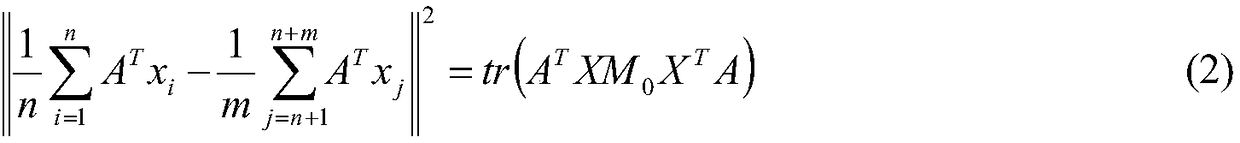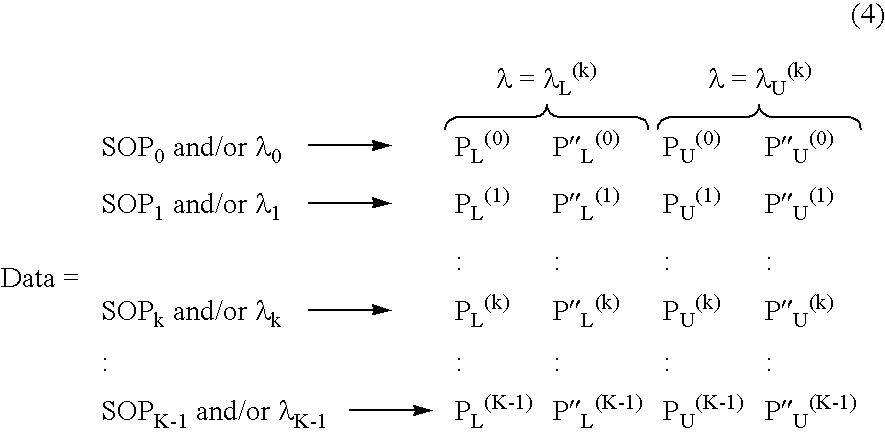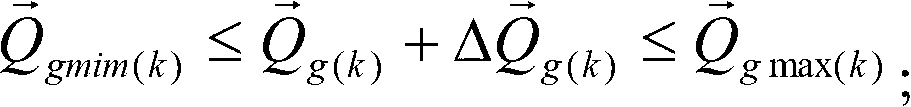Patents
Literature
83 results about "Mean square difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
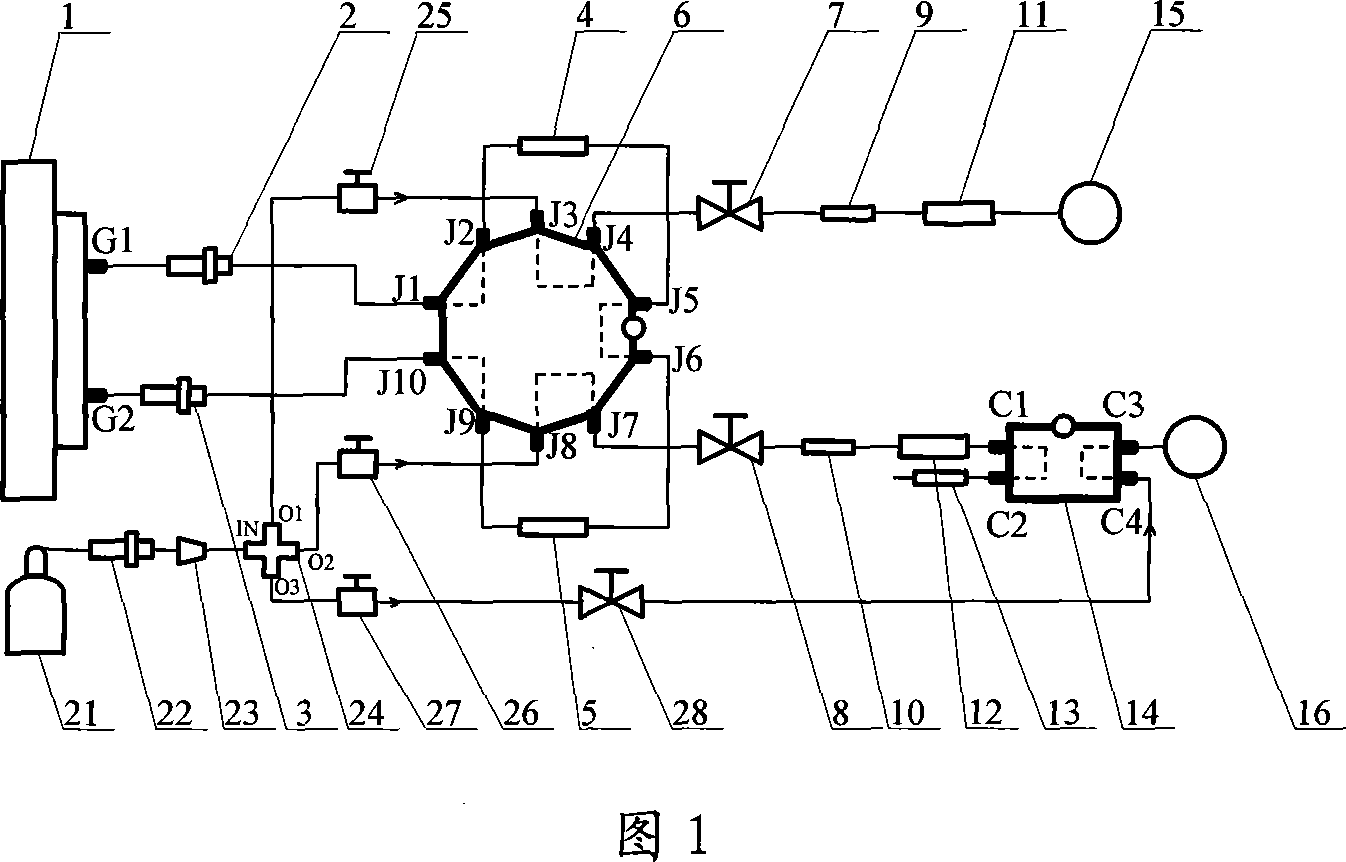
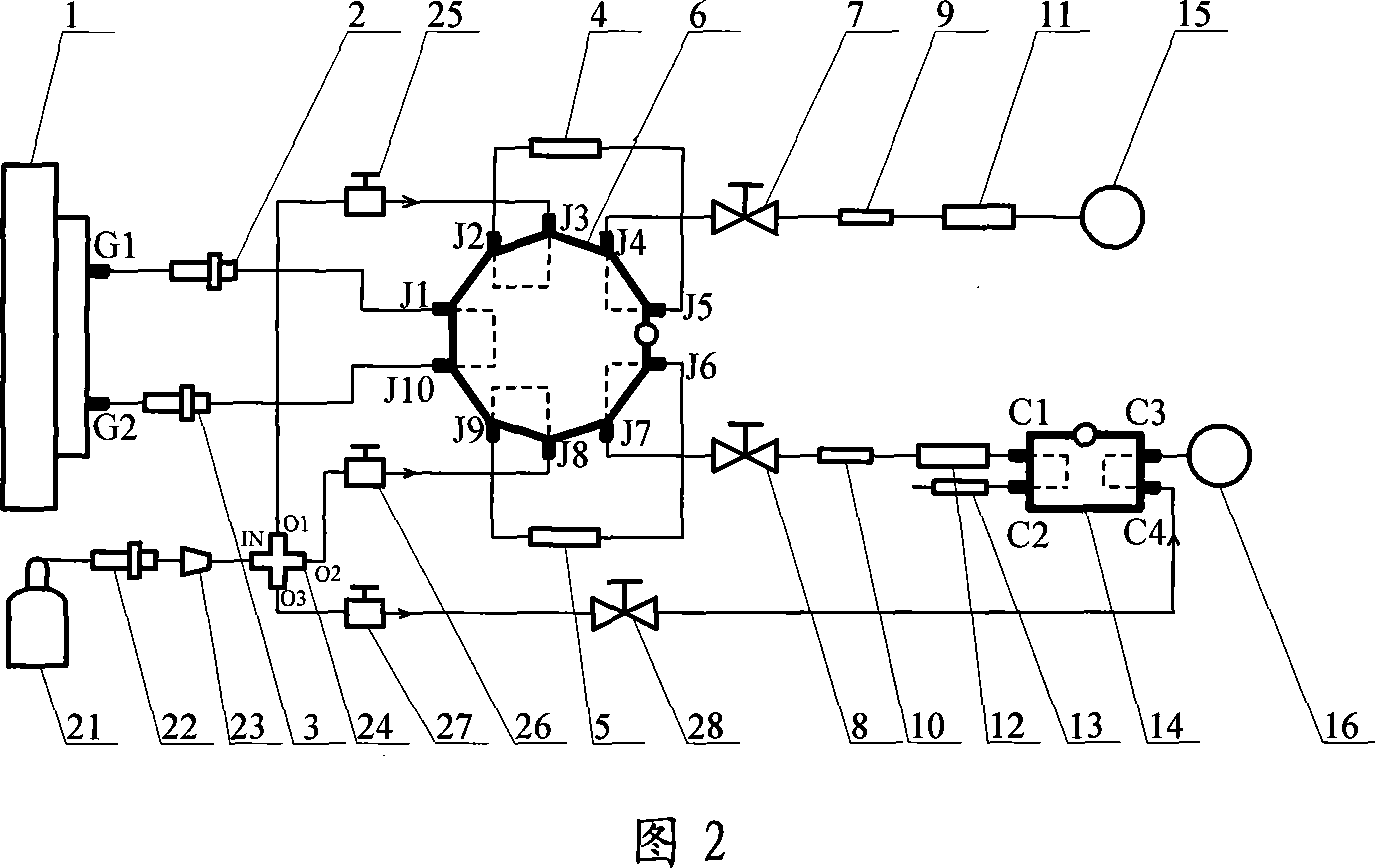
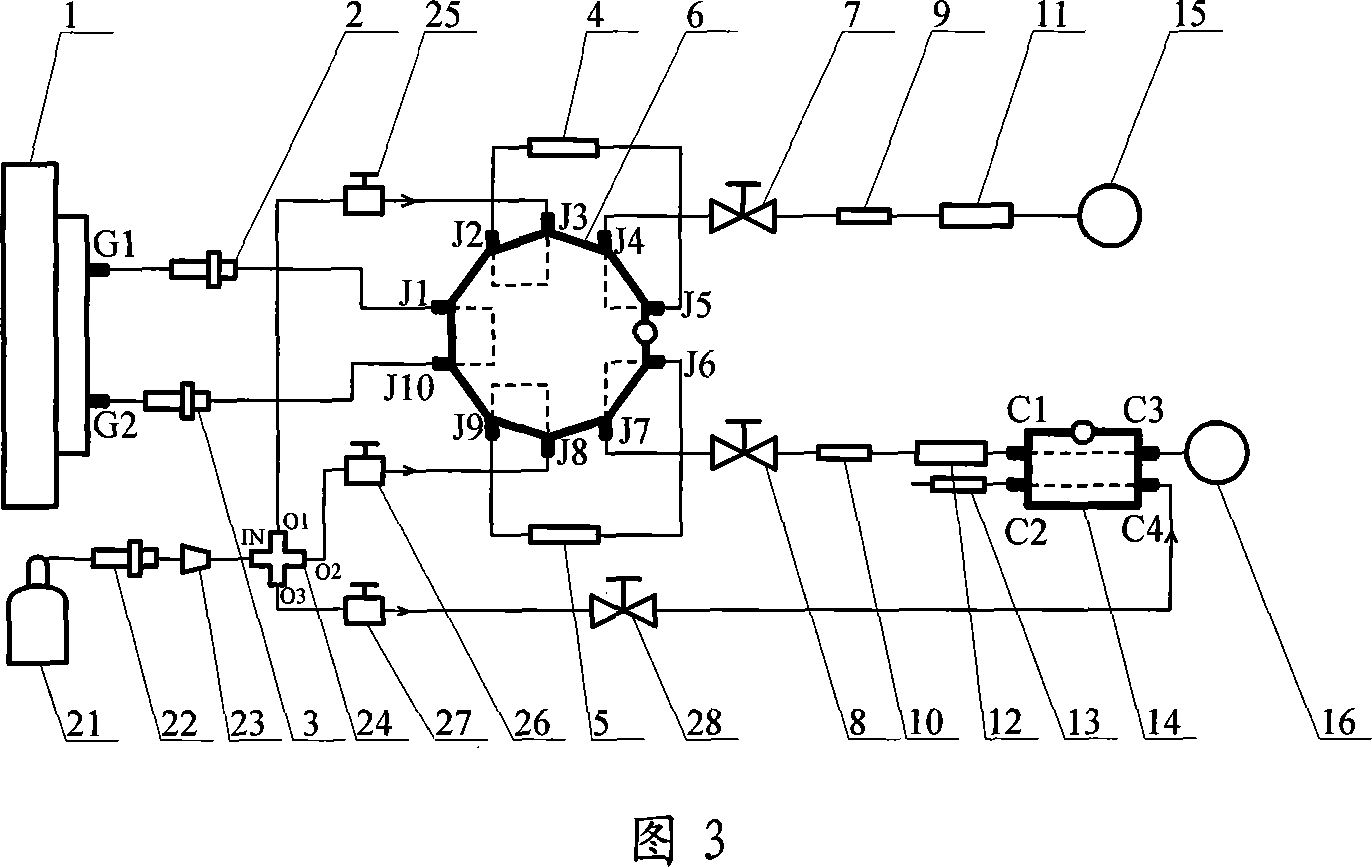
Characteristic point extraction-based three state data compression method of underground integrated monitoring system
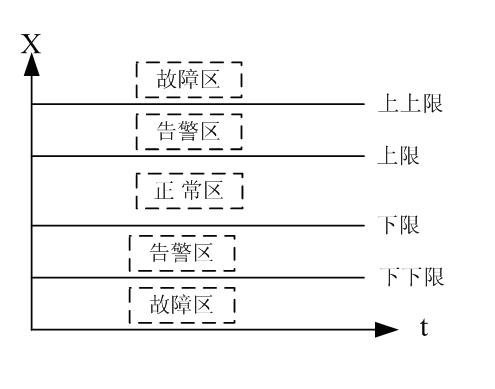
InactiveCN102437856AAvoid poor compression performanceGuaranteed compression accuracyCode conversionData packControl theory
The invention discloses a characteristic point extraction-based three state data compression method of an underground integrated monitoring system. Data point employed in the underground integrated monitoring system contains two types of data: an analog quantity and a switch quantity. The method comprises a step of analog quantity compression and a step of switching quantity compression. With regard to data quantity filtering of an analog quantity, an algorithm including dead zone compression, mean square deviation compression and slope compression of characteristic point extraction is provided; dynamic adjustment is carried out during a compression process, so that an error is controlled in a given range, compression precision is ensured and a high compression ratio is obtained. Compared with other compression algorithms, the provided compression method enables an on-site testing compression ratio to be improved by 50% to 90%, so that it is avoided that a compression performance is poor due to an unreasonable arrangement. According to the method in the invention, the performance of a historical database is stable; real-time data collection and data compression storage can be carried out simultaneously; and the data compression performance is outstanding.
