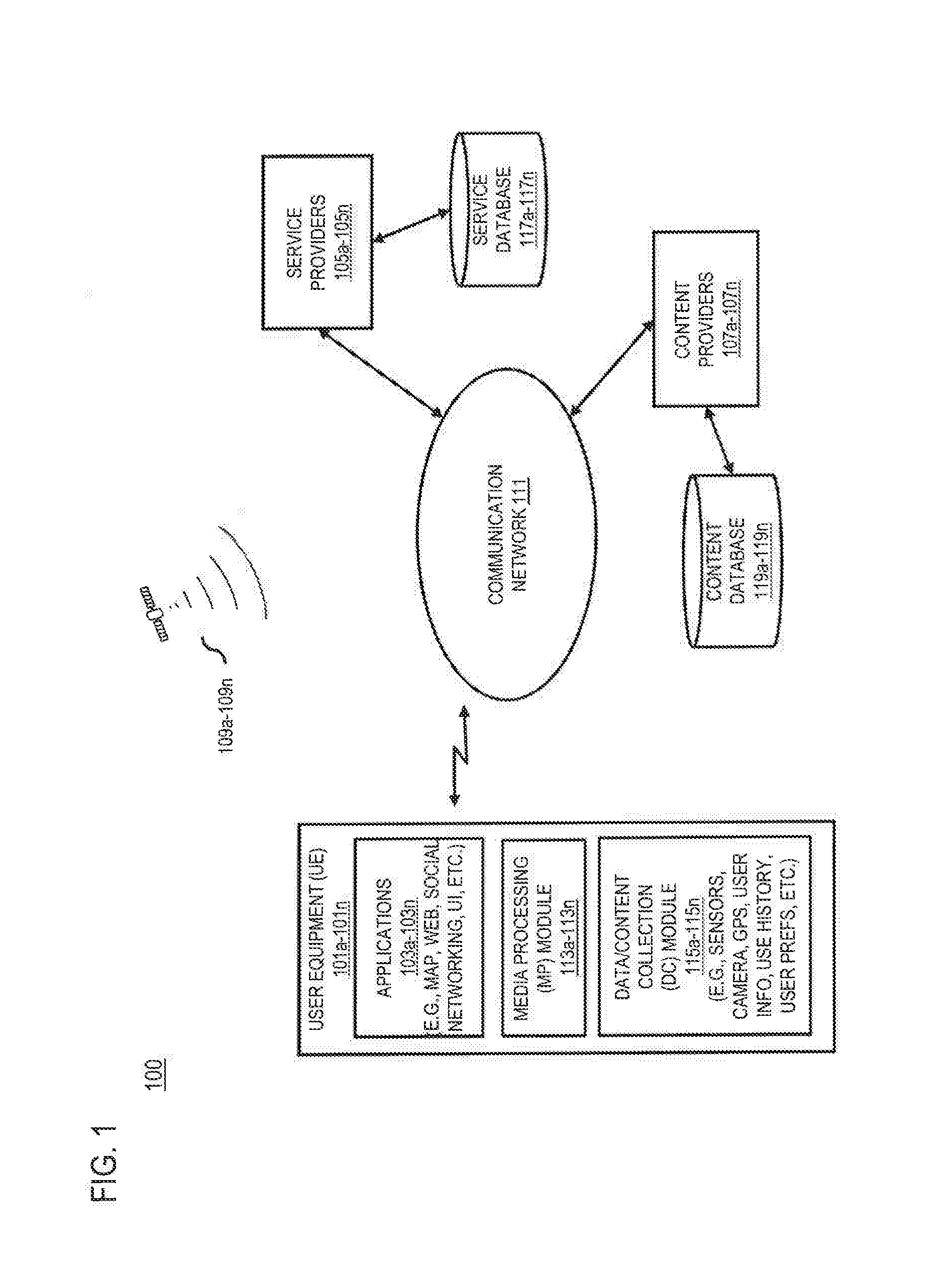
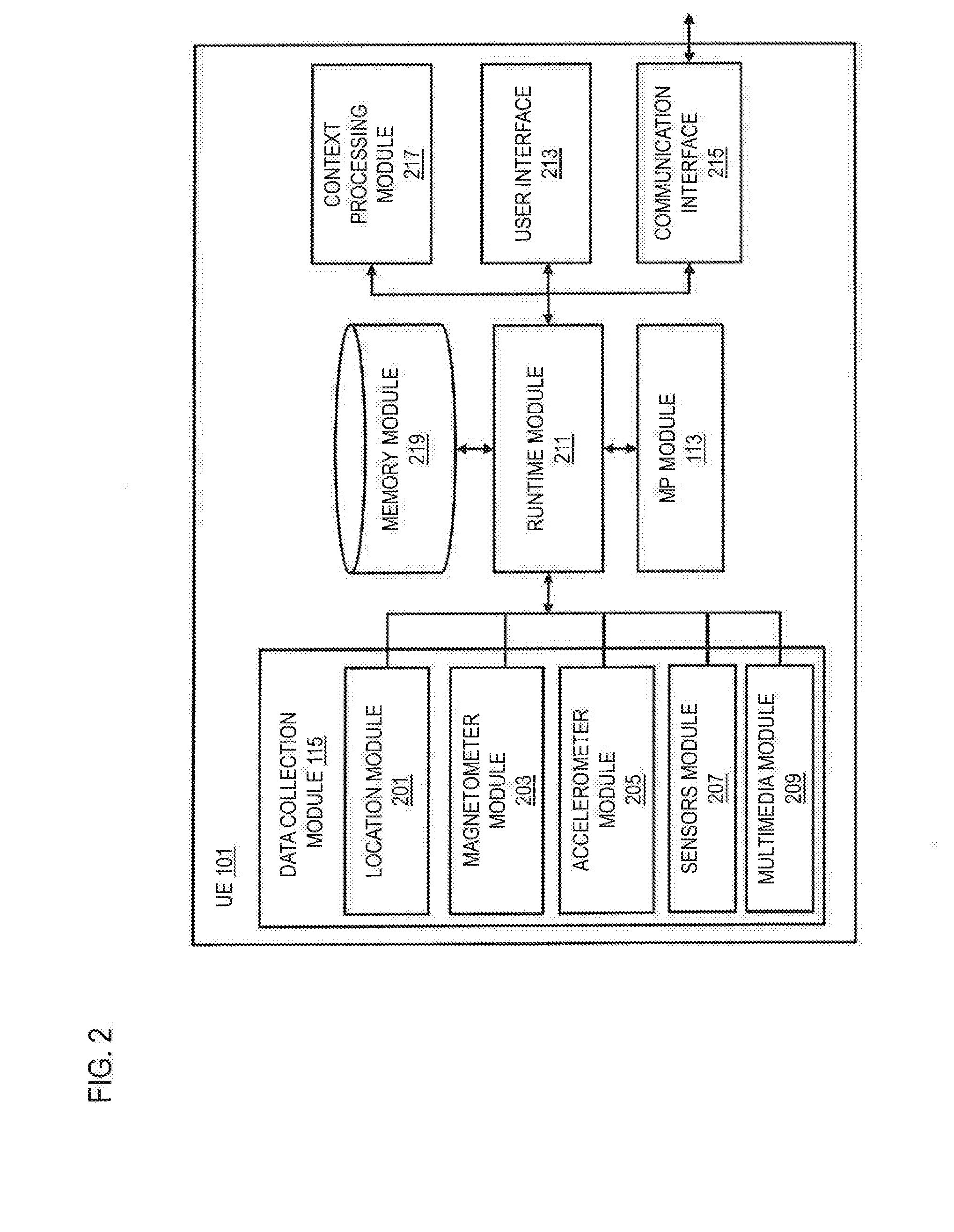
Patents
Literature
370 results about "3D rendering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
3D rendering is the 3D computer graphics process of converting 3D models into 2D images on a computer. 3D renders may include photorealistic effects or non-photorealistic styles.
Programs and methods for the display, analysis and manipulation of multi-dimensional data implemented on a computer
InactiveUS6750864B1Data processing applicationsDrawing from basic elementsData setSelection criterion
A GUI is disclosed including a set of visualization routines designed to improve display, visualization and manipulation of multi-dimensional data. Many of the routines combine 2D and 3D renderings with domain selecting criteria and stacking criteria with line segments connecting variable values between records in a given dataset or between corresponding variable values in records of related datasets. The GUI also employs active, persistent and slider variables to probe variable relationships, group relationships and dataset relationships.
Owner:GENESIS PARK
Method of Customizing 3D Computer-Generated Scenes
InactiveUS20090021513A1Low costRapid production3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)The Internet
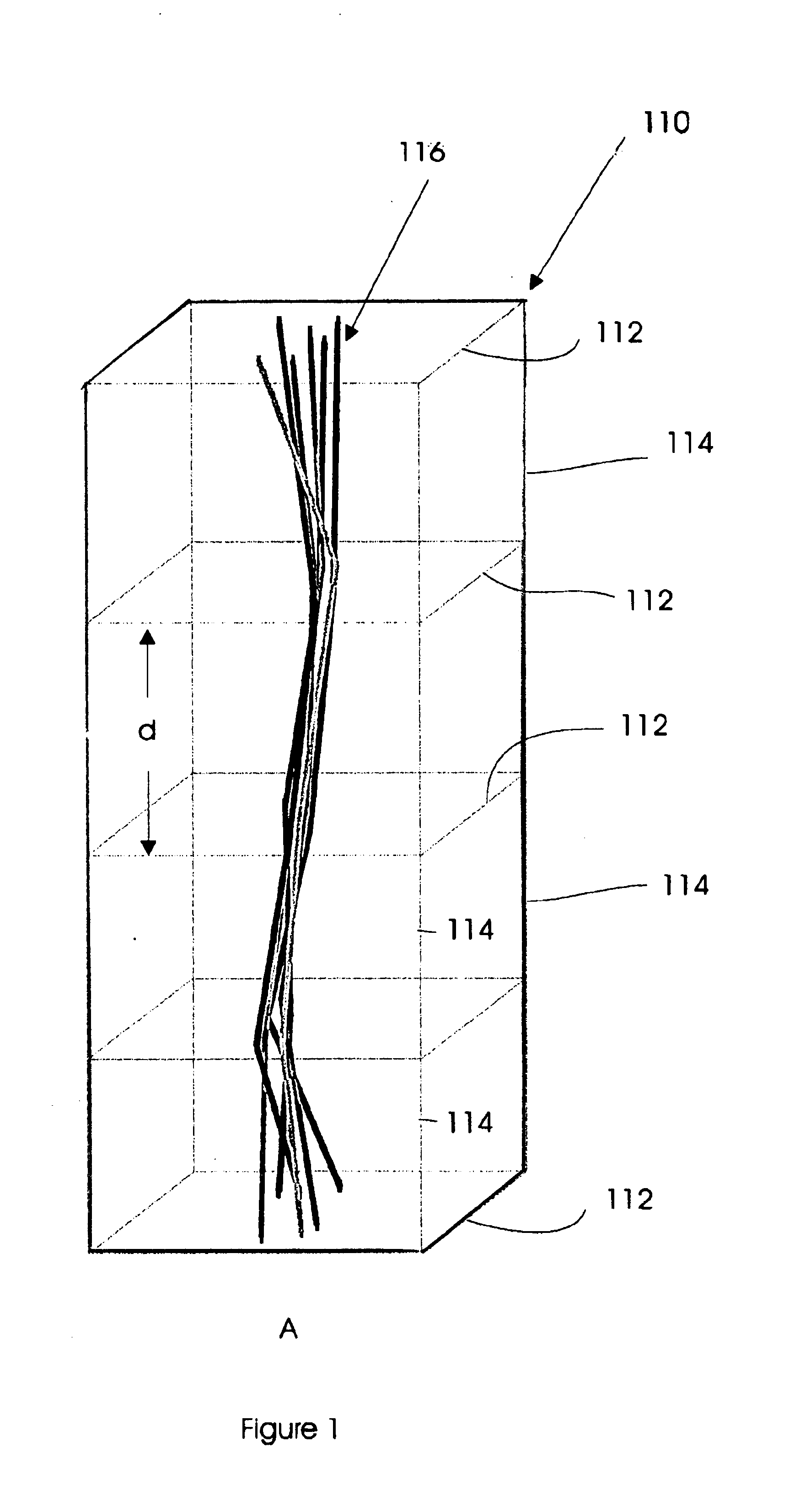
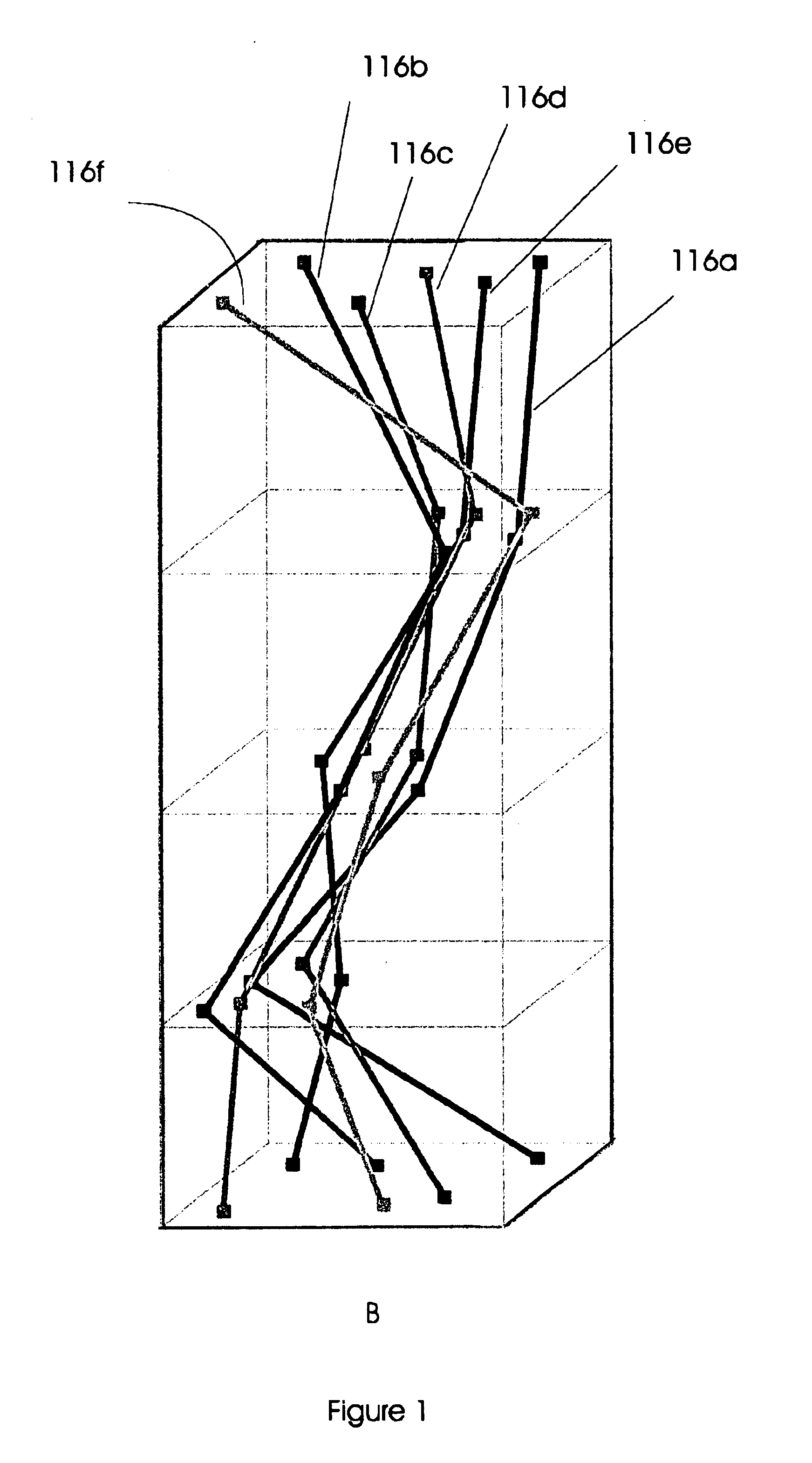
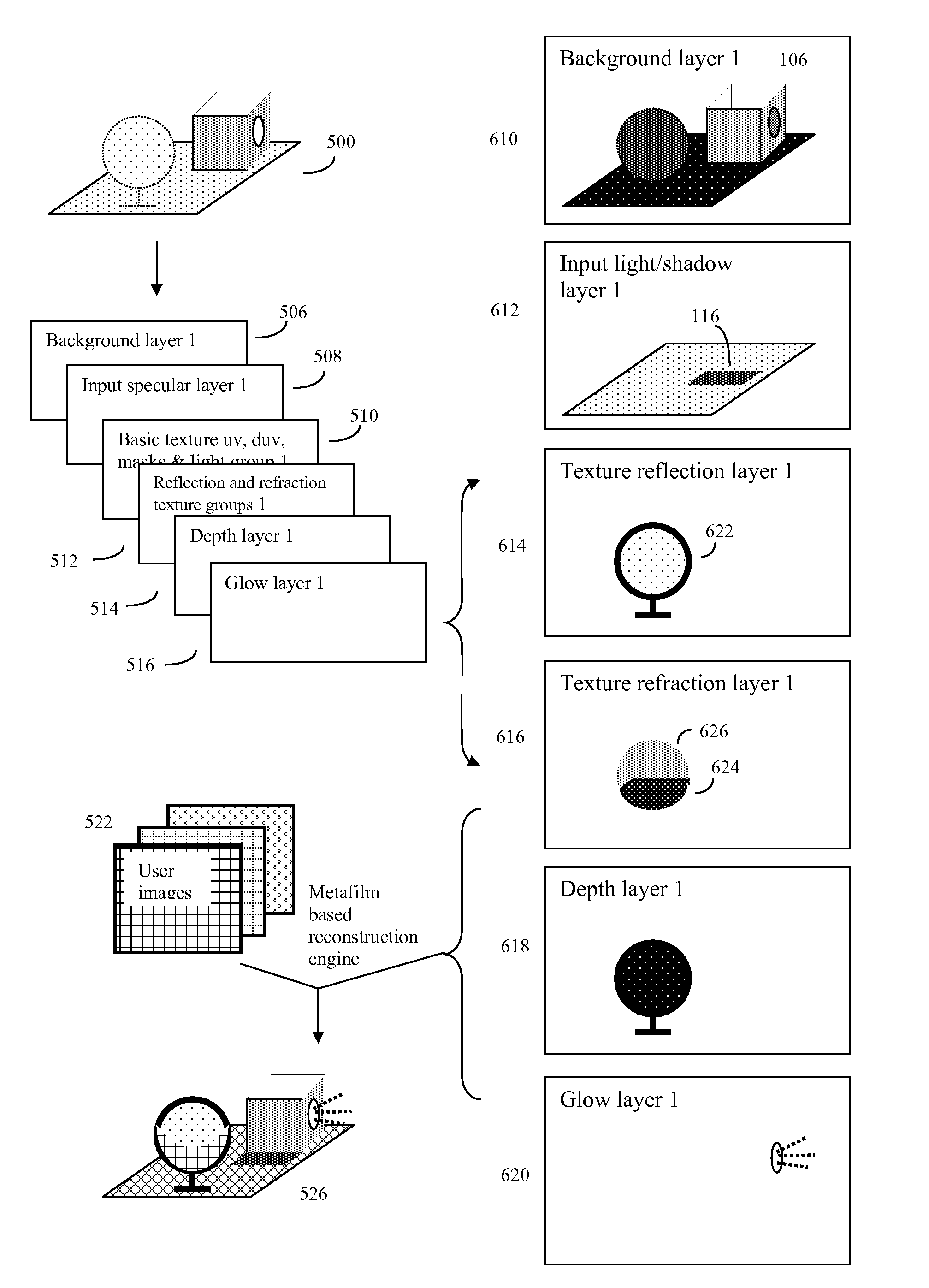
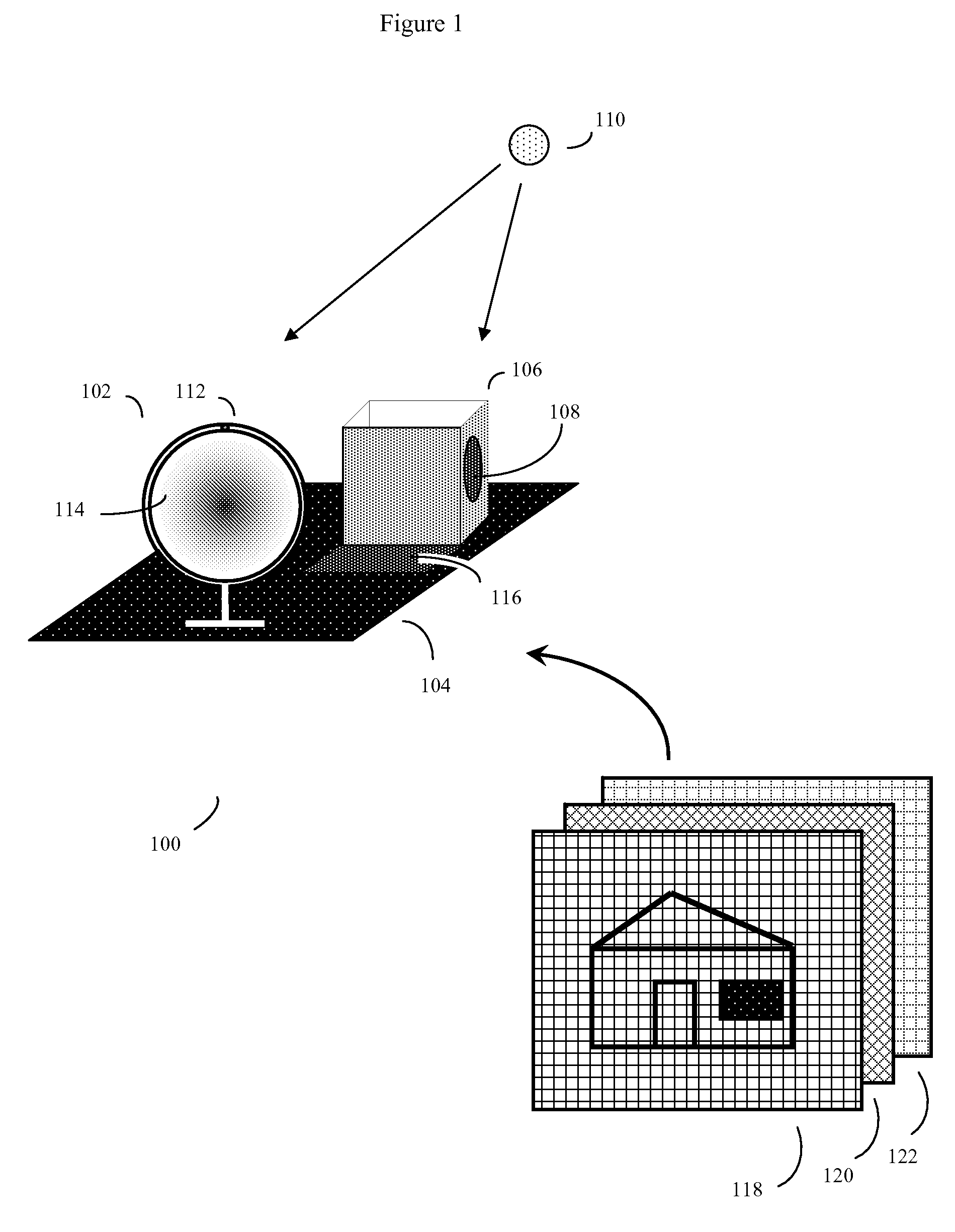
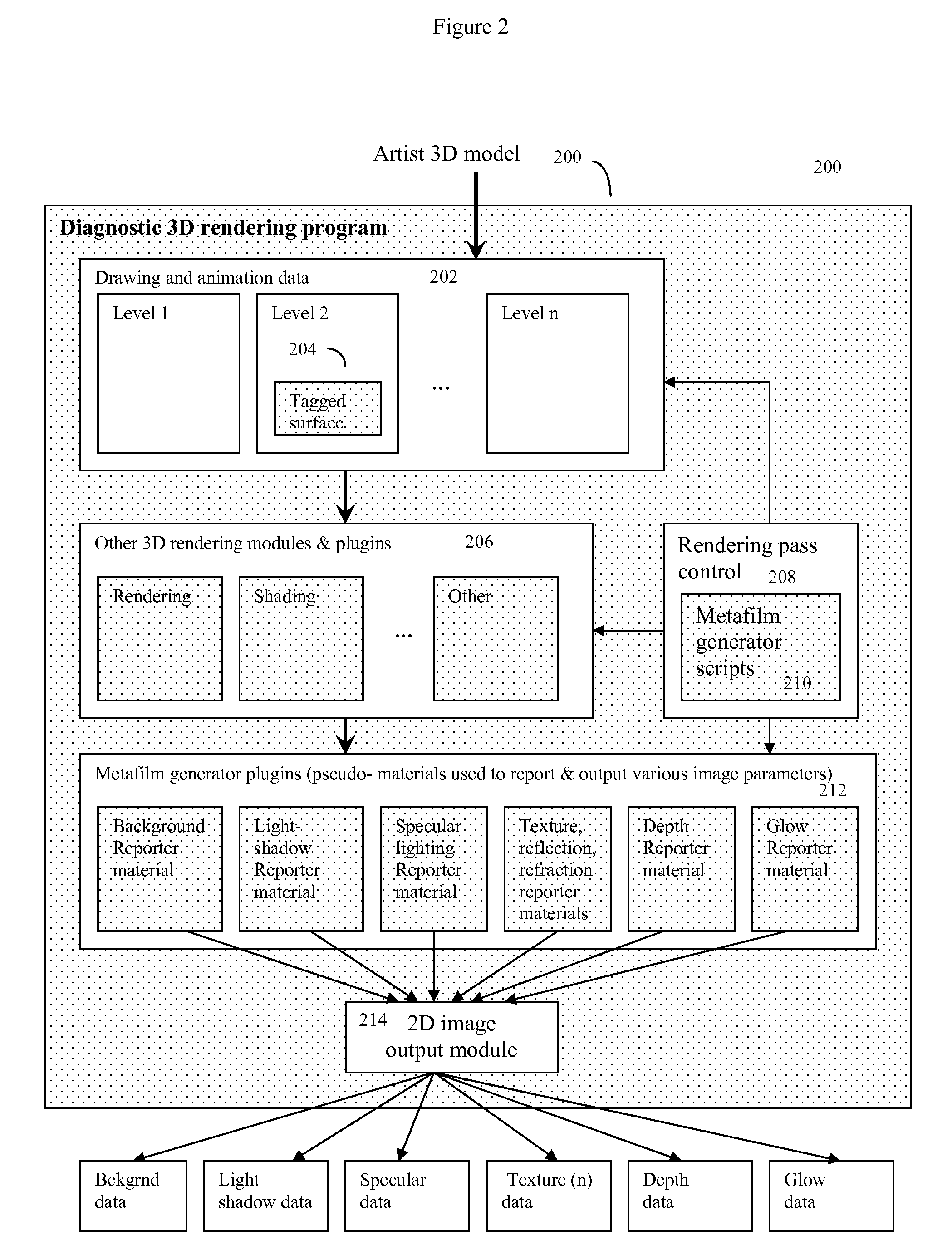
An automated method of rapidly producing customized 3D graphics images in which various user images and video are merged into 3D computer graphics scenes, producing hybrid images that appear to have been created by a computationally intensive 3D rendering process, but which in fact have been created by a much less computationally intensive series of 2D image operations. To do this, a 3D graphics computer model is rendered into a 3D graphics image using a customized renderer designed to automatically report on some of the renderer's intermediate rendering operations, and store this intermediate data in the form of metafilm. User images and video may then be automatically combined with the metafilm, producing a 3D rendered quality final image with orders of magnitude fewer computing operations. The process can be used to inexpensively introduce user content into sophisticated images and videos suitable for many internet, advertising, cell phone, and other applications.
