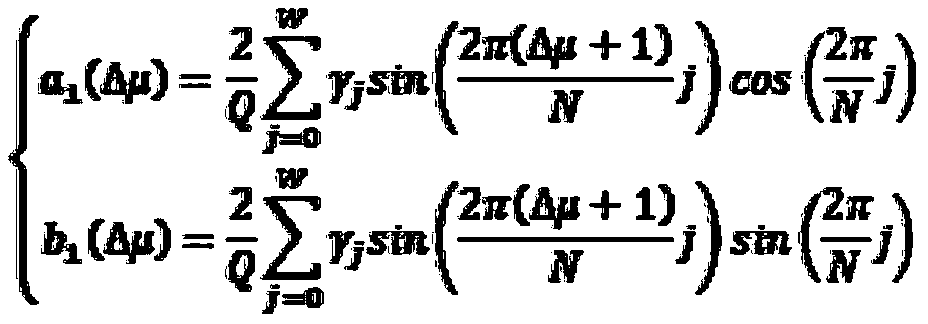Calculation method of quasi-synchronous DFT amplitude linear correction coefficient
A linear correction and calculation method technology, applied in the field of harmonic analysis, can solve the problems of untrustworthiness, large harmonic amplitude error of quasi-synchronous DFT algorithm, etc., and achieve the effect of simple algorithm
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
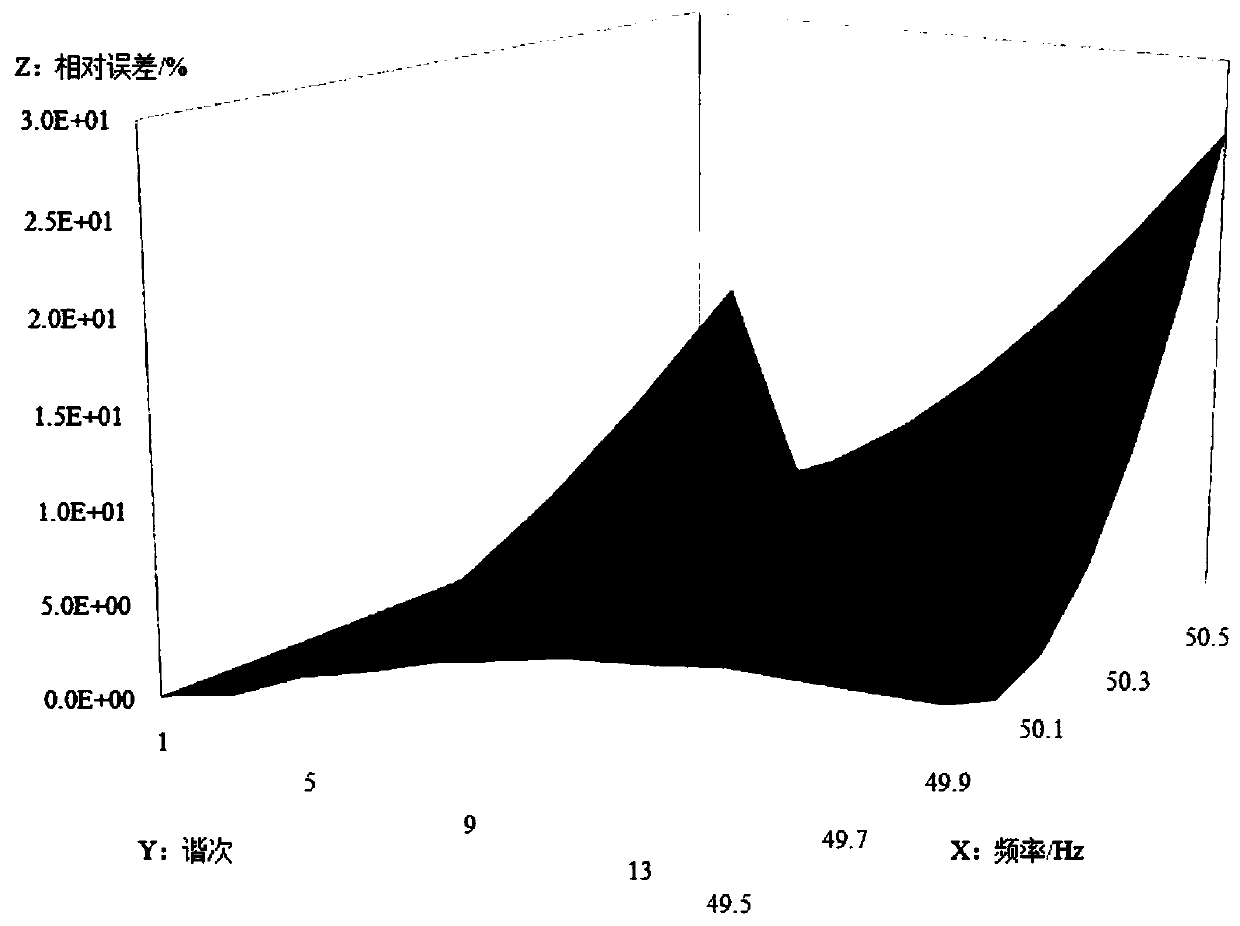
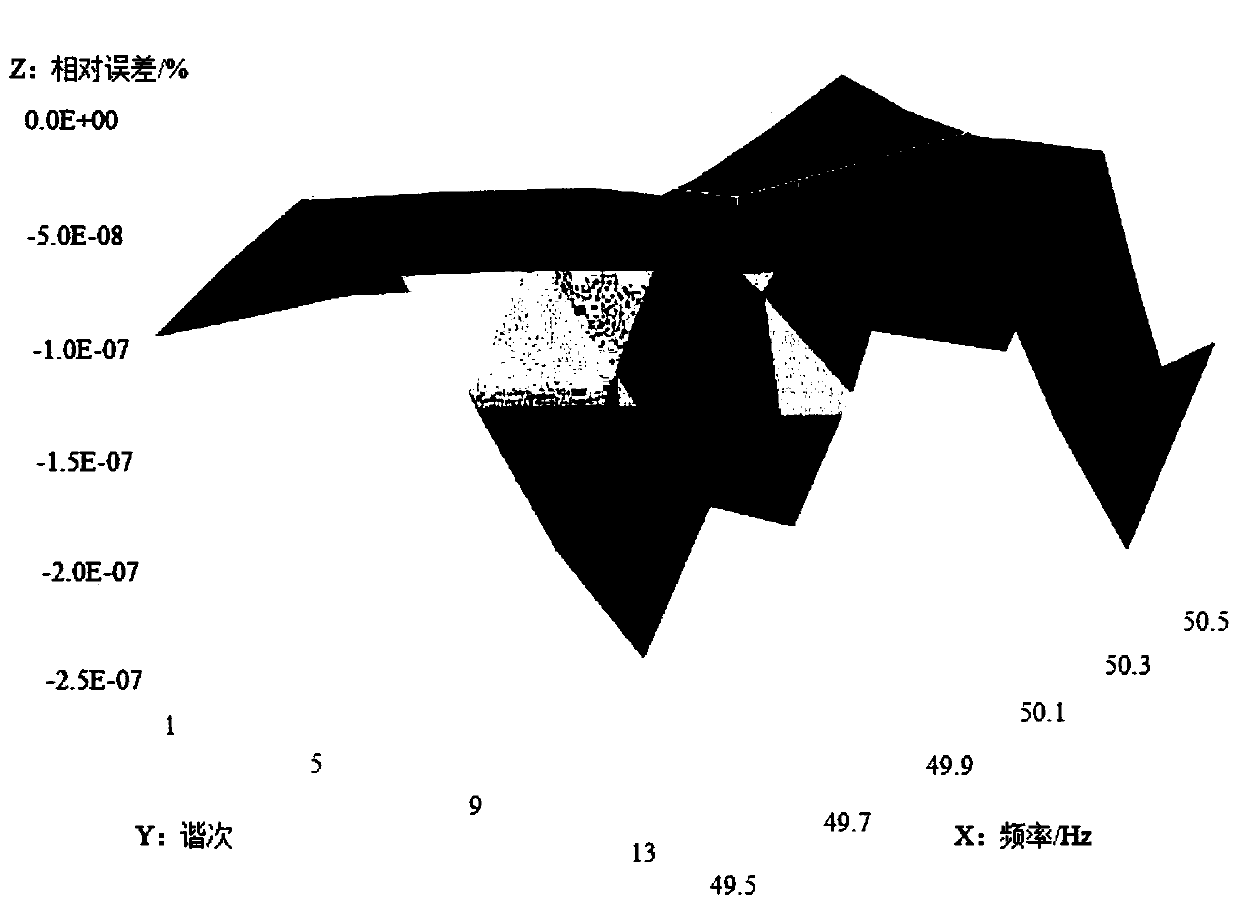
[0031] As shown in the figure, the quasi-synchronous DFT amplitude linear correction coefficient calculation method of the present invention includes 7 calculation steps:
[0032] Step 1. Δμ is in the range of [-30,30] and takes the value Δμ at an interval of 0.1 i , and according to the formula
[0033]
[0034] with
[0035]
[0036] Generate L=601 group A 1k data, and recorded as
[0037]
[0038] form;
[0039] Step 2, determine the positive integer M=10;
[0040] Step 3, according to Δμ i and M generate the array Δ;
[0041]
[0042] Step 4, according to the formula B=(Δ T Δ) -1 Δ T A
[0043] solve Step five, find the mean square error
[0044] Step 6. Increase the value of M to 20 one by one, repeat the above steps from Step 3 to Step 5, and record the corresponding G and B; Step 7, M and β to minimize G i That is, the amplitude linear correction coefficient of the quasi-synchronous DFT. When the integration method is the complex rectangular...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com