Owner:GUODIAN NANJING AUTOMATION
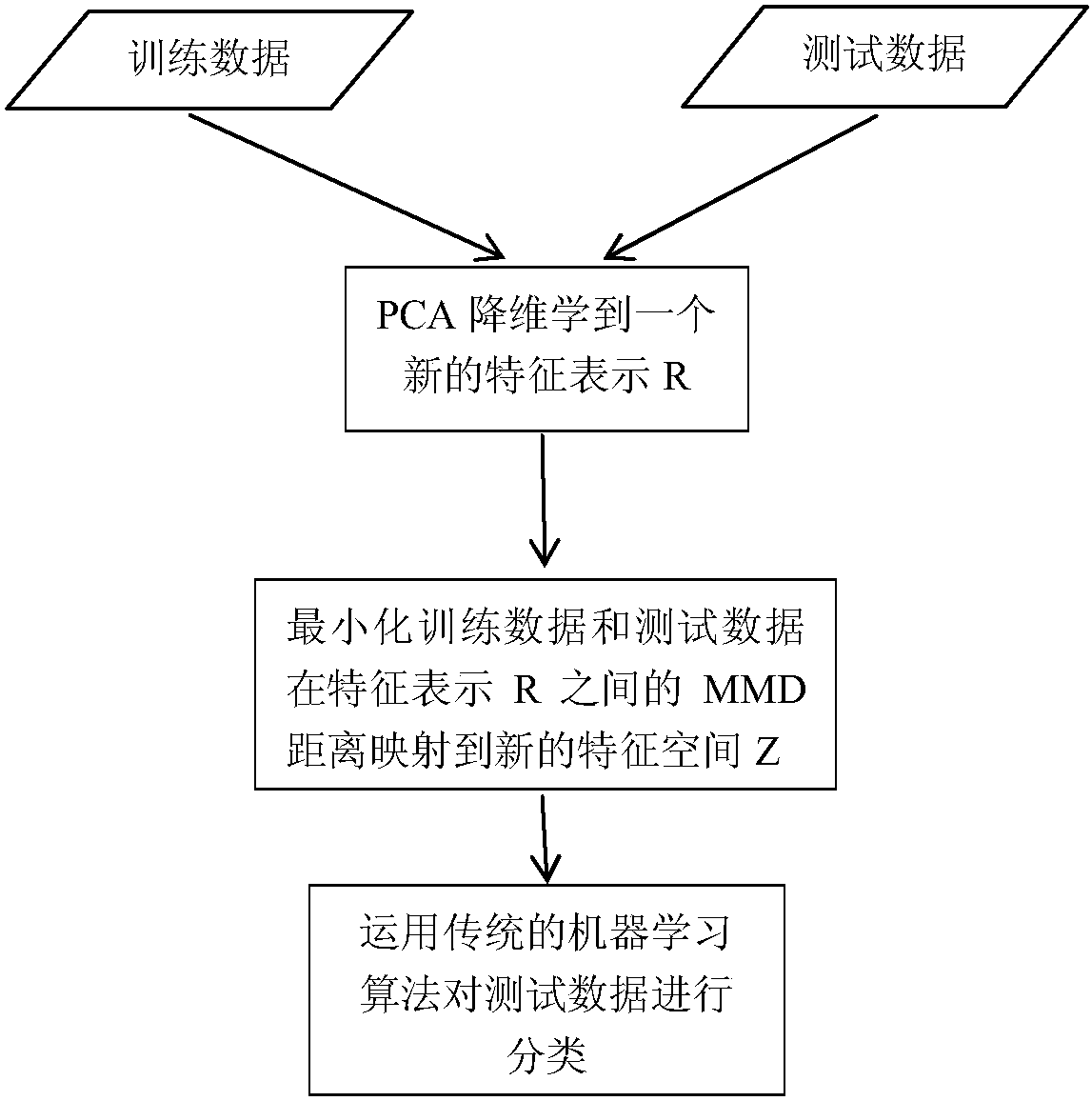
Software defect prediction method based on migration learning
ActiveCN108446711AGood defect prediction accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSoftware testing/debuggingDimensionality reductionPredictive methods
The invention discloses a software defect prediction method based on migration learning. The method is characterized in that the idea of dimensionality reduction migration learning is utilized, probability distribution and conditional probability distribution among different project data samples are comprehensively considered, a new feature representation between a source project and a target project is established, difference between the two in the new space is minimized, a new classifier is trained, and migration learning is realized. According to the method, firstly, a distance measurementmode between different distributions is employed, maximum mean square difference is utilized to quantify distribution difference and conditional distribution difference between source data and targetdata, a model is acquired through metric minimization, training data and test data mapped by the model have almost the same probability distribution and conditional probability distribution, and secondly, the test data is classified through the traditional machine learning algorithm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Automated picture montage method and apparatus
InactiveUS6549679B1AttractiveRapid productionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionEquipment computersMean square difference
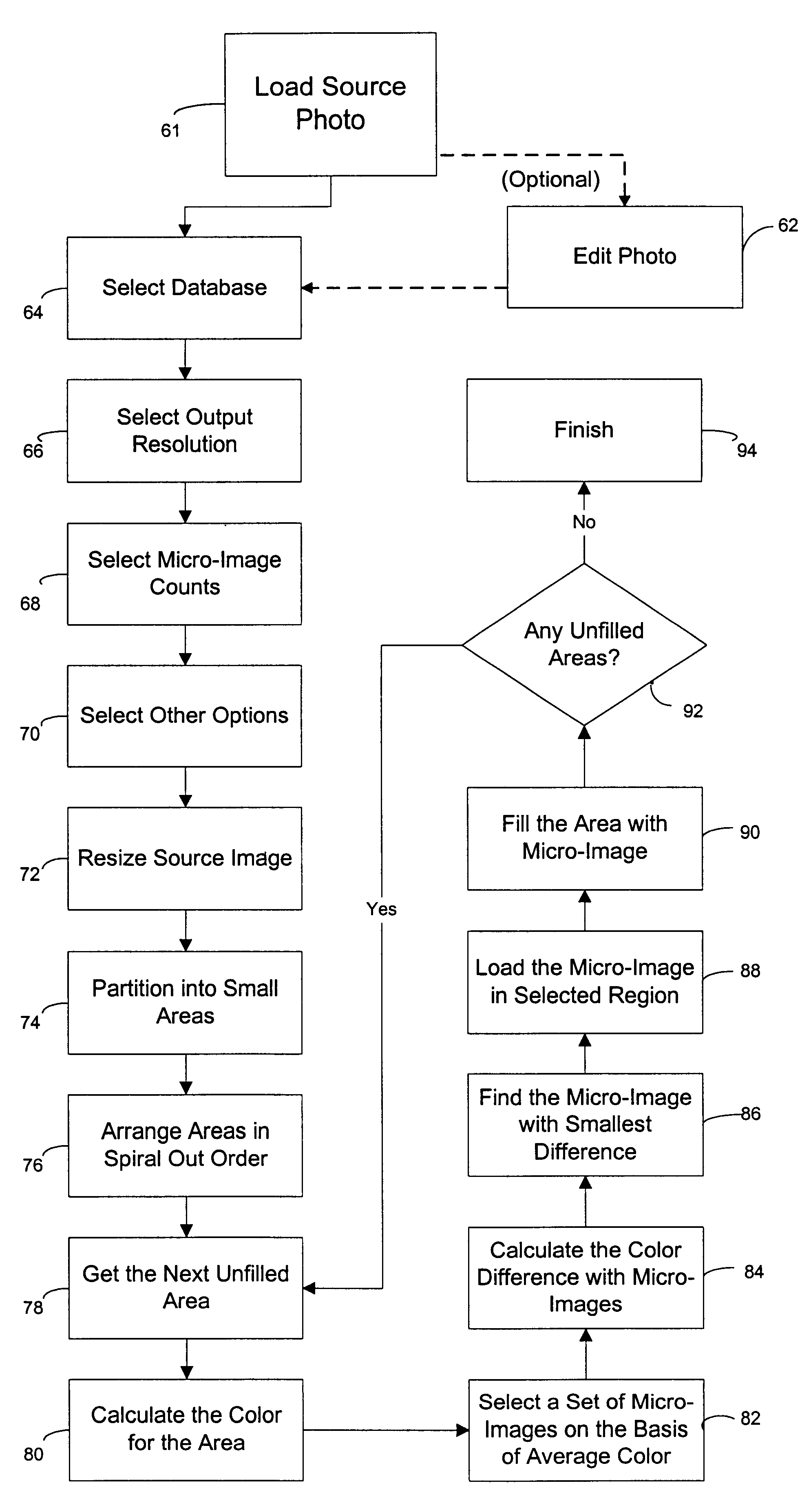
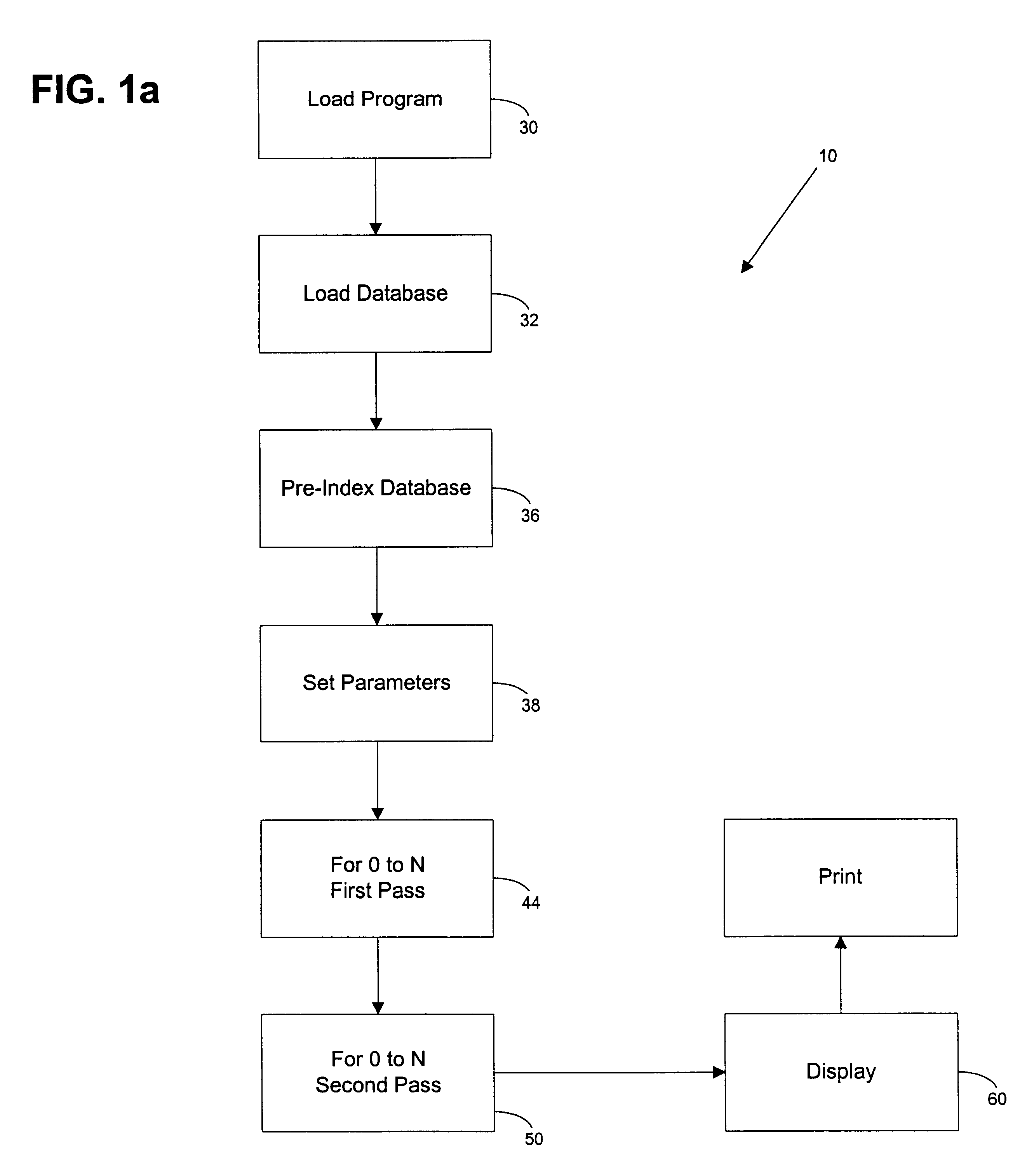
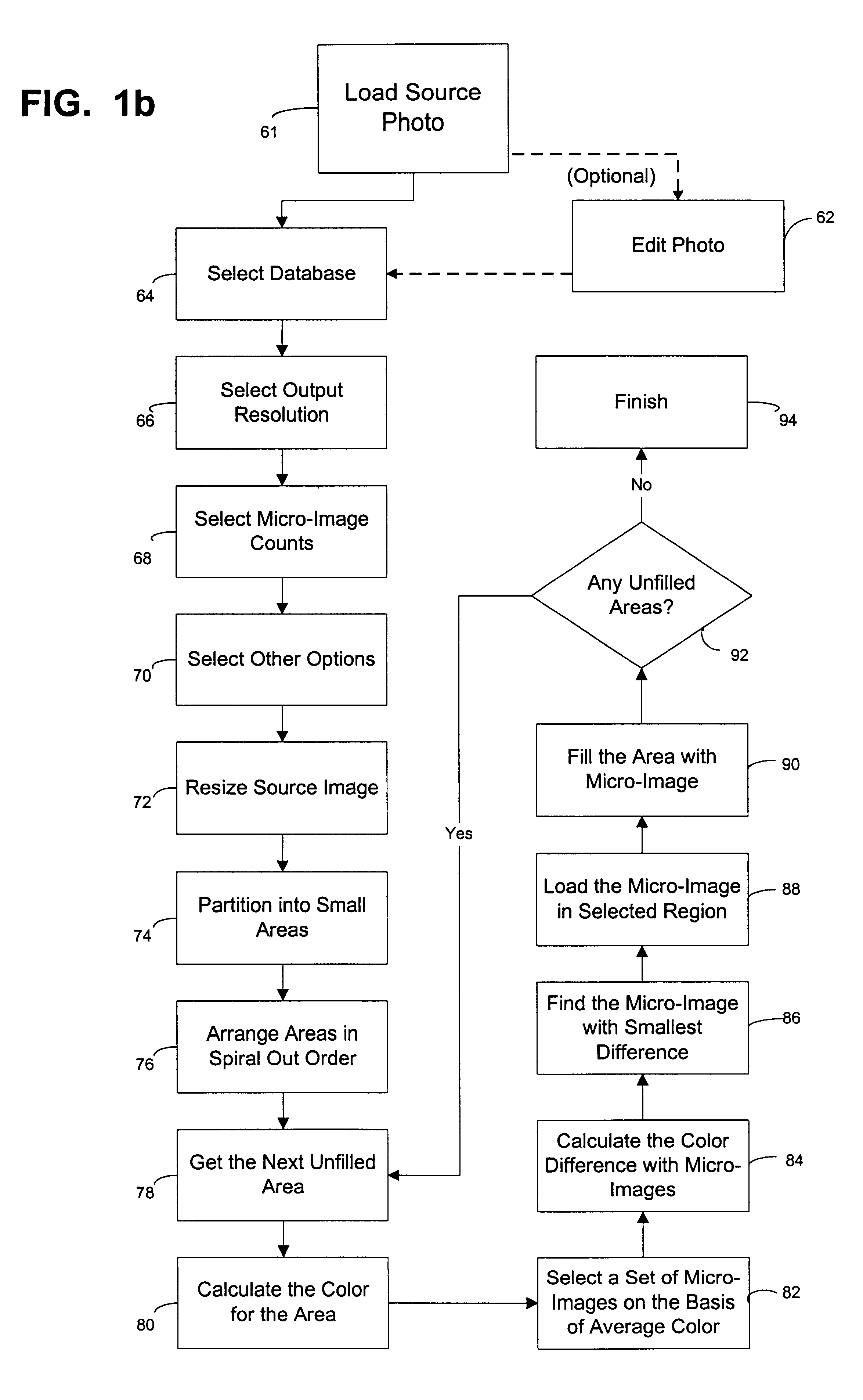
An automated picture montage method (10) and associated apparatus computer system (12) for accepting an original image (40) and a picture database (28) for creating a montage image (58) from a plurality of pictures (46) to approximate the original image (40). In a pre-index database operation (36), the database (28) is indexed so as to minimize the computational power required. In order to maximize the quality of image, tile regions (42) are analyzed beginning at a center tile region (54) in an outward spiraling order of progression (48). In order to speed the process, analysis is accomplished in a first pass operation (44) and a second pass operation (50). Pictures in the picture database (28) are first selected based on the average color difference of the pictures and the tile region (42). A best match picture is found based on the RGB mean square difference between picture subregions and tile subregions.
Owner:ARCSOFT
Small sample learning method based on multi-scale metric learning
ActiveCN111639679ASimple structureReasonable designCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningData setAlgorithm
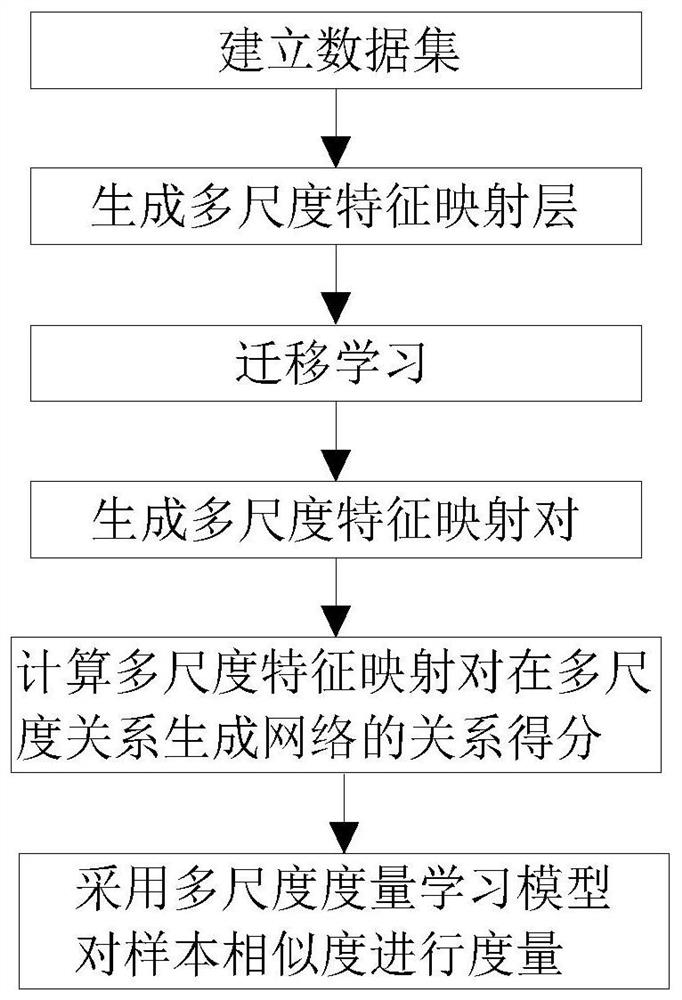
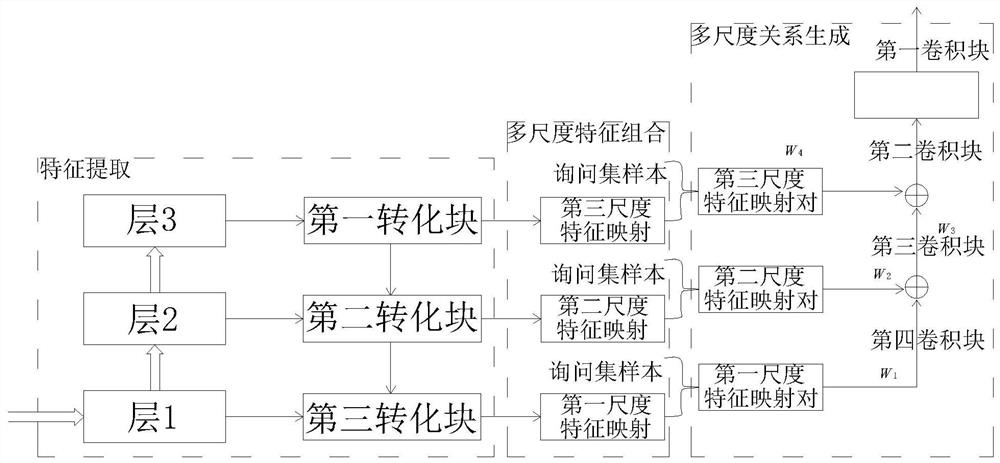
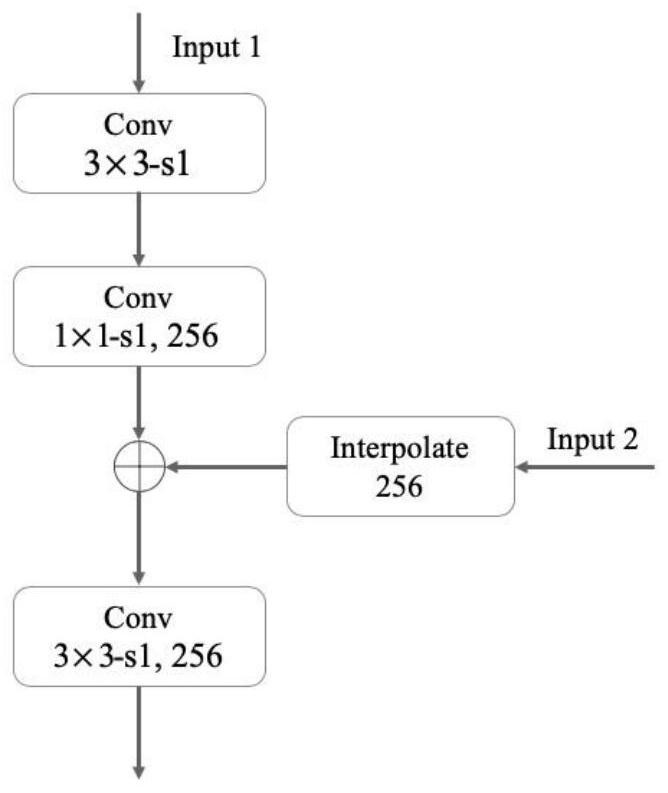
The invention discloses a small sample learning method based on multi-scale metric learning. The method comprises the following steps: 1, establishing a data set; 2, generating a multi-scale feature mapping layer; 3, performing transfer learning: performing secondary mapping on the multi-scale features of the sample by a conversion module; 4, generating a multi-scale feature mapping pair; 5, calculating a relationship score of the multi-scale feature mapping pair in the multi-scale relationship generation network; and 6, measuring the sample similarity by adopting a multi-scale measurement learning model. The method is simple in structure and reasonable in design, the multi-scale feature mapping pairs are obtained through transfer learning, the trained model has mobility, loss items brought to the whole model by sample spacing are added on the basis of a mean square error loss function to form a new loss function, metric learning is achieved, and the method adapts to training of smallsample learning.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
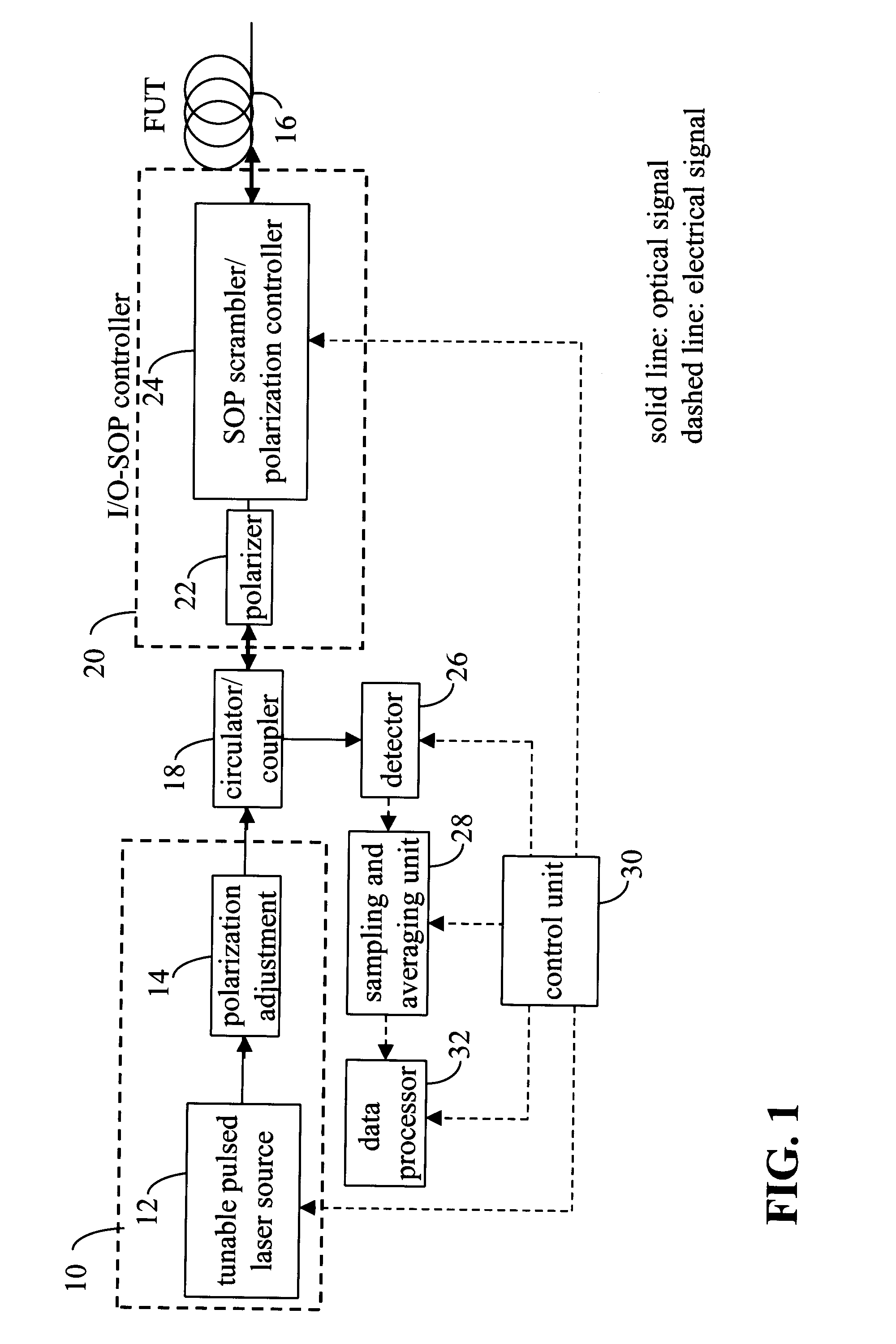
Polarization Optical Time Domain Reflectometer and Method of Determining PMD
InactiveUS20090244522A1Eliminate disadvantagesConvenient and accurateReflectometers dealing with polarizationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTime-domain reflectometerFiber
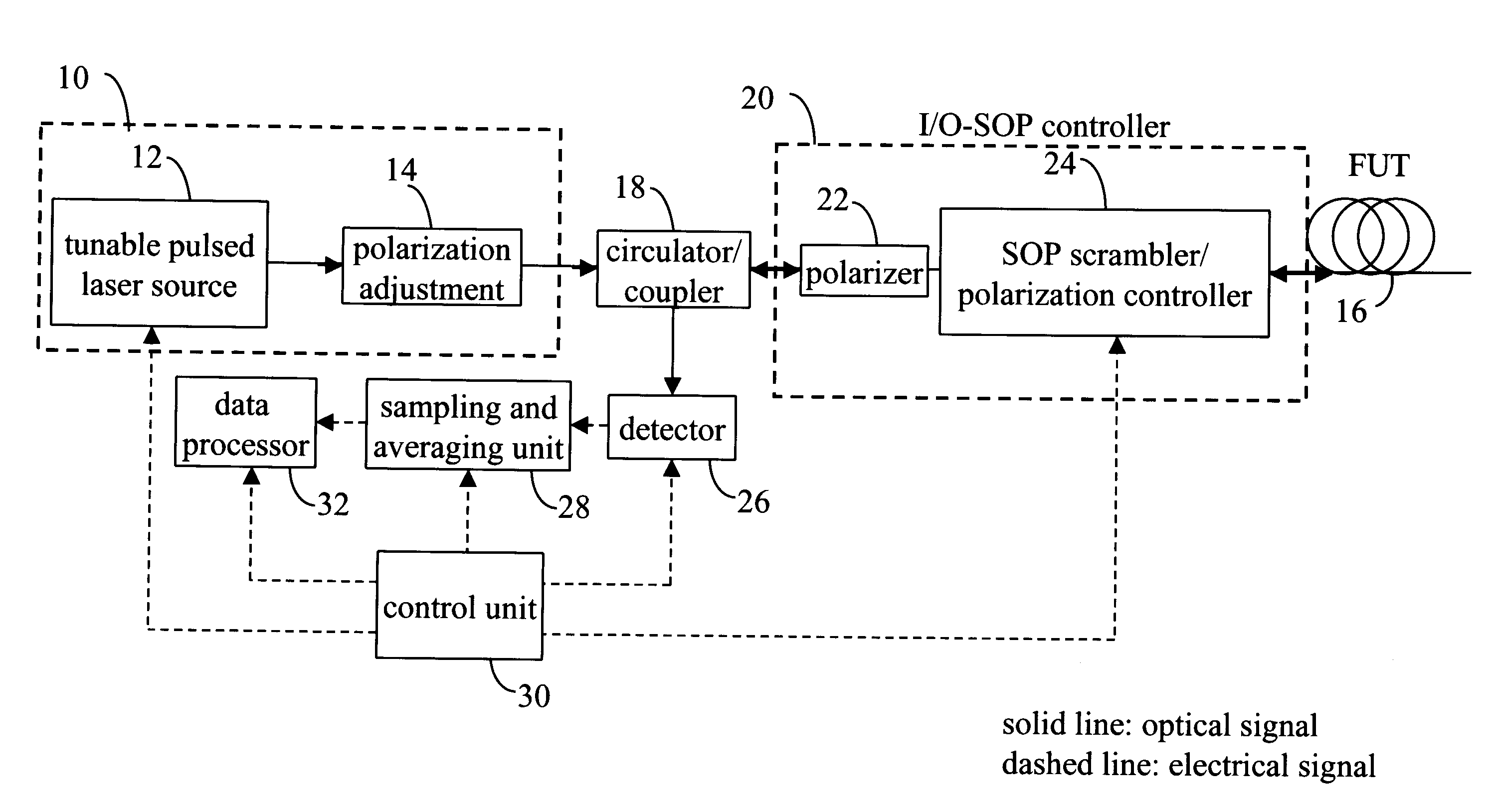
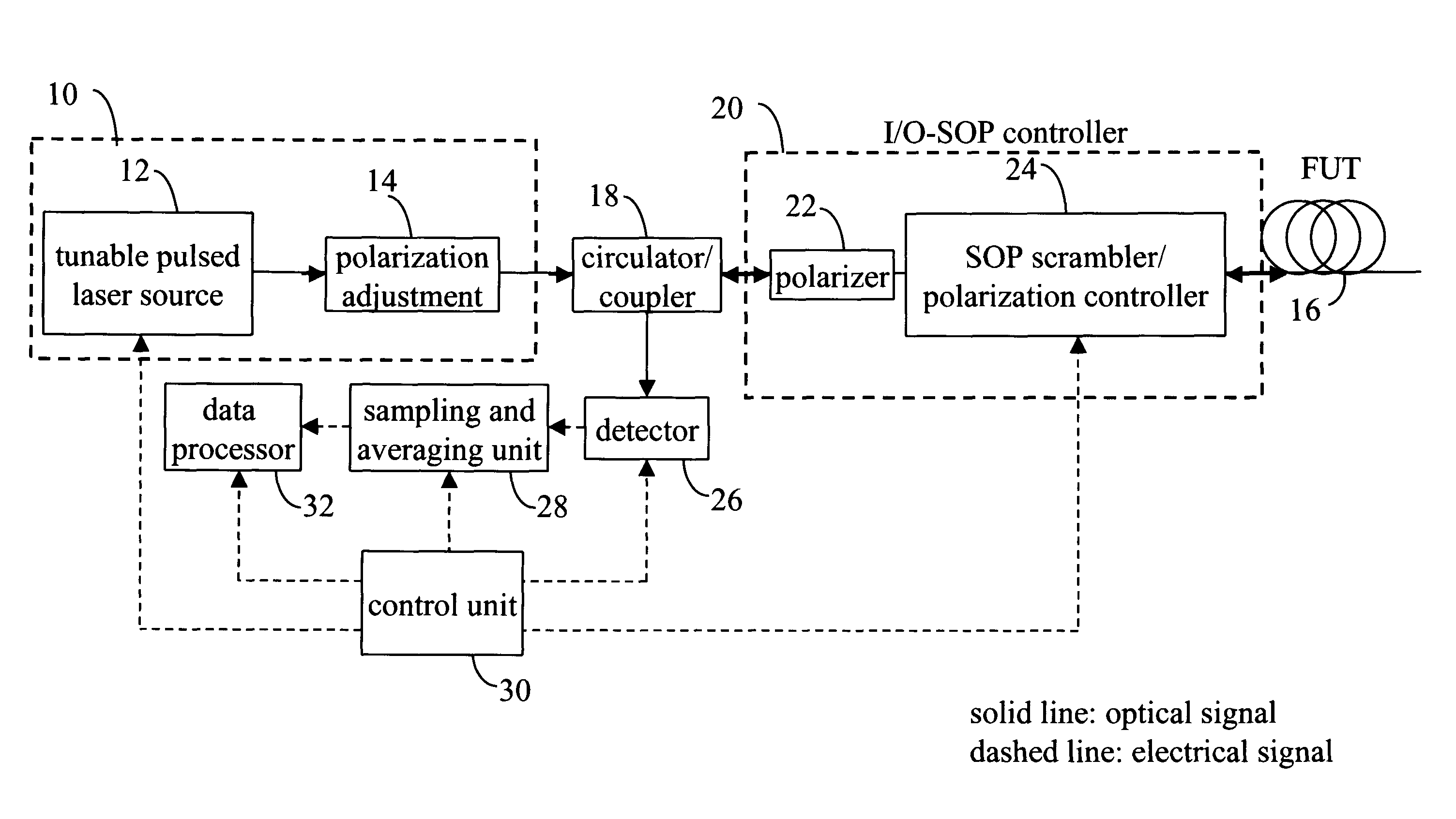
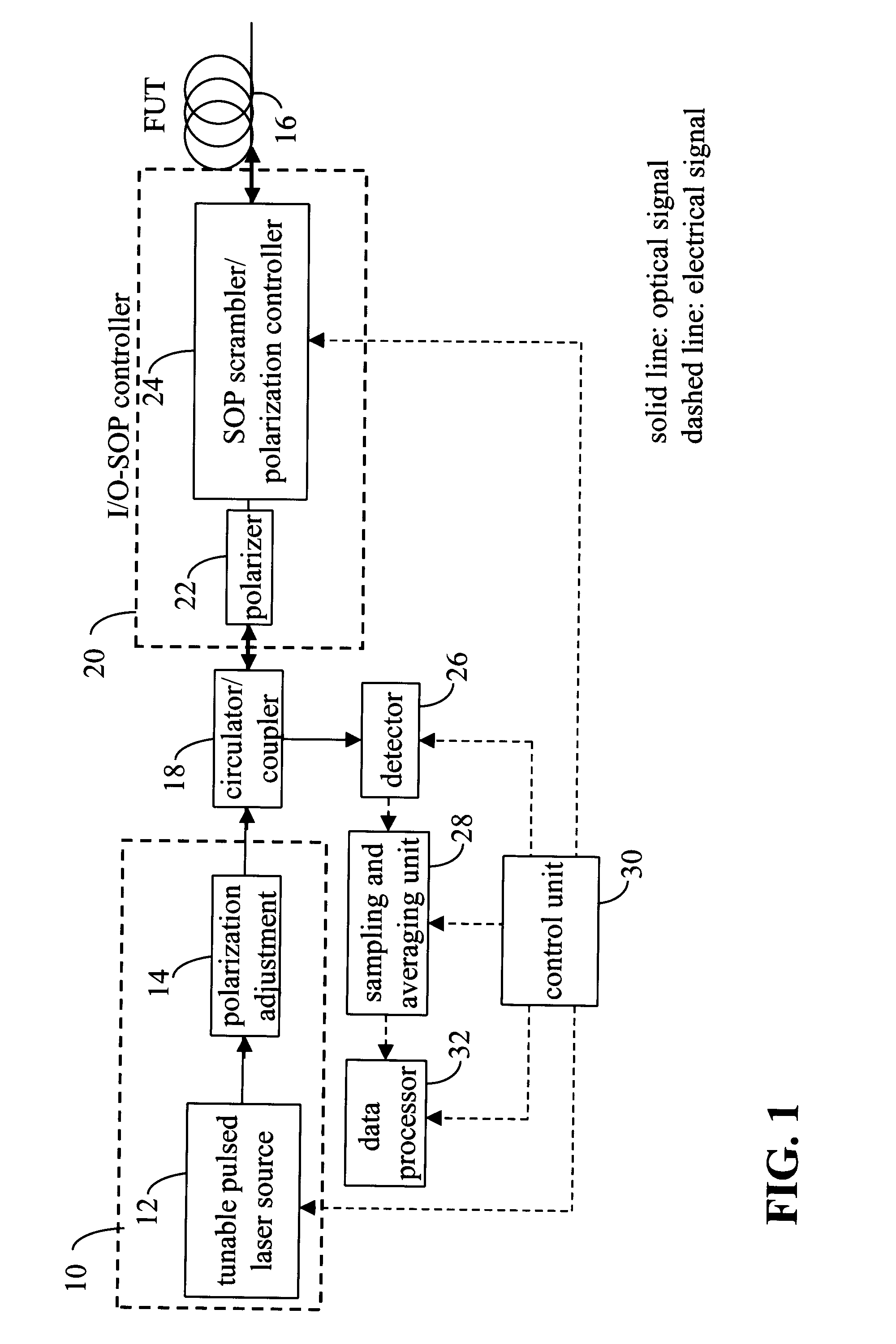
In a method of measuring cumulative polarization mode dispersion (PMD) along the length of a fiber-under-test (FUT), a polarization-sensitive optical time domain reflectometer (POTDR) is used to inject into the FUT plural series of light pulses arranged in several groups. Each group comprises at least two series of light pulses having different but closely-spaced wavelengths and the same state of polarization (SOP). At least two, and preferably a large number of such groups, are injected and corresponding OTDR traces obtained for each series of light pulses by averaging the impulse-response signals of the several series of light pulses in the group. The process is repeated for a large number of groups having different wavelengths and / or SOPs. The PMD then is obtained by normalizing the OTDR traces of all of the groups, then computing the difference between each normalized OTDR trace in one group and the corresponding normalized OTDR trace in another group, followed by the mean-square value of the differences. Finally, the PMD is computed as a predetermined function of the mean-square difference. The function may, for example, be a differential formula, an arcsine formula, and so on.
