A mechanically enhanced composite tissue engineering scaffold material and its preparation method
A technology of composite tissue and scaffold materials, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems of too fast degradation, long degradation cycle, unfavorable seed cell adhesion, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Embodiment 1, the preparation of composite support material
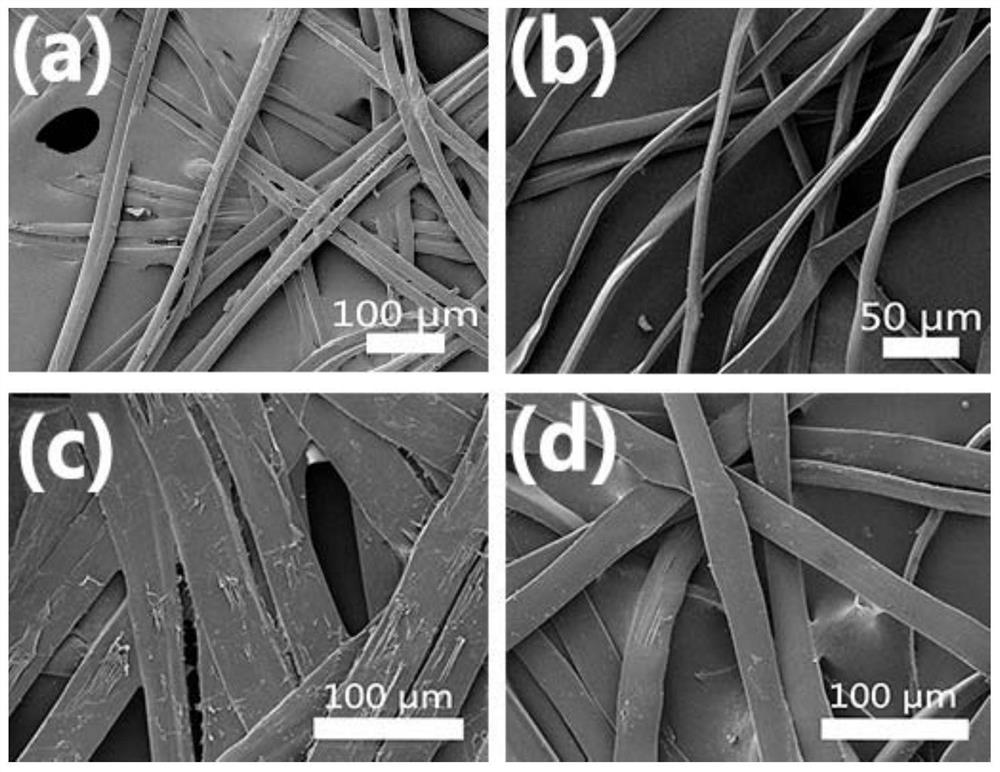
[0055] (1) Evenly stretch the degummed mulberry silk into a mesh structure, cut it into a silk mesh with a length of 7cm, a width of 4cm, and a thickness of 0.5cm, with a mass of 30mg, and spread the silk mesh into a mold of 7cm×4cm×1cm Inside.
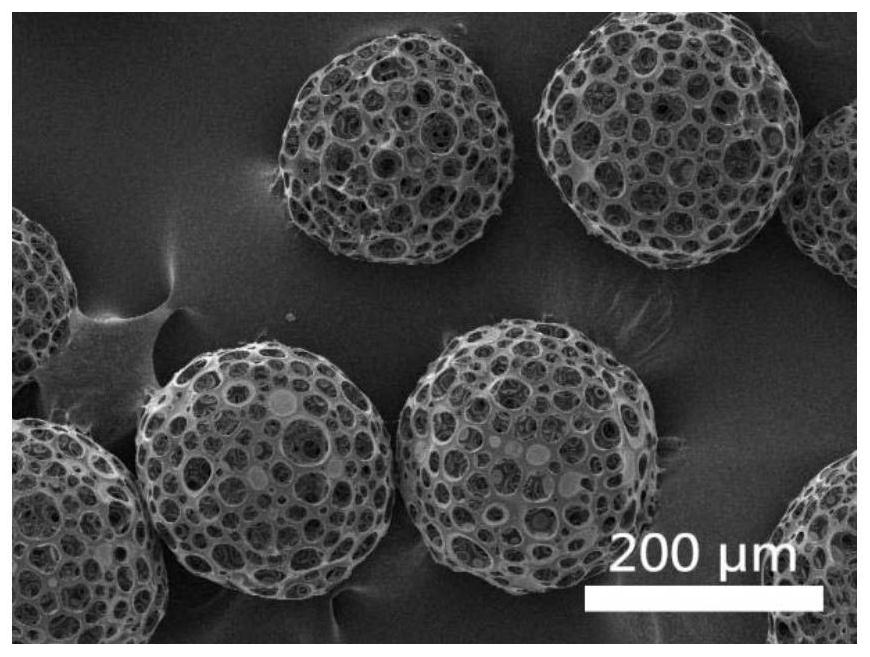
[0056] (2) 9 g of gelatin was dissolved in deionized water so that the concentration of the gelatin solution was 30%. 0 mg polylactic acid porous microspheres, 2.25 mL of silk fibroin protein solution with a concentration of 20 mg / mL and 1.5 mL of 30% gelatin solution were blended, and the volume of the resulting suspension was 15 mL, so that the concentration of porous microspheres was 0 mg / mL. The protein concentration is 3mg / mL, the gelatin concentration is 3wt%, and the gelatin mass in the suspension is 450mg.
