Wing-shaped optical fiber core adjustment structure
A core-tuning and optical fiber technology, applied in the field of X/Y-axis core-alignment alignment, can solve problems such as increasing the number of structural parts, material costs and processing costs, limited space for core-alignment structures, and occupying space for core-alignment optical fibers, etc., to achieve Avoid the decline in the quality of optical fiber fusion, ensure the quality of core alignment, and reduce the occupied space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
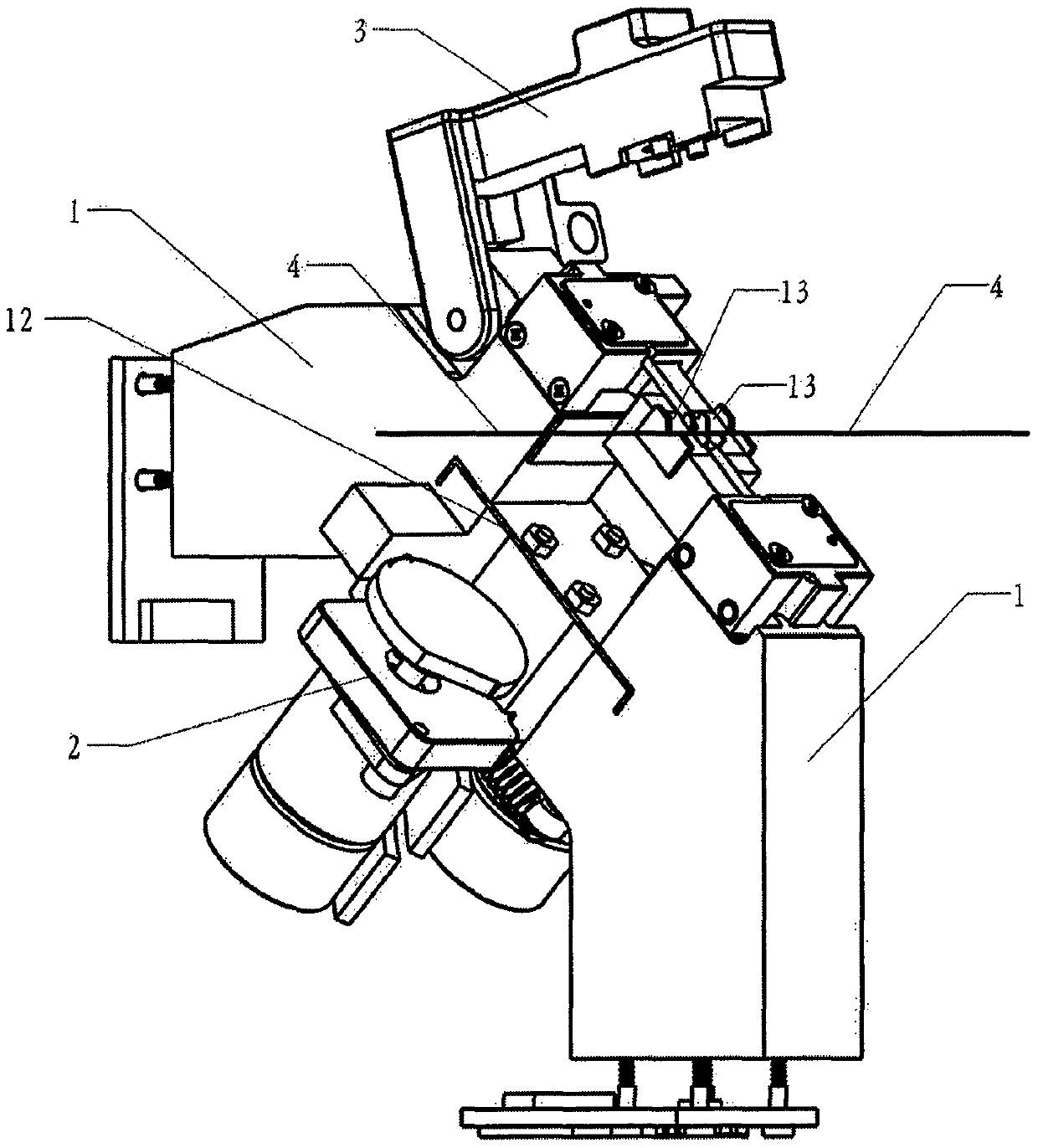
[0065] figure 1 It is the front view of the core structure of the airfoil fiber. As shown in the figure: two 1. main body components are connected as a whole through 12. connecting reeds. 2. The cam adjustment assembly is installed in the middle of 12. The connecting reed. 3. The hammer assembly is pivotally connected to the upper part of a 1. main body assembly, and can be opened and closed. The state shown in the figure is the open state. 4. The optical fiber is placed on the 13. V-groove of the two 1. body assemblies.
