A data synchronization system adaptive dynamic adjustment method and device
A data synchronization and dynamic adjustment technology, applied in database management systems, special data processing applications, structured data retrieval, etc., can solve problems such as inability to self-adjust, affect performance, lack of self-adaptive ability of worker threads, etc., to enhance the process The effect of adaptively adjusting processing power and improving overall performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
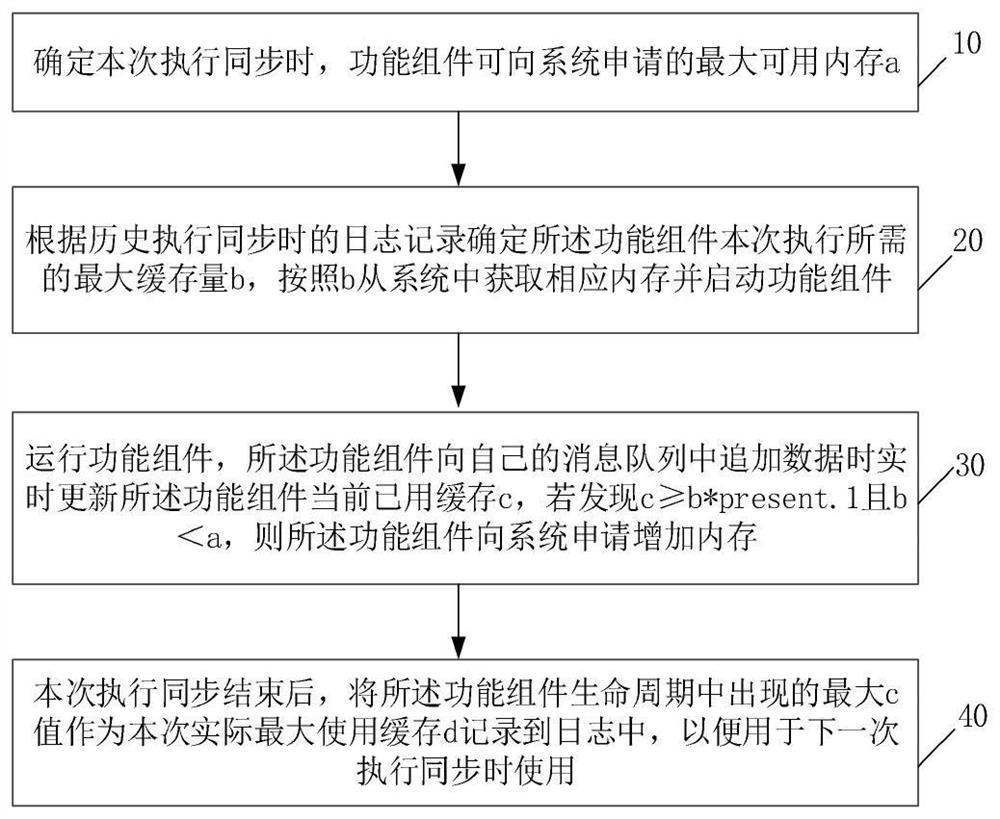
[0054] An embodiment of the present invention provides a data synchronization system adaptive dynamic adjustment method,
[0055] For the convenience of description, the letters a-e are used to represent different cache amounts, among which:
[0056] The value of a indicates the maximum amount of cache that the functional component can apply to the system during this execution, which is recorded as the maximum available memory: maxCacheSize;
[0057] The b value indicates the maximum cache size that the functional component has obtained from the system according to the maximum cache size it may need during this execution, which is recorded as the current available cache: currentAvailableCacheSize;
[0058] The c value indicates the amount of cache actually used by the functional component during this execution, which is recorded as the currently used cache: currentUsingCacheSize;
[0059] The d value indicates the maximum cache amount actually used in the life cycle of the fu...