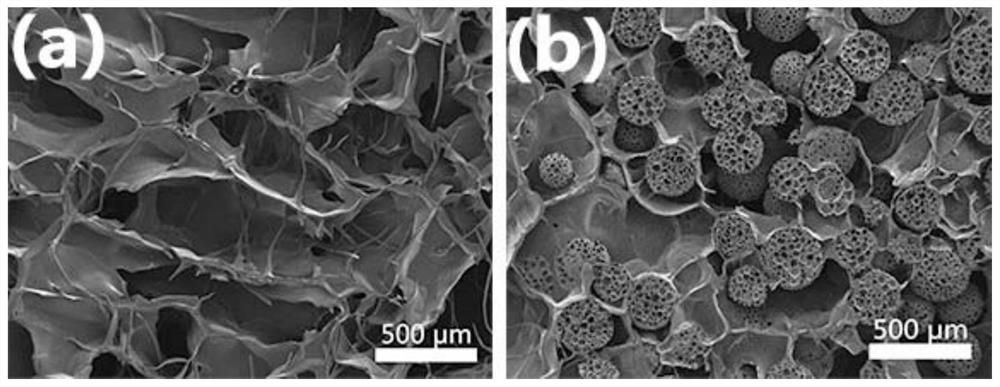
[0057] (3) Inject the suspension in step (2) into the mold in step (1), cool and shape at -20°C, and vacuum freeze-dry (the freeze-drying temperature i...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Embodiment 2, the preparation of composite support material
[0060] (1) Evenly stretch the degummed mulberry silk into a mesh structure, cut it into a silk mesh with a length of 7cm, a width of 4cm, and a thickness of 0.5cm, with a mass of 45mg, and spread the silk mesh into a mold of 7cm×4cm×1cm Inside.
[0061] (2) 9 g of gelatin was dissolved in deionized water so that the concentration of the gelatin solution was 30%. 225mg of polylactic acid porous microspheres and 9mL concentration of 25mg / mL silk fibroin protein solution and 4.5mL30% gelatin solution are blended to obtain 15mL of suspension, so that the concentration of porous microspheres is 15mg / mL, the concentration of silk fibroin protein It is 15mg / mL, the gelatin concentration is 9wt%, and the gelatin quality in the suspension is 1350mg.
[0062] (3) Inject the suspension in step (2) into the mold in step (1), cool and shape at -20°C, and vacuum freeze-dry (the freeze-drying temperature is -55°C) to init...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Embodiment 3, the preparation of composite support material
[0065] (1) Evenly stretch the degummed tussah silk into a mesh structure, cut it into a silk mesh with a length of 7cm, a width of 4cm, and a thickness of 0.5cm, with a mass of 40mg, and spread the silk mesh into a mold of 7cm×4cm×1cm Inside.
[0066] (2) 9 g of gelatin was dissolved in deionized water so that the concentration of the gelatin solution was 30%. 160mg of polylactic acid porous microspheres were blended with 7.5mL of silk fibroin protein solution with a concentration of 20mg / mL and 3.5mL of 30% gelatin solution to obtain a suspension of 15mL, so that the concentration of porous microspheres was 10.67mg / mL. The protein concentration is 10mg / mL, the gelatin concentration is 7wt%, and the mass of gelatin in the suspension is 1050mg.
[0067] (3) Inject the suspension in step (2) into the mold in step (1), cool and shape at -20°C, and vacuum freeze-dry (the freeze-drying temperature is -55°C) to i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap