Pulse shift circuit and frequency synthesizer
A pulse shifting and circuit technology, applied in phase shifter, pulse processing, pulse shaping, etc., can solve the problem of pulse signal output time shift
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
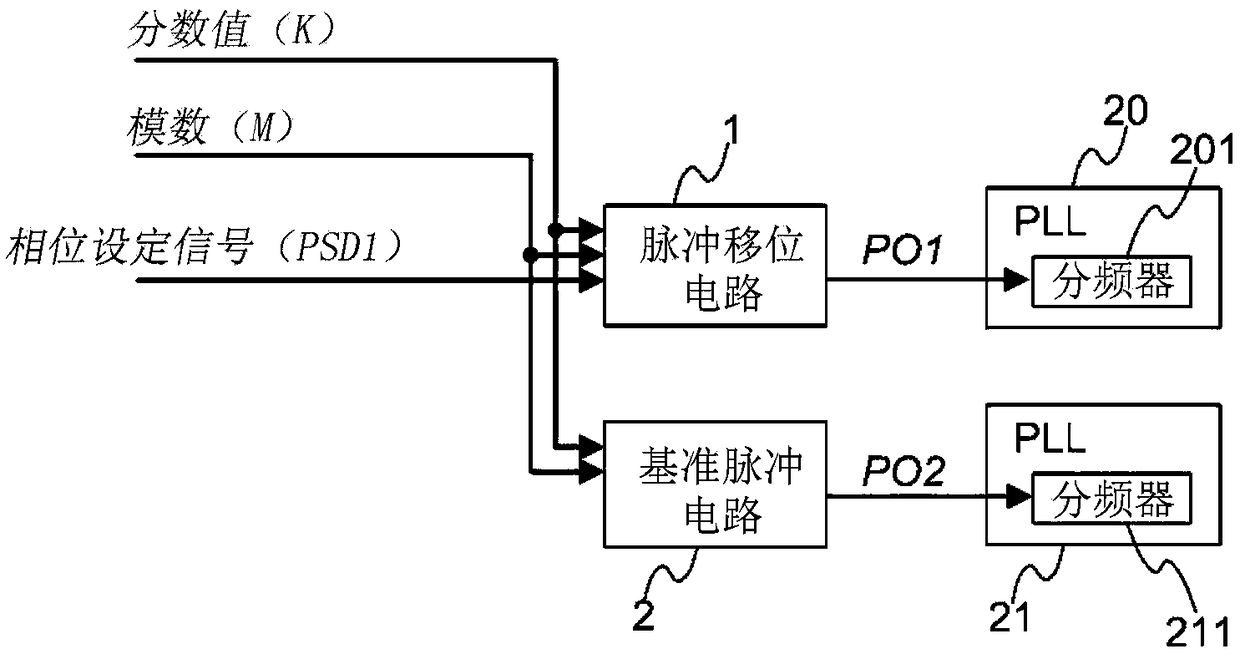
[0031] figure 1 It is a diagram showing an example of use of the pulse shift circuit according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
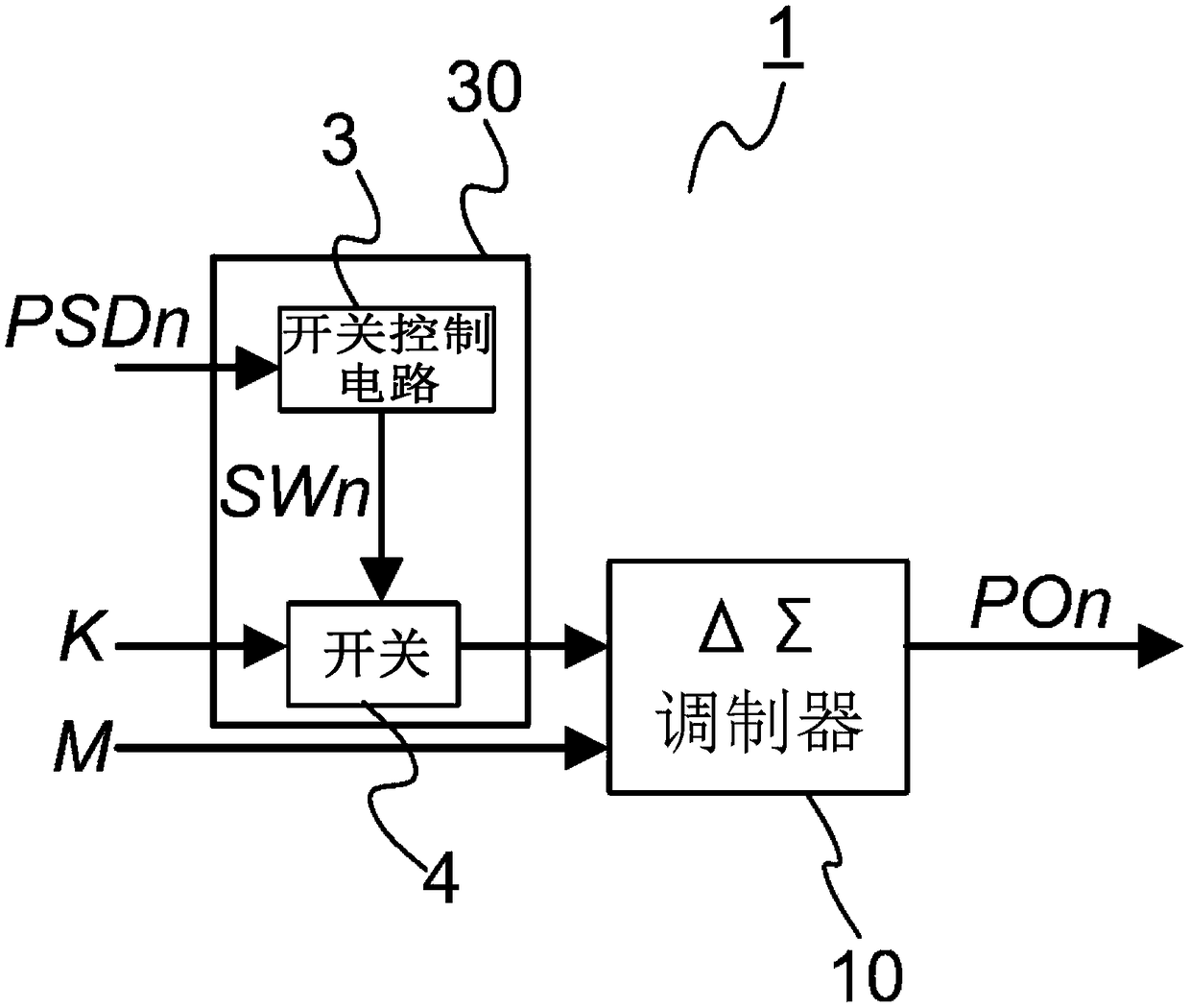
[0032] exist figure 1 Among them, pulse shift circuit 1, PLL 20, reference pulse circuit 2 and PLL 21 constitute a frequency synthesizer capable of controlling the phase difference of two PLL output signals. The pulse shift circuit 1 is connected to a frequency divider 201 built in the PLL 20 . The reference pulse circuit 2 is connected to a frequency divider 211 built in the PLL 21 . K (an example of the first signal) is frequency setting data and is generally called a fractional value. M (an example of the second signal) is frequency setting data and is generally called a modulus. PO1 and PO2 are the frequency division number control signals of the frequency divider 201 and the frequency divider 211 respectively, and are pulse signals output according to the cycle of M / K. The values below the decimal point of the frequency division...
