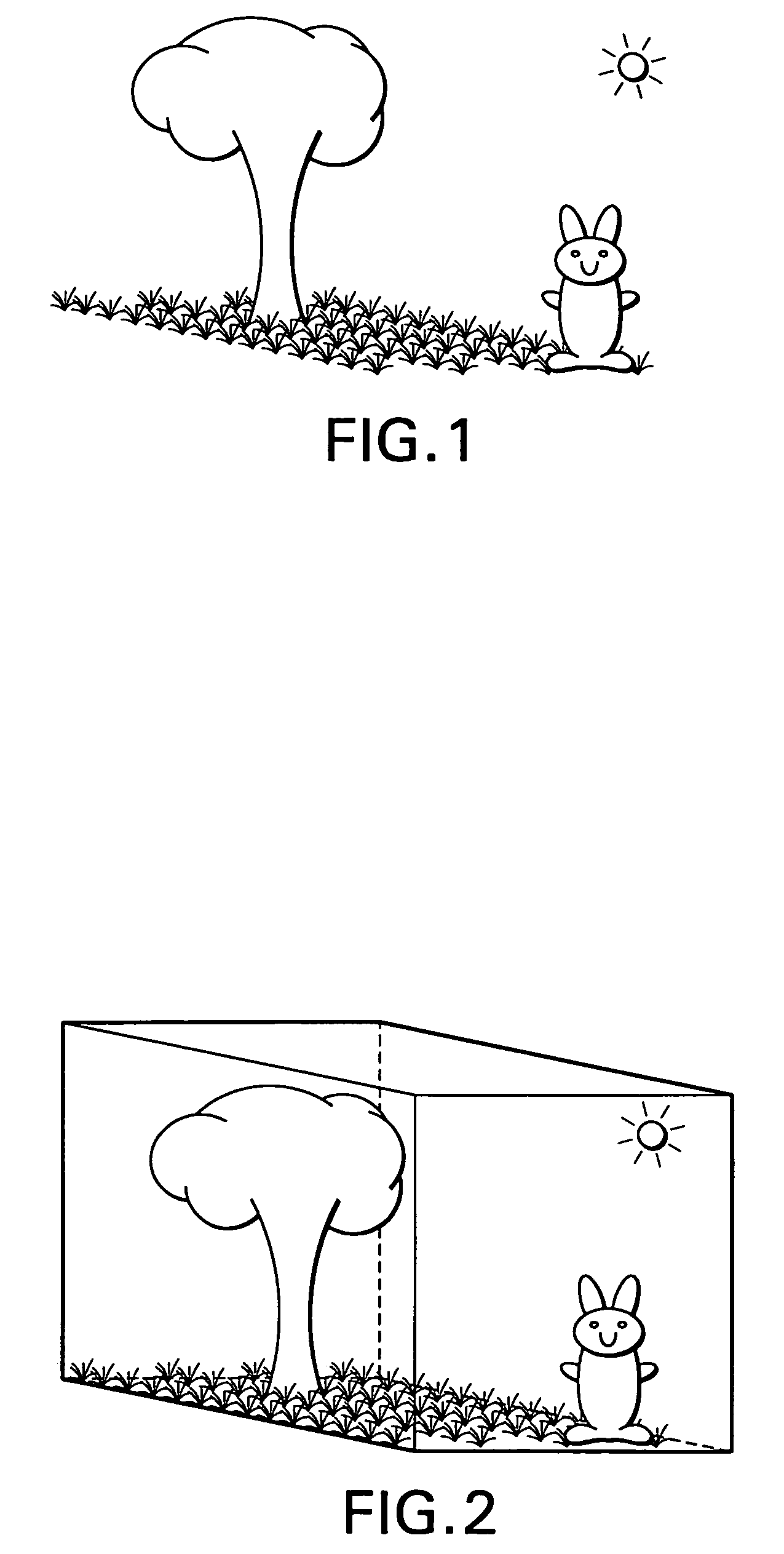
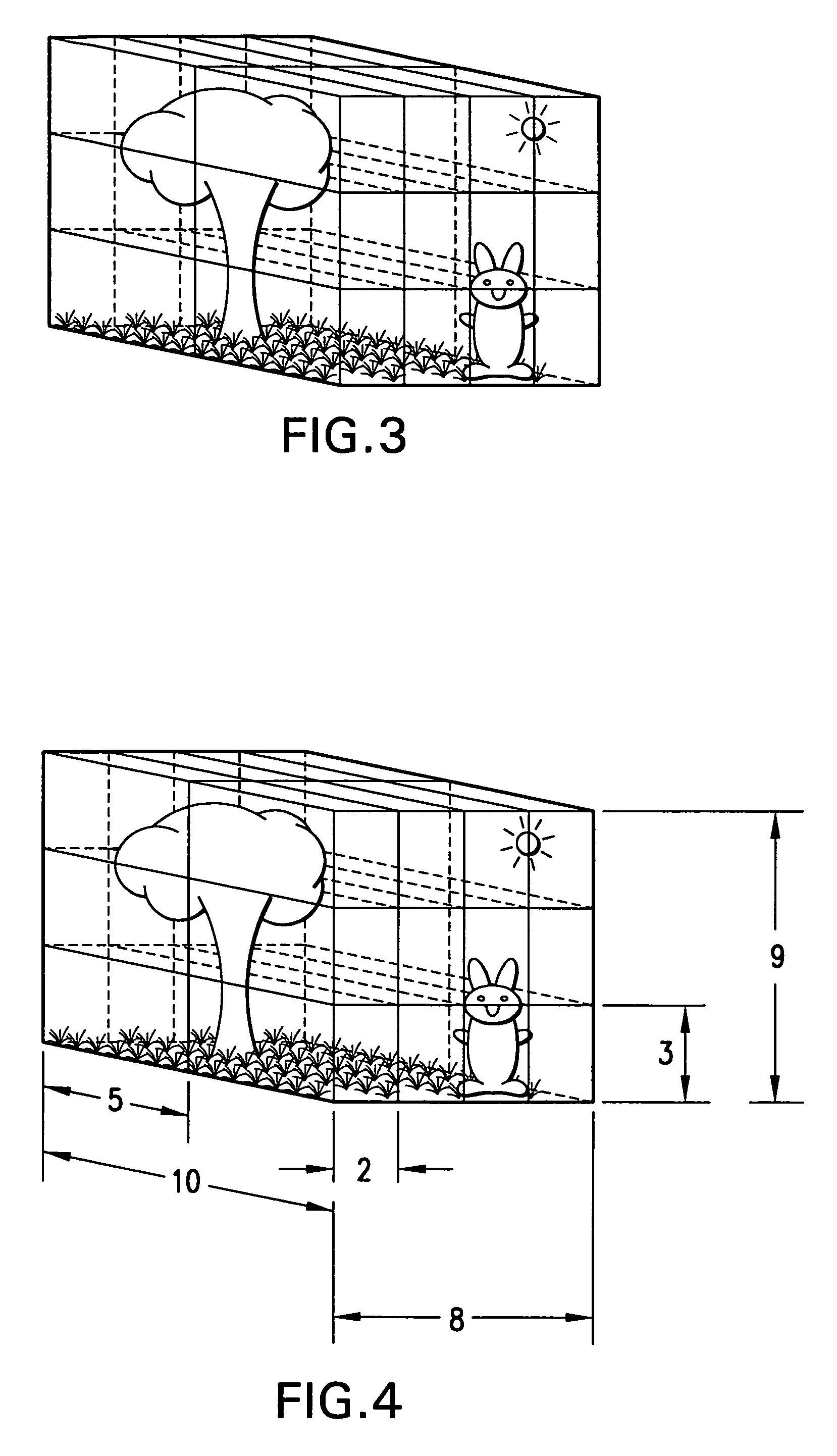
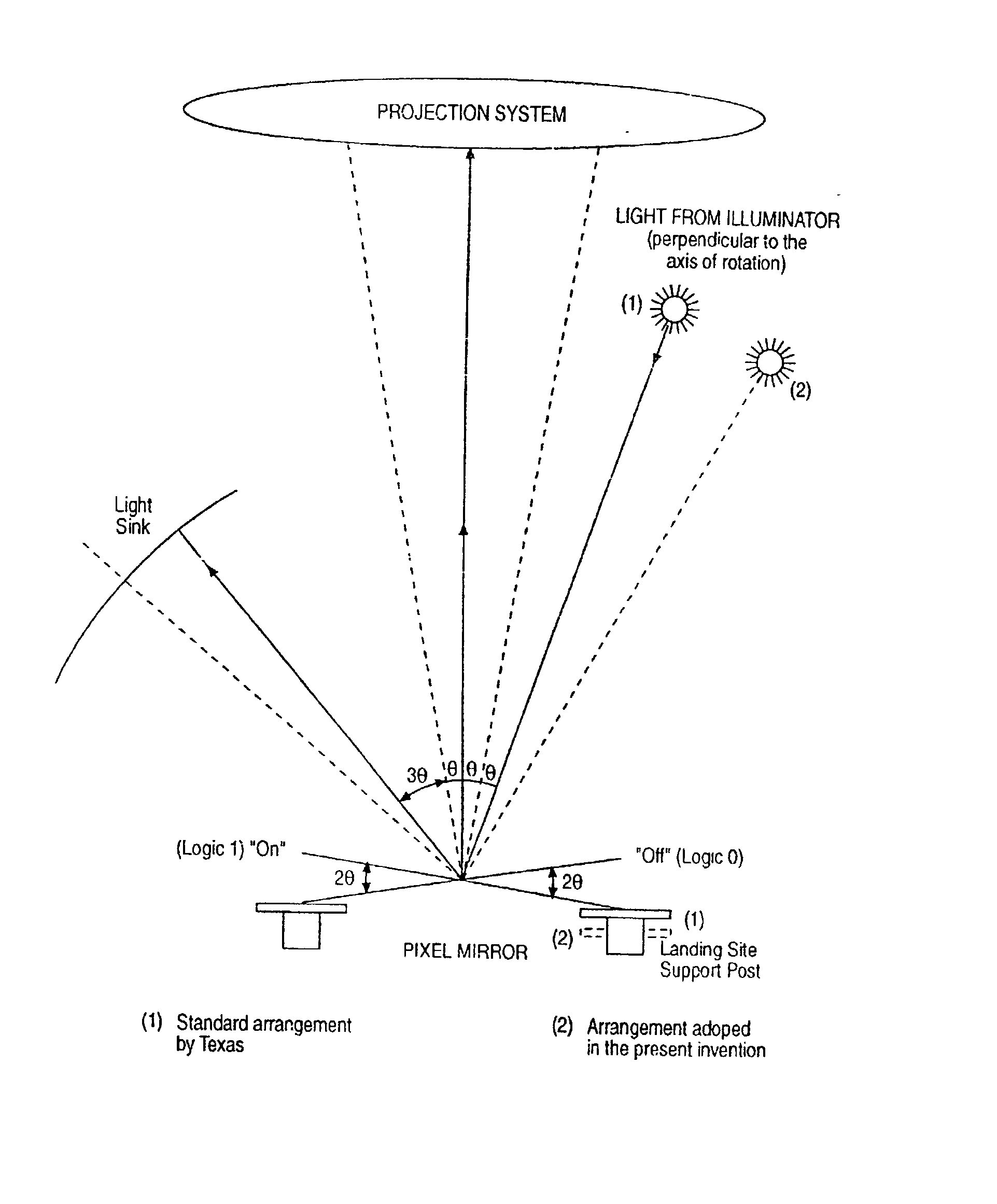
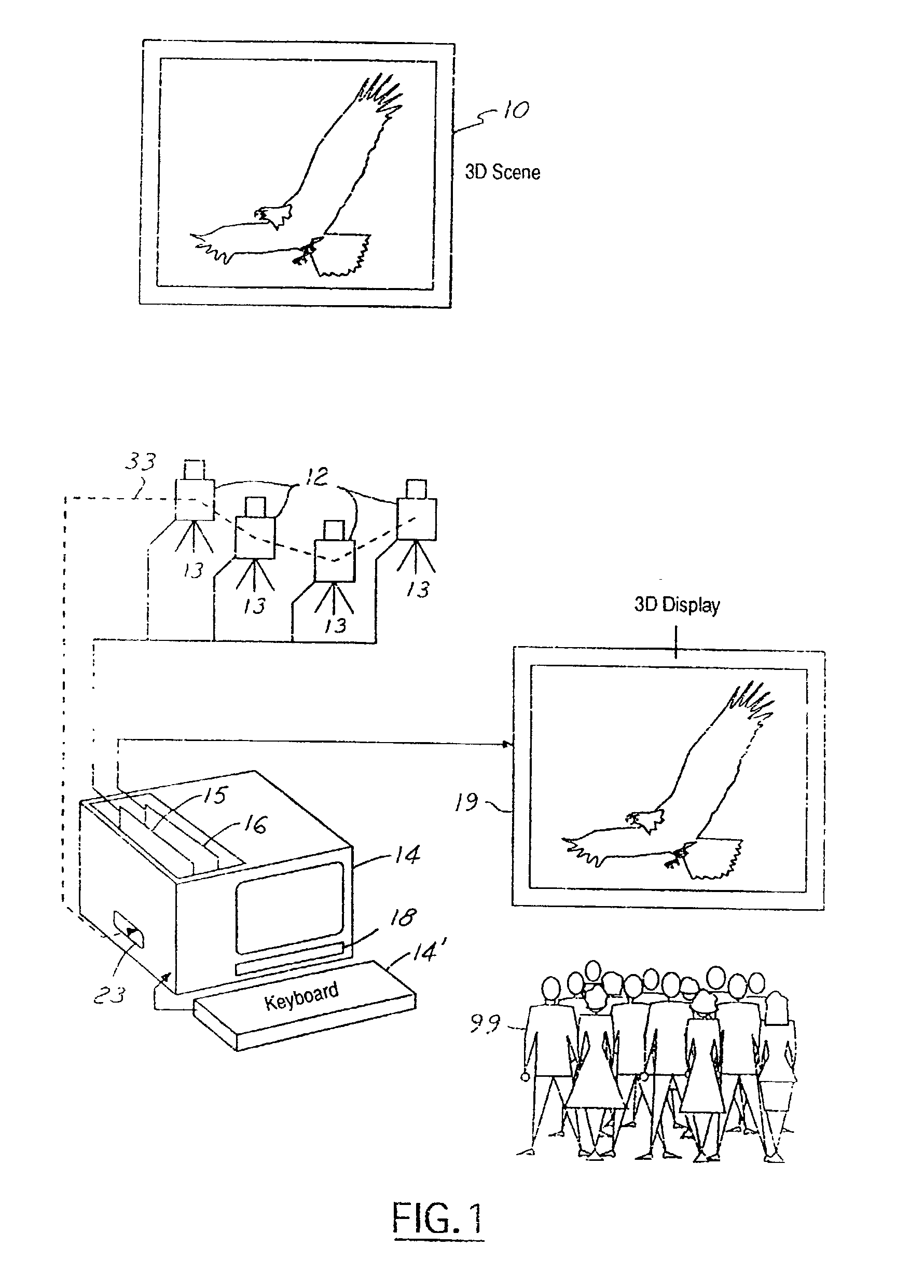
Patents
Literature
53 results about "3D computer graphics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
3D computer graphics, or three-dimensional computer graphics (in contrast to 2D computer graphics), are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering 2D images. The resulting images may be stored for viewing later (possibly as an animation) or displayed in real time.
Method of Customizing 3D Computer-Generated Scenes
InactiveUS20090021513A1Low costRapid production3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)The Internet
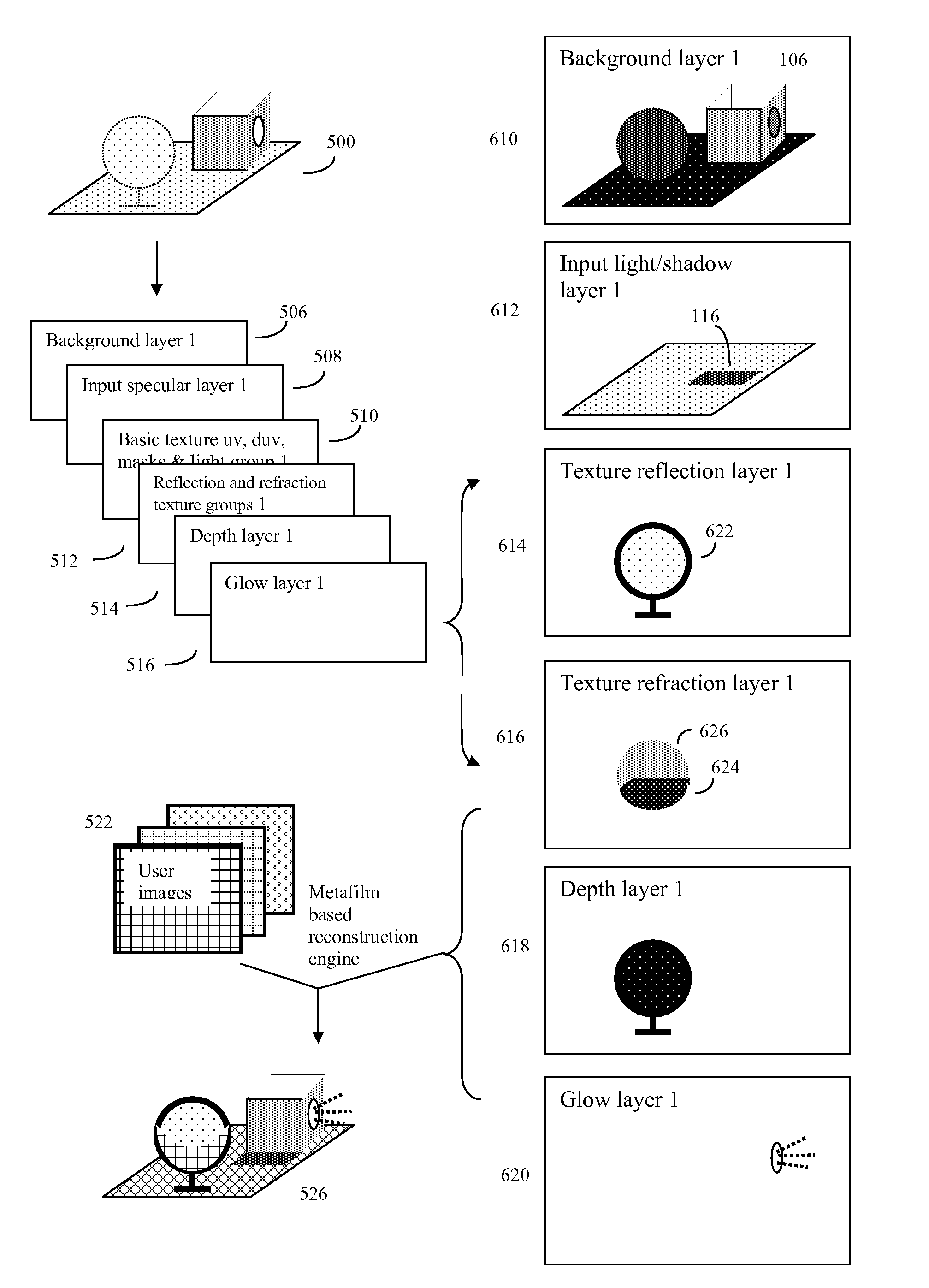
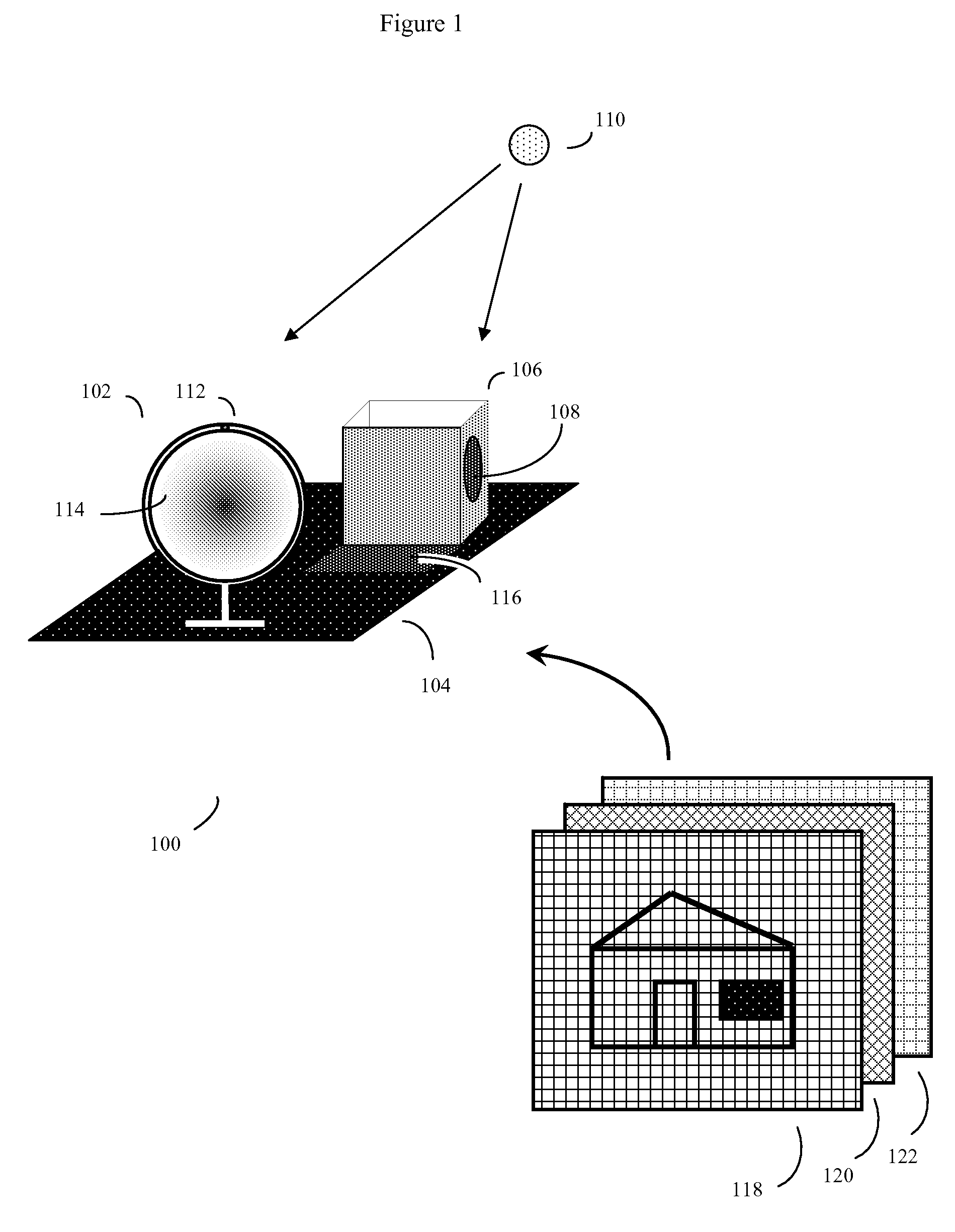
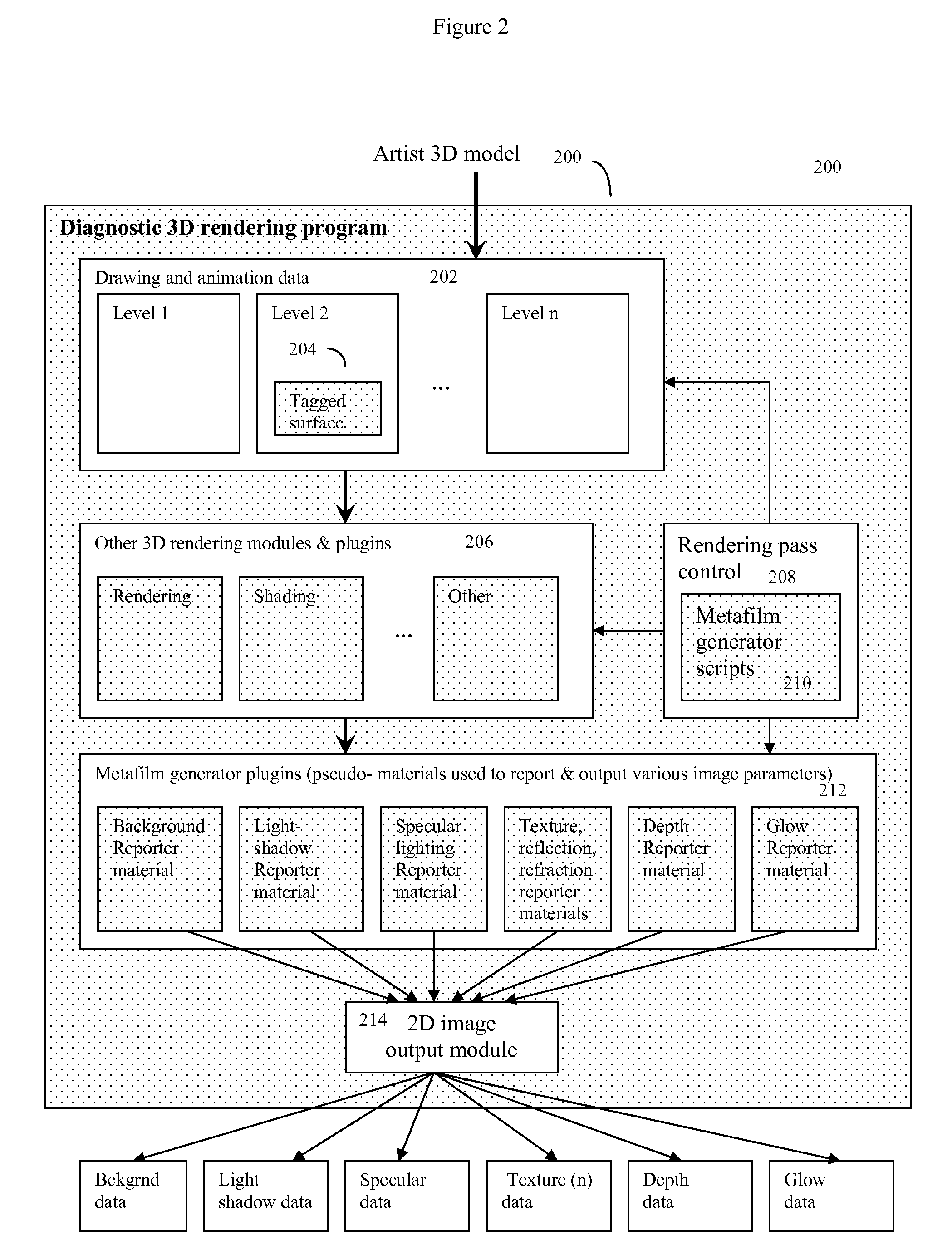
An automated method of rapidly producing customized 3D graphics images in which various user images and video are merged into 3D computer graphics scenes, producing hybrid images that appear to have been created by a computationally intensive 3D rendering process, but which in fact have been created by a much less computationally intensive series of 2D image operations. To do this, a 3D graphics computer model is rendered into a 3D graphics image using a customized renderer designed to automatically report on some of the renderer's intermediate rendering operations, and store this intermediate data in the form of metafilm. User images and video may then be automatically combined with the metafilm, producing a 3D rendered quality final image with orders of magnitude fewer computing operations. The process can be used to inexpensively introduce user content into sophisticated images and videos suitable for many internet, advertising, cell phone, and other applications.
Owner:PIXBLITZ STUDIOS
Information providing apparatus, information providing method, storage medium, and computer program
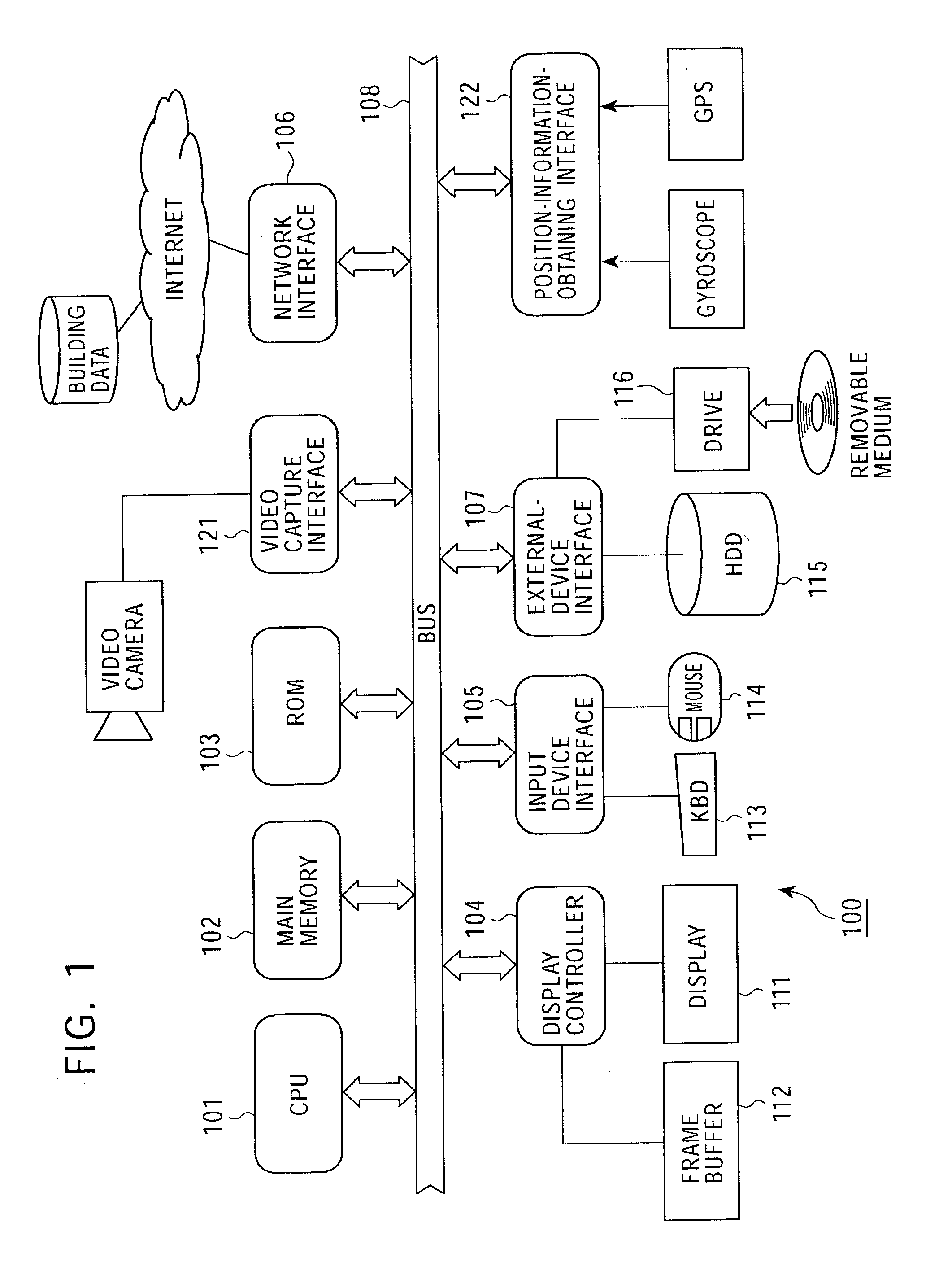
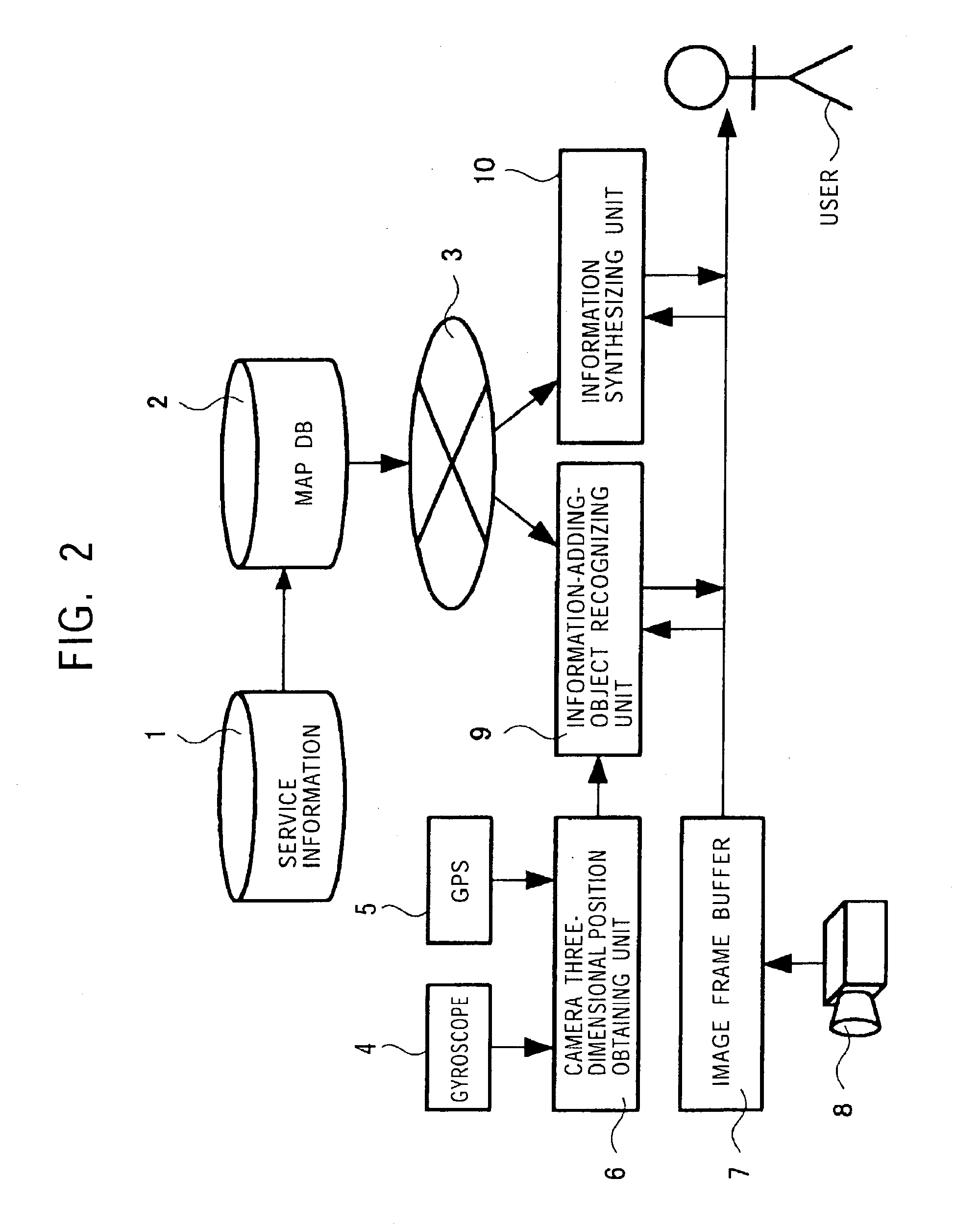
ActiveUS7119831B2Realize the operationEasy to understandColor signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay device3D computer graphics
A display device including a camera is used by inserting it in the direction of a user's gaze. Alternatively, an image of the same area as that of a scene from a windshield of an automobile may be obtained and the image may be displayed by using an information providing apparatus installed in the automobile. A system provides information to the user by adding a two-dimensional or three-dimensional computer graphics object to an image taken by the camera. The information is directly added to a scene in the direction of the user's gaze and is displayed to the user. Thus the user can easily understand the relationship between the information and the position to which the information is added.
