Weighted fraction Fourier transform domain double-time-slot diversity and multiplexing cooperated transmission method
A fractional Fourier and cooperative transmission technology, which is applied in the field of cooperative transmission of dual-slot diversity and multiplexing, can solve the problems that single-antenna systems cannot achieve diversity gain and multiplexing gain, and improve diversity gain and diversity gain Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
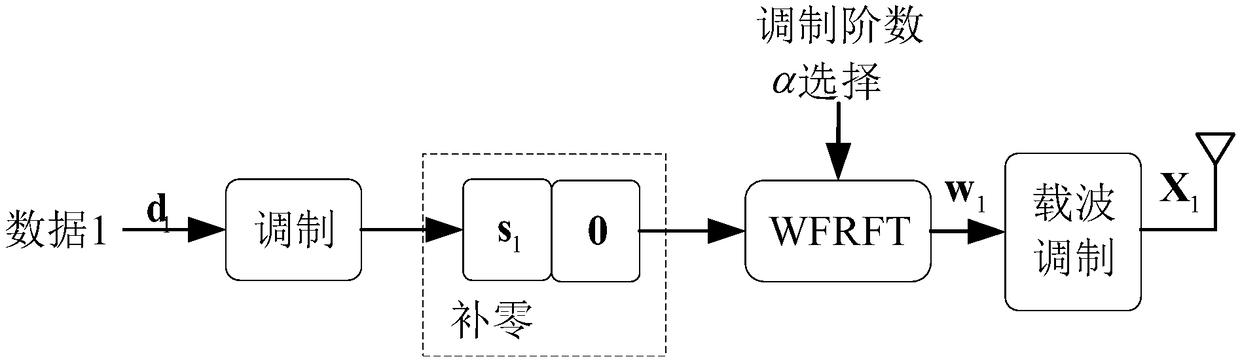
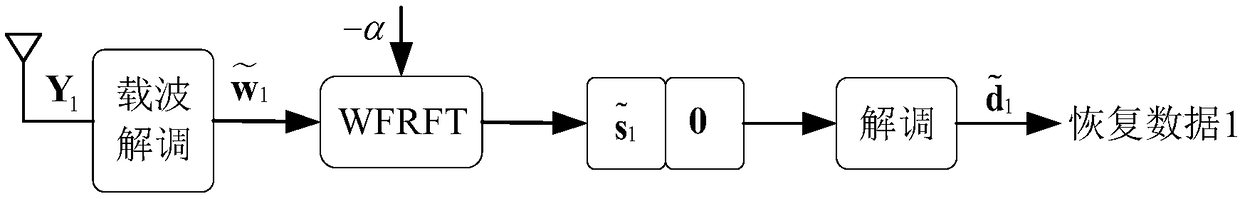
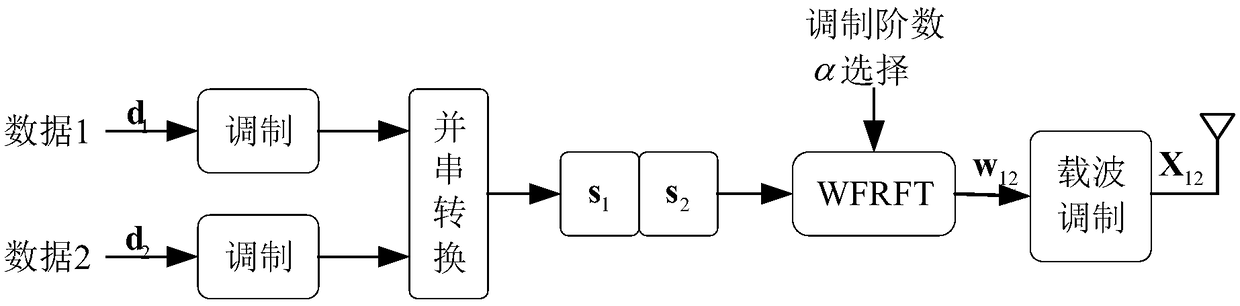
[0029] Specific implementation mode one: as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the weighted fractional Fourier transform domain dual-slot diversity and multiplexing coordinated transmission method described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0030] Step 1. Data d sent by the user at the sending end 1 Perform modulation to obtain the modulated baseband data s at the transmitting end 1 , and baseband data s at the sender 1 Carry out zero padding processing to obtain the data after zero padding processing;
[0031] Step 2. Perform a weighted fractional Fourier transform with an order of α on the zero-padding data obtained in step 1, and obtain the weighted fractional Fourier transformed data w 1 ;
[0032] Step 3, the data w obtained in step 2 1 Modulate to the corresponding carrier frequency to obtain the modulated data X 1 , and transmit a signal X through the antenna 1 , signal X 1 After being transmitted through the channel, it reaches the receiving end...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0043] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: the specific process of the step one is:
[0044] The user at the sending end sends data in a manner of equal probability and energy sharing, and the sent data d 1 The vector form of is:
[0045]
[0046] In the formula, s m (t) is M signal waveforms in digital phase modulation, M is M possible phases of the carrier, m=1, 2,..., M, used to transmit sending information, s m (t) represents the correspondence between each m and the transmitted signal, ε g is the energy of the signal pulse;
[0047] The data sent by the user at the sending end d 1 Perform modulation to obtain the modulated baseband data s at the transmitting end 1 ;
[0048] The signal generator at the sending end generates a series of m sequences, and each point passes through s m (t) corresponds to a modulated symbol, and these symbols finally form the transmission sequence ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0051] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the data d sent to the user at the sending end in step 1 1 For modulation, the modulation method adopted is the phase shift keying BPSK method.
[0052] For the phase-shift keying BPSK method of this embodiment, the modulated signal is a series of 01 sequences, and the present invention is compatible with various modulation methods, and this embodiment takes the phase-shift keying BPSK method as an example.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com