K-means non-uniform quantization algorithm for filter bank multi-carrier modulation optical communication system
A multi-carrier modulation and optical communication system technology, applied in the field of K-means non-uniform quantization algorithm, can solve the problems of high computational complexity, storage complexity, and large sample number requirements, and achieve good quantization performance, simple algorithm, and improved performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments. The following examples will help those skilled in the art to further understand the present invention, but do not limit the present invention in any form. It should be noted that those skilled in the art can make several changes and improvements without departing from the concept of the present invention. These all belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
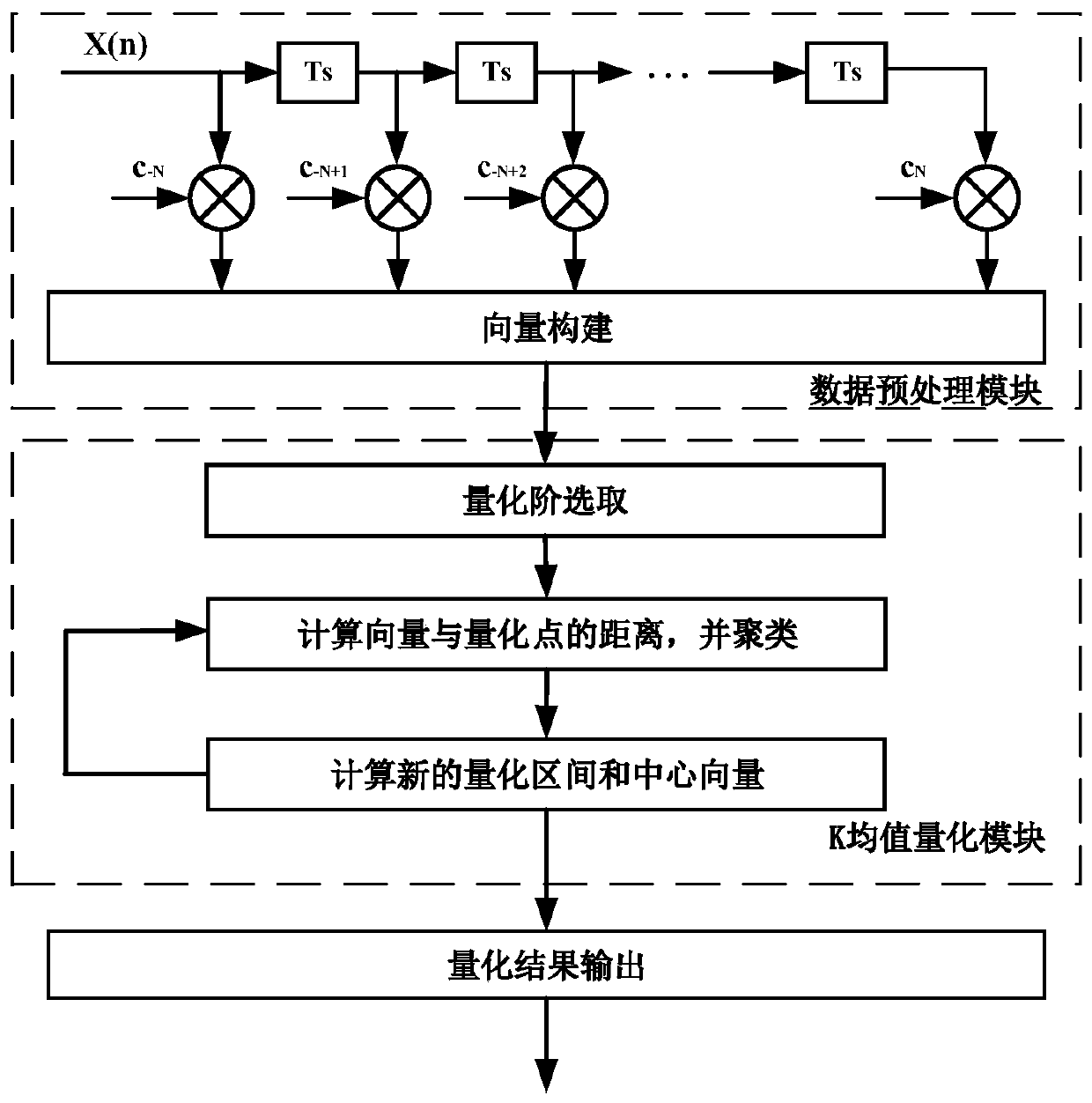
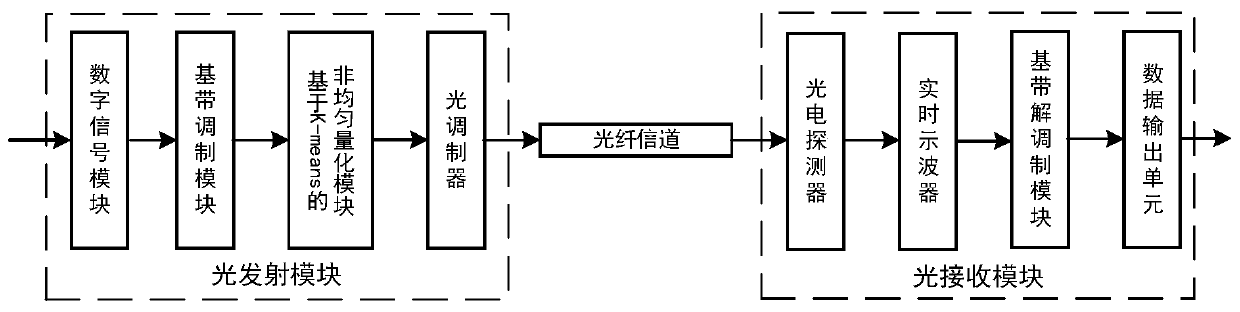
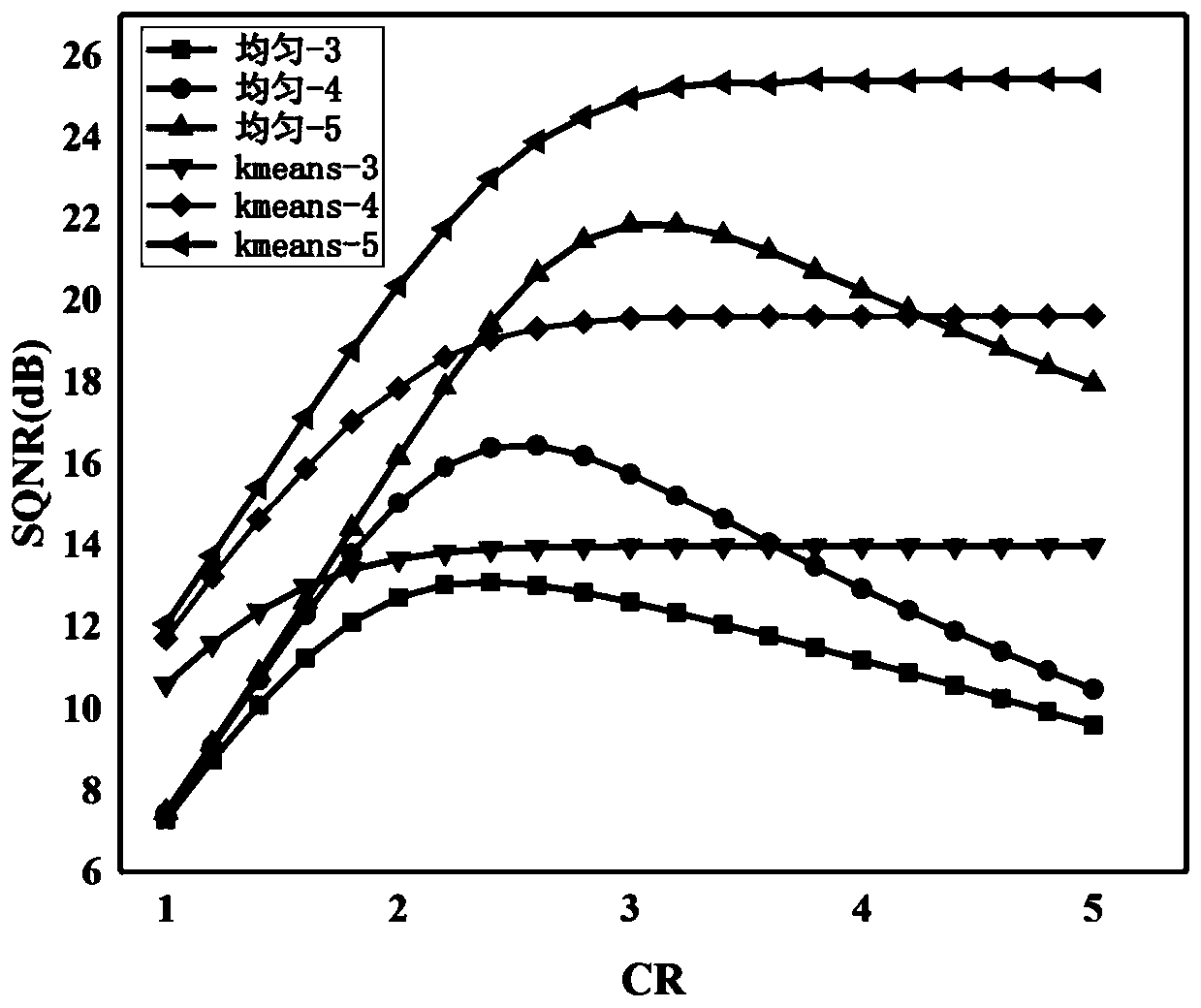
[0027] The invention provides a K-means non-uniform quantization algorithm used in a filter bank multi-carrier modulation optical communication system. Such as figure 1 As shown, the data preprocessing module preprocesses the input data sequence and forms the data sequence into M feature vectors. The K-means quantization module performs a clustering operation according to the Euclidean distance between the quantization order vector and each vector until the center vector does not change any more. The c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com