Method for identifying 28 good varieties of daucus carota, and special primer group thereof
An excellent variety, carrot technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, microbial assay/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as application research of unseen SSR markers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0137] Embodiment 1, be used for the development of the SSR primer of detection carrot fine variety
[0138] 1. Take the sand, sterilize at 130-170°C for 2 hours, and then pass it through a standard sieve (2.0mm in diameter) to collect the sand with a diameter below 2.0mm (that is, the sand under the standard sieve).
[0139] 2. After completing step 1, put the collected sand in the seed box, plant the seeds of Dongyang Qicun, and finally put the seed box in the incubator, and cultivate it at 25°C under alternating light and dark conditions. After 14 days, collect 30 seedlings of equal quality Mix the samples to get sample 1.
[0140] According to the above method, replace Dongyang Qicun with Dongyang Xinxiu, Qishan Black Crown, Qishan Zihuangguan, Qishan Caiguan, Sheng-Qihongguan, Qishan Super Three Reds, Super Eight-inch Ginseng, Three Red Seven Inch Ginseng, Touxin Red, Pheasant Red, Super Red Crown Eight Inch Ginseng, Huayu No. 1, South Korea Jinhongfu, Osaka Three Red Se...
Embodiment 2
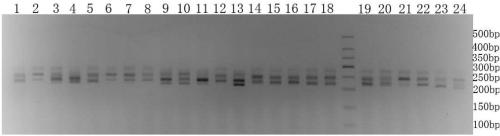
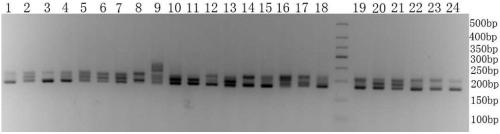
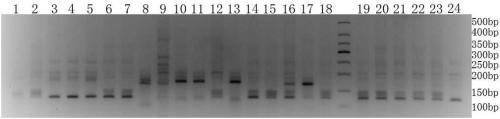
[0145] Embodiment 2, using the SSR primers developed in Example 1 to detect 28 fine varieties of carrots
[0146] 1. Extraction of Carrot Genomic DNA
[0147] A simple method for extracting DNA using improved SDS (Li Li, Zheng Xiaoying. The establishment of EST-SSR composite markers for the identification of Chinese cabbage and Chinese cabbage varieties. Acta Horticultural Science, 2009, 37 (11): 1627-1634) Extraction Example 1 Samples in (sample1, sample2, sample3, sample4, sample5, sample6, sample7, sample8, sample9, sample10, sample11, sample12, sample13, sample14, sample15, sample 16. Genomic DNA of sample 17, sample 18, sample 19, sample 20, sample 21, sample 22, sample 23, sample 24, sample 25, sample 26, sample 27 or sample 28), to obtain the genomic DNA of the sample.
[0148] 2. PCR amplification
[0149] Using the genomic DNA of the sample as a template, perform PCR amplification with primer pair 2-7A, primer pair 2-10H, primer pair SSR-I, primer pair FJ816243 or p...
Embodiment 3
[0169] Embodiment 3, accuracy experiment
[0170] The 13 seeds to be tested are the seeds of excellent carrot varieties that have been phenotyped.
[0171] See columns 1 to 4 in Table 4 for the name, delivery year, delivery company, and phenotypic identification information of each seed to be tested.
[0172] Table 4. Basic information of good carrot seeds to be tested
[0173]
[0174] 1. Obtaining samples to be tested
[0175] (1) Take the sand, sterilize it at 130-170°C for 2 hours, then pass it through a standard sieve (2.0mm in diameter) to collect the sand with a diameter below 2.0mm (that is, the sand under the standard sieve).
[0176] (2) After completing step (1), put the collected sand in the seed box, plant the seeds to be tested respectively, and finally place the seed box in the incubator, and cultivate at 25°C under alternating light and dark conditions. After 14 days, 30 seedlings were collected. Mix the samples with equal mass to obtain the corresponding...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com