Method for detecting water mist on inner surface of windshield
A technology for windshields and inner surfaces, applied to measuring devices, using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves to analyze solids, and using sound waves/ultrasonic waves/infrasonic waves for material analysis, etc., which can solve the problems affecting heat transfer, energy consumption, and difficult process implementation And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
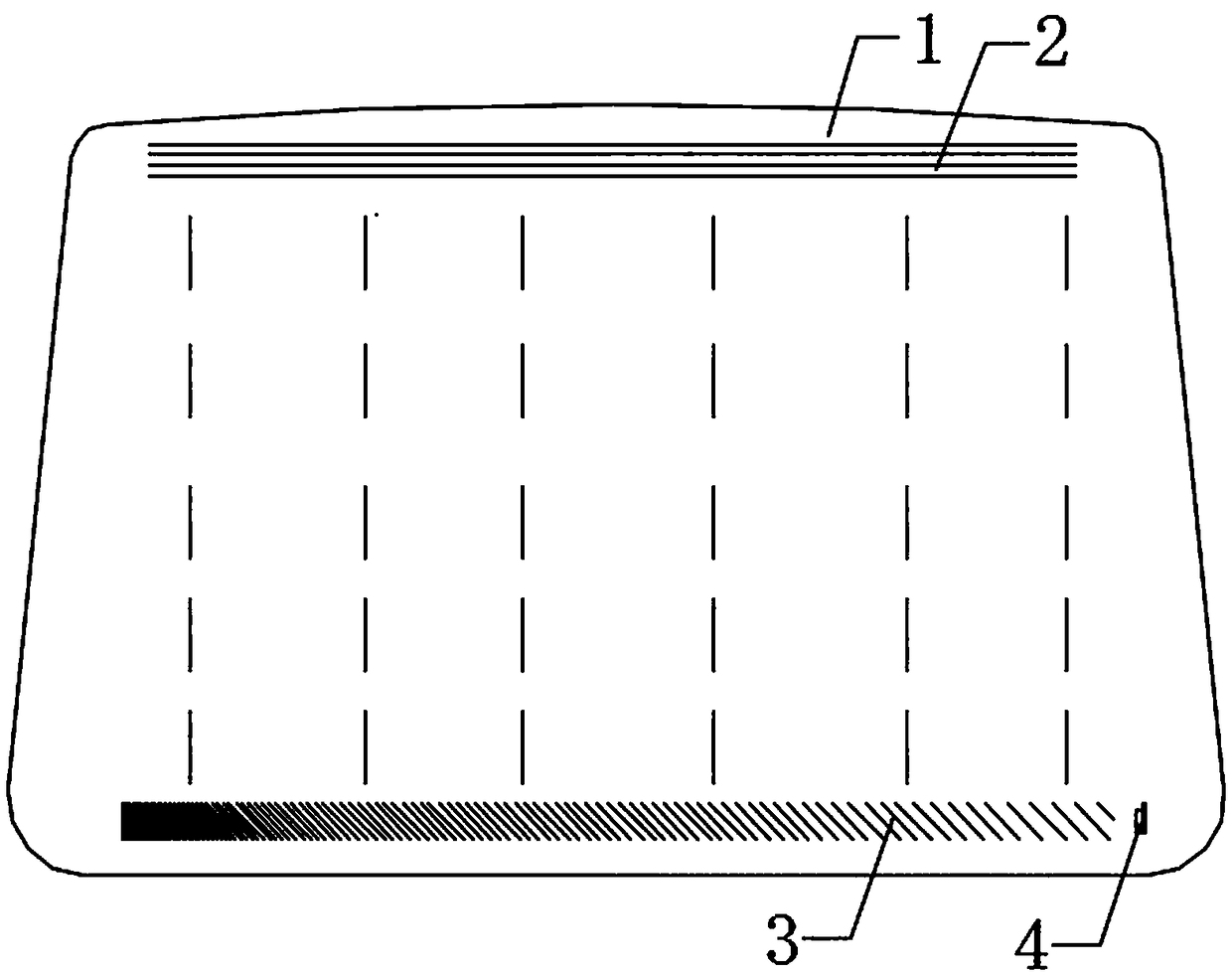
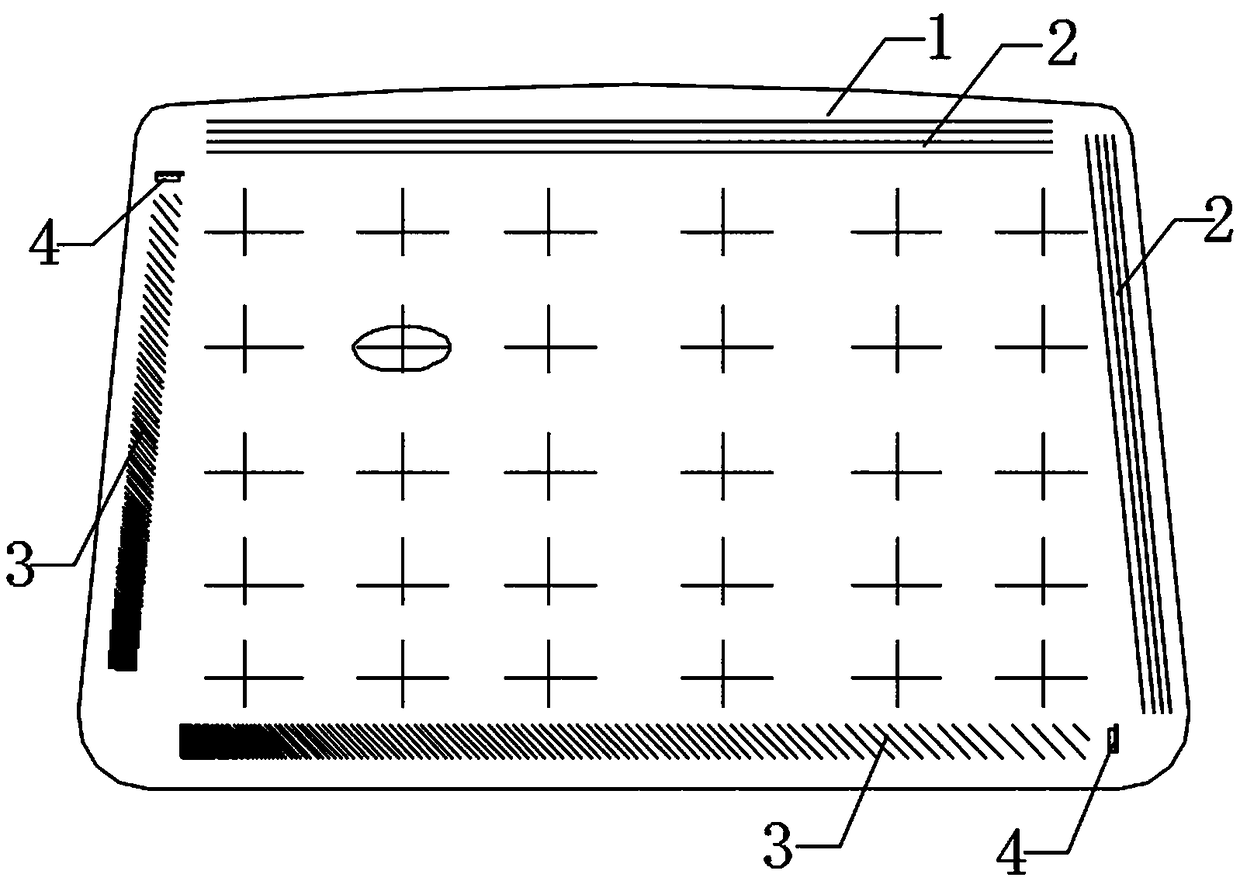
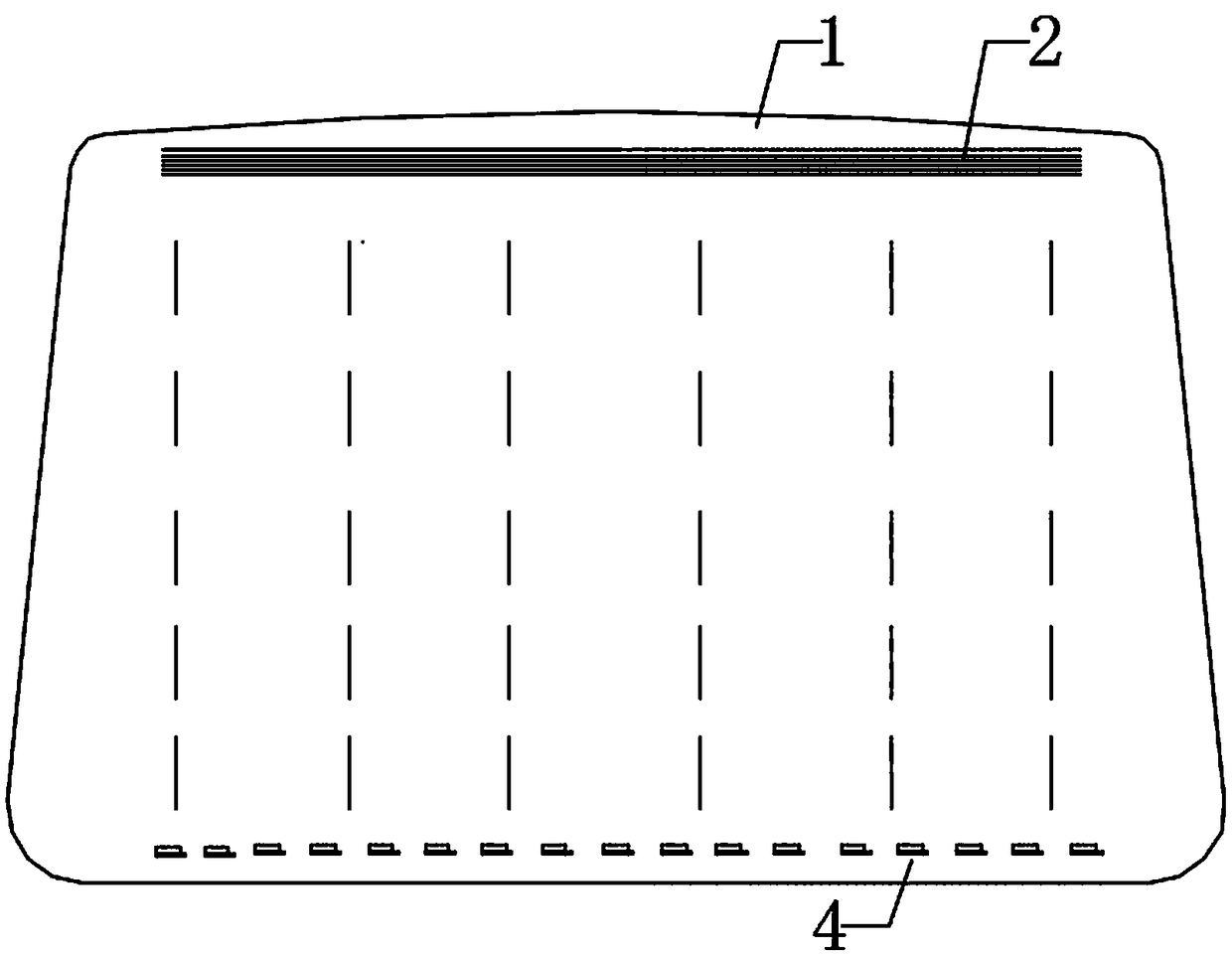
[0057] This embodiment discloses a method for detecting water mist on the inner surface of a windshield, which uses surface ultrasonic waves to detect the water mist on the inner surface 1 of the glass. Specifically, the detection method is as follows: the controller (not shown in the figure) controls the ultrasonic transceiver assembly to form a surface ultrasonic detection area on the inner surface 1 of the glass. When water mist is generated on the inner surface 1 of the glass, the The surface ultrasonic wave is absorbed and attenuated, and the controller determines the position of the water mist on the inner surface 1 of the glass according to the received attenuation signal.
