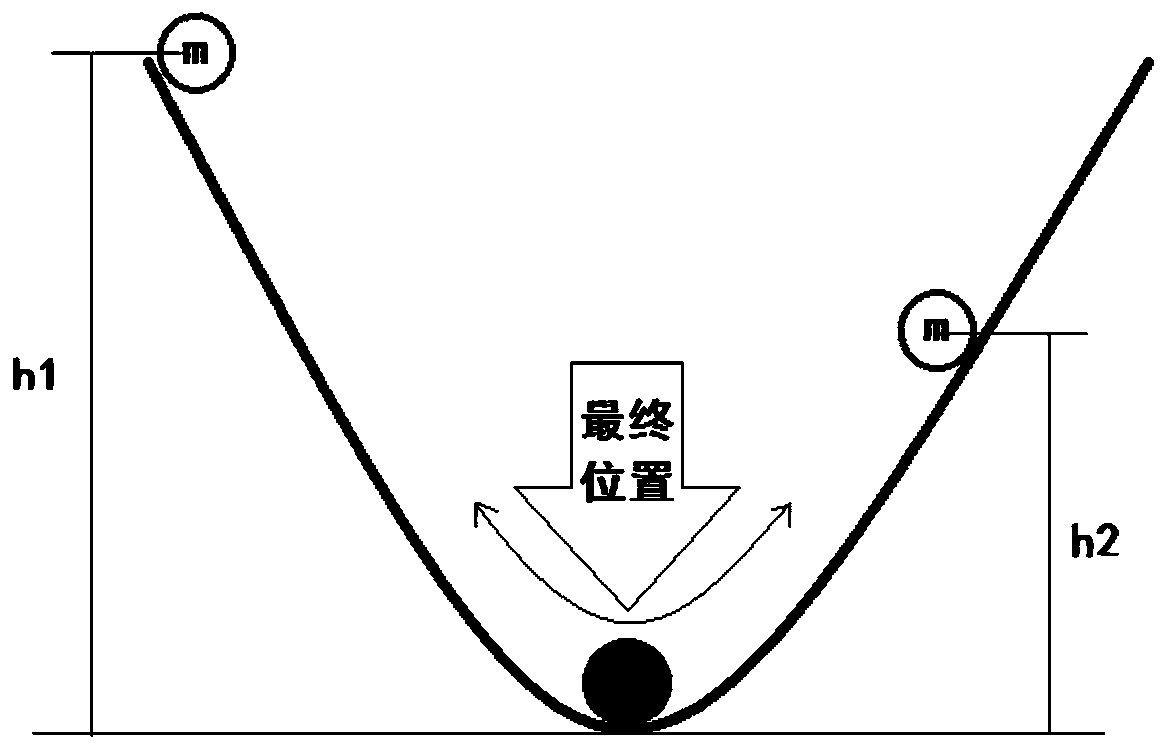
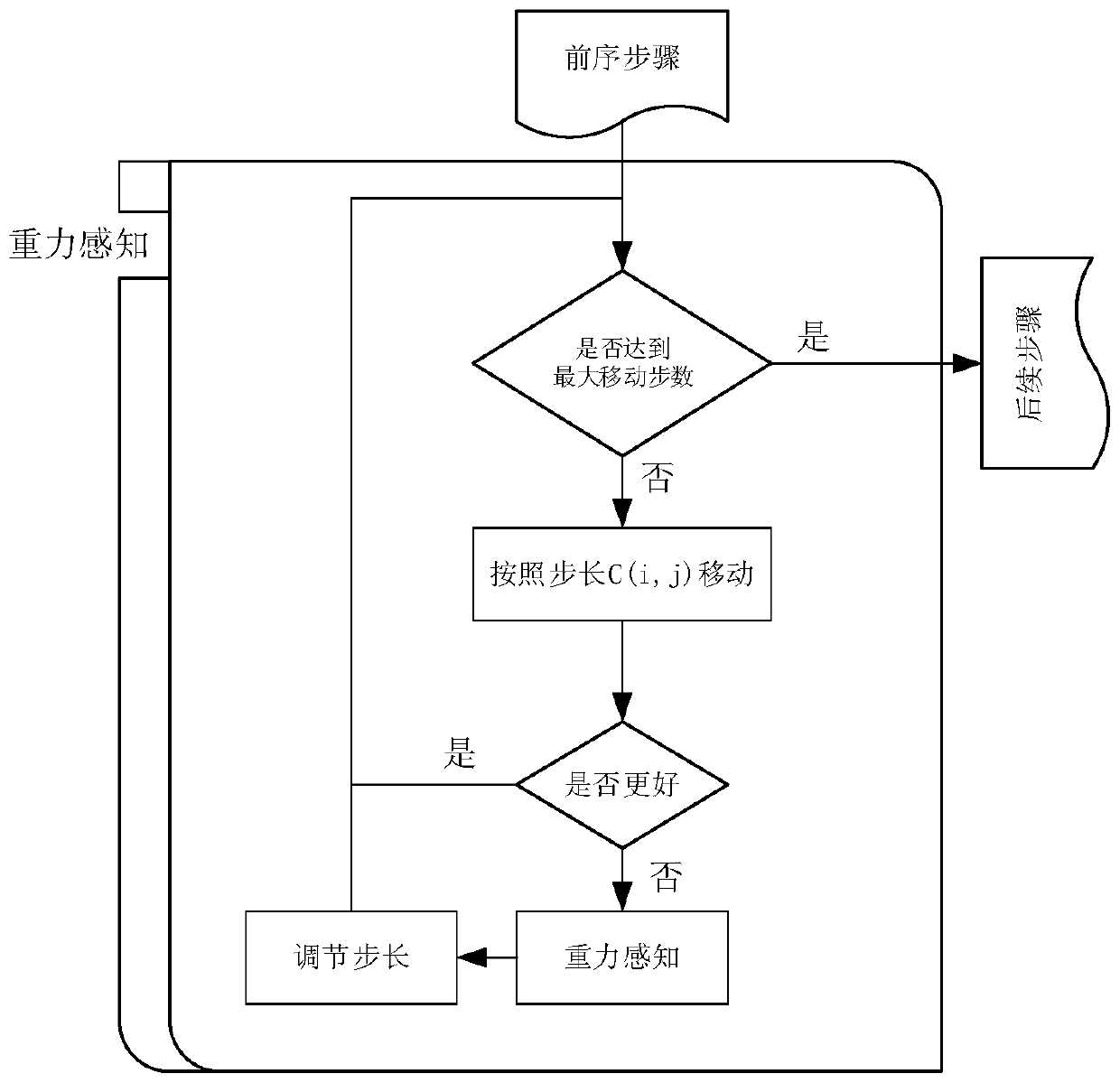
A bacterial foraging optimization method based on gravity induction
A bacterial foraging algorithm and bacterial foraging technology, applied in the directions of instruments, computational models, biological models, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to find the optimal solution, difficult to determine the step size, and reducing the optimization accuracy, so as to increase the search efficiency. The effect of excellent accuracy, reduced step size, and fast iterative convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
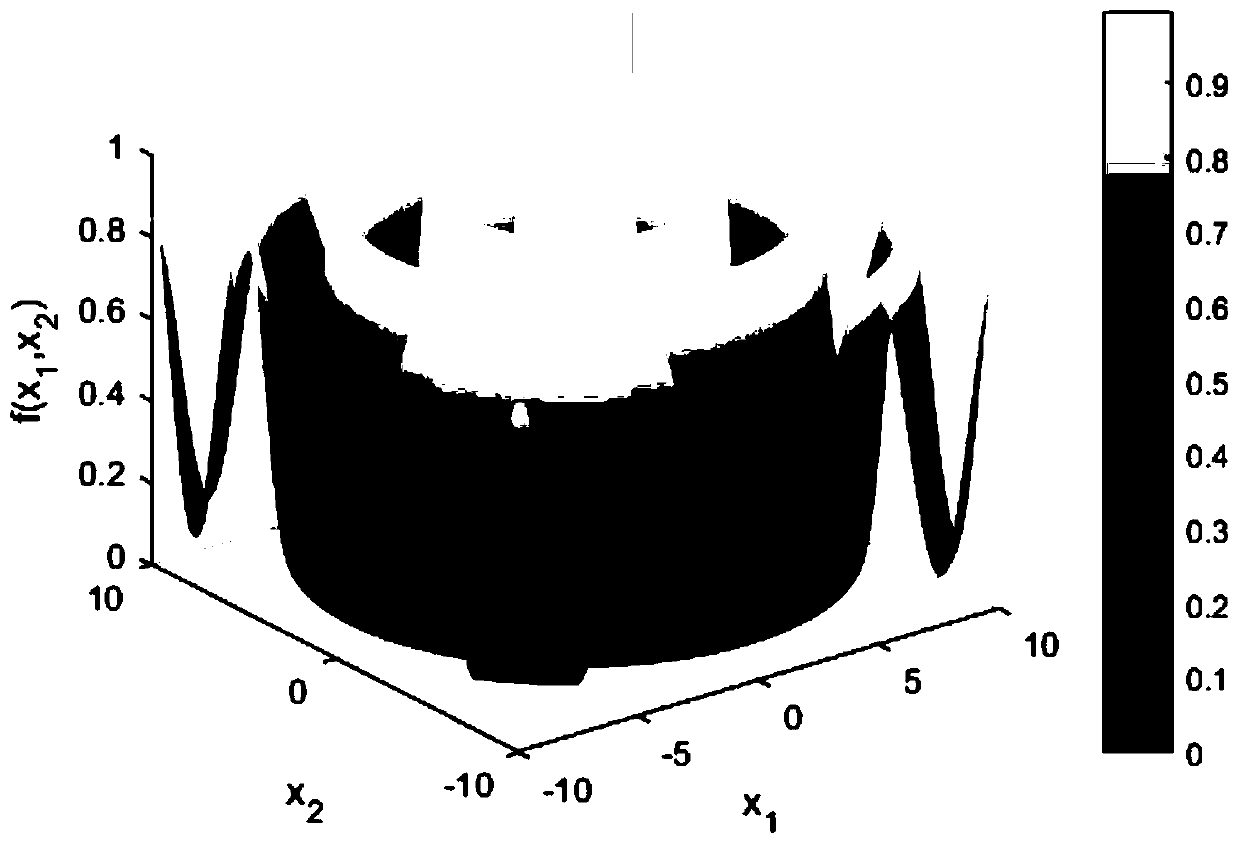
[0066] Using the Schaffer function
[0067] where -10≤x 1 ,x 2 ≤10, both numbers are between -10 and 10, verifying the optimization ability of the gravity-aware bacterial foraging algorithm. Such as image 3 is the three-dimensional