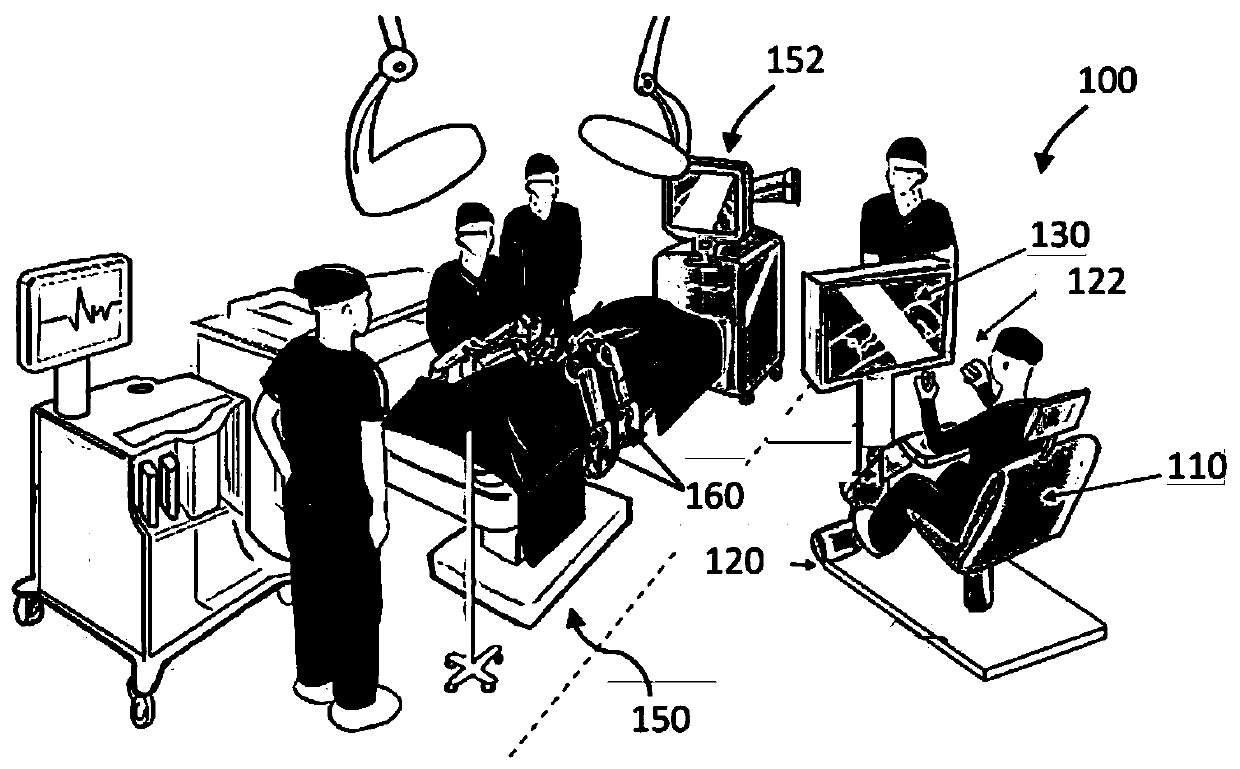
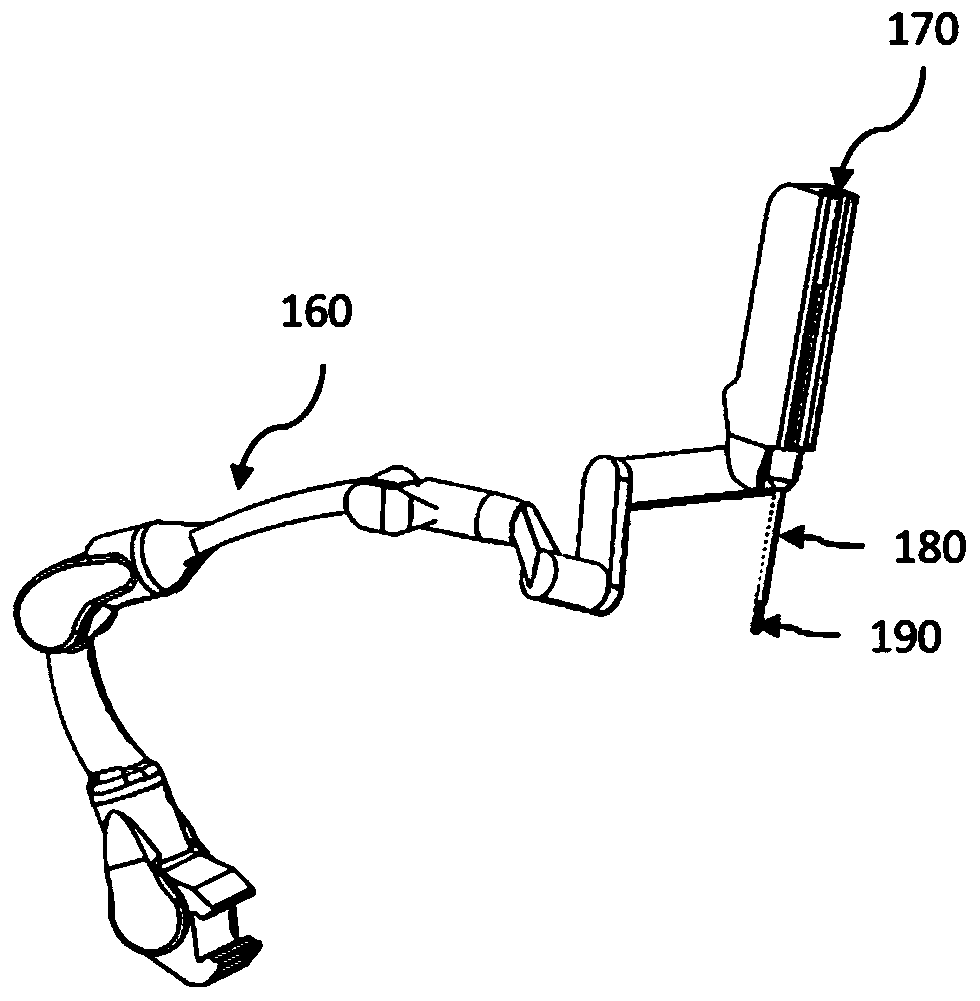
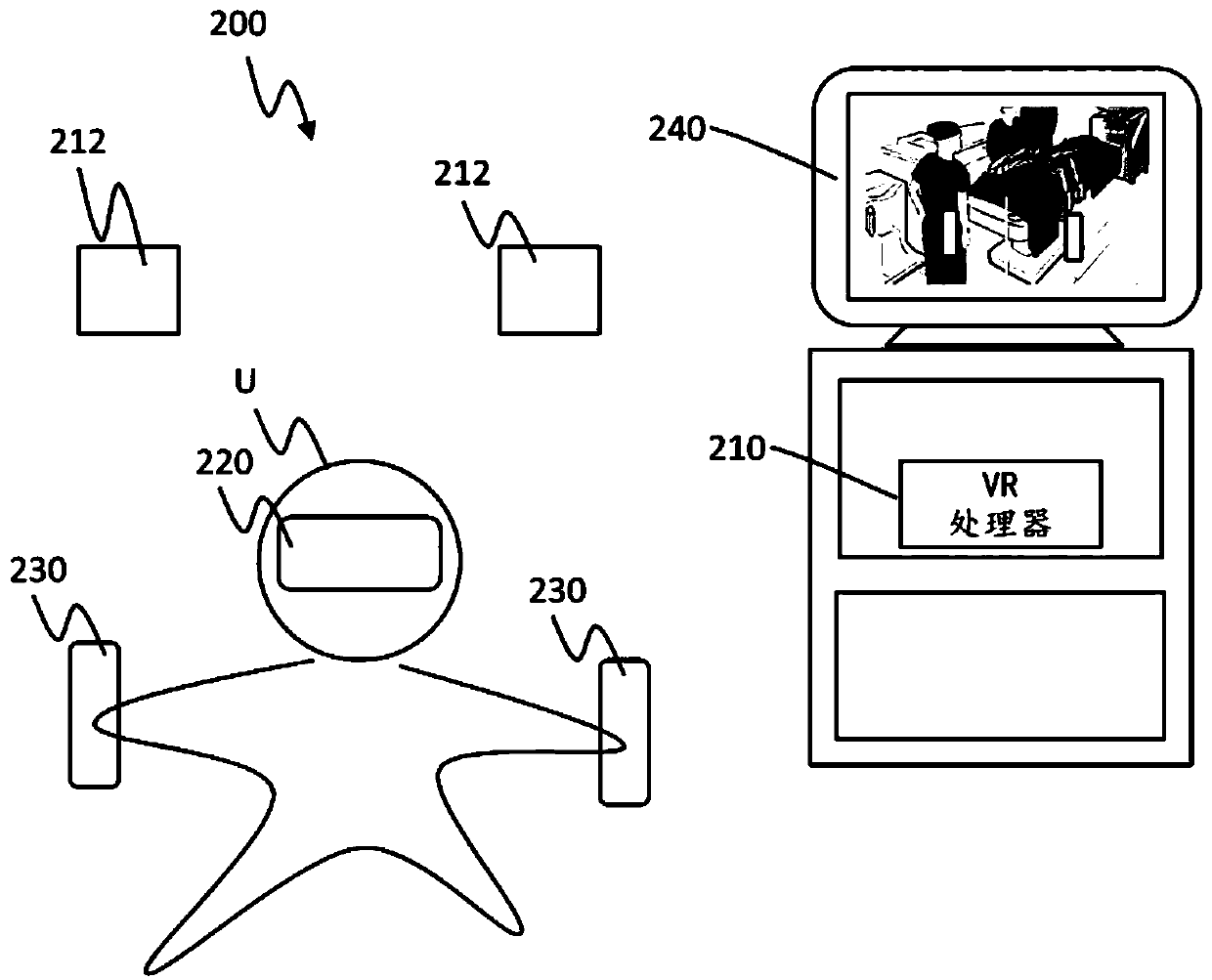
Virtual reality training, simulation, and collaboration in a robotic surgical system
A surgical operation and virtual reality technology, applied in surgical navigation system, surgical system user interface, surgical robot, etc., can solve the problems of accumulating expensive and time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0164] Example 1 - Cross bed
[0165] A user may use the virtual reality system to simulate a bed crossing scenario where the user is adjacent to a hospital bed or table and operates a robotic surgical system and manual laparoscopic tools. Such simulations may be used for training, surgical planning, and the like. For example, a user may use virtual robotic tools and virtual hand tools to suture tissue in a targeted segment of a virtual patient's bowel.
[0166] In this example, a user wears a head-mounted display that provides an immersive view of a virtual reality environment, and can use a handheld controller to navigate within the virtual reality environment to be adjacent to a virtual operating