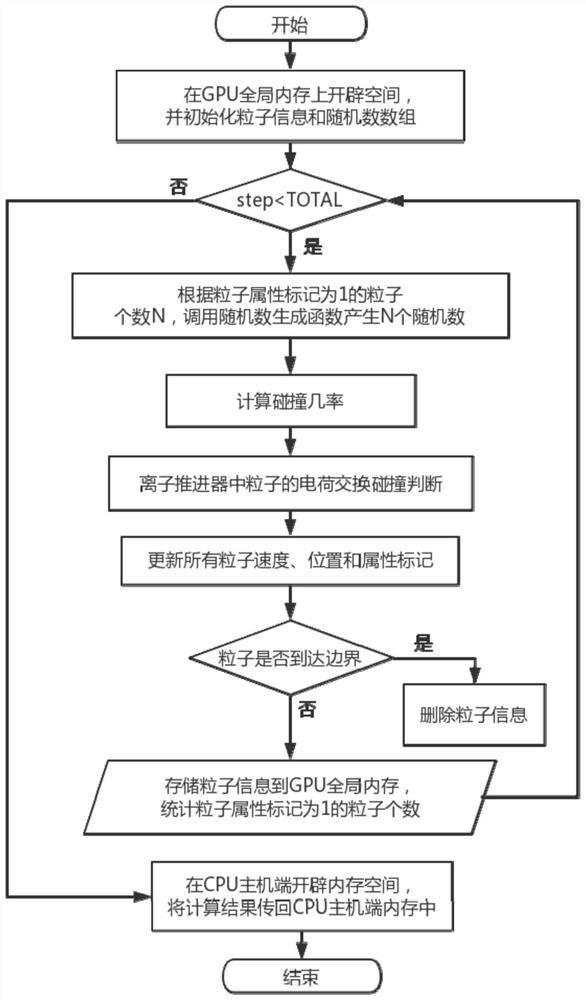
A Charge Exchange Collision MCC Method for Numerical Simulation of Ion Thrusters
A technology of ion propulsion and charge exchange, applied in CAD numerical modeling, geometric CAD, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency and time-consuming calculation, and achieve the effect of saving calculation time and improving calculation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawings and examples.
[0025] In the example, a two-dimensional axisymmetric plume model was tested, using xenon gas as the example of an ion thruster as the propellant. Its cross-sectional diagram is shown in Figure 4 As shown, the charge exchange collision of the ion thruster is simulated in the way of 2D3V. The number of simulated xenon ions is 1 million, and the initial velocity of xenon ions is υ bi , the initial positions of xenon ions are evenly distributed at the gate exit, and the collision cross section of charge exchange collision between xenon ions and xenon atoms is expressed as:
[0026] σ cex =(k 1 lnυ bi +k 2 ) 2 ×10 -20 m 2 (1)
[0027] For xenon ions, the constant coefficient k in the formula 1 =-0.8821,k 2 = 15.1262.
[0028] The probability of a charge exchange collision occurring is expressed as:
[0029] P=1-exp(-n 0 σ cex υ bi Δt) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com