Owner:EXFO ELECTRO OPTICAL ENG
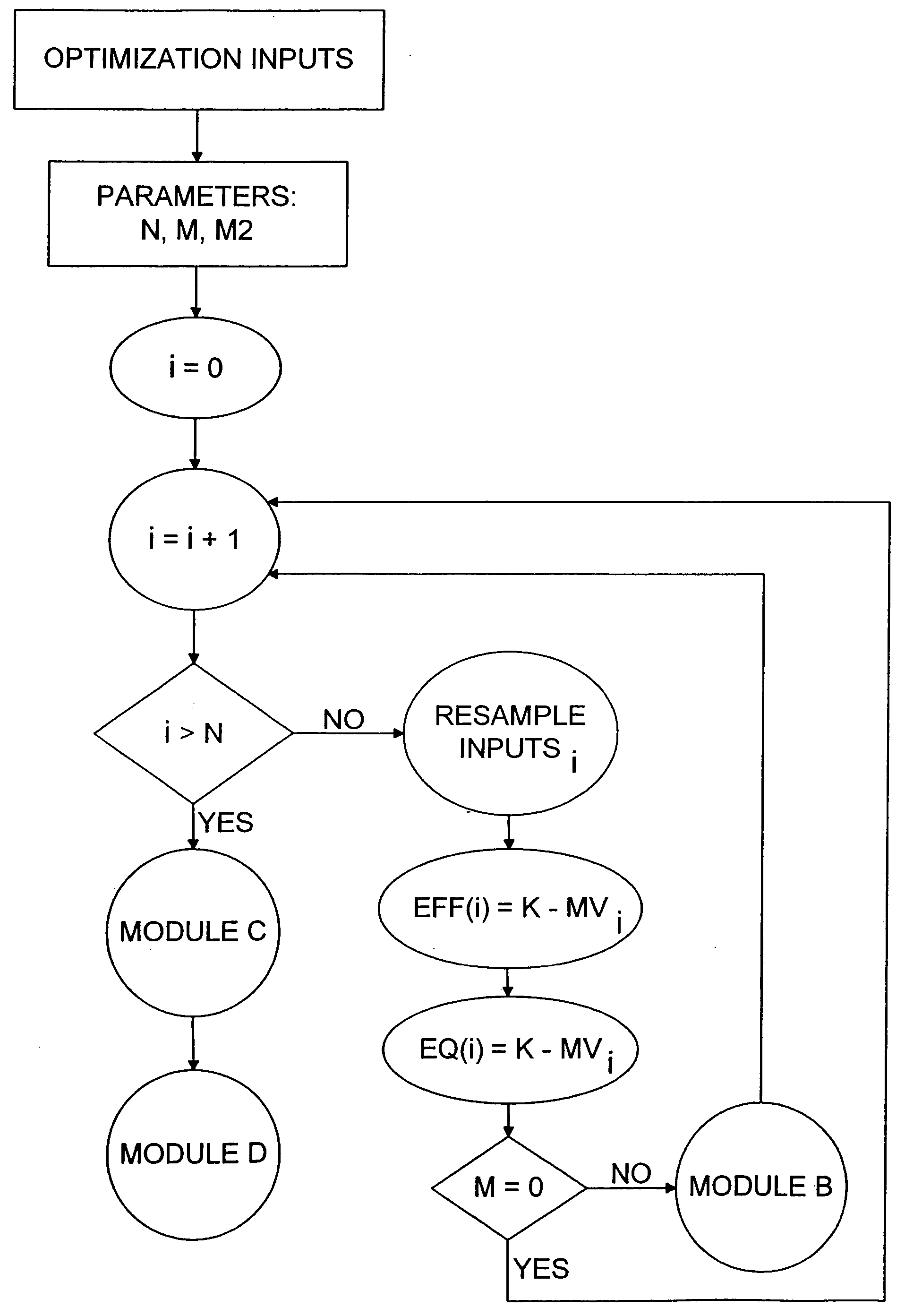
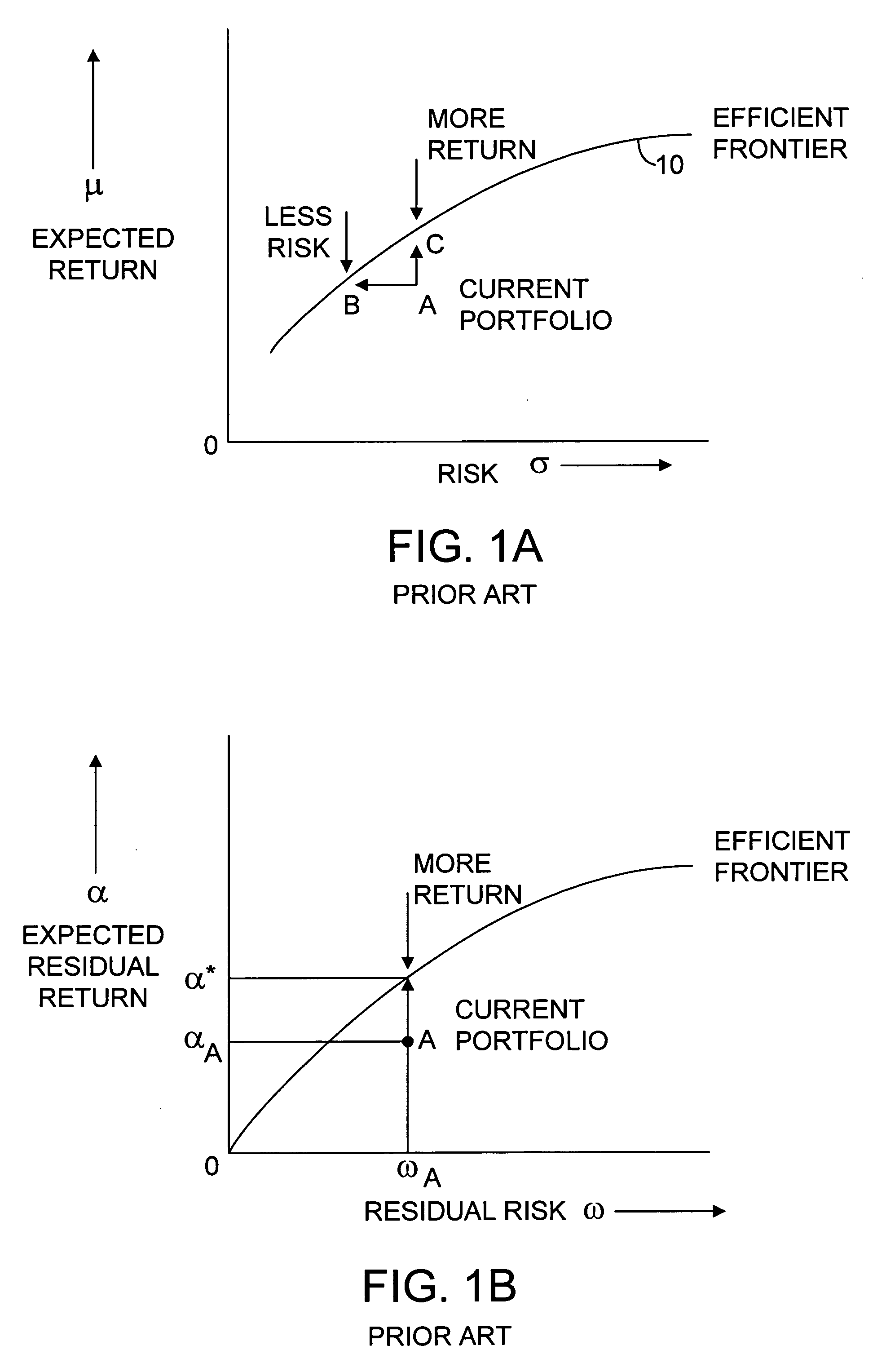
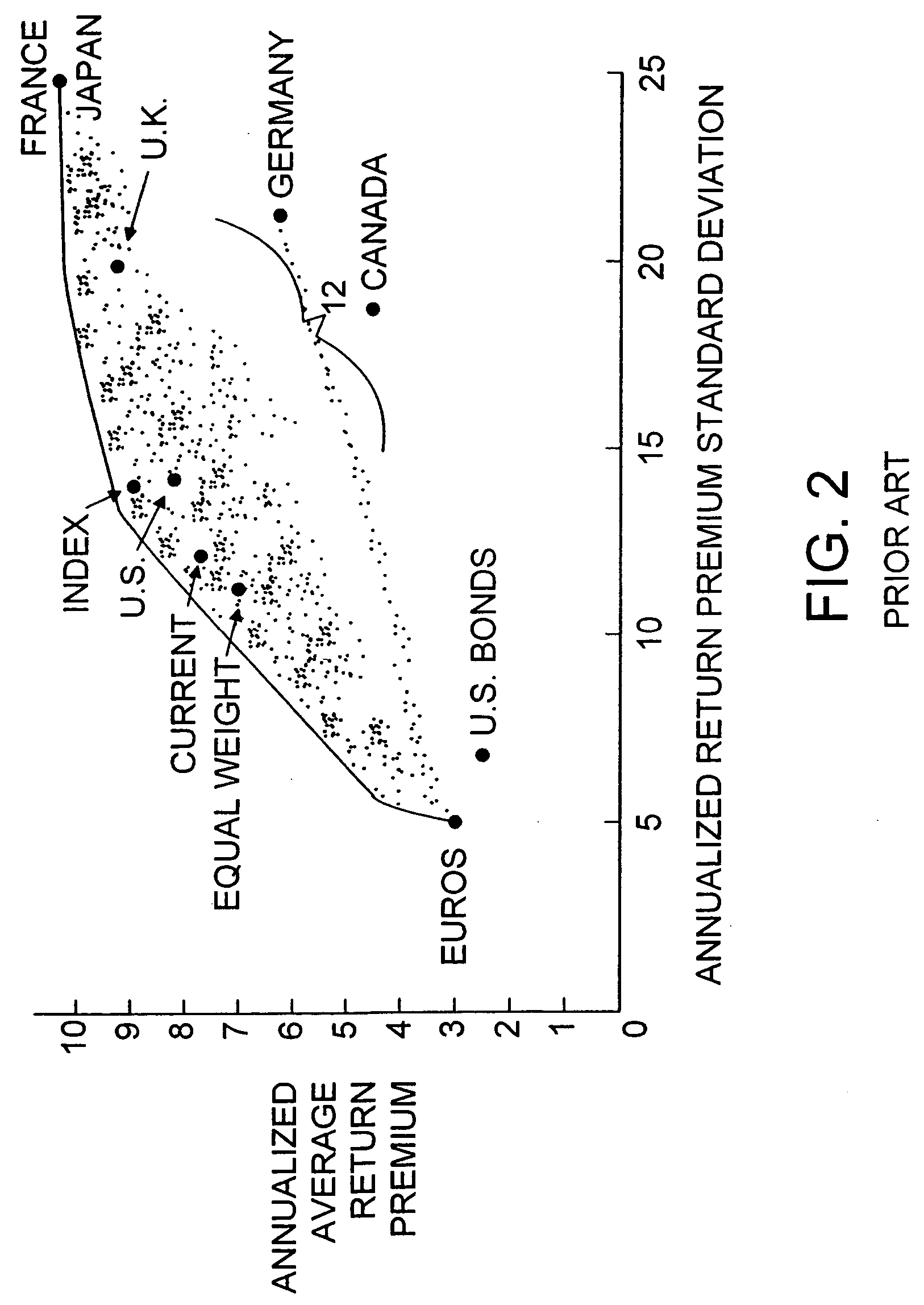
Portfolio rebalancing by means of resampled efficient frontiers with forecast confidence level
A computer-implemented method and computer program product for selecting a portfolio weight (subject to specified constraints) for each of a plurality of assets of an optimal portfolio. A mean-variance efficient frontier is calculated based on input data characterizing the defined expected return and the defined standard deviation of return of each of the plurality of assets. Multiple sets of optimization inputs are drawn from a distribution of simulated optimization inputs consistent with the defined expected return, the defined standard deviation of return of each of the plurality of assets and then a simulated mean-variance efficient frontier is computed for each set of optimization inputs. A meta-resampled efficient frontier is determined as a statistical mean of associated portfolios among the simulated mean-variance efficient frontiers, and a portfolio weight is selected for each asset from the meta-resampled efficient frontier according to a specified investment objective. The number of simulations and the number of simulation periods is determined on the basis of a specified level of forecast certainty.
Owner:MICHAUD PARTNERS
Polarization optical time domain reflectometer and method of determining PMD
InactiveUS7920253B2Convenient and accurateImprove accuracyReflectometers dealing with polarizationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFiberTime domain
In a method of measuring cumulative polarization mode dispersion (PMD) along the length of a fiber-under-test (FUT), a polarization-sensitive optical time domain reflectometer (POTDR) is used to inject into the FUT plural series of light pulses arranged in several groups. Each group comprises at least two series having closely-spaced wavelengths and the same state of polarization (SOP). At least two of such groups are injected and corresponding OTDR traces obtained for each series by averaging the impulse-response signals of the several series in the group. The process is repeated for a number of groups. The PMD is obtained by normalizing the OTDR traces of all of the groups, then computing the difference between each normalized OTDR trace in one group and the corresponding normalized OTDR trace in another group, followed by the mean-square value of the differences. Finally, the PMD is computed as a predetermined function of the mean-square difference.
Owner:EXFO ELECTRO OPTICAL ENG
Self-adaptive monitoring method for gas dissolved in oil of traction transformer, and the device thereof
InactiveCN101059525AReduce adverse effectsExtended service lifePreparing sample for investigationSensor arrayEngineering
The invention discloses a self-adaptive detect method of the gas dissolved in the oil of a drawing transformer, and a relative device, wherein the invention uses a high-density gas sensor array to check the object gas to obtain a first check value, when the first check value is higher than a preset threshold value, using the first check value as the check result, or else, uses a low-density gas sensor array to check the object gas again, using the second check value as the check result. And the invention judges if the ratio between the average value and mean square difference of the check values of all sensors in the array is over a preset value to check the condition of the array. The invention has high measuring accuracy, better repeatability, long service life, and low check cost.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
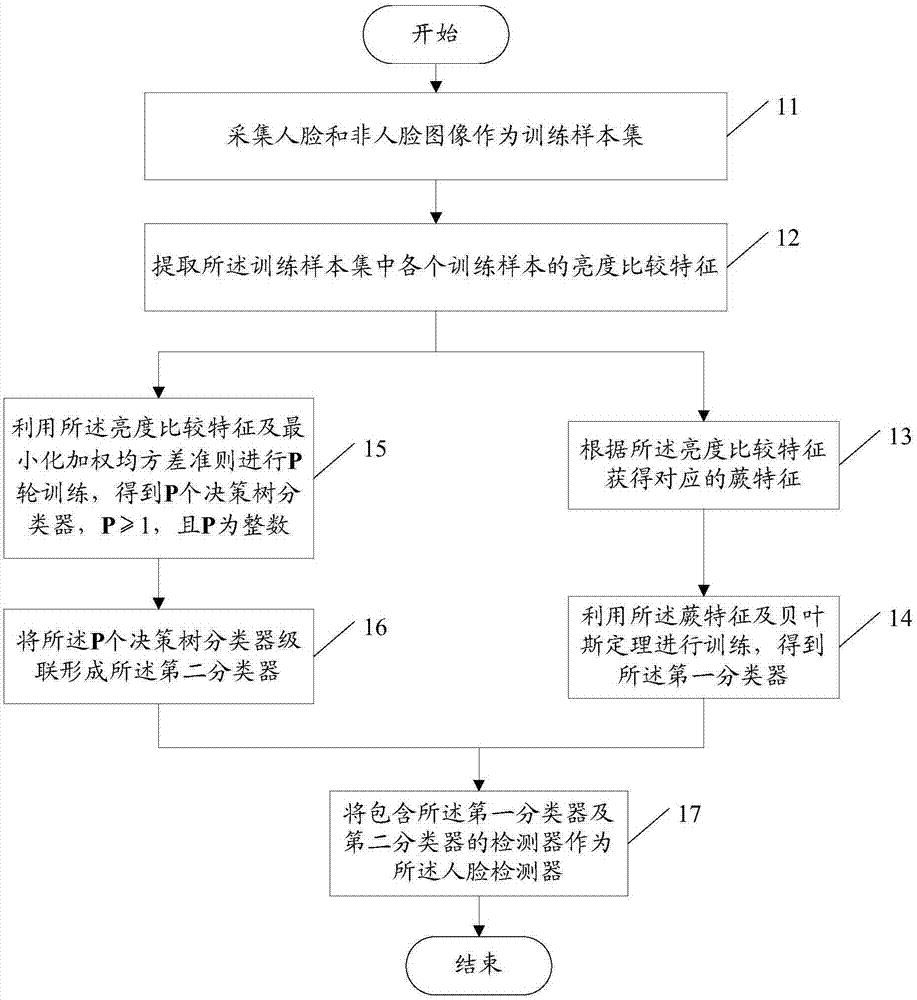
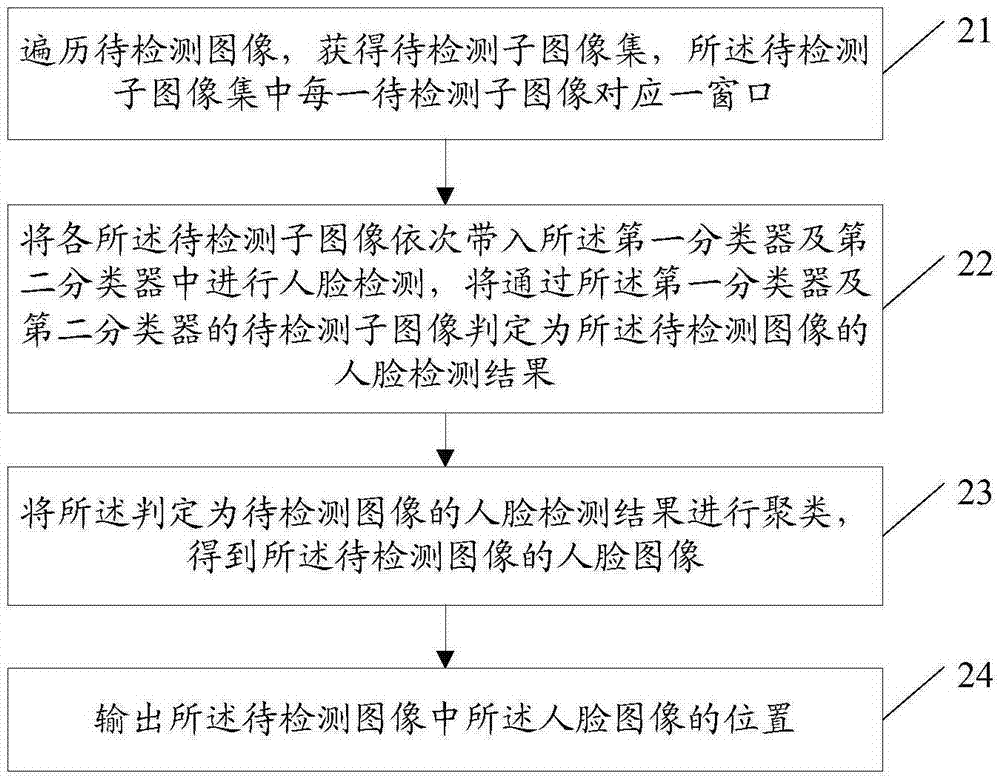
Face detection training method, detection method and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN106874825AReduce complexityReduce the amount of calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionPattern recognition