Owner:PIXBLITZ STUDIOS
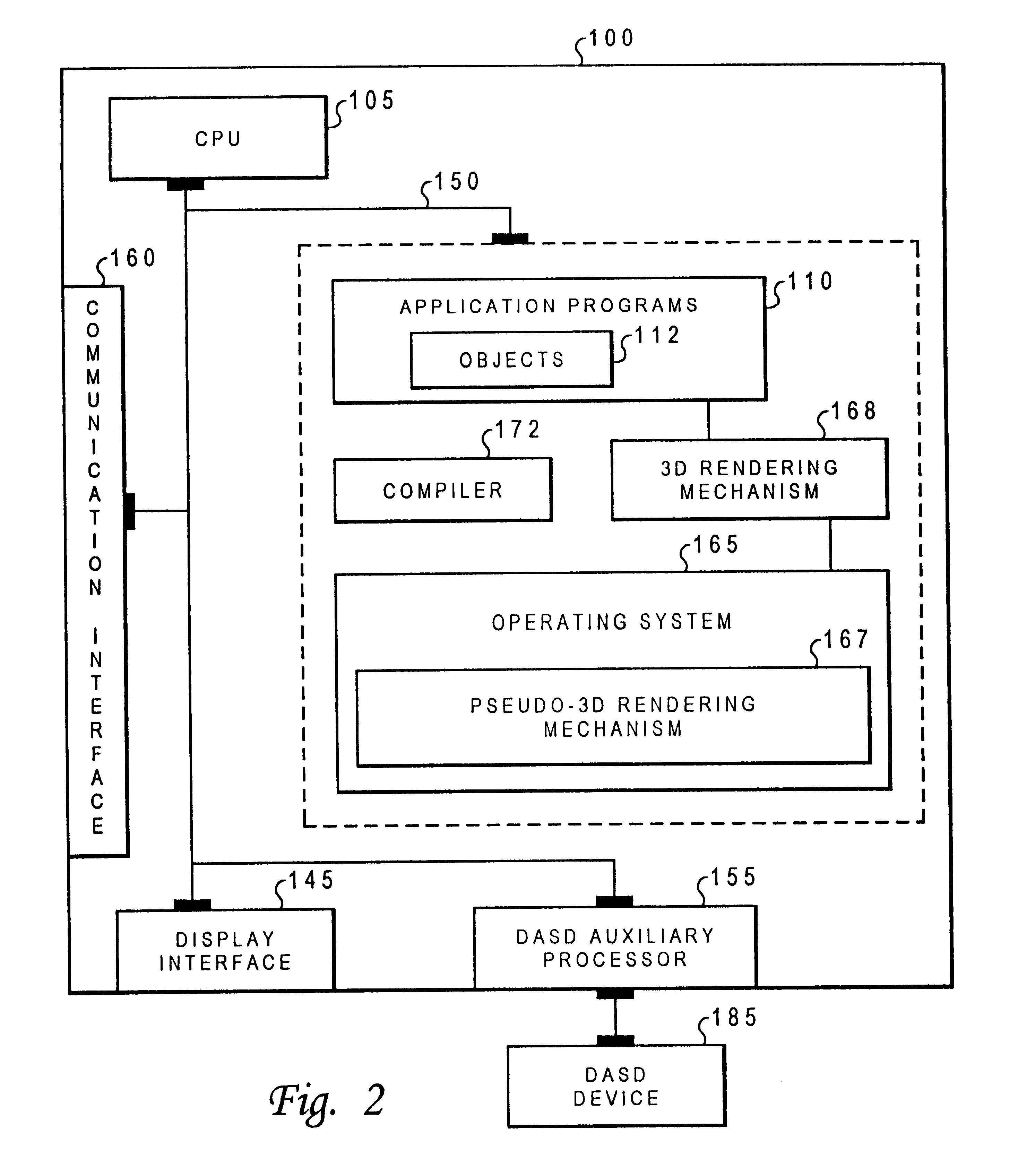
Method and apparatus for providing pseudo-3D rendering for virtual reality computer user interfaces
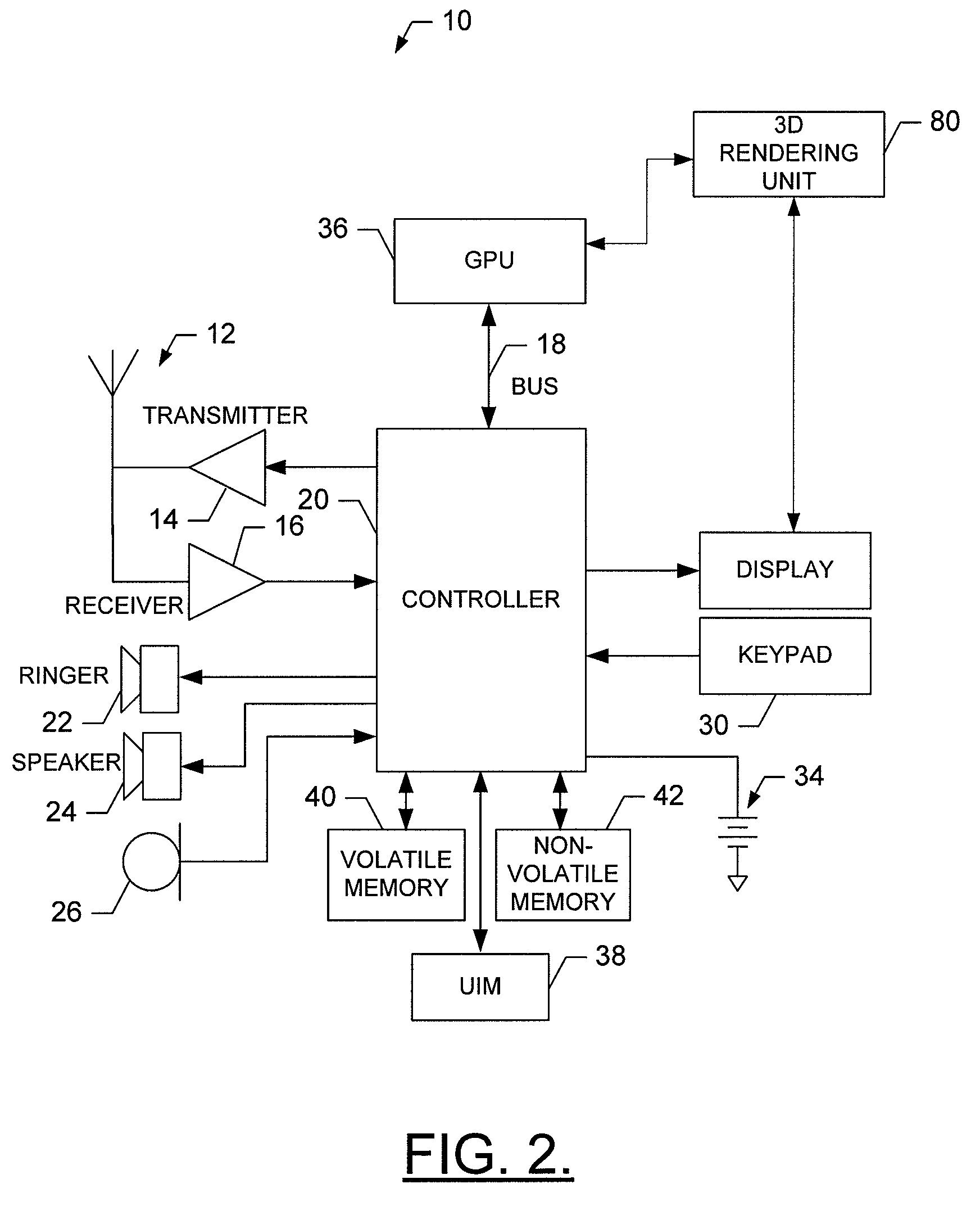
InactiveUS6426757B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer usersDisplay device
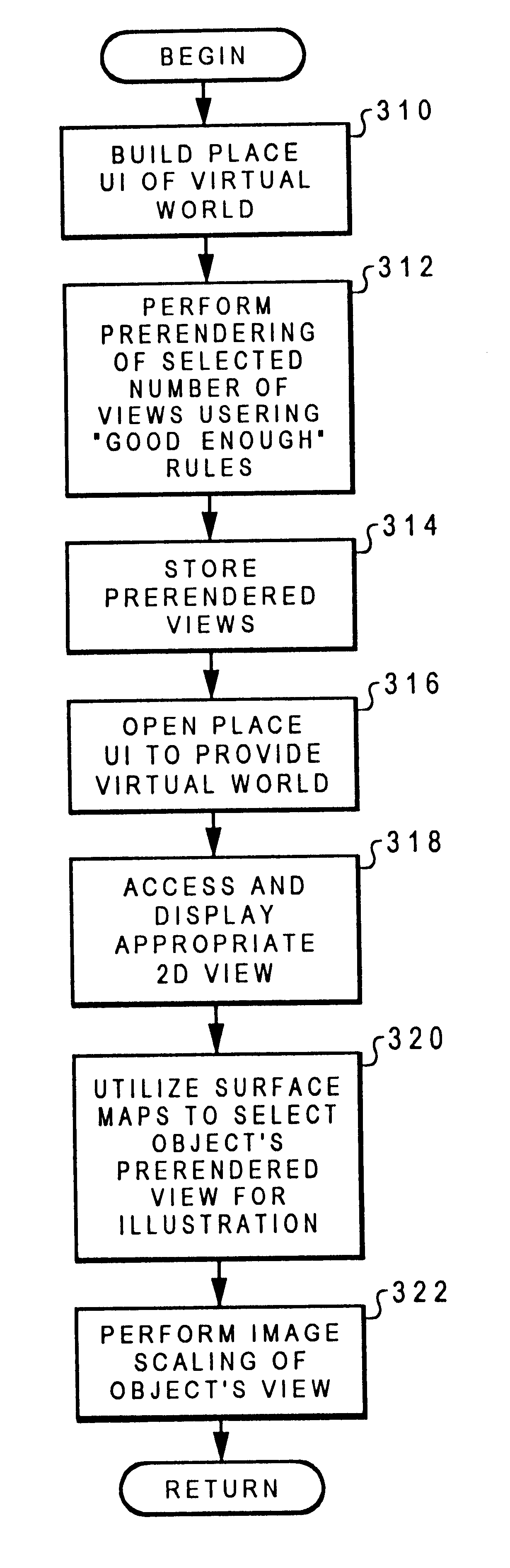
A computer system which includes a central processing unit, a bus, and a memory store coupled to the central processing unit that includes a psuedo 3D rendering mechanism. Typically, the rendering mechanism is loaded in the memory store, but can be implemented in an application's specific integrated circuit further coupled to the central processing unit via the bus. The psuedo 3D rendering mechanism is used to generate a psuedo 3D rendered virtual image using only two dimensional prerendered selected views of 3D objects to be displayed. As the viewing orientation shifts from point to point, an adequate three-dimensional rendering is provided based on these selected views. These selected views are designed for display on a display device further connected to the computer system.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
Camera Projection Meshes
InactiveUS20130021445A1Improve performanceLess complexSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingShadow mappingVideo sequence
A 3D rendering method is proposed to increase the performance when projecting and compositing multiple images or video sequences from real-world cameras on top of a precise 3D model of the real world. Unlike previous methods that relied on shadow-mapping and that were limited in performance due to the need to re-render the complex scene multiple times per frame, the proposed method uses, for each camera, one Camera Projection Mesh (“CPM”) of fixed and limited complexity per camera. The CPM that surrounds each camera is effectively molded over the surrounding 3D world surfaces or areas visible from the video camera. Rendering and compositing of the CPMs may be entirely performed on the Graphic Processing Unit (“GPU”) using custom shaders for optimal performance. The method also enables improved view-shed analysis and fast visualization of the coverage of multiple cameras.
Owner:FORTEM SOLUTIONS
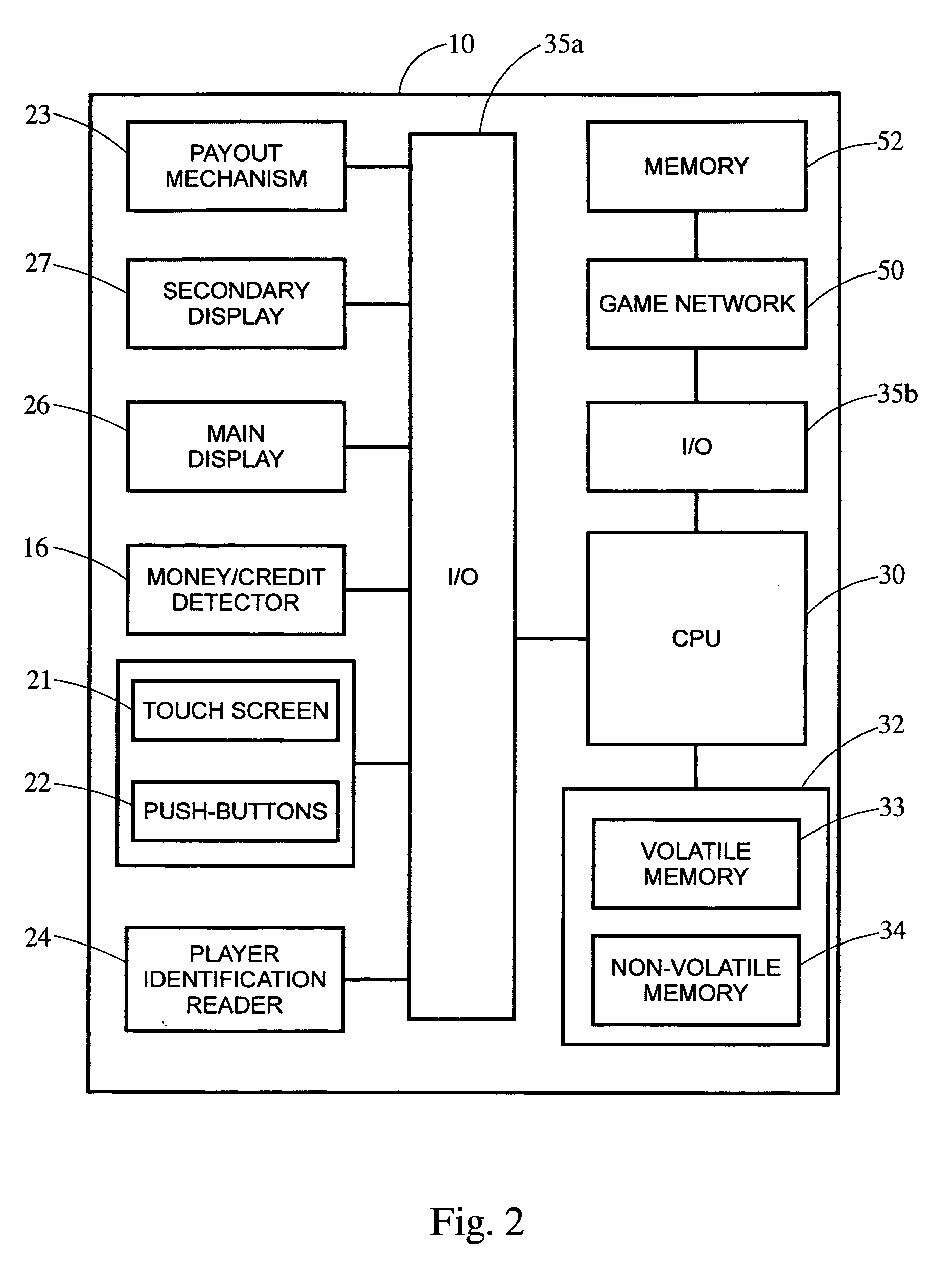
Wagering game with 3D rendering of a mechanical device
A stand-alone or server-linked gaming terminal that displays on a plasma display in the top-box area a 3D-rendered mechanical device that is pre-rendered or rendered in real time using a 3D-graphics processor or the like. The 3D-rendered mechanical device depicts the game outcome or a bonus game displayed in the top box display. The images or animation representing the 3D-rendered mechanical device may be stored on a digital video recorder (DVR) within the gaming terminal or downloaded remotely from a storage device coupled to the gaming terminal. The DVR outputs the mechanical device images as analog video, and is capable of receiving analog video input, converting the analog video to a digital format such as MPEG, and storing the converted video on a storage media. Additional structural elements such as a frame may be arranged about the top-box display to add depth or dimensionality to the 3D-rendered images displayed thereon.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
3D scene rendering
InactiveUS20170116781A1Image analysisDetails involving 3D image dataPoint cloudComputer graphics (images)
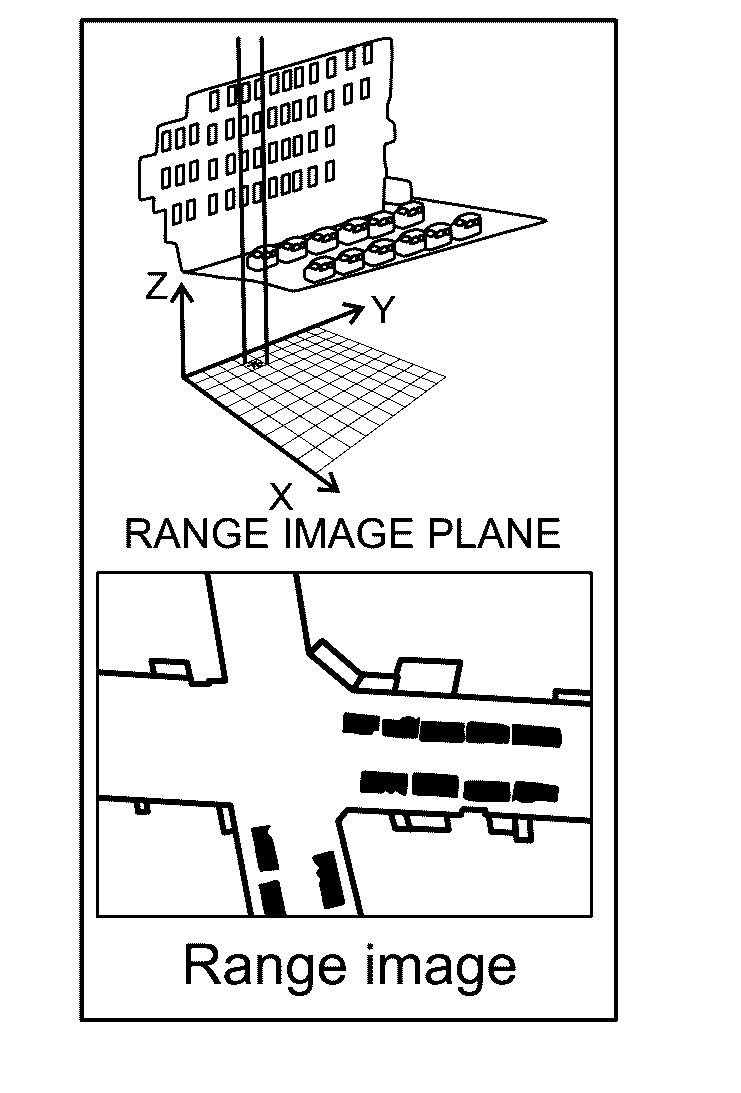
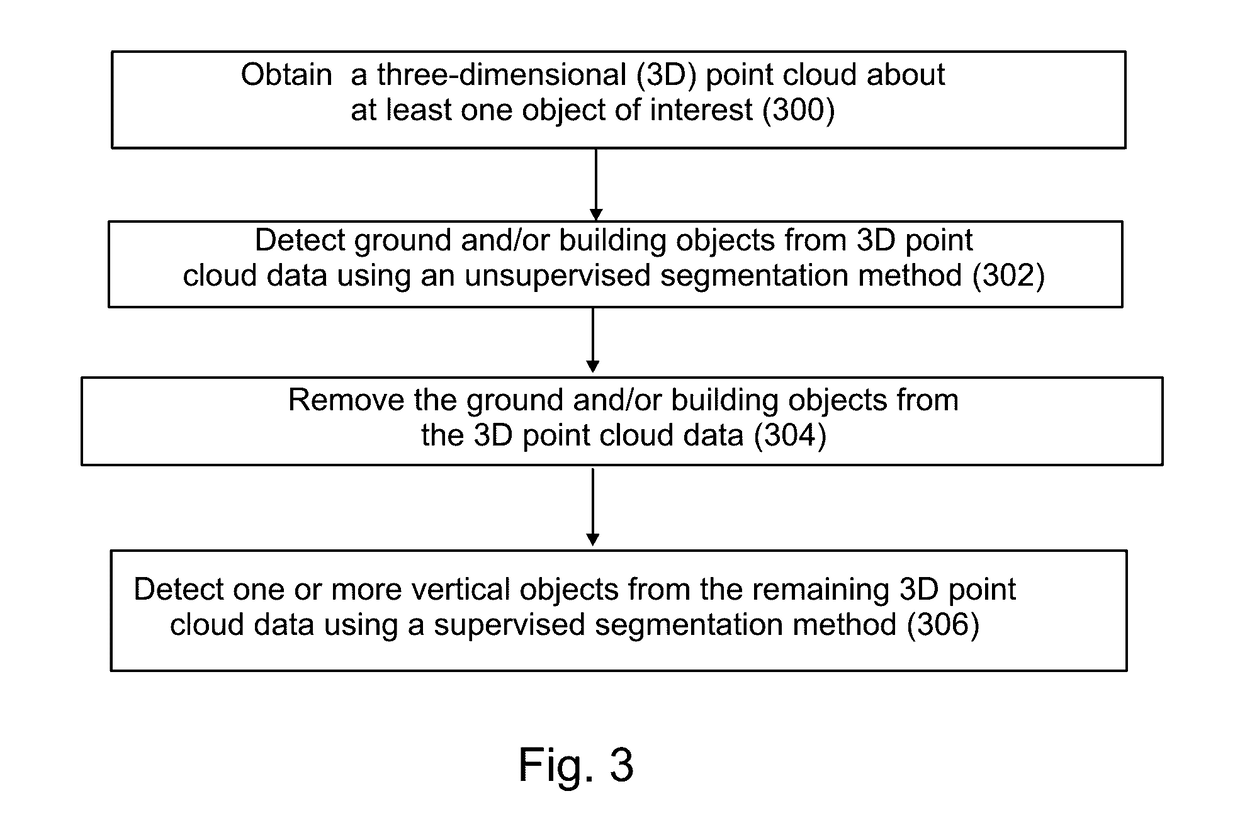
A method comprising: obtaining a plurality of three-dimensional (3D) point clouds about a plurality of objects of interest, each of said 3D point clouds being labelled to a category of objects of interest; rendering facades for the objects of interests categorized as buildings using an ambient occlusion method, where illumination of the point cloud is calculated based on light coming from a theoretical hemisphere or sphere around the object of interest; and rendering shapes of the objects of interests categorized as non-buildings by fitting predefined templates of street view objects to the point clouds labelled as non-buildings.
Owner:PIECE FUTURE PTE LTD
Apparatus and method for processing manipulation of 3D virtual object
InactiveUS20140015831A1Imparting and convenienceImprove overall senseImage analysisInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Unit model
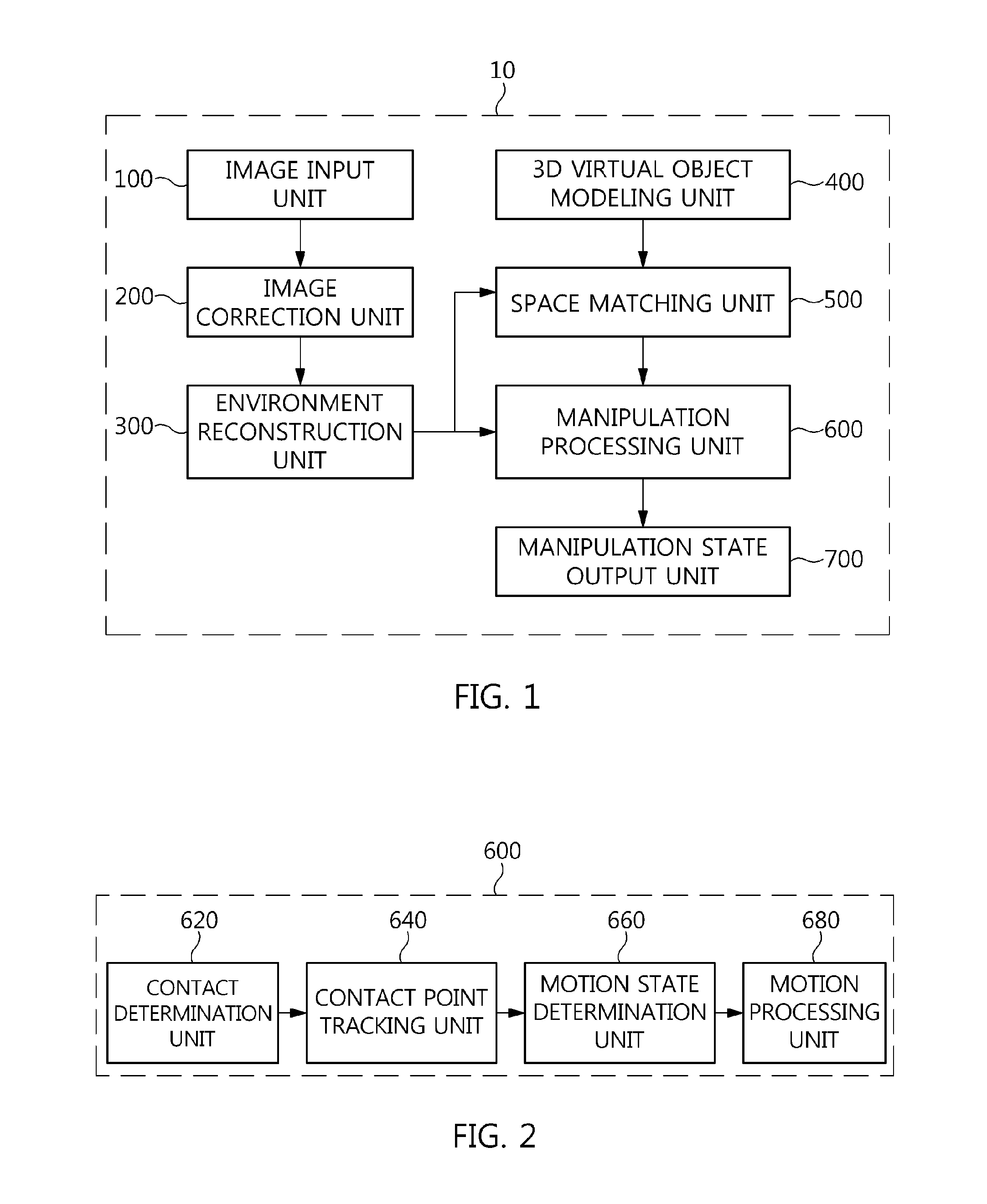
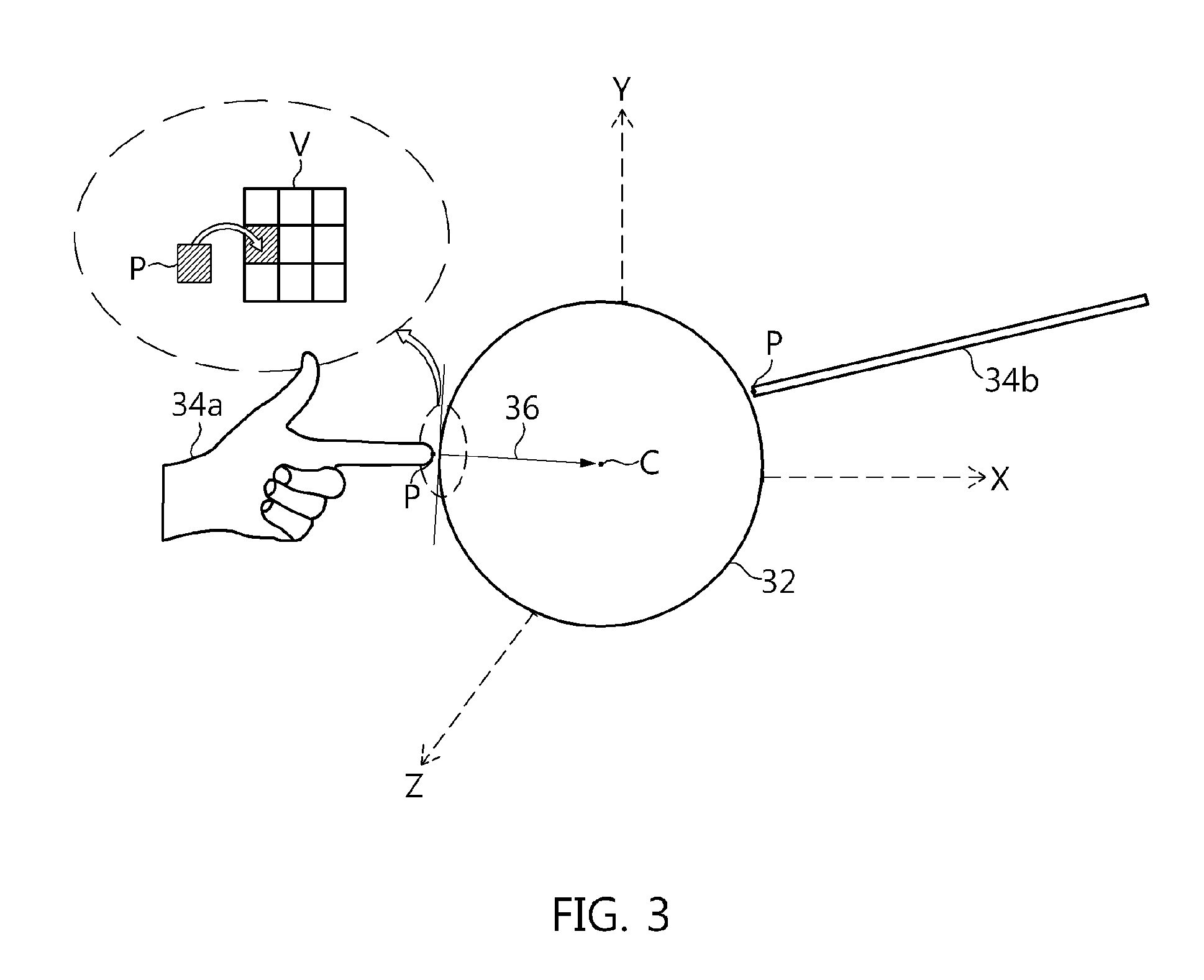
Disclosed herein are an apparatus and method for processing the manipulation of a three-dimensional (3D) virtual object. The apparatus includes an image input unit, an environment reconstruction unit, a 3D object modeling unit, a space matching unit, and a manipulation processing unit. The image input unit receives image information generated by capturing a surrounding environment including a manipulating object. The environment reconstruction unit reconstructs a 3D virtual reality space. The 3D object modeling unit models a 3D virtual object that is manipulated by the manipulating object, and generates a 3D rendering space. The space matching unit matches the 3D rendering space to the 3D virtual reality space. The manipulation processing unit determines whether the manipulating object is in contact with the surface of the 3D virtual object, and tracks the path of a contact point and processes the motion of the 3D virtual object.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
3D visualization method and system of natural resource data
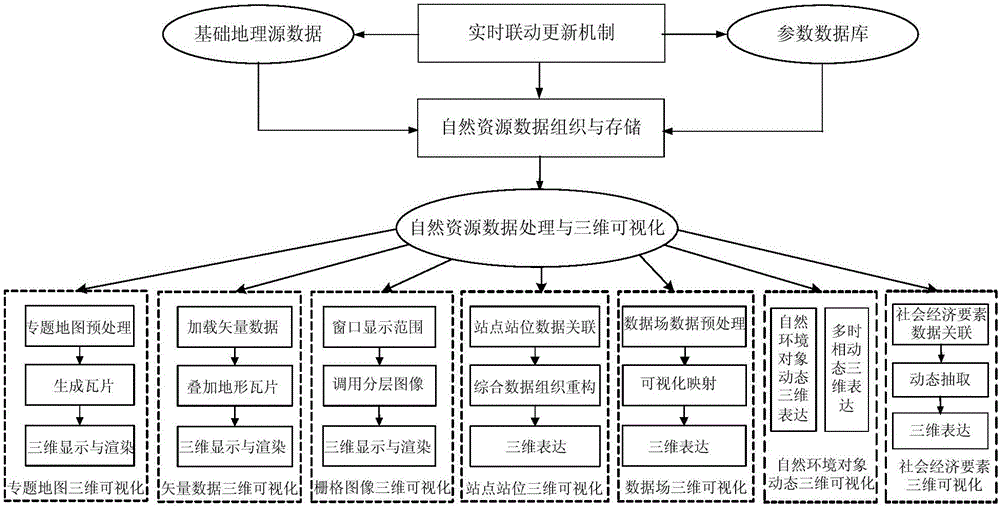
InactiveCN105069020AReal-time online 3D rendering displayRealize high-performance 3D visualization expressionGeographical information databasesOther databases browsing/visualisationData setEmbedded database
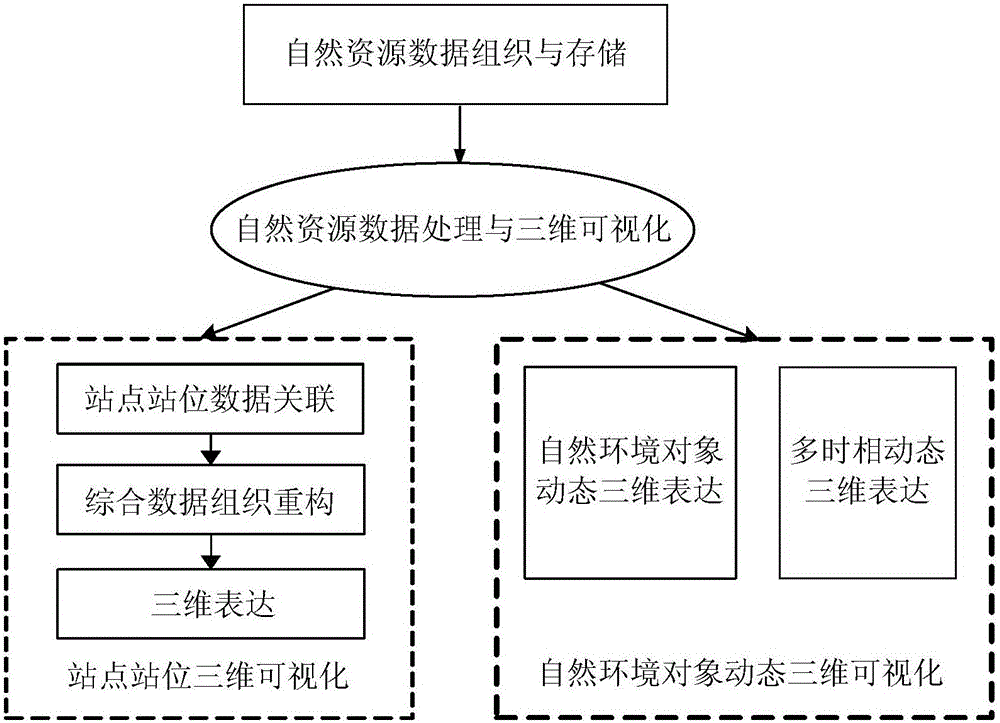
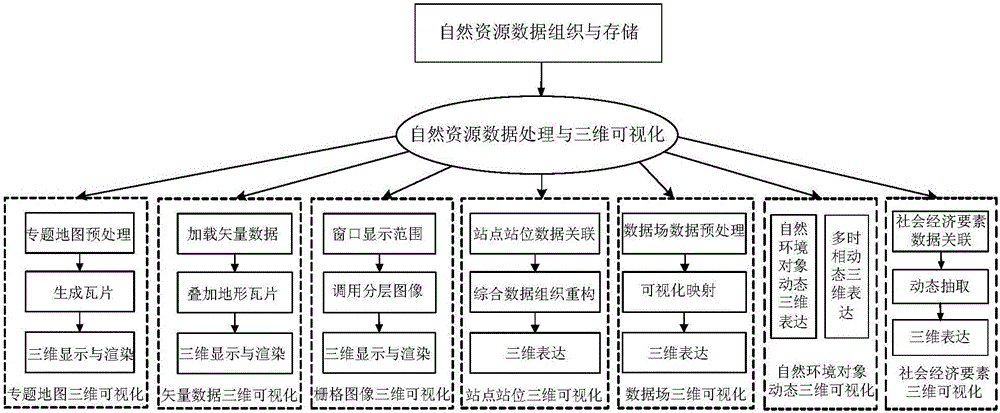
The present invention relates to an on line 3D visualization method and system of natural resource data. The method mainly includes a step of natural resource data organization and storage and a step of natural resource data processing and 3D visualization. The step of natural resource data organization and storage includes: according to natural resource data characteristics and service characteristics, dividing data types, and making the natural resource data as tile image data formed by a plurality of tiles by adopting a pyramid model, then encoding each tile, and establishing a tile data set based on an embedded database technology, storing the tile data set in database, and establishing a quadtree index of space for each tile. The step of natural resource data processing and 3D visualization includes site and position 3D visualization and natural environment object dynamic 3D visualization. The method achieves real time on line 3D rendering display for all kinds of natural resources and geographic space information data in a high-performance 3D visualization environment.
