Fluorescence-lifetime imaging microscopy method having time-correlated single-photon counting, which method permits higher light intensities
A single photon counting, fluorescence lifetime technique, applied in the field of microscopy, which can solve the problems of cost realization, time resolution and signal utilization limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
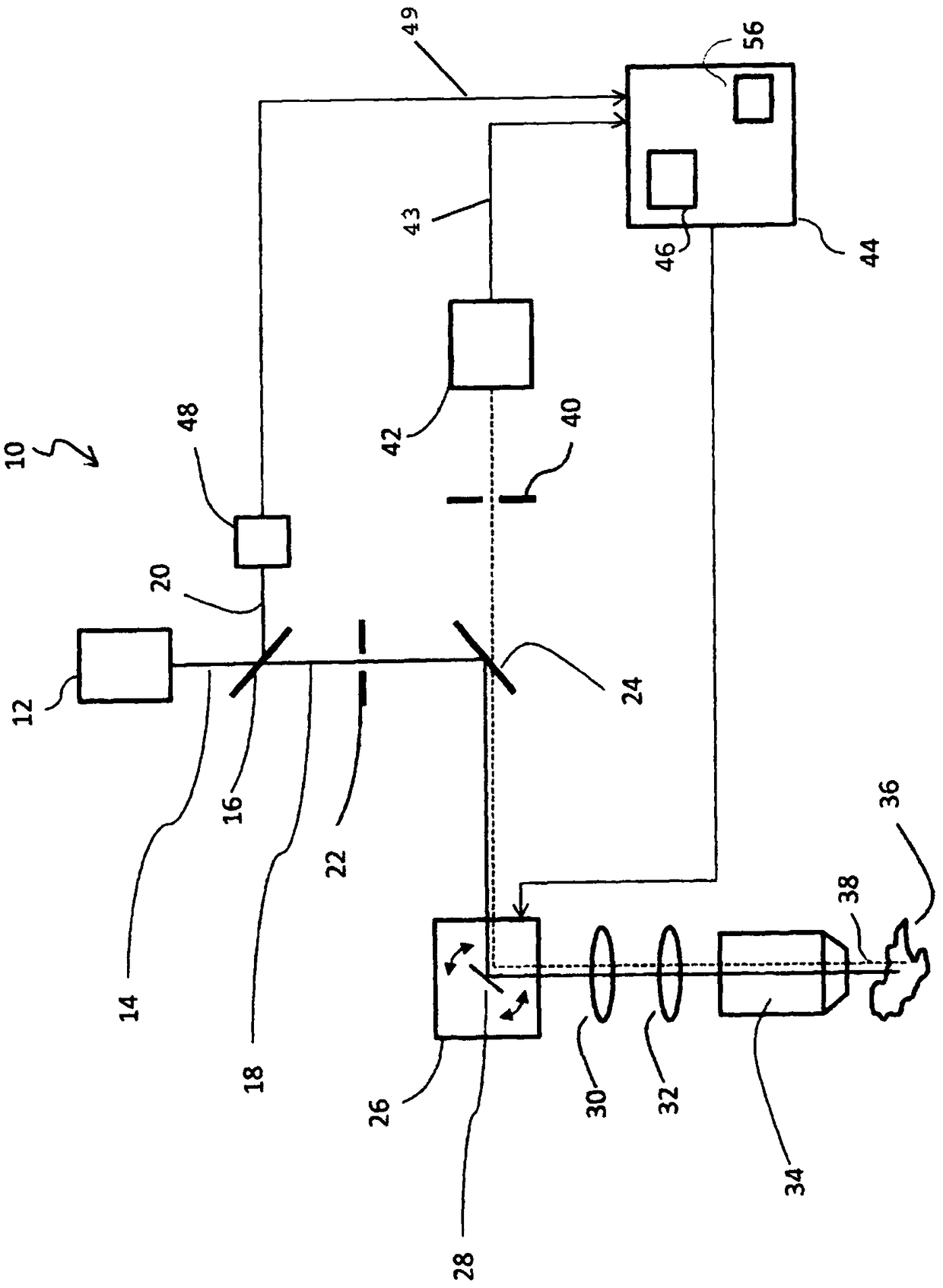
[0052] figure 1 A confocal scanning microscope 10 is shown, which is an embodiment of a microscope according to the invention.