A face detection training method, a detection method and an apparatus thereof are disclosed. A face detector comprises a first classifier and a second classifier. The training method comprises the following steps of collecting face and non-face images as training sample sets; extracting a brightness comparison characteristic of each training sample in the training sample sets; according to the brightness comparison characteristic, acquiring a corresponding fern characteristic; using the fern characteristic and a Bayes theorem to carry out training and acquiring the first classifier; using the brightness comparison characteristic and a minimized weight mean square error criterion to carry out P-round training, and acquiring P decision tree classifiers, wherein the P is greater than or equal to 1 and the P is an integer; and cascading the P decision tree classifiers so as to form the second classifier. The face detector acquired through applying the training method is used to carry out face detection so that complexity and a calculated amount of face detection can be reduced and detection efficiency can be increased.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (TIANJIN) INC
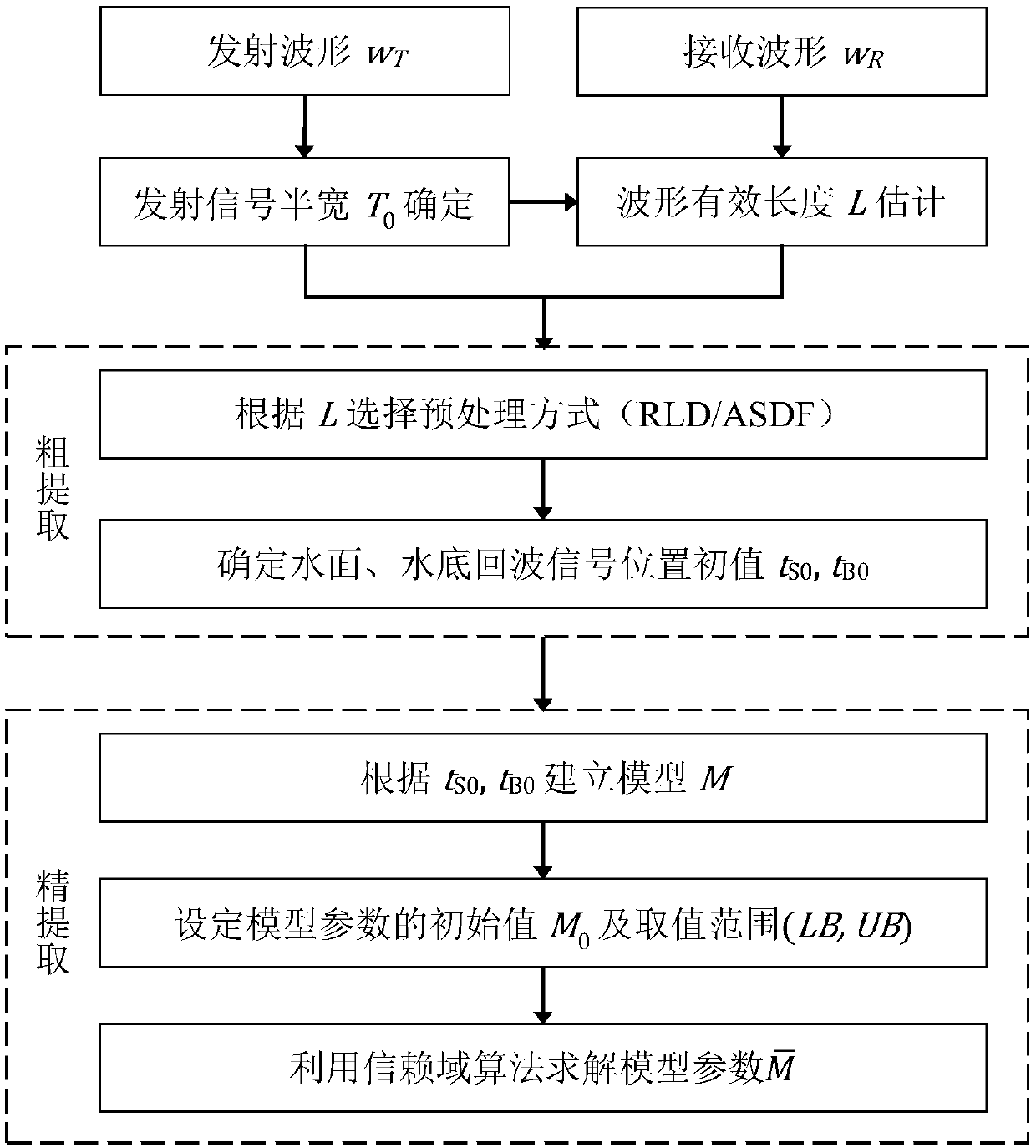
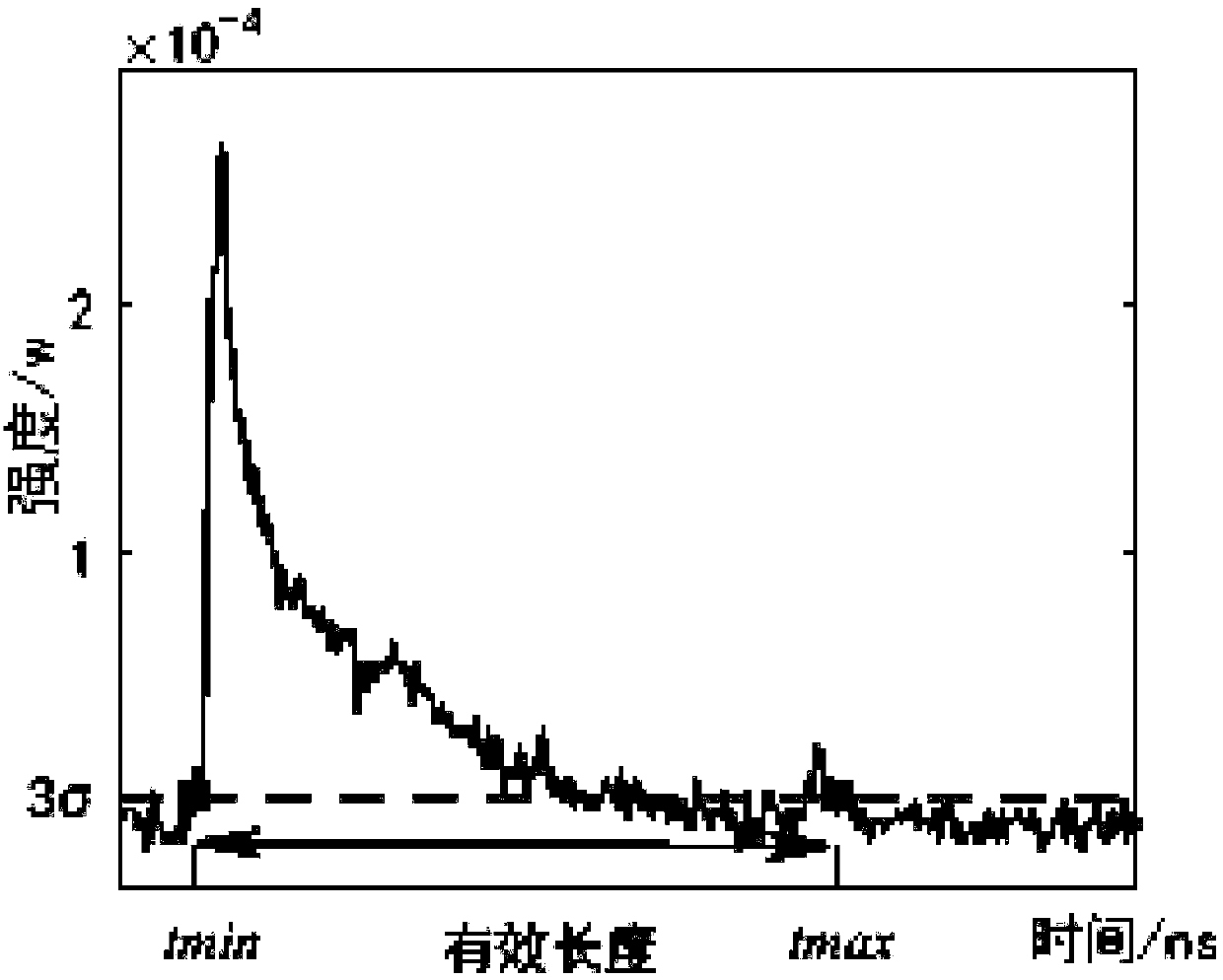
Denoising processing method for airborne laser sounding received waveform and system thereof
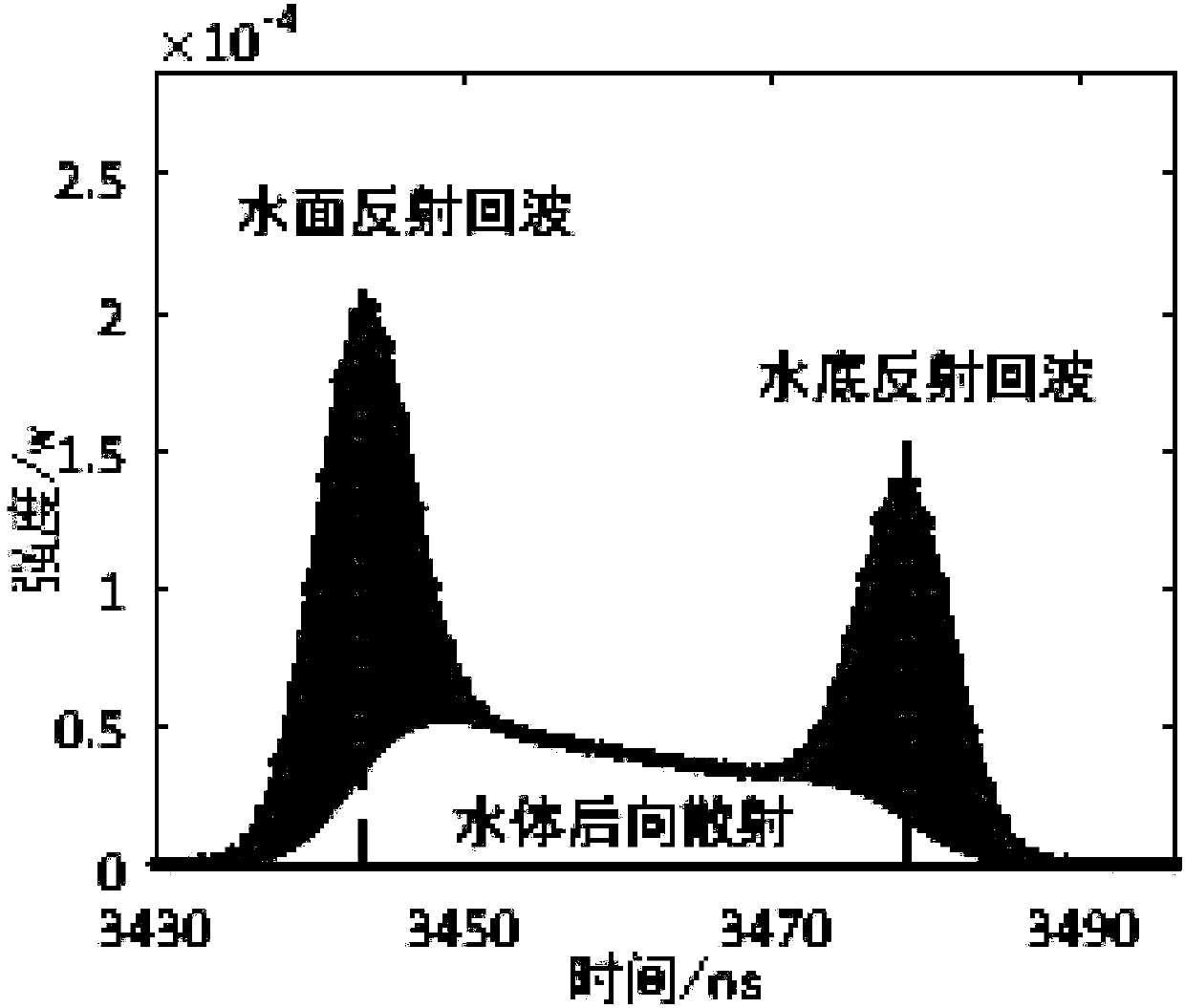
ActiveCN110133670AImprove denoising effectHigh-resolutionMachines/enginesWater resource assessmentEffective lengthFunction method
The invention relates to a denoising processing method for airborne laser sounding received waveform and system thereof, and the method specifically comprise the following steps: acquiring waveforms to be processed, estimating corresponding water depth to be measured according to the waveforms, and dividing corresponding water depths to be measured into at least deep water and shallow water basedon an estimation result; processing the waveforms corresponding to the deep water depth to be measured by a mean square difference function method, and processing the waveforms corresponding to the shallow water depth to be measured by a Richardson-Lossian deconvolution method. The method provided by the invention calculates the effective length of the received waveform and is used for approximateestimation of water depth; and then different preprocessing modes are adopted for the received waveform according to the water depth approximate value, so that the preprocessing is more targeted, andthe processing result and the denoising effect are better.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Image threshold segmentation method and device based on fuzzy set and Otsu
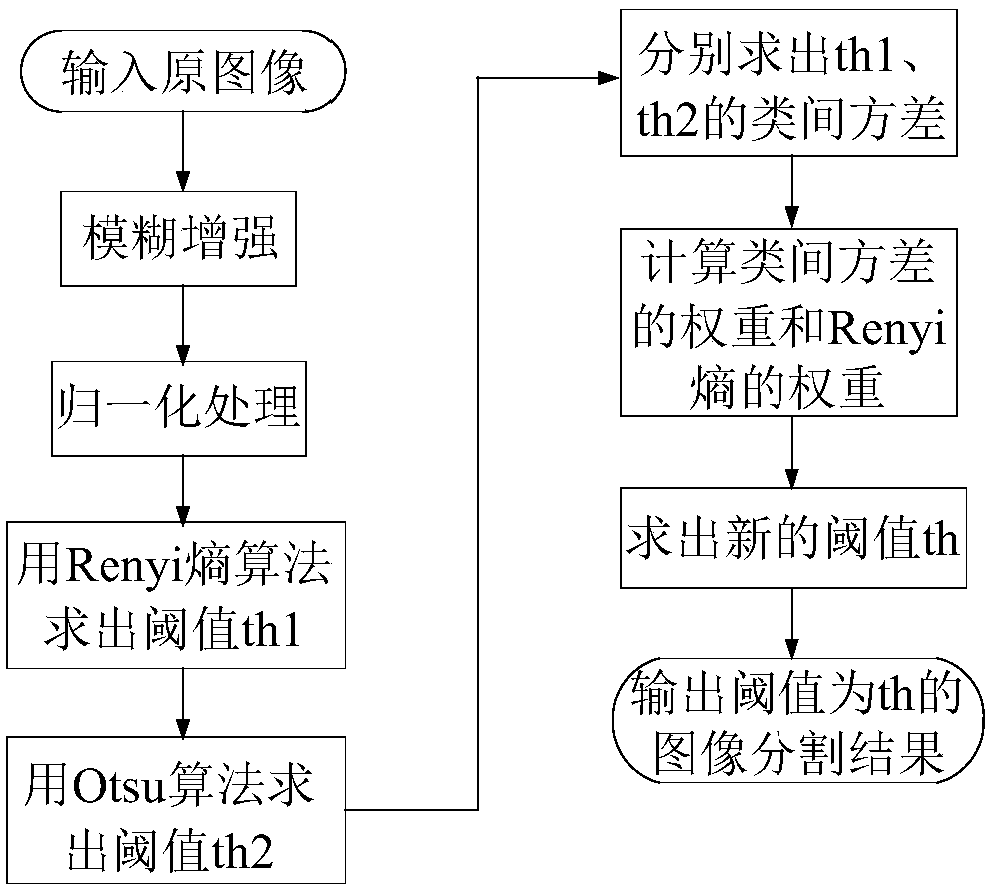
The present invention belongs to the image segmentation field and relates to an image threshold segmentation method and device based on a fuzzy set and the Otsu. According to the method and device ofthe invention, a new fuzzy enhanced membership function is provided based on the fuzzy set; the inter-class variance of the Otsu is constructed through using a discretization method of mean square error; and with the Renyi entropy theory used in combination and weight calculation introduced, the Renyi entropy of an image is provided, and the threshold of a maximum Renyi entropy is adopted to accomplish image segmentation. Compared with a traditional threshold segmentation algorithm, the method of the invention has advantages of high edge segmentation accuracy, high robustness to noises, high stability and favorable segmentation effect, and can effectively improve the accuracy of image segmentation.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Techniques for entry of less-than-perfect-passwords
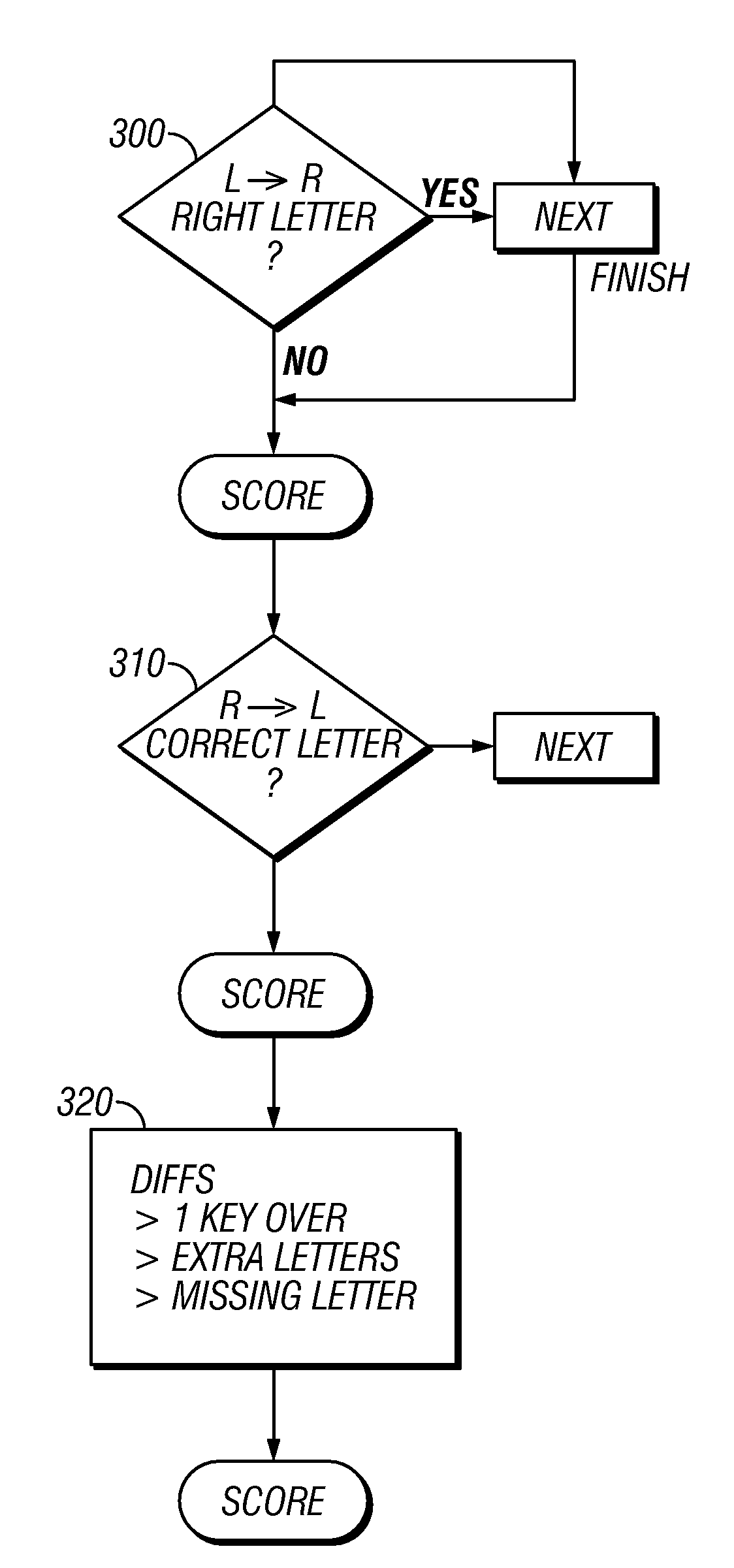
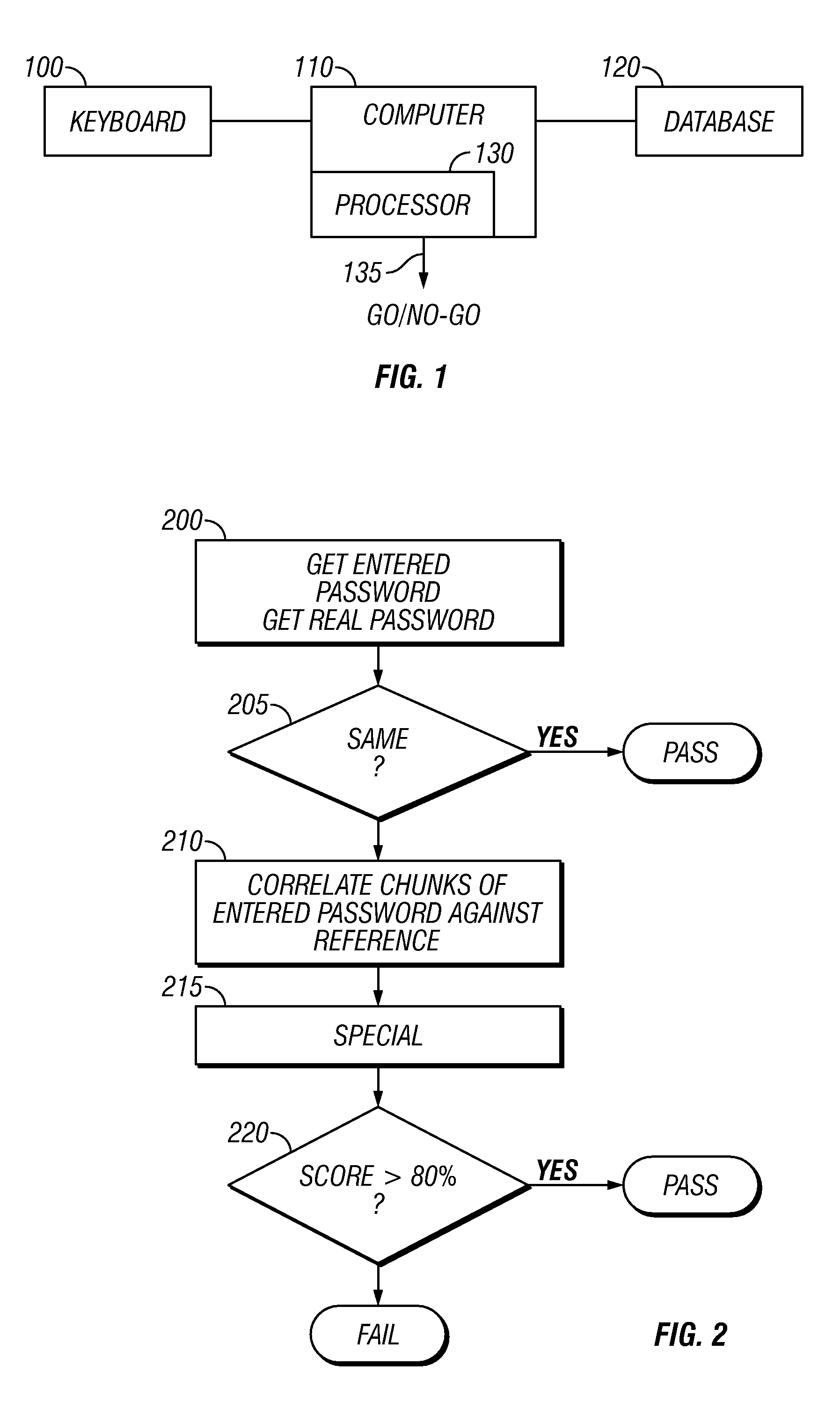
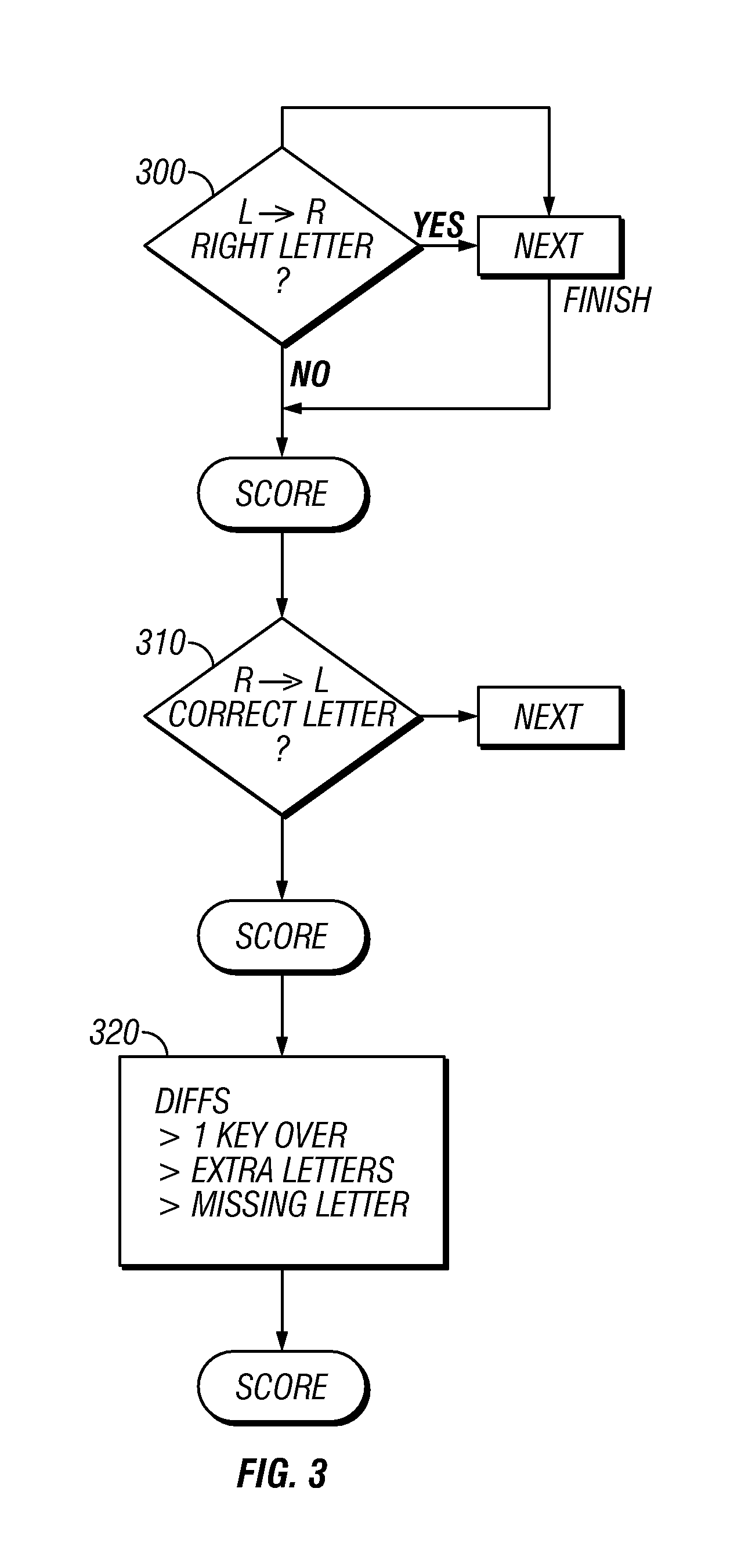
InactiveUS7467403B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordMean square difference
A technique of allowing entry of the password which is not 100% correct. This password would be used to verify identity and / or login information in low security techniques. The password is scored relative to the correct password. The scoring can take into effect least mean squares differences, and other information such as letter groups, thereby detecting missed characters or extra characters, as well as shift on the keyboard.