Owner:国家信息中心
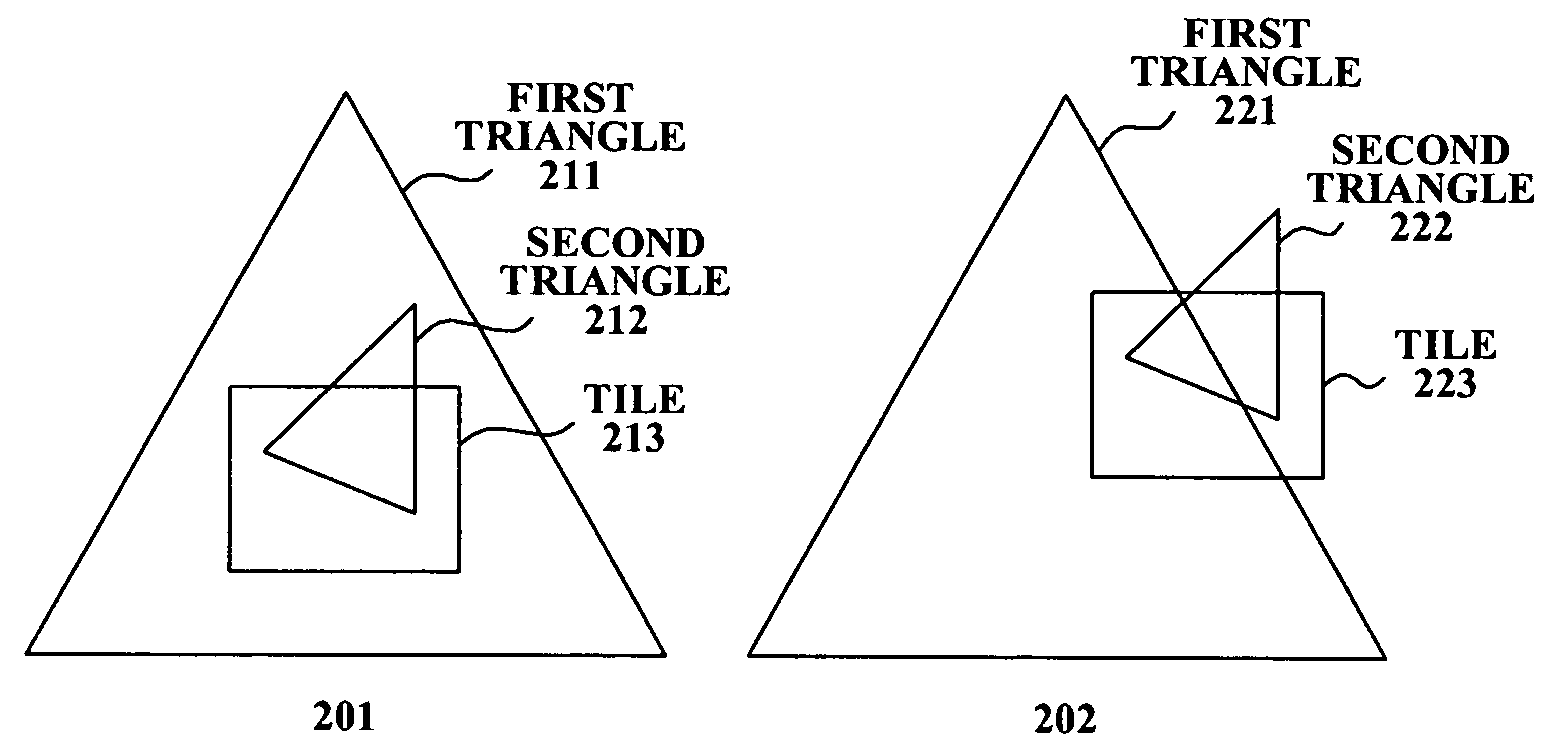
Method And System For Compressing Tile Lists Used For 3D Rendering
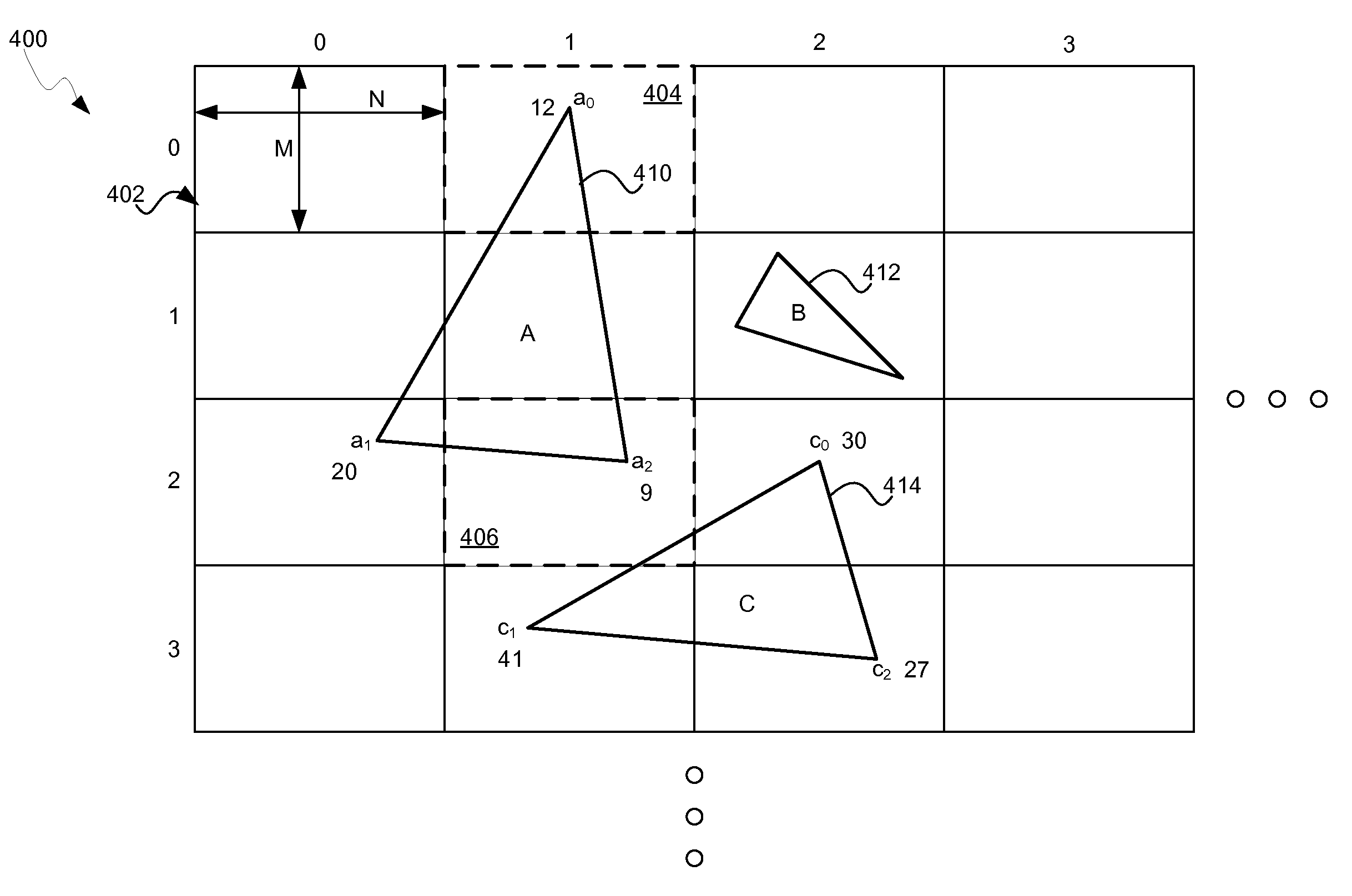
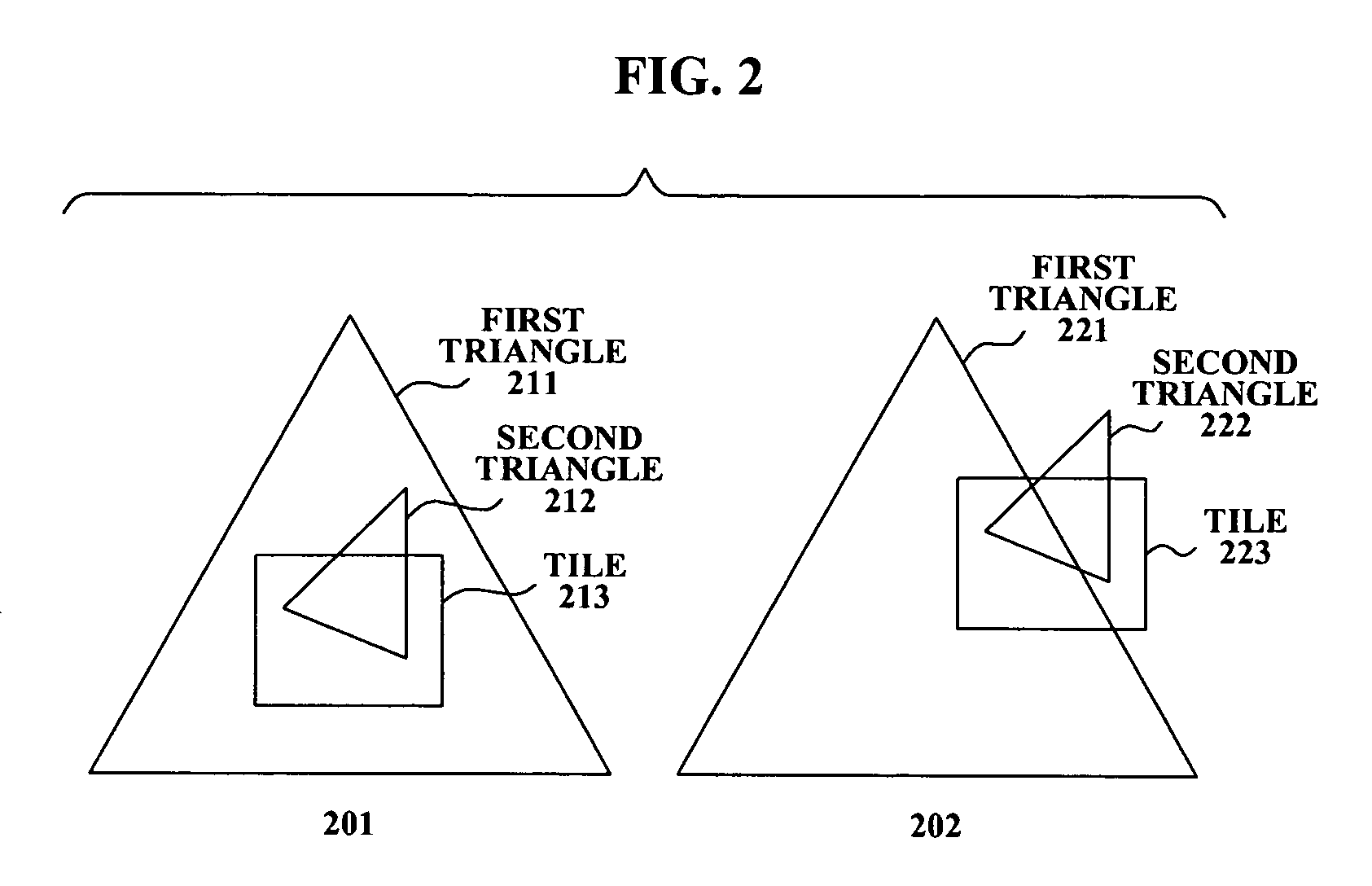
ActiveUS20110216069A1Drawing from basic elementsImage data processing detailsGraphicsTiled rendering
A graphics processing device may generate coordinates for vertices of graphics primitives in a view-space. Tiles are defined within the view-space and are associated with tile lists. Primitives and / or vertices which overlap a tile are determined. Tile lists comprise differentially encoded indices and / or spatial coordinates for overlapping primitives. The differential encoding may or may not be byte aligned. During tile mode graphics rendering, tile lists are utilized to reference vertex attributes and / or primitives. Graphics rendering comprises a tile binning phase and a tile rendering phase. The primitives may comprise a triangle and / or joined triangles that share one or more vertices. For multiple joined primitives, information about shared vertices may be encoded without repetition for each primitive. Coordinates and / or corresponding weights for new vertices are encoded in a tile list and utilized for interpolating properties of the new vertices based on attributes of the original vertices.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for real-time volume rendering on thin clients via render server
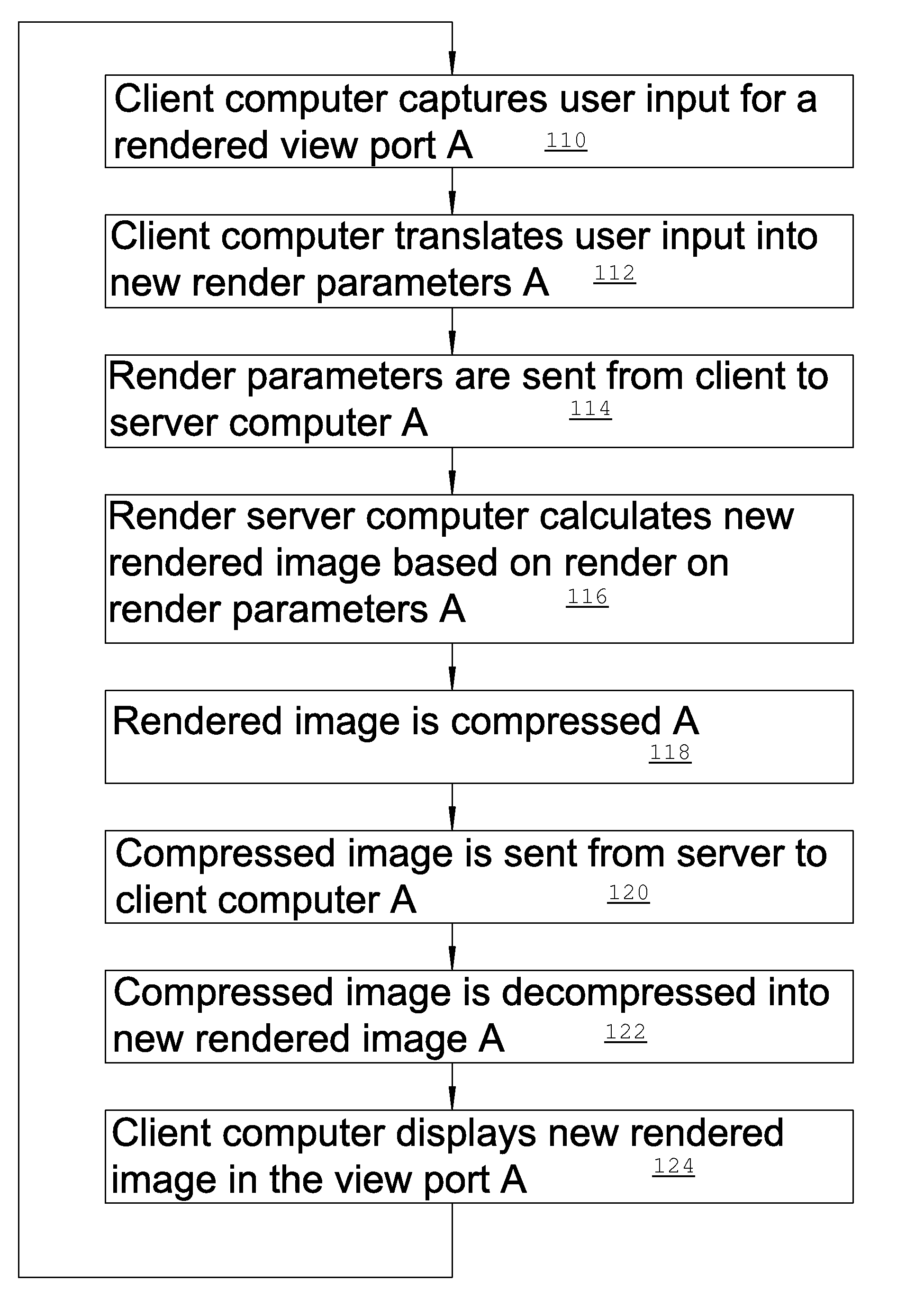
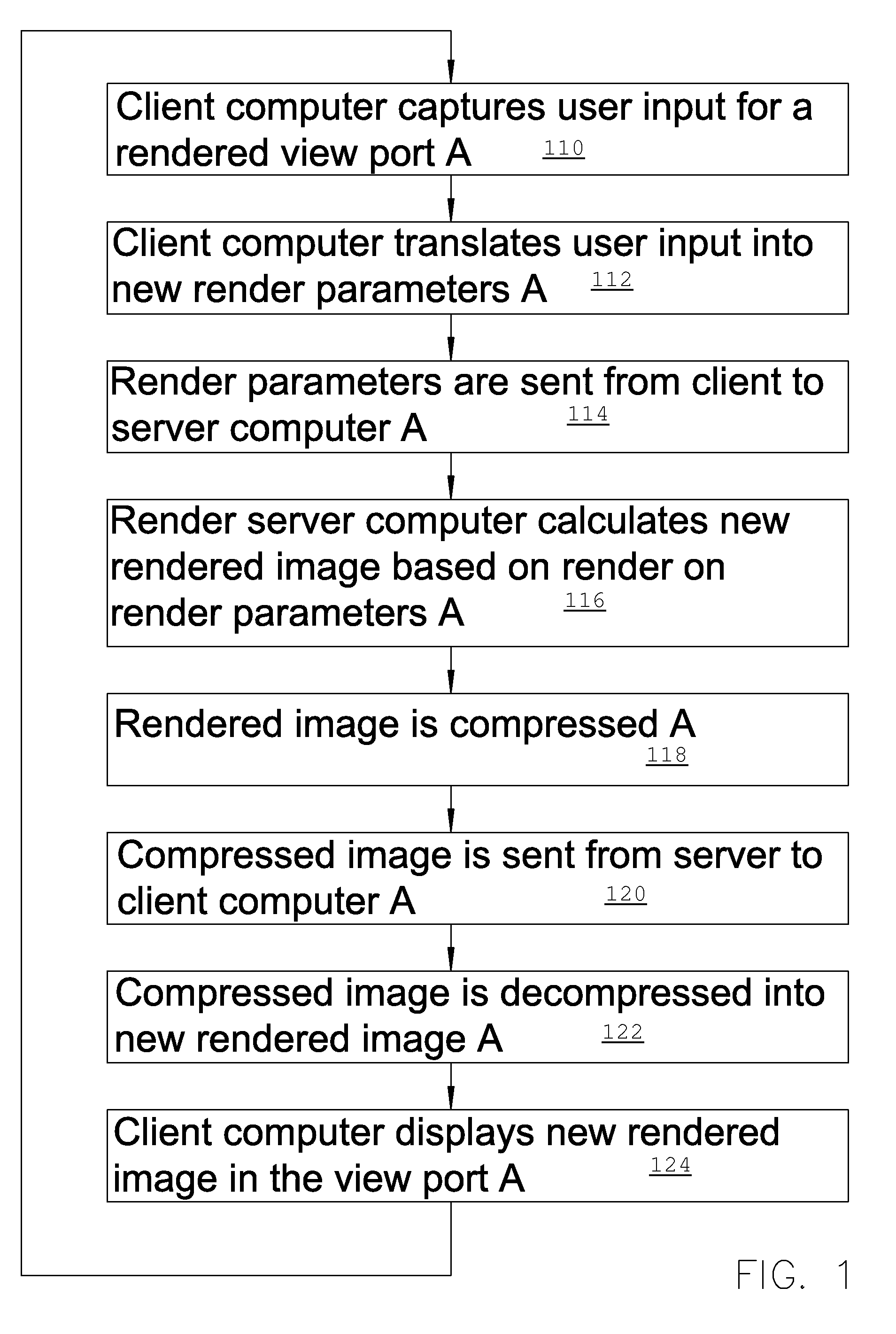
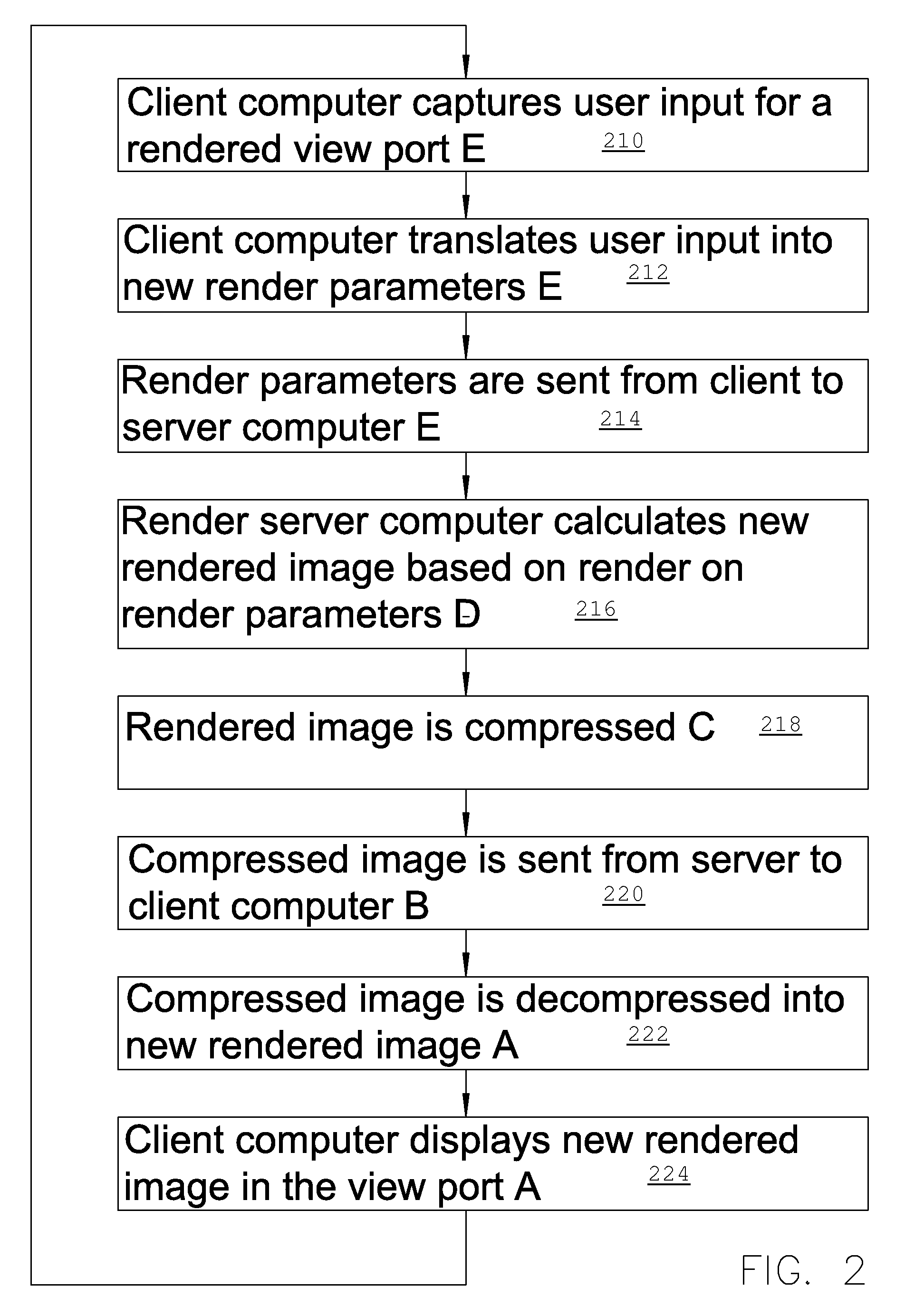
ActiveUS8508539B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer graphics (images)Client-side
A method of server site rendering 3D images on a server computer coupled to a client computer wherein the client computer instructs a server computer to load data for 3D rendering and sends a stream of rendering parameter sets to the server computer, each set of rendering parameters corresponding with an image to be rendered; next the render computer renders a stream of images corresponding to the stream of parameter sets and the stream of images is compressed with a video compression scheme and sent from the server computer to the client computer where the client computer decompresses the received compressed video stream and displays the result in a viewing port. The rendering and communication chain is subdivided in successive pipeline stages that work in parallel on successive rendered image information.