[0058] In this embodiment, the frequency of the surface ultrasonic waves is set to 1.1-10 MHz, which is applicable to windshields of different thicknesses.
Embodiment 2
[0060] This embodiment discloses a method for detecting water mist on the inner surface of a windshield, which uses surface ultrasonic waves to detect the water mist on the inner surface 1 of the glass. Specifically, the detection method is as follows: the controller (not shown in the figure) controls the ultrasonic transceiver assembly to form a surface ultrasonic detection area on the inner surface 1 of the glass. When water mist is generated on the inner surface 1 of the glass, the The surface ultrasonic wave is absorbed and attenuated, and the controller determines the position of the water mist on the inner surface 1 of the glass according to the received attenuation signal.
[0061] In this embodiment, when the attenuation signal received by the controller is higher than the set value, it indicates that the amount of water mist on the inner surface 1 of the glass is relatively large, and it is determined that the amount of water mist on the inner surface 1 of the glass af...
Embodiment 3
[0063] This embodiment discloses a method for detecting water mist on the inner surface of a windshield, which uses surface ultrasonic waves to detect the water mist on the inner surface 1 of the glass. Specifically, the detection method is as follows: the controller (not shown in the figure) controls the ultrasonic transceiver assembly to form a surface ultrasonic detection area on the inner surface 1 of the glass. When water mist is generated on the inner surface 1 of the glass, the The surface ultrasonic wave is absorbed and attenuated, and the controller determines the position of the water mist on the inner surface 1 of the glass according to the received attenuation signal.
[0064] In this embodiment, when the attenuation signal received by the controller is higher than the set value, it indicates that the amount of water mist on the inner surface 1 of the glass is relatively large, and it is determined that the amount of water mist on the inner surface 1 of the glass af...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com