Owner:HARRIS TECHNOLOGY
Purple clay teapot seal retrieval method
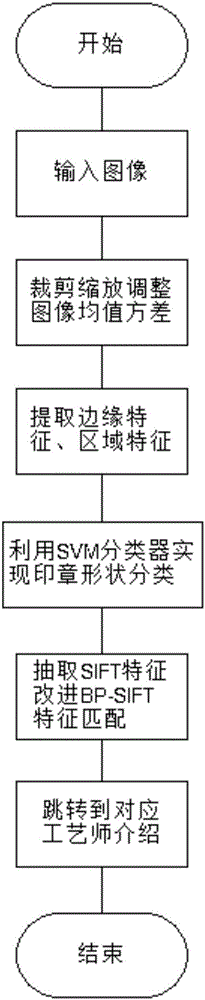
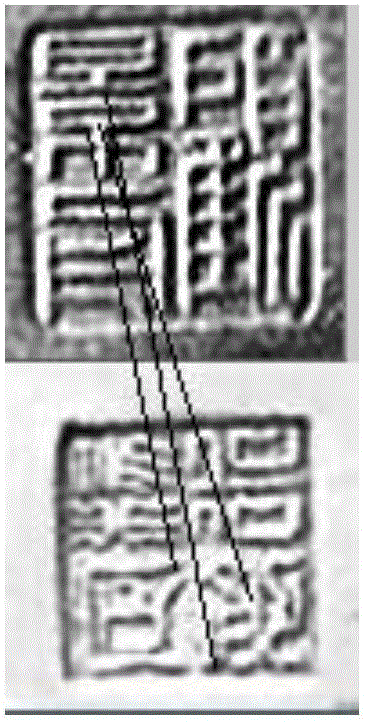
ActiveCN106570475AImprove retrieval accuracyShorten the timeCharacter and pattern recognitionMean squareSvm classifier
The invention discloses a purple clay teapot seal retrieval method. The method is characterized by cutting and zooming a purple clay teapot seal image photographed by a mobile phone; through adjusting a mean value and a mean square error of the image, changing image brightness and contrast and acquiring a standard image; in the standard image, extracting an edge characteristic and a shape area characteristic of a purple clay teapot seal; after characteristic fusion is performed, using a trained SVM classifier to coarsely divide the seal into four types of a round shape, a triangle, rectangle and an irregular shape; extracting a SIFT characteristic of the purple clay teapot seal image, introducing a geometric constraint condition, and using an improved matching method based on belief propagation to match with the image in a template database; and simultaneously using a clustering method to optimize retrieval time and completing seal retrieval. By using the method of the invention, good robustness is possessed to uneven illumination and affine transformation of rotation, zooming, side looking and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
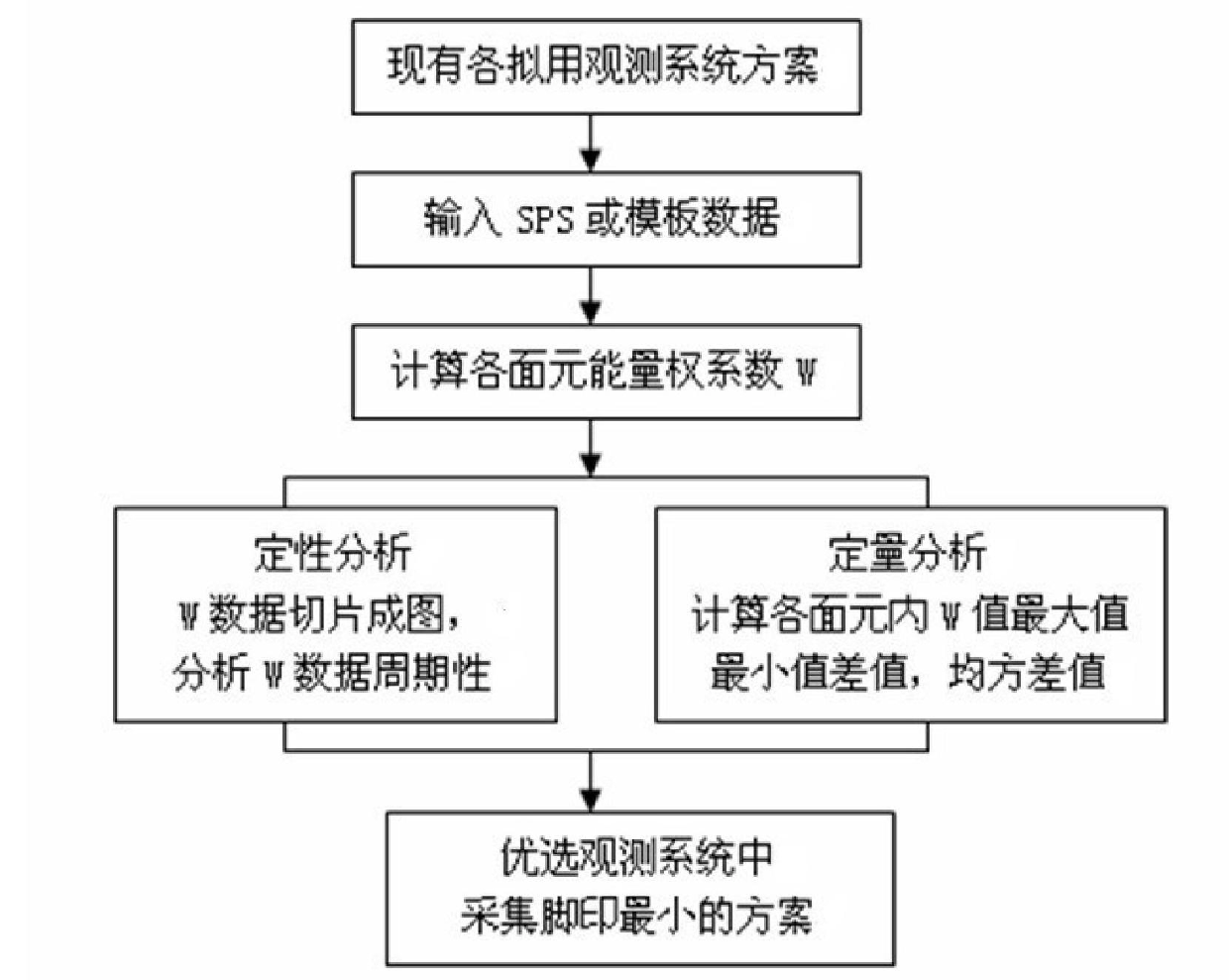
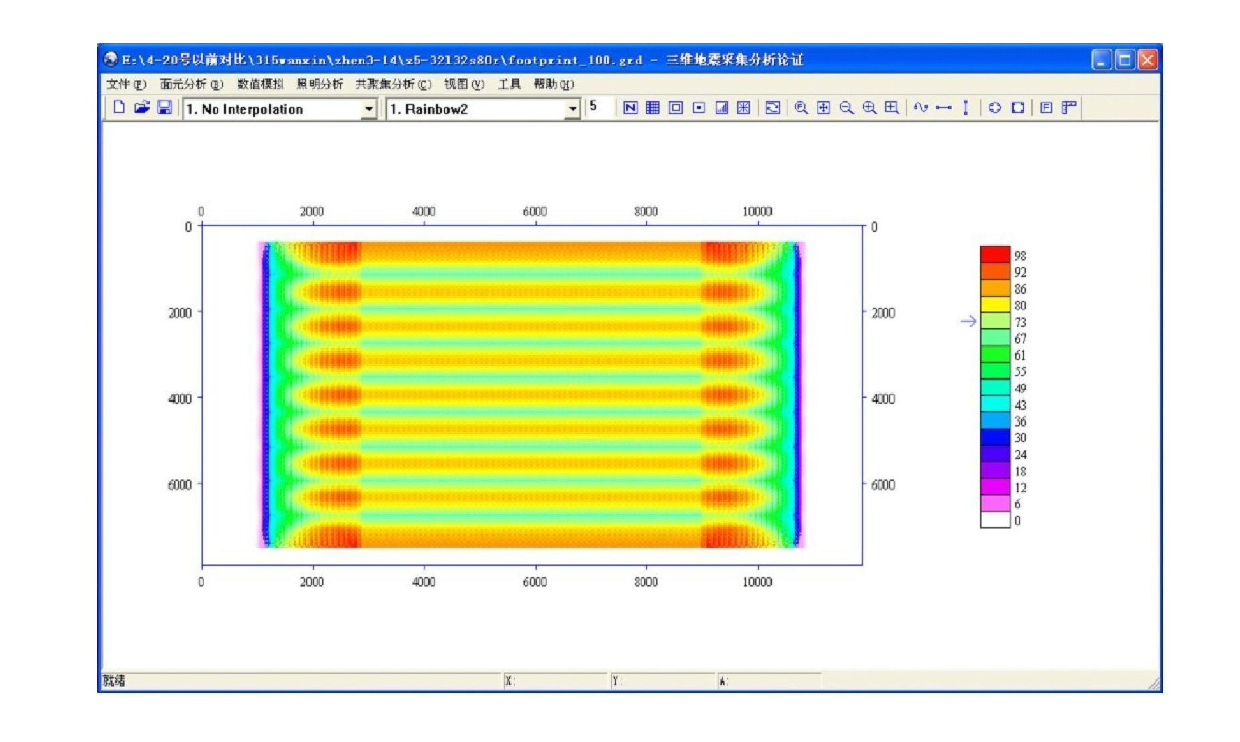
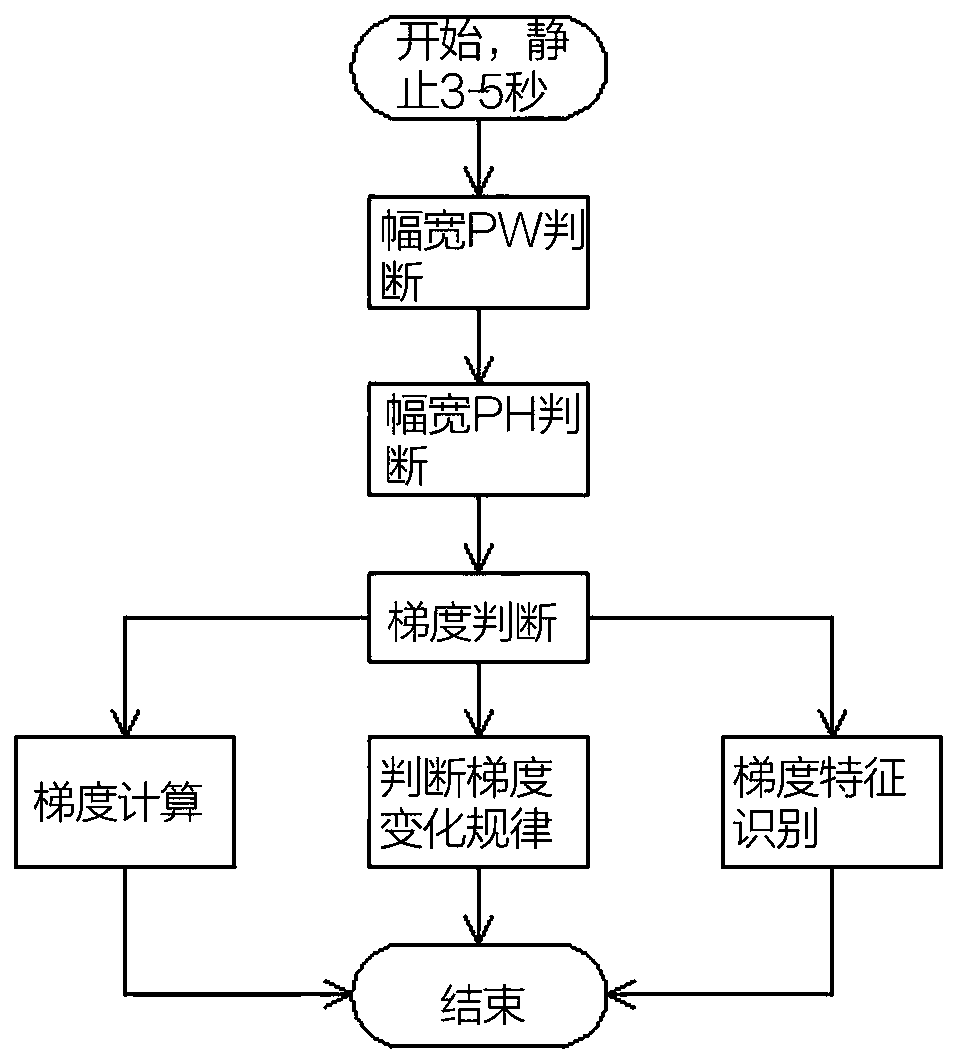
Quantitative analysis method for collected footprints by three-dimensional observation system
ActiveCN102023312AImprove research precisionGuaranteed accuracySeismic signal processingDesign planSystems design
The invention relates to a quantitative analysis method for collected footprints by a three-dimensional observation system, which comprises the following steps of: inputting SPS (Symbolic Programming System) data according to the designed plan of the three-dimensional observation system and calculating the energy change weight coefficient value W of each surface element in the three-dimensional observation system; carrying out qualitative analysis on the collected footprints by the three-dimensional observation system according to value W distribution of all surface elements; carrying out quantitative analysis on the collected footprints by the three-dimensional observation system by calculating and analyzing difference, mean value and mean square error value of the values W of all surface elements; and comparatively selecting the designed plan of the three-dimensional observation system with smallest collected footprint. The invention can be used for carrying out qualitative and quantitative analysis on the collected footprints caused by the three-dimensional observation system and quantitatively comparing the performance difference before and after change of the three-dimensional observation system so that the collected footprints are minimized in the design stage of the observation system, thereby ensuring the accuracy and continuity of the sectional amplitude and providingguarantee for improving the forecast of reservoir stratum, oil pool description and AVO(earthquake amplitude and phase relationship) research precision.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
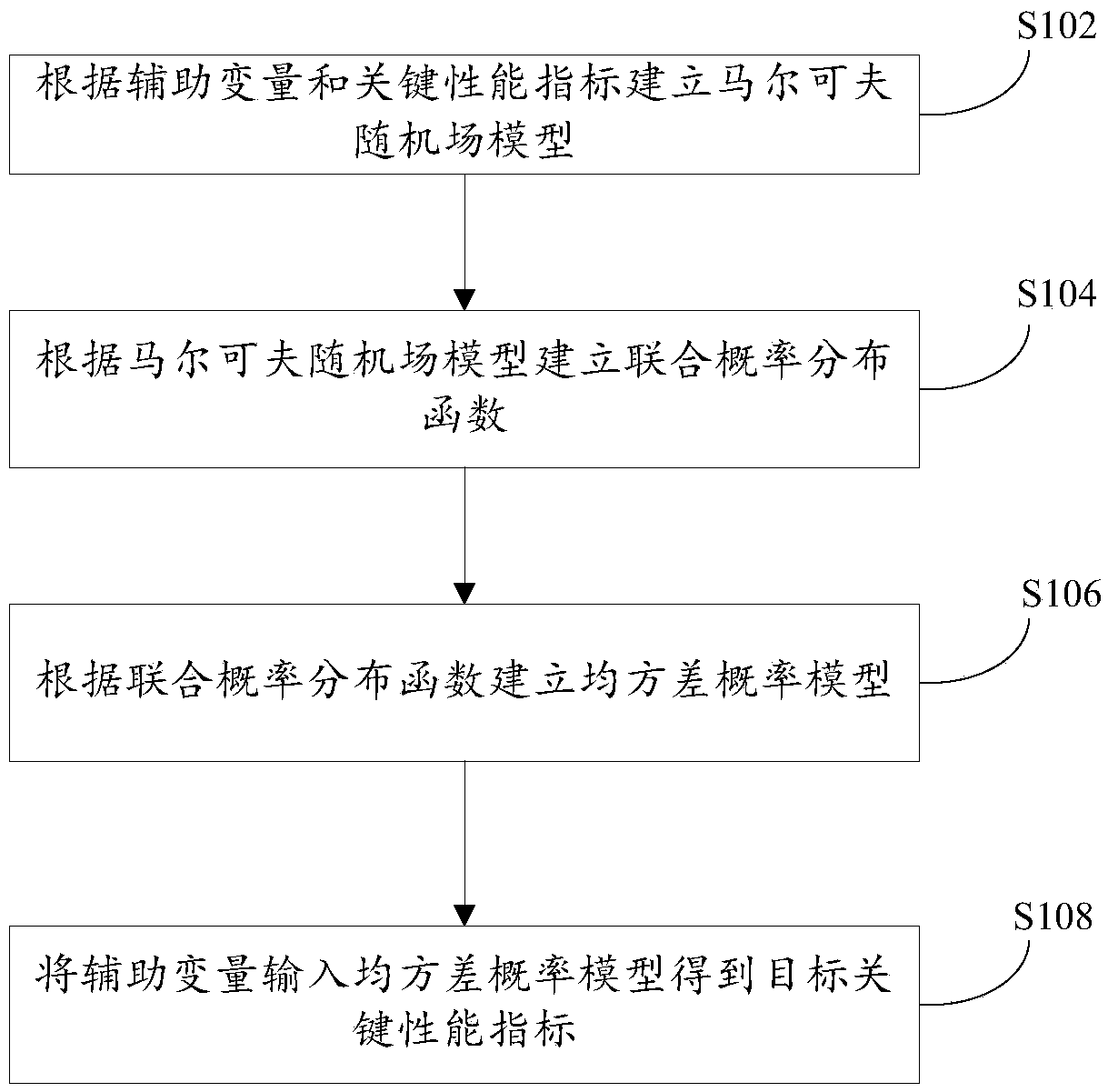
Soft sensing method based on Markov random field and EM algorithm
InactiveCN109241493ASimple structureClear expressionResourcesManufacturing computing systemsMean squarePerformance index
The invention discloses a soft sensing method of key performance index based on Markov random field and EM algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a Markov random field model according to auxiliary variables and key performance indicators, and then establishing a joint probability distribution function according to the Markov random field model, wherein, the joint probability distribution function is a joint probability distribution among auxiliary variables and / or a joint probability distribution among key performance indicators; According to the joint probability distribution function, the mean square deviation probability model is established, where the mean square deviation probability model is the relationship between the expectation of the key performance index and the target key performance index when the auxiliary variable is given, and the target key performance index is the key performance index when the mean square deviation probability model approaches zero; the auxiliary variables are inputted into the mean square deviation probability model to obtain the target key performance index, thus solving the technical problem of the prior art that the key performance index in the industrial process can not be accurately measured in real time.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Neural network based rock destroy strength determination method
InactiveCN103226080AAvoiding Hyperadaptation ProblemsImprove adaptabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesNeural learning methodsPrincipal stressNerve network
The invention discloses a neural network based rock destroy strength determination method. The method is characterized in that a neural network is used to research the rock strength criterion under a uniaxial or triaxial loading condition, various collected rock related data are randomly divided into training and verifying subsets, the compressive strength and the smallest principal stress are used as input values and the largest principal stress value is used as an output value to train the neural network, and the trained neutral network is used to predict largest principal stress value during the test rock destroy. The method mainly comprises a step of experiment data analysis and a step of ANN based largest principal stress value prediction. The method shows the mean square deviation of the neutral network prediction result is reduced by 30-40%, and the determination coefficient is increased by 0.05-0.08 and is more close to 1. The use of the ANN to predict the rock strength has a wide adaptive loading range, so the method is suitable for rock-kind-changeable complex non-linear conditions, and is flexible and accurate.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
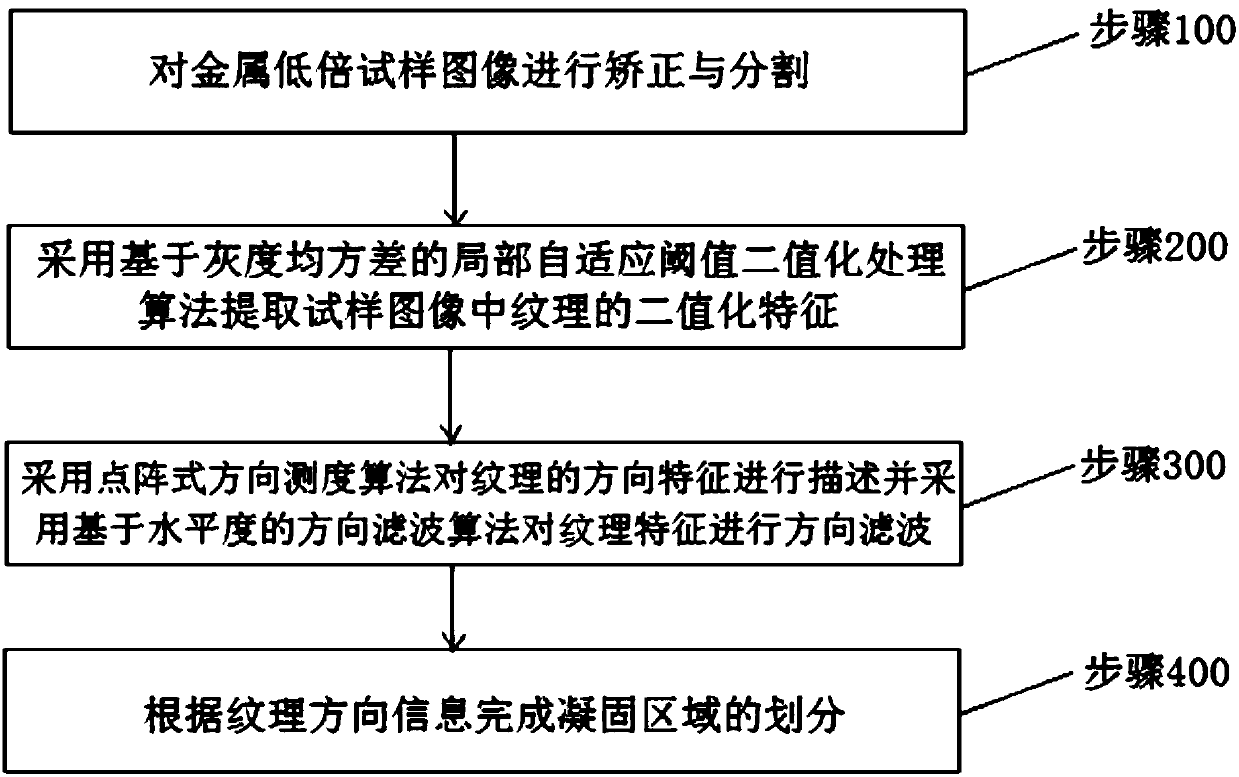
Method and system for identifying metal solidification area with texture
ActiveCN107657620AEliminate distractionsImprove detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisDot matrixFeature extraction
