Zero-emission treatment system and process for volatile phenol in salt-containing wastewater
A technology of salt-containing wastewater and volatile phenol, applied in water/sewage treatment, heating water/sewage treatment, flotation water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of limiting size scale, limiting reactor size, reactor clogging, etc. Achieve the effect of reducing the cost of materials, less welding seams, and less clogging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
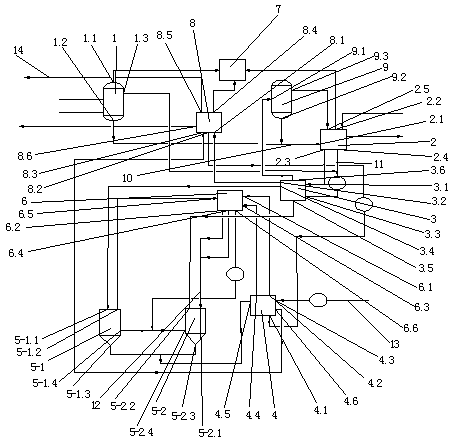
[0029] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, a zero-emission treatment system for volatile phenols in saline wastewater, including air flotation tank 1, multi-effect evaporator 2, No. 1 preheating heat exchanger 3, No. 2 preheating heat exchanger 4, supercritical Reactor, multi-stream heat exchanger 6, incineration torch 7, concentration equipment 8, flash tank 9, the supercritical reactor is provided with the upper feed port of the supercritical reactor and the lower feed port of the supercritical reactor, the supercritical The feed inlet of the lower part of the reactor is located in the middle and lower part of the side wall of the supercritical reactor, and the supercritical reactor is provided with two respectively No. 1 supercritical reactor 5-1 and No. 2 supercritical reactor 5-2, and an air flotation tank 1 The gas charged is inert gas, the gas outlet 1.1 of the air flotation tank is connected with the incineration torch 7, the water outlet 1.2 of the air flotation tank ...
Embodiment 2
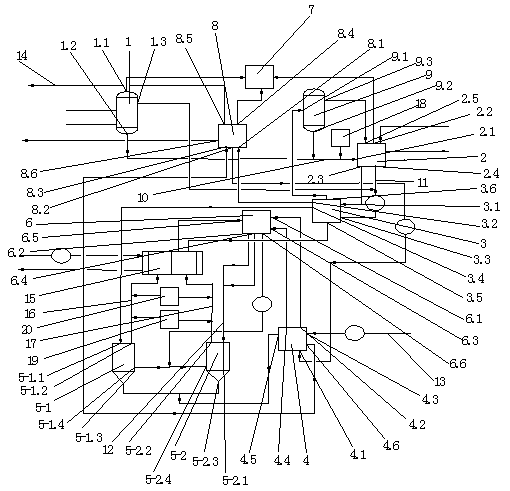
[0030] Embodiment 2: as figure 2 As shown, a zero-emission treatment system for volatile phenols in saline wastewater, including air flotation tank 1, multi-effect evaporator 2, No. 1 preheating heat exchanger 3, No. 2 preheating heat exchanger 4, supercritical Reactor 5, multi-stream heat exchanger 6, incineration torch 7, concentration equipment 8, flash tank 9, supercritical reactor 5 is provided with supercritical reactor upper feed inlet and supercritical reactor lower feed inlet, The feed inlet of the lower part of the supercritical reactor is located at the middle and lower part of the side wall of the supercritical reactor 5, and the supercritical reactor 5 is provided with two respectively No. 1 supercritical reactor 5-1 and No. 2 supercritical reactor 5-2, The gas outlet 1.1 of the air flotation tank is connected with the incineration torch 7, the water outlet 1.2 of the air flotation tank is connected with the feed liquid inlet 2.1 of the multi-effect evaporator th...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Embodiment 3: as figure 1 As shown, a zero-emission treatment process for volatile phenol in saline wastewater includes the following steps: the salt-containing phenol wastewater is separated from oil, gas, and waste water through the air flotation tank 1, and the waste gas separated by the air flotation tank 1 is incinerated The torch 7 is incinerated, the waste water at the separation place of the air flotation tank 1 is evaporated by the multi-effect evaporator 2, the waste gas of the multi-effect evaporator 2 is incinerated by the torch 7, and the concentrated waste water after the multi-effect evaporation is heated by the No. 1 preheating heat exchanger 3 After entering the concentration equipment 8 to concentrate, the waste gas produced after concentration is sent to incineration torch 7 for incineration, the concentrated steam is discharged outside, and the concentrated liquid after concentration is heated by No. 2 preheating heat exchanger 4 and then passed throu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com