table on which a virtual patient lies. The proximal end of the virtual robotic arm is attached to the virtual operating table, and the distal end of the virtual robotic arm supports a virtual tool driver that actuates a virtual gripper positioned within the virtual patient's abd...
Embodiment 2
[0168] Example 2 - Collision Resolution from User Console
[0169] When using a virtual reality system, a user may desire to resolve collisions between virtual components of a virtual robotic surgery system, even though the user may not be adjacent to the colliding virtual components (e.g., the user may be seated at a distance away from the virtual operating table , such as at the virtual user console). In this example, a user wears a head-mounted display that provides an immersive view provided by a virtual endoscope placed inside a virtual patient's abdomen. The proximal ends of the two virtual robotic arms are attached to separate locations on the virtual operating table on which the virtual patient lies. The distal end of the virtual robotic arm supports a corresponding tool driver that actuates a virtual gripper positioned within the virtual patient's abdomen. The user manipulates the handheld controller to manipulate two robotically controlled virtual grippers that m...
Embodiment 3
[0172] Example 3 - Coordinated Repositioning of Multiple Surgical Instruments from a User Console
[0173]When using a virtual reality system, the user may find that essentially staying in the endoscopic view and repositioning multiple virtual surgical instruments (e.g., end effectors, cameras) as a group rather than individually within the virtual patient Local repositioning is useful, saving time and making it easier for the user to maintain contextual awareness of the instrument relative to the virtual patient's anatomy. In this example, a user wears a head-mounted display that provides an immersive view provided by a virtual endoscope placed inside a virtual patient's abdomen. The proximal ends of the two virtual robotic arms are attached to separate locations on the virtual operating table on which the virtual patient lies. The distal end of the virtual robotic arm supports a corresponding tool driver that actuates a virtual gripper positioned in the pelvic region of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com