A deep space landing geometric orbit determination method, system and deep space lander
A lander, geometric technology, applied in the direction of the integrated navigator, etc., can solve the problems affecting the successful implementation of the mission, GNC command execution errors, altitude calculation errors, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0103] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment the present invention is described in further detail:
[0104] The specific calculation process of the method for geometric orbit determination and attitude determination of deep space landing utilizing ranging and velocity measuring information in the present invention is as follows:
[0105] 1. Determine the representation of the direction vector of the lander relative to Mars in the body coordinate system, and obtain the distance of the lander relative to the center of Mars according to the direction vector:
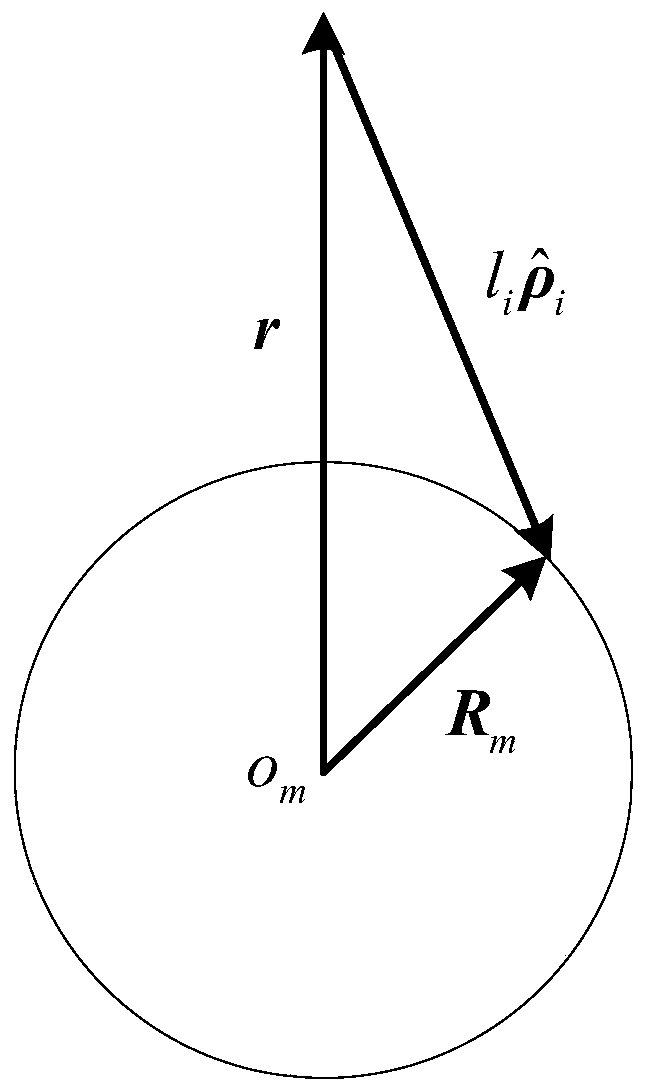
[0106] For the dynamic descent stage of the soft landing mission, Mars can be approximated as a sphere, and the measurement geometry of the ranging sensor, such as figure 1 As shown, you can get:
[0107]
[0108] Where: r is the position vector of the lander relative to the center of Mars, is the direction vector of the beam of the ranging sensor, l is the observation value of the ran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com