The invention discloses a method for identifying a metal solidification area with a texture. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: Step 100, correcting and segmenting a metal low-magnification sample image; Step 200, adopting a local self-adaptive threshold binaryzation processing algorithm based on grayscale mean square difference to extract binarization features of the texture in the sample image; Step 300, describing the direction characteristics of the texture by adopting a dot matrix type direction measurement algorithm, and carrying out direction filtering onthe texture features by adopting a direction filtering algorithm based on the levelness; Step 400, dividing the solidification area according to the texture direction information. According to the invention, a digital image processing technology is used to perform preprocessing, feature extraction, pattern recognition and the like on a solidification area image of a casting blank macrostructure soas to realize automatic recognition and quantization and improve the detection precision. Meanwhile, the labor intensity is reduced and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
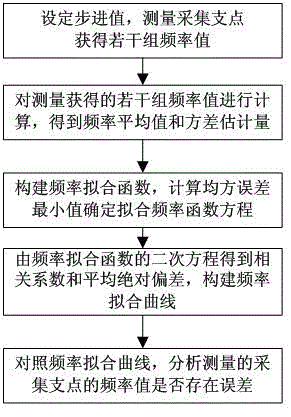
Parameter estimation and fitting method for collecting supporting point frequency in vibrating wire mode
InactiveCN104794358ATimely correctionHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientVibrating wire
The invention discloses a parameter estimation and fitting method for collecting supporting point frequency in a vibrating wire mode. The method comprises the following steps that a stepping value is set, and collecting supporting points are measured to obtain a plurality of sets of frequency values; the frequency values obtained through measurement are calculated, and an average frequency value and a variance estimator are obtained; a frequency fitting function is constructed, the minimum value of a mean square error is calculated, and a fitting frequency functional equation is determined; a mean square error is calculated, a quadratic equation of the frequency fitting function is obtained through fitting, a correlation coefficient and mean absolute deviation are obtained through the quadratic equation of the frequency fitting function, and a frequency fitting curve is constructed; compared with the frequency fitting curve, whether errors exist in the frequency values of the collecting supporting points under the current stepping value or not is analyzed. The precision of fitting can be further improved, the fitting curve is generated, the frequency values can be corrected in time, and therefore the method can be used in the process of determining the parameters of the collecting supporting points of a communication network well.
Owner:WUXI WISEN INNOVATION TECH
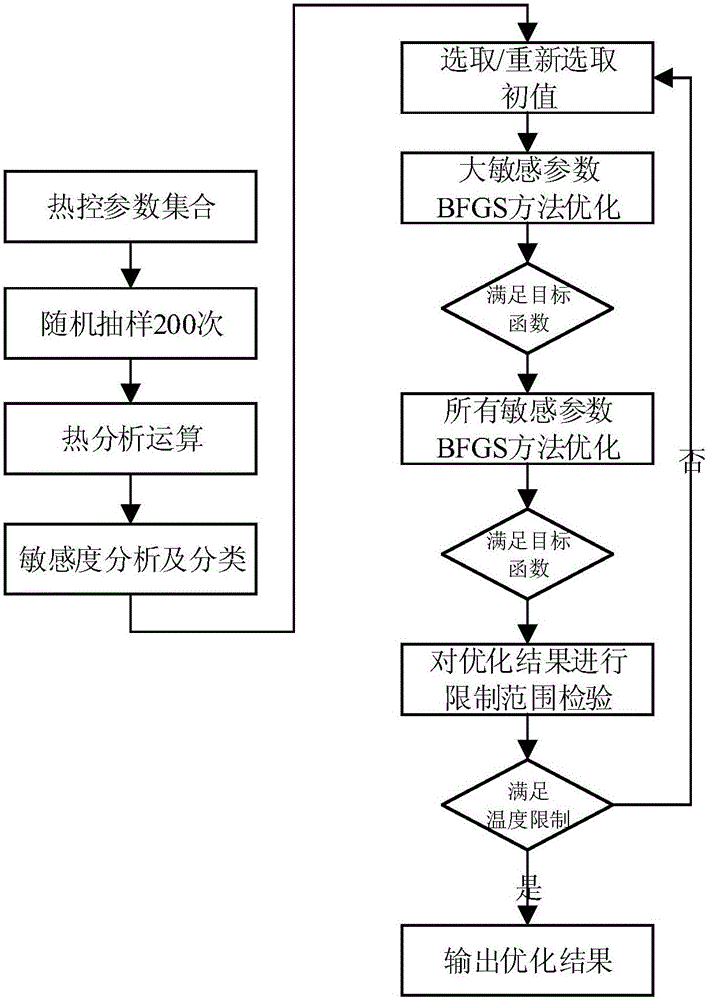
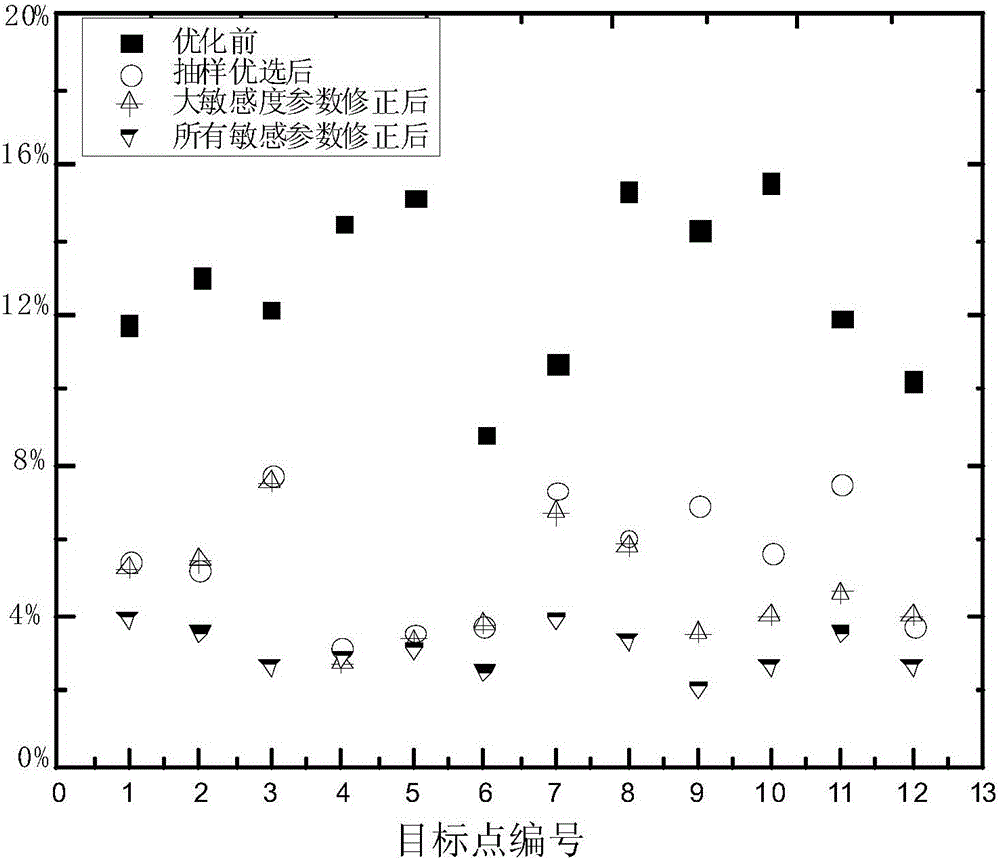
Design optimization method for spacecraft passive thermal control parameters
InactiveCN105975712AIn line with the actual work situationHigh cost-effectiveGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCost effectivenessMean square
The invention discloses a design optimization method for spacecraft passive thermal control parameters. The design optimization method comprises the following steps that firstly, statistics is carried out on a thermal control parameter set to be designed and the design scope of the thermal control parameter set, and objective temperatures and the optimum value and the limit range of the objective temperatures are determined; secondly, an objective function is established, the sensitivity of the objective function on the thermal control parameters is analyzed, and the parameters are classified according to sensitivity; then, a sampled optimal sample serves as an initial value, and step-by-step optimization is carried out on the thermal control parameters through a quasi-linear algorithm according to the sensitivity classification; finally, whether an optimized value meets the temperature limitation or not under various thermal working conditions is detected, and if not, a suboptimum sample is selected again to serve as an initial value for optimization until the optimized value meeting the temperature limitation is acquired. The establishing method for the objective function with a weight mean square error, a sensitivity analysis classifying method for multiple working condition mean square errors on the thermal control parameters, the thermal control parameter step-by-step optimizing method and the like are put forward, and the effective optimization design method is provided for improving the cost-effectiveness and reliability of a spacecraft thermal control system to meet the harsh requirements of a current spacecraft.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Extreme value wind speed recurrence period determination method and device considering wind speed extra-large value
ActiveCN110334406AFix inaccurate estimatesWide applicabilityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMean squareEstimation methods
The invention discloses an extreme value wind speed recurrence period determination method and device considering a wind speed extra-large value. The extreme value wind speed recurrence period determination method comprises the following steps: checking and selecting an extra-large value in a sequence from an average wind speed sequence with the maximum wind speed of 10min over the years; and by constructing an expectation and mean square error calculation method under the condition of containing an extra-large value, on the basis of empirical frequency calculation, estimating position parameters and scale parameters of a Gunn Bell extreme value distribution model, enabling the recurrence period of the extra-large value to be subjected to iterative trial calculation until the error requirement is met, and obtaining the final recurrence period and distribution model parameters. The extreme value wind speed recurrence period determination method provided by the invention can effectivelysolve the problem of unreliable design wind speed value caused by inaccurate estimation of an extra-large value recurrence period when a frequency distribution model is adopted to analyze a maximum 10min average wind speed sequence over the years. According to the extreme value wind speed recurrence period determination method, a reliable extra-large value recurrence period estimation method is provided, and the design wind speed obtained on the basis can ensure the wind resistance reliability of the project.