Owner:SONY CORP
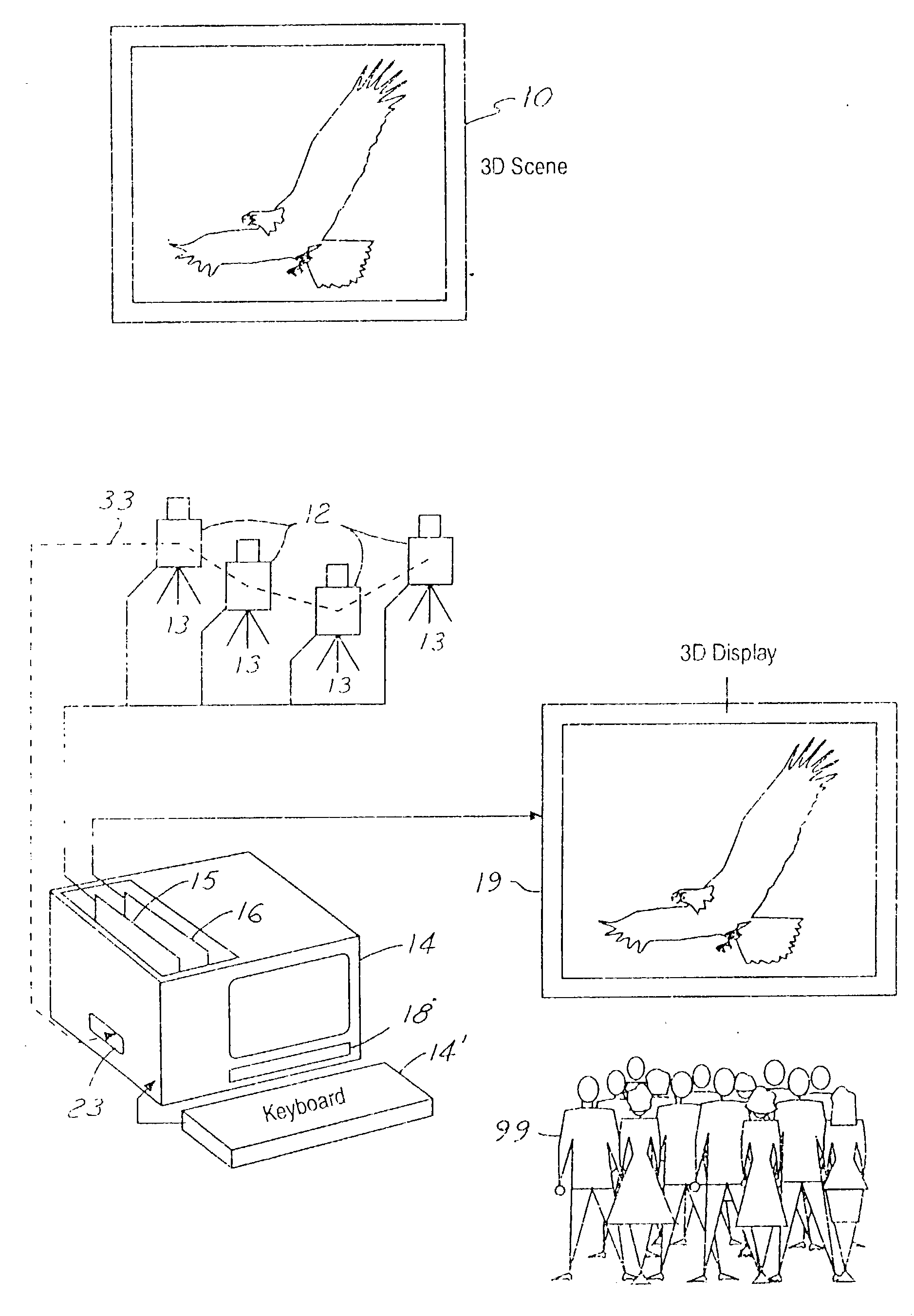
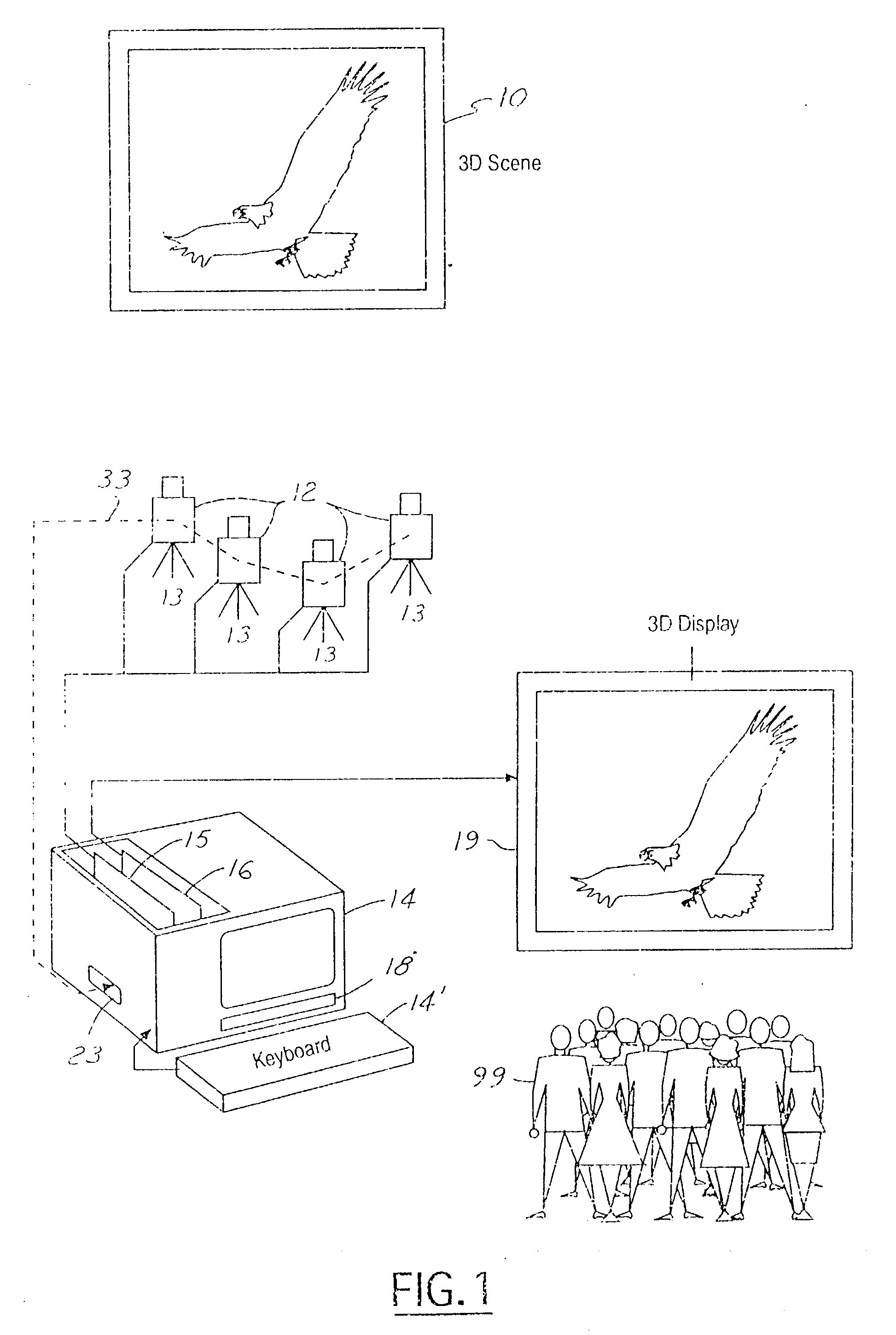
Three-dimensional display system: apparatus and method
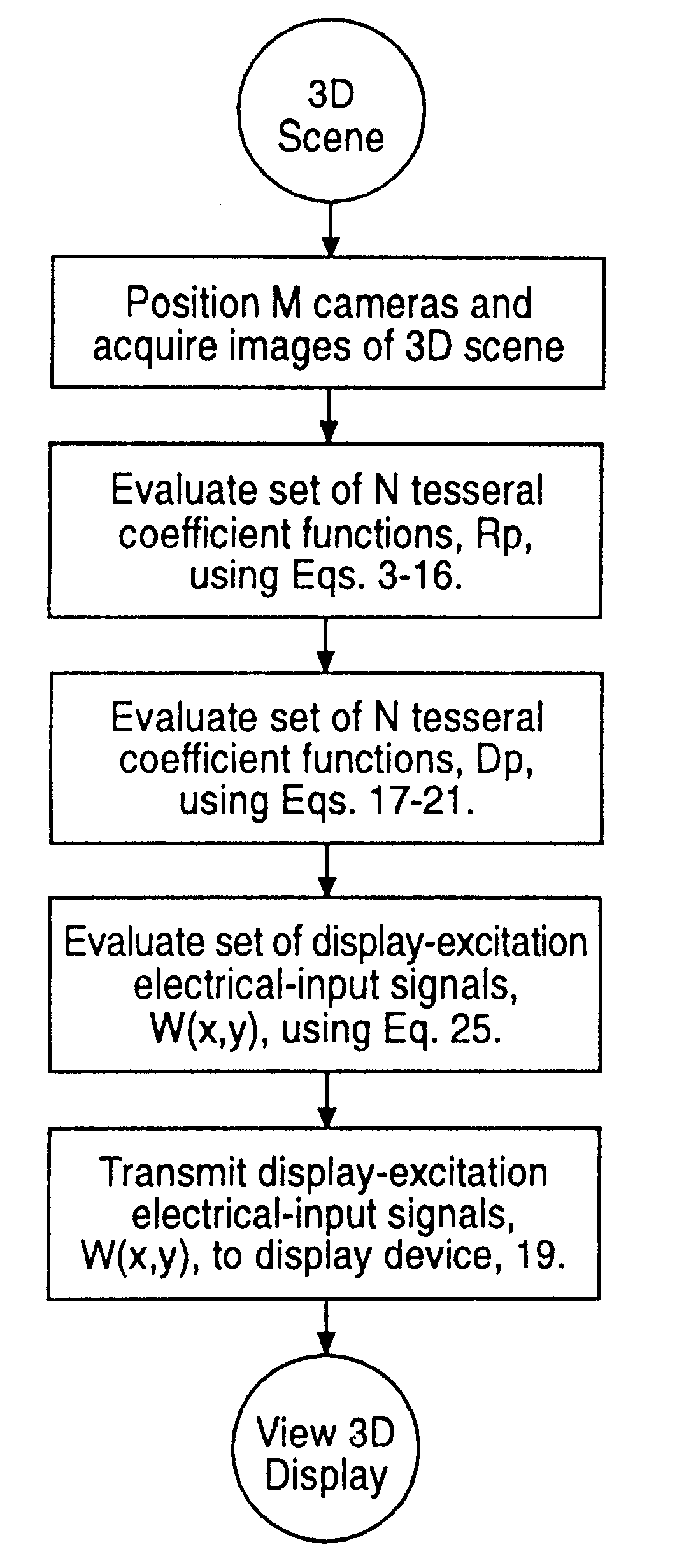
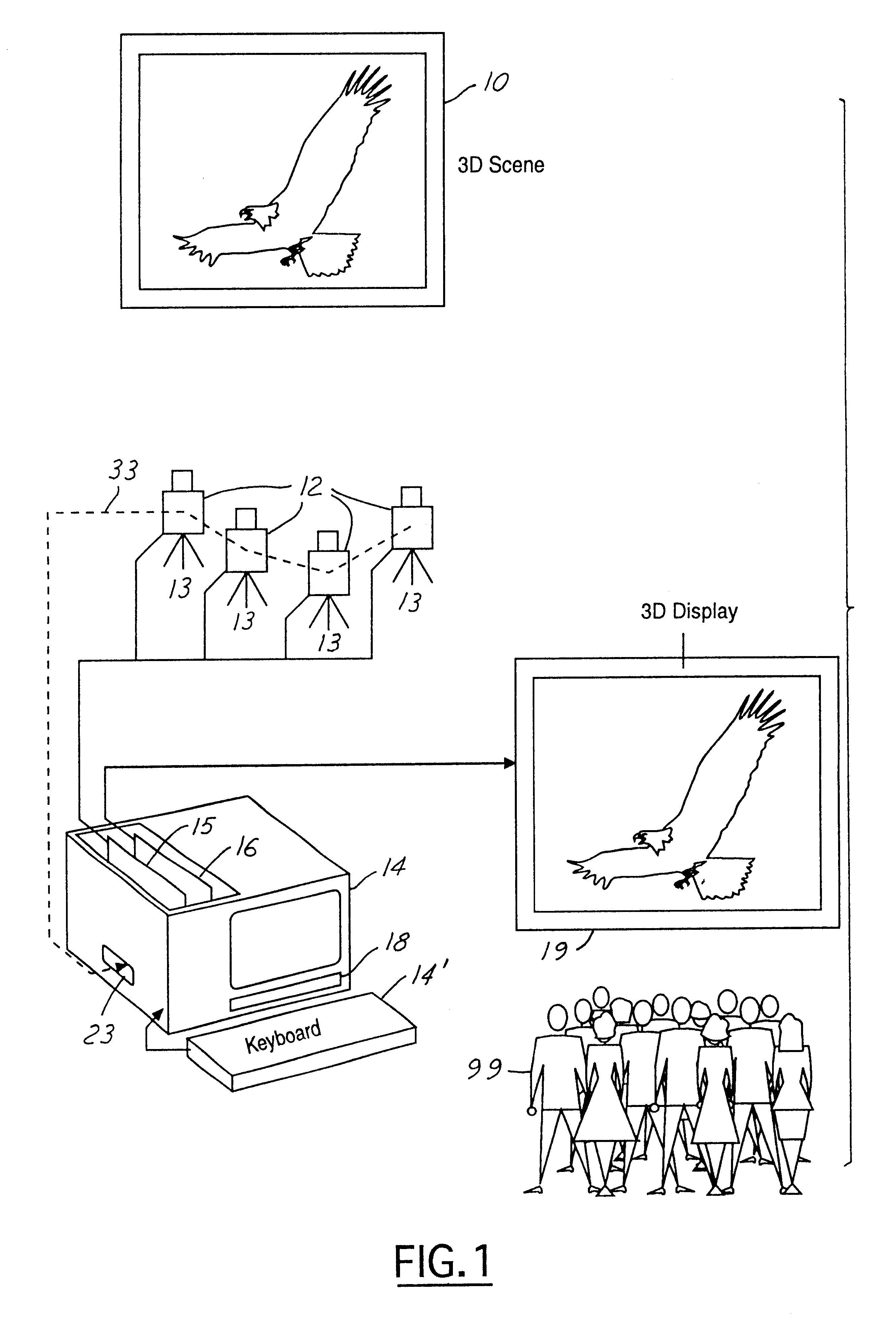
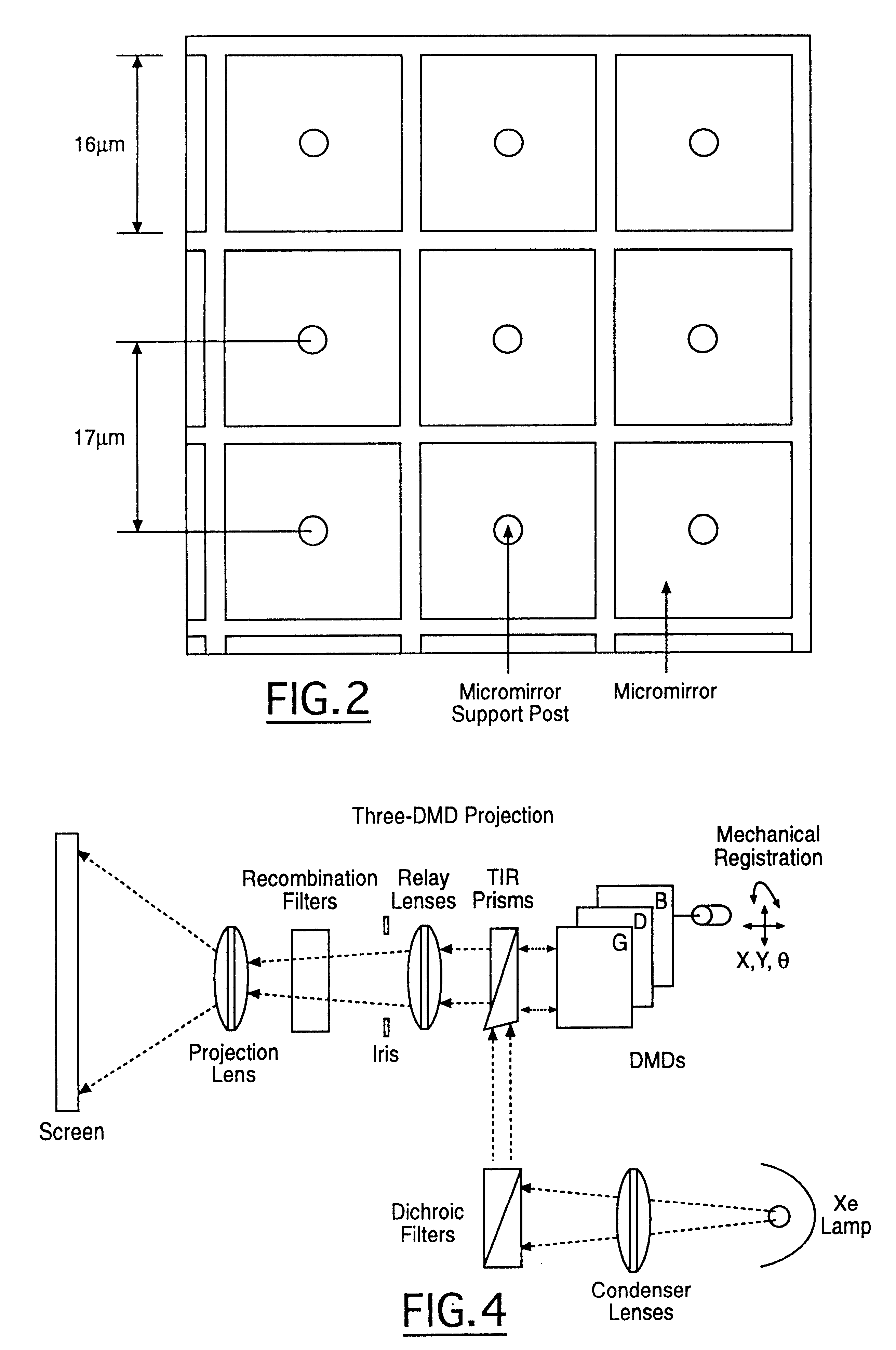
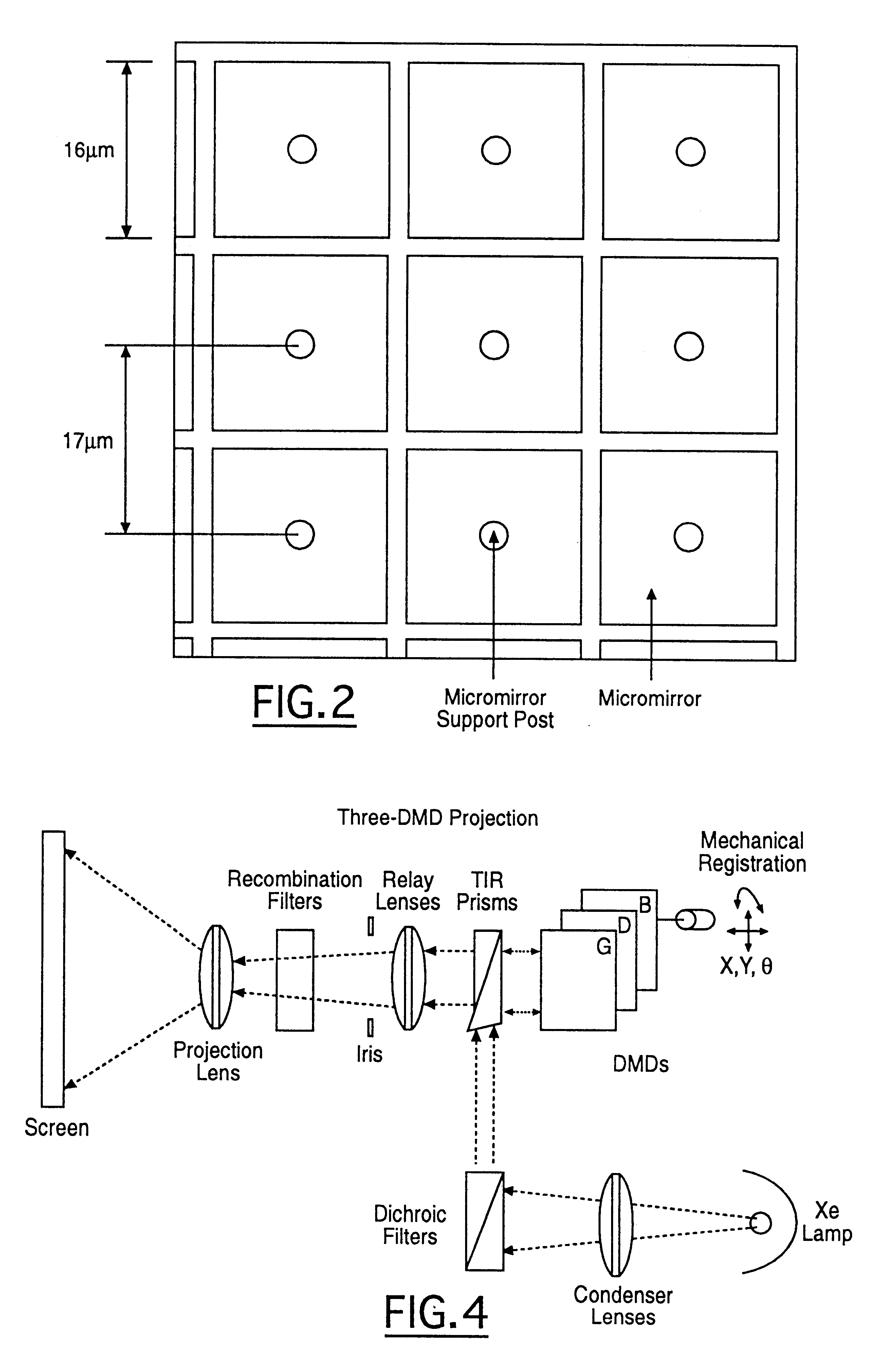
InactiveUS6329963B1Little time delayEfficient storageTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using projection devicesRadiance3D computer graphics
In a presently preferred embodiment of the invention, a three-dimensional scene is reproduced on a specialized light display which offers full multiviewpoint capability and auto-stereoscopic views. The displayed image is produced using a set of M two-dimensional images of the scene collected at a set of distinct spatial locations. These M two-dimensional images are processed through a specialized mathematical encoding scheme to obtain a set of NxK display-excitation electrical-input signals, where K is the number of pixels in the display, and N<=M is the number of individual light-radiating elements within one pixel. The display is thus comprised of a total of NxK light-radiating elements. Each of the K pixels is adapted for control of their associated radiance patterns. The display is connected for response to the set of NxK display-excitation electrical-input signals. In this manner, the display provides a multiviewpoint and autostereoscopic three-dimensional image associated with the original three-dimensional scene. An alternative embodiment of the invention is utilized to provide efficient storage and display of 3D computer graphics images.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
Three-dimensional display system: apparatus and method
InactiveUS6304263B1Little time delayEfficient storageTelevision system detailsImage enhancementRadiance3D computer graphics
A three-dimensional scene is reproduced on a specialized light display which offers full multiviewpoint capability and autostereoscopic views. The displayed image is produced using a set of M two-dimensional images of the scene collected at a set of distinct spatial locations. These M two-dimensional images are processed through a specialized mathematical encoding scheme to obtain a set of NxK display-excitation electrical-input signals, where K is the number of pixels in the display, and N>=M is the number of individual light-radiating elements within one pixel. The display is thus comprised of a total of NxK light-radiating elements. Each of the K pixels is adapted for control of their associated radiance patterns. The display is connected for response to the set of NxK display-excitation electrical-input signals. The display provides a multiviewpoint and autostereoscopic three-dimensional image associated with the original three-dimensional scene. An alternative embodiment of the invention is utilized to provide efficient storage and display of 3D computer graphics images.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
Three-dimensional digital magnifier operation supporting system
ActiveUS8253778B2Details involving processing stepsImage enhancementVisual field lossSupporting system
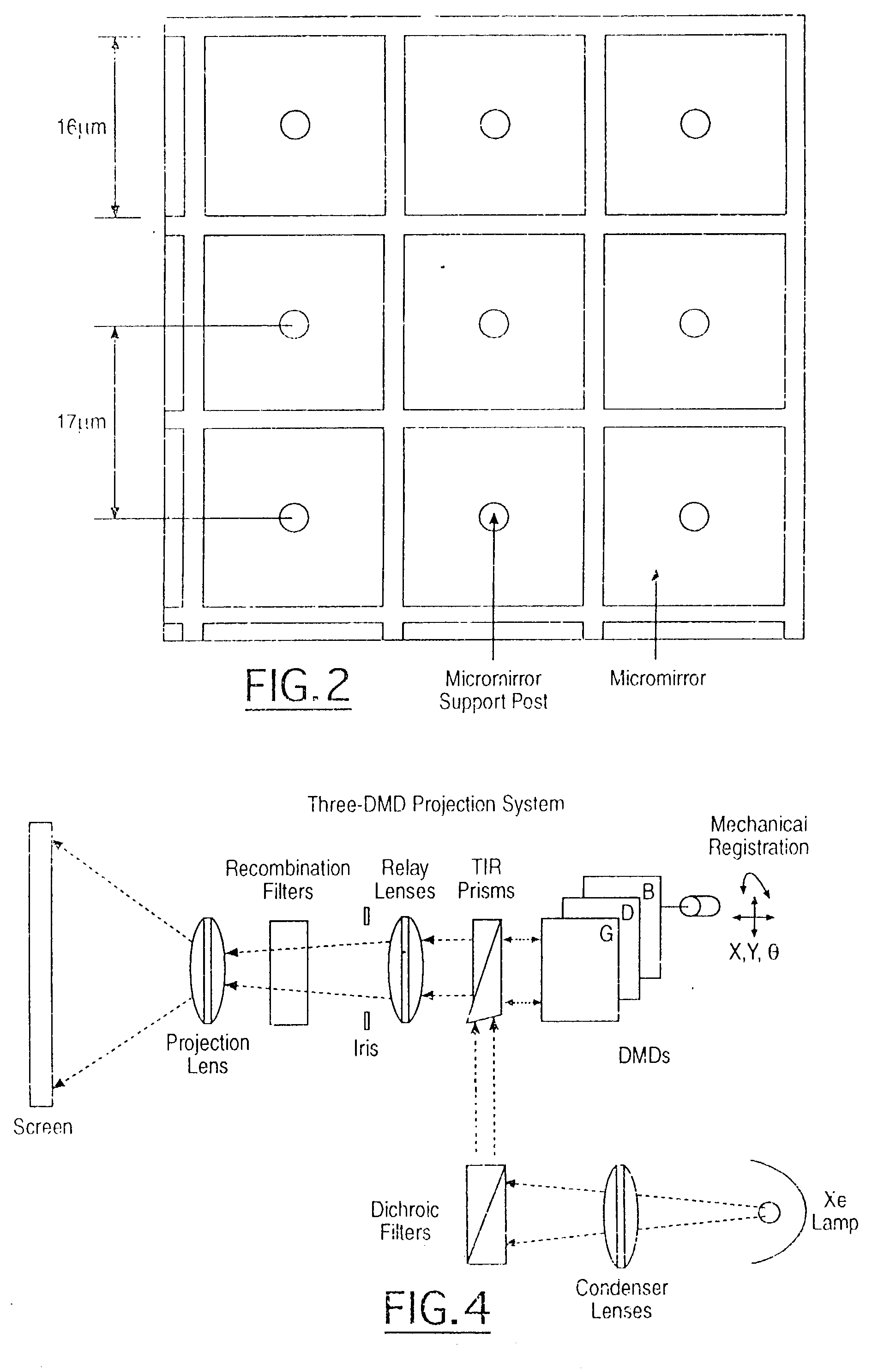
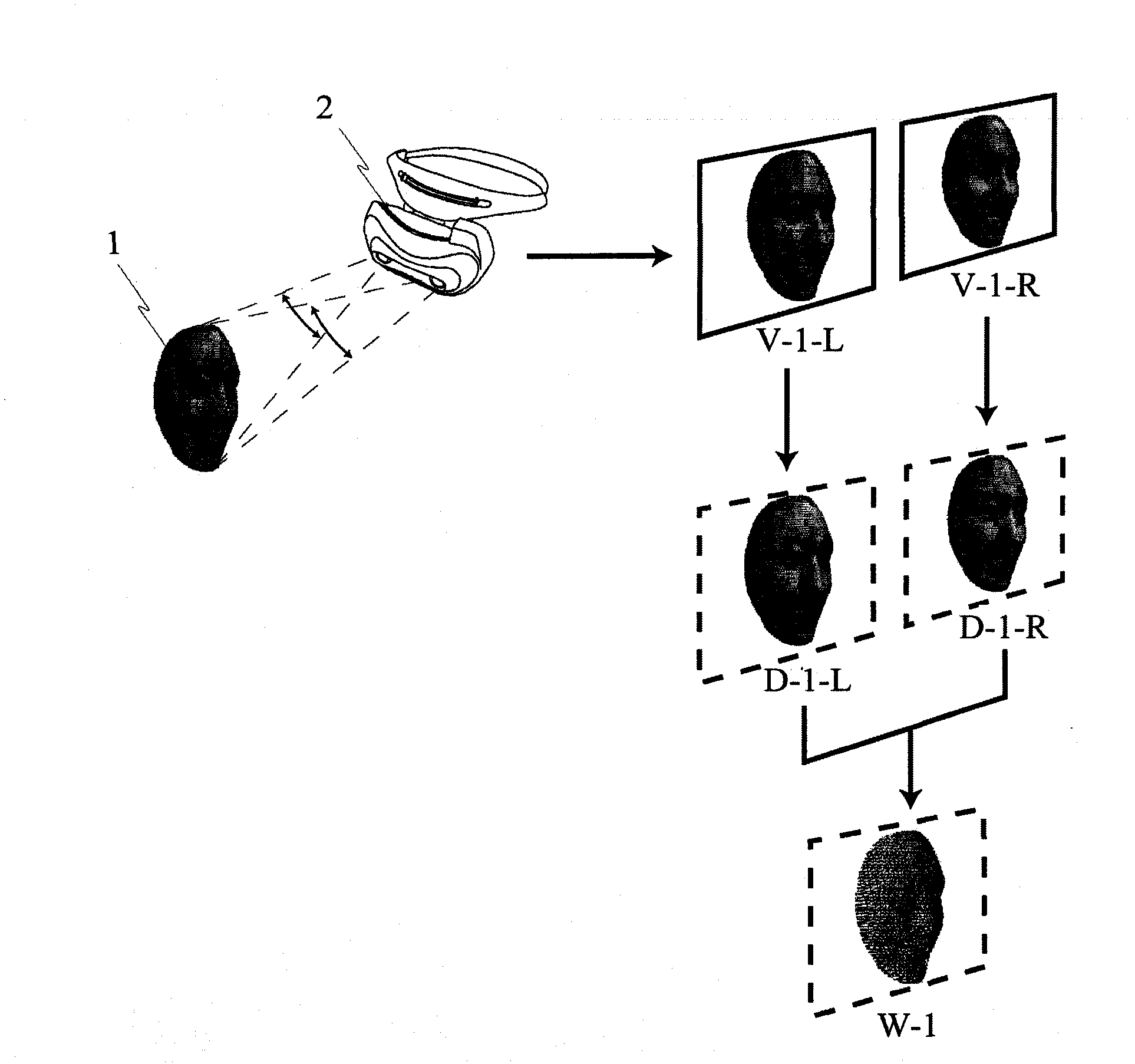
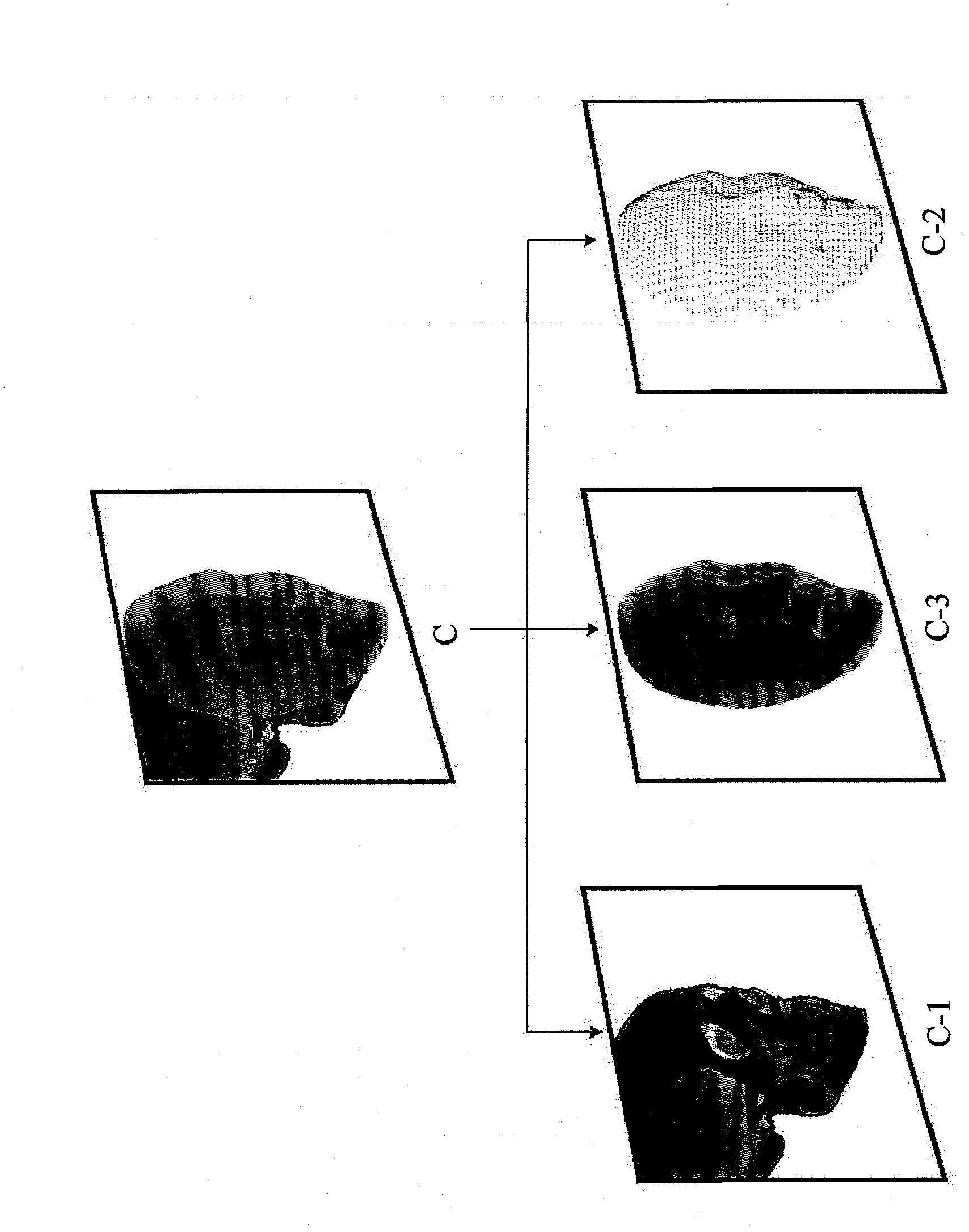
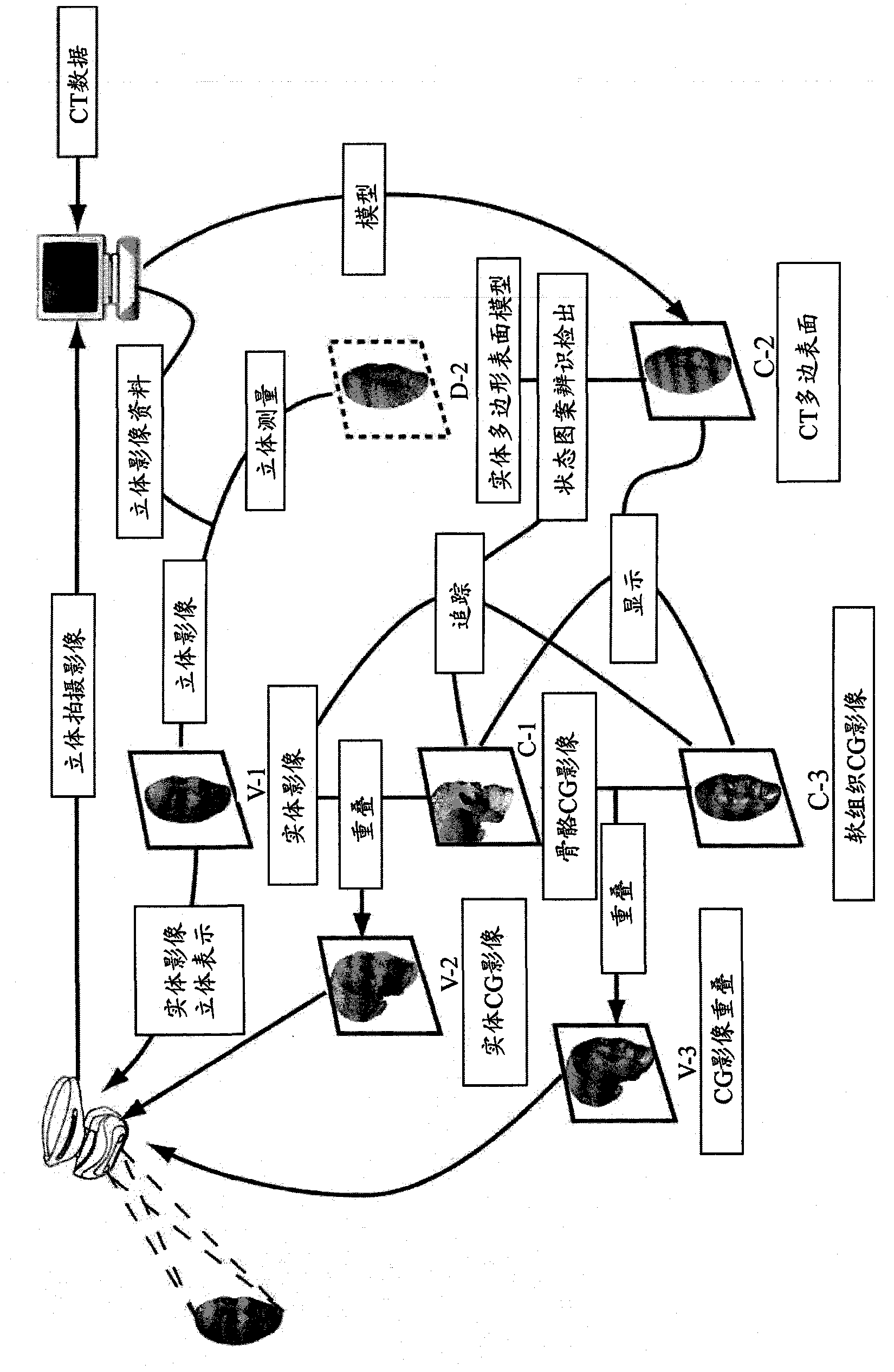
The simulation regarding the state change of the subject in a real space provides a system which represents impacts to three-dimensional computer graphics caused by changes of state of three-dimensional computer graphics composed and fixed to subject, and state of image taking space by simulation, surface polygon model and similar surface polygon model 1 is selected, according to shape pattern, from surface polygon model 2 measures, in a three-dimensional way, subject image existing in the same space, a tracking process is performed on the computer graphics, following to the relative position change of the position changes of the subject and the camera caused in real three-dimensional space, subjects in the visual field of the camera and virtual three-dimensional computer graphics image is unified and displayed by displaying computer graphics image having the same relative position change on the image.