Owner:AGFA HEALTHCARE NV
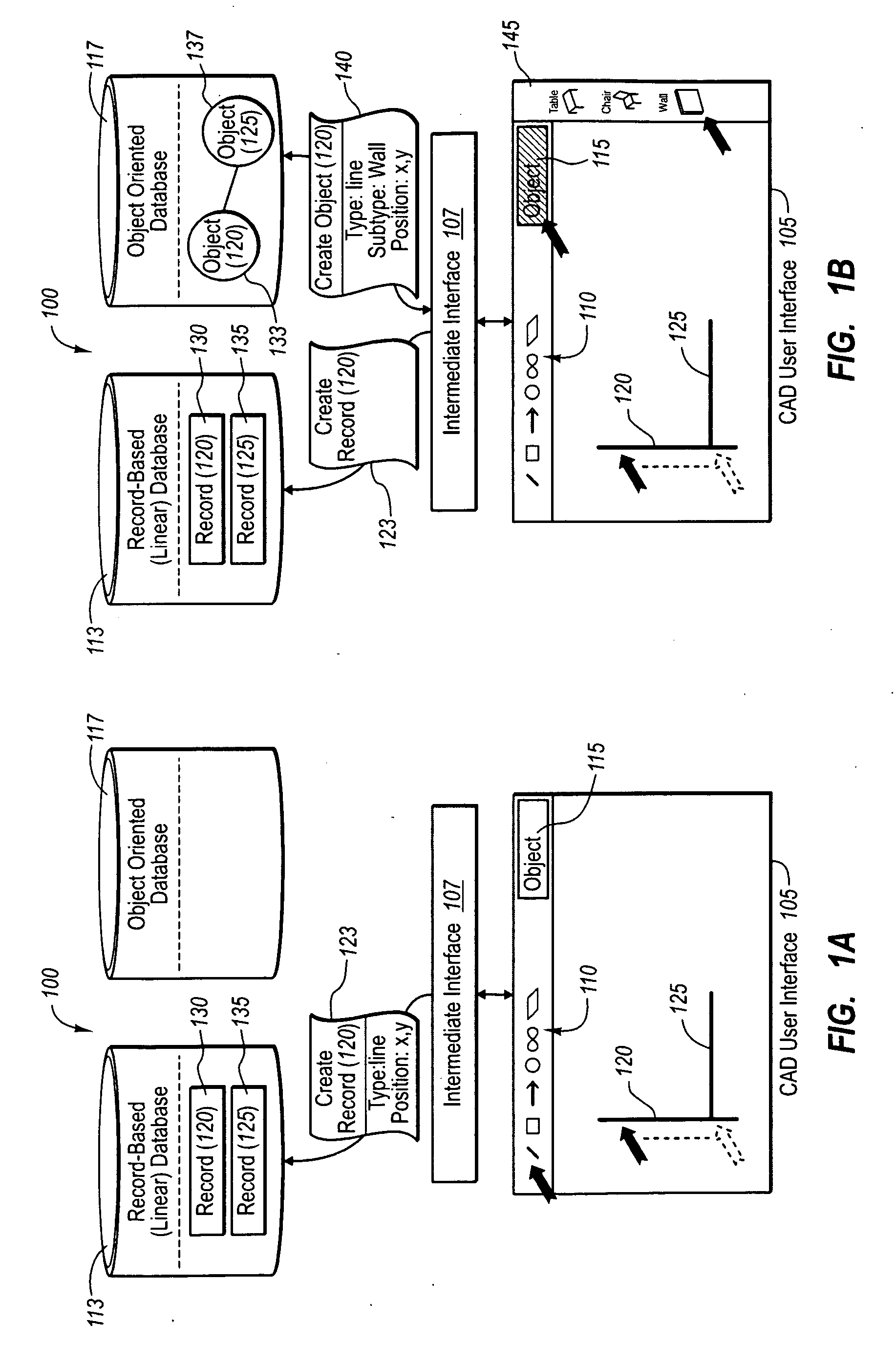
Rendering and modifying cad design entities in object-oriented applications
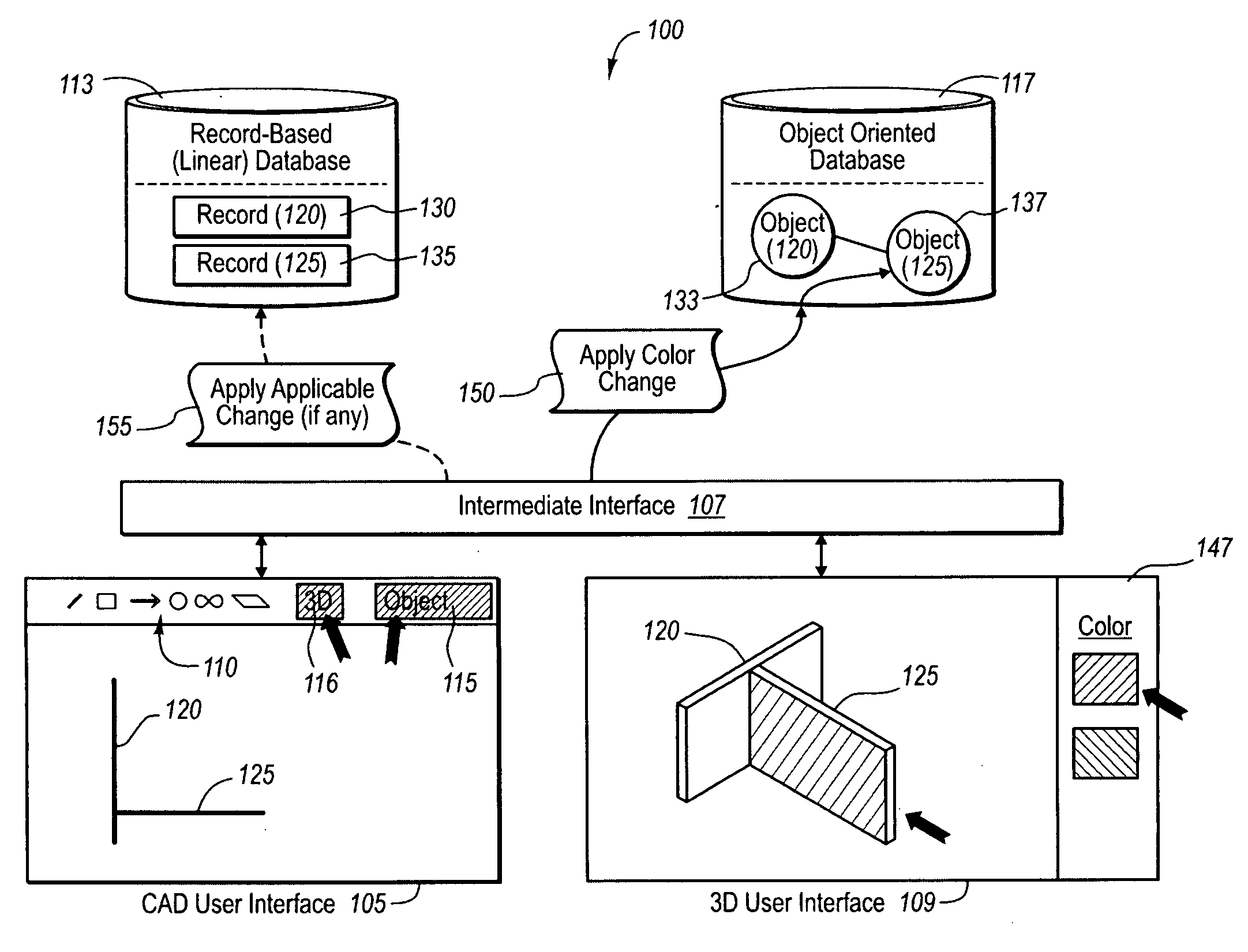
ActiveUS20100268513A1View effectivelyGuaranteed accuracyGeometric CADSpecific program execution arrangementsImage resolutionSoftware engineering
An object-oriented design program provides is configured to instantly render in a three-dimensional interface user CAD designs received as CAD-based design elements (e.g., CAD blocks or lines). The object-oriented program renders the user CAD designs regardless of whether the user designs are practical, or use finishes or colors that are in-stock for the selected design elements. In addition, the object-oriented program can also create intelligent software objects for the CAD-based elements at a later time, upon request by the user. The intelligent software objects can be configured to automatically resolve themselves in view of one or more system limitations and rules in related components, and to replicate any such resolution back to the CAD-based blocks if desired. Thus, a user can have the benefits of instant 3D rendering of CAD drawings with or without the automatic resolution provided by intelligent software objects, depending on the situation.
Owner:ARMSTRONG WORLD INDUSTRIES +1
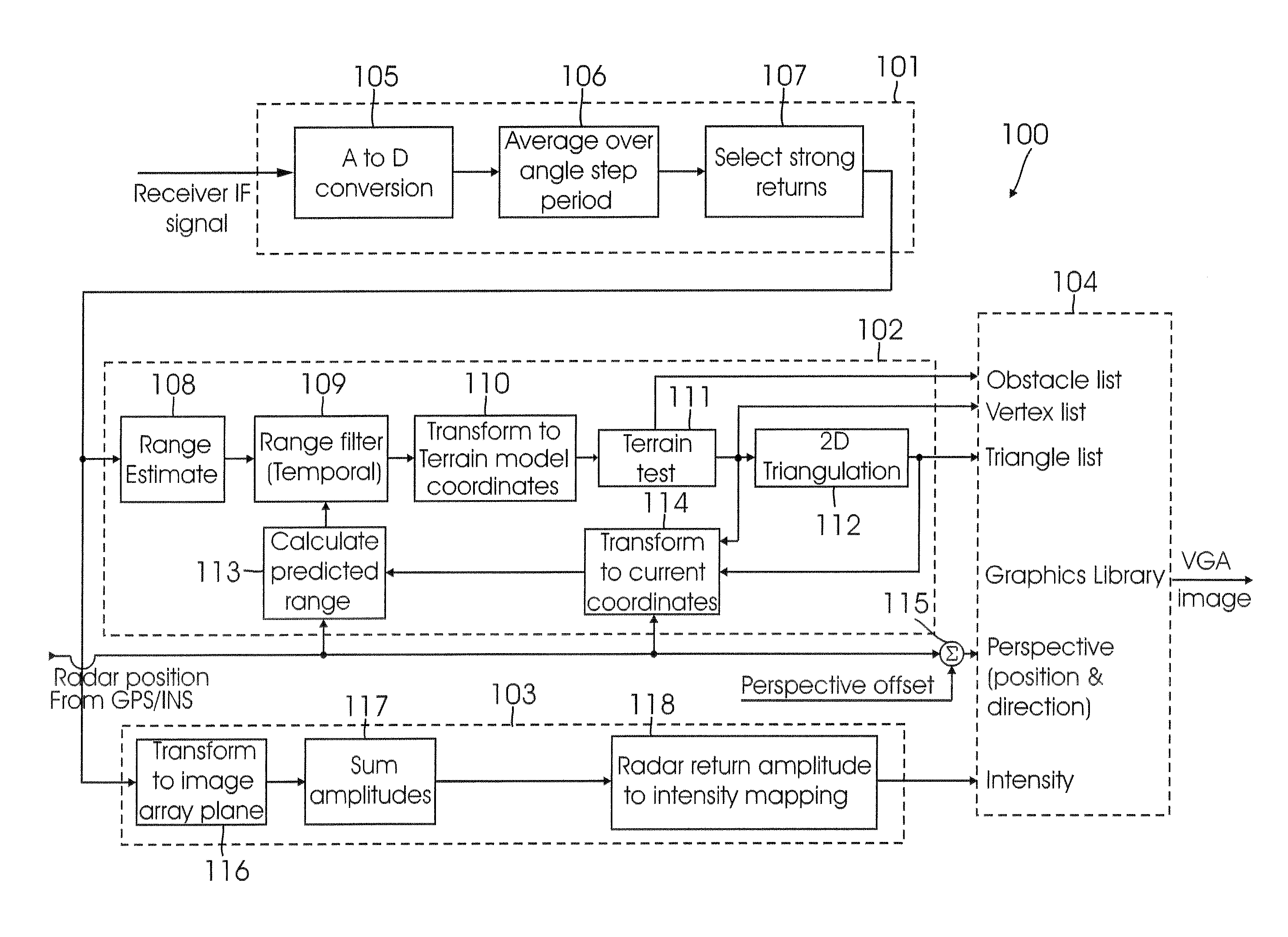
System and method for 3D radar image rendering
ActiveUS20080074312A1Improve usabilityEasy to explainRadio wave reradiation/reflection3D-image renderingTerrain3d image
A 3D rendered image of a radar-scanned terrain surface is provided from a radar return signal from the surface, wherein the return signal includes data indicative of azimuth, elevation, and range of a radar-illuminated area of the surface. The data are processed for transformation into X, Y, and Z coordinates. The X and Y coordinates corresponding to each illuminated area are triangulated so as to create a mesh of triangles representing the terrain surface, each of the triangles in the mesh being defined by a vertex triplet. 3D imaging information (grey scale shading and / or coloring information) is added to each triangle in the mesh, based on the amplitude of the radar return signal from the coordinates represented by each vertex in the triplet and the value of the Z coordinate at each vertex, so as to form the 3D rendered image.
Owner:SIERRA NEVADA CORP
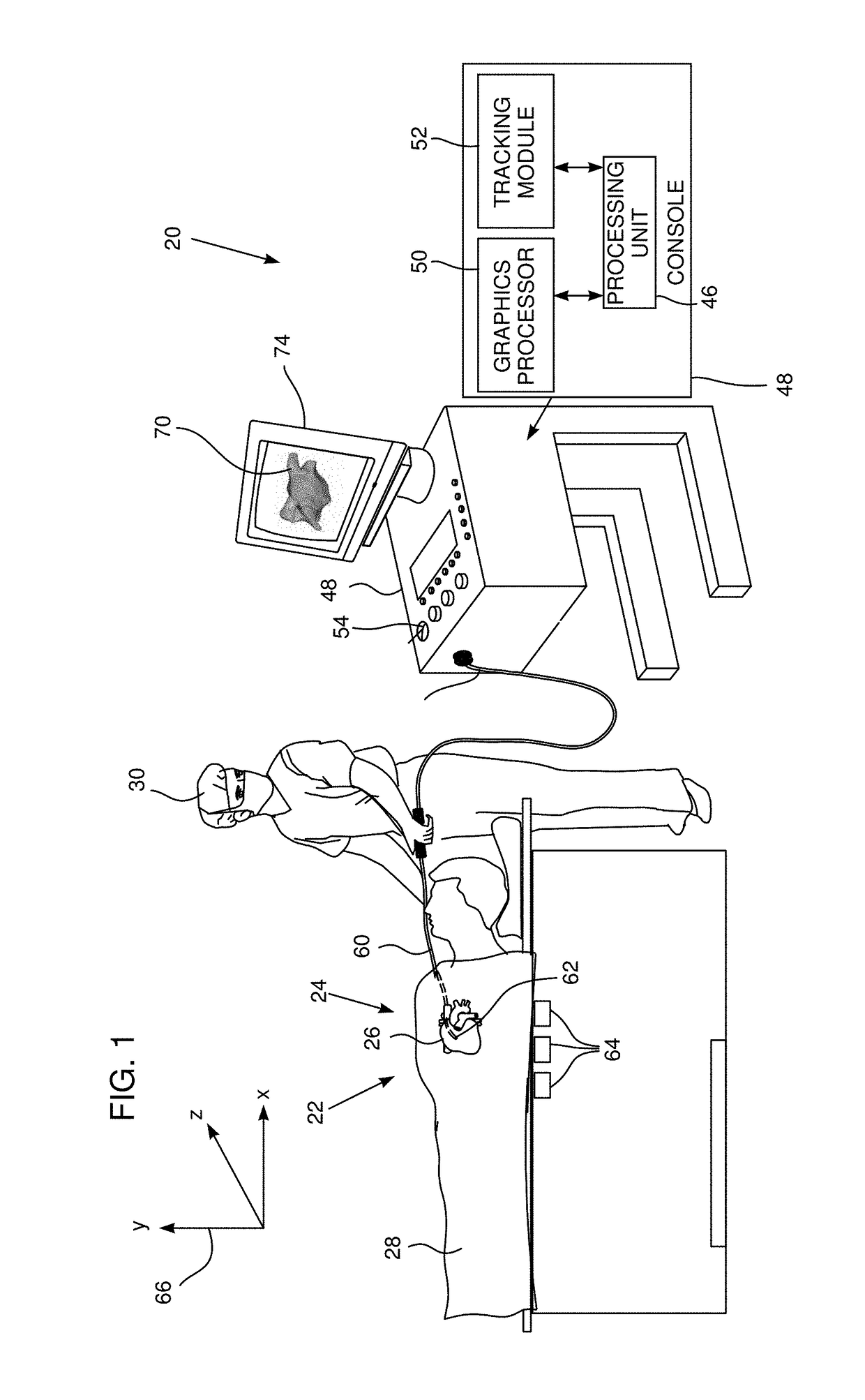
Alignment ct
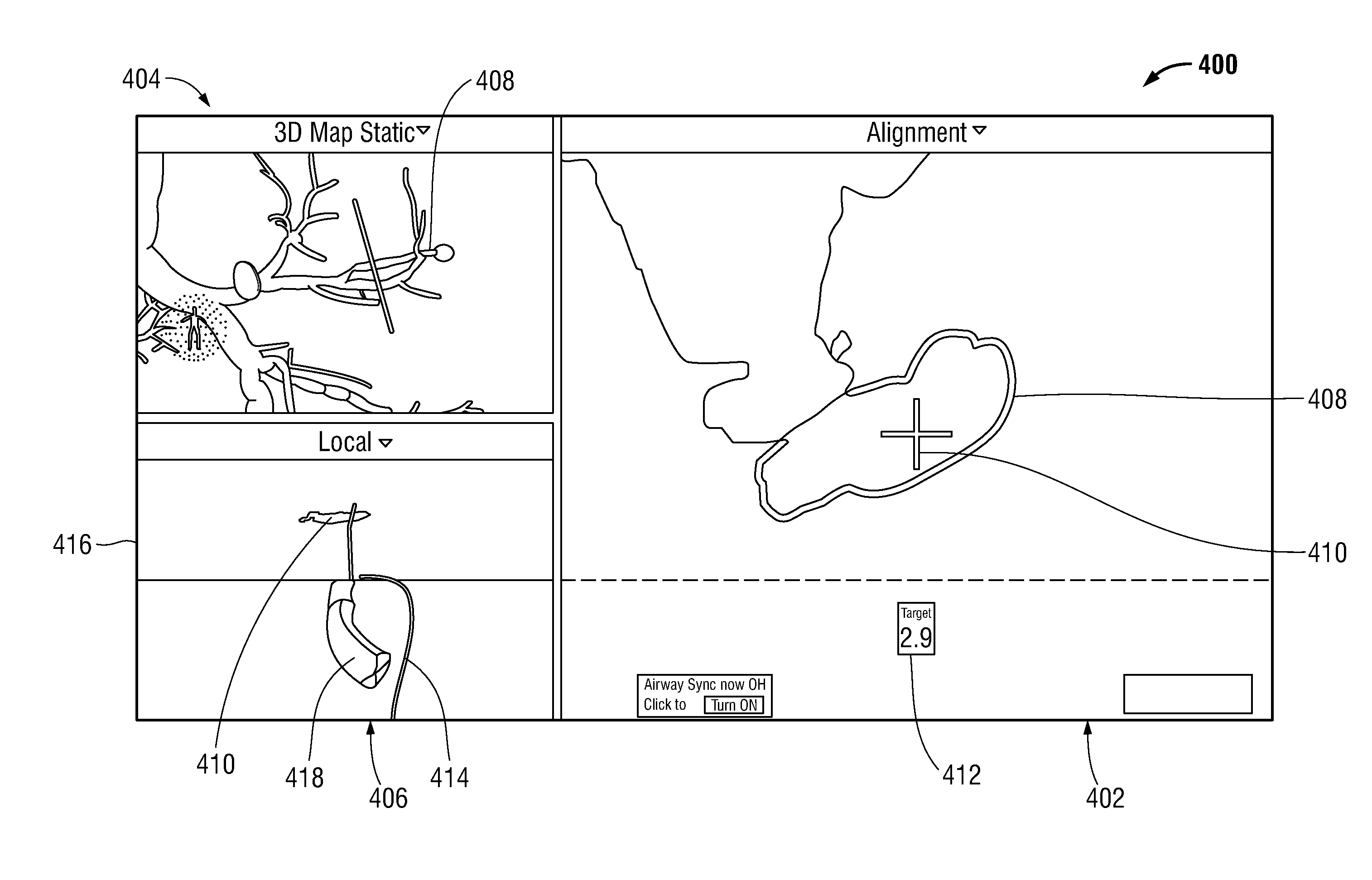
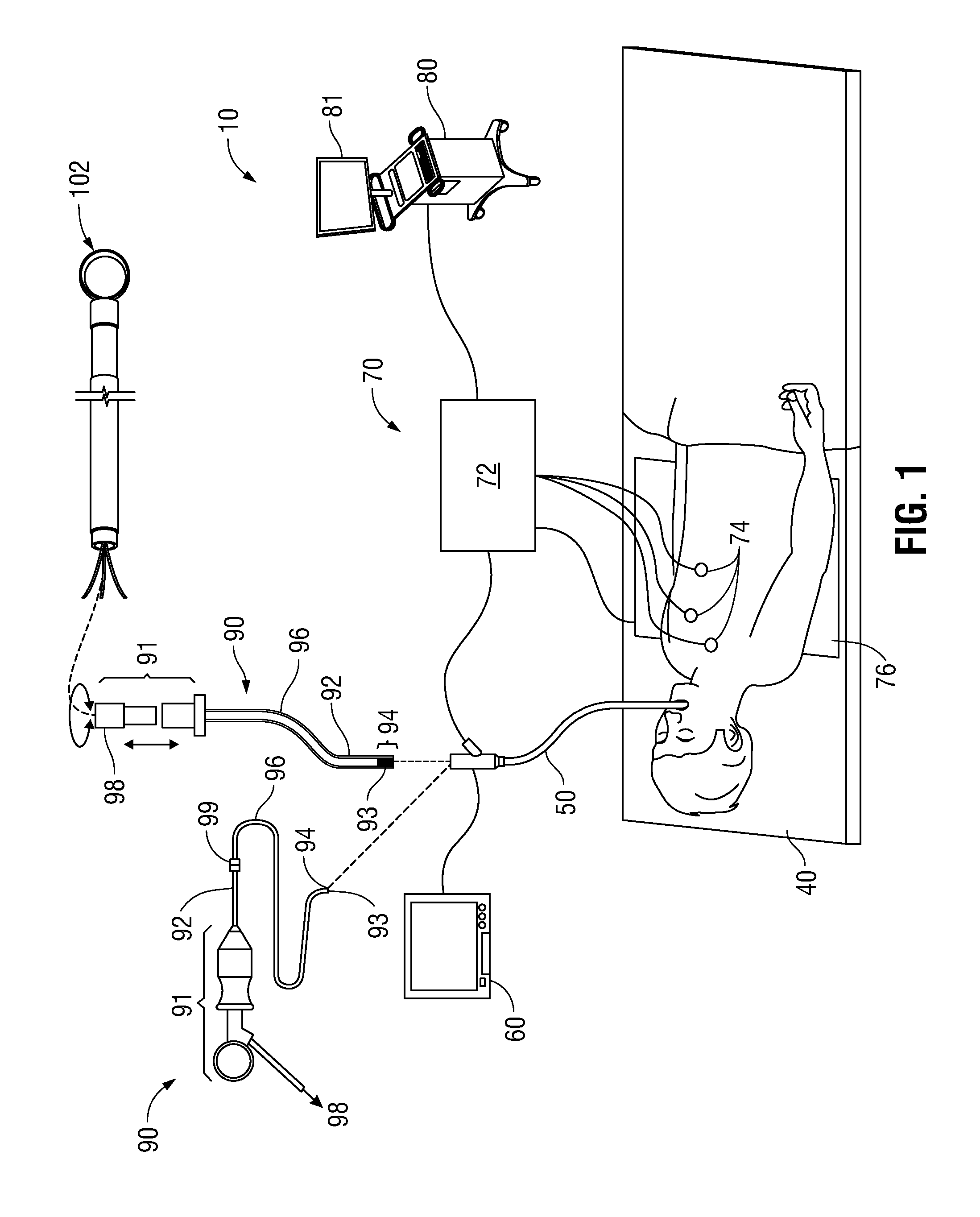
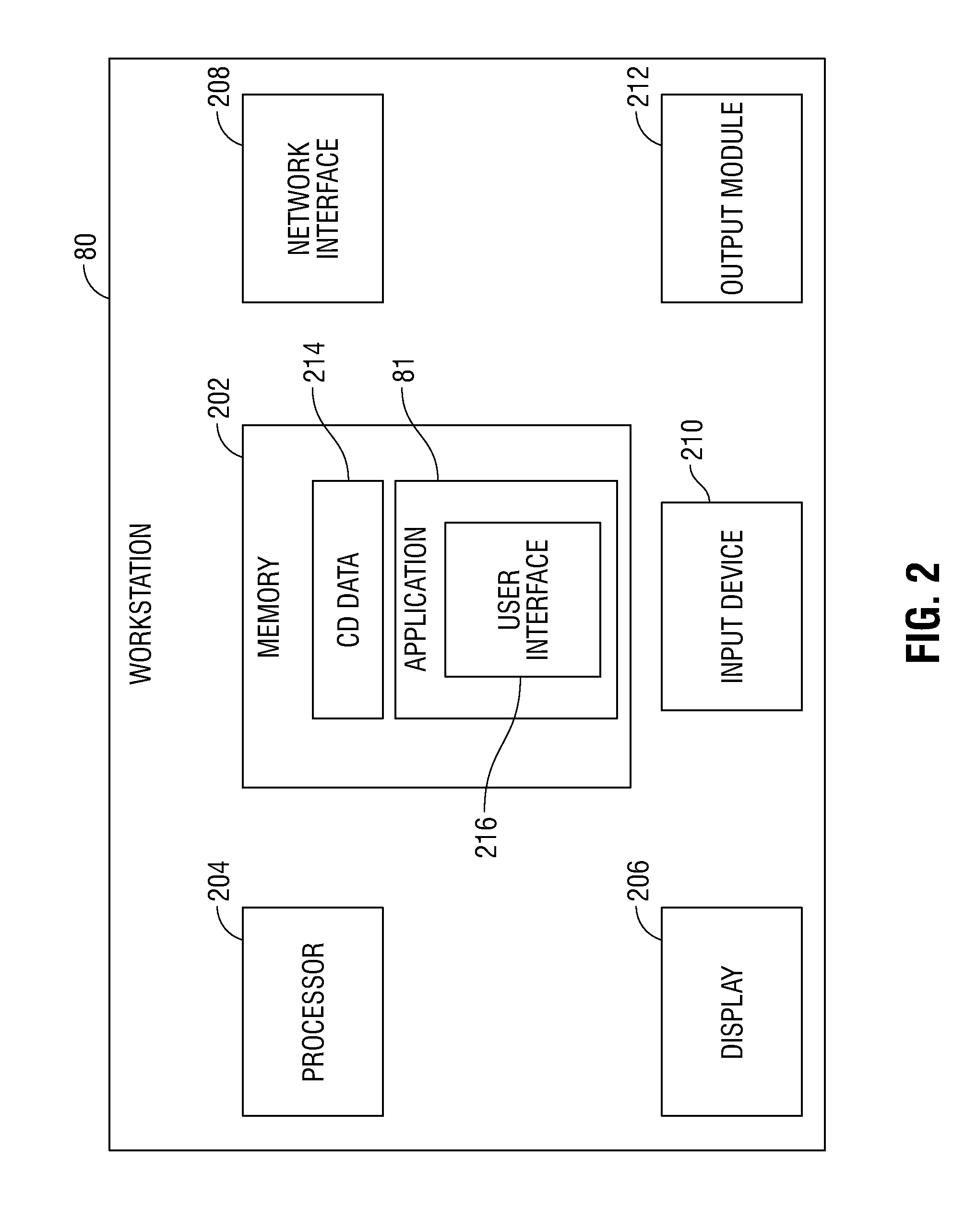
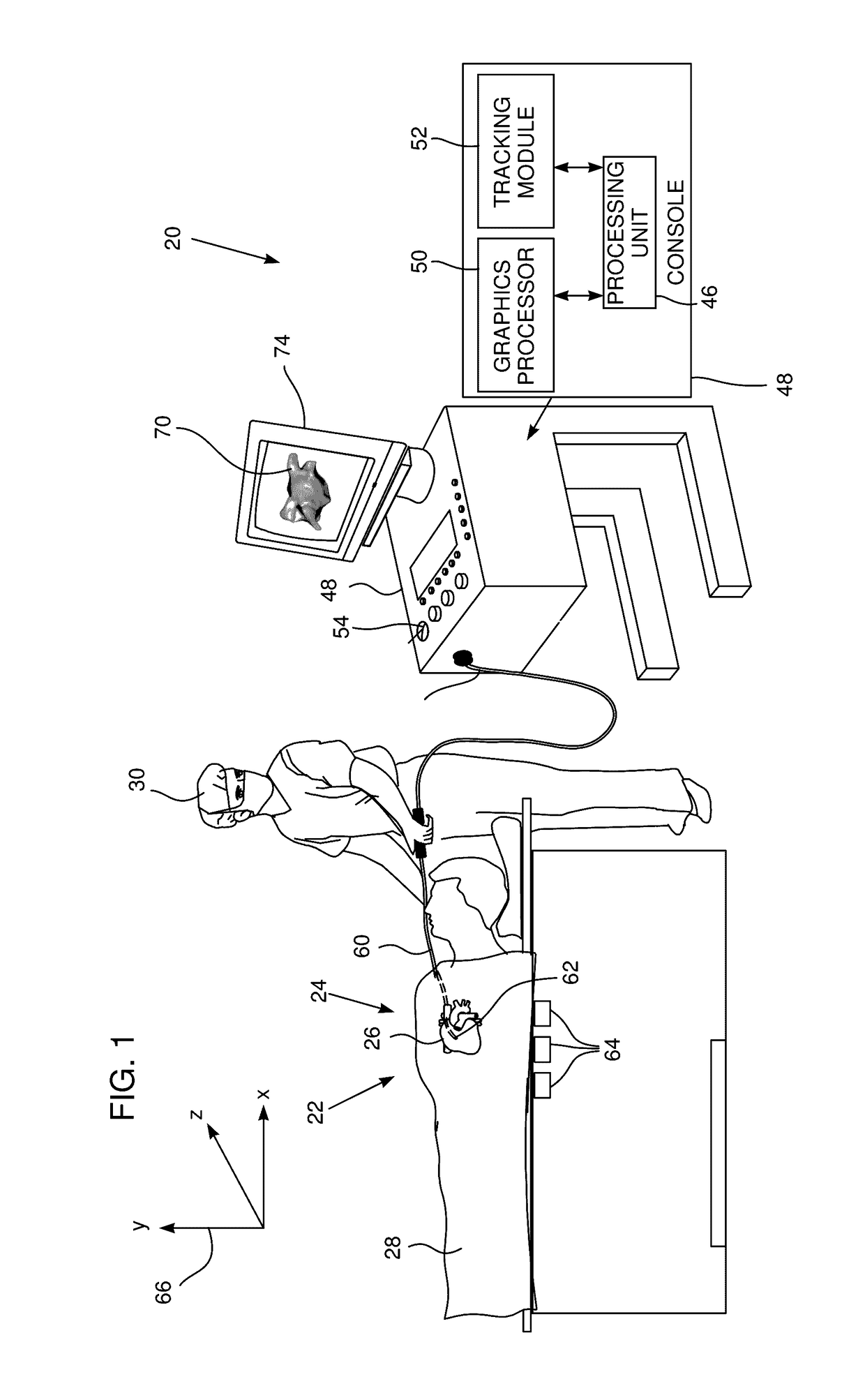
Methods and systems for navigating to a target through a patient's bronchial tree are disclosed including a bronchoscope, a probe insertable into a working channel of the bronchoscope including a location sensor, and a workstation in operative communication with the probe and the bronchoscope the workstation including a user interface that guides a user through a navigation plan and is configured to present a three-dimensional (3D) view for displaying a 3D rendering of the patient's airways and a corresponding navigation plan, a local view for assisting the user in navigating the probe through peripheral airways of the patient's bronchial tree to the target, and a target alignment view for assisting the user in aligning a distal tip of the probe with the target.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Joy-stick like graphical user interface to adjust 3D cross sectional plane in 3D volume
ActiveUS20070291000A1Facilitates userProcess controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsJoystick
Methods for a joy-stick graphical control in 3D space are disclosed. 3D data are rendered with a certain orientation in a 3D rendering space within a region of a 2D screen. One or more cross sectional views of the 3D data are rendered in the 3D rendering space where the cross sectional views are derived based on corresponding one or more 3D planes cutting through the 3D data at a 3D location. On one 3D plane, a joy-stick control is rendered in the 3D space at a pose determined based on the joy stick.
