Control method of fuel cell system of hybrid electric vehicle
A technology for fuel cell systems and hybrid electric vehicles, applied in battery/fuel cell control devices, electric vehicles, vehicle energy storage, etc., can solve the problems of reduced durability and reduced life of fuel cell stacks, and achieve improved life and durability performance, avoid frequent start and stop, and avoid idling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
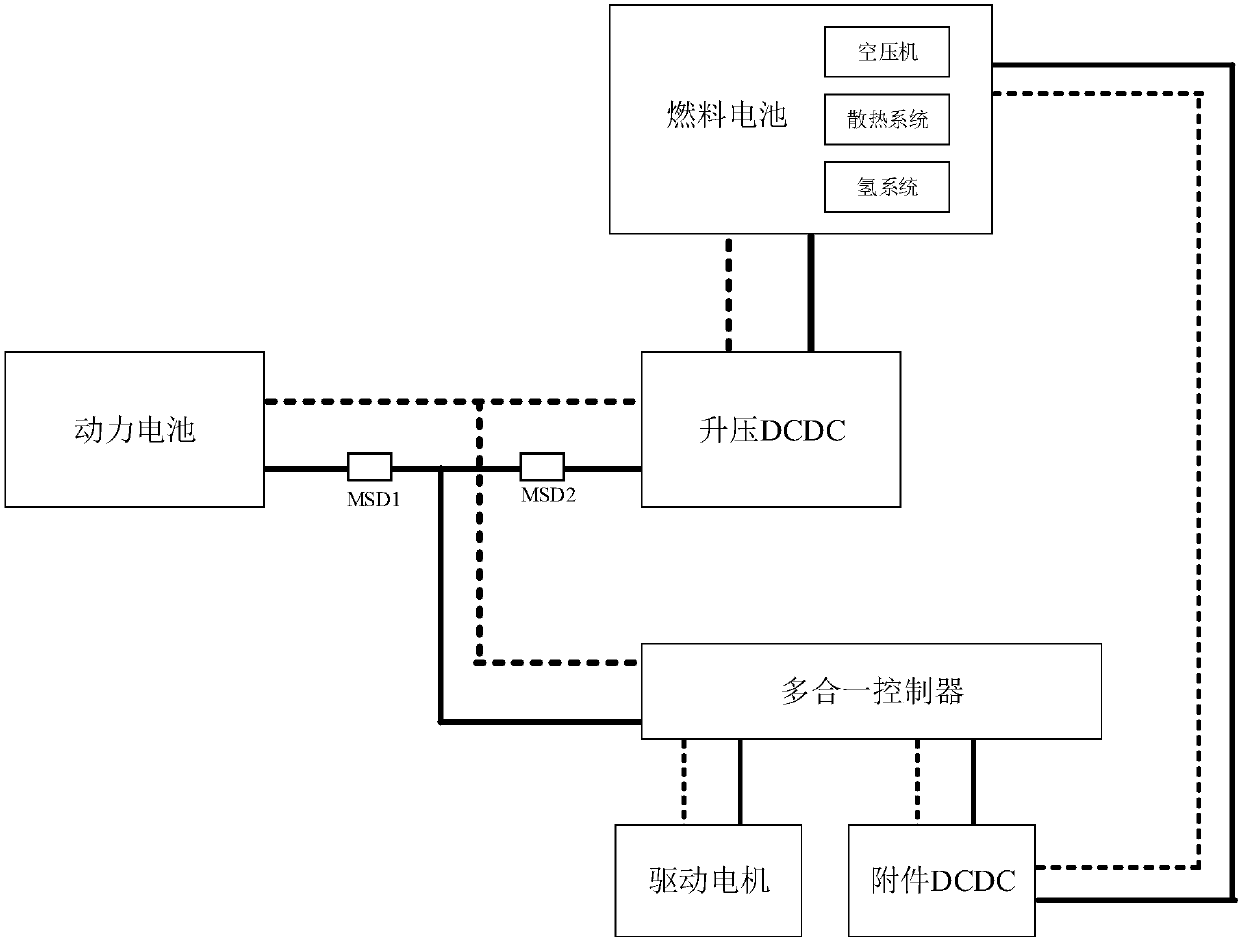
[0041] This embodiment 1 provides a fuel cell system for a hybrid electric vehicle, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes fuel cell, power battery, boost DCDC, all-in-one controller, drive motor and accessory DCDC, where the fuel cell is connected to the power battery through the boost DCDC, and the boost DCDC and power battery are connected in parallel to the all-in-one Among the controllers, the all-in-one controller distributes power to the drive motor and accessories DCDC; the fuel cell accessories include an air machine, heat dissipation system and hydrogen system, which are powered by the accessories DCDC; the preferred step-up DCDC is a unidirectional step-up DCDC. figure 1 Among them, MSD1 and MSD2 are manual maintenance switches.