Owner:ATSUSHI TAKAHASHI
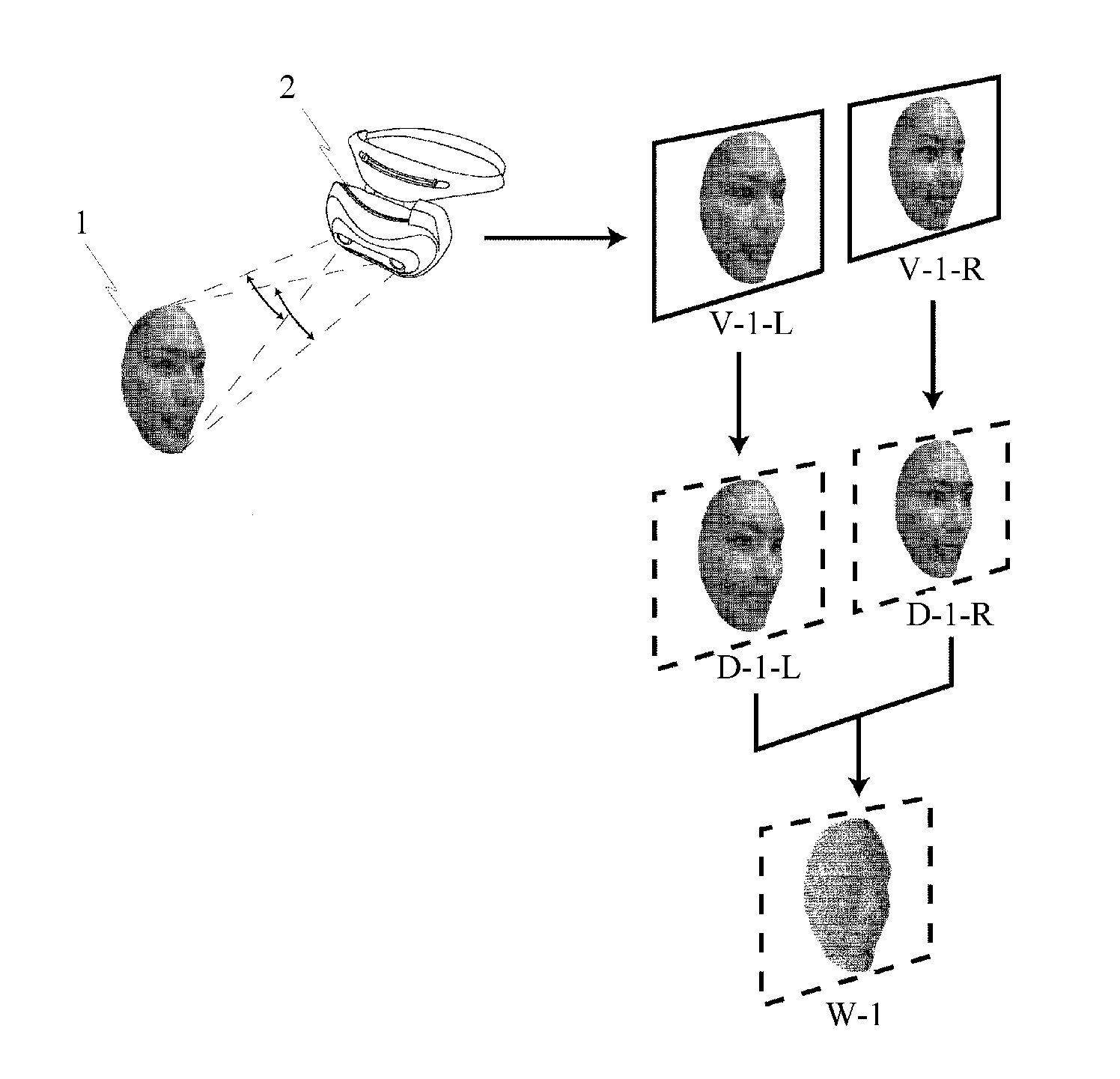
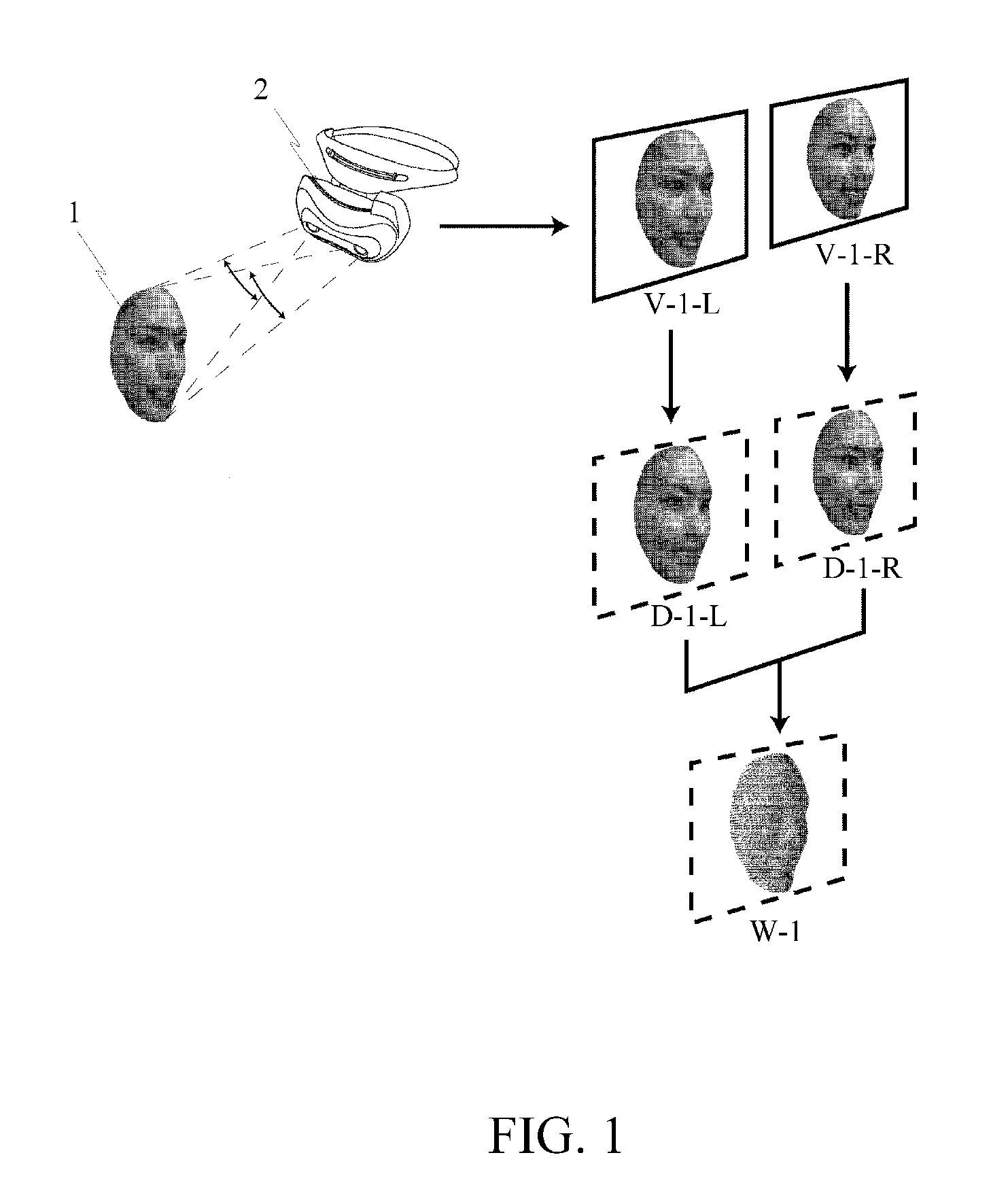
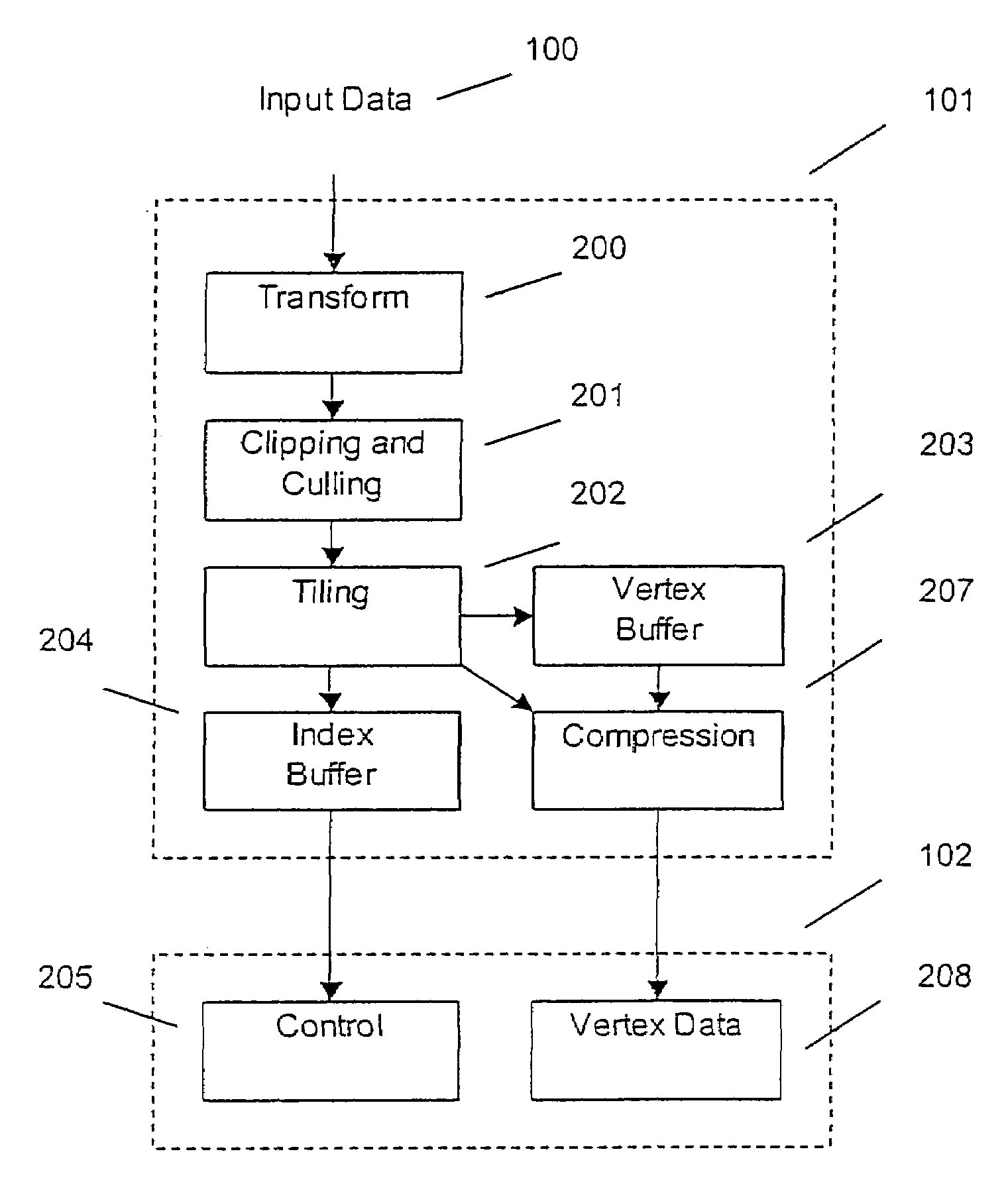
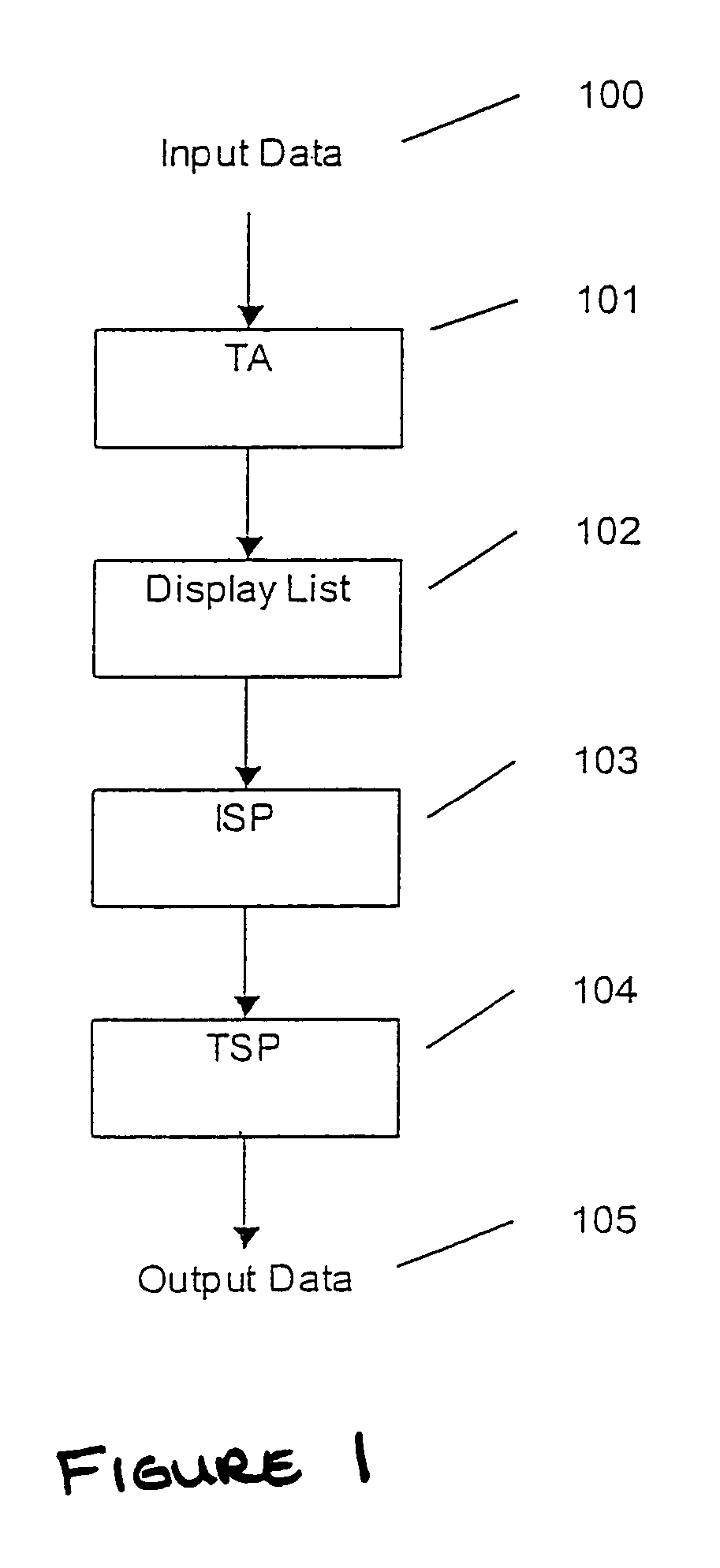
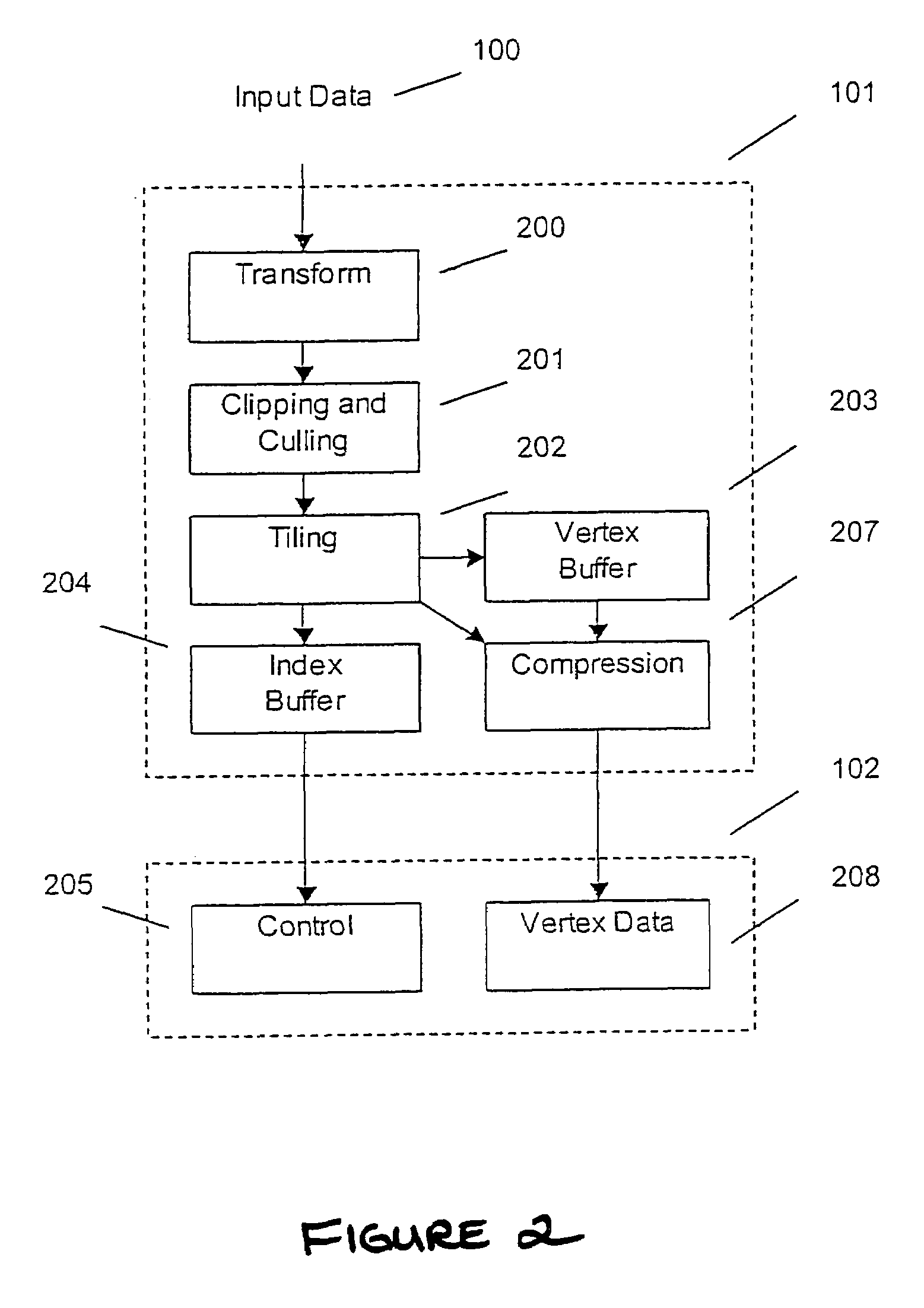
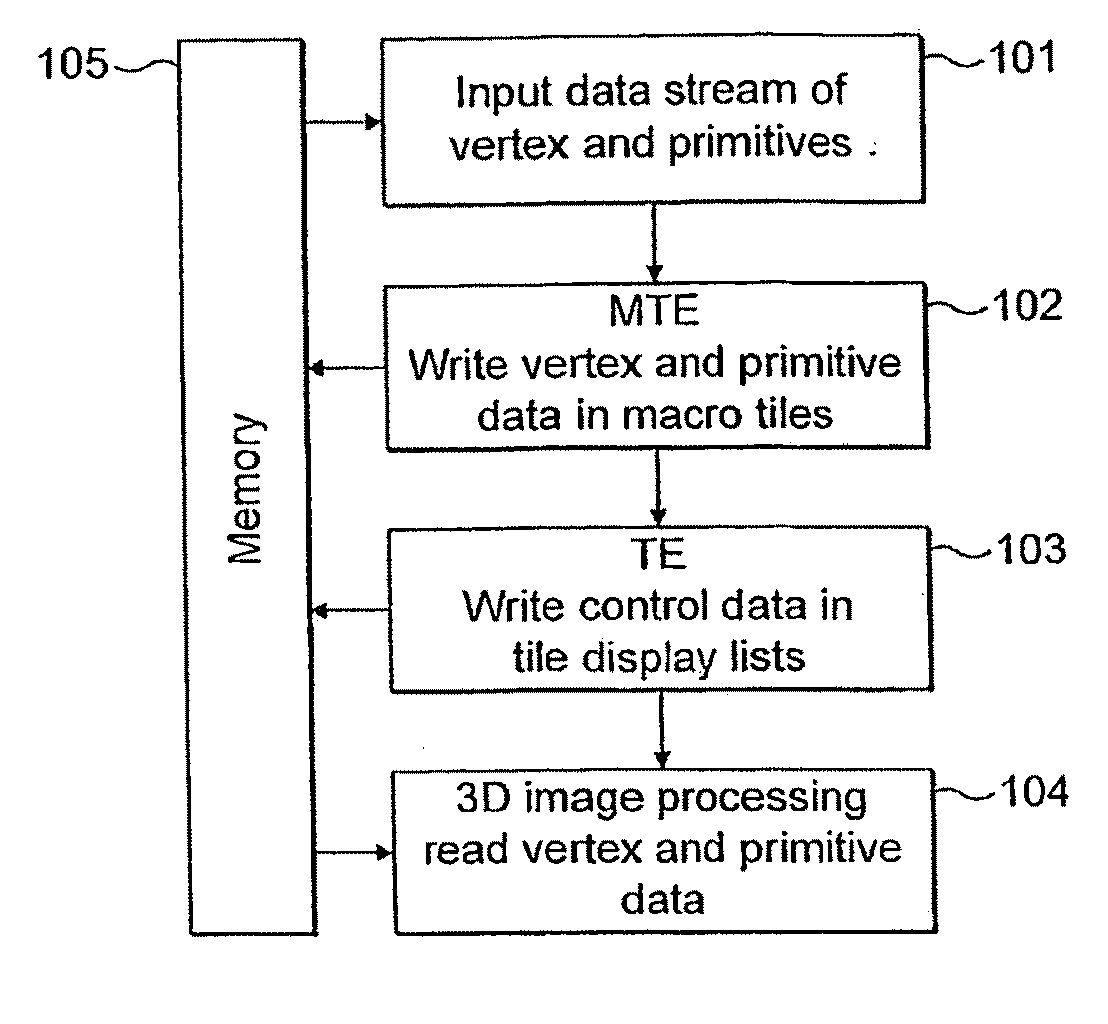
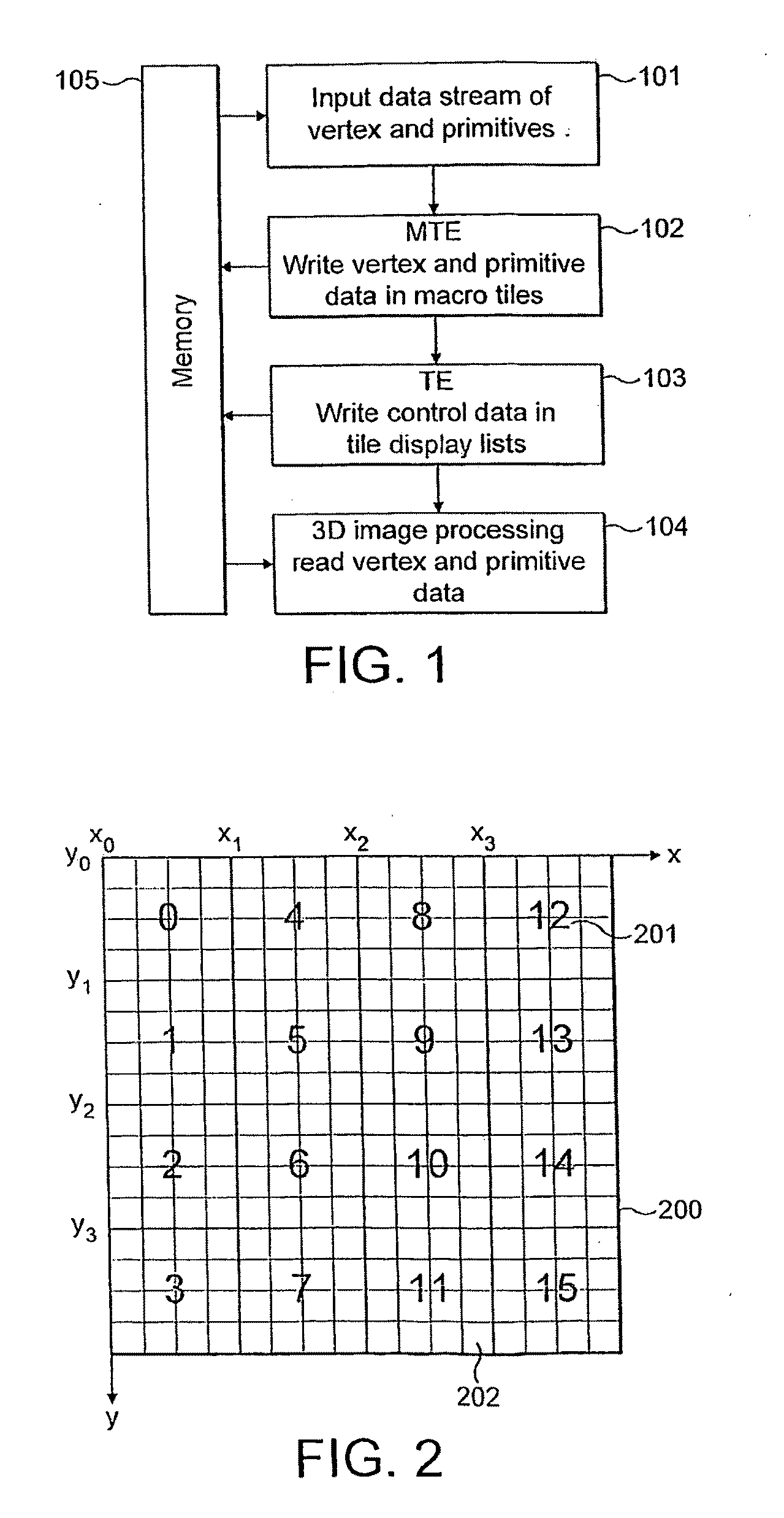
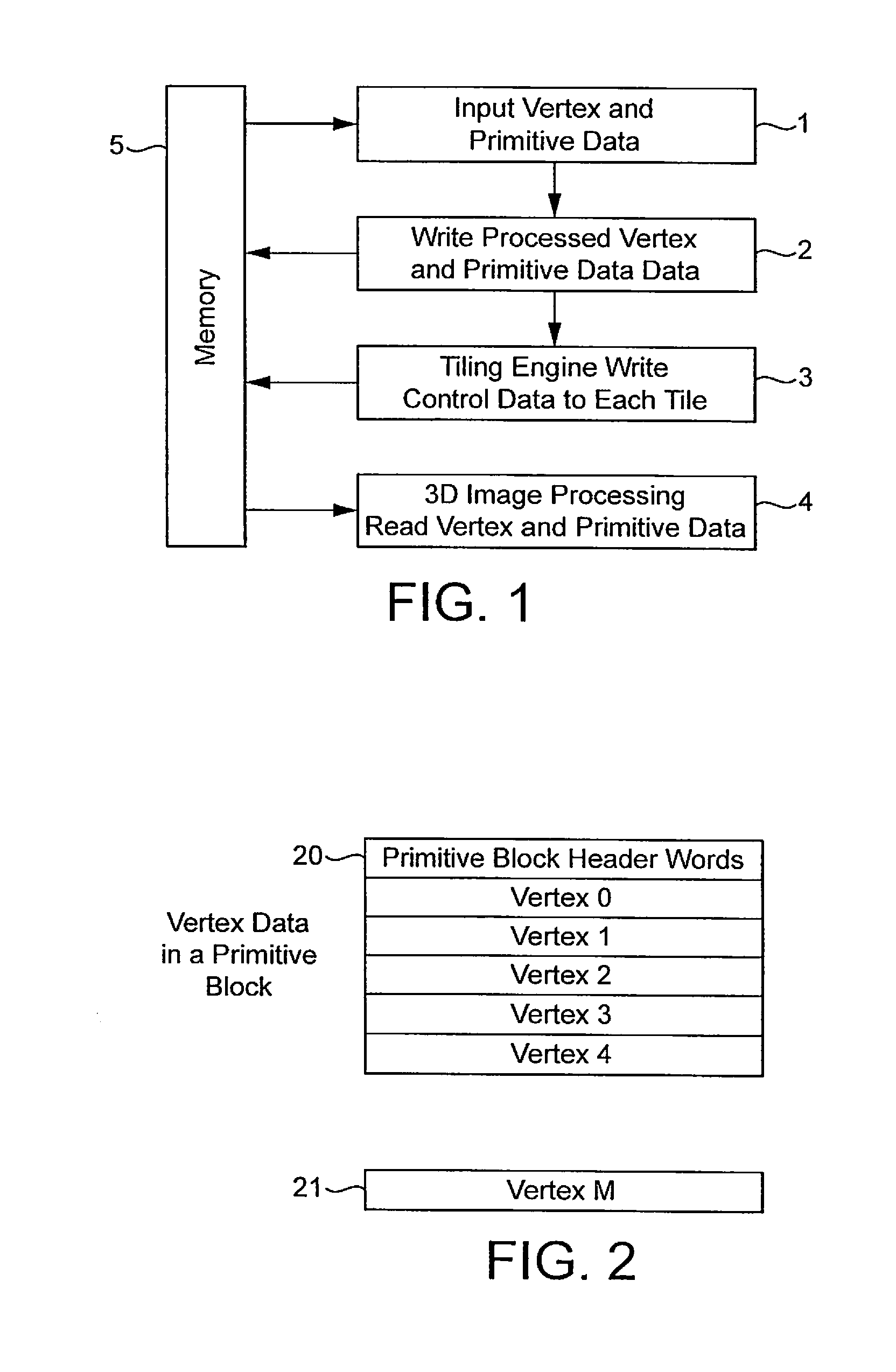
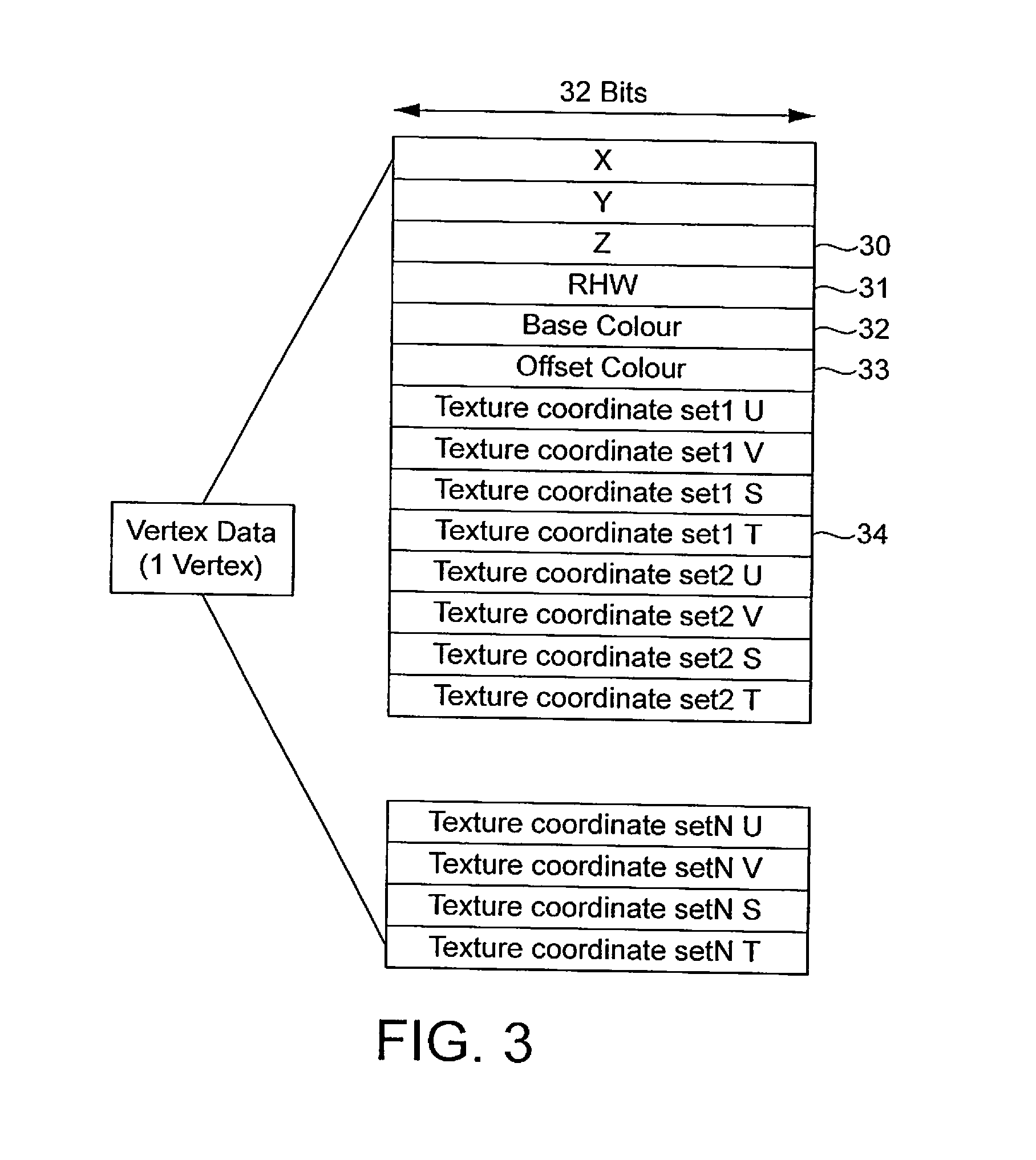
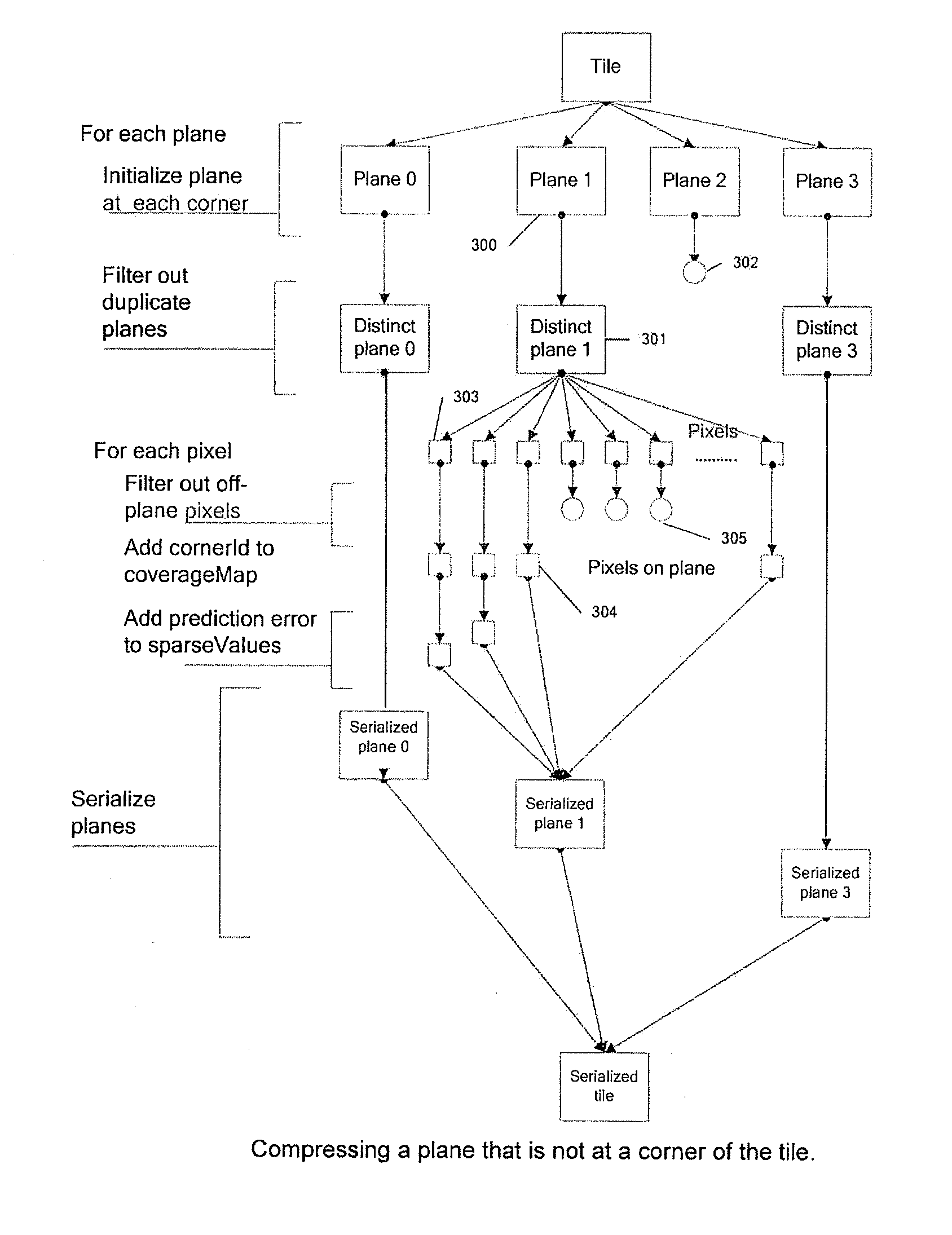
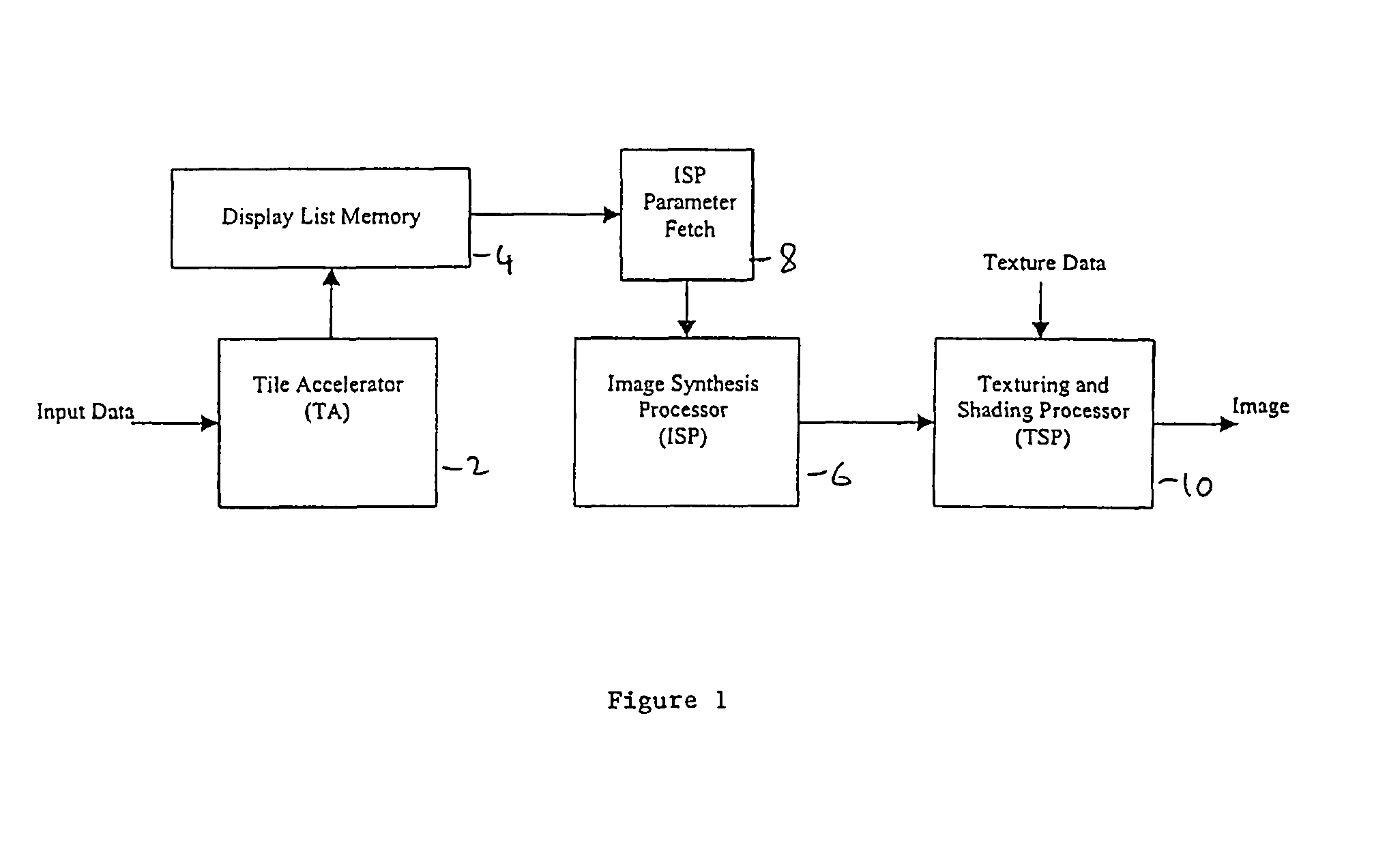
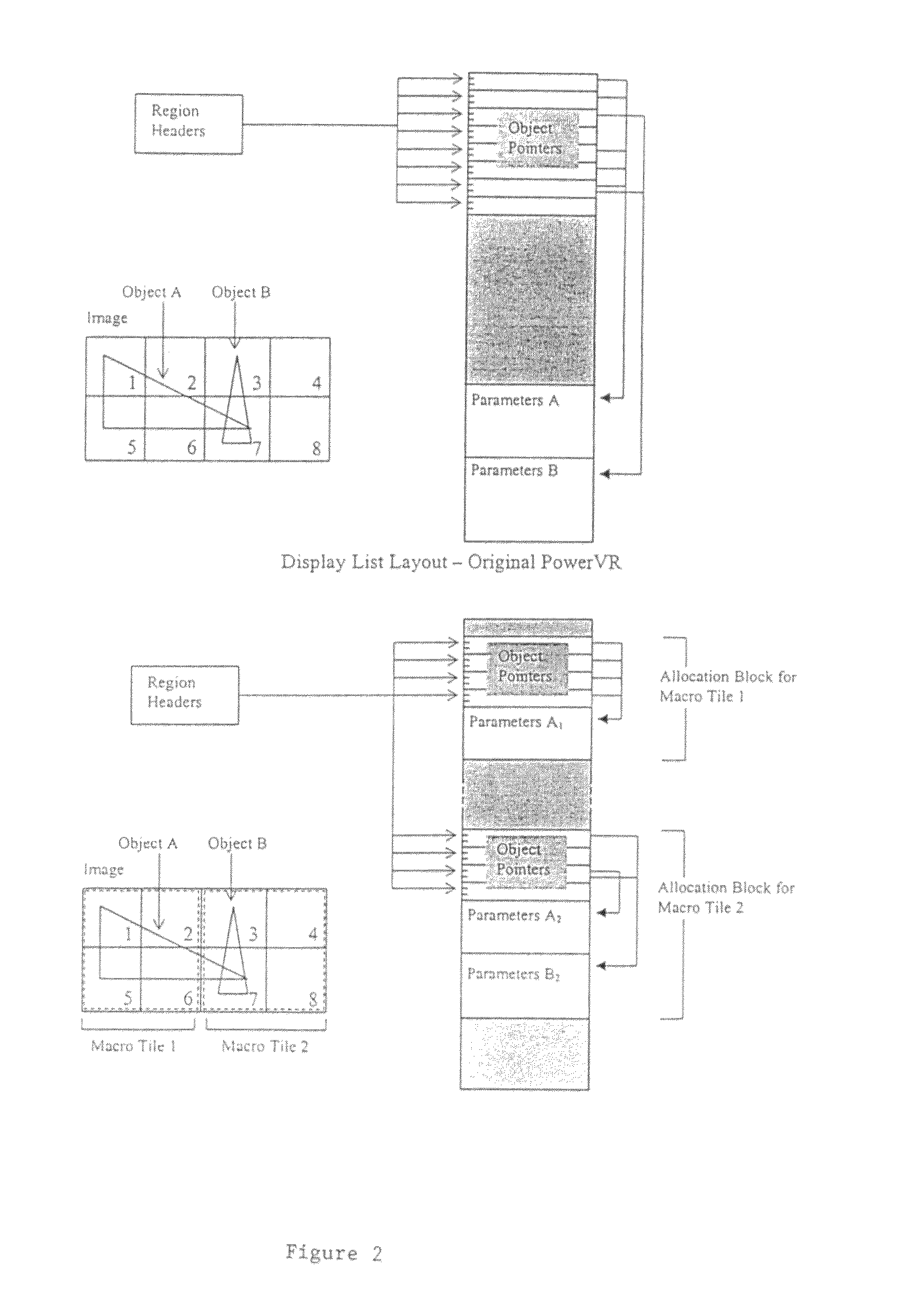
Display list compression for a tiled 3-D rendering system
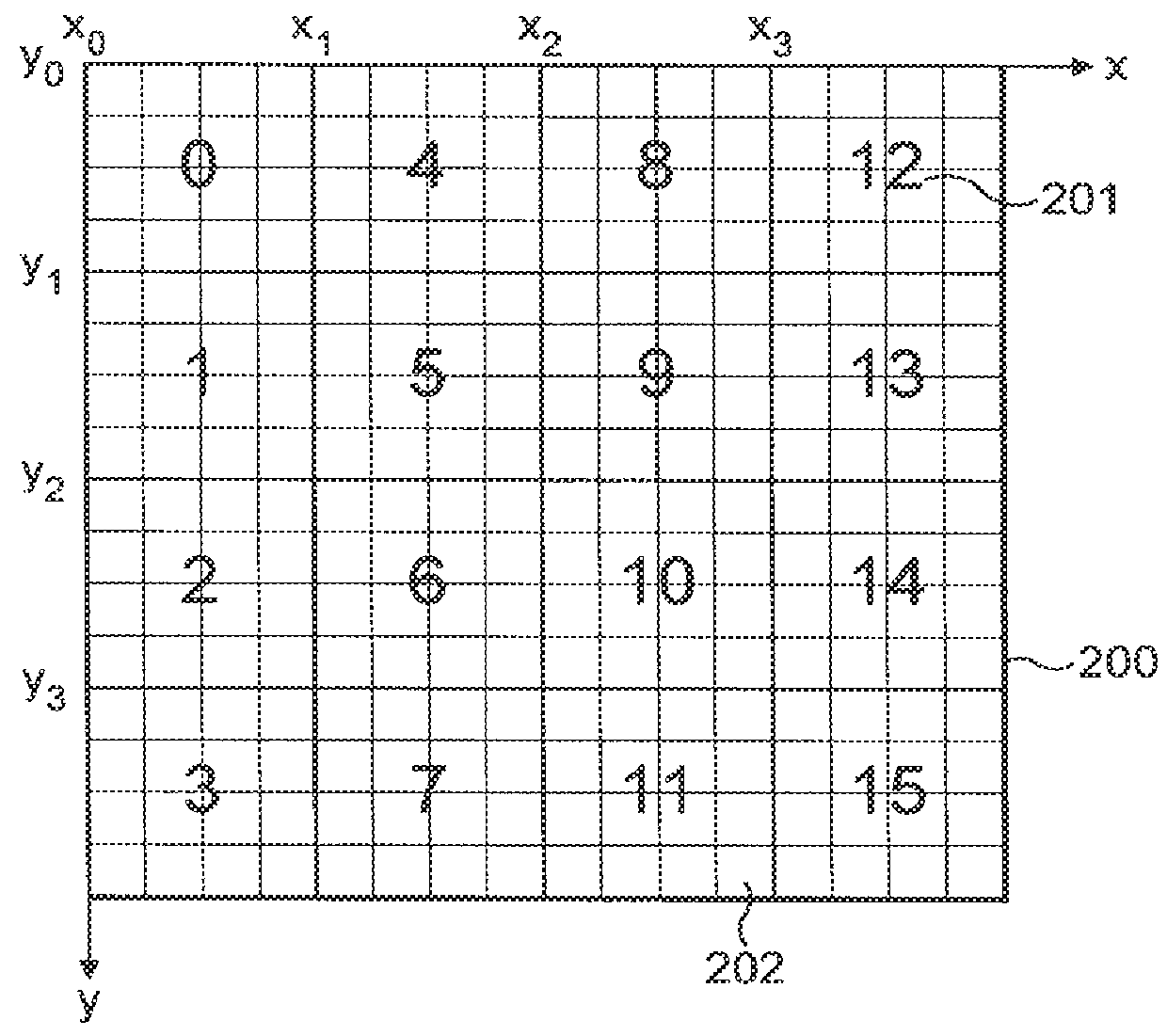
InactiveUS7324115B2Reduce memory bandwidthSmall sizeImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay list3D computer graphics
A 3-dimensional computer graphics rendering system receives object data for a scene to be rendered. This includes vertex data and index data. The scene is subdivided into priority of rectangular areas (202). Object 8 of each rectangular area in the scene is assembled (203) and subsequently compressed (207). This data can subsequently be retrieved and decompressed and used for producing a properly shaded and texted image for display.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
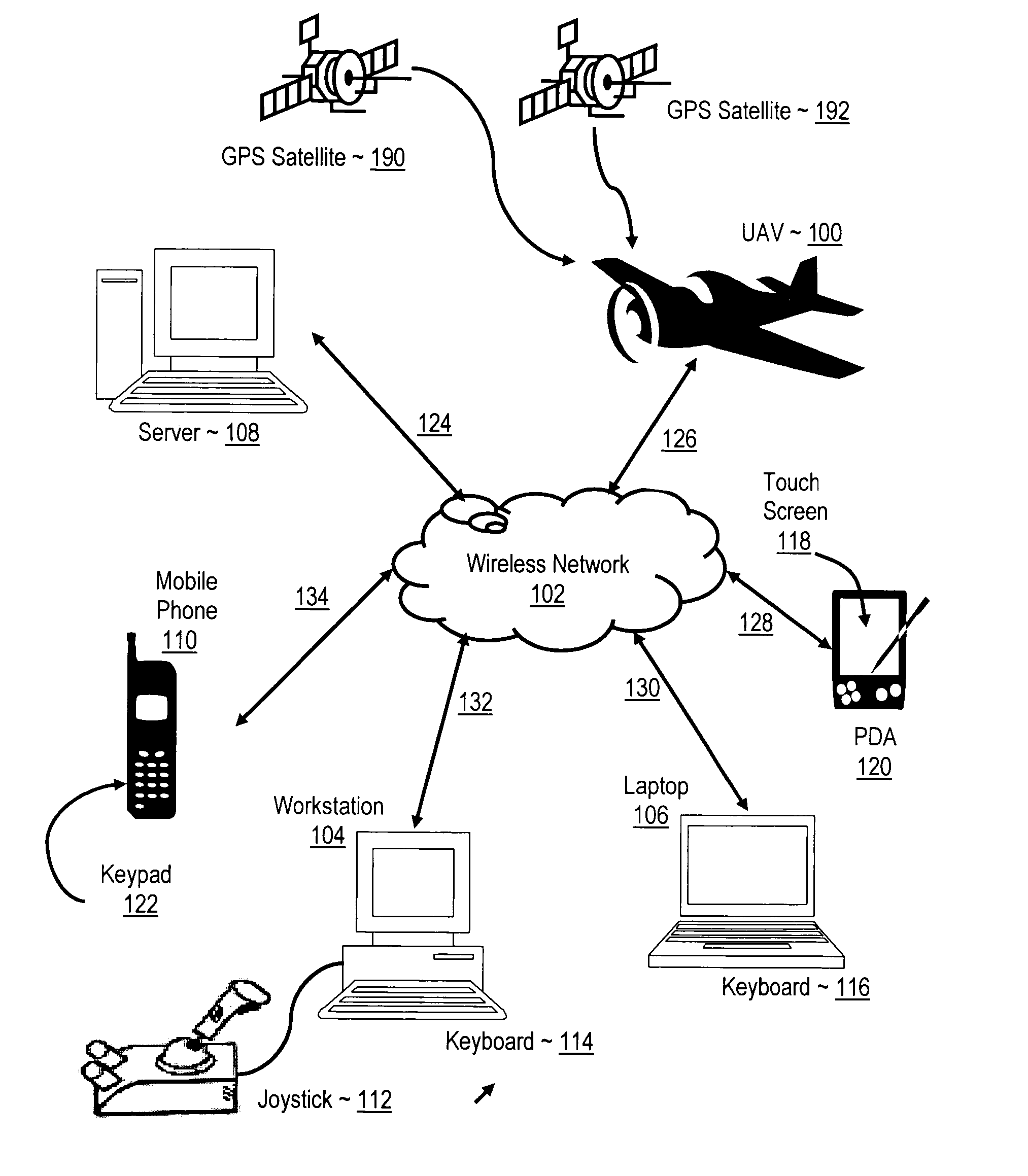
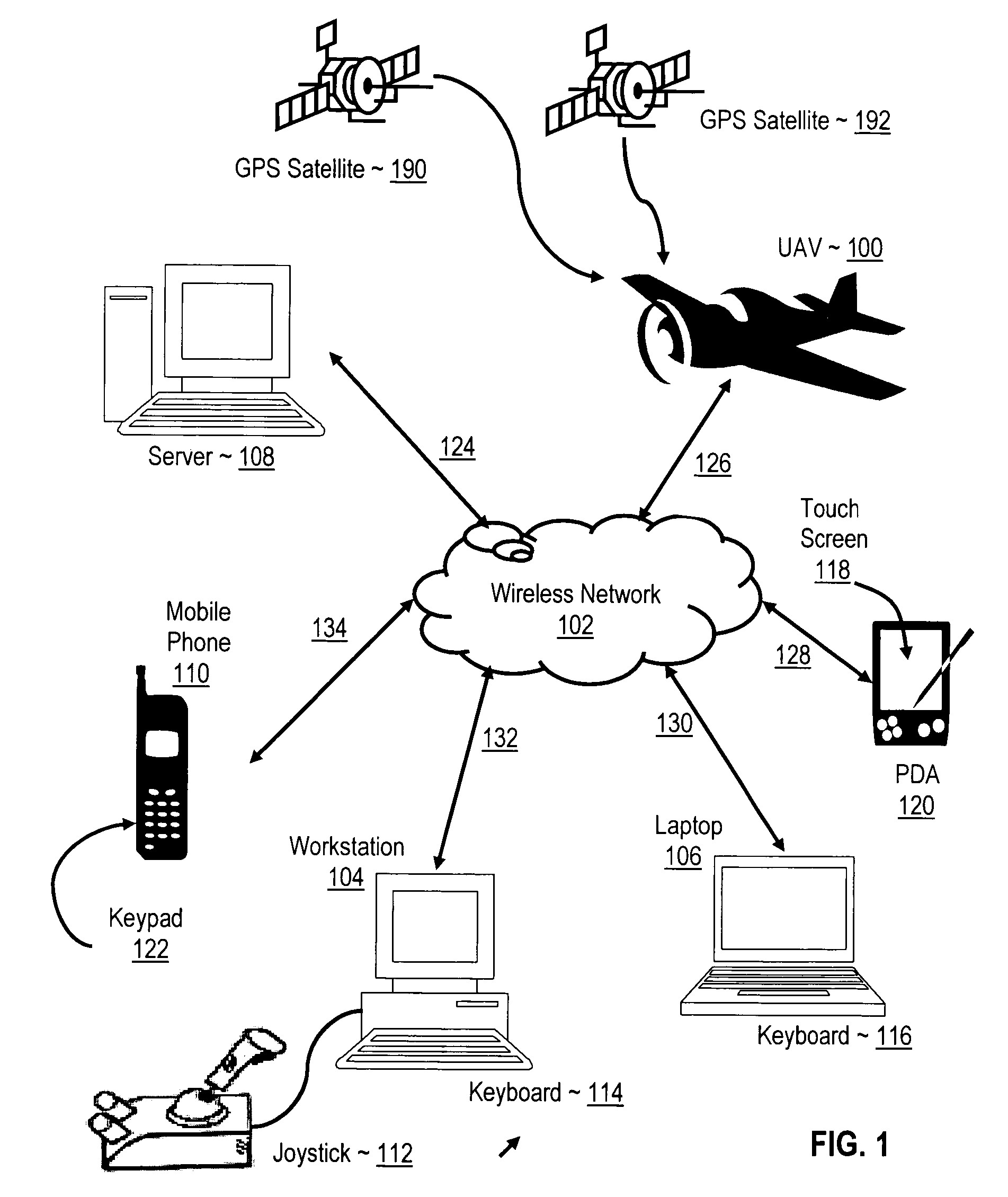
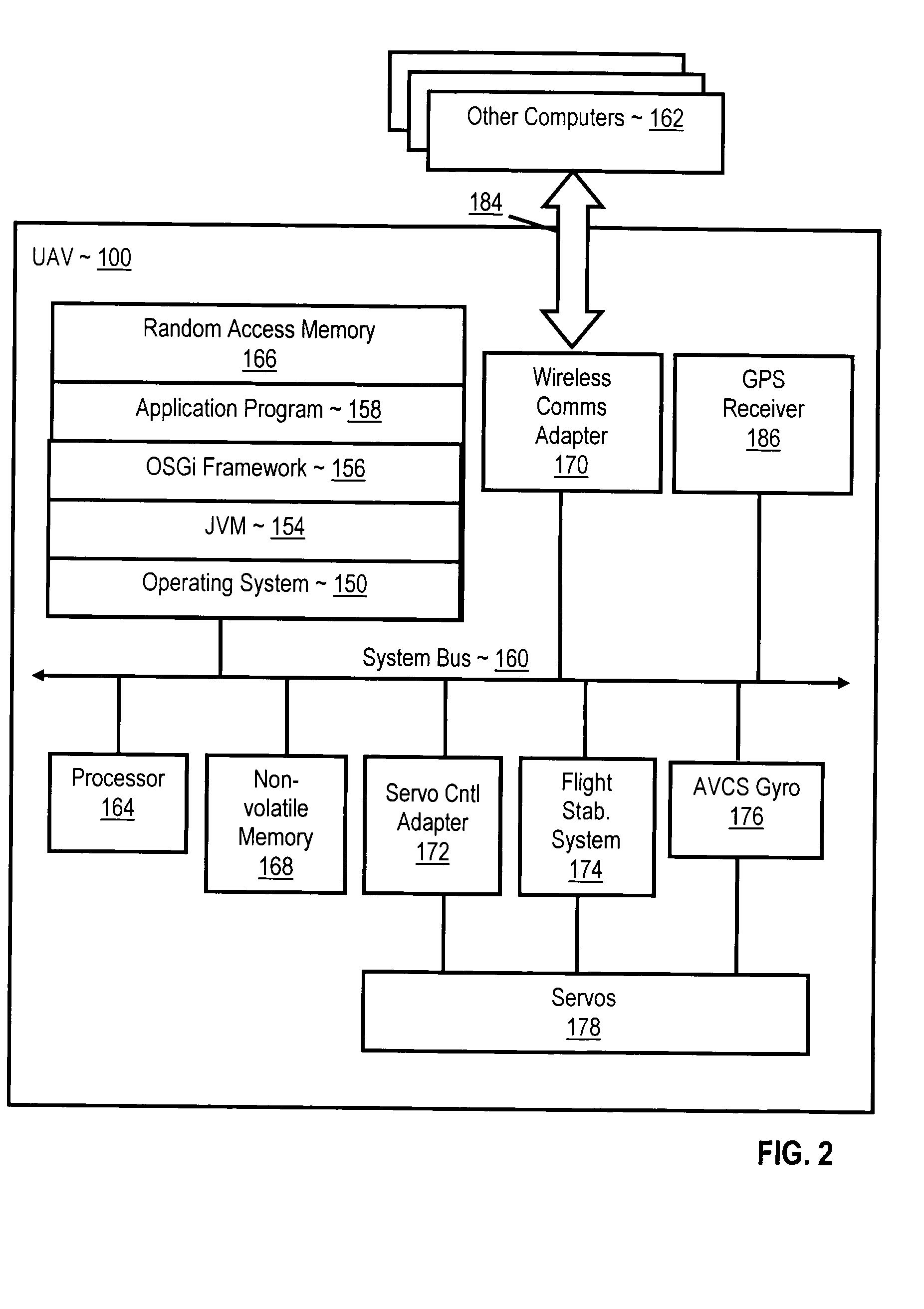
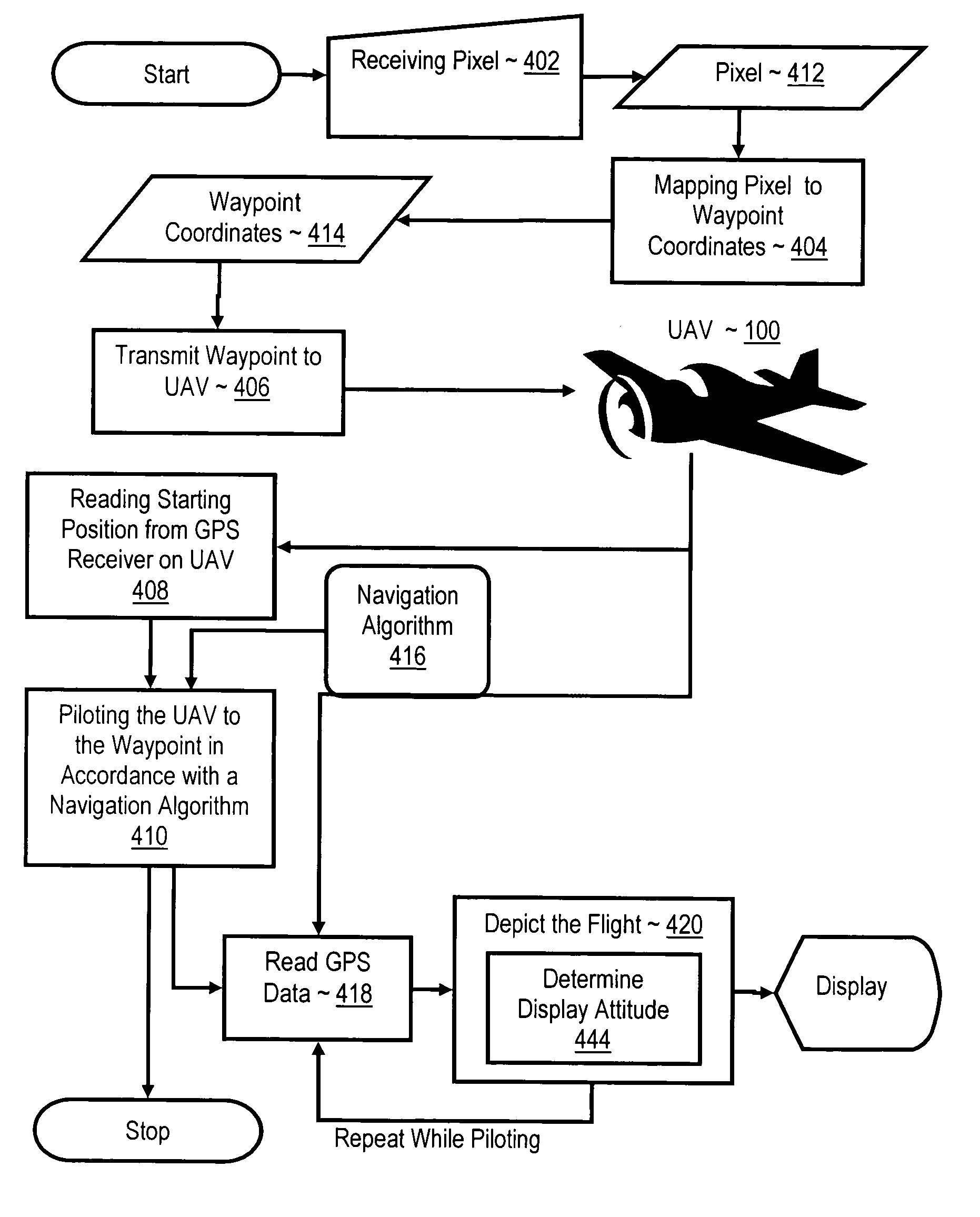
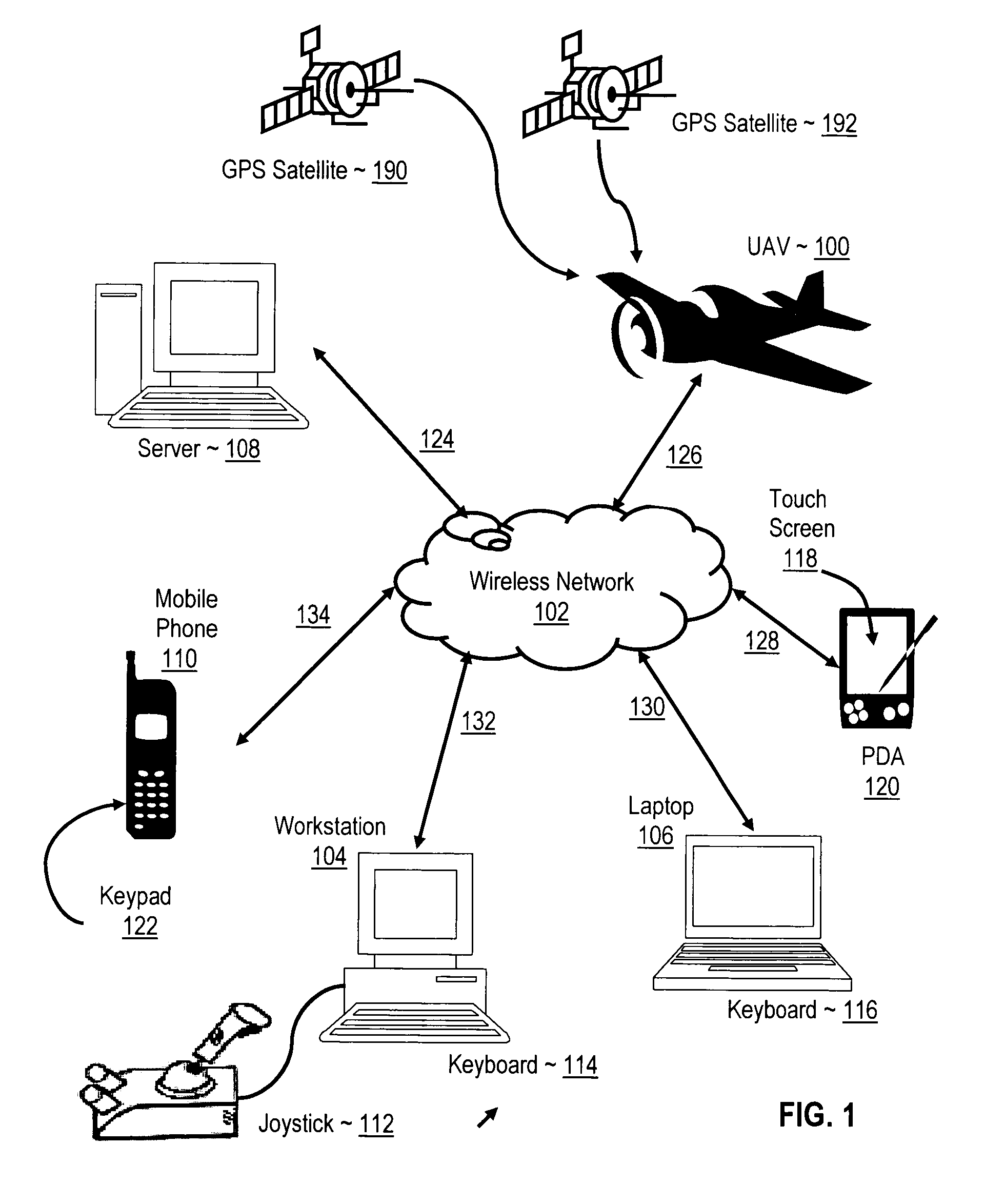
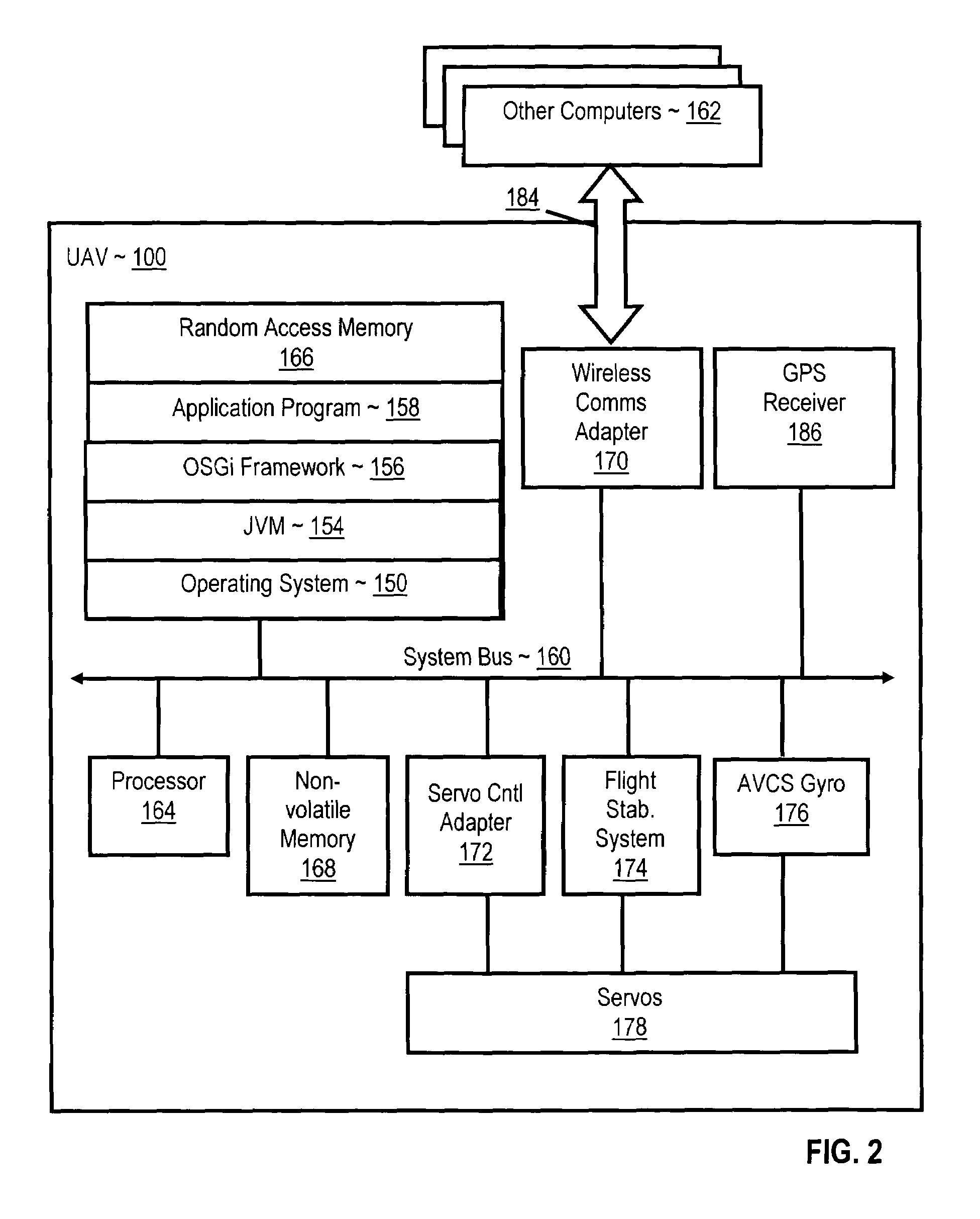
Navigating a UAV with on-board navigation algorithms with flight depiction
InactiveUS20060217877A1Navigation instrumentsVehicle position/course/altitude controlRemote controlOn board