Owner:EDDA TECH
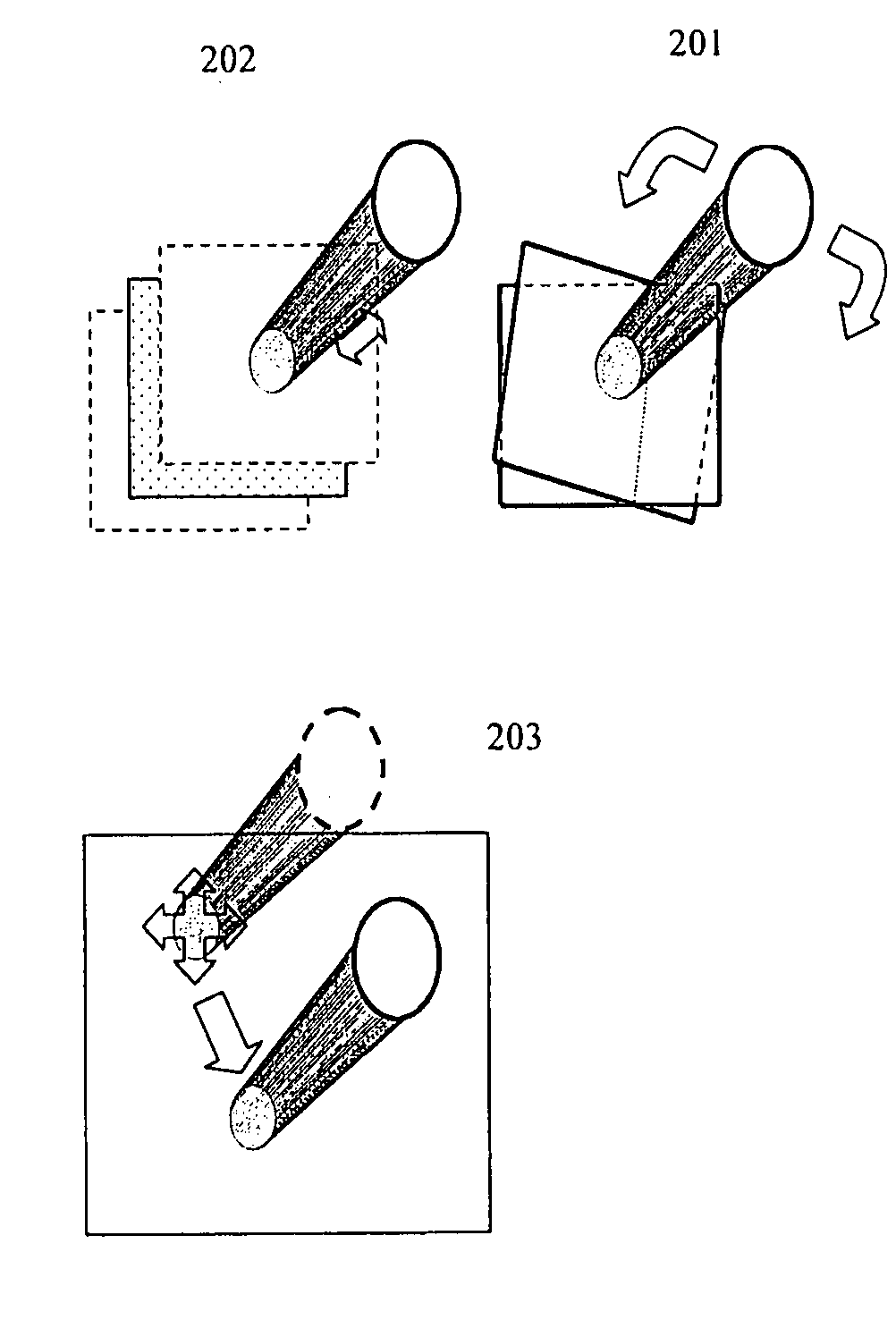
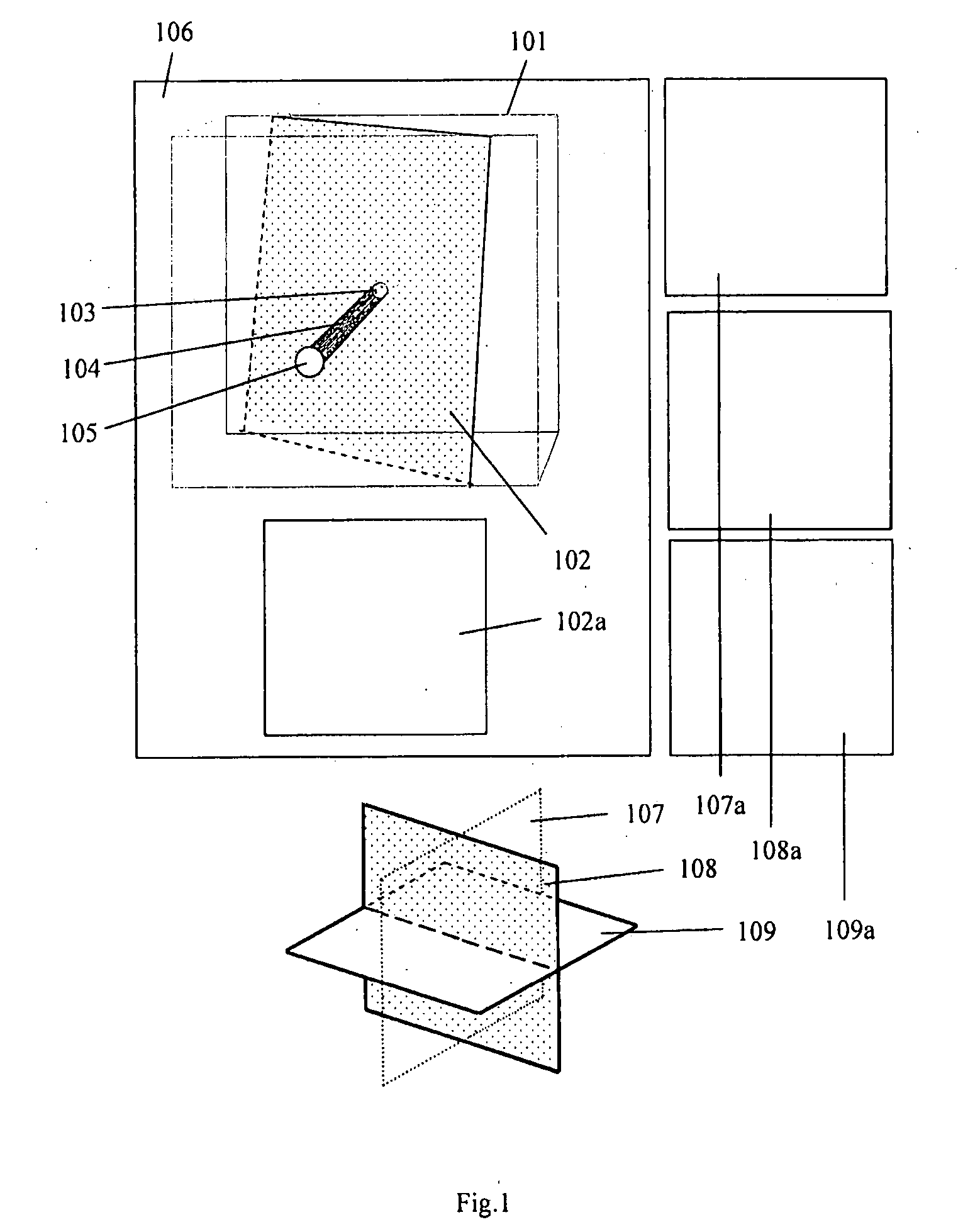
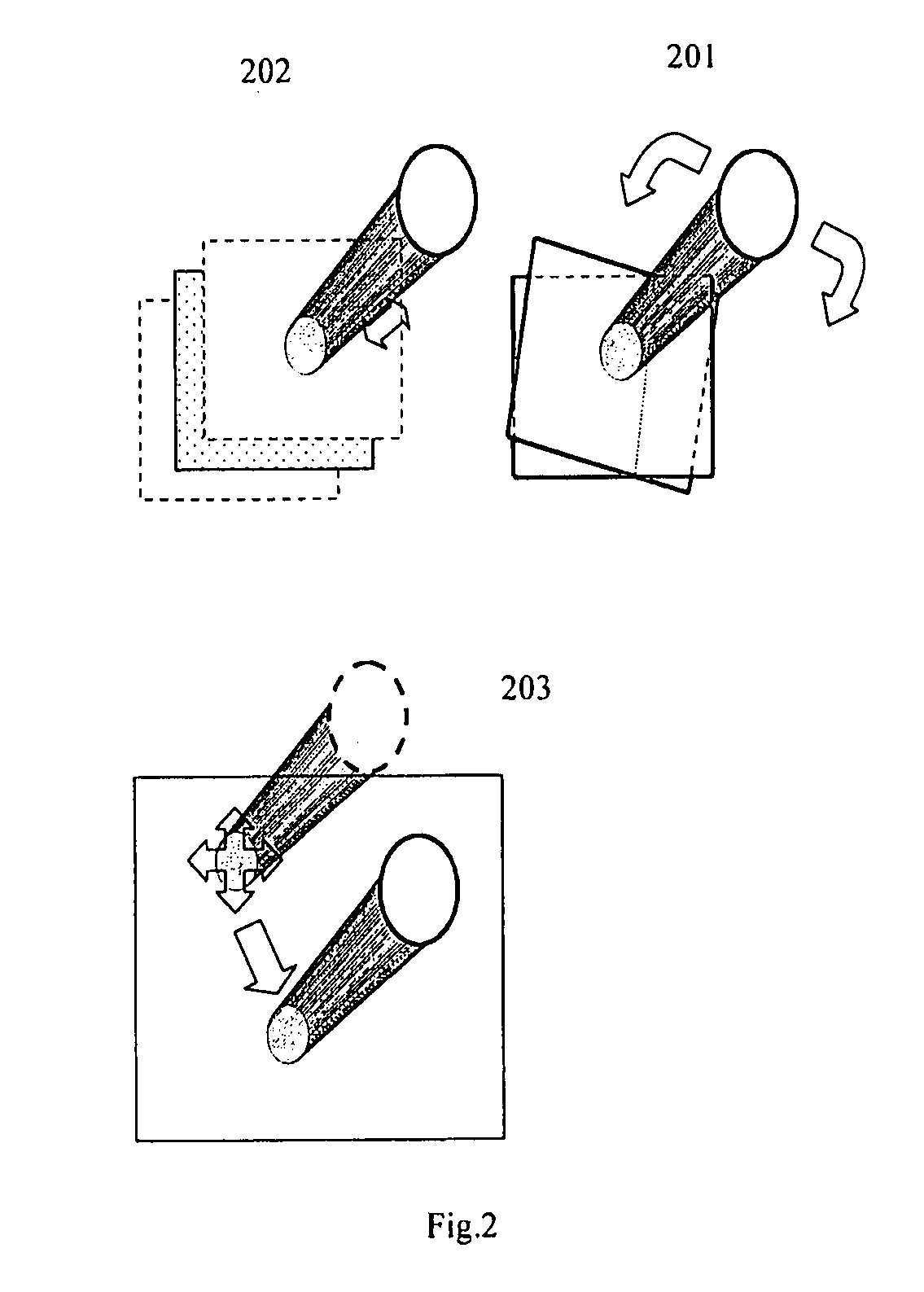
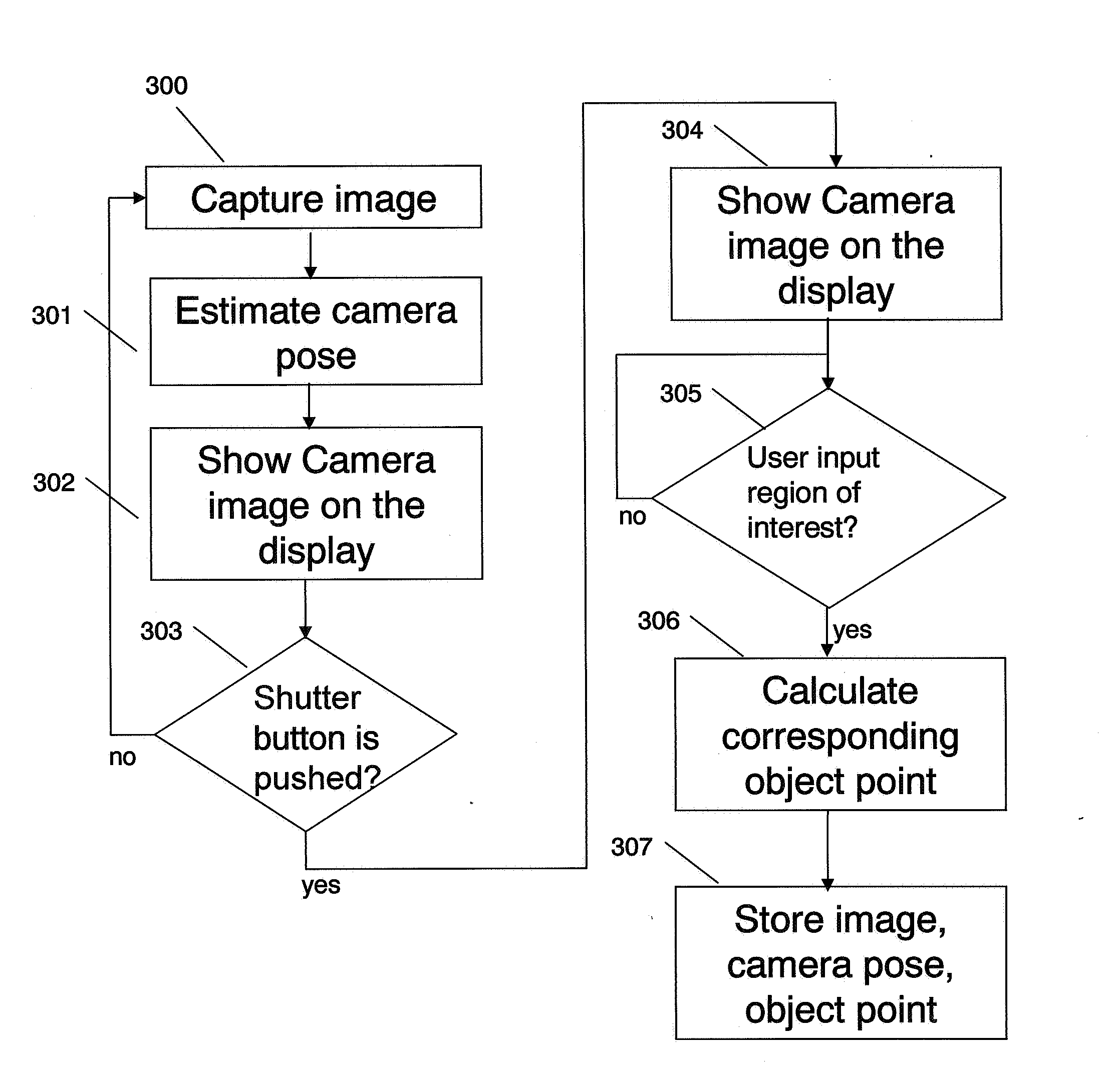
Ar navigation for repeat photography and difference extraction
Systems and methods for repeat photography and difference extraction that help users take pictures from the same position and camera angle as earlier photos. The system automatically extracts differences between the photos. Camera poses are estimated and then indicators are rendered to show the desired camera angle, which guide the user to the same camera angle for repeat photography. Using 3D rendering techniques, photos are virtually projected onto a 3D model to adjust them and improve the match between the photos, and the difference between the two photos are detected and highlighted. Highlighting the detected differences helps users to notice the differences.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
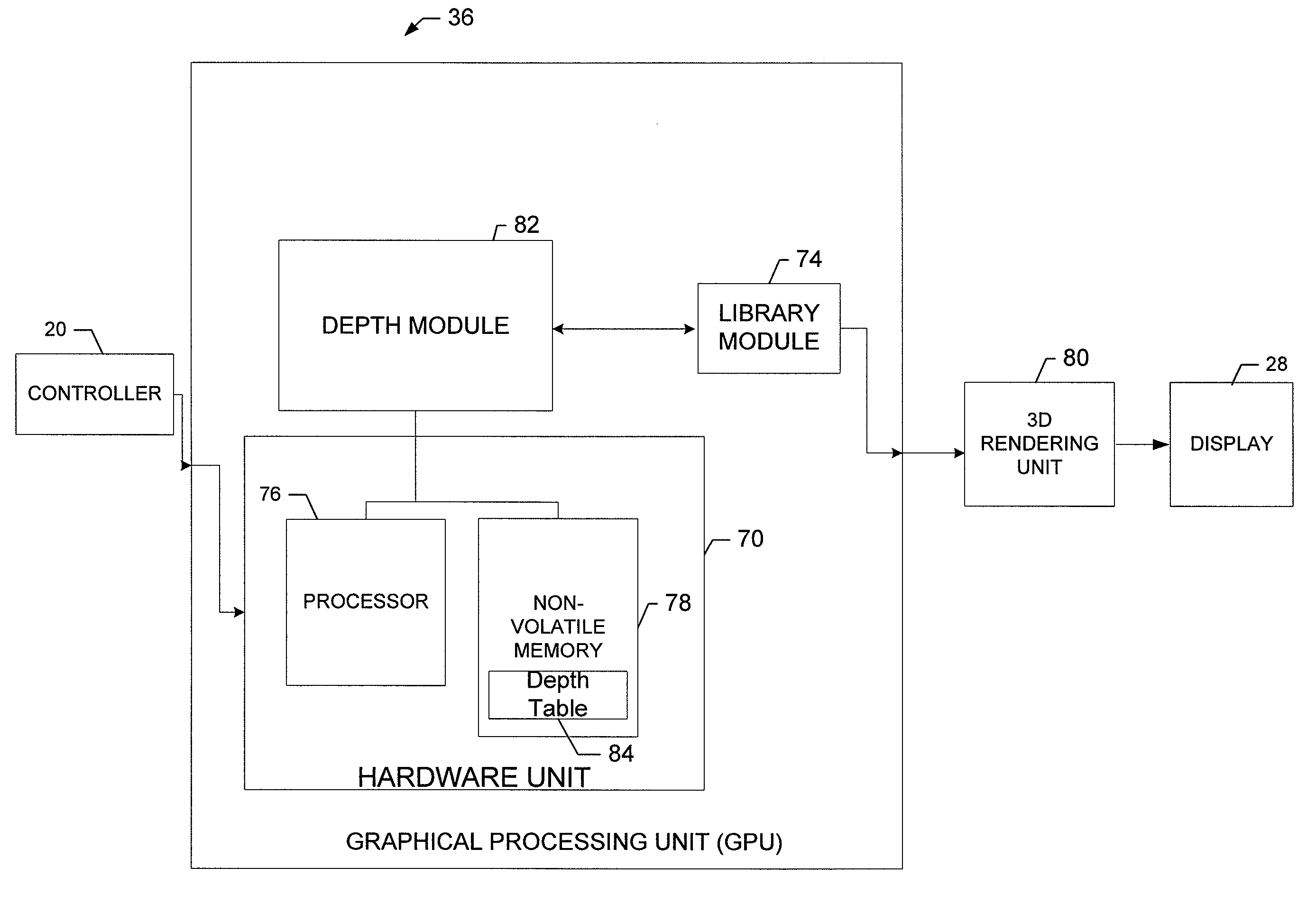
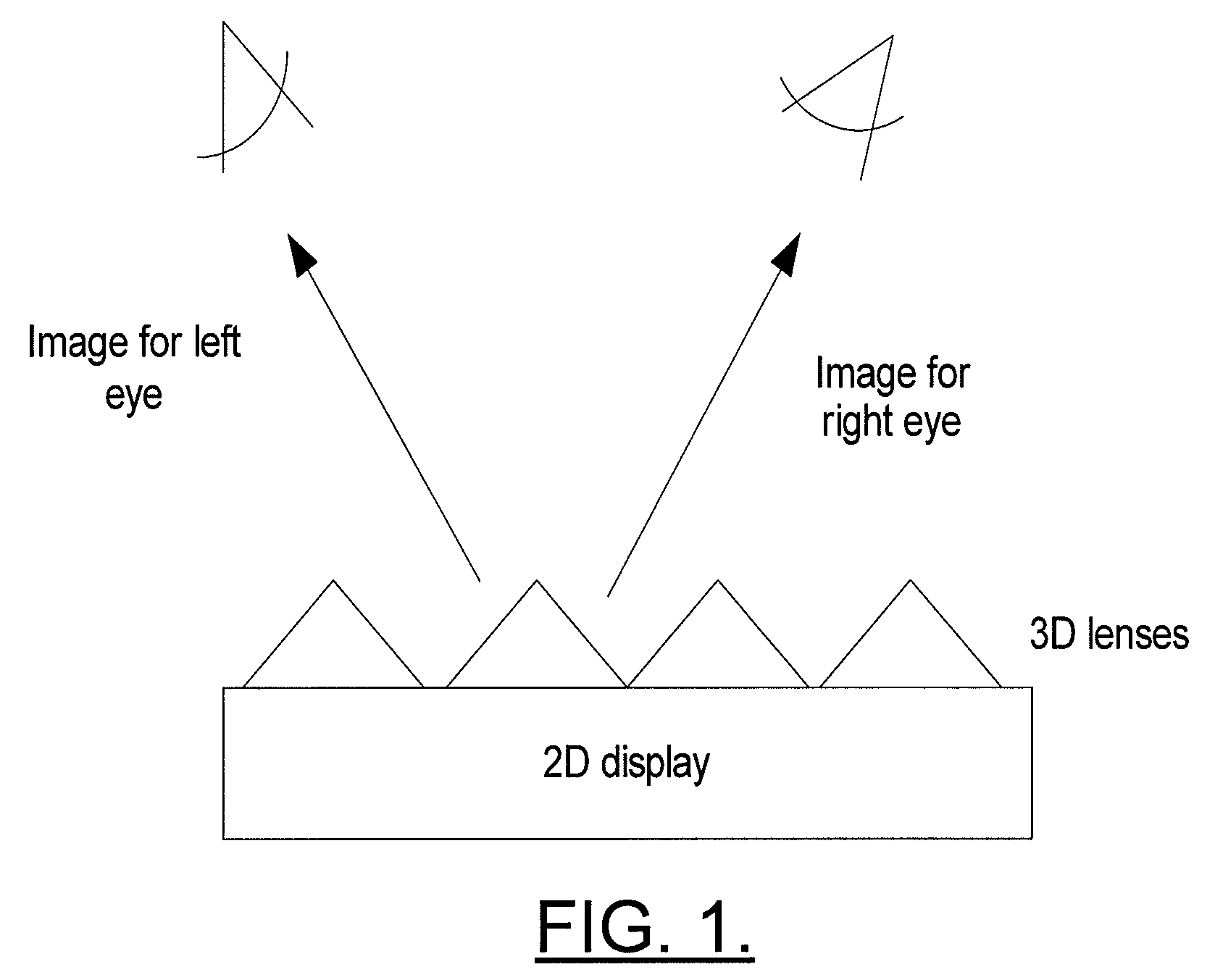
Method, apparatus and a computer program product for utilizing a graphical processing unit to provide depth information for autostereoscopic display
InactiveUS20090002368A1Reduce processing loadReduce processSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingGraphics3d image
A device for generating a 3D image based on 2D graphical content of an image and depth information (i.e., Z-map) to be displayed on a display includes an application processor, a graphical processing unit (GPU), a 3D rendering unit and a display. The application processor is capable of sending 2D graphical content to the GPU, which is stored in memory. The GPU also includes a depth table having predefined depth information corresponding to the 2D graphical content. The GPU includes a depth module which monitors or identifies the 2D graphical content and requests a graphics library to paint a corresponding area in the Z-map that has the same size and position in the Z-map as that of the 2D graphical content. The GPU sends the 2D graphical content and the painted Z-map to a 3D rendering unit which creates a 3D image to be shown on a display.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Device and method for outputting indoor soft decoration 3D (three-dimensional) effect drawing designs
InactiveCN102609584ALower requirementReduce data transfer volumeSpecial data processing applicationsLeading edgeComputer graphics (images)
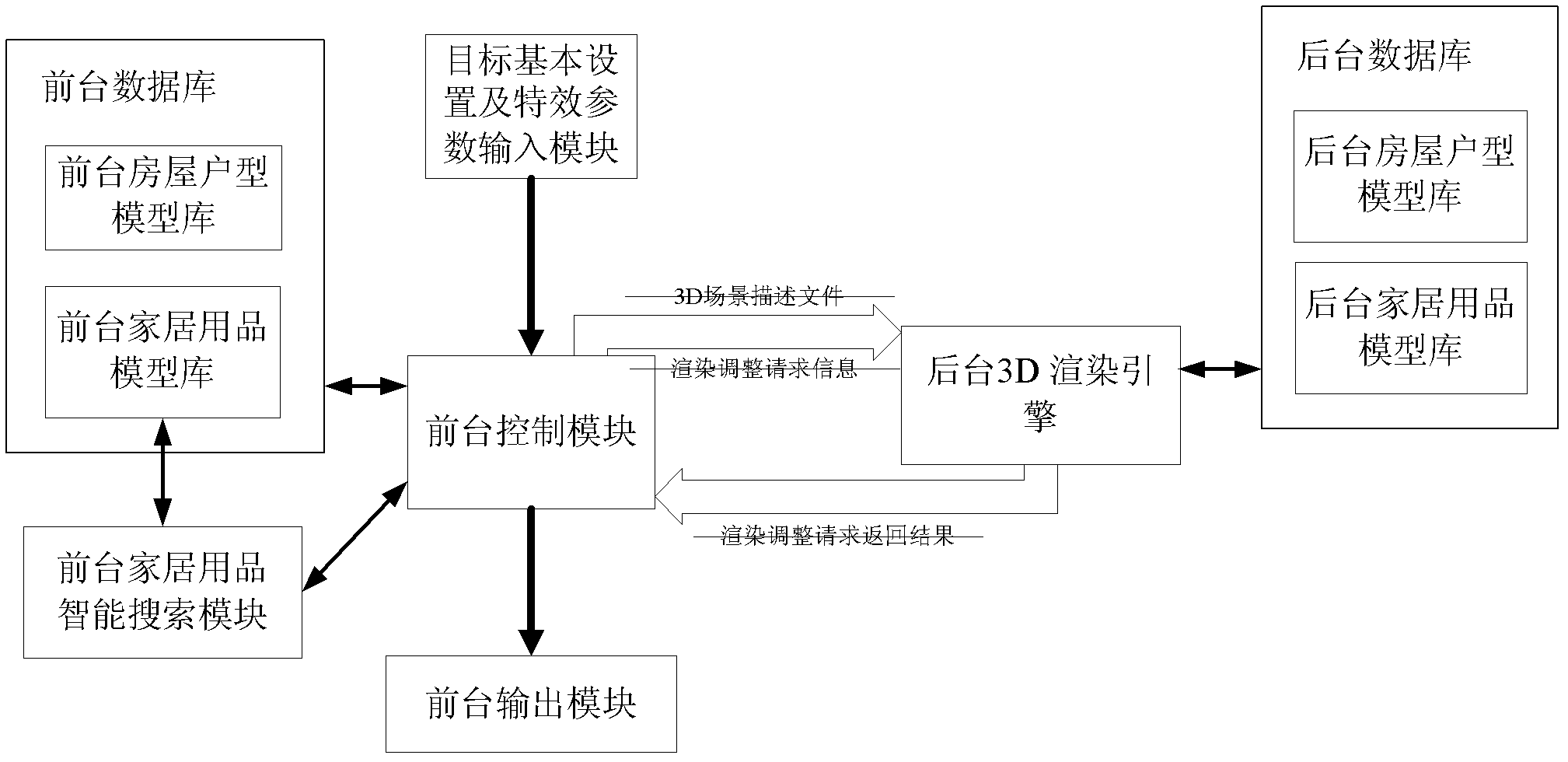
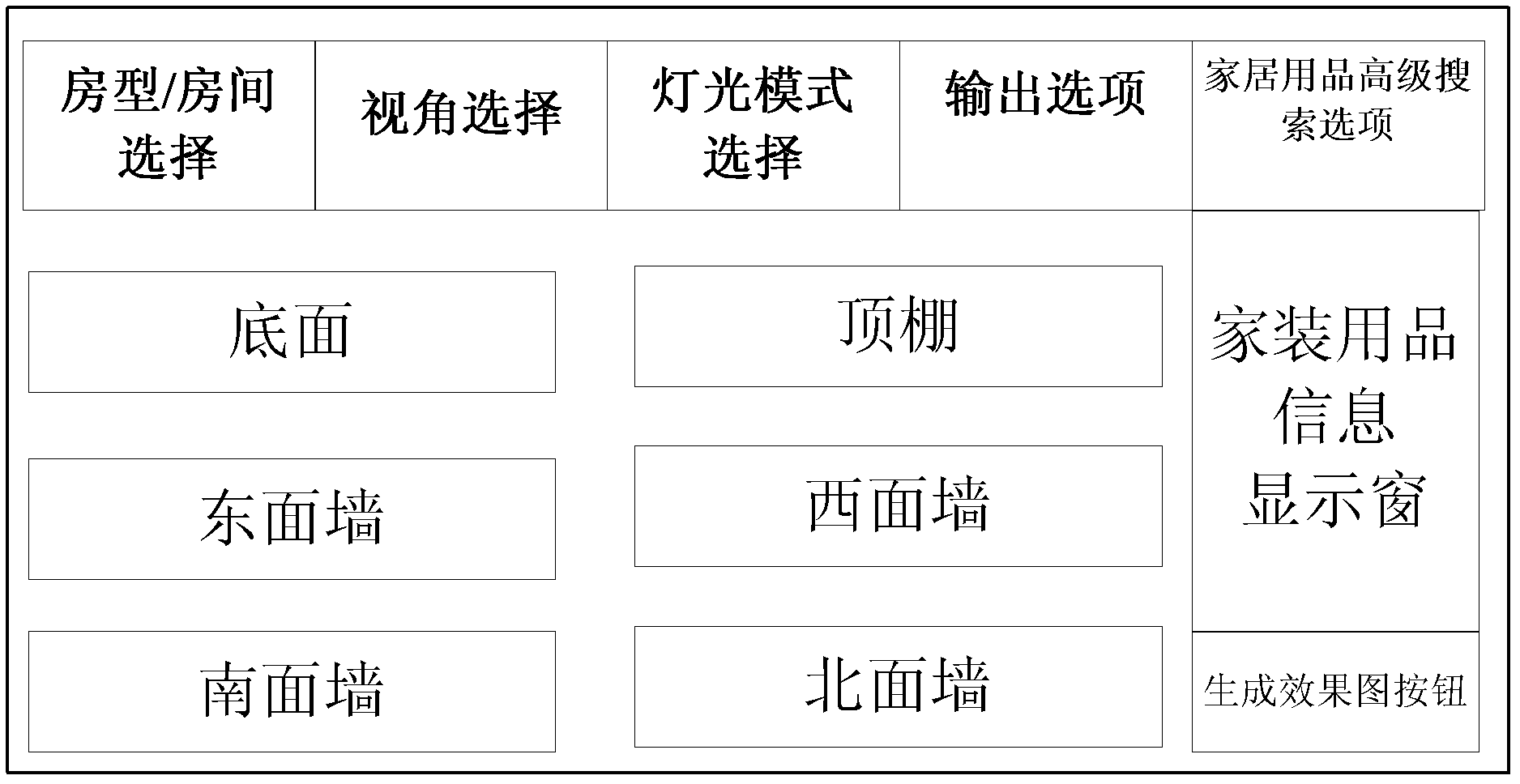
The invention relates to a device and a method for outputting indoor soft decoration 3D (three-dimensional) effect drawing designs. The method includes the steps: splitting adjustment output of a 3D effect drawing into two steps of preview of 2D (two-dimensional) six walls and final generation of a 3D scene by arranging a foreground input / output module, a foreground control module, a foreground database, a background database and a background 3D rendering engine, utilizing the foreground database with small data size as a leading edge for preliminary interaction with a user, and then invoking a background 3D model with large data size to generate the 3D effect drawing after adjustment is completed. By the aid of the method, the data transmission quantity during data interaction of a foreground and a background is decreased, requirements on foreground terminal hardware are lowered, operation is accelerated, and the method is particularly applicable to wireless or remote application.
