Method for producing halimasch strain by utilizing waste gastrodia elata fungi
A technology for Armillaria and waste bacteria is applied in the field of producing Armillaria strains by using Gastrodia elata waste mushroom materials, which can solve the problems of high transportation cost of cottonseed hulls, increase the pressure of forest ecological resource protection, etc., so as to ensure normal growth and reduce production. cost, the effect of reducing dependence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
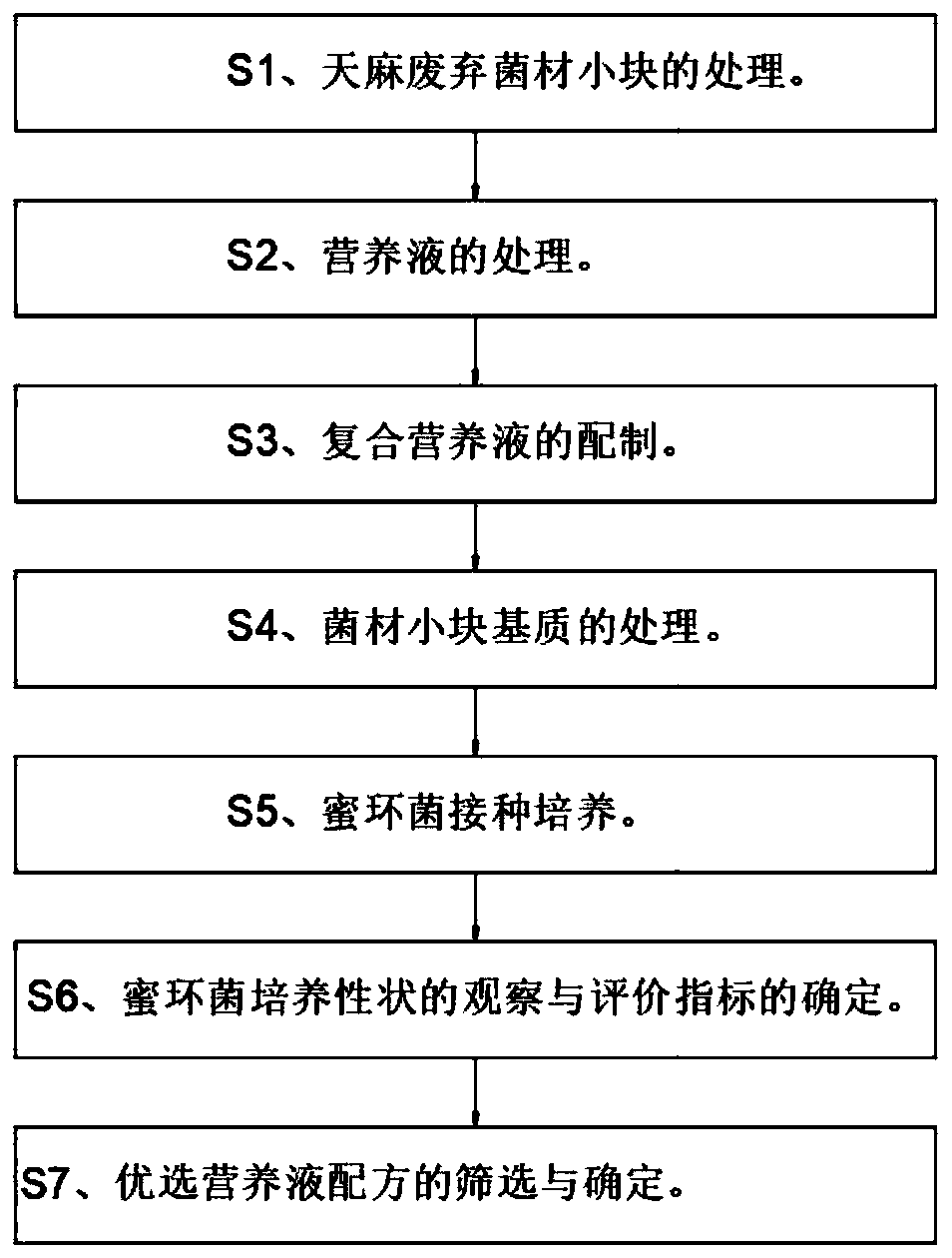
[0028] see figure 1 , the present invention provides a technical solution: a method for producing Armillaria strains by utilizing the waste bacterium of Gastrodia elata, comprising the steps of:
[0029] S1. Treatment of small pieces of waste gastrodia elata;
[0030] S2, the treatment of nutrient solution;
[0031] S3, preparation of compound nutrient solution;
[0032] S4, the processing of bacterial material small block matrix;
[0033] S5, armillaria inoculation culture;
[0034] S6. Observation of Armillaria armillaria culture traits and determination of evaluation indexes;
[0035] S7. Screening and determination of optimal nutrient solution formula.
[0036] Specifically, in the S1: the waste gastrodia elata fungus is mainly Qinggang wood or cork oak, and after cleaning the soil on the surface of the waste fungus, it is processed into small pieces with a length of 1-2 cm and a width of about 1 cm for later use.
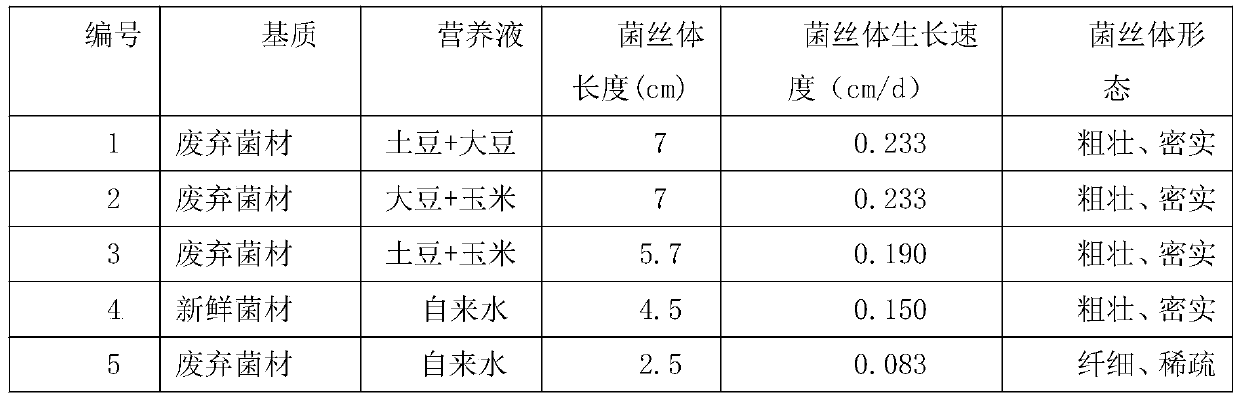
[0037] Specifically, in the S2: according to the am...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com