Navigating a UAV including receiving in a remote control device a user's selection of a GUI map pixel that represents a waypoint for UAV navigation, mapping the pixel's location on the GUI to Earth coordinates of the waypoint, transmitting the coordinates of the waypoint to the UAV, reading a starting position from a GPS receiver on the UAV, and piloting the UAV, under control of a navigation computer on the UAV, from the starting position to the waypoint in accordance with a navigation algorithm. While piloting the UAV from the starting position to the waypoint, such embodiments include reading from the GPS receiver a sequence of GPS data representing a flight path of the UAV, and depicting the flight of the UAV with 3D computer graphics, including a computer graphic display of a satellite image of the Earth, in dependence upon the GPS data.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Navigating a UAV with on-board navigation algorithms with flight depiction
InactiveUS7107148B1Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsRemote controlOn board
Navigating a UAV including receiving in a remote control device a user's selection of a GUI map pixel that represents a waypoint for UAV navigation, mapping the pixel's location on the GUI to Earth coordinates of the waypoint, transmitting the coordinates of the waypoint to the UAV, reading a starting position from a GPS receiver on the UAV, and piloting the UAV, under control of a navigation computer on the UAV, from the starting position to the waypoint in accordance with a navigation algorithm. While piloting the UAV from the starting position to the waypoint, such embodiments include reading from the GPS receiver a sequence of GPS data representing a flight path of the UAV, and depicting the flight of the UAV with 3D computer graphics, including a computer graphic display of a satellite image of the Earth, in dependence upon the GPS data.