Owner:孙华良
3-D rendering texture caching scheme
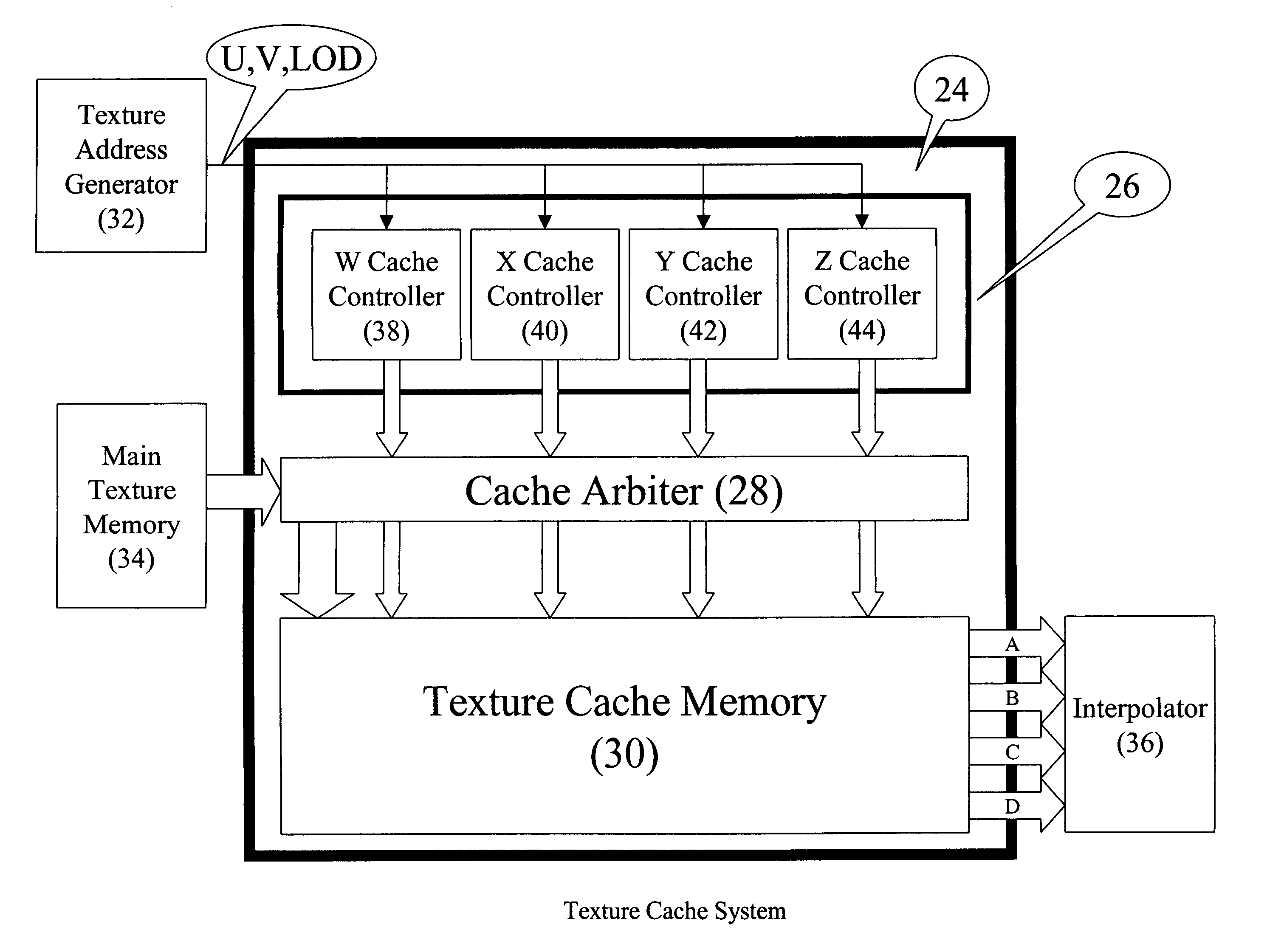
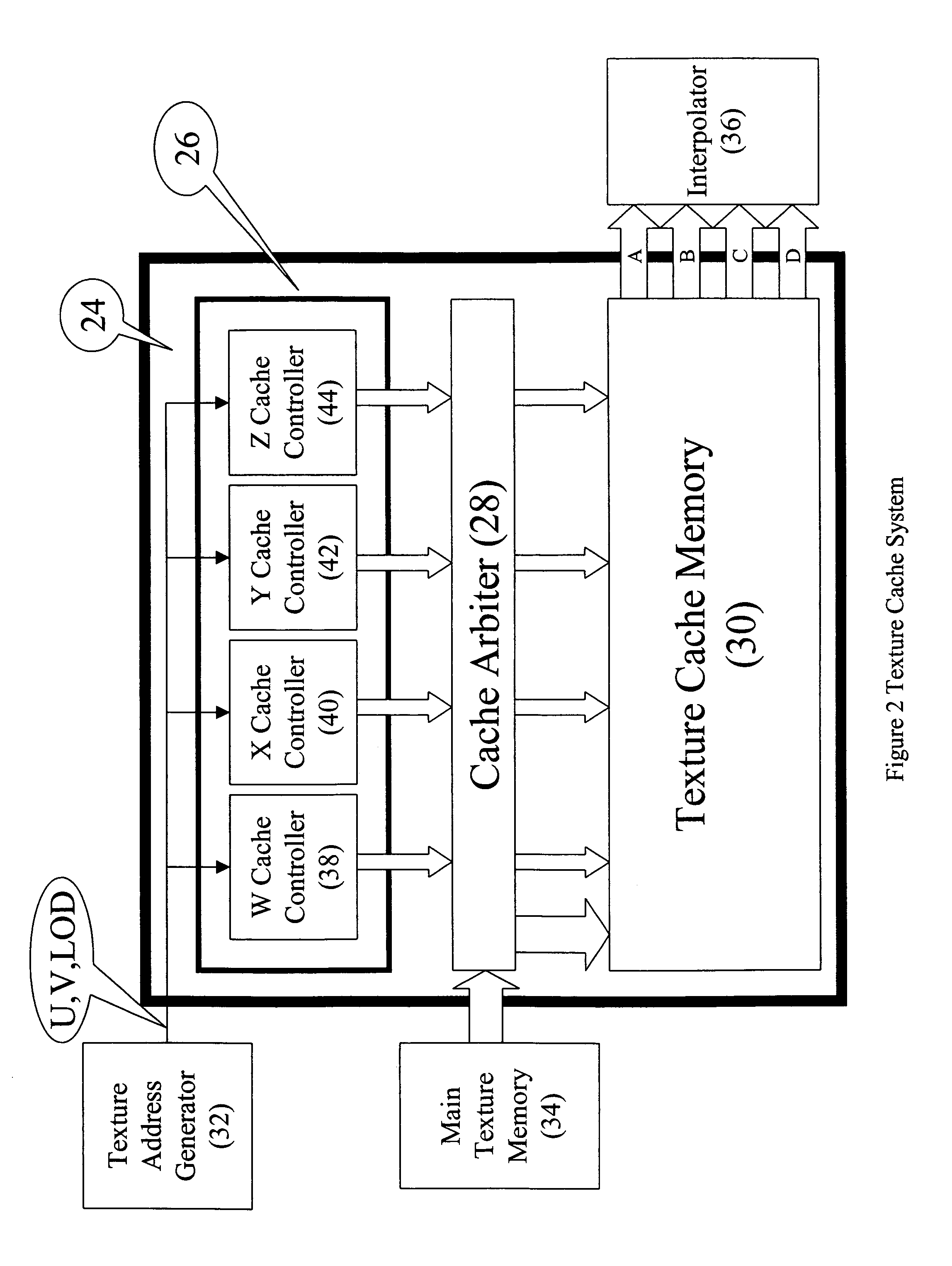
InactiveUS7050063B1Improve efficiencyEliminate significant numberMemory adressing/allocation/relocationImage memory managementComputational scienceParallel computing
A 3D rendering texture caching scheme that minimizes external bandwidth requirements for texture and increases the rate at which textured pixels are available. The texture caching scheme efficiently pre-fetches data at the main memory access granularity and stores it in cache memory. The data in the main memory and texture cache memory is organized in a manner to achieve large reuse of texels with a minimum of cache memory to minimize cache misses. The texture main memory stores a two dimensional array of texels, each texel having an address and one of N identifiers. The texture cache memory has addresses partitioned into N banks, each bank containing texels transferred from the main memory that have the corresponding identifier. A cache controller determines which texels need to be transferred from the texture main memory to the texture cache memory and which texels are currently in the cache using a least most recently used algorithm. By labeling the texture map blocks (double quad words), a partitioning scheme is developed which allow the cache controller structure to be very modular and easily realized. The texture cache arbiter is used for scheduling and controlling the actual transfer of texels from the texture main memory into the texture cache memory and controlling the outputting of texels for each pixel to an interpolating filter from the cache memory.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for medical ultrasound navigation user interface
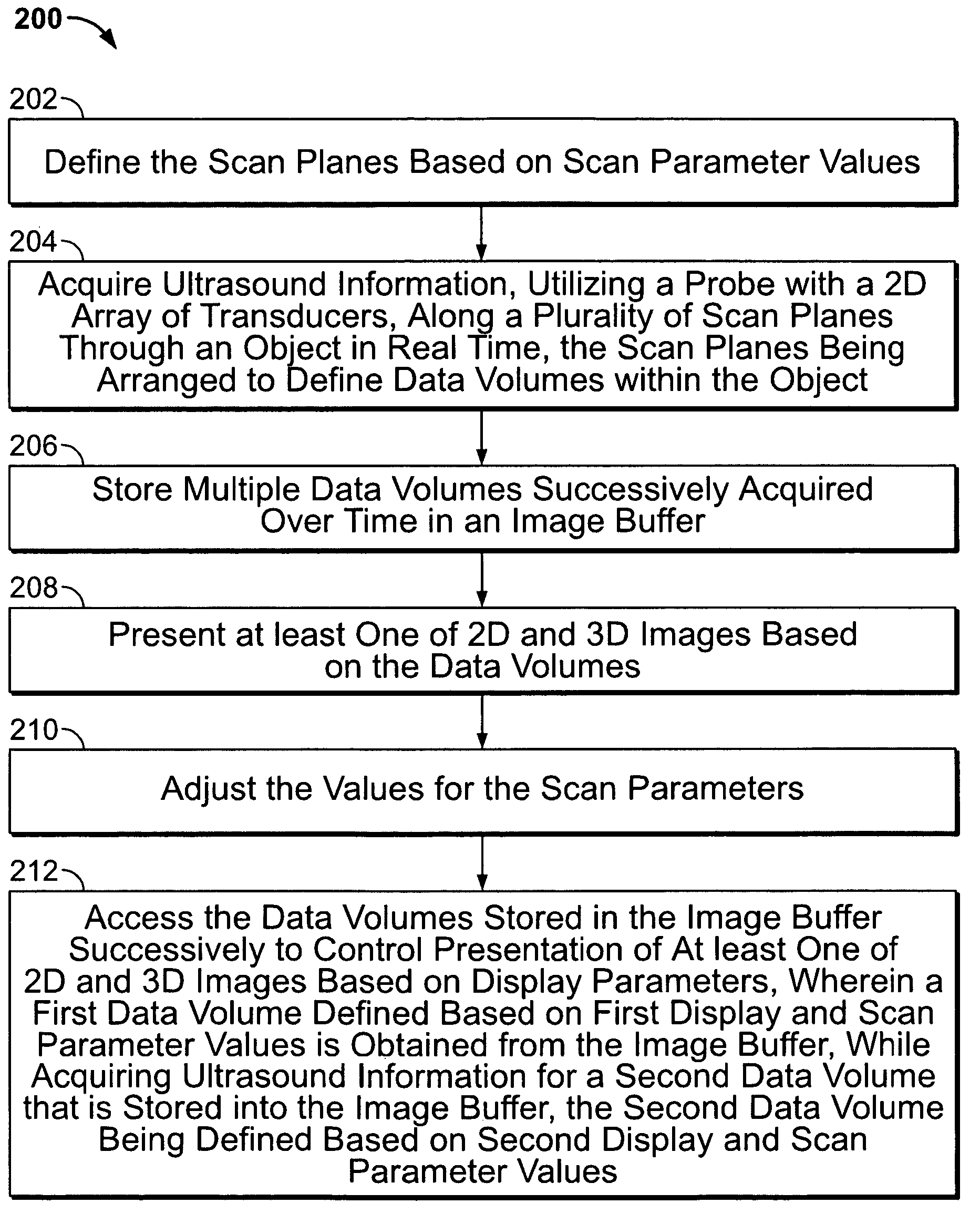
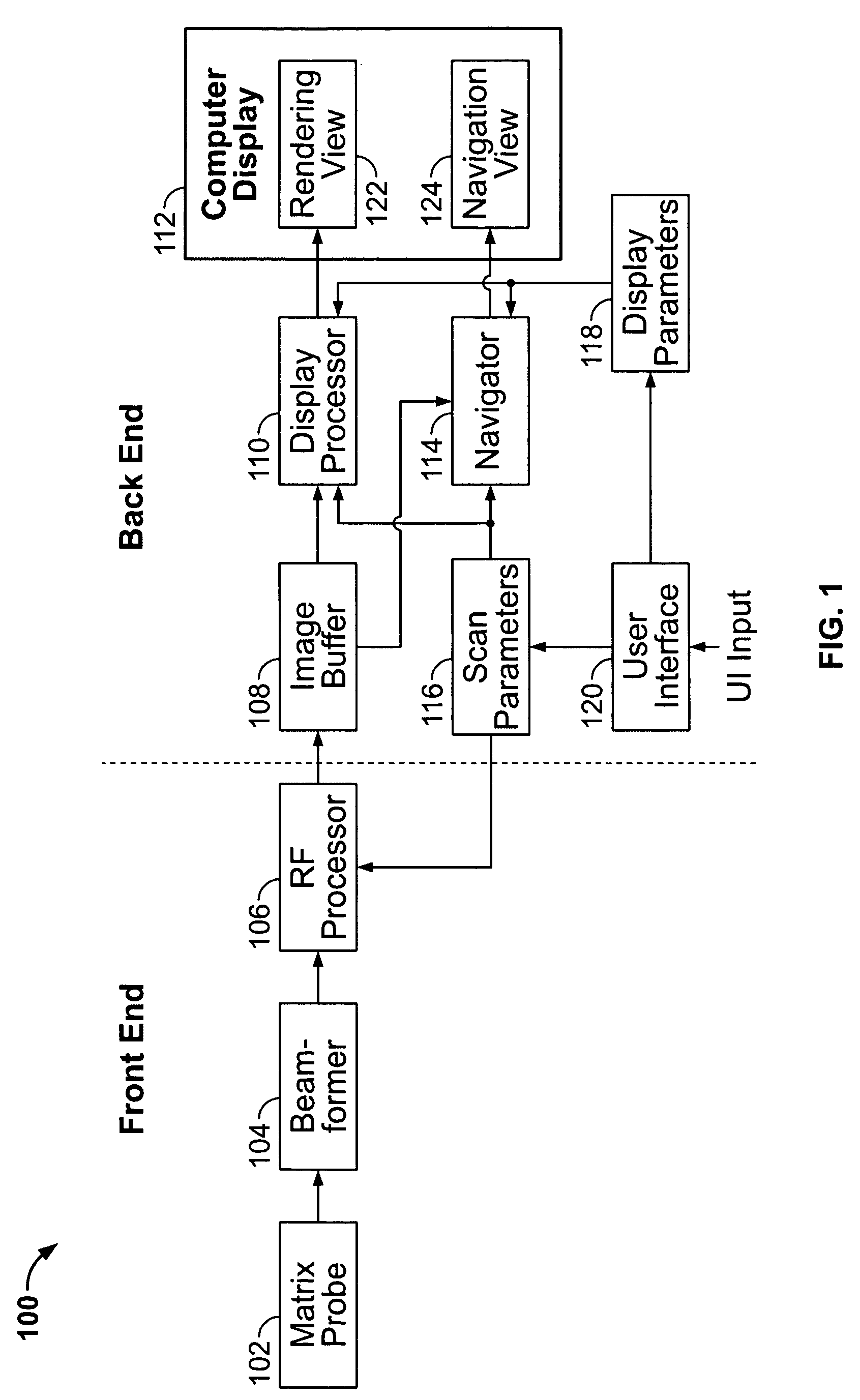
ActiveUS20050283079A1Multiple-port networksHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesUltrasonographySonification
In one embodiment, an ultrasound system is provided that includes a probe having a 2D array of transducers for acquiring ultrasound information along a plurality of scan lines through an object in real time. The scan lines are arranged to define volumetric data corresponding to a volume of interest (VOI) in a subject or patient. One such VOI may include the human heart or some portion of the human heart. The system includes a beamformer configured with scan parameter values that define the scan lines. An image buffer stores multiple data volumes acquired over time that are successively retrieved and processed by a display processor. The display processor accesses the data volumes stored in the image buffer successively to control generation of at least one of 2D and 3D renderings based on display parameters, wherein the display processor obtains from the image buffer a first data volume defined based on first scan parameter values, while the probe acquires ultrasound information for a second data volume that is entered into the image buffer. The second data volume is defined based on second scan parameter values. A navigation view presents in real time the renderings generated by the display processor with their corresponding 3D orientation. A navigator is provided that controls the display of the navigation view in real time such that, as the user adjusts a display parameter value to change a view plane, images presented in the navigation view are updated to reflect the view plane. A user interface is provided for adjusting the scan and display parameter values.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
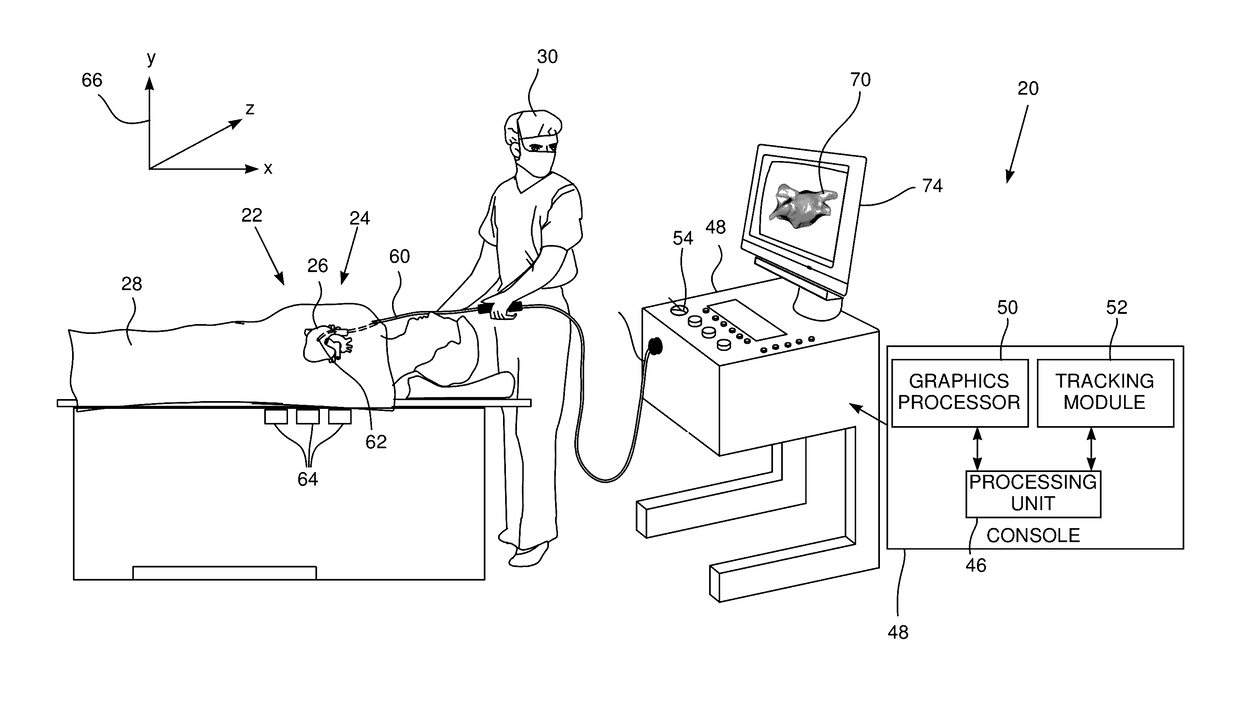
System for three-dimensional medical instrument navigation
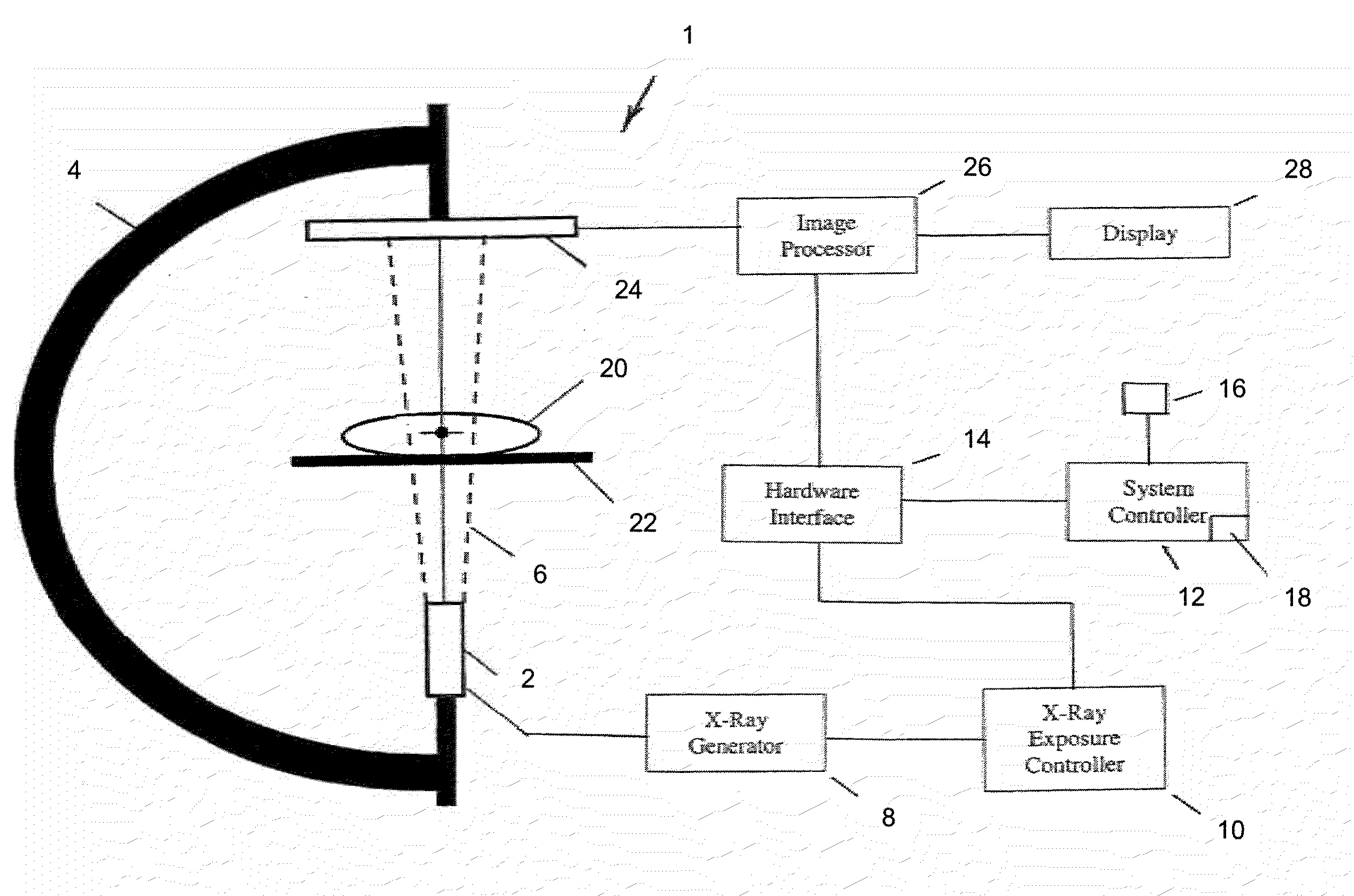
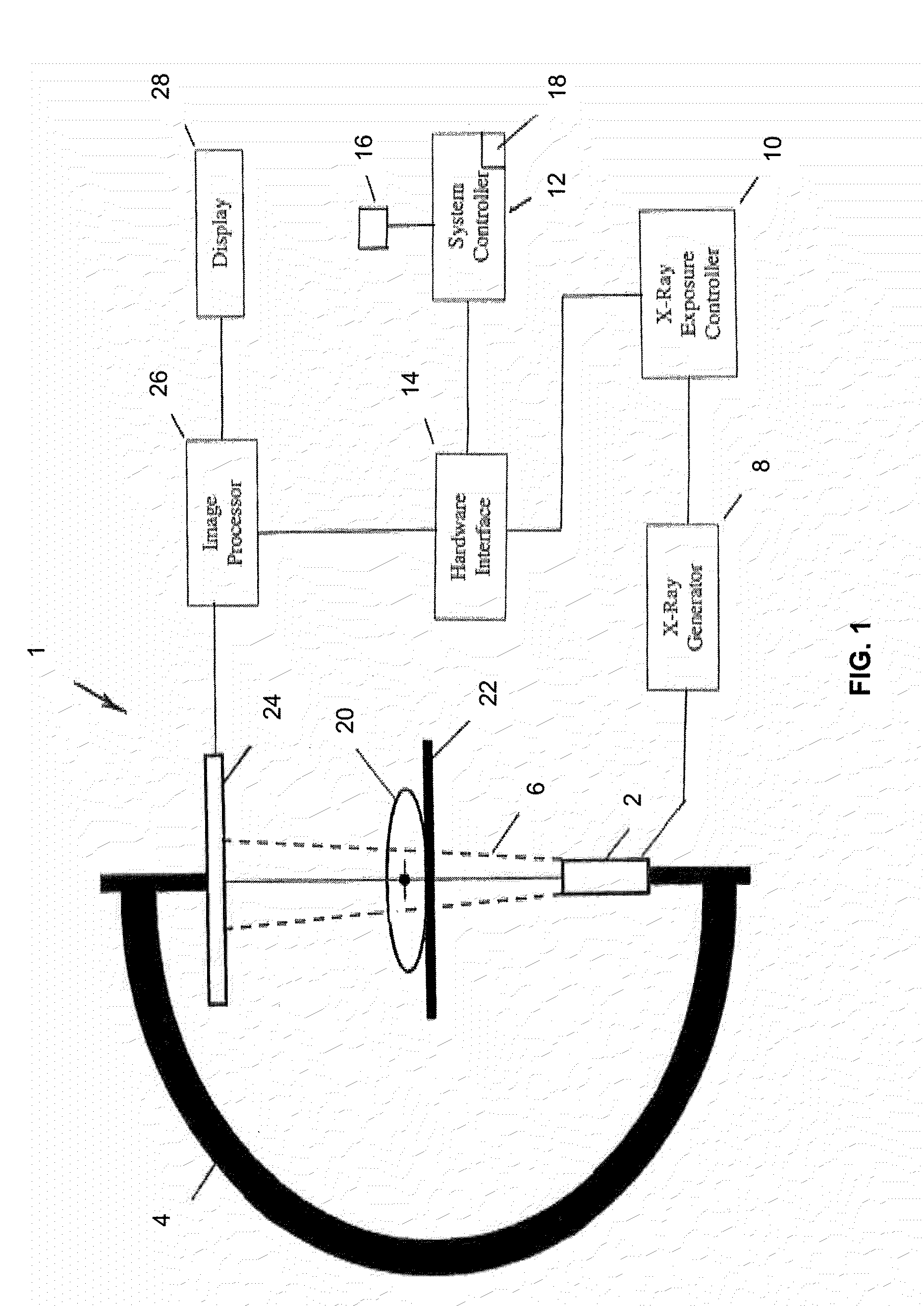
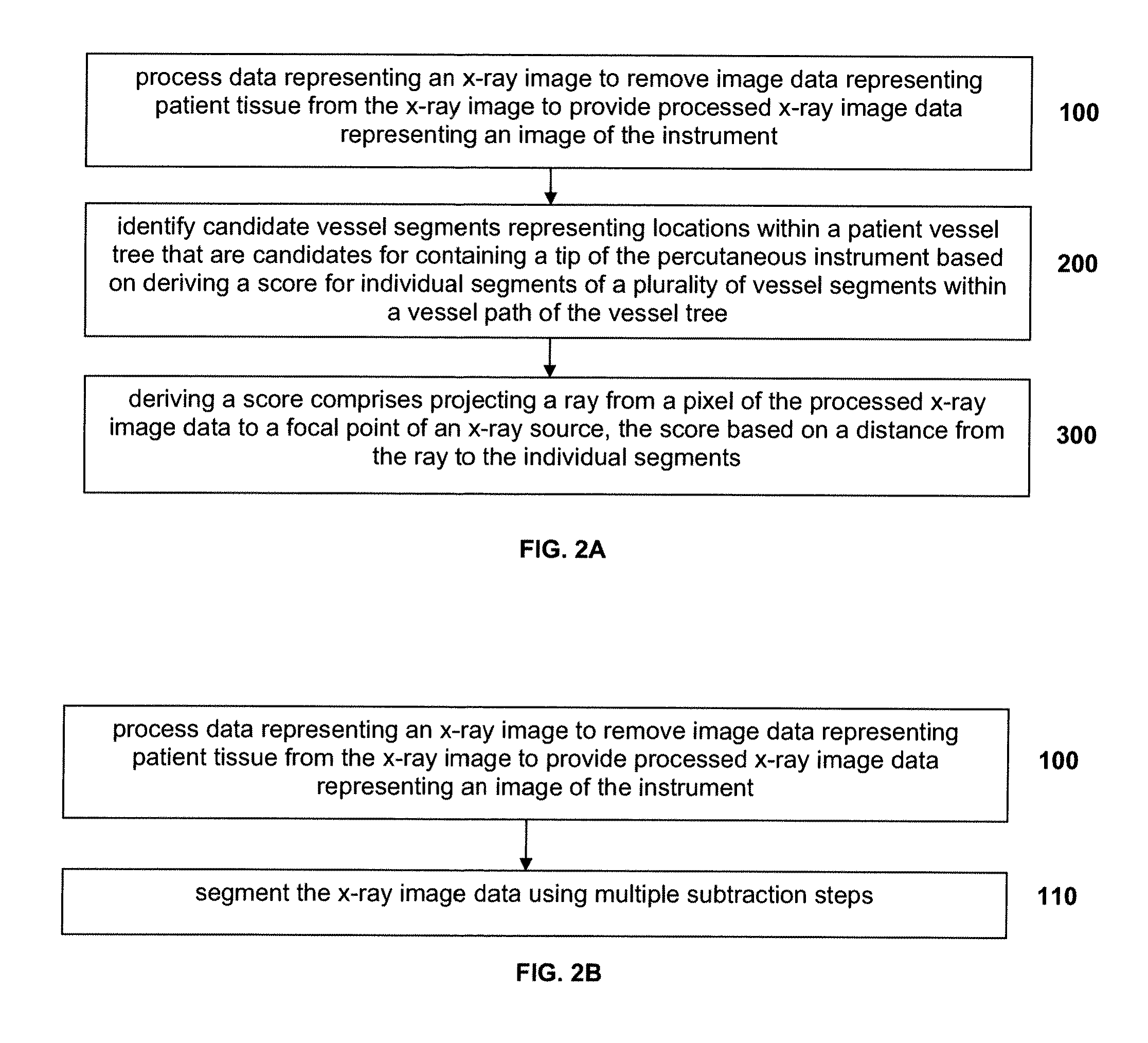
InactiveUS20090279767A1Image enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluoroscopic imageFluorescence
A system and method are disclosed for reconstructing an instrument in 3 dimensions for use during interventional medical procedures to provide enhanced instrument visualization with respect to a patient's vasculature. A patient vessel tree volume is co-registered with a live fluoroscopic image of a percutaneously-inserted instrument, such as a guidewire. The fluoroscopic image is segmented to eliminate images of surrounding tissue and to retain the guidewire image. The black pixels of the image are backprojected to the focal point of the x-ray source, through the co-registered vessel tree. The vessel tree is divided into segments that are scored based on proximity to the backprojected black pixels. Candidate instrument-containing vessel paths are identified based on the scores of the segments, and errant candidate vessel paths are eliminated to produce a refined list of candidate paths. Thresholding and visualization are performed to further refine the candidate vessel paths. 3D curve fitting is used to reconstruct an image of the instrument along with a 3D rendering of the final vessel path.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
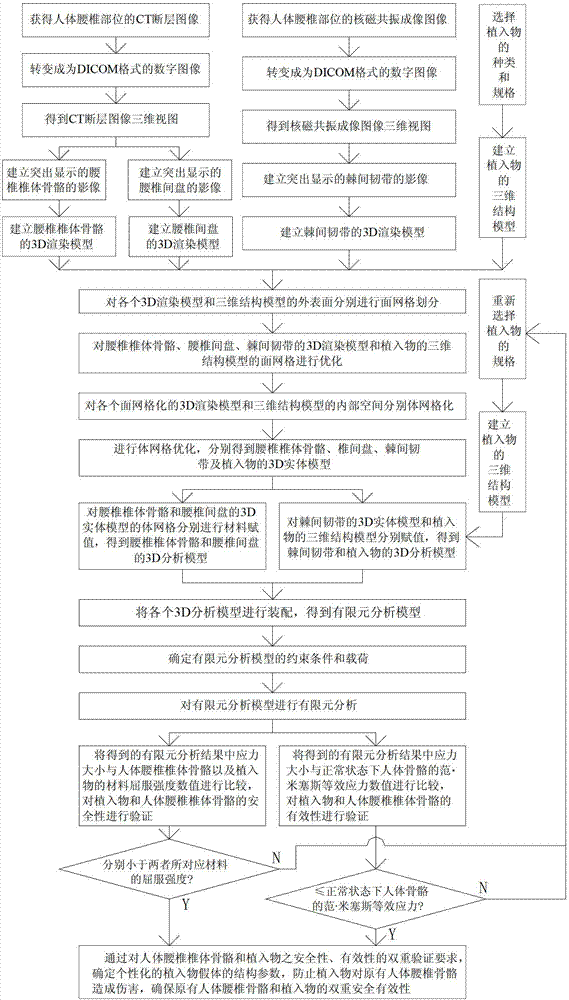
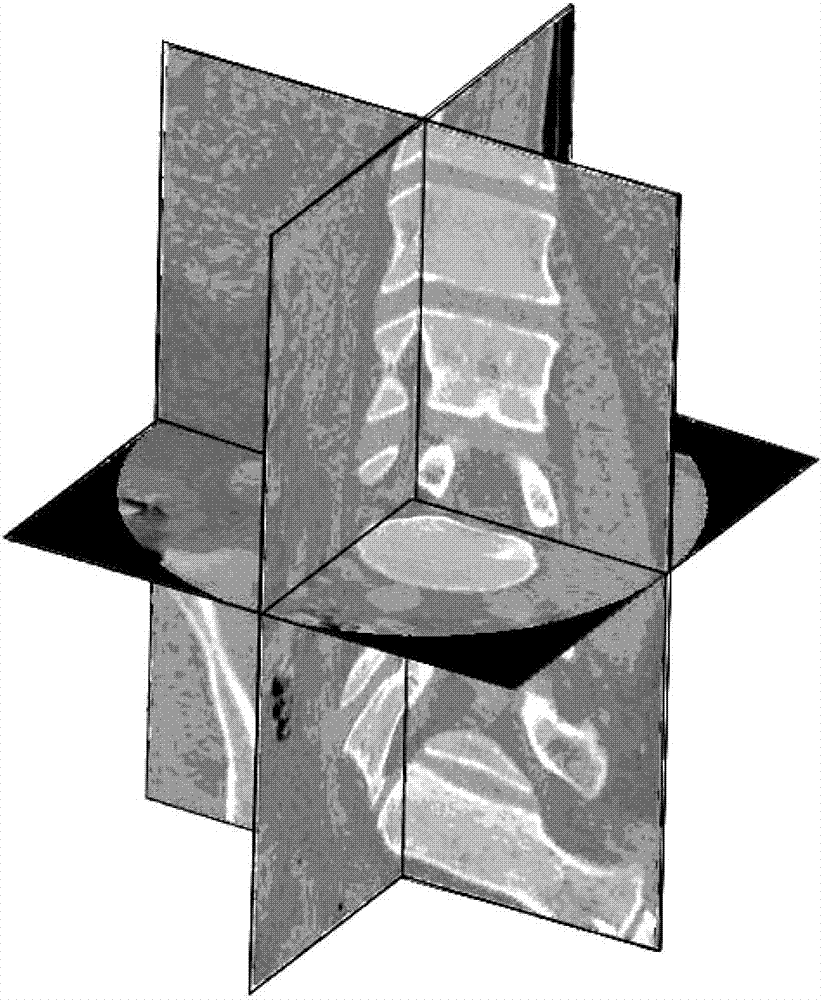
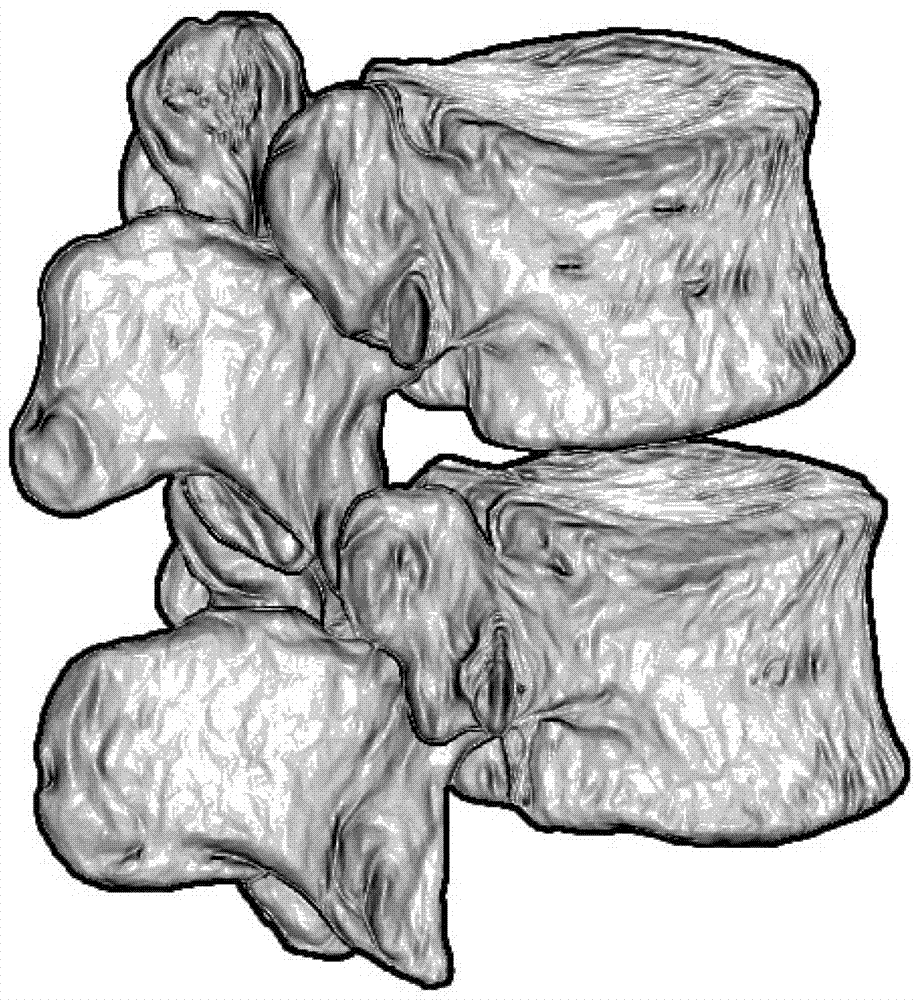
Double safety and effectiveness inspection method of human lumbar bone and implant
InactiveCN102920537AEnsure safetyGuaranteed validityJoint implants3D modellingHuman bodyManufacturing cost reduction
