Anti-saliency tangentially magnetized multi-phase permanent magnet fault-tolerant motor
A permanent magnet fault-tolerant, salient-pole technology, applied in synchronous motors with static armatures and rotating magnets, synchronous machine parts, magnetic circuit rotating parts, etc., can solve the mutual constraints between normal operation performance and fault tolerance, etc. problem, to achieve excellent normal operation performance and fault-tolerant operation ability, reduce permanent magnetic flux, change the effect of air gap magnetic density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
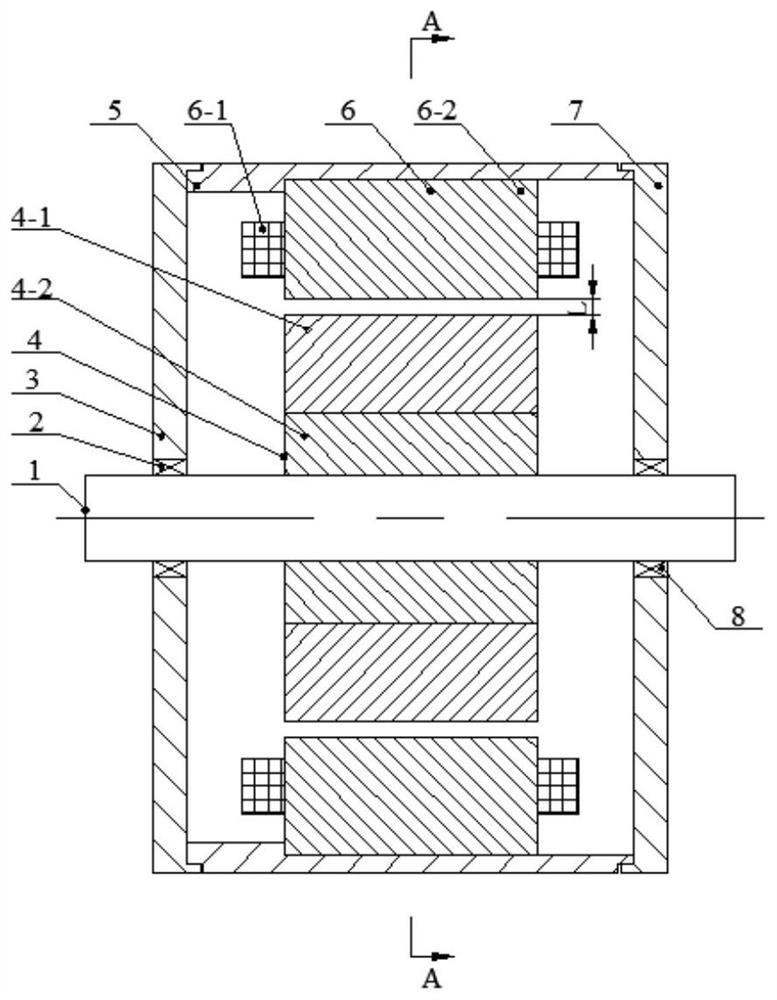
[0019] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 2 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment includes a rotating shaft 1, a first bearing 2, a left end cover 3, a rotor 4, a casing 5, a stator 6, a right end cover 7, and a second bearing 8. The direct axis reactance of the motor is greater than the quadrature axis reactance;
[0020] The ports on the left and right sides of the casing 5 are respectively provided with a left end cover 3 and a right end cover 7, the stator 6 is fixed on the inner wall of the casing 5, the rotor 4 is fixed on the rotating shaft 1, and the rotating shaft 1 passes through the first bearing 2 and the second bearing 8 are respectively rotated and fixed on the left end cover 3 and the right end cover 7, and there is a radial air gap L between the rotor 4 and the stator 6;
[0021] The stator 6 includes a stator core 6-2 and an m-phase stator winding 6-1. The stator winding 6-1 is a multi-phase fractional slot conc...
