Application of L-aspartic acid beta-hydroxamate in preparation of drugs for inhibiting choroidal neovascularization, and choroidal neovascularization treatment method
A hydroxamate and aspartic acid technology, applied in drug delivery, pharmaceutical formulation, drug combination, etc., can solve the problems of retinal and choroidal atrophy, side effects, intraocular infection, etc., and achieve the effect of inhibiting choroidal neovascularization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
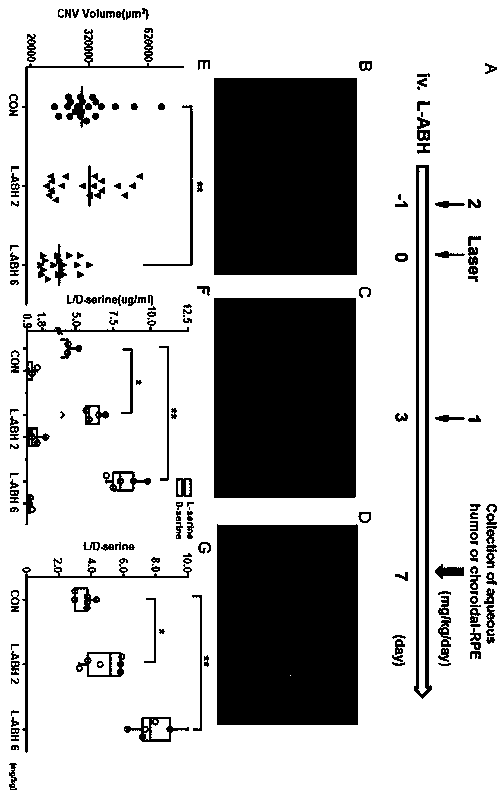
[0016] experimental method:
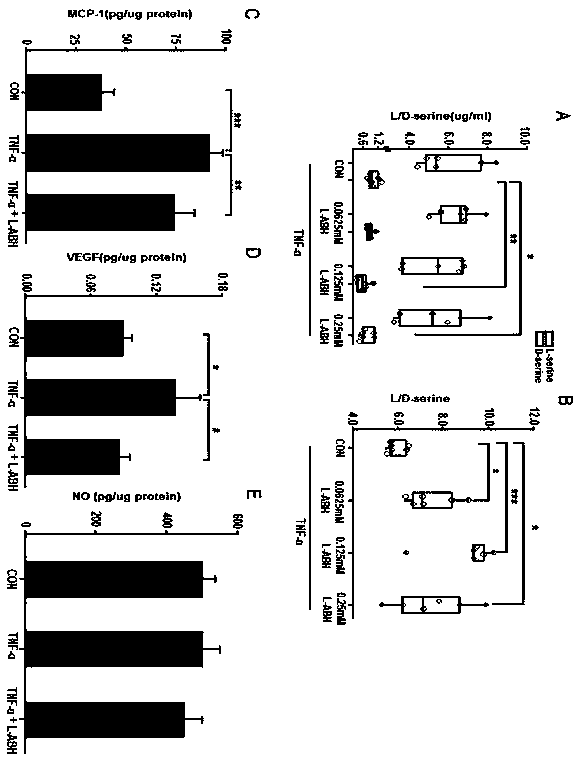
[0017] Using the animal model of exAMD, in C57 / B6 mice, using Krypton red laser (0.05 s interval, 0.07 s duration, and 240 mW power), do fundus irradiation to create CNV mouse model. Serine racemase competitive inhibitor, L-Aspartic acid β-hydroxamate (l-Aspartic acid β-hydroxamate) was injected intravenously at a dose of 6 mg / kg on the day before laser and 3 mg / kg on the third day after laser. -hydroxamate, L-ABH). On day 7 after laser injury, choroid / retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPEs) were spread and stained with Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated isolectin GS-IB4 to analyze CNV volume. And using primary RPEs in vitro, study the inhibitory effect of L-ABH on the production of VEGF and MCP-1 induced by TNFα in RPEs. And use RPEs and macrophage co-culture, research L-ABH pretreatment RPEs, inhibit the migration of macrophages.
[0018] Intravenous injection of L-ABH inhibits laser-induced choroidal neovascularization as a result of figure 1 shown...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com