image of the function, Figure 4 is a two-dimensional graph. This function is a relatively complex two-dimensional function, and the minimum point is f(0,0)=0; because this function has a strong oscillation form, it is difficult to find the global optimal value.
[0068] S1: There are two variables that directly affect the value of the function, so X={x 1 ,x 2};
[0069] S2: The optimization value (fitness) of the problem to be studied is the function
[0070] S3: Initialize gravity sensing parameters and bacterial foraging parameters:
[0071] S31: Initialize gravity perception parameters: slope angle α=45°, drag coefficient c=0.5, air density ρ=1.293g / L, wind impact area S=1m 2 ;
[0072] S32: Initialize the relevant parameters of ...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Using the Rastrigrin function where -5≤x 1 ,x 2 ≤5, verify the optimization ability of the gravity-aware bacterial foraging algorithm. This function is a relatively complex two-dimensional function, the minimum point is f(0,0)=0, this function has countless minimum value points, it is easy to fall into a local optimum, and it is difficult to find the minimum value of the whole play, such as Figure 5 , Figure 6 .
[0086] S1: There are two variables that directly affect the value of the function, so X={x 1 ,x 2};
[0087] S2: The optimization value (fitness) of the problem to be studied is the function
[0088] S3: Initialize gravity sensing parameters and bacterial foraging parameters:
[0089] S31: Initialize gravity perception parameters: slope angle α=45°, drag coefficient c=0.5, air density ρ=1.293g / L, wind impact area S=1m 2 ;
[0090] S32: Initialize the relevant parameters of the bacteria foraging algorithm: initial step size Cstart=0.1, the numb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com