Embodiment approach 2
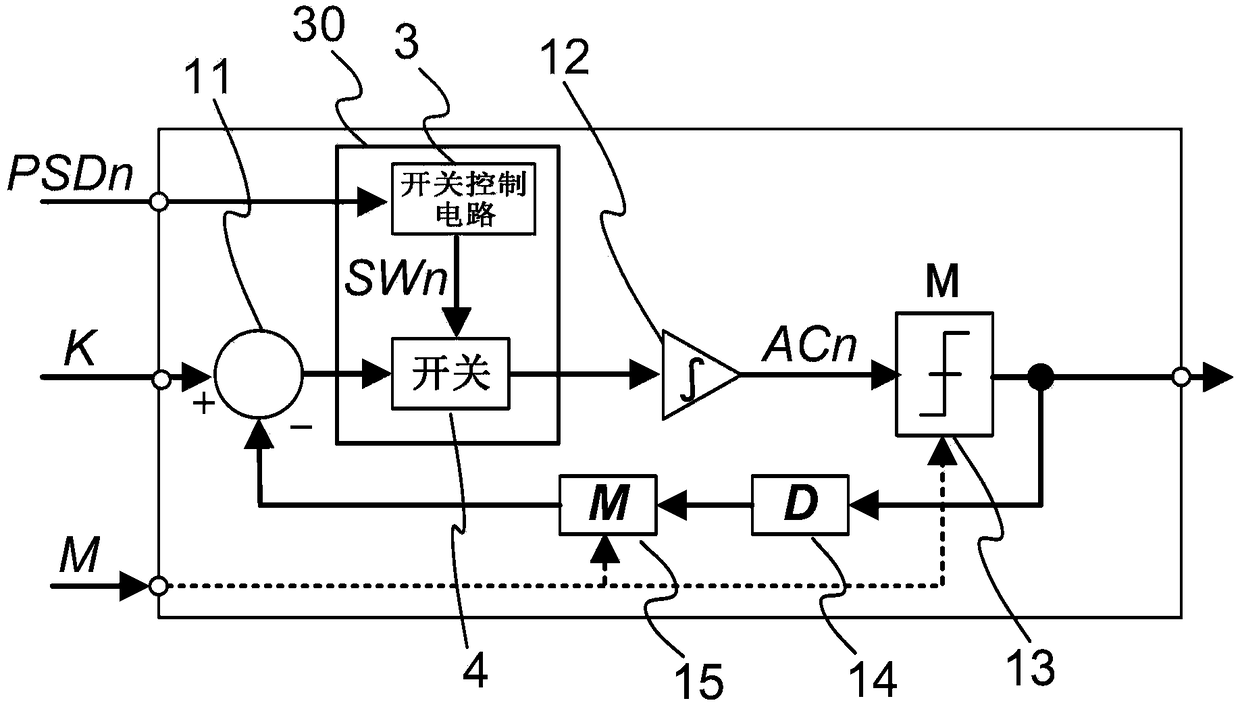
[0066] Embodiment 1 shows a circuit configuration in which, in the pulse shift circuit, the signal input to the integrator 12 of the ΔΣ modulator 10 is held constant for several clocks according to the phase setting signal, thereby realizing frequency division. The shift of the digital control signal (PO1). Here, a circuit configuration is shown in which the frequency division number control signal is shifted with one clock in the pulse shift circuit. Accordingly, the operating time of the circuit can be reduced, and an effect of reducing power consumption of the circuit can be obtained.
[0067] Figure 6 It is a configuration diagram showing a configuration example of a pulse shift circuit according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The input signal control circuit 31 is different from the pulse shift circuit 1 of the first embodiment in that it is composed of an addition bit generation circuit 5 and an adder 6 .
[0068] The addition bit generation circuit 5 is a...
Embodiment approach 3
[0081] In Embodiment 1, the case where K of the pulse shift circuit is fixed is shown. Here, the case where K of the pulse shift circuit changes with time is shown. Thus, in an F-PLL that generates an FM (Frequency Modulation: Frequency Modulation) signal such as a chirp signal, pulse shifting for phase difference control can be realized.
[0082] Figure 9 It is a configuration diagram showing a configuration example of a pulse shift circuit according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. The pulse shift circuit of Embodiment 3 is the same as that of Embodiment 1 figure 2 The input side of the shown pulse shift circuit 1 has an FM control circuit 41 , an integrator 42 and an addition circuit 43 .
[0083] The FM control circuit 41 is an FM control circuit that outputs a derivative amount of K corresponding to a frequency change amount in FM. For example, the FM control circuit 41 uses a logic circuit of FPGA.
[0084] The integrator 42 is an integrator that integrat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com