The invention provides a double safety and effectiveness inspection method of human lumbar bone and implant, and belongs to the field of medicine. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a 3D (three-dimensional) rendering model of lumbar body bone, lumbar disc and interspinous ligament by a 3D reconstruction technology; performing 3D grid division to the 3D rendering model, and giving attributes of a heterogeneous material to the 3D rendering model; performing 3D modeling to an implant; assembling the lumbar body bone, the lumbar disc, the interspinous ligament and the implant, and analyzing stress and strain of the assembly by adopting uniformly distributed nodal load through a finite element analysis method; simulating visible finite element analysis by a computer before the implant is implanted into a human body. Therefore, the verification requirement to bone and implant double safety and effectiveness can be fulfilled, the damage of the implant to original human lumbar bones can be prevented, double safety and effectiveness of the bones and implant can be guaranteed, the manufacture cost can be effectively reduced along with convenience and quickness, and individual and industrial manufacturing of a human lumbar bone implant can be realized. The method is applicable in the field of implant stress-strain analysis in the orthopedics department.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
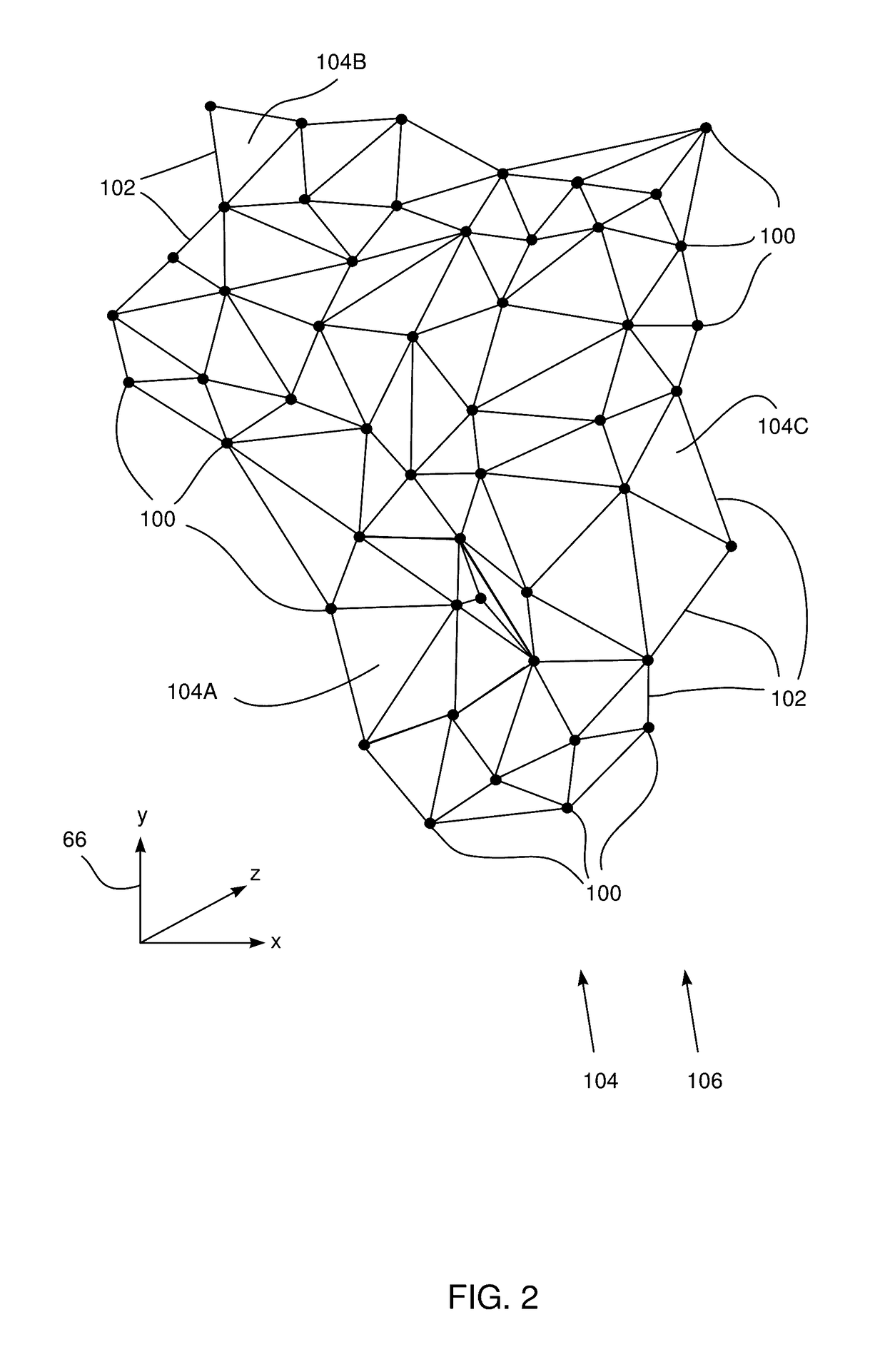
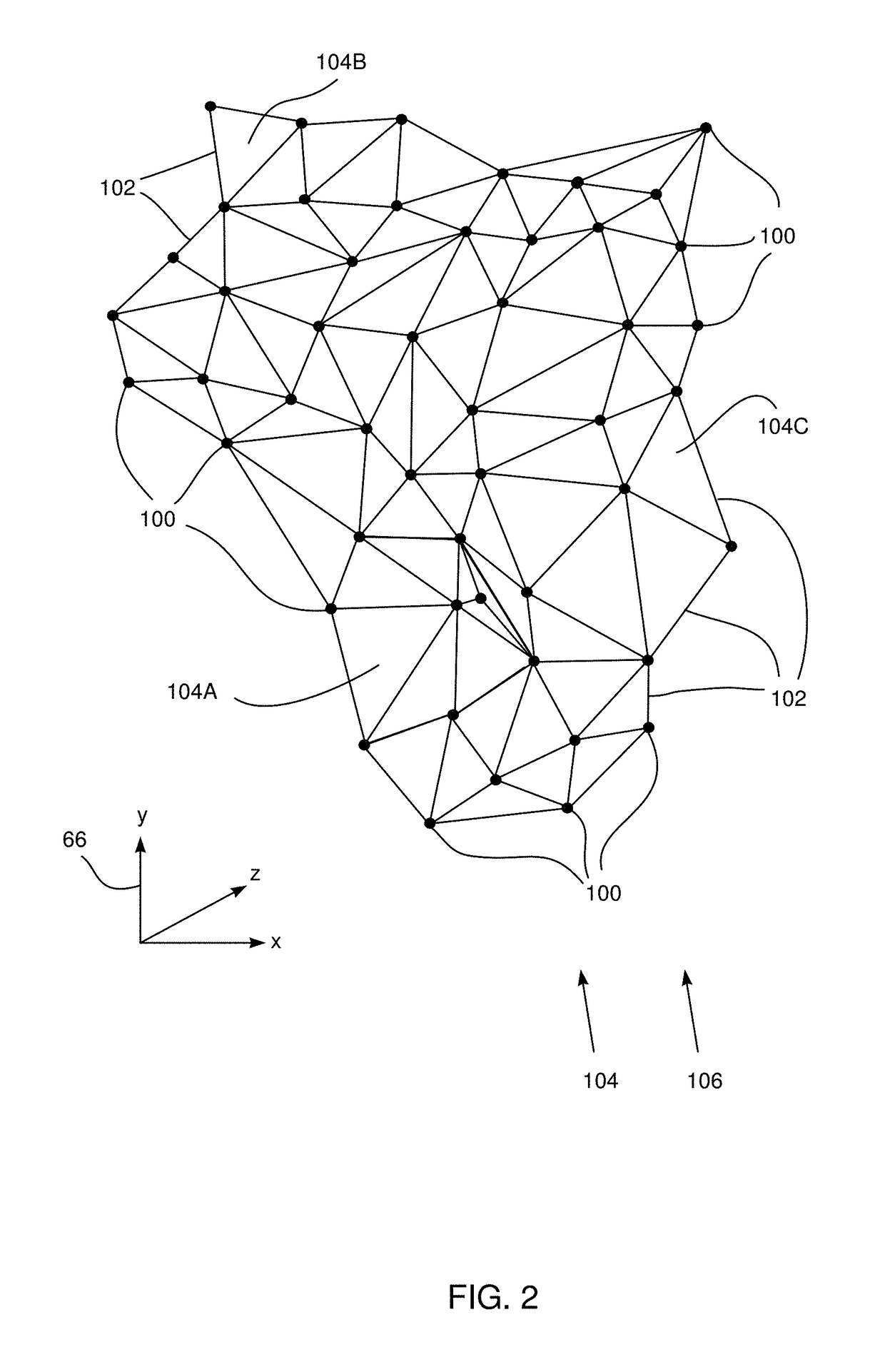
Voxelization of a mesh
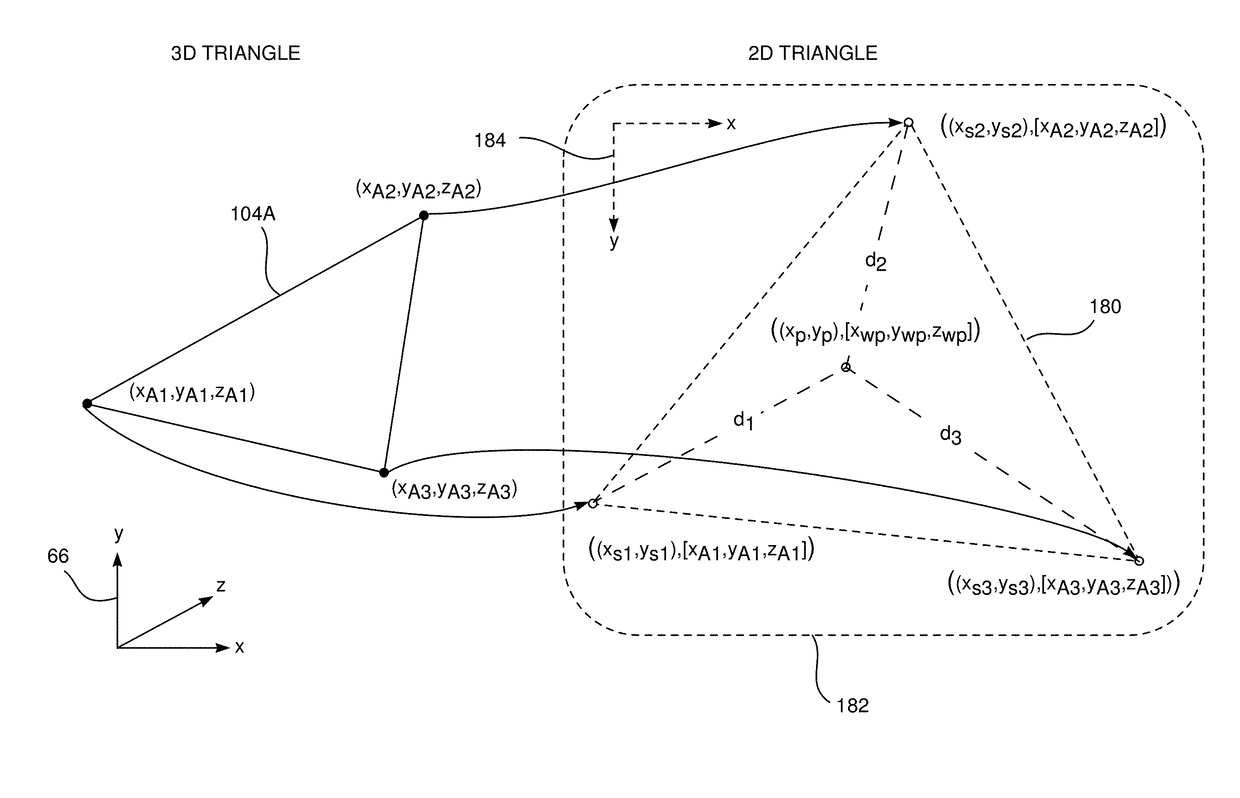
A method for 3D rendering, including receiving a group of 3D triangles defining a mesh of a surface, each 3D triangle in the group having 3D vertices with respective 3D coordinates, and transforming each 3D triangle into a 2D triangle having 2D vertices corresponding respectively to the 3D vertices, each 2D vertex having respective 2D pixel coordinates and a triplet of pixel attributes corresponding to the 3D coordinates of a corresponding 3D vertex. Each 2D triangle is passed to a graphics processor, which treats the triplet of pixel attributes of each 2D vertex as interpolatable values. The graphics processor computes respective triplets of interpolated pixel attributes for pixels within each 2D triangle by interpolation between the pixel attributes of the 2D vertices, and a 3D image of the surface is rendered by converting the interpolated pixel attributes computed by the graphics processor into voxel coordinates in the 3D image.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Method and system for early Z test in title-based three-dimensional rendering
InactiveUS20080068375A1Reduce performanceEasy to operate3D-image rendering3D modellingComputer graphics (images)3D rendering
A method and system for an early Z test in a tile-based three-dimensional rendering is provided. In the method and system for an early Z test, a portion which is not displayed to a user is removed prior to performing a rasterization process, and thereby performing the 3D rendering efficiently. The method includes segmenting a scene into tiles for performing a rendering with respect to a triangle; selecting a first tile of the tiles, which has a tile Z value less than a minimum Z value of the triangle; and performing the rendering with respect to the triangle in remaining tiles excluding the selected first tile of the tiles.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
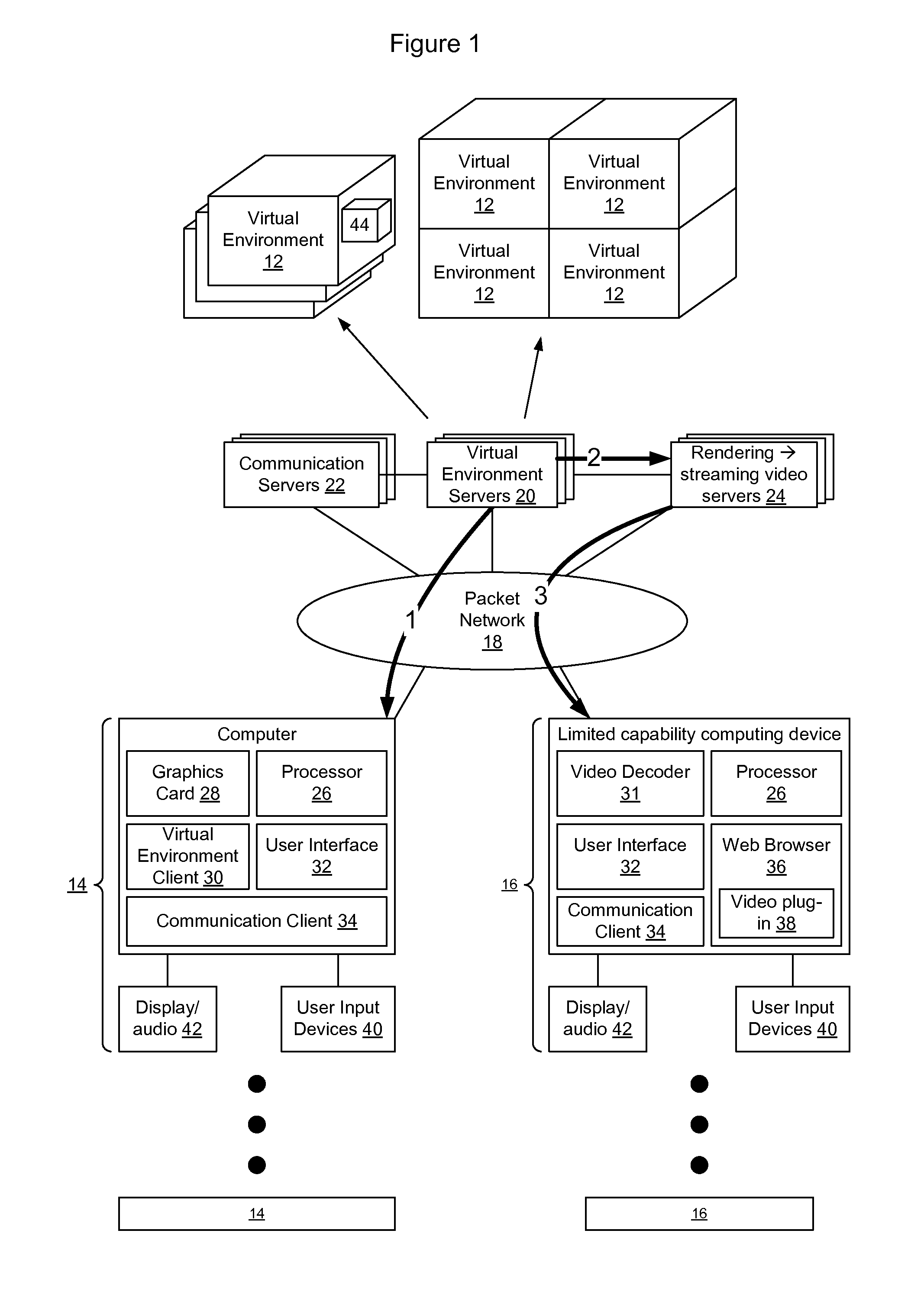
Method and System for Remote Visualization Client Acceleration
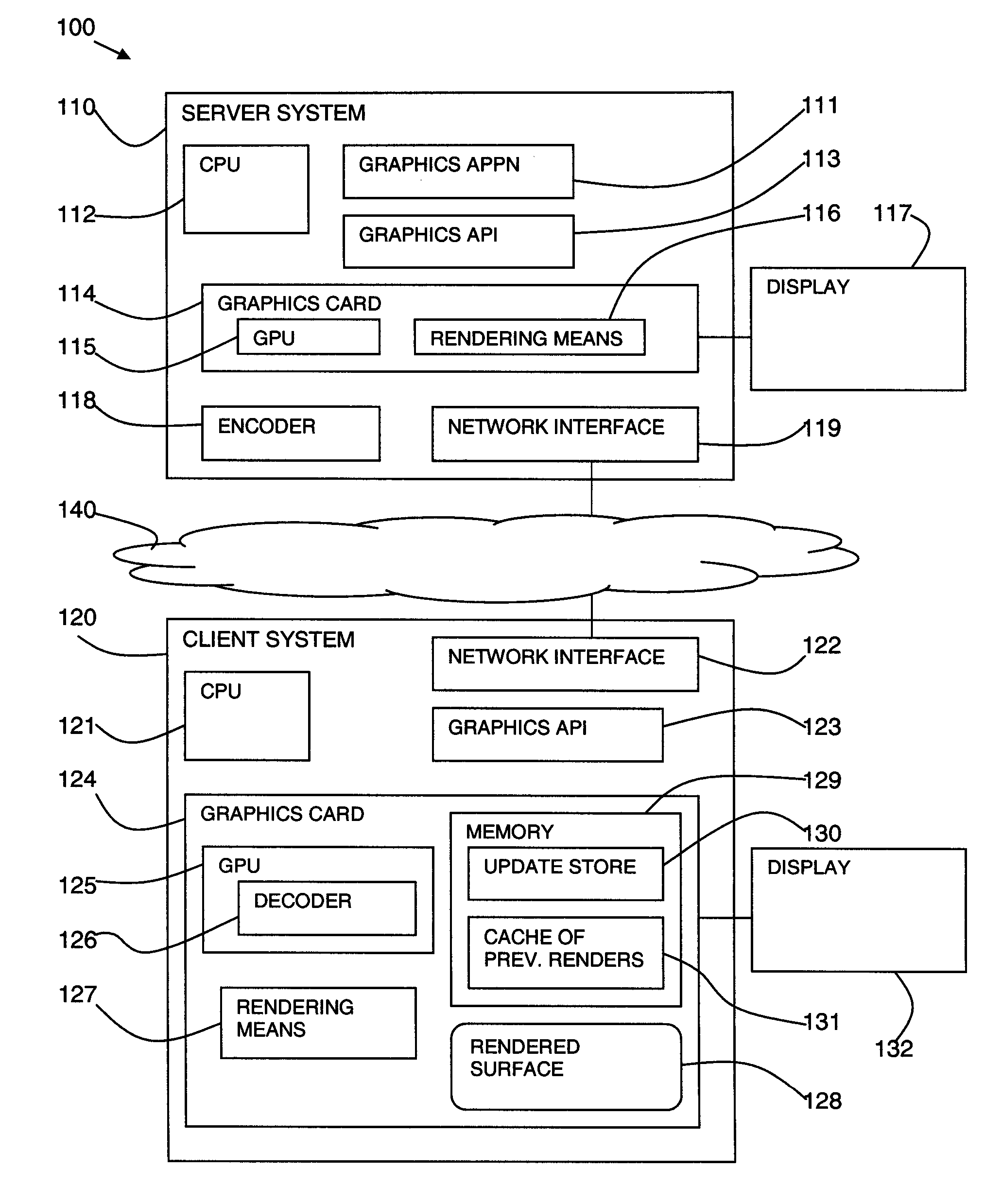
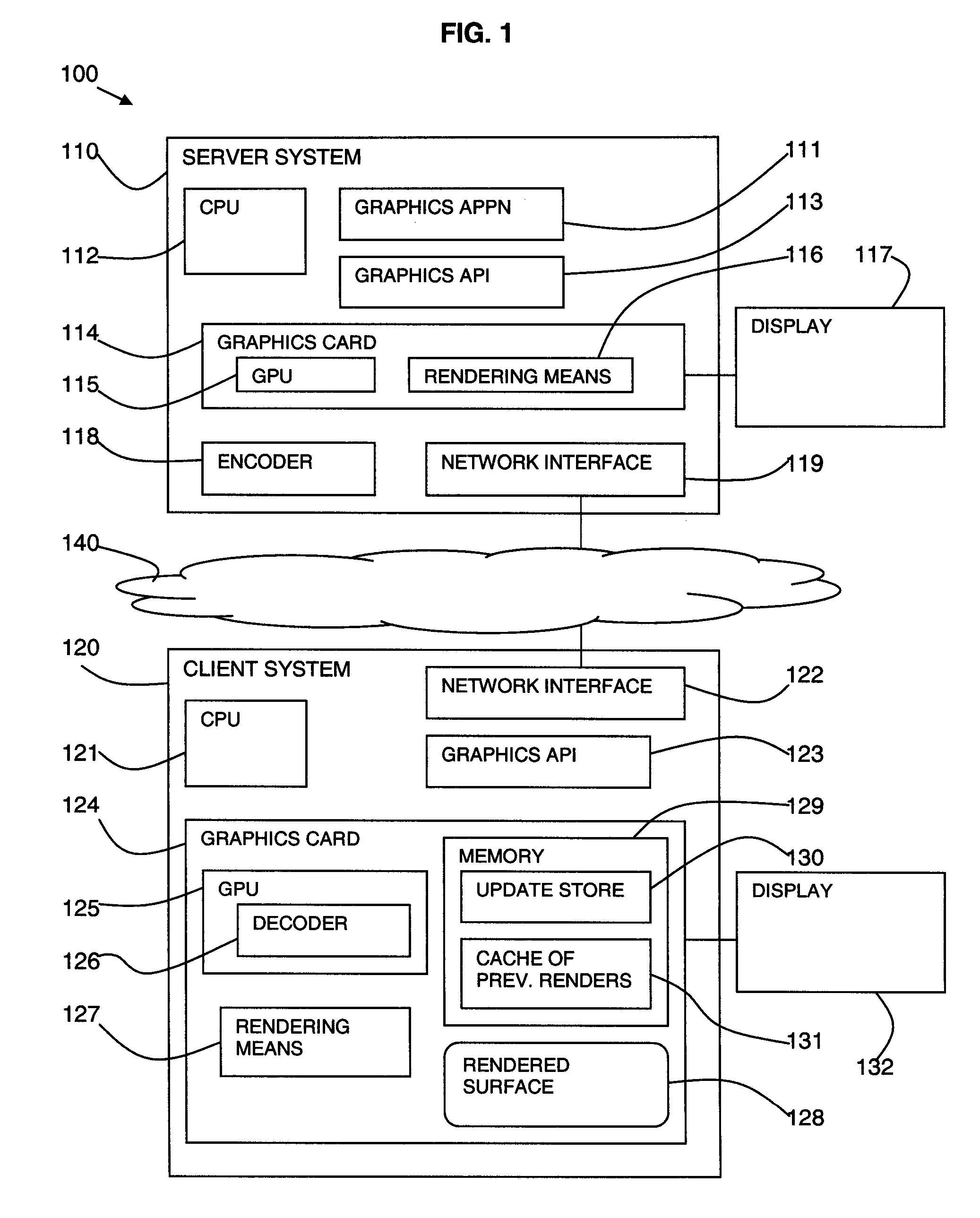
InactiveUS20100001995A1Optimize costly image decompressionStatic indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingGraphic cardClient-side
A method, system, and program product is disclosed for remote visualization in which a server window contents is displayed remotely at a client. The client creates a 3D rendering surface on a client graphics card to display a server window contents and receives update data from the server relating to the server window contents. The update data is uploaded to the client graphics card and the graphics processing unit (GPU) is used to decode the update data and render the update data to the 3D rendering surface. The graphical processing unit includes general purpose computing on graphics processing unit functionality to provide the decoding processing.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for visualization of geo-located media contents in 3D rendering applications
ActiveUS20160335796A1Input/output processes for data processing3D-image renderingComputer visionMetadata
An approach is provided for accurate processing and registering of media content for rendering in 3D maps and other applications. The approach includes determining at least one first pixel of at least one image that geometrically corresponds to at least one second pixel of at least one rendered three-dimensional map. Further, the approach includes processing and / or facilitating a processing of (a) the at least one first pixel; (b) the at least one second pixel; (c) metadata associated with at least one of the at least one first pixel and the second pixel; or (d) a combination thereof to determine at least one confidence value, wherein the at least one confidence value is indicative of an estimated level of geometric distortion resulting from projecting the at least one first pixel onto the at least one second pixel. Furthermore, the approach includes determining whether to cause, at least in part, a rendering of the at least one first pixel onto the at least one rendered three-dimensional map based, at least in part, on the confidence value.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Voxelization of a mesh
