Power assisting device and power assisting bicycle
A technology of power-assisted bicycles and power-assisted devices, which is applied to chain/belt transmission devices, vehicle components, vehicle gearboxes, etc., which can solve the problems of lower device reliability, short center distance, and increased maintenance costs, and achieve isolation from muddy water and sewage material, improve service life, and avoid improper consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
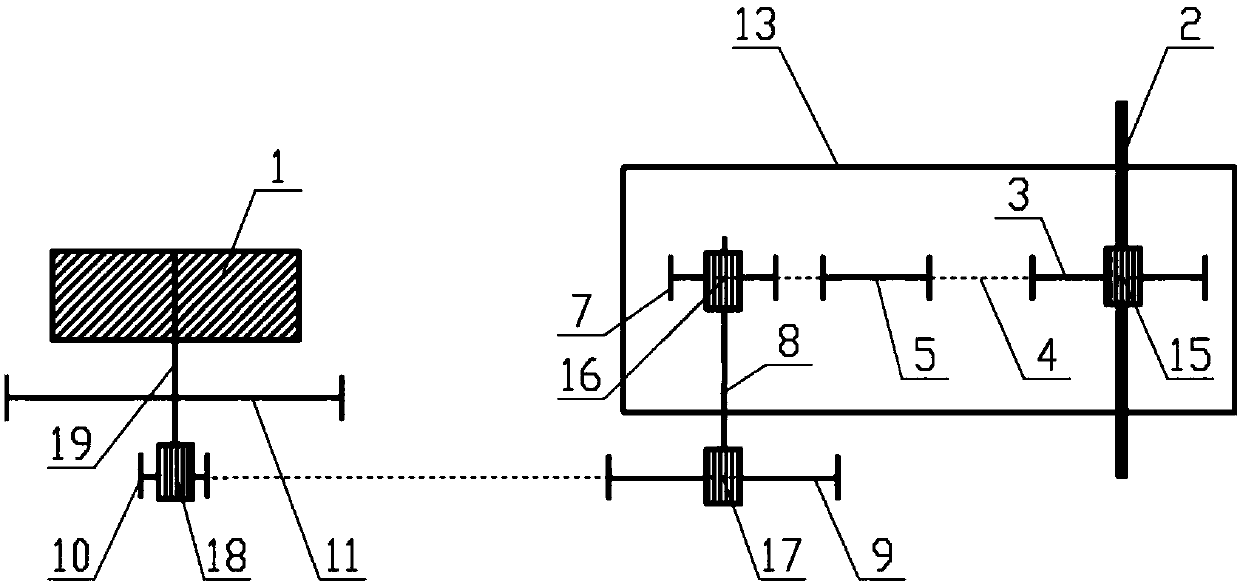
[0059] Such as figure 1 , 6 , 7 and 8, the booster device of the present invention includes a crankshaft 3, a drive shaft 8, a flywheel 10, a first drive wheel 7, a second drive wheel 9 and a pedal force measuring device (not shown), a motor 1 and motor controller 27.
[0060] A transmission connection is established between the tooth plate 3 and the first driving wheel 7 through the first chain 4, and the transmission connection between the second driving wheel 9 and the flywheel 10 is established through the second chain 12 or the second belt (not shown). The first driving wheel 7 and the second drive wheel 9 are all installed on the drive shaft 8, and the torque on the first drive wheel 7 can act on the second drive wheel 9.
[0061] The chainring 3 , the first chain 4 , the first driving wheel 7 and the pedal force measuring device are all integrated in a housing 13 , and the second driving wheel 9 , the second chain 12 and the flywheel 10 are arranged outside the housin...
Embodiment 2
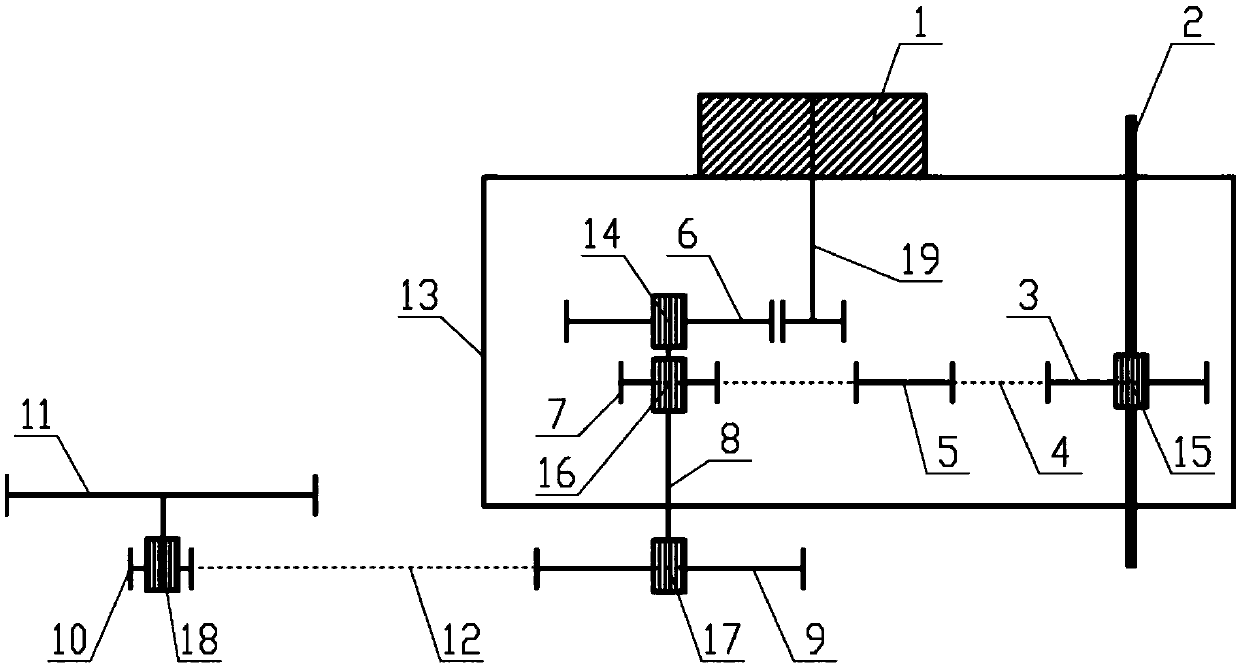
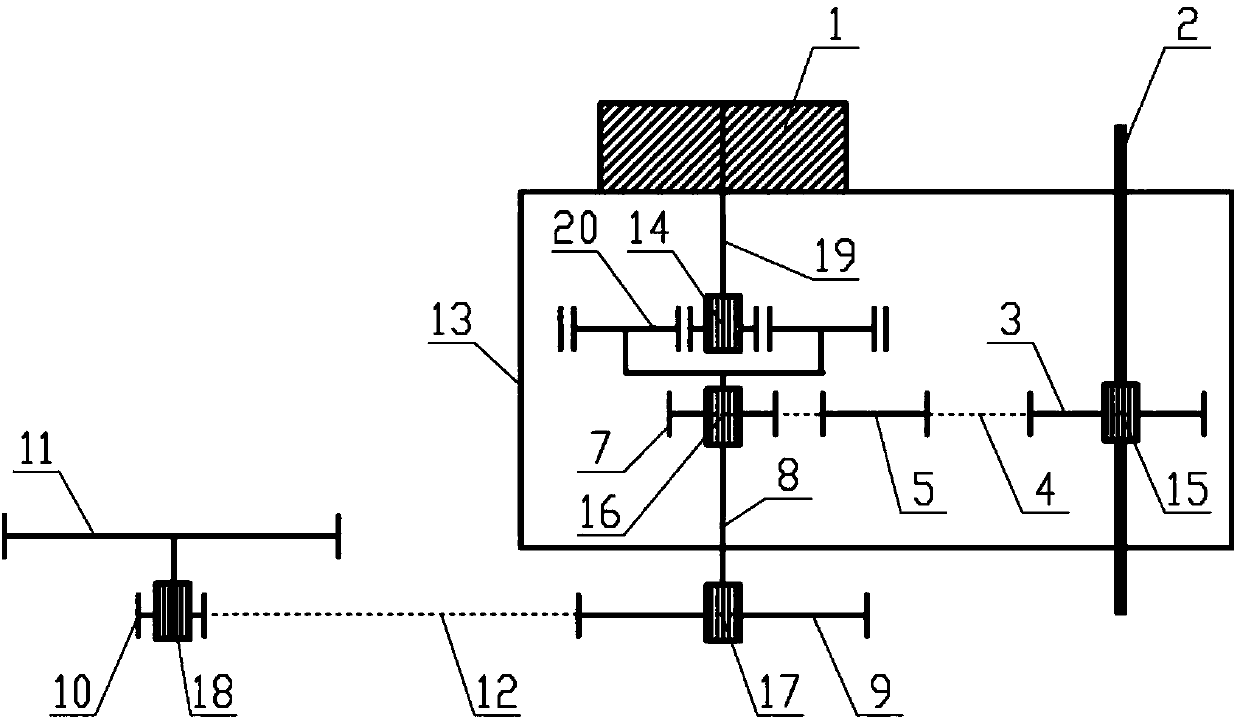