[0042] The set power is not less than the power required for the normal operation of the fuel cell accessory to ensure that the fuel cell accessory still operates normally when the fuel cell has no power demand, and that the fuel cell does...
Embodiment 2
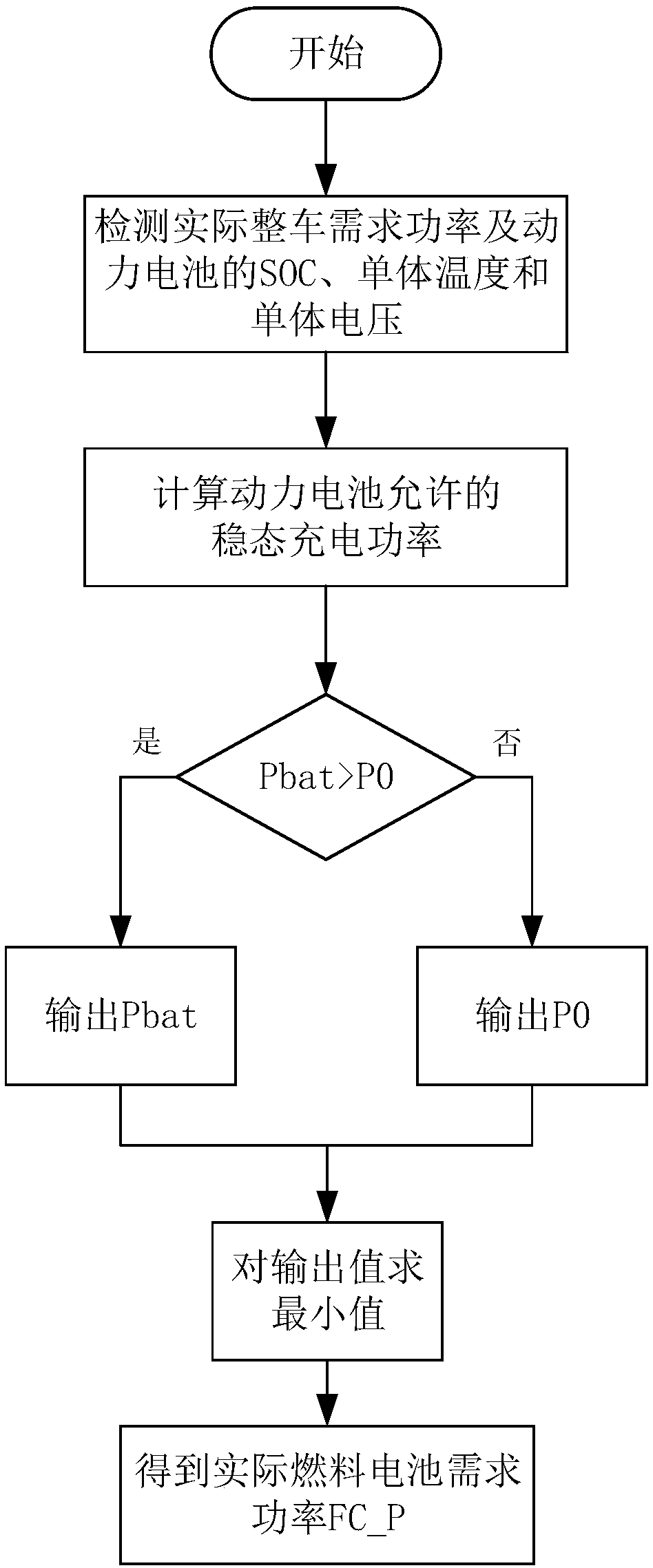
[0052]In order to ensure the constant power output of the fuel cell and the balance of the SOC of the vehicle, on the basis of Embodiment 1, this Embodiment 2 provides a control method for a fuel cell system of a hybrid electric vehicle, such as image 3 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0053] Step S1, detecting the actual required power of the whole vehicle, the SOC of the power battery, the temperature and the voltage of the single cells.
[0054] The vehicle controller obtains the corresponding actual required power P of the vehicle, the SOC of the power battery, the cell temperature and the cell voltage through the sensors or controllers corresponding to the above detection objects.
[0055] Step S2, calculating the actual required power and the allowable steady-state charging power of the power battery.
[0056] By comparing the relationship between SOC and its set value and the relationship between P and its set value, the actual demanded power is obtained...