Owner:IBM CORP
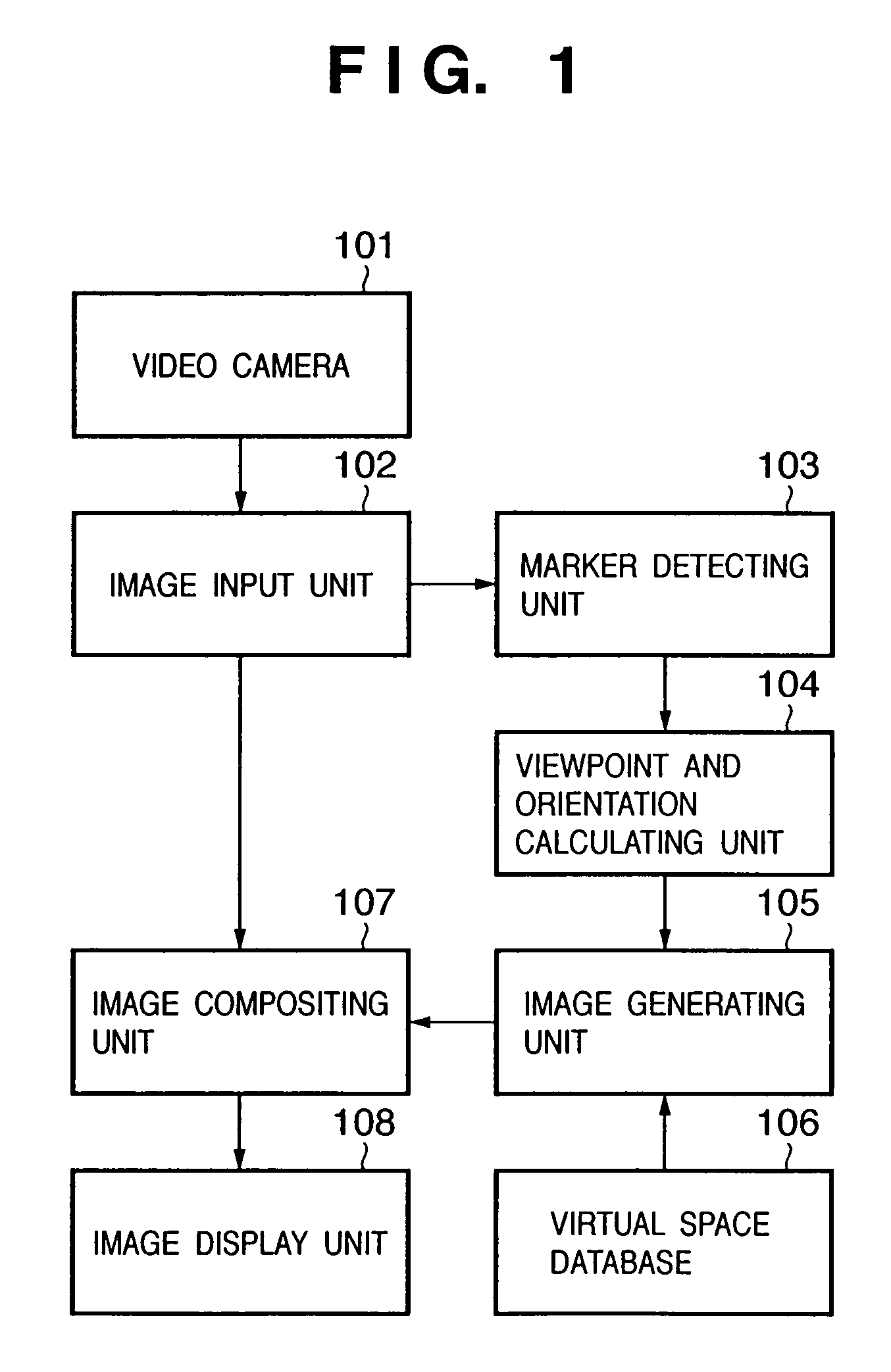
Image display apparatus and method
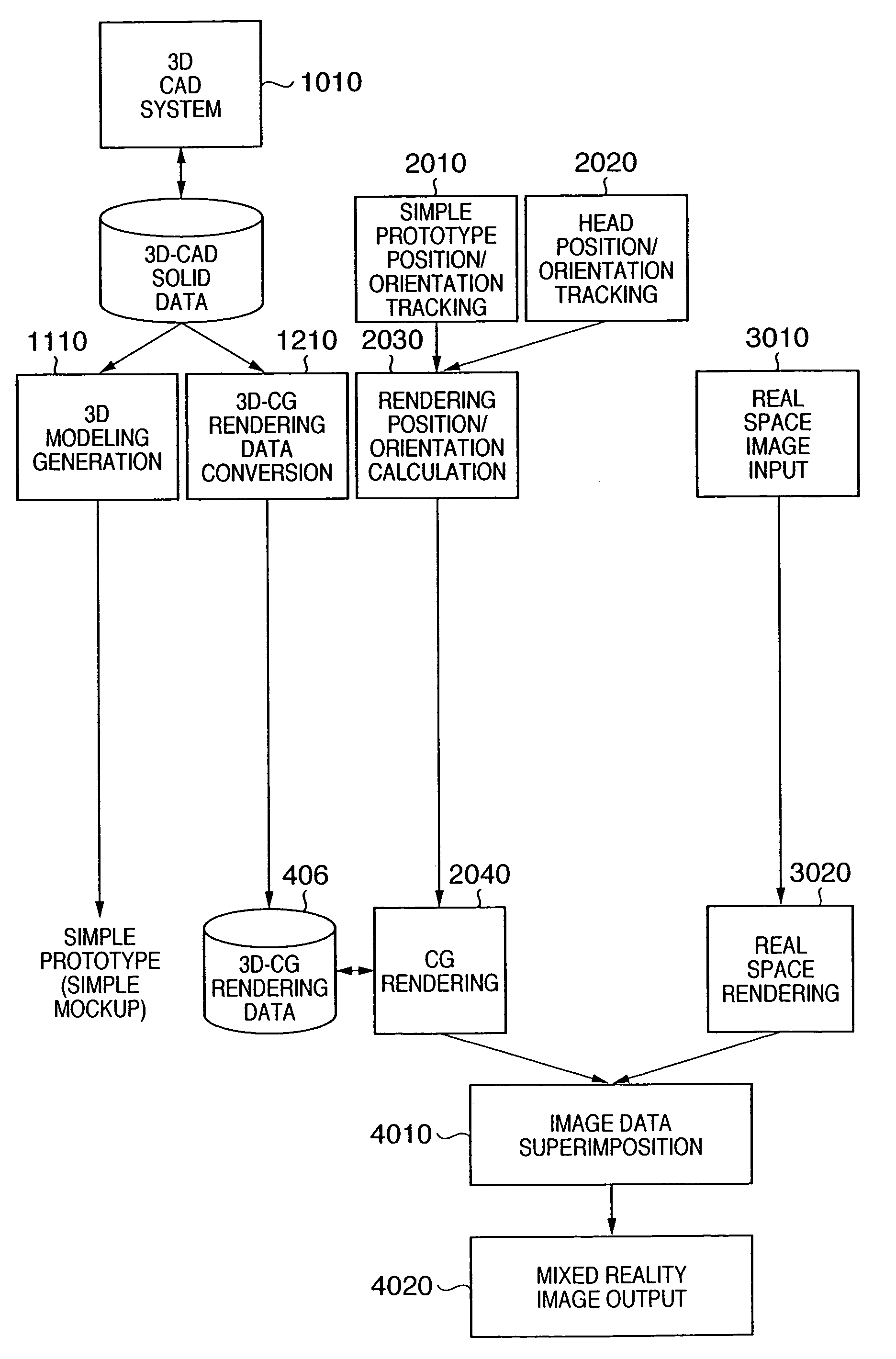
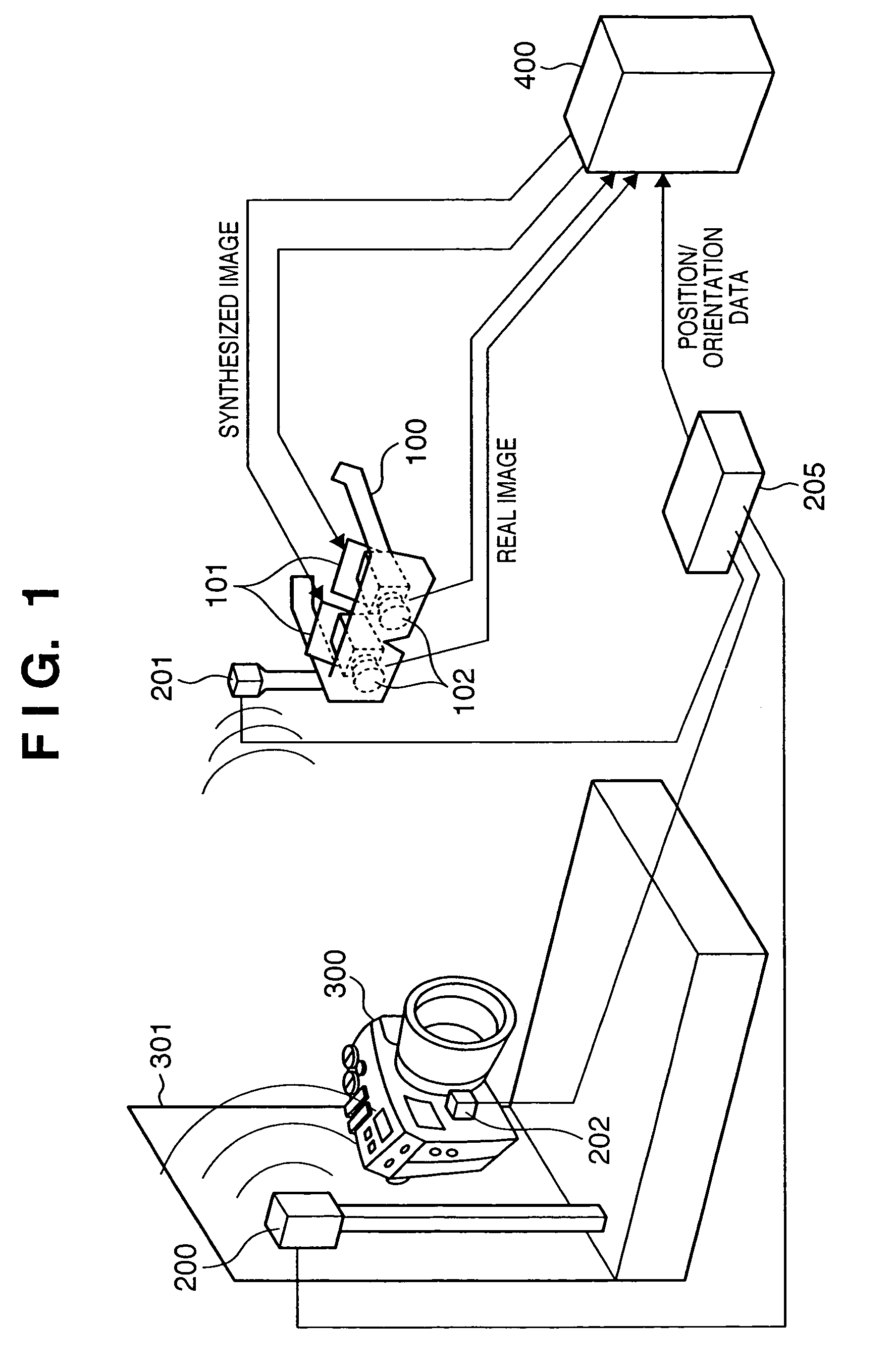
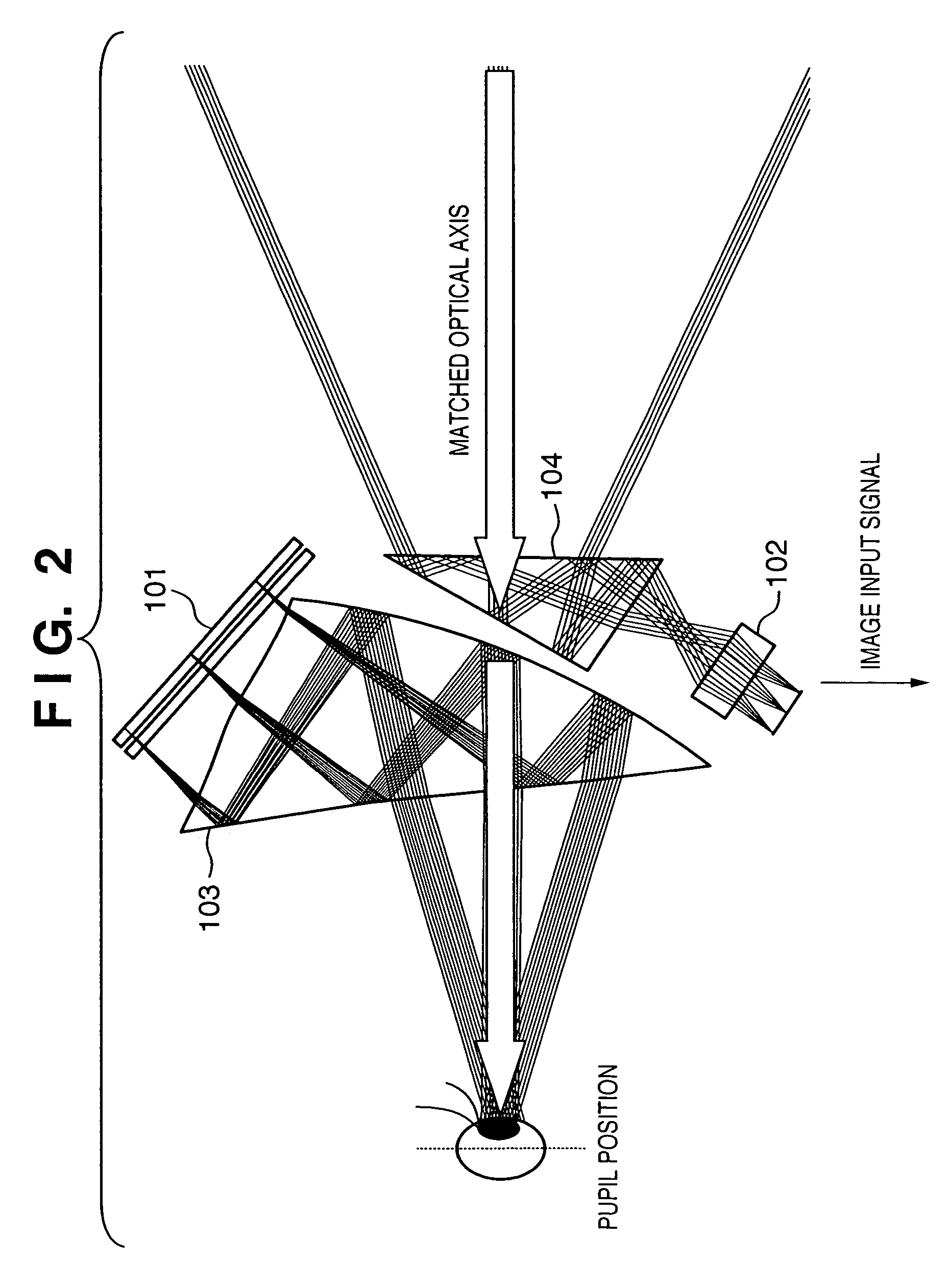
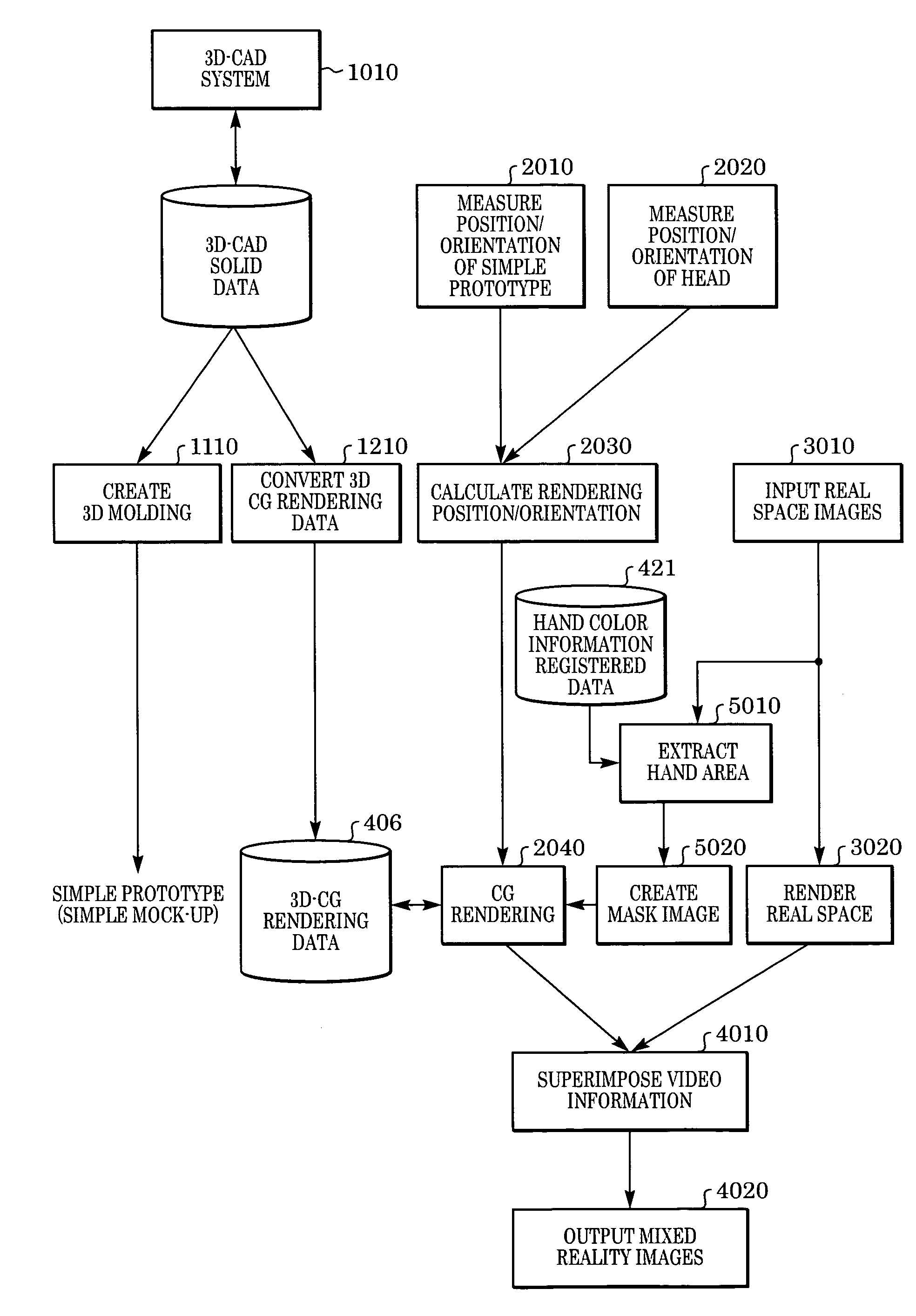
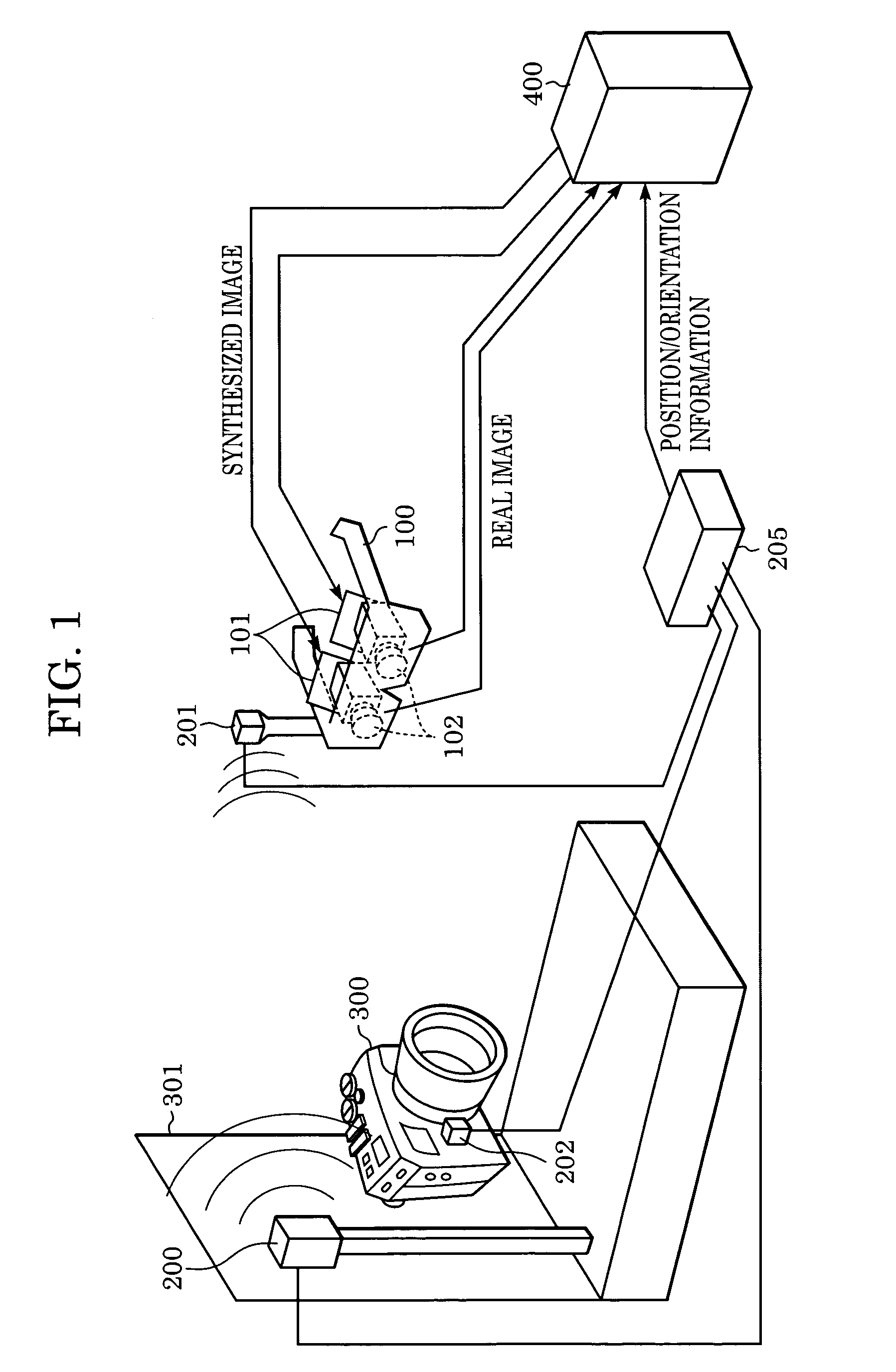
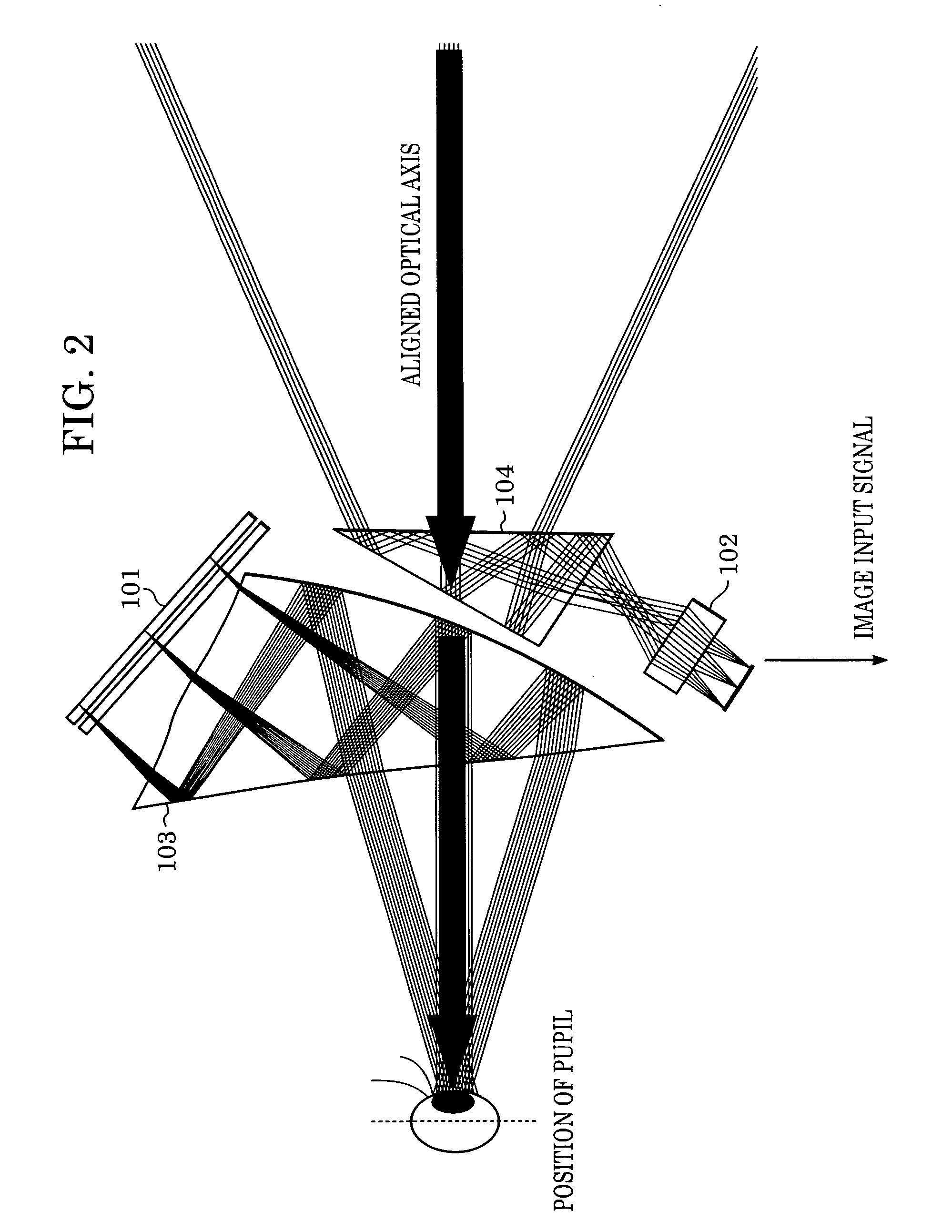
Image display method of superimposing virtual space image data on real space image data at an arbitrary viewpoint and exhibiting the superimposed image to a viewer is provided. When real space image data, including a prototype generated based on three-dimensional CAD data, is captured by an image sensing device, the position and orientation of the image sensing device and the prototype are tracked, and position / orientation data indicative of the position and orientation of the prototype in the image is acquired. Based on the position / orientation data and the three-dimensional CAD data, a three-dimensional computer graphic image is rendered so as to overlap the prototype in the image, thereby synthesizing the image with the three-dimensional computer graphic image. The synthesized image is then displayed.