[0084] like figure 2 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that, in order to increase the assist torque, a planetary gear reducer 20 is also installed in the housing 1, and its sun gear (not shown) is installed on the output shaft 19 of the motor 1 The planetary carrier (not shown) is installed on the drive shaft 8, and the power assist torque output by the motor 1 is amplified by the planetary gear reducer 20 and acts on the drive shaft 8 to achieve greater driving force. Based on this, the torque that the motor 1 actually needs to provide is reduced, and the volume and mass of the motor 1 are also small, which is conducive to the installation of the motor 1 and the weight reduction of the bicycle; in addition, the planetary gear reducer 20 can reduce the length of the housing 13 so that reduce its overall size.
[0085] The fifth one-way device 16 can be arranged between the sun gear and the output shaft 19 of the electric machine 1 .
Embodiment 3
[0087] like image 3 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the motor 1 is arranged outside the casing 13 to directly drive the front wheel 21 or the rear wheel 11 of the bicycle. Preferably, the output shaft 19 of the motor 1 is connected to the rear wheel 11 . After the first sensor detects the pedaling force, the motor 1 outputs an assist torque to directly act on the rear wheel 11 . In this embodiment, the motor 1 is a hub motor. Since the motor 1 is not arranged in the casing 13, there is no need to arrange a breathable and waterproof valve on the casing 13.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com