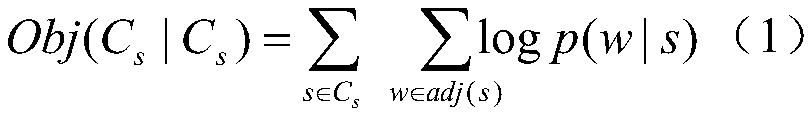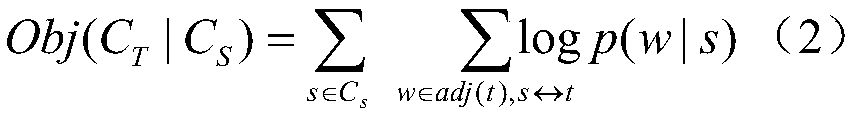Cross-language text classification method based on cross-language word vector representation and classifier joint training
A text classification and word vector technology, applied in natural language translation, natural language data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of low classification accuracy, long training time, large amount of corpus, etc., to achieve strong practicability, good performance, good performance performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
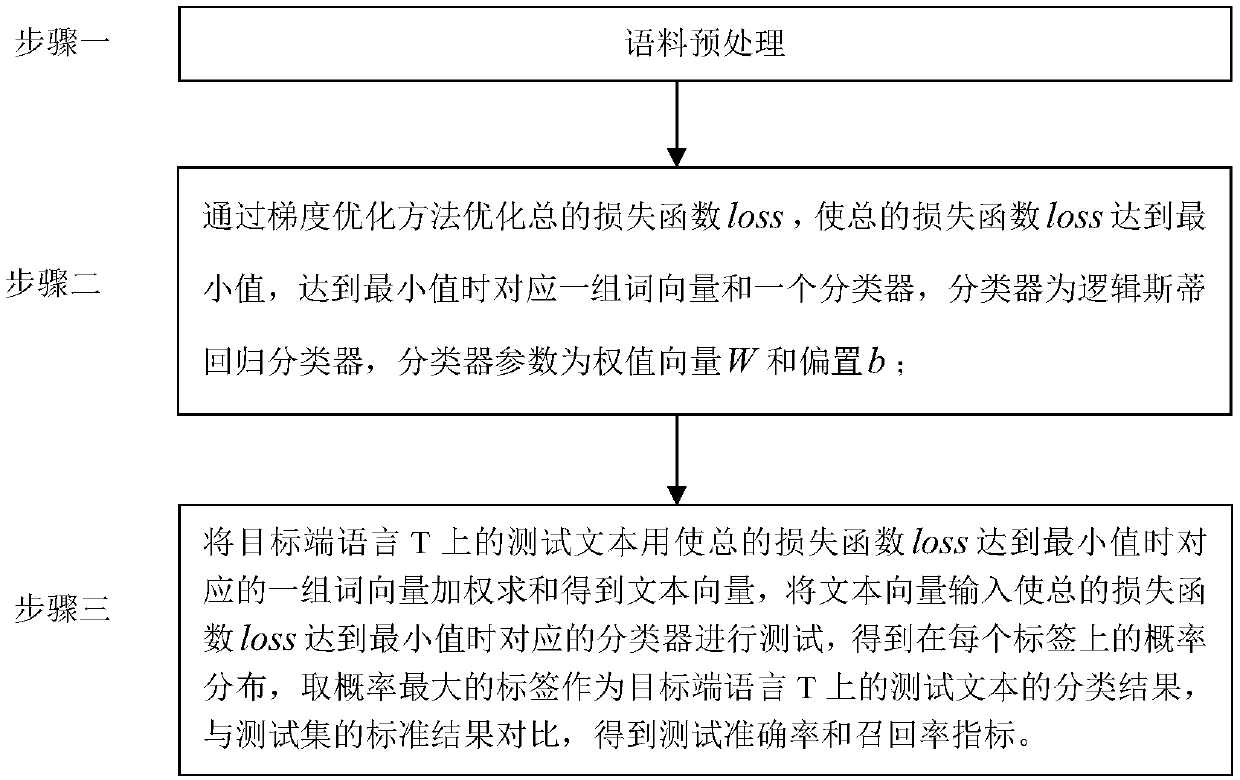
[0025] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, the specific process of the cross-language text classification method based on cross-language word vector representation and classifier joint training in this embodiment is:
[0026] Traditional text classification tasks usually represent a word as a one-hot vector, and represent the text as a high-dimensional text vector through the word bag model. The dimension of the vector is the same as the size of the vocabulary, and the components of the vector in each dimension represent The weight of a word in the text, the common useful word frequency indicates the weight or 0 and 1 represent the existence or non-existence of the word. Using this bag of words representation will cause serious sparsity and dimensionality problems. In large-scale text classification, more computing resources are required. In addition, the word bag representation ignores the context information and word order info...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the specific solution process of the total loss function loss in step 2 is:
[0050] The total loss function consists of three items:
[0051] One is the source language loss, that is, the loss on the source language S, which is obtained from the source language part in the parallel corpus;
[0052] The second is the target-side language loss, that is, the loss on the target-side language T, which is obtained from the target-side language part in the parallel corpus;
[0053] The third is the classifier loss;
[0054] Construct the total loss function loss according to the source-side language loss, target-side language loss and classifier loss.
[0055] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0056] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the source language loss, that is, the loss on the source language S, is obtained from the source language part in the parallel corpus; the specific process is:
[0057] in C s Medium, monolingual (C only s ) loss is:
[0058]
[0059] Among them, C s Represents the source language part; Obj(C s |C s ) represents the monolingual loss in the source language in the parallel corpus; w represents one of the words in the context of the word s in the source language; p(w|s) represents the probability of predicting the window of s under the condition that the central word is s ; adj(s) represents the word in the context of the word s in the source language;
[0060] The probability value p in the formula is obtained by a two-layer fully connected feedforward neural network; the process is:
[0061] Will C s The word vectors of all the words in are input into the neural network as the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com