Owner:CANON KK
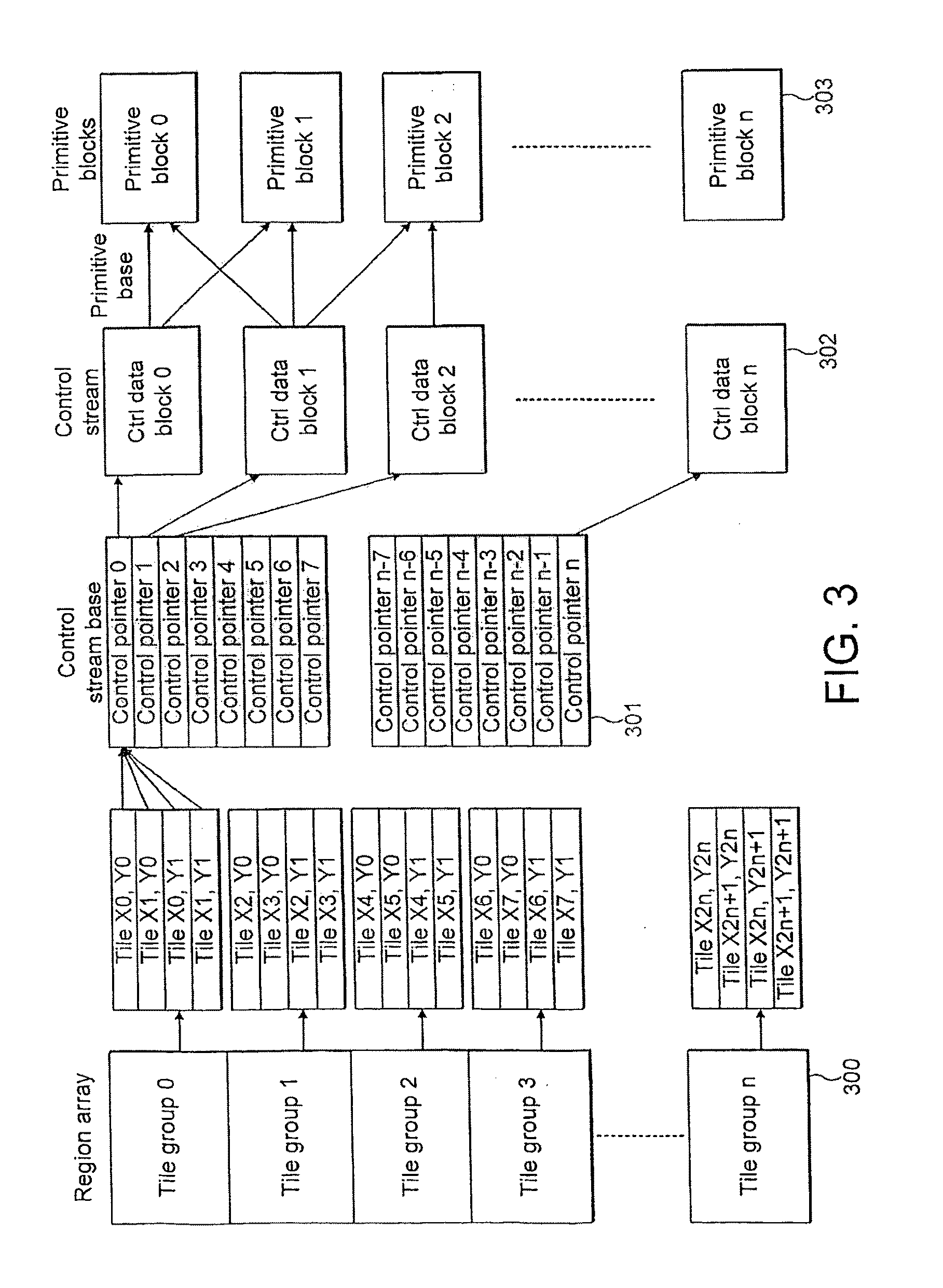
Display list control stream grouping in tile based 3D computer graphics system
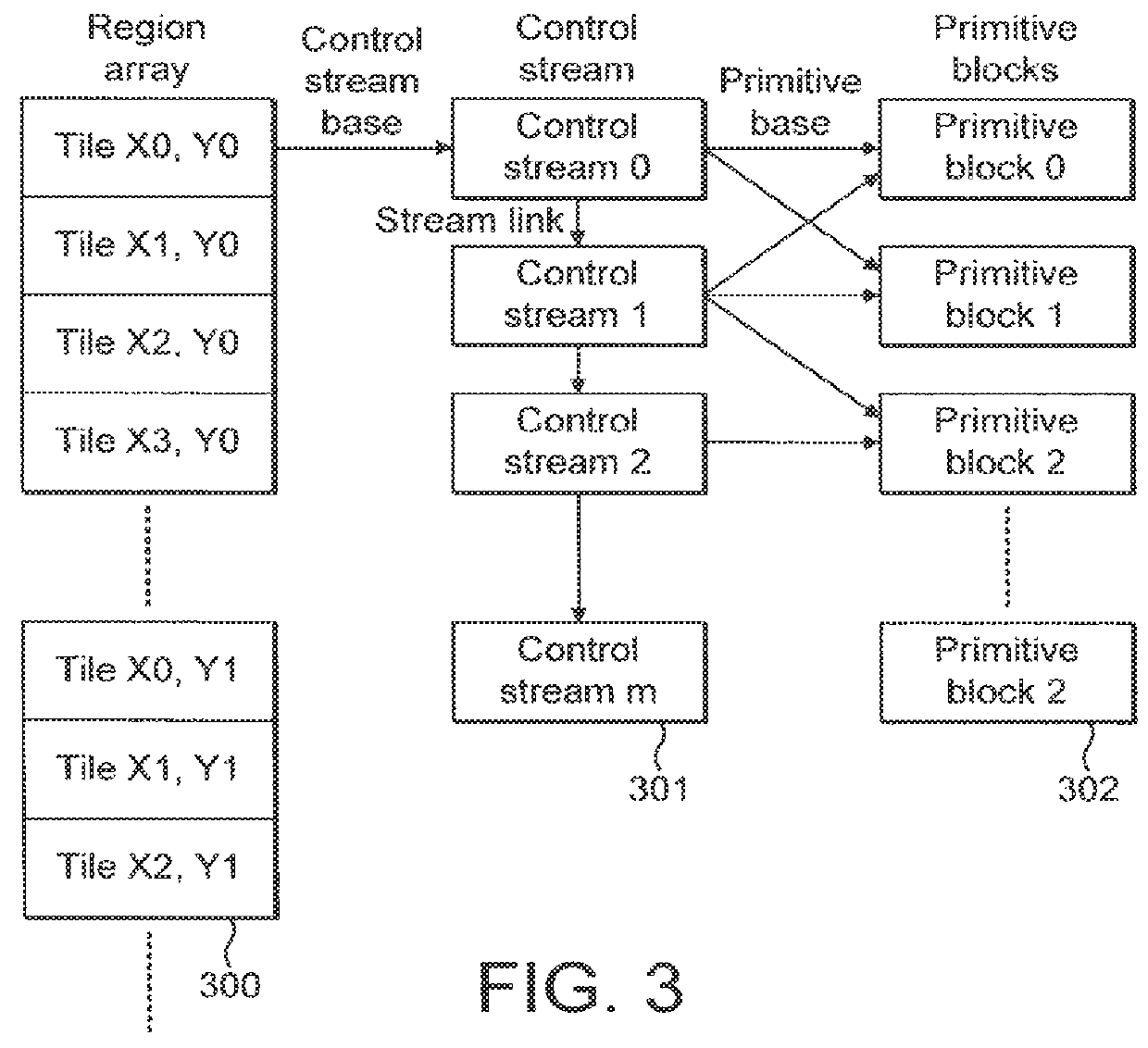
ActiveUS20110304608A1Improve efficiencyReduces internal parameter memory bandwidthImage generationFilling planer surface with attributesStreaming dataGraphic system
A method and apparatus are provided for rendering a 3 dimensional computer graphics image. The image is subdivided into a plurality of rectangular areas and primitives which may be visible in the image are assigned to respective ones of a plurality of primitive blocks. A determination is made as to which primitive blocks contain primitives which intersect each rectangular area. The rectangular areas are then grouped into a plurality of fixed size groups and control stream data for each of the fixed size groups is derived, this control stream data including data which determines which primitive blocks are required to render the rectangular areas in each respective first fixed size group. The control stream data is then used to render the image for display.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
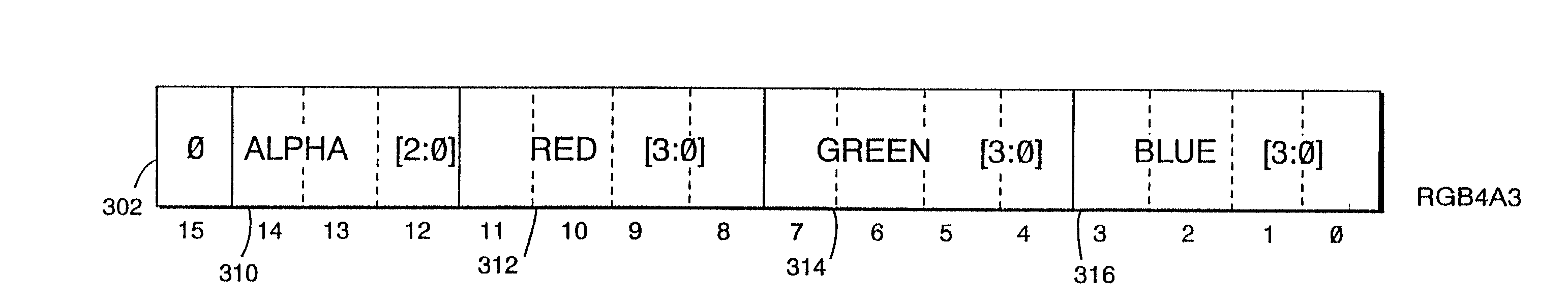
Variable bit field encoding
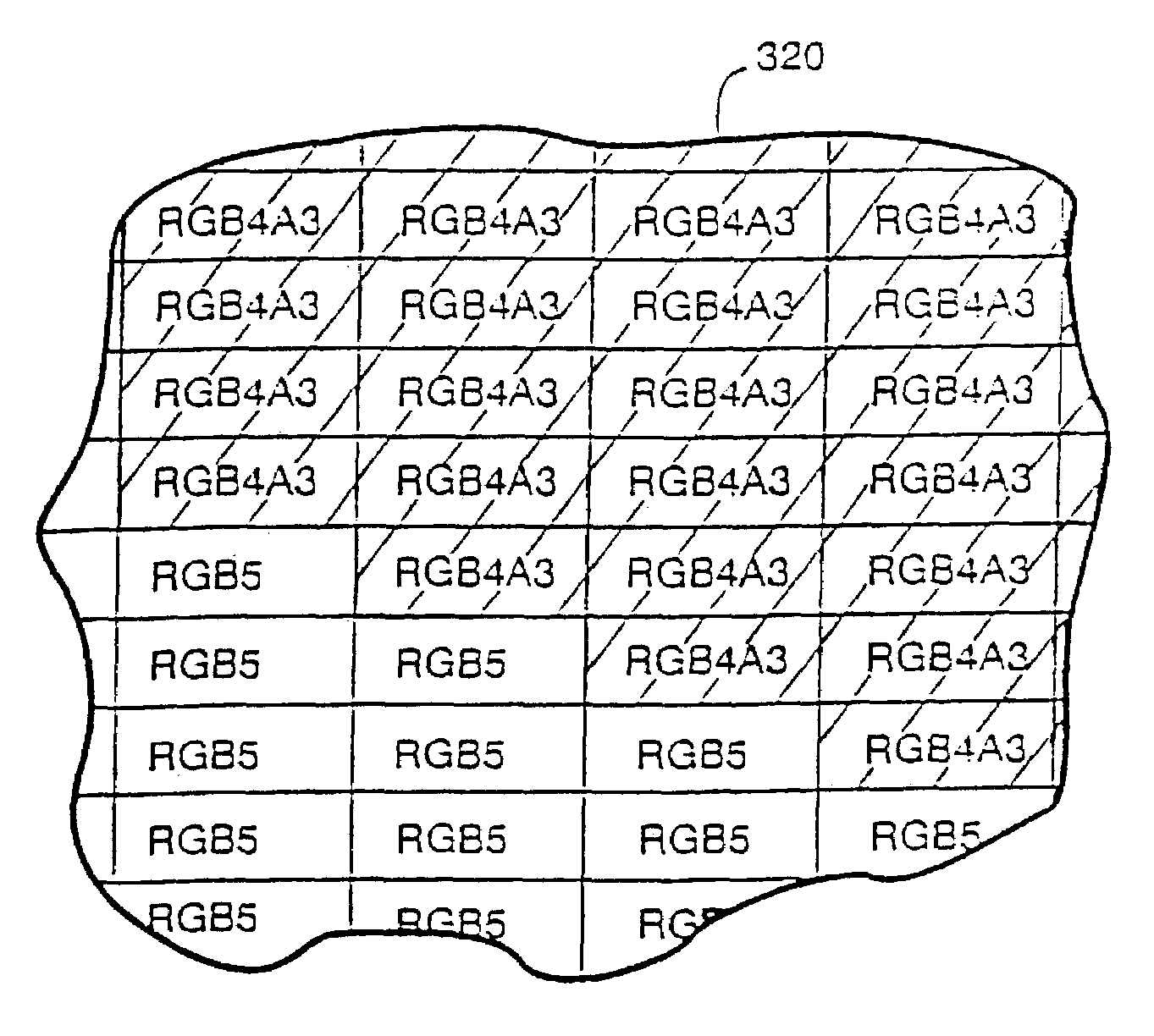
InactiveUS7119813B1Improve image qualityHigh color resolutionTexturing/coloringCathode-ray tube indicatorsBit fieldImage resolution
A compact image element encoding format selectively allocates a bit field within the format to alternately encode either multi-bit alpha resolution or increased color resolution. This encoding technique may be advantageously used to allocate encoding bits to model semi-transparency while using those same bits for other purposes (e.g., higher color resolution) in instances where semi-transparency is not required (e.g., for opaque image elements). In one advantageous embodiment, the same encoding format can provide either RGB5 or RGB4A3, on an image-element-by-image-element basis. Applications include but are not limited to texture mapping in a 3D computer graphics system such as a home video game system or a personal computer.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Efficient bump mapping using height maps
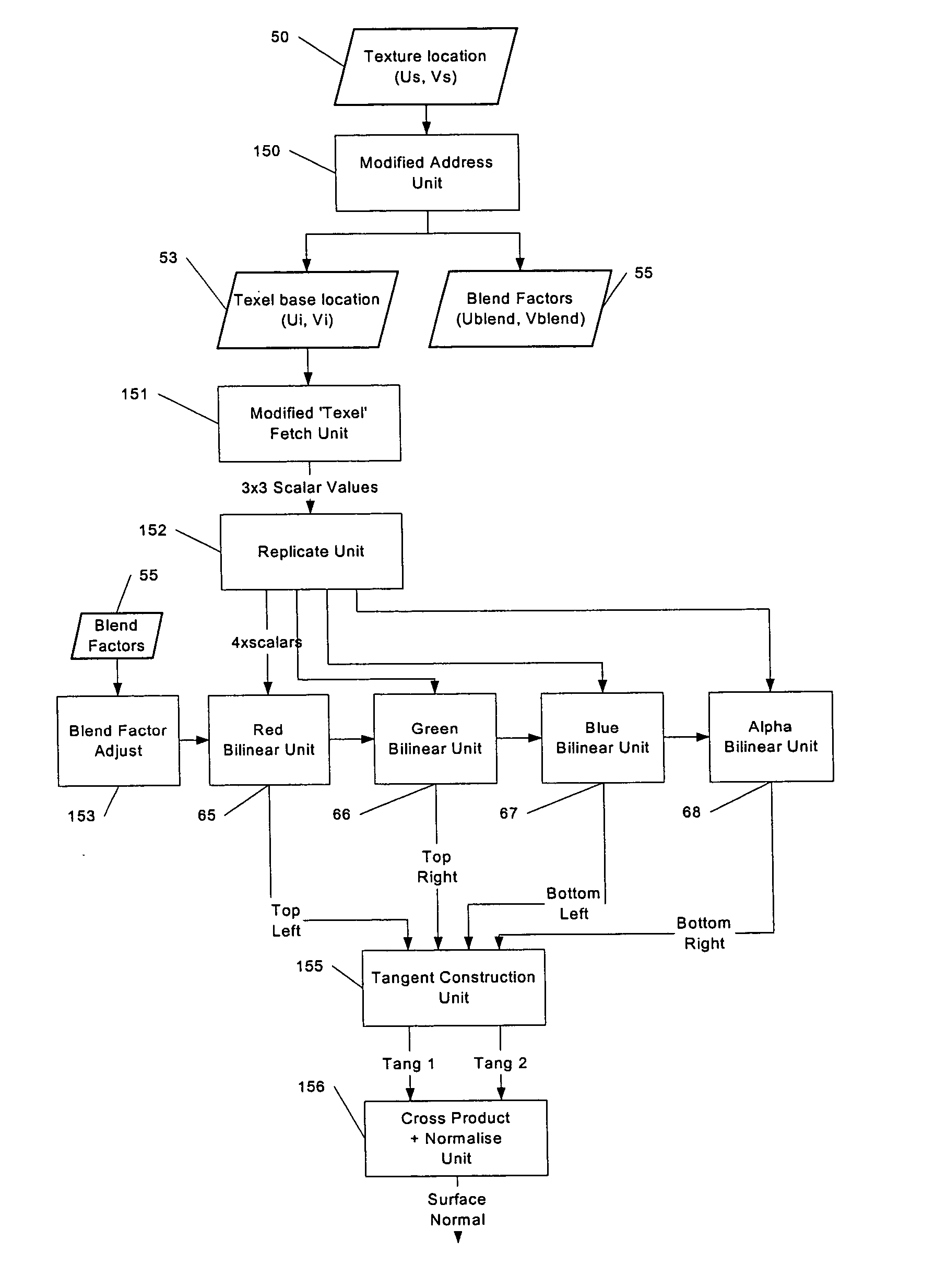
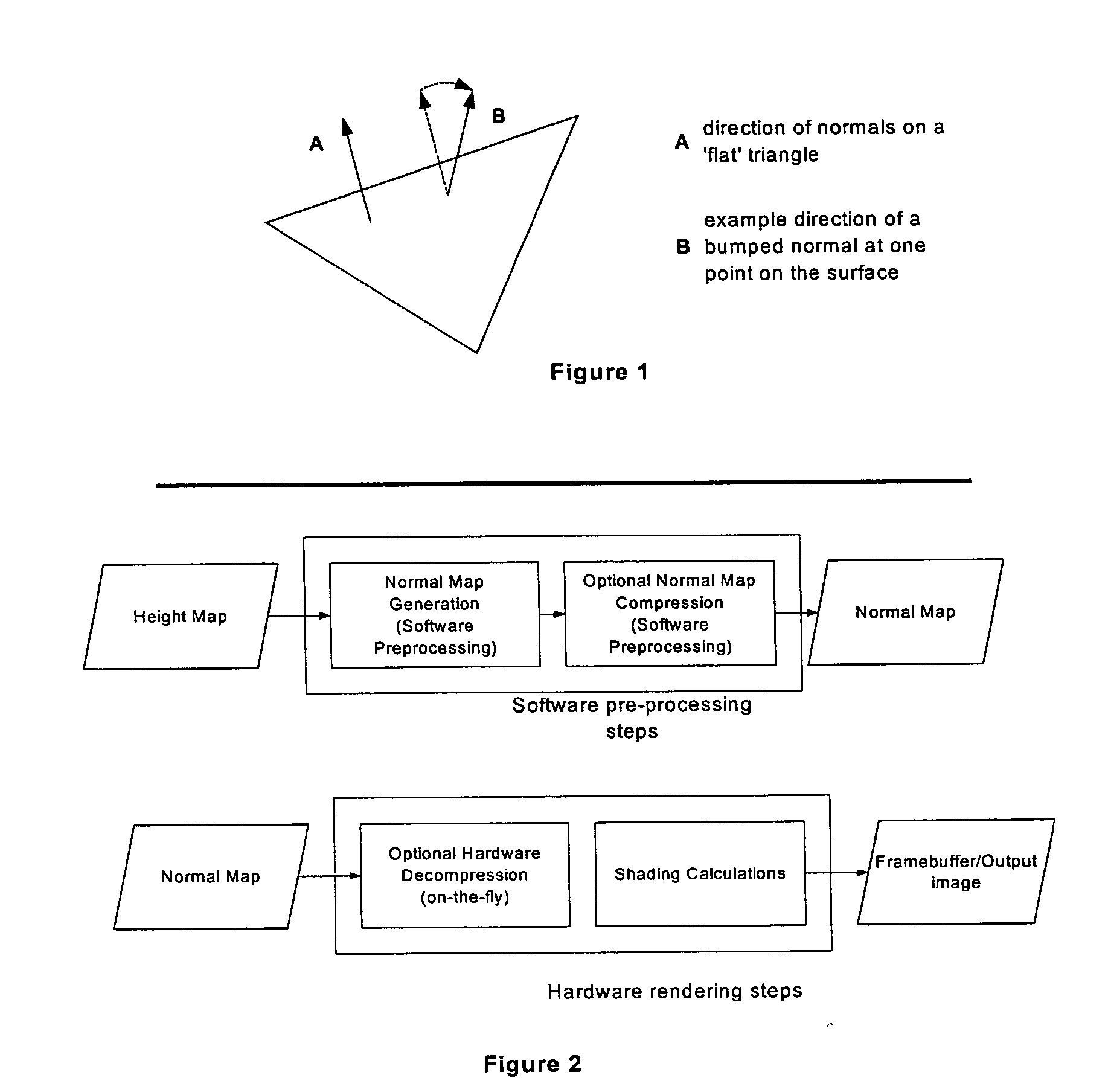
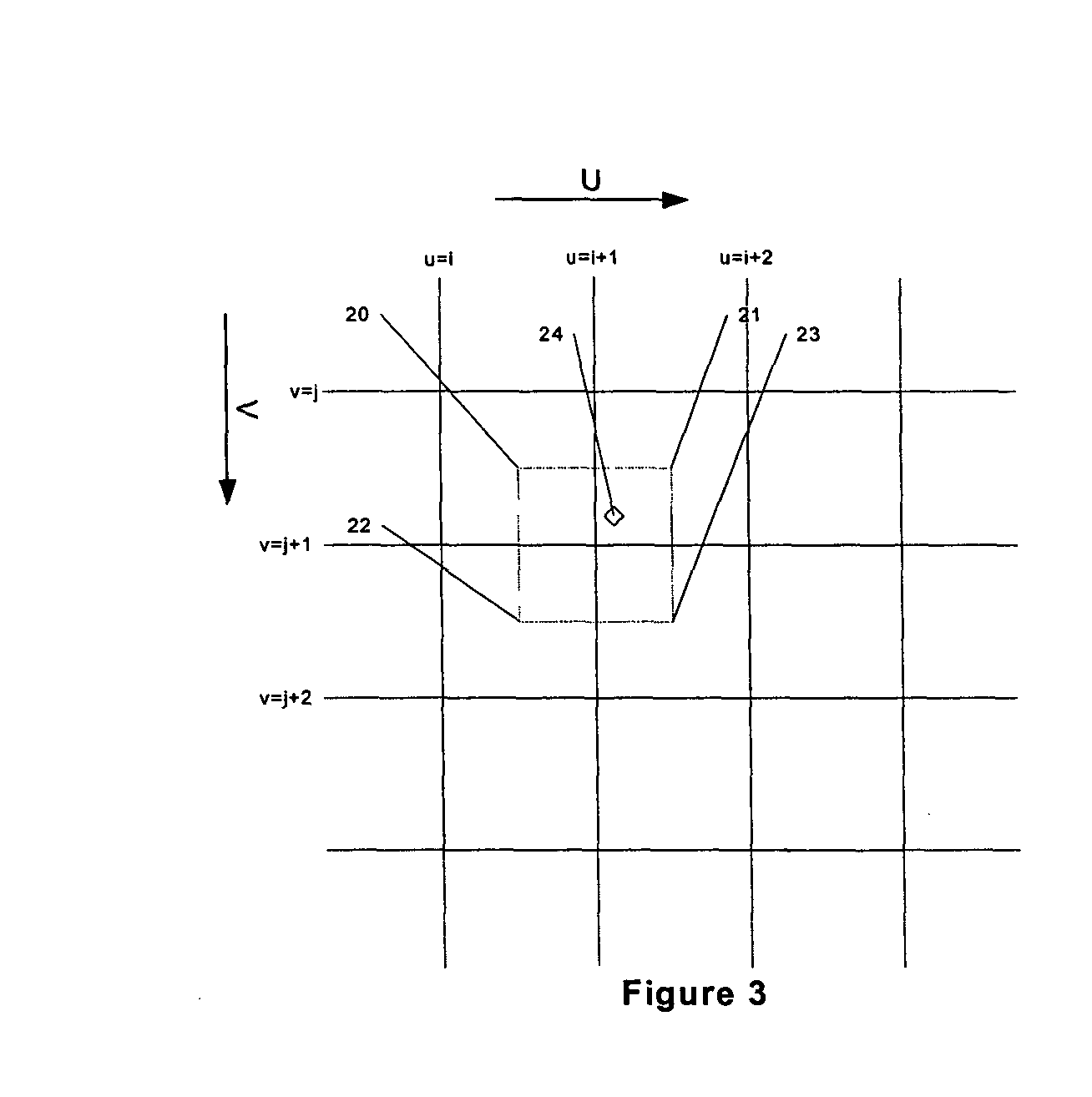
A method for generating bump map data substantially in real time for use in a 3-dimensional computer graphics system. Data is received which defines an area to which a texture is to be applied. Texture data to apply to the area is also received. This data includes surface height data. A set of partially overlapping samples of texture data are then filtered and surface tangent vectors derived therefrom. A bump map surface normal is then derived from the tangent vectors.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
Method and system for presenting three-dimensional computer graphics images using multiple graphics processing units
InactiveUS7405734B2Improve scalabilityScaling geometrically specific textureCathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinations3D computer graphicsGraphics processing unit
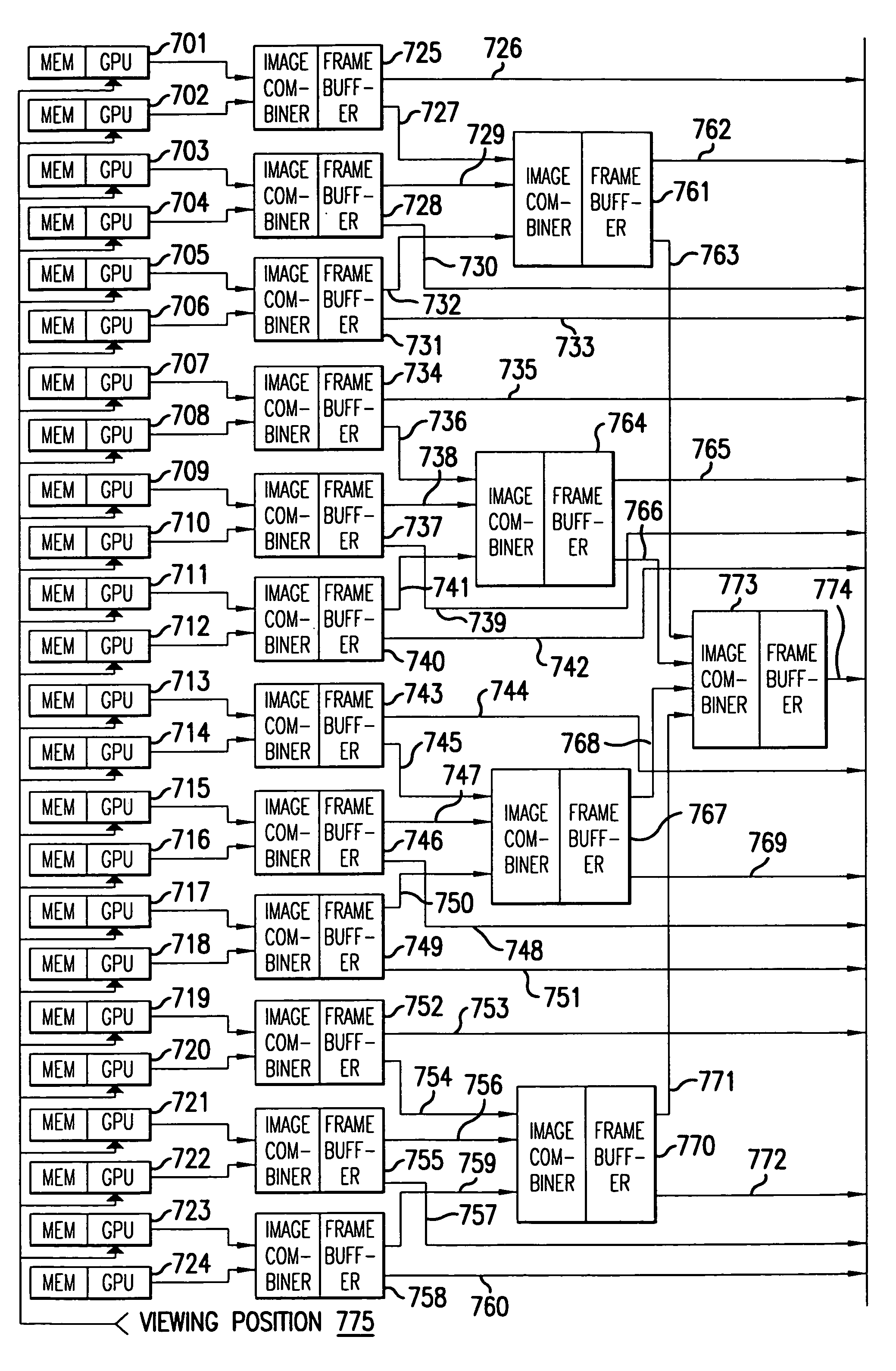
The present invention provides a method and system for presenting three-dimensional computer graphics images using multiple graphics processing units. The dimensions of the scene to be rendered are bounded by a rectangular volume decomposed into rectangular subvolumes. Vertices of graphics primitives are compared with subvolume boundaries to determine to which subvolume a graphics primitive should be assigned. A GPU is assigned to each subvolume to render the graphics data that lies within it. A viewing position point is determined and communicated to each GPU. Rendered graphics data from each GPU are ordered based upon the viewing position Outputs of the individual GPUs are combined by blending within an image combiners. Outputs of image combiners can be presented for viewing or further combined in a subsequent stage image combiner.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
Three-dimensional display system: apparatus and method
InactiveUS20030071813A1Readily and more reliably producedLittle time delayImage enhancementTelevision system detailsRadiance3D computer graphics
In a presently preferred embodiment of the invention, a three-dimensional scene is reproduced on a specialized light display which offers full multiviewpoint capability and auto-stereoscopic views. The displayed image is produced using a set of M two-dimensional images of the scene collected at a set of distinct spatial locations. These M two-dimensional images are processed through a specialized mathematical encoding scheme to obtain a set of NxK display-excitation electrical-input signals, where K is the number of pixels in the display, and N<=Ed is the number of individual light-radiating elements within one pixel. The display is thus comprised of a total of NxK light-radiating elements. Each of the K pixels is adapted for control of their associated radiance patterns. The display is connected for response to the set of NxK display-excitation electrical-input signals. In this manner, the display provides a multiviewpoint and autostereoscopic three-dimensional image associated with the original three-dimensional scene. An alternative embodiment of the invention is utilized to provide efficient storage and display of 3D computer graphics images.
Owner:MONSELLA MGMT NY
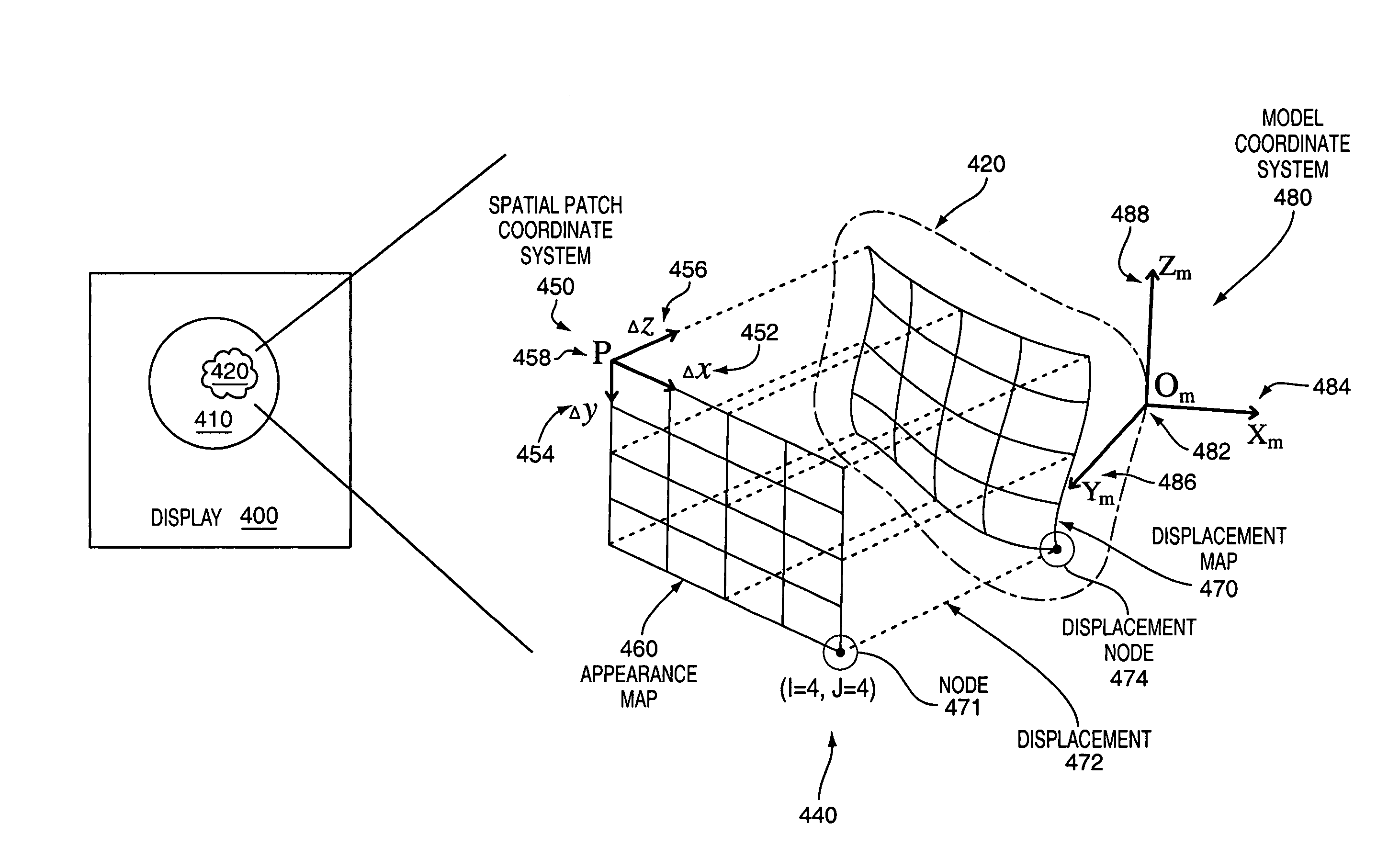
Spatial patches for graphics rendering
InactiveUS7102636B2Drawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicators3D computer graphicsParallel processing
Described are a novel graphical element known as a spatial patch and a system and method for rendering the spatial patch to create computer graphics. The spatial patch may include appearance data and displacement data for each of a plurality of nodes that together specify the color and geometry for typically a small portion of a surface of an object. The appearance and displacement data may be independent and irregular for each of the nodes in order to represent complexly colored and structured objects. The spatial patch may be processed independently and may have internal topology or structure to facilitate parallel processing. Accordingly, the spatial patch offers many quality and processing advantages over polygon mesh representations that have previously been used to create three-dimensional computer graphics.
Owner:MOSCOW STATE UNIVERSITY +1
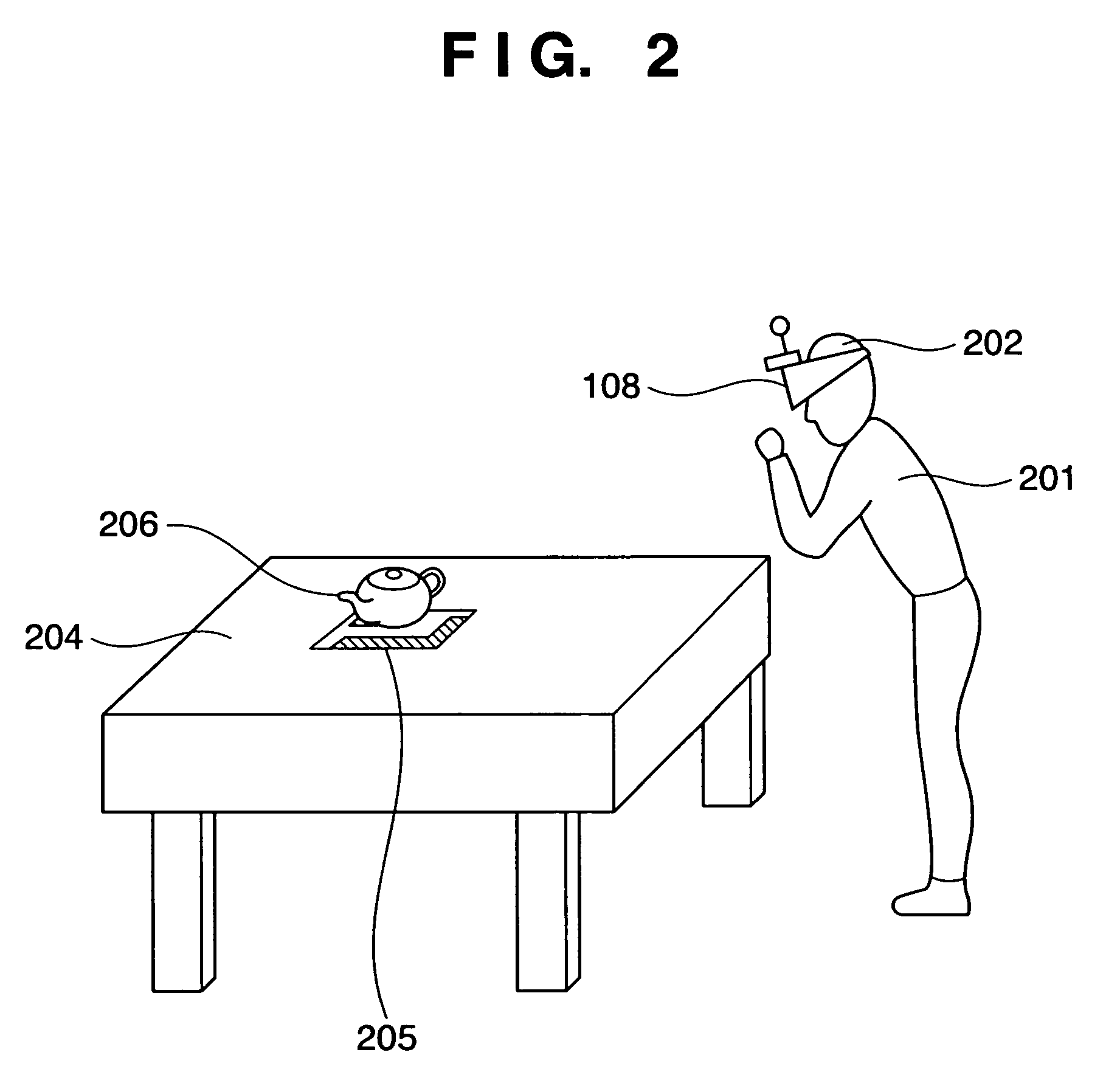
Image display method and image display system
Real space image including a simple prototype created based on three-dimensional CAD data is captured by an image input apparatus. A position / orientation measuring apparatus measures positions and orientations of the image input apparatus and simple prototype. An information processor captures position / orientation information representing the position and orientation of the simple prototype in the image captured by the image input apparatus 102. The information processor further extracts a hand area from an image, renders a three-dimensional computer graphic image on the simple prototype, excluding the extracted hand area, in the image based on the position / orientation information and the three-dimensional CAD data, and synthesizes the image and the three-dimensional computer graphic image. Here, the simple prototype has a different color from a color of the hand area.
Owner:CANON KK
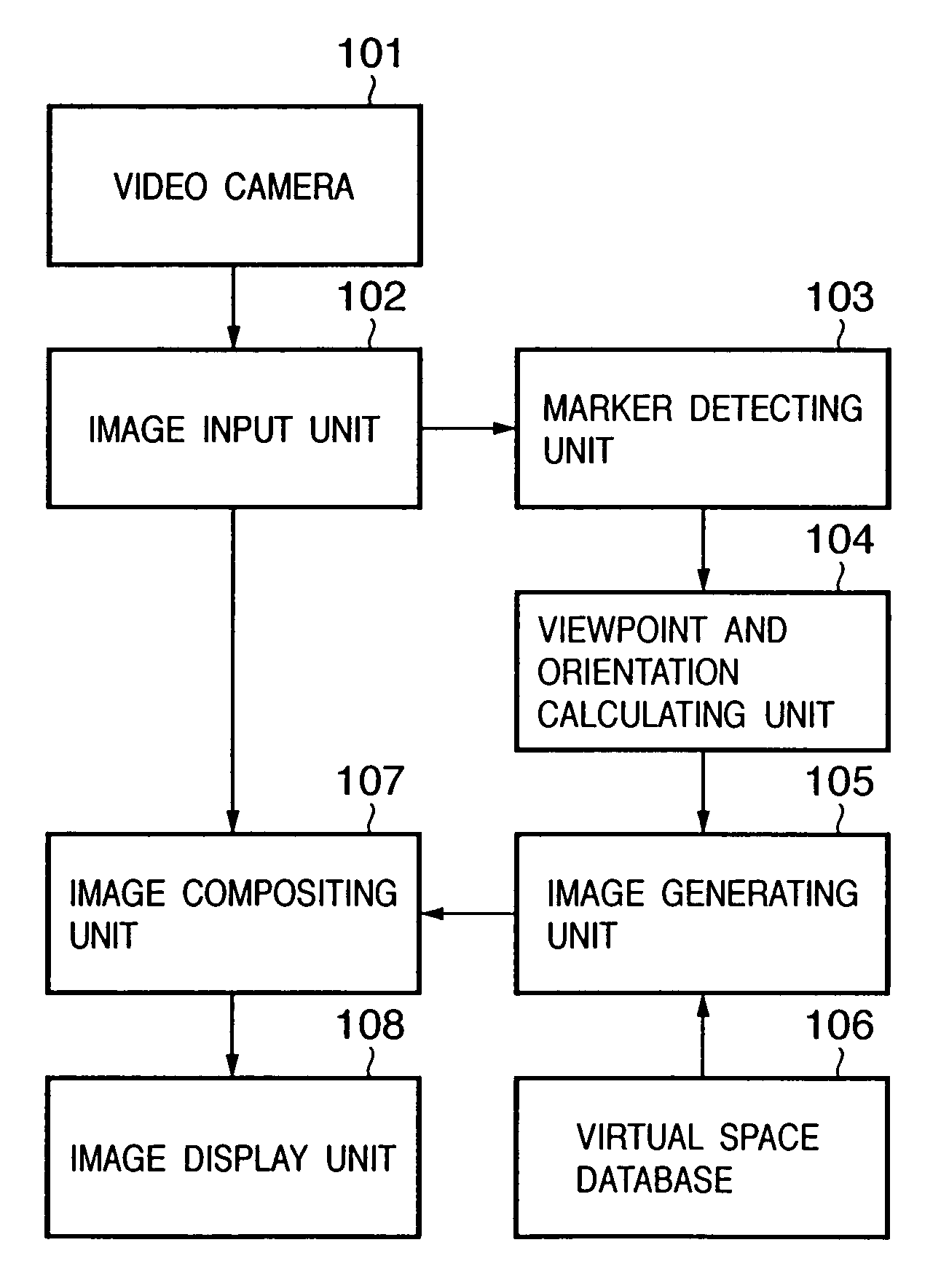
Image compositing method and apparatus for superimposing a computer graphics image on an actually-sensed image
InactiveUS7928977B2Efficient arrangementImage enhancementImage analysis3D computer graphicsComputer science
Owner:CANON KK
Three-dimensional display system: apparatus and method
InactiveUS20030103047A1Readily and more reliably producedQuality improvementTelevision system detailsImage enhancementComputer graphics (images)Radiology
In a presently preferred embodiment of the invention, a three-dimensional scene is reproduced on a specialized light display which offers full multiviewpoint capability and auto-stereoscopic views. The displayed image is produced using a set of M two-dimensional images of the scene collected at a set of distinct spatial locations. These M two-dimensional images are processed through a specialized mathematical encoding scheme to obtain a set of NxK display-excitation electrical-input signals, where K is the number of pixels in the display, and N<=M is the number of individual light-radiating elements within one pixel. The display is thus comprised of a total of NxK light-radiating elements. Each of the K pixels is adapted for control of their associated radiance patterns. The display is connected for response to the set of NxK display-excitation electrical-input signals. In this manner, the display provides a multiviewpoint and autostereoscopic three-dimensional image associated with the original three-dimensional scene. An alternative embodiment of the invention is utilized to provide efficient storage and display of 3D computer graphics images.