Embodiment approach 2
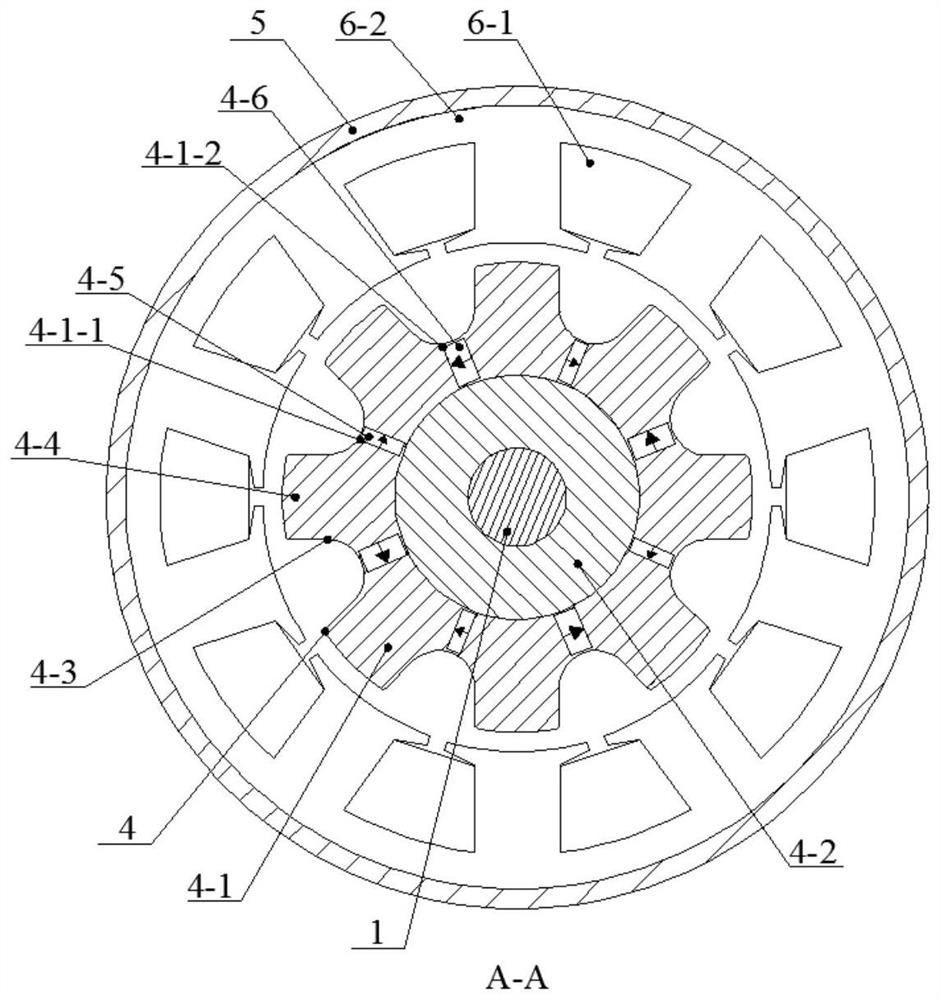
[0033] Implementation mode two: the following combination figure 1 and image 3 This embodiment will be described. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, there are multiple arc-shaped magnetic barrier slots 4-7 on the 2p ferromagnetic poles 4-4, and the multiple magnetic barrier slots 4-7 are sequentially arranged along the radial direction. Arranged and symmetrical with respect to the first permanent magnet pole slot 4-1-1 or the second permanent magnet pole slot 4-1-2.
[0034] By arranging multiple magnetic barrier slots 4-7, the difference between the direct axis inductance and the quadrature axis inductance can be further increased, which is beneficial to increase the reluctance torque of the motor.
specific Embodiment approach 3
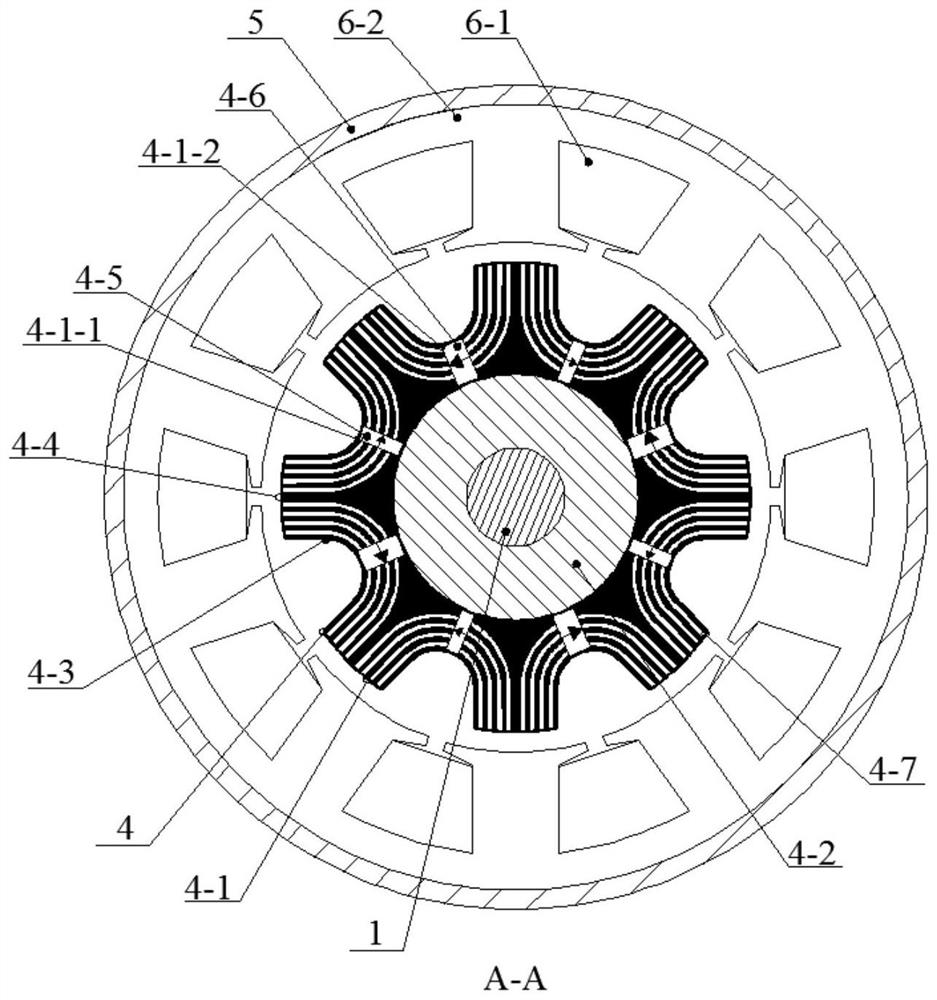
[0035] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, a certain phase winding in the m-phase stator winding 6-1 has a short-circuit fault, and the multi-phase full-bridge inverter will The end of the faulty phase winding is short-circuited, and at the same time, the current in the remaining m-1 phase normal windings in the stator winding 6-1 is controlled to control the magnetic state of the p second permanent magnets 4-6, so that the p second permanent magnets 4-6 The operating point of the permanent magnets 4-6 is lowered, and even reversely magnetized to reduce the size of the permanent magnetic field in the air gap, thereby suppressing the short-circuit current of the faulty phase winding.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com