A method for 3D rendering, including receiving a group of 3D triangles defining a mesh of a surface, each 3D triangle in the group having 3D vertices with respective 3D coordinates, and transforming each 3D triangle into a 2D triangle having 2D vertices corresponding respectively to the 3D vertices, each 2D vertex having respective 2D pixel coordinates and a triplet of pixel attributes corresponding to the 3D coordinates of a corresponding 3D vertex. Each 2D triangle is passed to a graphics processor, which treats the triplet of pixel attributes of each 2D vertex as interpolatable values. The graphics processor computes respective triplets of interpolated pixel attributes for pixels within each 2D triangle by interpolation between the pixel attributes of the 2D vertices, and a 3D image of the surface is rendered by converting the interpolated pixel attributes computed by the graphics processor into voxel coordinates in the 3D image.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
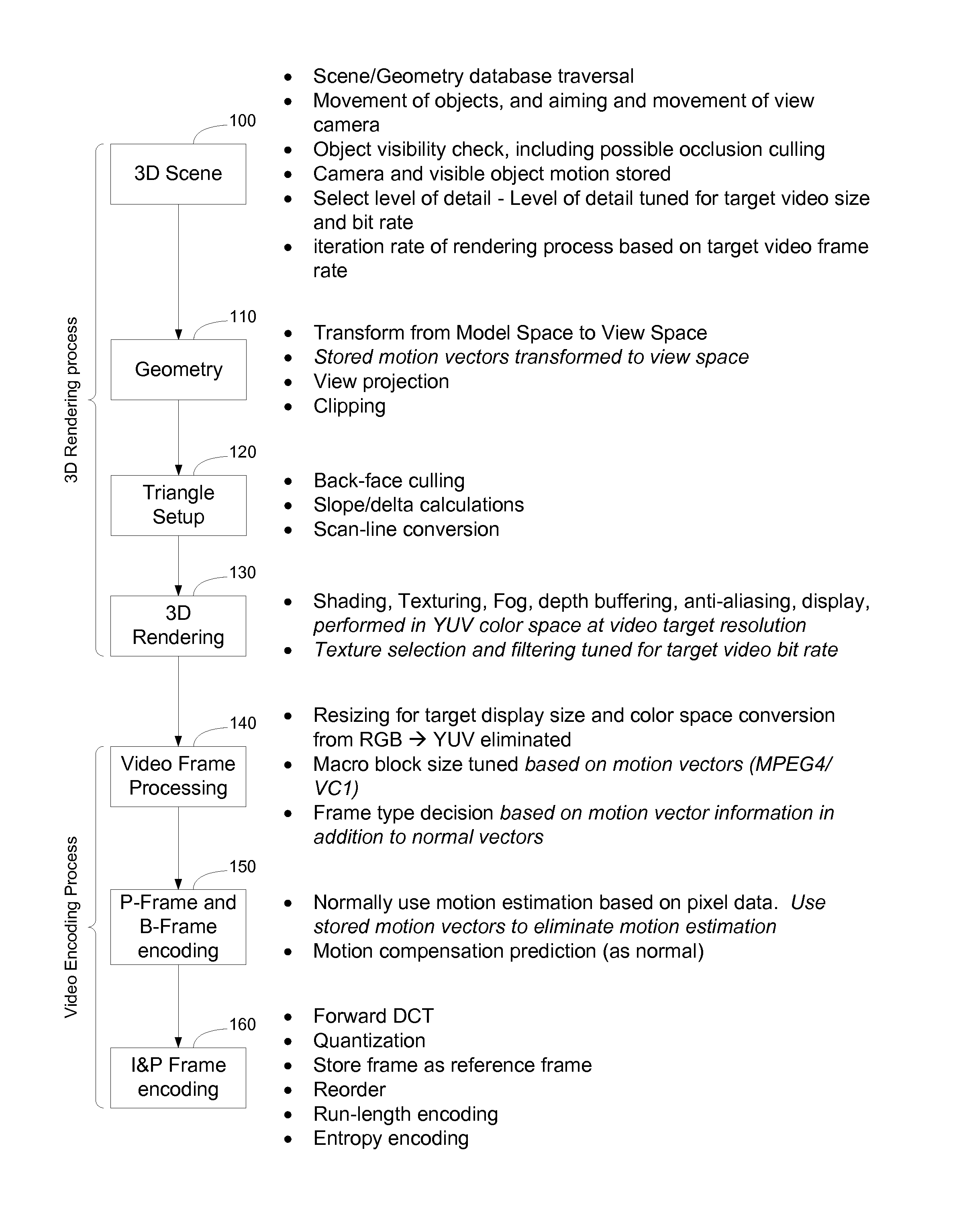
Method and Apparatus for Providing a Video Representation of a Three Dimensional Computer-Generated Virtual Environment
InactiveUS20110221865A1Optimized for encodingReduce complexityImage codingDigital video signal modificationVideo encodingLevel of detail
A server process renders instances of a 3D virtual environment as video streams that may then be viewed on devices not sufficiently powerful to implement the rendering process natively or which do not have native rendering software installed. The server process is broken down into two steps: 3D rendering and video encoding. The 3D rendering step uses knowledge of the codec, target video frame rate, size, and bit rate from the video encoding step to render a version of the virtual environment at the correct frame rate, in the correct size, color space, and with the correct level of detail, so that the rendered virtual environment is optimized for encoding by the video encoding step. Likewise, the video encoding step uses knowledge of motion from the 3D rendering step in connection with motion estimation, macroblock size estimation, and frame type selection, to reduce the complexity of the video encoding process.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
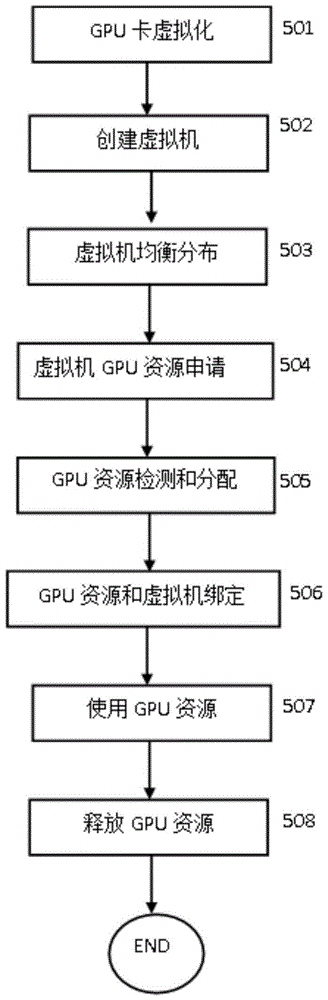
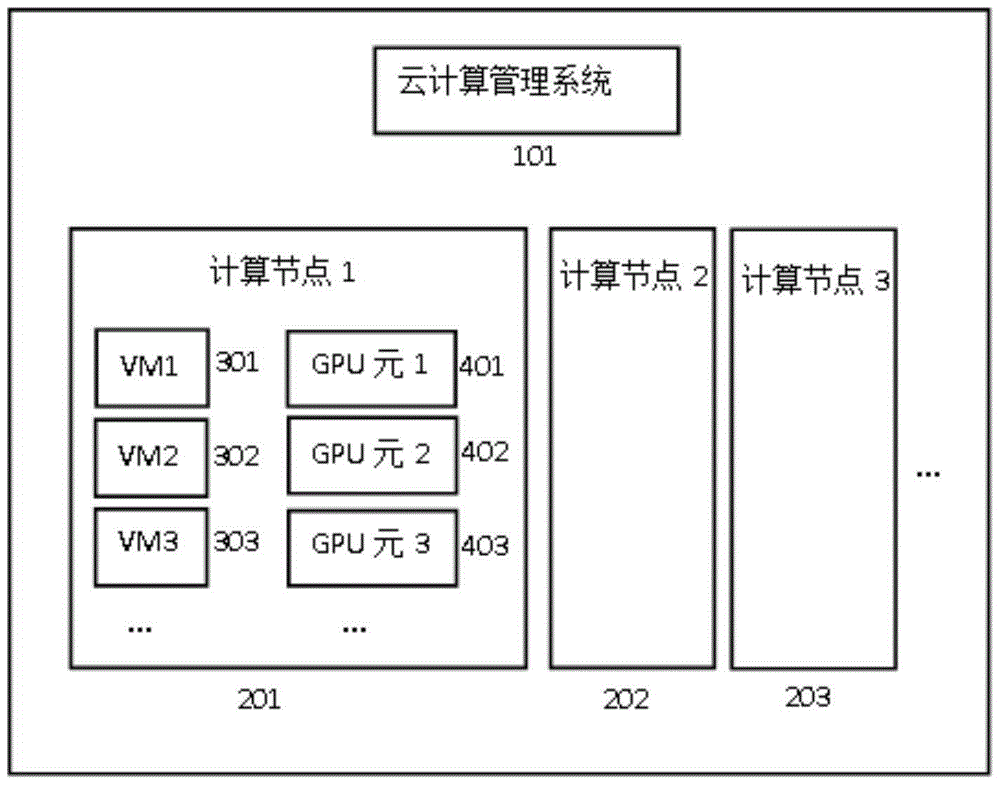
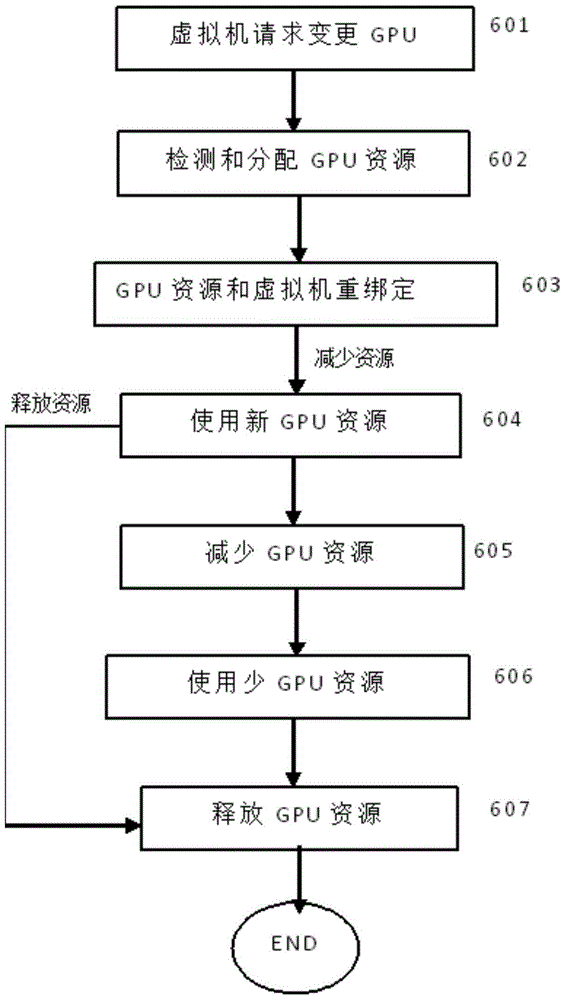
Method and system for cloud computing system to allocate GPU resources to virtual machine
InactiveCN105242957AEasy to useLoad balancingResource allocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationResource poolHigh-definition video
The present invention provides a method and a system for a cloud computing system to allocate GPU resources to a virtual machine. By applying the method, the virtual machine does not need to be constantly allocated with certain GPU resources; when the virtual machine needs to perform related high-definition video or 3D rendering, the virtual machine can apply to the cloud computing management system for the GPU resources; after the virtual machine uses the GPU resources, the resources are released and return to a GPU resource pool, so that large amounts of the GPU resources are saved; and the cloud computing management system evenly distributes virtual machines in need of the GPU resources to computing nodes with GPU cards according to created GPU usage identifiers of the virtual machines, thereby achieving usage effects of load balance and GPU resource optimization.
Owner:广州云晫信息科技有限公司
GPS Based Spectator and Participant Sport System and Method
ActiveUS20080198230A1Improve accuracyAchieve accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesClosed circuit television systemsData setDriver/operator
A spectator sport system and method that displays different views of a sporting event and, in particular, uses a position selected by the spectator to assist in displaying a view from the selected position. The spectator, using an internet device, can zoom, pan, tilt and change the view, as well as change the view to another position, such as a finish line, goal, or a participant position (e.g. Driver of car #3 or Tiger Wood's position). The starting position can be specified, as well as the target position or orientation from the starting position. Vital information on the sporting event or a participant can be appended to the view. In some forms, augmented reality or any geographic referenced datasets can be used and combined, such as 3D imagery or 3D renderings, to enhance the experience.
Owner:SPATIAL REALITY LLC
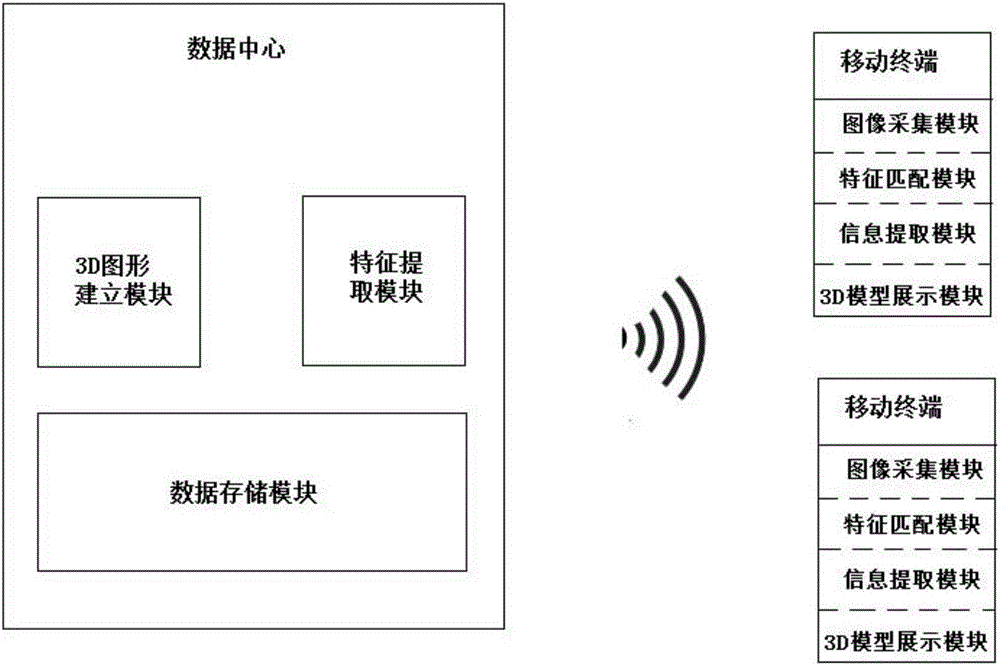
Electric equipment information extraction and display method and system based on augmented reality
InactiveCN106097425AEasy to understandLow cost3D-image rendering3D modellingTerminal equipmentComputer terminal
The invention provides an electric equipment information extraction and display method based on augmented reality (AR), comprising the steps of: building an electric equipment model database; the camera of mobile terminal equipment aligning at electric entity equipment to be identified; a program collecting picture information passed back by the camera in a data frame mode, extracting characteristics to contrast with stored identification object characteristics in the database, and returning corresponding equipment information if the characteristics match stored identification object characteristics in the database; and a mobile terminal maintaining the picture position information of a matched model, performing 3D rendering at the position, displaying the matched model and related information on a screen, and keeping a following state, i.e., recalculating the position of the model if the mobile terminal equipment is moved. According to the technical scheme, the mobile terminal equipment can be employed to scan an electrical equipment model, and to rapidly and vividly display correlated information, thereby greatly facilitating learning equipment for maintainers, and further reducing equipment maintenance costs.
Owner:TIANDAQIUSHI ELECTRIC POWER HIGH TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com