Owner:MONSELLA MGMT NY
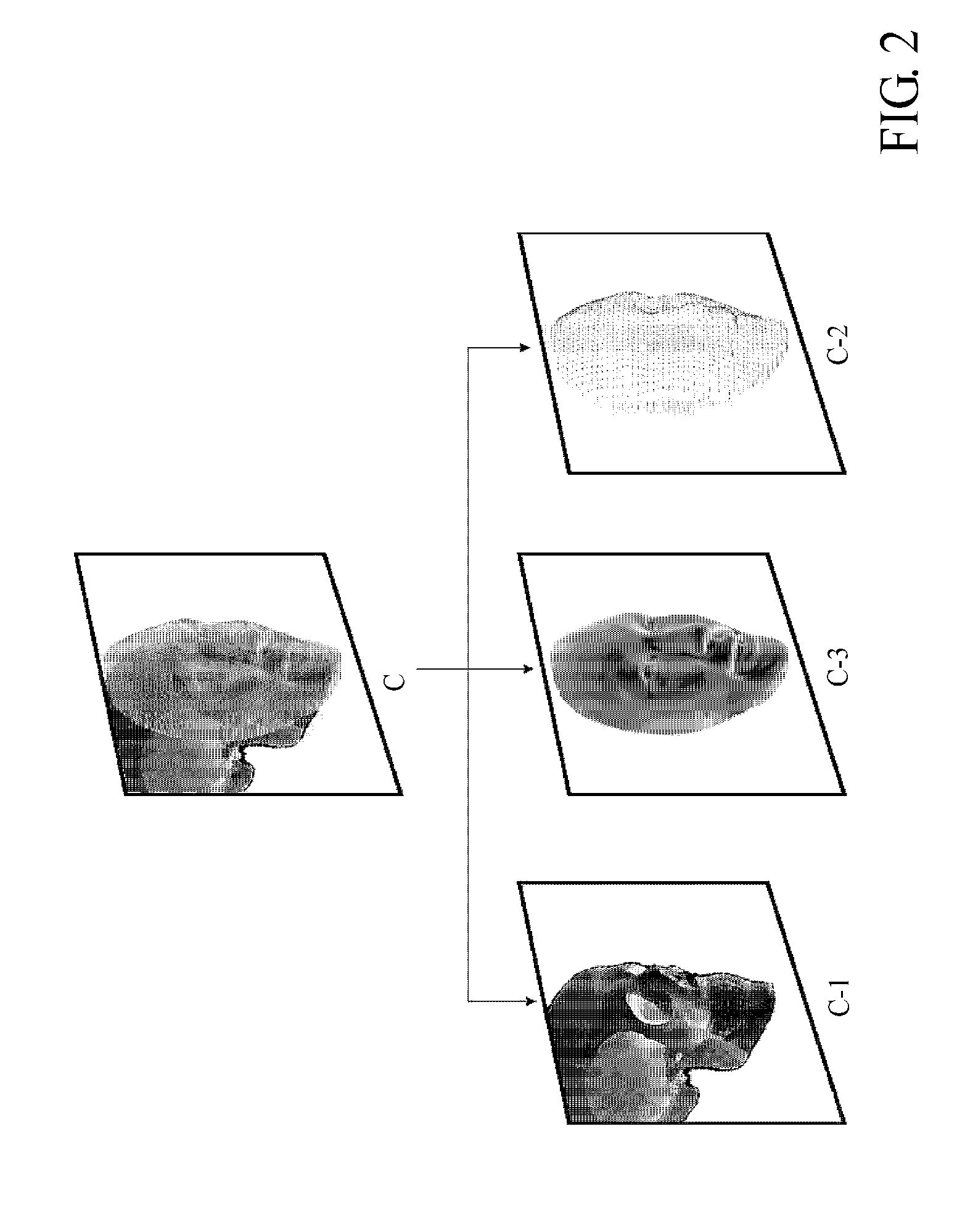
Three-dimensional digital magnifier operation supporting system
InactiveCN102036616AImprove qualityImprove work efficiencyImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsSupporting systemState variation
Provided is a system for displaying indirect influence of the variations of the state of the imaged space and the state of the displayed three-dimensional computer graphics images fixed to and combined with a subject by simulation of the variation of the state of the subject in a real space on the three-dimensional computer graphics. From among surface polygon models (2) made by three-dimensionally measuring a subject image present in the same space, a surface polygon model having a shape similar to the surface polygon model (1) is discriminated and detected by shape pattern recognition. A computer graphics picture is tracked. A computer graphics image reflecting the variation of the real relative positions is displayed superimposedly on the captured image in accordance with the variation of the relative position of the subject with respect to the imaging device occurring in the real three-dimensional space. With this, a combined image position complement tracking system for displaying the subject in the field of view of the imaging device and the virtual three-dimensional computer graphics image in such a way that the subject and the virtual three-dimensional computer graphics images are viewed integrally.
Owner:高桥淳
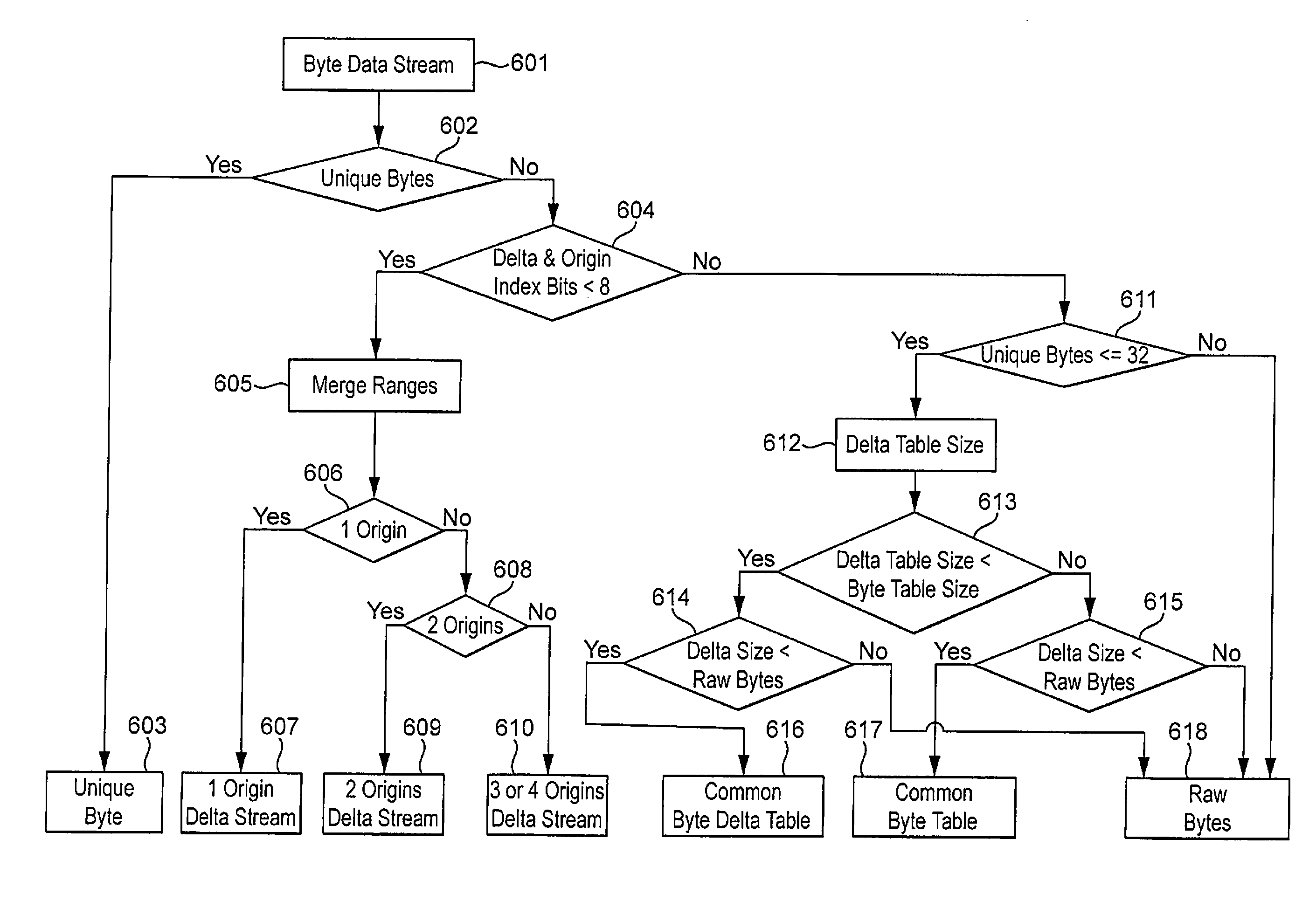
Random accessible lossless parameter data compression for tile based 3D computer graphics systems
ActiveUS20120062553A1Reduce memory requirementsLimited storage buffer requirementImage codingDigital video signal modificationData compression3D computer graphics
A method and apparatus are provided for compressing vertex parameter data in a 3D computer graphic system, where the vertex parameter data is a data block relating to a plurality of vertices used for rendering an image. The data relating to each vertex includes multiple byte data relating to at least one parameter. The parameters include X, Y and Z coordinates and further coordinates for texturing and shading. Decompression is also provided for decompressing vertex parameter data thus compressed. These are able to access randomly the compressed data, rather than having to read a stream of data.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
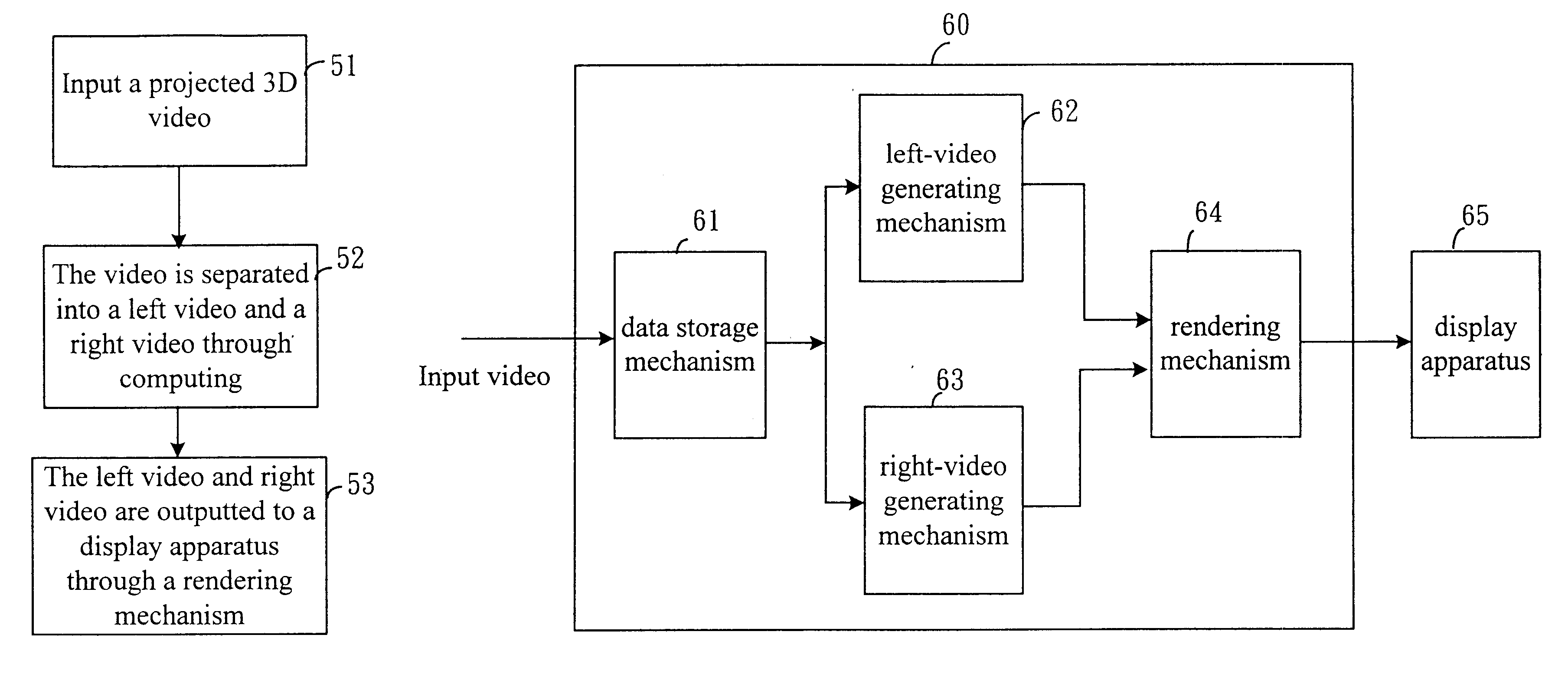
Apparatus and method for adjusting 3D stereo video transformation
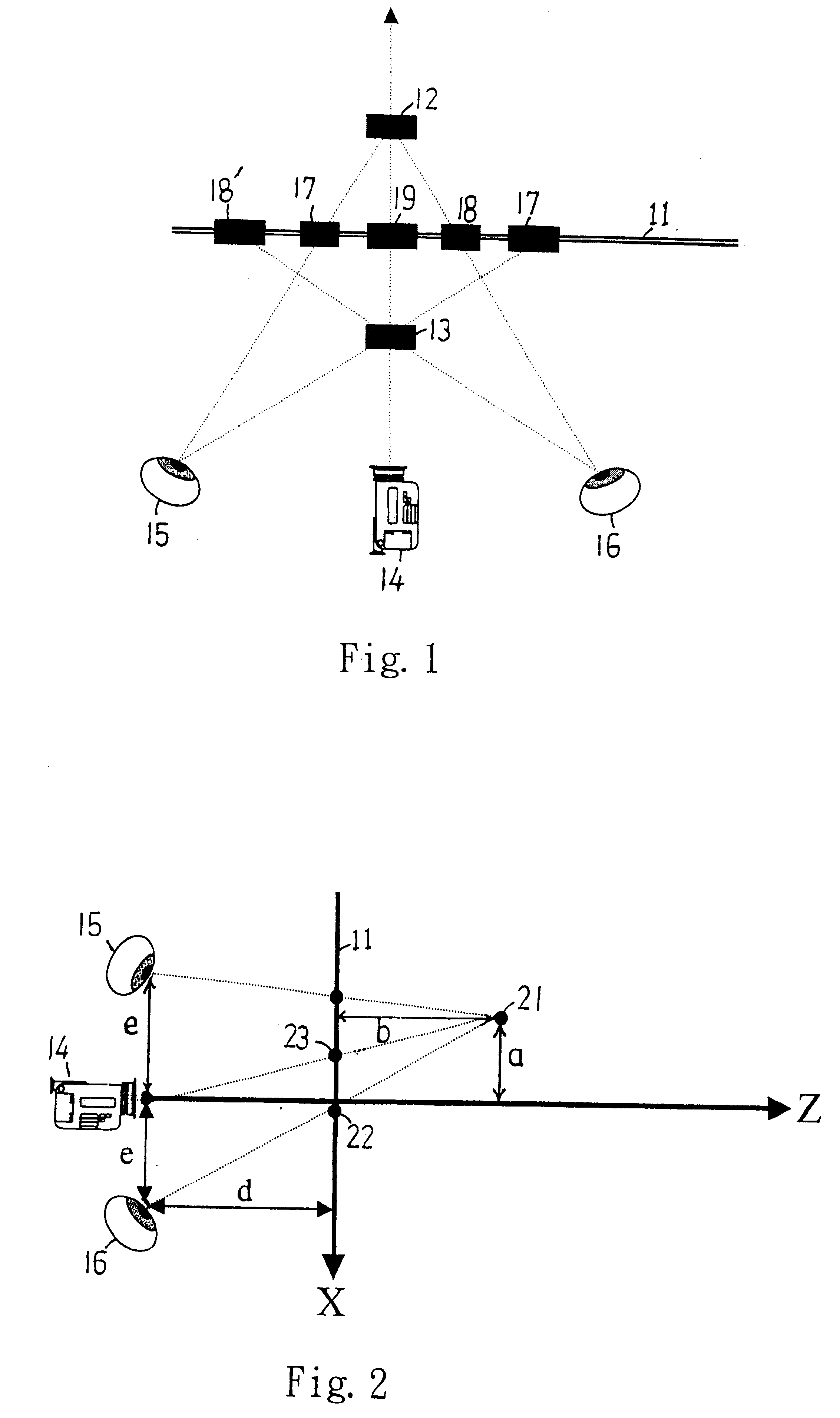
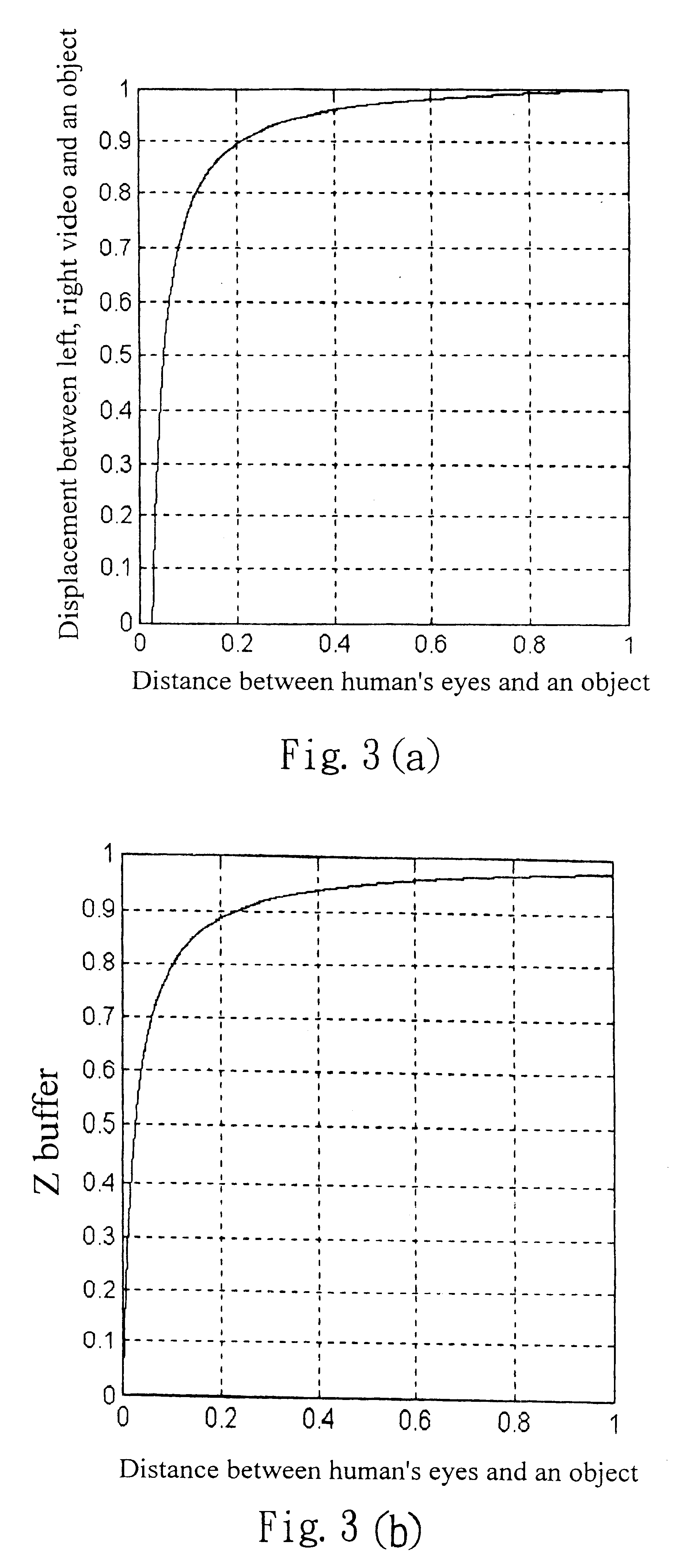
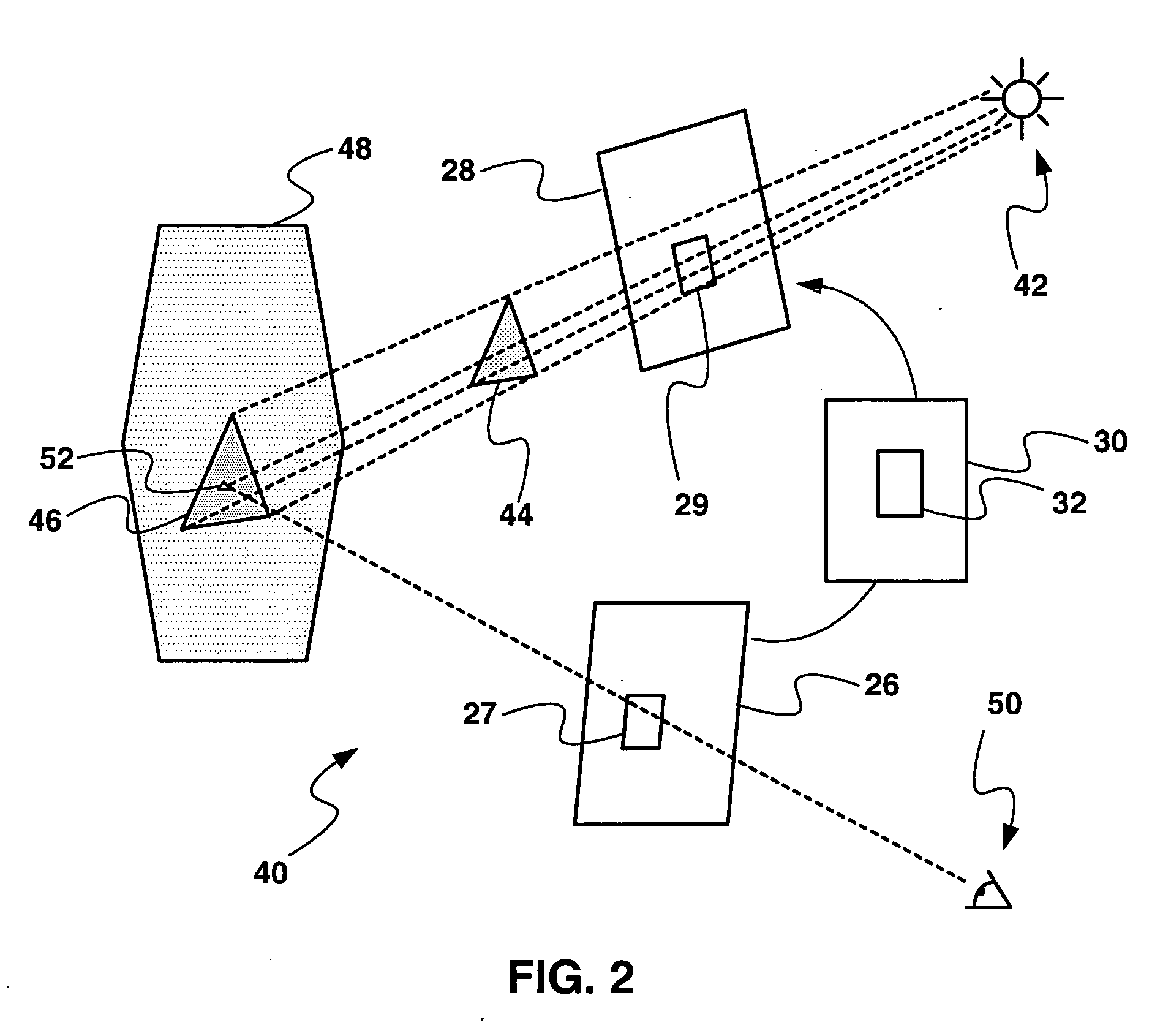
InactiveUS6466208B1Reduce workloadDrawback can be obviatedSteroscopic systems3D-image rendering3D computer graphicsVisual perception
The present invention discloses an apparatus and method for adjusting 3D transformation applied in a 3D computer graphic processing system, using a simple and practical computing method to simulate visual effect of human's eyes to separate input video into a left video and a right video. By the focus effect of the left video and the right video, a user can feel effect of changing depth of the input video, and creating 3D effect. Additionally, the present invention provides many parameters for convenience in adjusting the video depth and location in a display plane by users.
Owner:XGI TECHNOLOGY
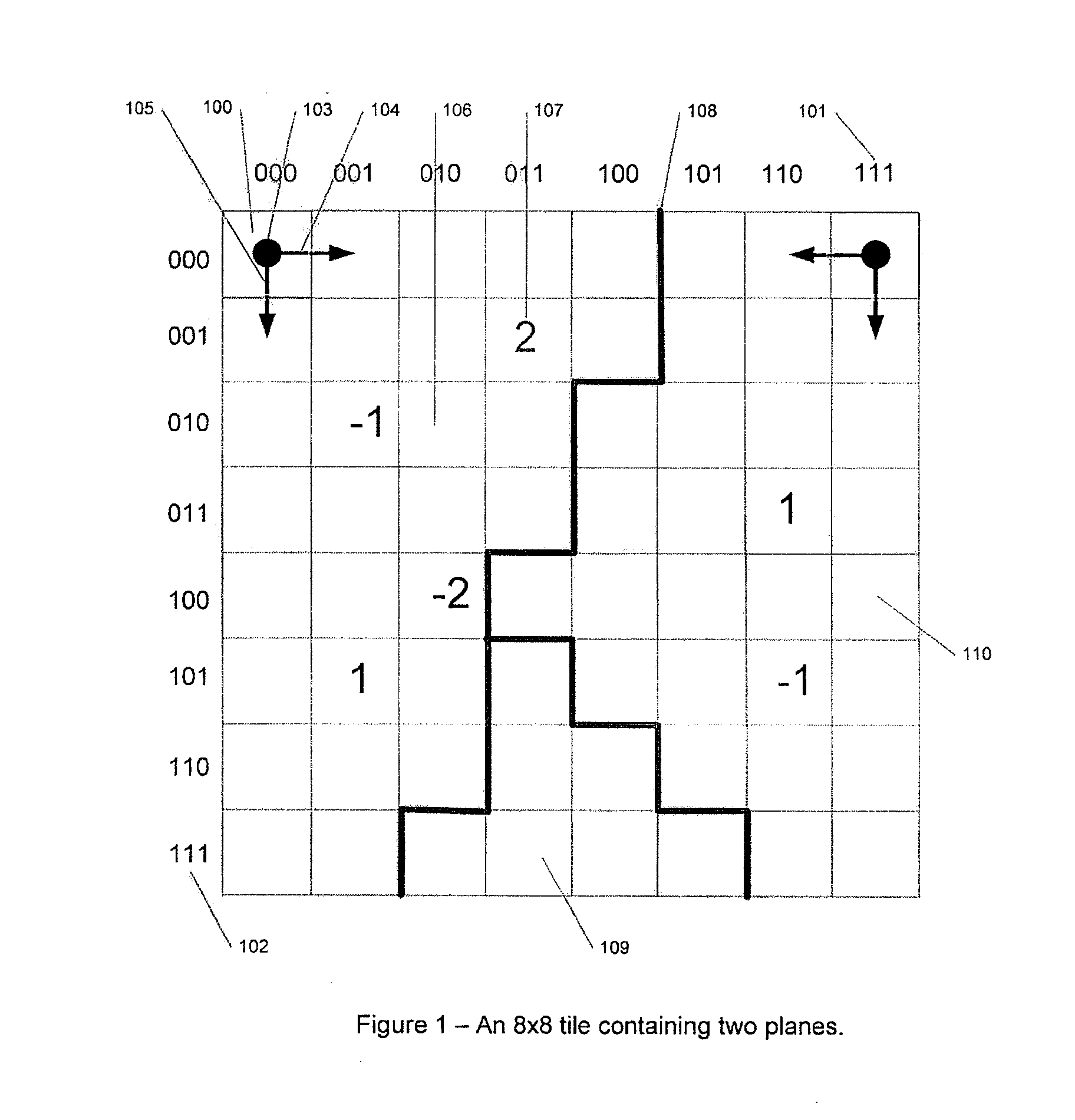
Method and apparatus for tile based depth buffer compression
ActiveUS20120212489A1Image codingDetails involving image processing hardware3D computer graphicsZ-buffering
A method and apparatus are provided for compressing depth buffer data in a three dimensional computer graphics system. The depth buffer data is divided into a plurality of rectangular tiles corresponding to rectangular areas in an associated image. The number of starting point locations in a tile are identified and a difference in depth value determined between each starting point and depth values of each of at least two further locations. Using this information depth values are predicted at a plurality of other locations in the tile and where these predicated values substantially match an actual depth value at location is assigned to a plane associated with respective starting point. Starting point location depth value difference data and plane assignment data for each tile and locations in the tile not assigned to a plane, then stored.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
Tiling system for 3D rendered graphics
ActiveUS7834872B2Easy to useCheap methodImage generationFilling planer surface with attributesPattern recognitionDisplay device
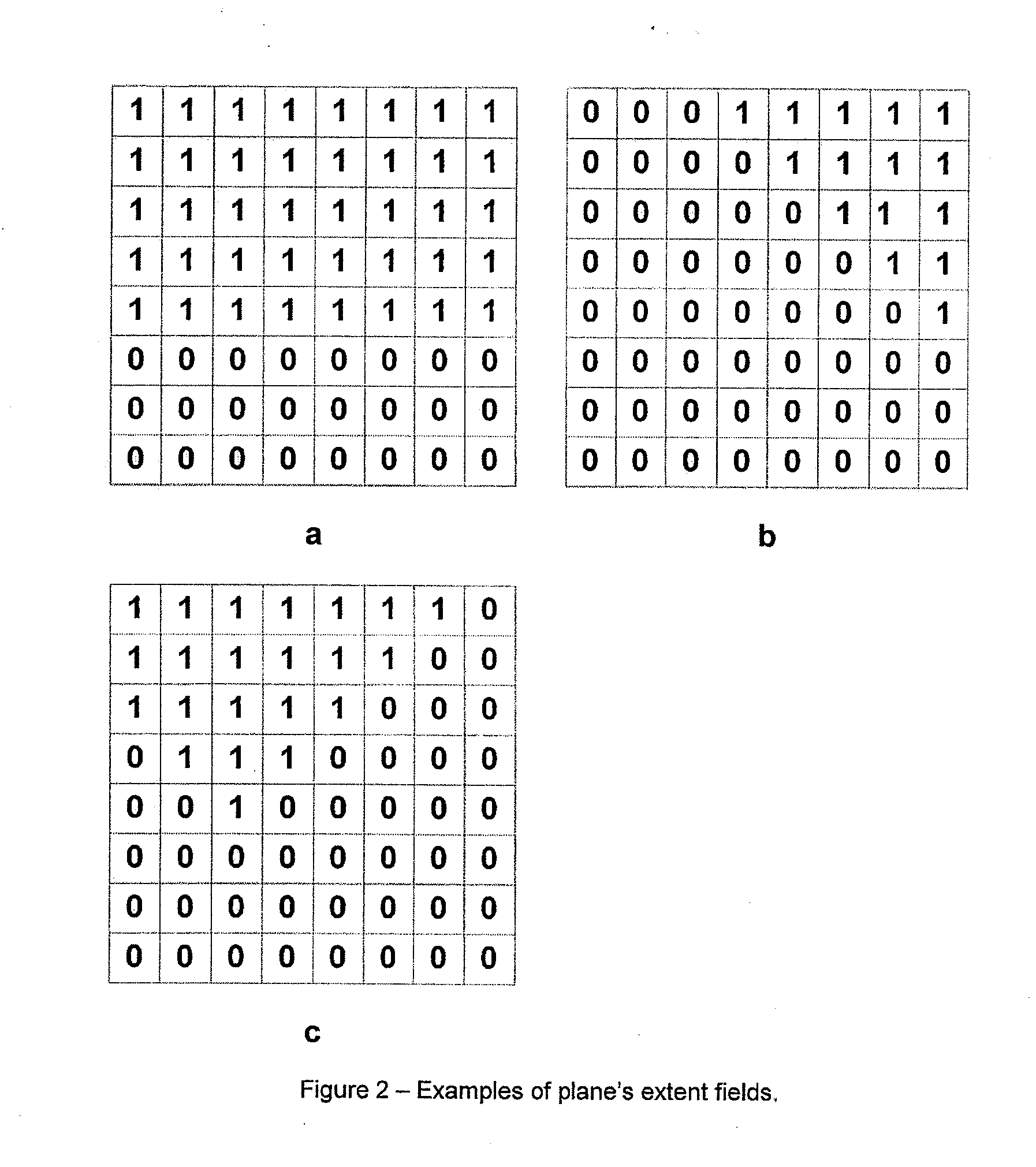
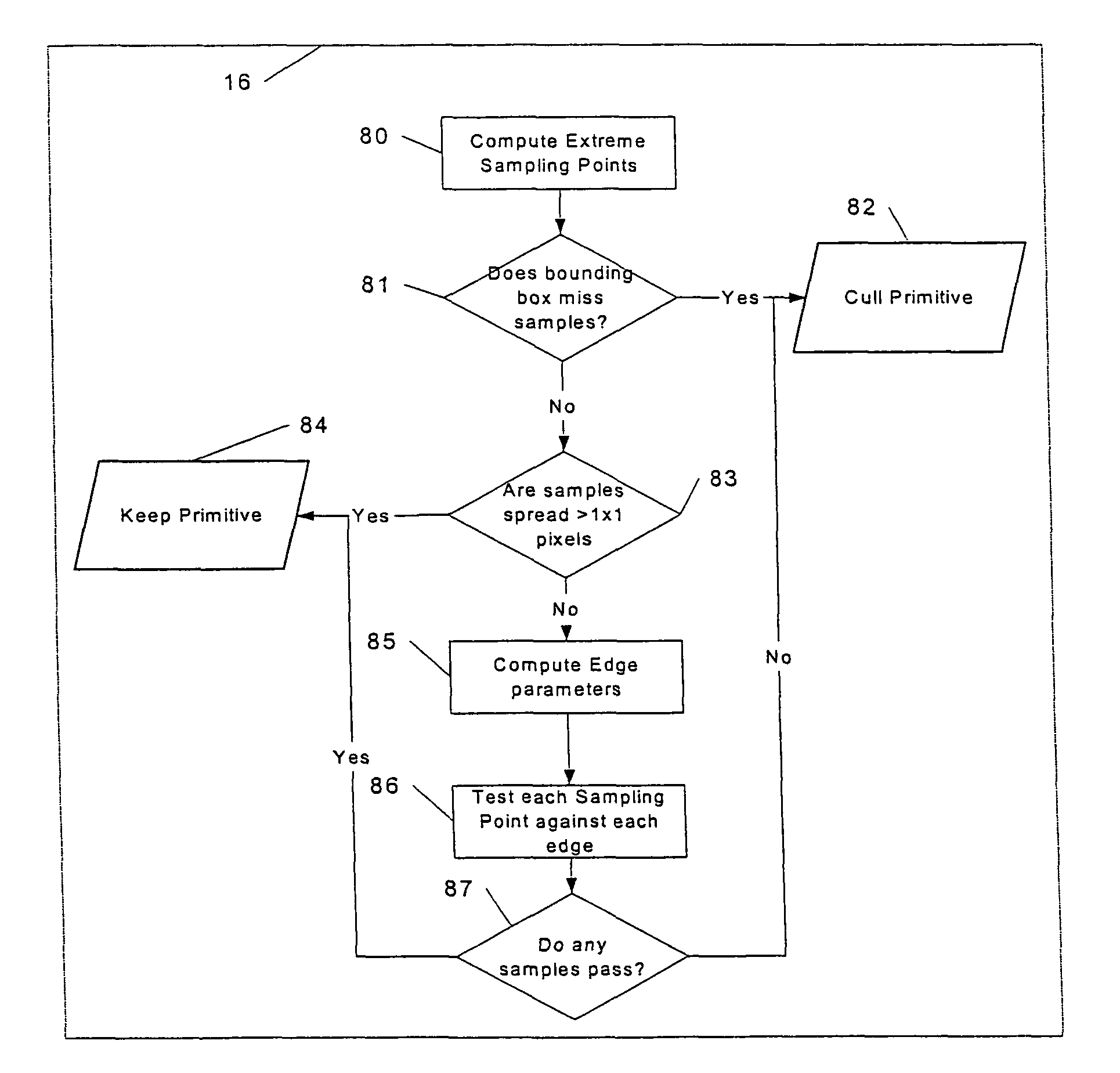
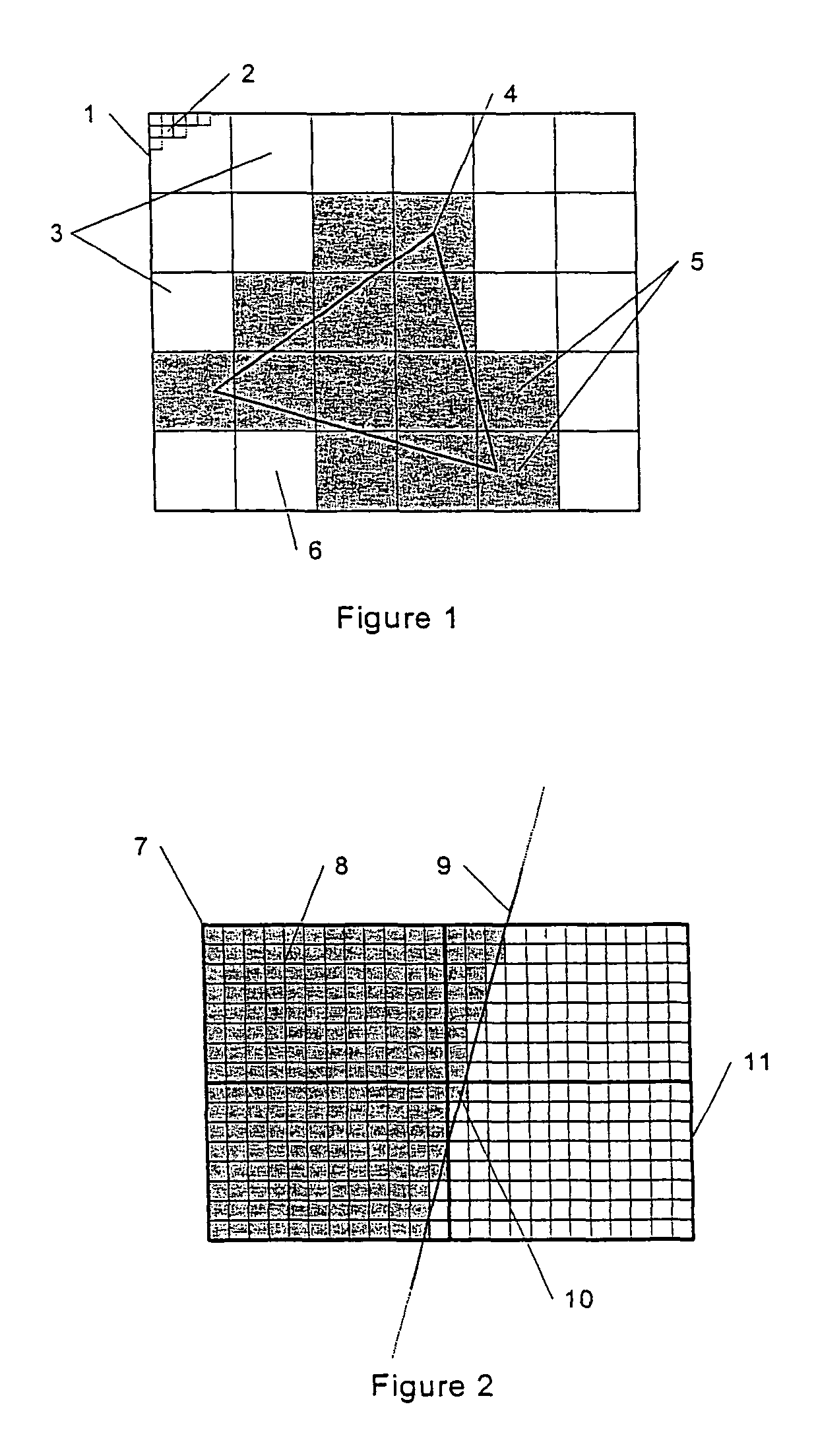
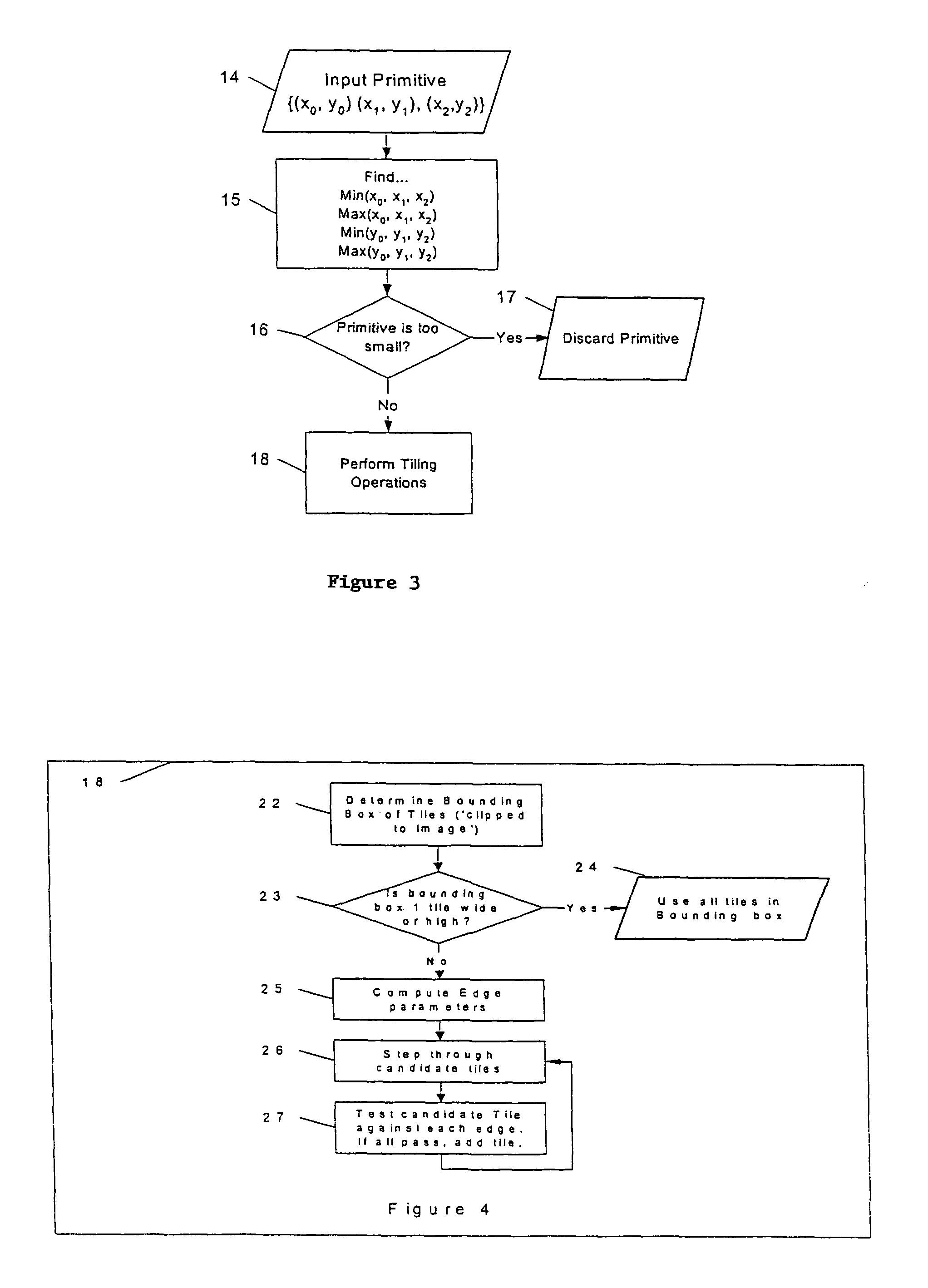
A method and an apparatus for shading three-dimensional computer graphic images is provided. A display on which the image is to be viewed is subdivided into a plurality of rectangular areas. For each rectangular area, a list of objects in the image which may be visible is determined, and this list is used to determine how the rectangular area should be shaded for display. In deriving the list of objects, a determination of maximum and minimum values for each object in x and y directions is used, and a set of sampling points is determined from these values. If a bounding box surrounding the object covers any of the sampling points, the object is added to the object list or otherwise rejected. Also provided is a method and an apparatus for testing an edge information for each object against the sample points to determine whether or not the object falls into the rectangular area in the bounding box surrounding the object. The step of testing the edge information includes shifting the edge information by a predetermined amount based on the orientation of each edge.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
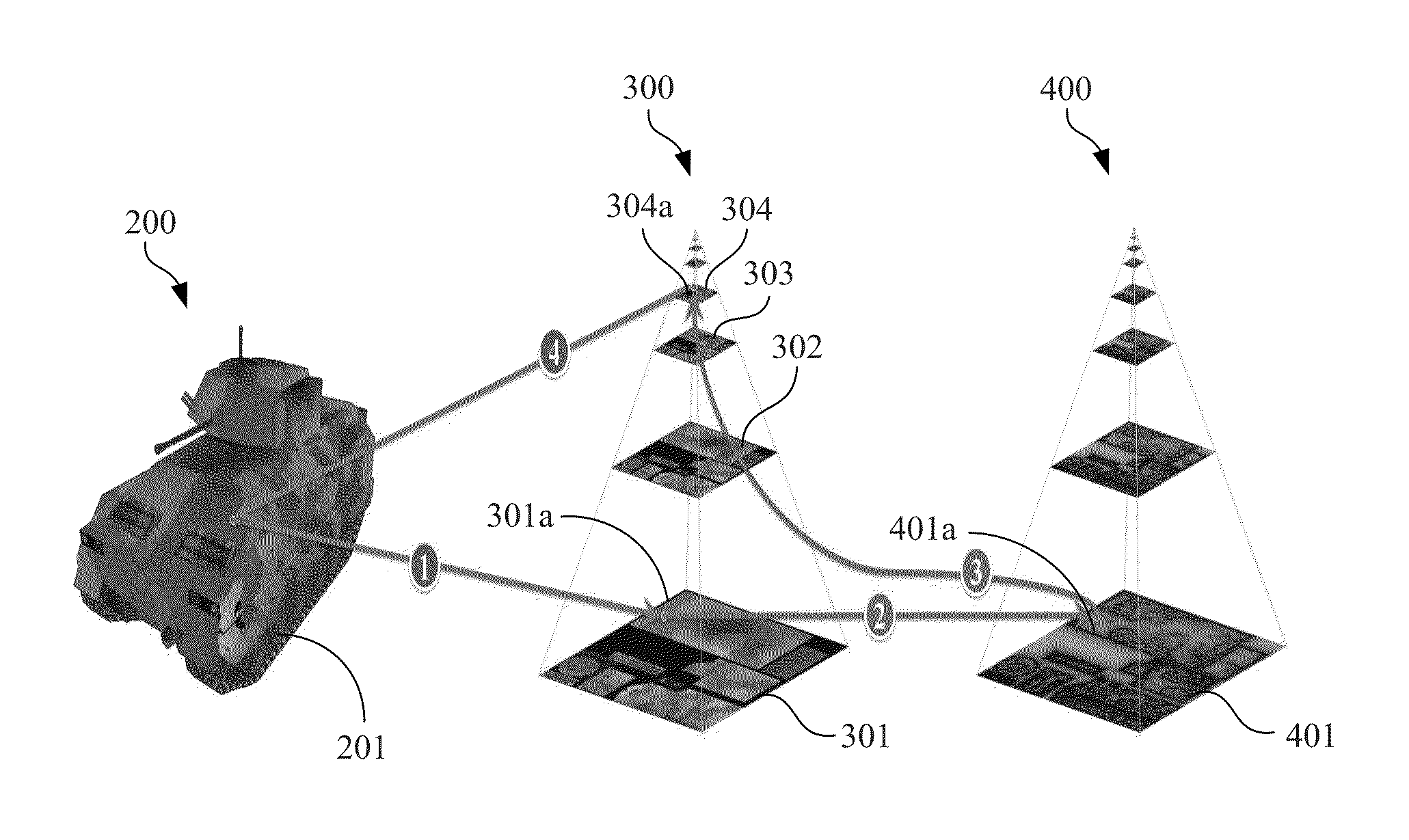
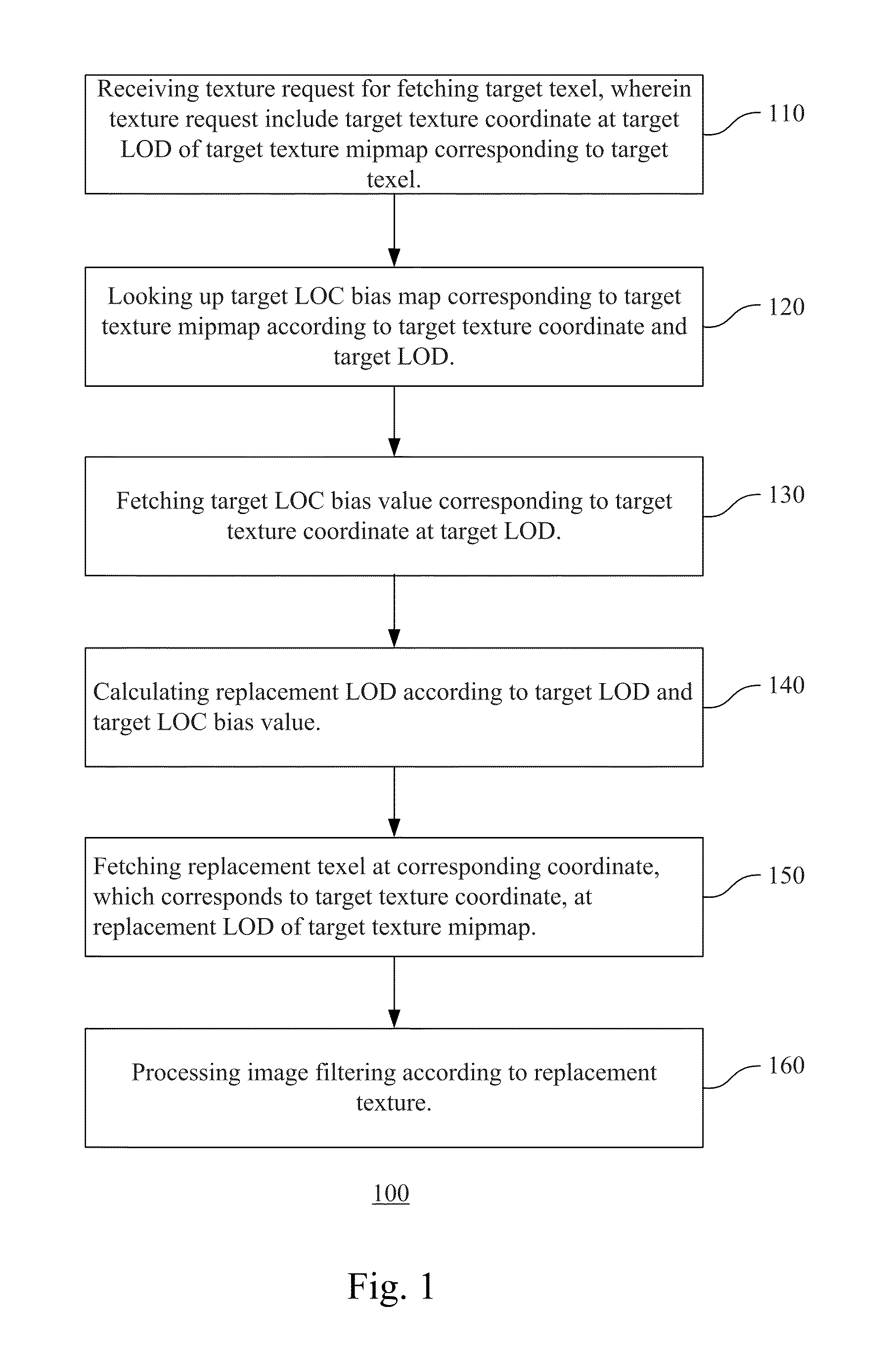
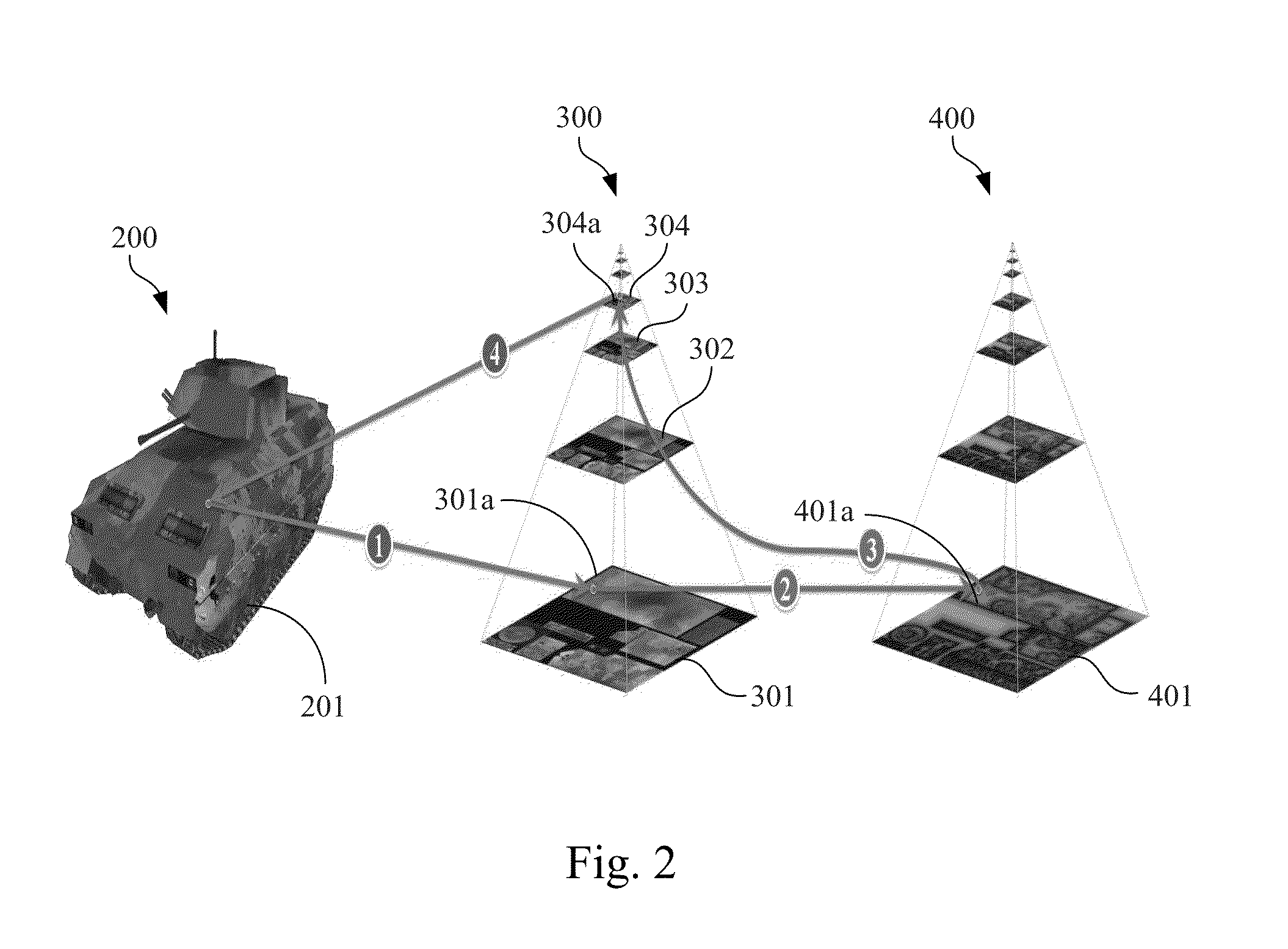
Method and Apparatus for Processing Texture Mapping in Computer Graphics by Biasing Level of Detail According to Image Content and Computer Readable Storage Medium Storing the Method
InactiveUS20130278601A1Reduce required transmission bandwidthReduce power consumptionImage generation3D-image renderingLevel of detail3D computer graphics
