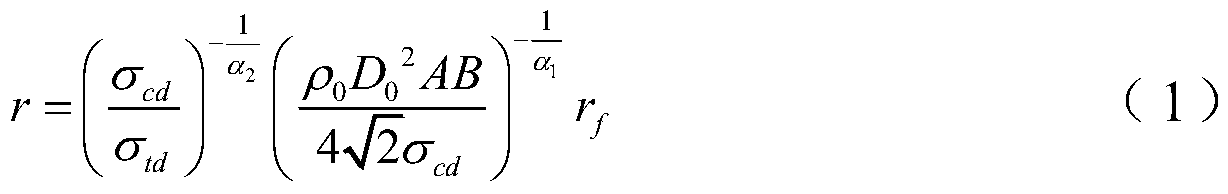Explosive model construction method based on equivalent radius of phase transition and fracturing of liquid carbon dioxide
A technology of liquid carbon dioxide and radius, which is applied in computational theoretical chemistry, instrumentation, computer material science, etc., and can solve problems such as the inability to accurately analyze the effect of cracking and anti-reflection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
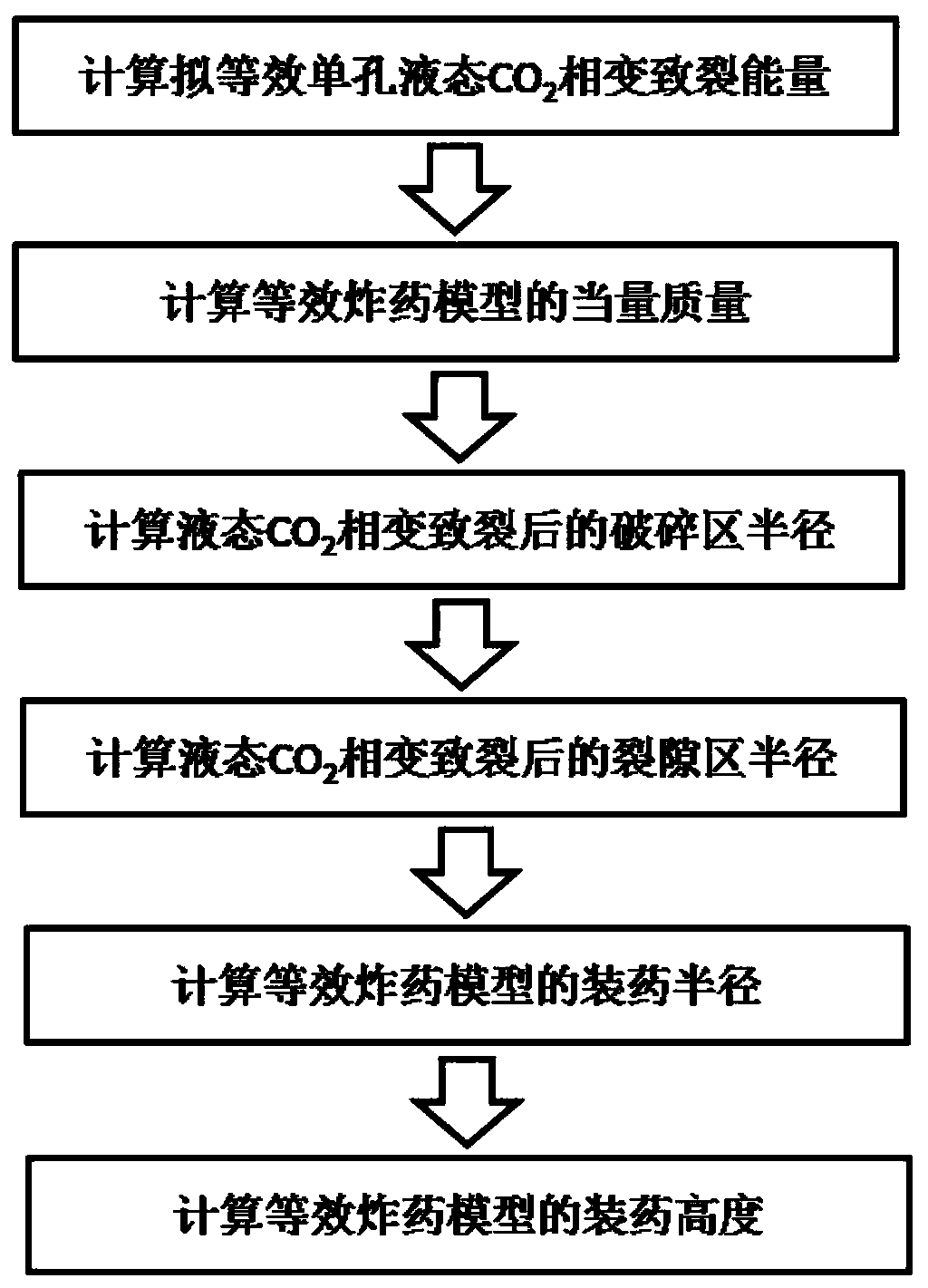
[0072] A method for constructing an explosive model based on the equivalent cracking radius of liquid carbon dioxide phase transition, comprising the following steps:
[0073] Step 1: If the to-be-equivalent object is the MZT275-51 / 1000 liquid carbon dioxide cracker commonly used in underground wells (drilling radius is 30mm): the length of the liquid storage tube is 1.0m, the outer diameter of the liquid storage tube is 51 mm, and the volume of the liquid storage tube is 1.0 m. It is 1.32L, the filling mass of liquid carbon dioxide is 0.7Kg, and the release pressure is 275MPa. According to formula (3), the explosion energy released when the quasi-equivalent liquid carbon dioxide phase transitions and cracks is calculated: E=1027.3KJ.
[0074] Step 2: Based on the equal explosion energy, the single-hole liquid carbon dioxide phase-transition-induced cracking explosion source in step 1 is equivalent to the TNT explosive explosion source of the single-hole columnar coupling char...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com