Treatment of diseases mediated by vascular hyperpermeability
A technology of permeability and blood vessels, applied in the direction of sensory diseases, serum albumin, organic active ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as vascular leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0151] Example 1: Effect of LMWFHSA on Permeability of Retinal Endothelial Cells
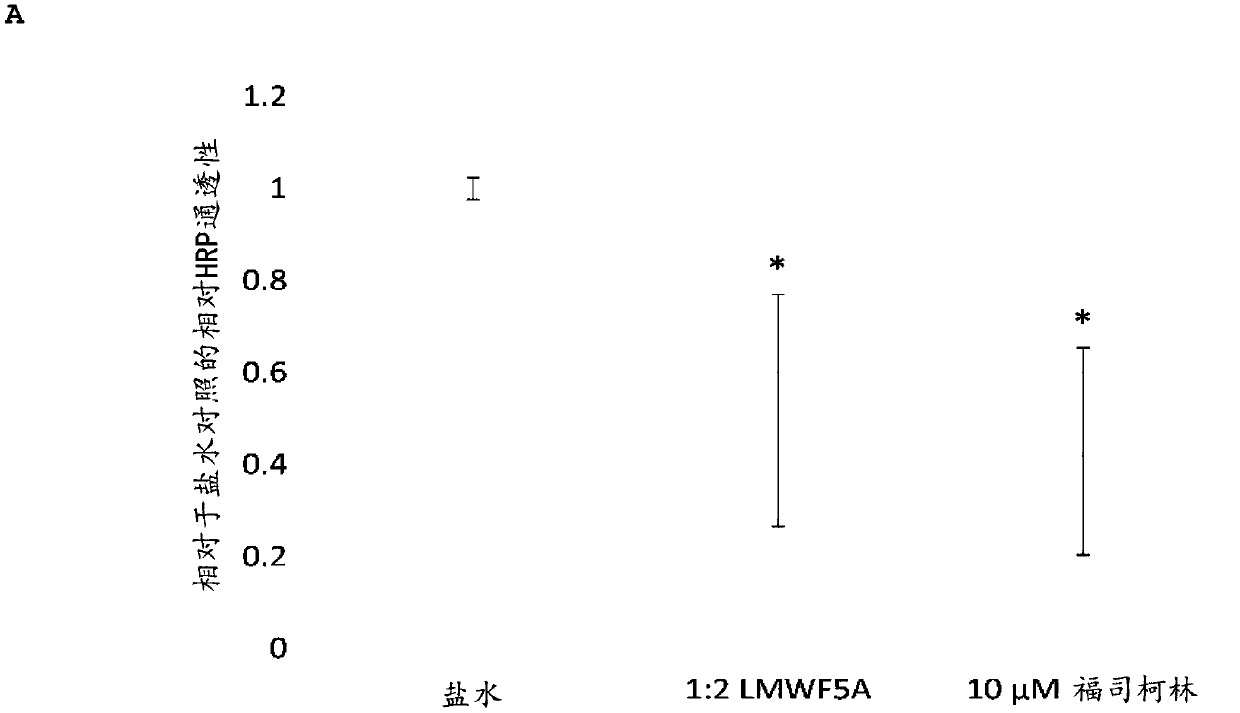
[0152] To assess the effect of LMWFHSA on vascular permeability, two in vitro assays were employed. First, passage of HRP was measured between confluent HREC monolayers established on multiwell transwell inserts. Such as Figure 1A It was seen that LMWFHSA ("LMWF5A") significantly reduced HRP permeability in this model by 48% compared to saline-treated controls (p<0.025; n=3). A similar reduction was achieved by treatment with 10 [mu]M forskolin.