A method for processing texture mapping by biasing level of detail (LOD) according to image content includes: a texture request for fetching a target texel is received. The texture request includes a target texture coordinate at a target LOD of a target texture mipmap corresponding to the target texel. A target level of content (LOC) bias map corresponding to the target texture mipmap is looked up according to the target texture coordinate and the target LOD to fetch a target LOC bias value corresponding to the target texture coordinate at the target LOD. A replacement LOD is calculated according to the target LOD and the target LOC bias value. A replacement texel is fetched at a corresponding coordinate, which corresponds to the target texture coordinate, at the replacement LOD of the target texture mipmap. Texture filtering is processed according to the replacement texel.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
Rendering 3D Computer Graphics Using 2D Computer Graphics Capabilities
Method for generating and displaying 3D graphic images on the display of a terminal device using 2D graphic environments, where every possible scene is modeled by one or more objects that can be represented by polygons using a suitable modeling method. The geometry of the polygons that correspond to each object is projected for any desired orientation of the objects, onto the plane of the display. For each object, curves connecting the projections of the vertices of its corresponding mesh of polygons in all different orientations of that object and consisting of a plurality of discrete points, is created, such that every point on each curve is stored according to its (x,y) position on the plane, and such that the resolution of each curve is determined according to the number of points. A visibility analysis is performed for every mesh that corresponds to a specific orientation, thereby determining the distance of the points from the viewer. Hidden polygons and / or edges or portions thereof are deleted and the geometry for all orientations is optimally encoded. Then 3D graphic images are displayed in the 2D environments by using the encoded geometry for reconstructing a portion of, or all, the remaining polygons and filling the remaining polygons according to predefined rules.
Owner:REVOLVER
System and method for shadow rendering
InactiveUS20050017974A1Latency and needed storage capacityReduce processing time3D-image renderingDisplay device3D computer graphics
A system and method for providing shadow information for 3D computer graphics objects on a display for a graphic computer system are disclosed. The 3D objects are processed only once and the rendering and shadow generation information is stored in memory. In a subsequent two-dimensional pass, the shadow information is used to provide the color value at each rendered pixel. Thus, the latency and the need for storage capacity due to the multiple 3D pass processing are eliminated.
Owner:S3 GRAPHICS
Multilevel display control list in tile based 3D computer graphics system
ActiveUS9336623B2Reduce amountImprove performanceFilling planer surface with attributes3D-image renderingLevel structureOriginal data
A method and apparatus are provided for rendering a 3 dimensional computer graphics image. The image is divided into plurality of rectangular tiles which are arranged in a multi level structure comprising a plurality of levels of progressively larger groupings of tiles. Image data is divided into a plurality of primitive blocks and these are assigned to groupings of tiles within the multi level structure in dependence on the groupings each one intersects. Control stream data is derived for rendering the image and this comprises references to primitive blocks for each grouping of tiles within each level of the multi level structure, the references corresponding to the primitive blocks assigned to each grouping and control stream data is used to render the primitive data into tiles within the groupings of tiles for display. This is done such that for primitive blocks which intersect a plurality of tiles within a grouping, control stream data is written for the grouping of tiles rather than for each tile within the grouping.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
Variable bit field color encoding
InactiveUS7129956B2Increase volumeQuantity minimizationTexturing/coloringCathode-ray tube indicatorsBit fieldGraphic system
A compact image element encoding format selectively allocates a bit field within the format to alternately encode either multi-bit alpha resolution or increased color resolution. This encoding technique may be advantageously used to allocate encoding bits to model semi-transparency while using those same bits for other purposes (e.g., higher color resolution) in instances where semi-transparency is not required (e.g., for opaque image elements). In one advantageous embodiment, the same encoding format can provide either RGB5 or RGB4A3, on an image-element-by-image-element basis. Applications include but are not limited to texture mapping in a 3D computer graphics system such as a home video game system or a personal computer.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
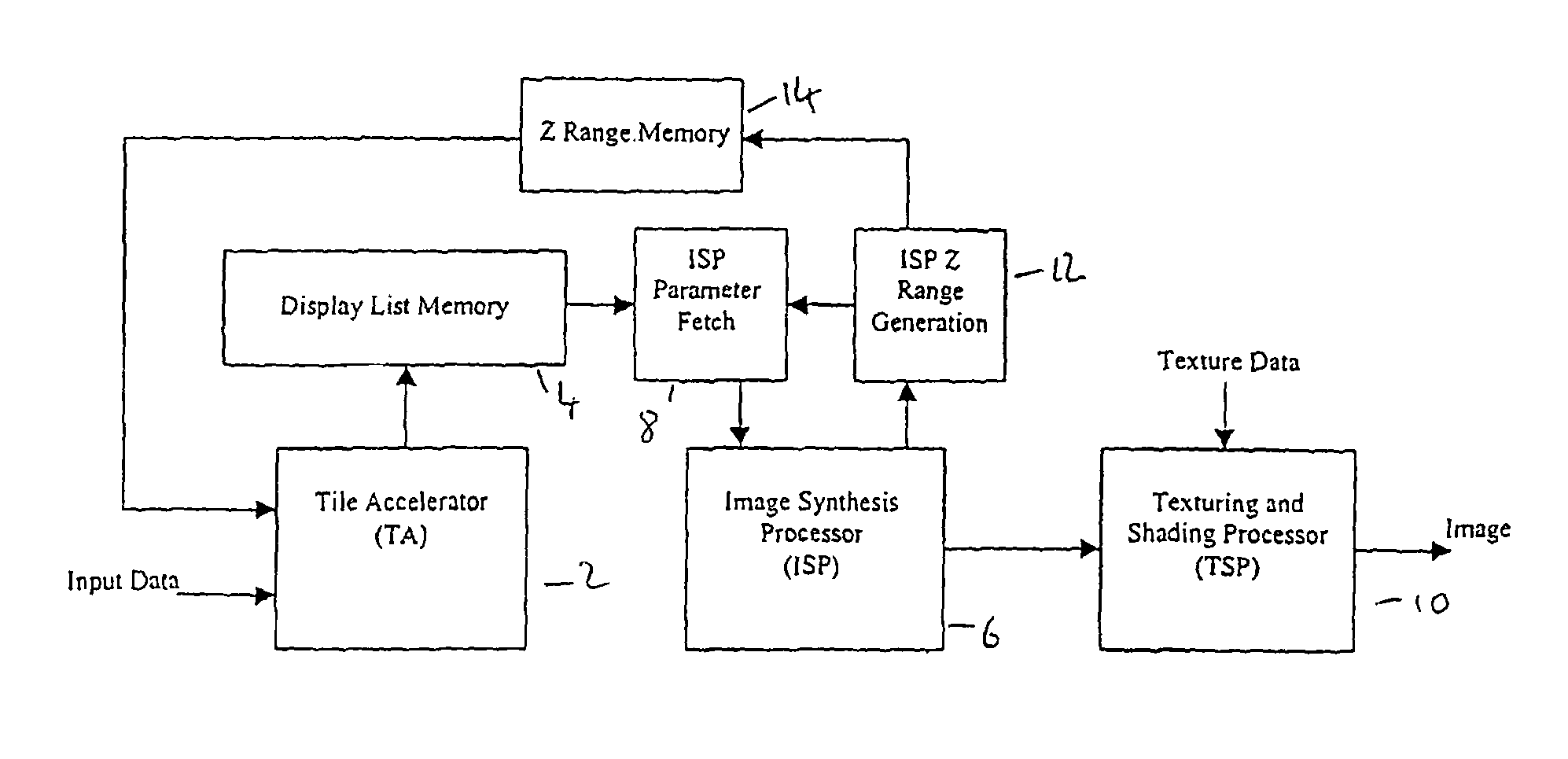
Three dimensional graphics system with early occlusion culling using Z-ranges
ActiveUS8686998B2Impact performanceLimited amount of memoryDetails involving 3D image dataDetails involving image processing hardwareThree dimensional graphics3D computer graphics
An apparatus and a method for generating 3-dimensional computer graphic images. The image is first sub-divided into a plurality of rectangular areas. A display list memory is loaded with object data for each rectangular area. The image and shading data for each picture element of each rectangular area are derived from the object data in the image synthesis processor and a texturizing and shading processor. A depth range generator derives a depth range for each rectangular area from the object data as the imaging and shading data is derived. This is compared with the depth of each new object to be provided to the image synthesis processor and the object may be prevented from being provided to the image synthesis processor independence on the result of the comparison.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
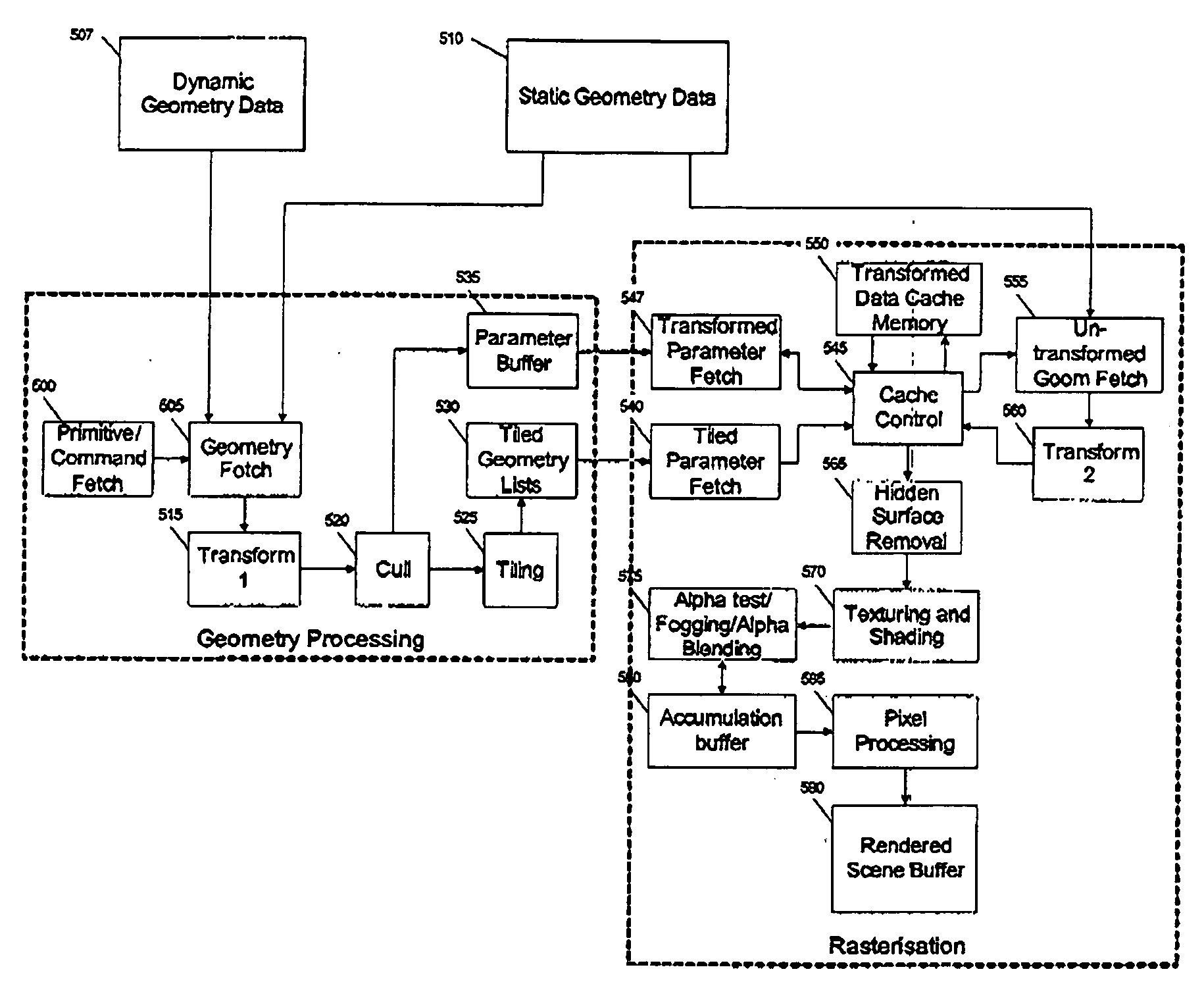
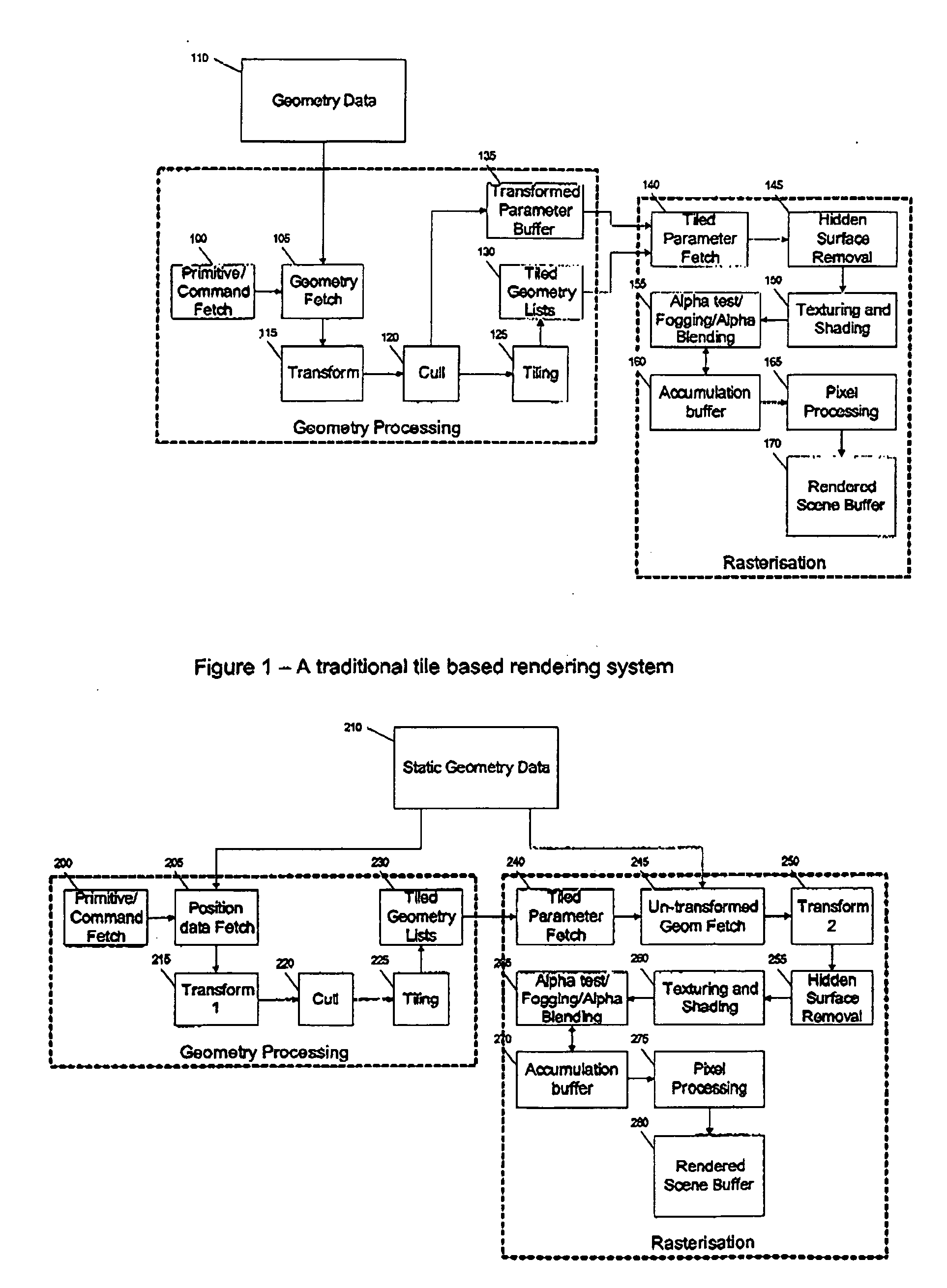
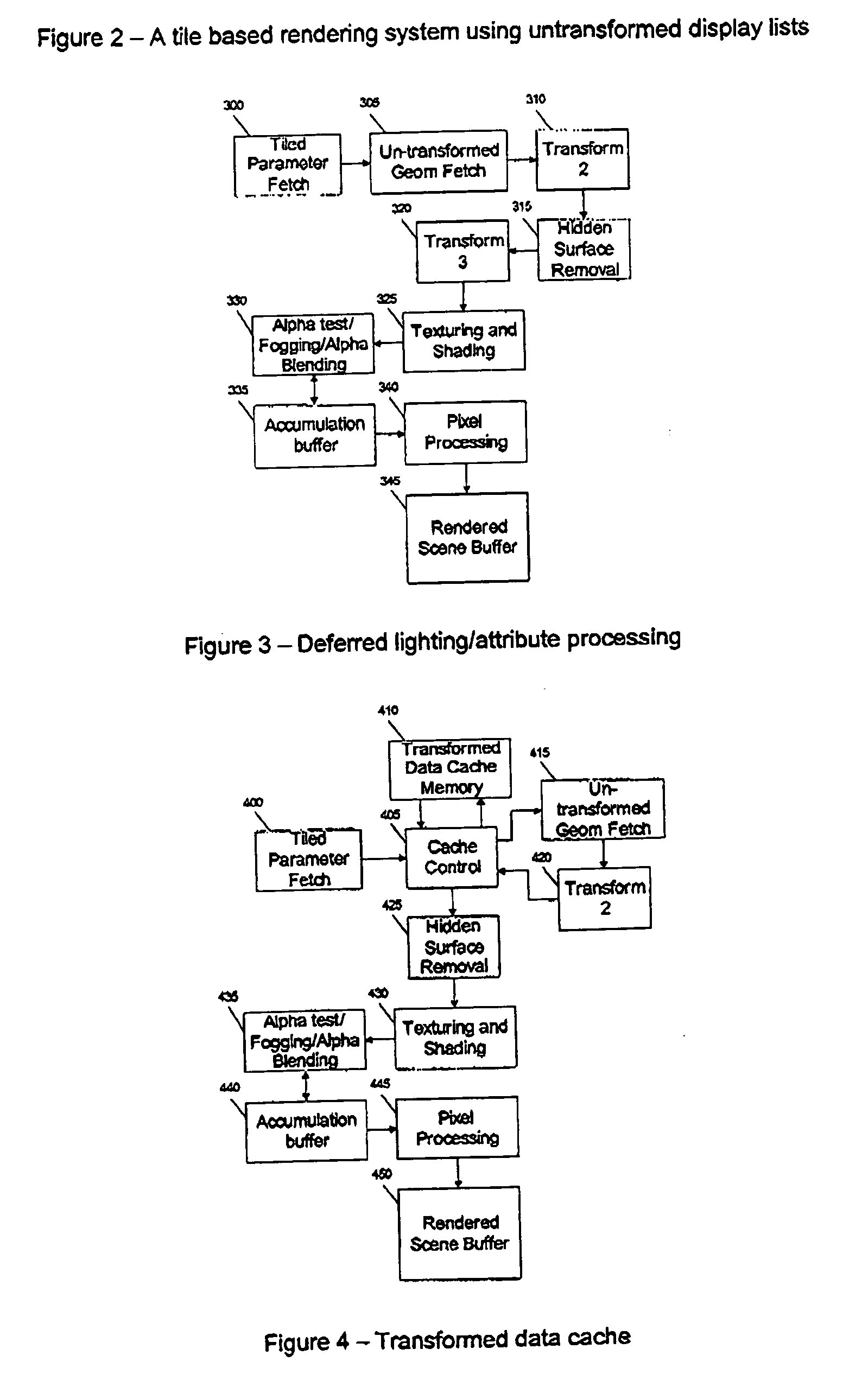
Untransformed display lists in a tile based rendering system
ActiveUS20090256844A1Reduce storageImage memory managementCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay list3D computer graphics
A three-dimensional computer graphics rendering system allows a tile-based rendering system to operate with a reduced amount of storage required for tiled screen space geometry by using an untransformed display list to represent the screen's geometry.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com