Embodiment 3
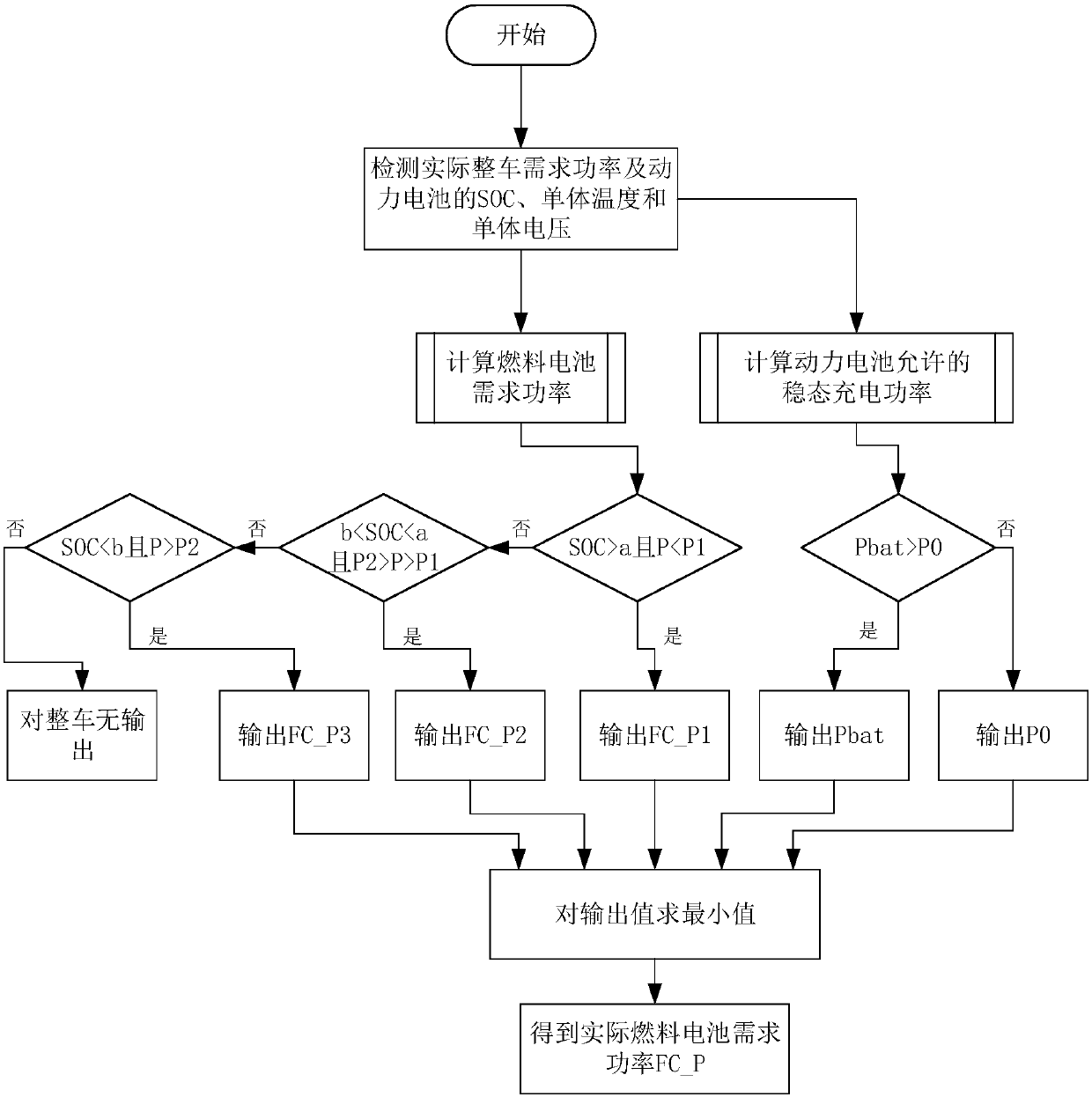
[0063] In order to avoid the overload of the fuel cell, on the basis of embodiment 2, this embodiment 3 provides a control method for a fuel cell system of a hybrid electric vehicle, such as Figure 4 As shown, the specific process also includes obtaining the loadable power limit of the fuel cell system when the fuel cell is started after step 1 of the above-mentioned embodiment 2.
[0064] When the fuel cell controller supplies power, it receives an instruction to start the fuel cell, controls the start of the fuel cell, and calculates the loadable power of the fuel cell system at this time, and outputs the limit value of the loadable power; in step S3 of embodiment 2 The loadable power limit is also compared with the actual demand power and the steady-state charging power or the set steady-state charging power to find the minimum value.
[0065] When the actual required power and charging required power are higher than the loadable power limit of the fuel cell system, the se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com