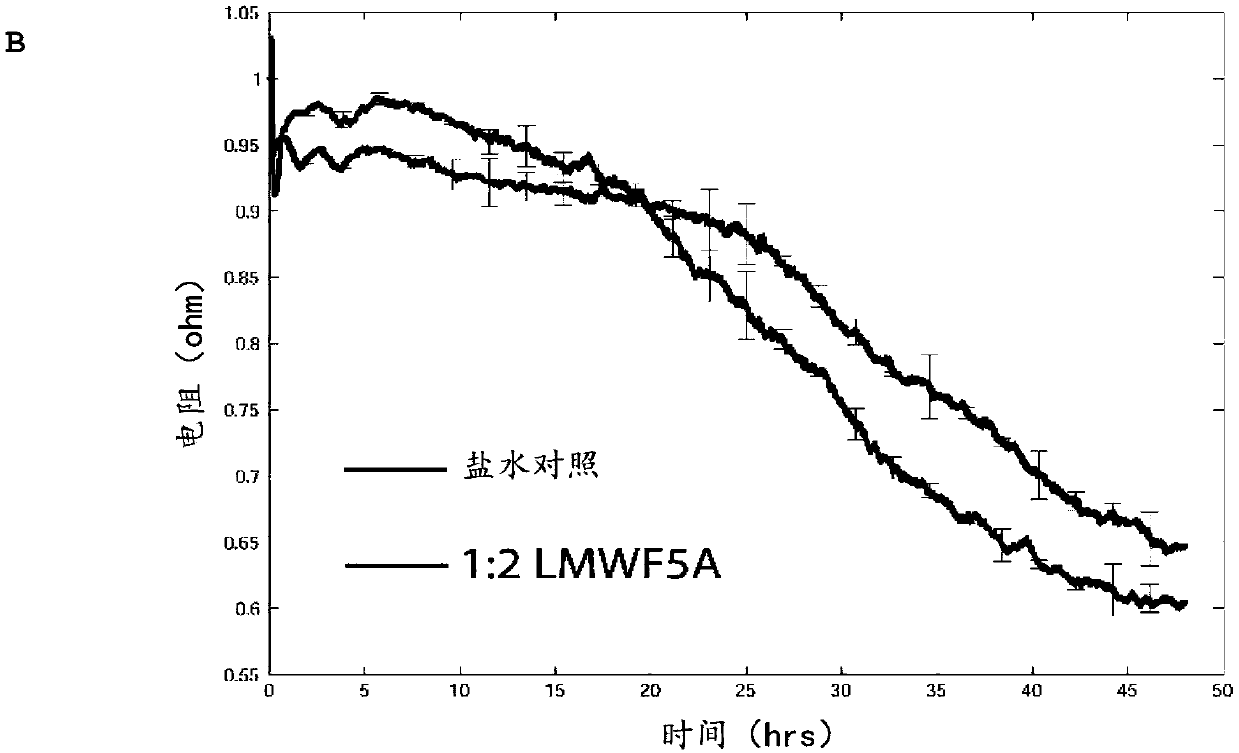
[0153] Having established that LMWFHSA reduces macromolecular permeability, transendothelial resistance was then monitored for up to 48 hours after treatment. In this assay, an immediate increase in electrical resistance was observed for 30 minutes following exposure to LMWFHSA, followed by a 2-5% decrease compared to saline for about 15 hours ( Figure 1B ). However, after 24 hours, LMWFHSA-treated cells exhibited an increase in electrical resist...
Embodiment 2
[0154] Example 2: Temporal and phenotypic changes in HRECα-tubulin acetylation induced by LMWFHSA
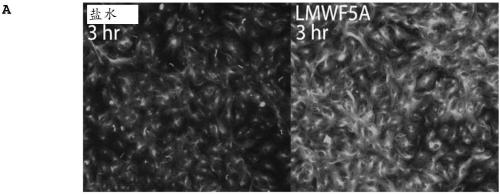
[0155] Previous studies demonstrated that LMWFHSA treatment of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells resulted in a reduction of cytoplasmic stress fibers that coincided with the formation of filopodia-like protrusions around the cell periphery (Bar-Or D, et al. Low Molecular Weight Fraction of Commercial Human Serum Albumin Induces Morphologic and Transcriptional Changes of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Transl Med2015; 4:945-955). However, in HREC, no appreciable changes in f-actin were observed after treatment (data not shown). In contrast, immunofluorescence (IF) staining revealed that HRECs exhibited a marked increase in α-tubulin acetylation, a sensory marker of microtubule stabilization, 3 hours after exposure to LMWFHSA ( Figure 2A ). Figure 2B Depicted is a representative IF experiment in which temporal changes in LMWFHSA-induced tubulin ...
Embodiment 3
[0157] Example 3: LY294002 (PI3-kinase inhibitor) reduces LMWFHSA-induced α-tubulin acetylation, while SB203580 (p38MAPK inhibitor) enhances LMWFHSA-induced α-tubulin acetylation
[0158] This example evaluates the effect of inhibition of PI3-kinase and inhibition of p38MAPK on LMWF5A-induced α-tubulin acetylation of HRECs. HREC were treated with LMWFHSA in the presence of specific inhibitors and IF was performed 3 hr later. Such as Figure 4A As seen, inhibition of PI3-kinase with 10 μM LY294002 reduced LMWFHSA-induced acetylation (p=0.025 vs. LMWF5A+DMSO; n=6). When percent inhibition was calculated for four separate experiments performed in triplicate, LY294002 was found to reduce LMWFHSA-induced acetylation by 24% (95% CI 29-19). In contrast, inhibition of p38MAPK with SB203580 significantly acetylated α-tubulin relative to both saline-DMSO control (p Figure 4B ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com