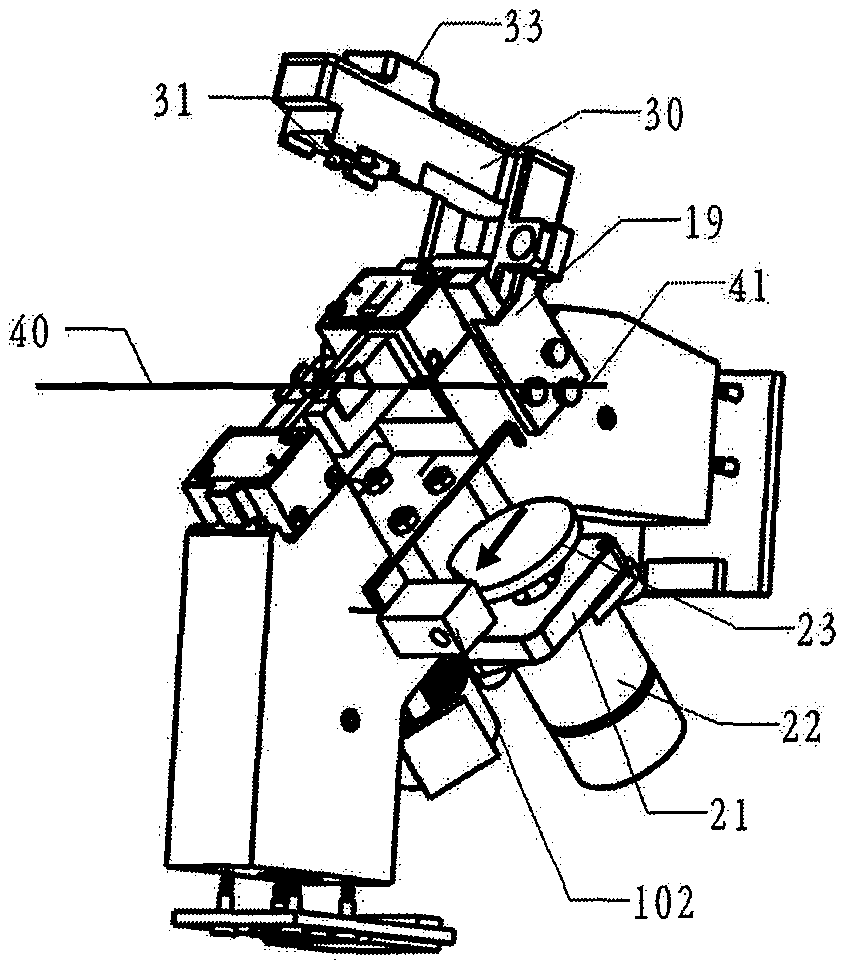
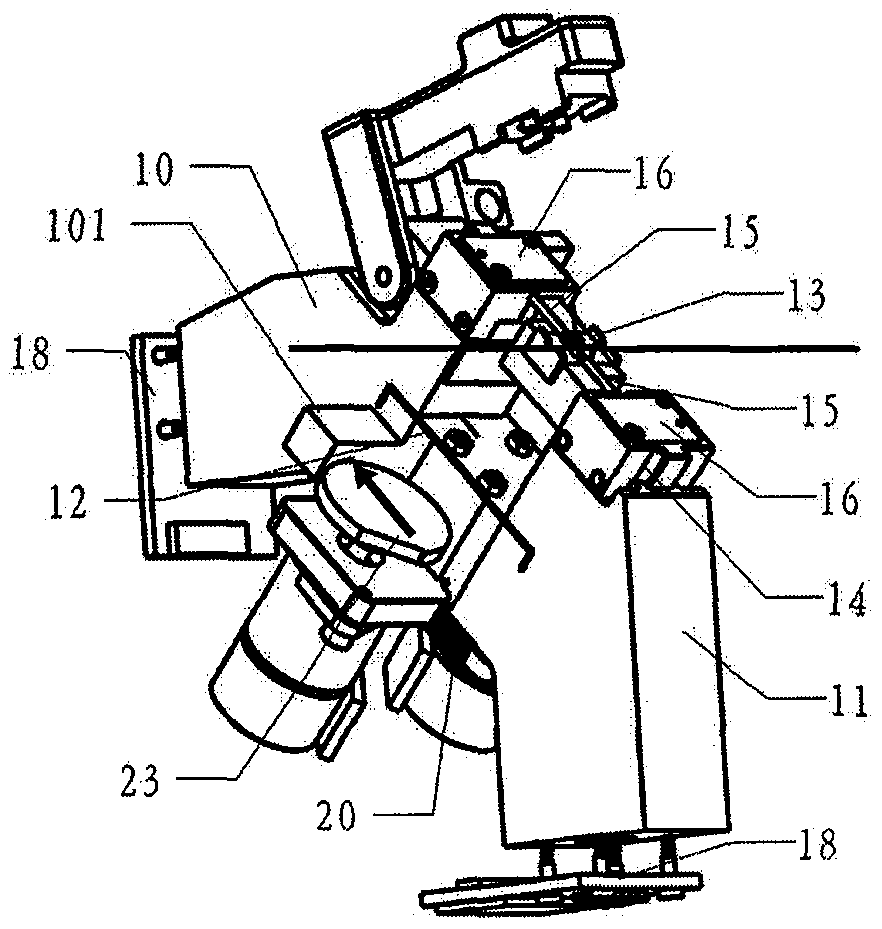
[0066] Figure 2A / Figure 2B It is the left and right side structure diagram of the airfoil fiber core adjustment structure. Yes figure 1 Further detailed structure diagram, as shown in the figure: take 12. connecting spring as the boundary, one side is 10. left assembly, 13. V-shaped groove, 14. V-shaped groove support frame, 15. electrode, 16. electrode fixing Board and connecting line, 18. CCD imaging board, 19. pressure hammer stopper, directly ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com