A two-lane cellular automata microscopic traffic simulation method for simulating dynamic lane-changing behavior
A micro-traffic simulation and cellular automata technology, applied in the field of traffic engineering, can solve problems that do not conform to real traffic conditions and cannot be well simulated.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
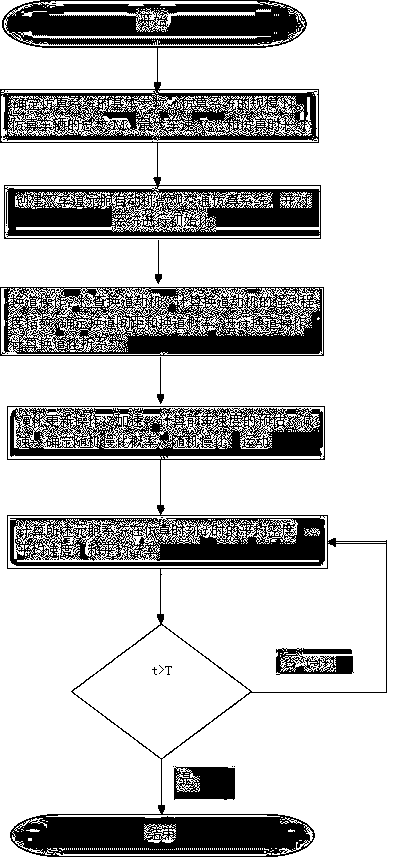
[0040] A two-lane cellular automaton micro-traffic simulation method for simulating dynamic lane-changing behavior, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0041] S1. Determine the basic parameters of the simulation system: the basic parameters include at least the scale N of the simulation system, the total number of simulated vehicles M, and the maximum vehicle speed V max and the simulation time T, where the size N of the simulation system refers to the length of the simulation lane, that is, the number of cells contained in each simulation lane. The entire two-lane cellular automaton simulation system has 2N cells in total. A vehicle occupies a cell, and its speed can take values 0,1,2,...,V max .
[0042] S2. Create a two-lane cellular automaton micro-traffic simulation system and initialize the system. In the created simulation system, the value of each cell is 0 or 1; 0 means that the cell is not occupied by a simulated vehicle. 1 means that the ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com