Embodiment 2
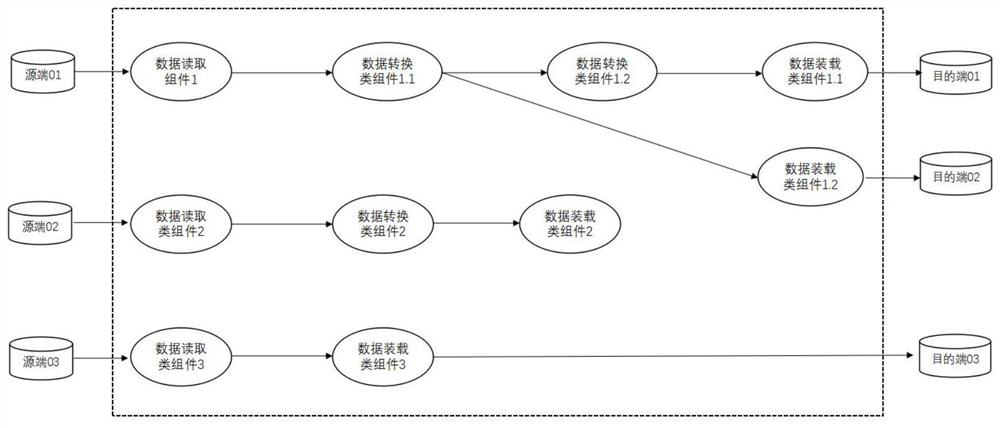
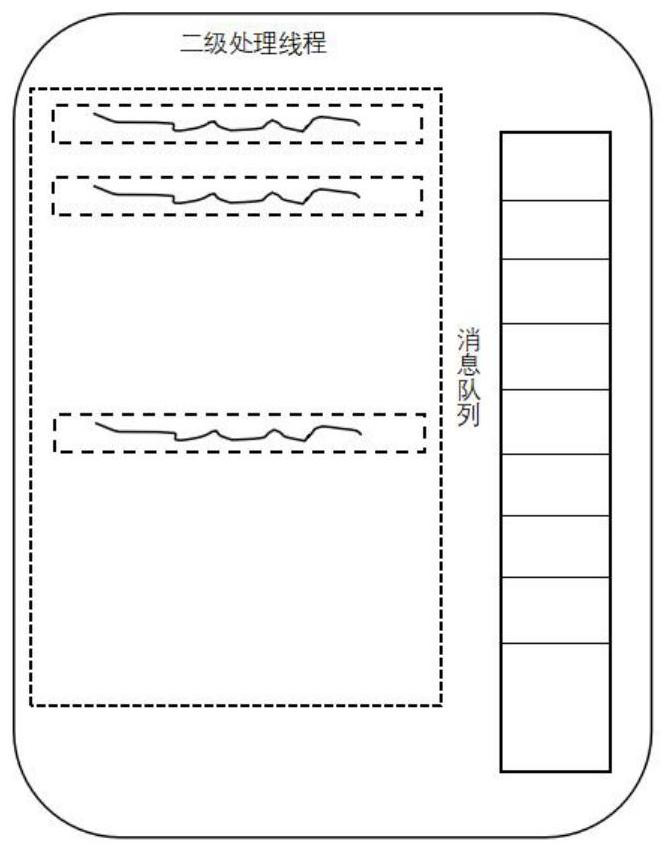
[0076] On the basis of Embodiment 1 above, the embodiment of the present invention provides a specific implementation method for dynamically adding primary threads and secondary threads during the synchronization process. It can be seen from Embodiment 1 that in the step 30, when the functional component adds data to its own message queue, if c≥b*present.1 is found, the functional component notifies its downstream component to add a secondary thread . In addition, the functional component can also notify its upstream component to add a secondary thread, specifically, when the functional component reads data from the message queue of its upstream component, if it finds that the message queue of the upstream component is empty or the message If the amount of cached data in the queue is less than the preset threshold, it means that the processing capability of the upstream component to read data or convert data is too low to keep up with the processing speed of the functional com...
Embodiment 3
[0088] On the basis of a data synchronization system adaptive dynamic adjustment method provided in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, the present invention also provides a data synchronization system adaptive dynamic adjustment device that can be used to implement the above method, such as Image 6 Shown is a schematic diagram of the device architecture of the embodiment of the present invention. The data synchronization system adaptive dynamic adjustment device of this embodiment includes one or more processors 21 and memory 22 . in, Image 6 A processor 21 is taken as an example.
[0089] The processor 21 and the memory 22 may be connected via a bus or in other ways, Image 6 Take connection via bus as an example.
[0090] The memory 22, as a non-volatile computer-readable storage medium of a data synchronization system adaptive dynamic adjustment method, can be used to store non-volatile software programs, non-volatile computer-executable programs and modules, as in Embodim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com