[0053] The confocal scanning microscope 10 has a pulsed laser source 12 which is designed to emit light with periodic excitation light pulses. exist figure 1 Excitation light, denoted by 14 , enters a beam splitter 16 , which splits the excitation light 14 into a transmissive portion 18 and a reflective portion 20 .
[0054] Excitation light 18 transmitted through beam splitter 16 passes through excitation aperture 22 and is then reflected on dichroic beam splitter 24 in the direction of scanning unit 26 . Scanning unit 26 includes a gimbaled scanning mirror 28 which reflects excitation light 14 in the direction of scanning lens 30 . After passing through scan lens 30 and tube lens 32 , the excitation light enters microscope objective 34 , which directs excitation light 18 onto sample 36 .
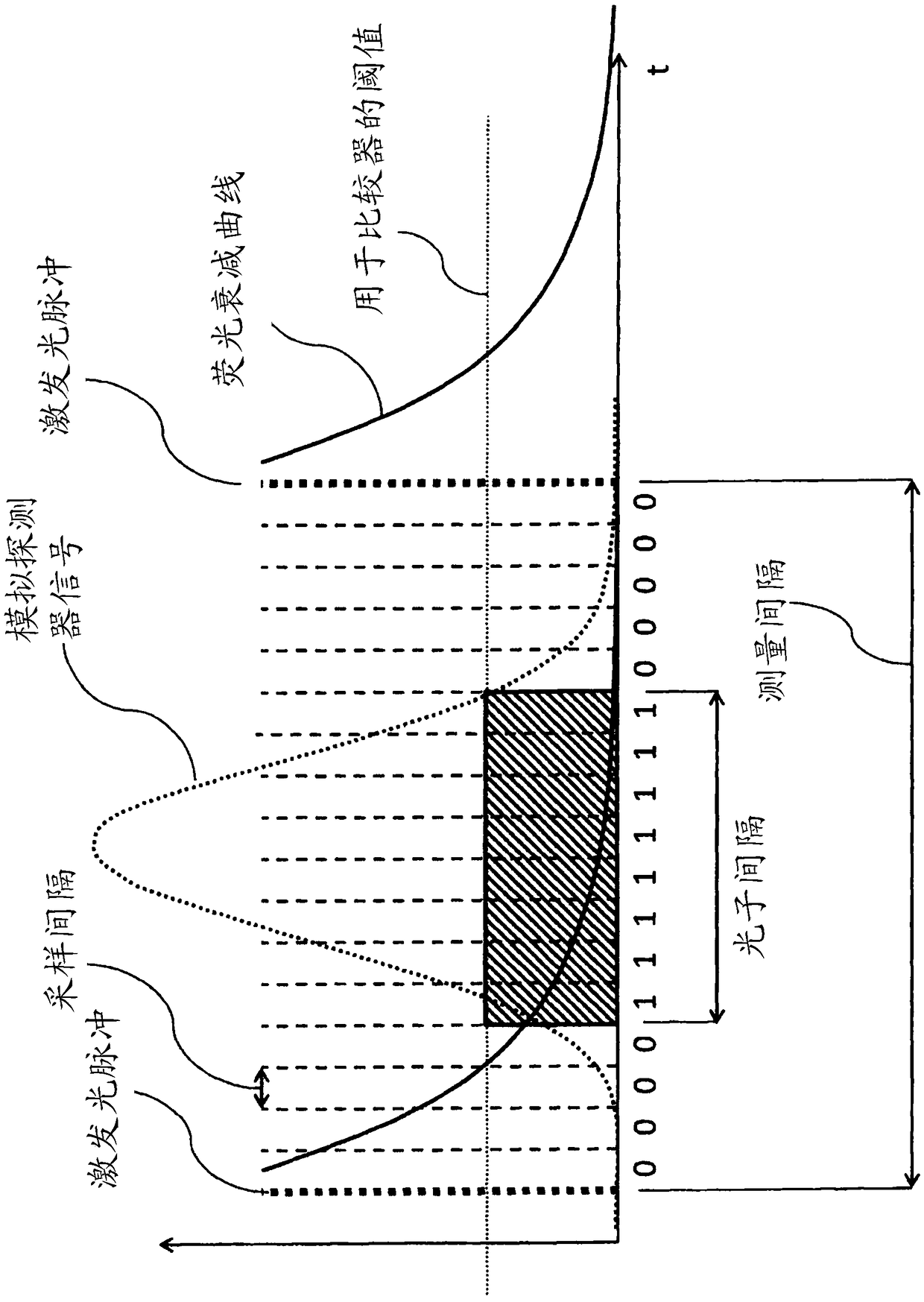
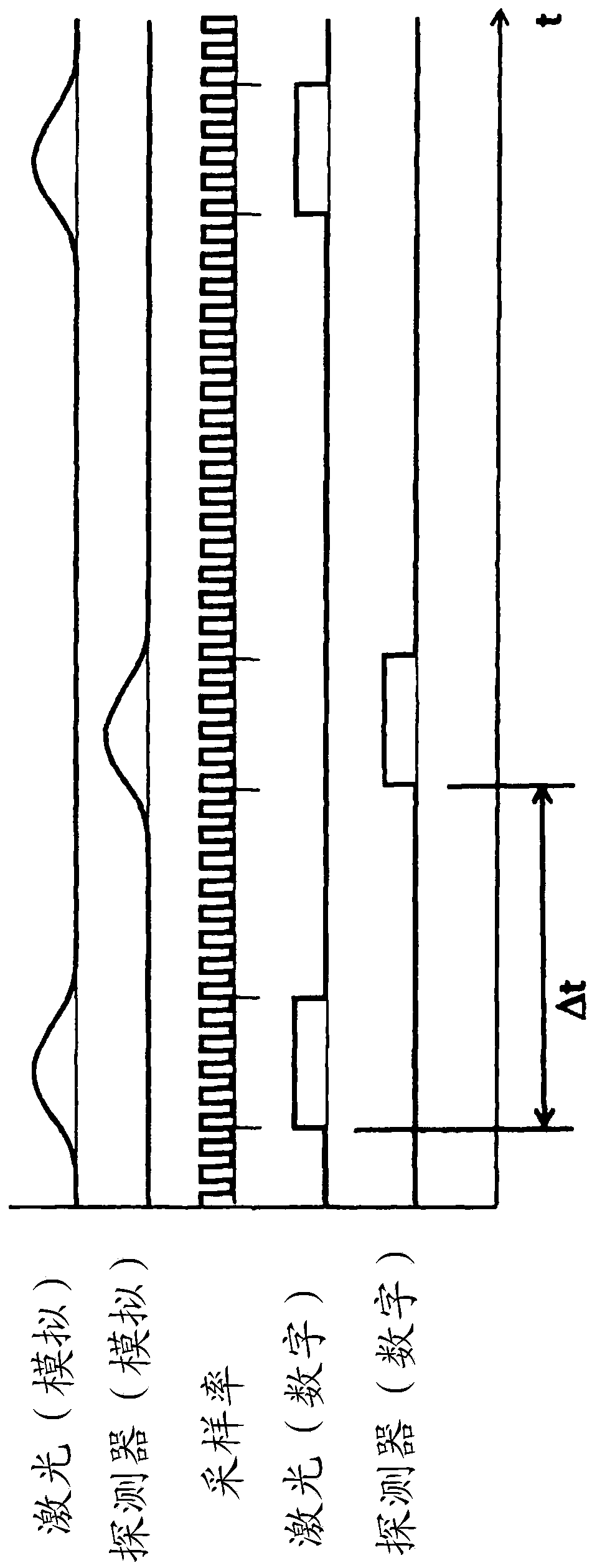
[0055] In the region of the sample 36 irradiated with t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com