Owner:CEEC JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST
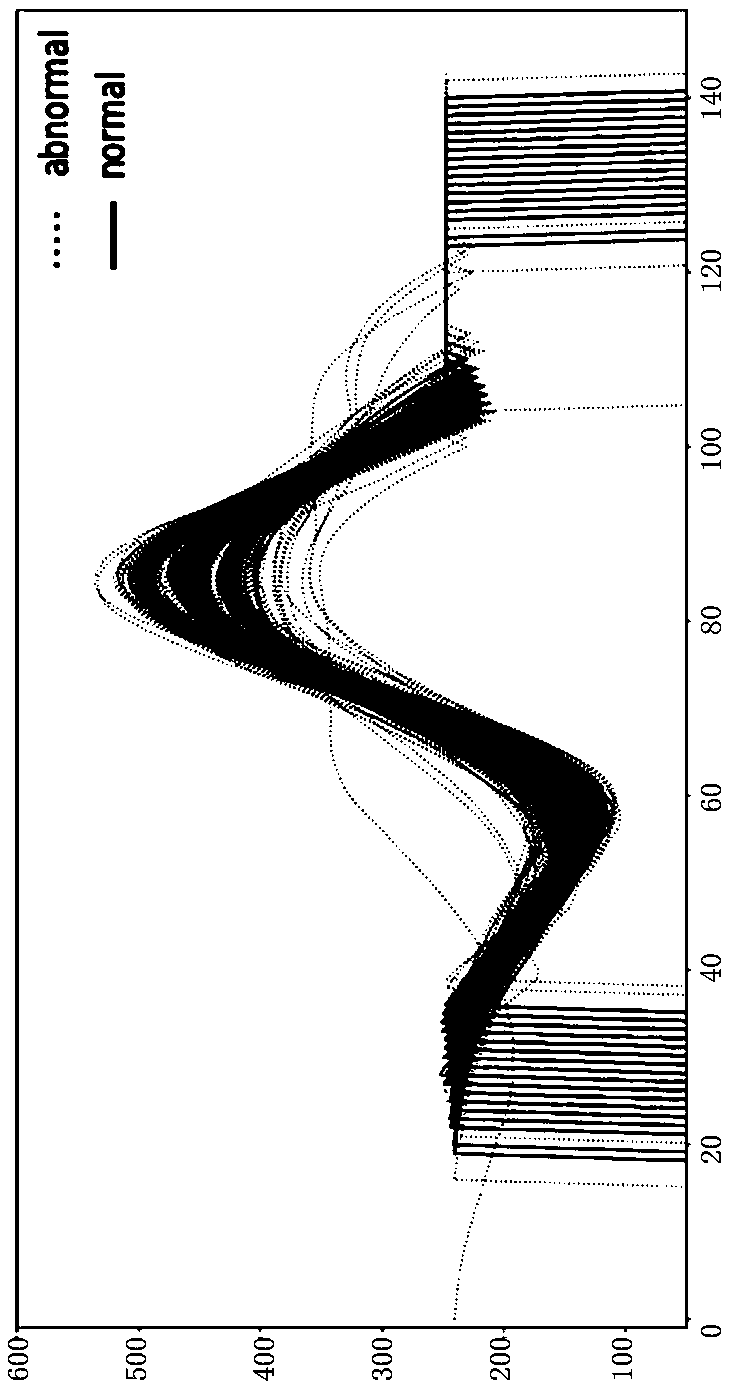
Object reciprocating motion distance evaluation method based on deep learning
PendingCN111353208AJudgment operation is fastMake up for the errorDesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesData setObject motion
The invention relates to an object reciprocating motion distance evaluation method based on deep learning, and the method comprises the following steps: carrying out the data sampling, and collectingthe motion acceleration change data of an object; segmenting a pressing waveform in a pulse form; correcting the data label so as to clearly see the discrete condition of the curve; marking data, integrating all pulse waveform data, calculating the weighted mean square error of each waveform, marking whether a single waveform is normal or abnormal according to the overall weighted mean square error range of the correct waveform and the abnormal waveform, disturbing a data set after marking is completed, and selecting a training set and a test set according to a certain proportion; establishinga convolutional neural network model for training, debugging parameters, optimizing the model, and storing the model to a file for subsequent reciprocating motion distance evaluation; evaluating data: putting to-be-evaluated data into the trained convolutional neural network model, and judging whether an evaluation result is normal or abnormal; and outputting an evaluation result to evaluate whether the object movement distance is proper.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
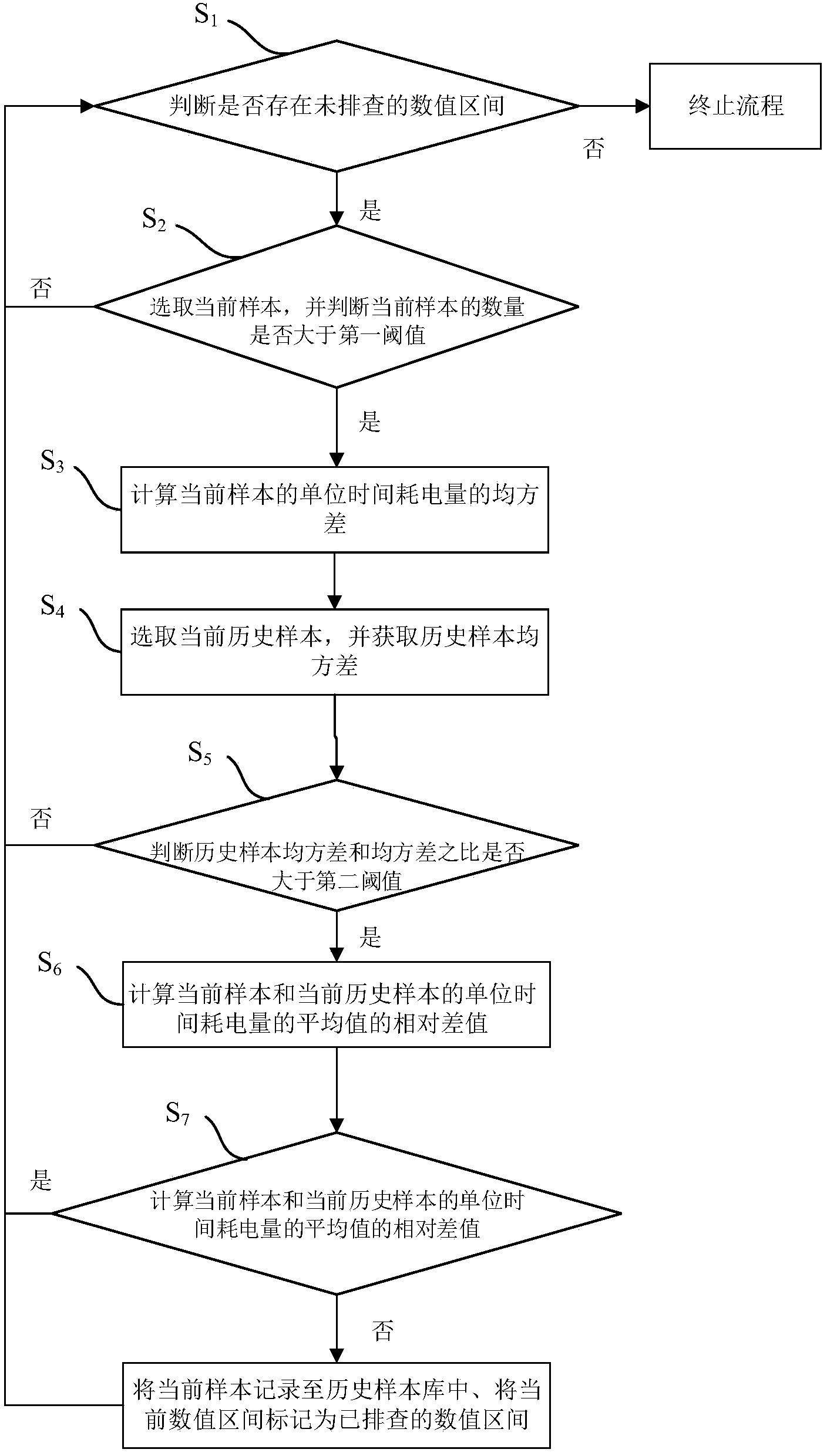
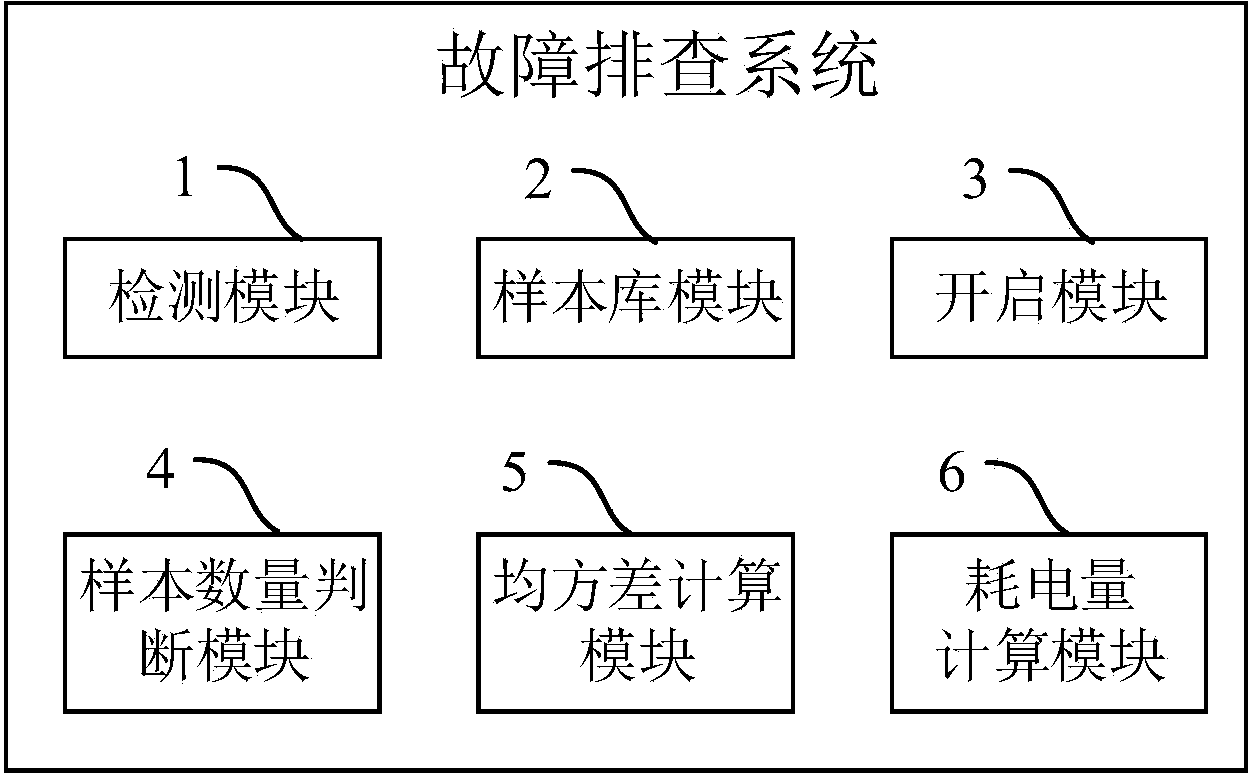
Troubleshooting method and troubleshooting system for energy-saving lamps
ActiveCN103687254AFind faults in timeGuarantee energy saving effectElectric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesComputer scienceBrightness perception
The invention discloses a troubleshooting method and a troubleshooting system for energy-saving lamps. The troubleshooting method includes acquiring power consumption in unit time and ambient brightness values of the energy-saving lamps in real time; storing samples which are the power consumption in unit time and the ambient brightness values in a temporary sample library and an original sample library; presetting a plurality of numerical value intervals of the ambient brightness values; analyzing and comparing mean-square difference values and relative difference values of sample data in the temporary sample library and sample data in a historical sample library; performing troubleshooting on the energy-saving lamps with excessively high power consumption in unit time. A plurality of samples are stored in the historical sample library, and each sample comprises the power consumption in unit time and the ambient brightness value of the corresponding energy-saving lamp. The troubleshooting method and the troubleshooting system for the energy-saving lamps have the advantages that running states of the energy-saving lamps can be comprehensively monitored without labor consumption, the energy-saving lamps can be analyzed and subjected to troubleshooting objectively via the historical data, accordingly, failures of all energy-saving lamps can be timely and accurately found out, and energy-saving effects of the energy-saving lamps can be guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHENTONG METRO
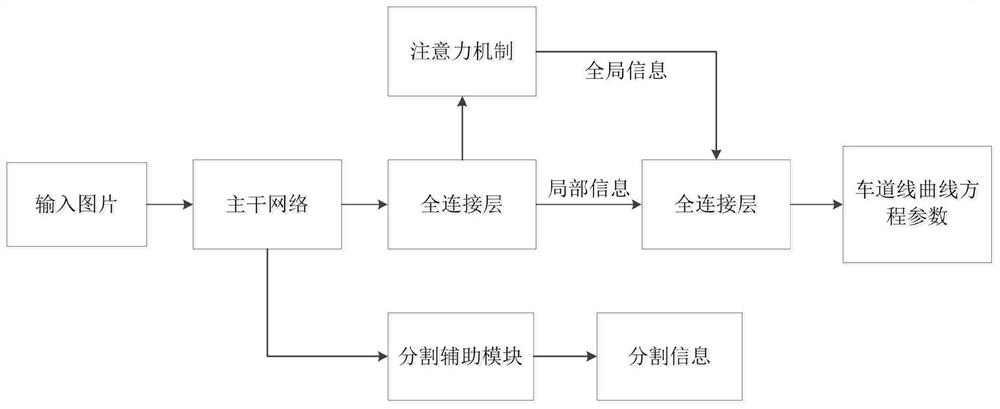
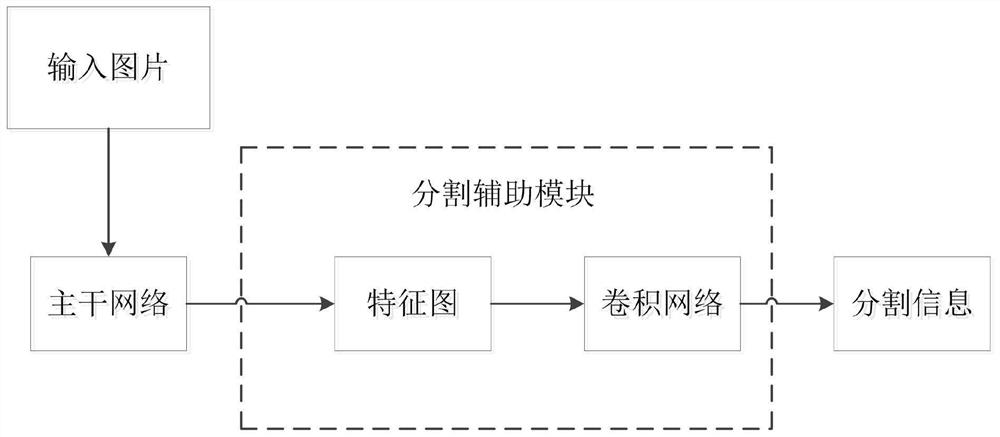
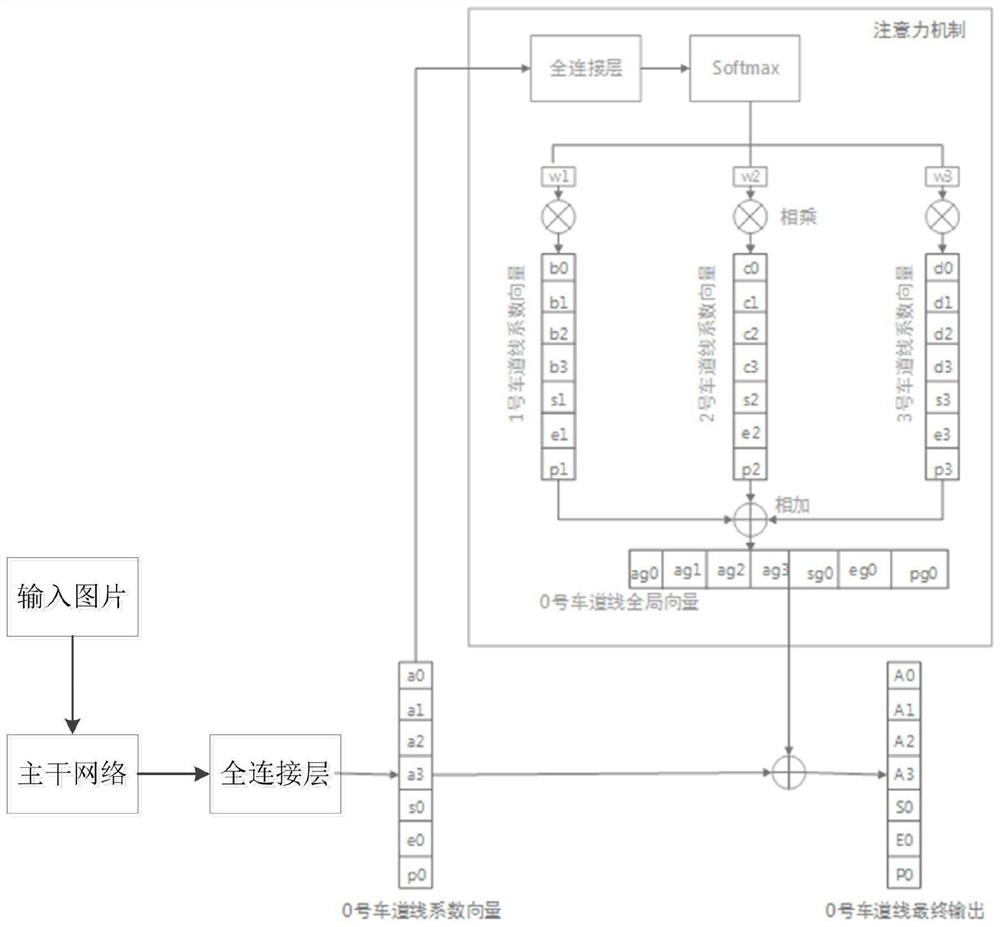
A semantic segmentation and attention mechanism-combined lane line detection method and system
The invention discloses a semantic segmentation and attention mechanism-combined lane line detection method and system, and relates to the technical field of lane line detection, and the method comprises the following steps: inputting a picture to a backbone network to extract lane line features in the picture, inputting the features extracted by the backbone network into a full connection layer, and carrying out the processing of the full connection layer for obtaining local features of each lane line; inputting the local features of each lane line into an attention mechanism module to obtain global features of each lane line, and superposing the global features with the local features to obtain final lane line parameters; and comparing with a real lane line in an input picture, respectively calculating mean square error loss of the lane line and cross entropy loss of a mask graph, calculating a gradient of a corresponding convolutional layer, updating parameters of the convolutional layer and a full connection layer by using a back propagation algorithm, and continuously iterating until the model converges. According to the method, the convergence speed of the model is increased and the robustness of the model is improved under the condition that the operand is not increased.
Owner:深圳瑞为智能科技有限公司
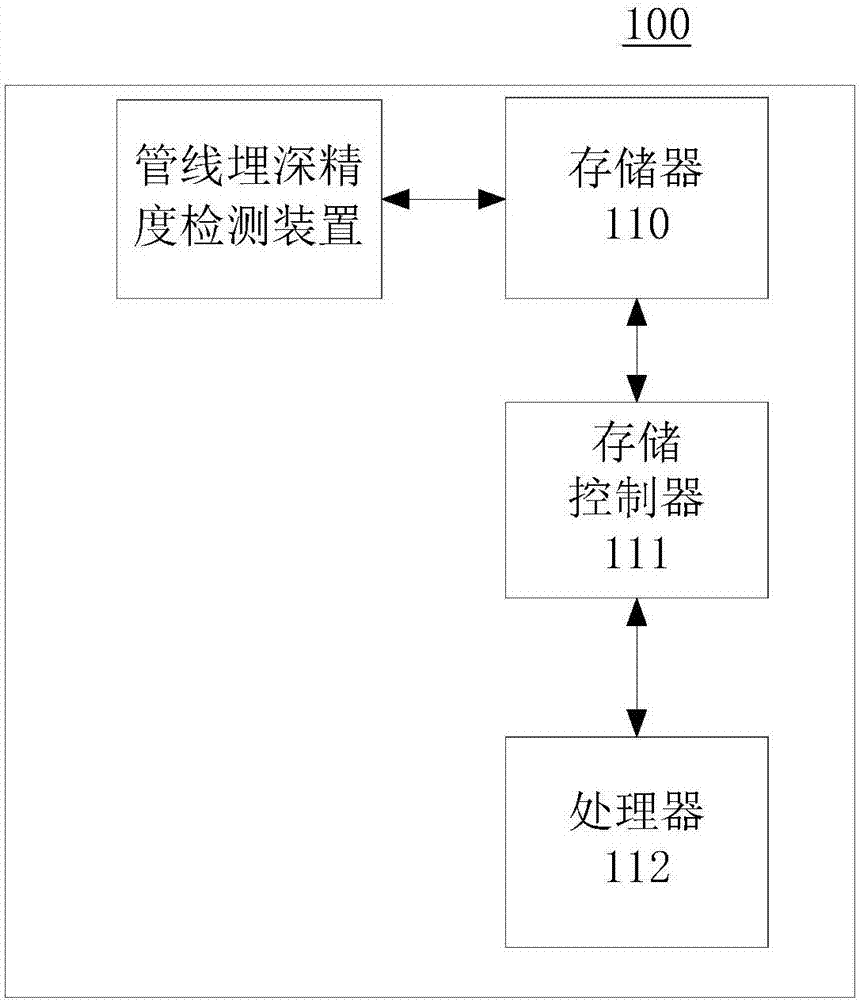
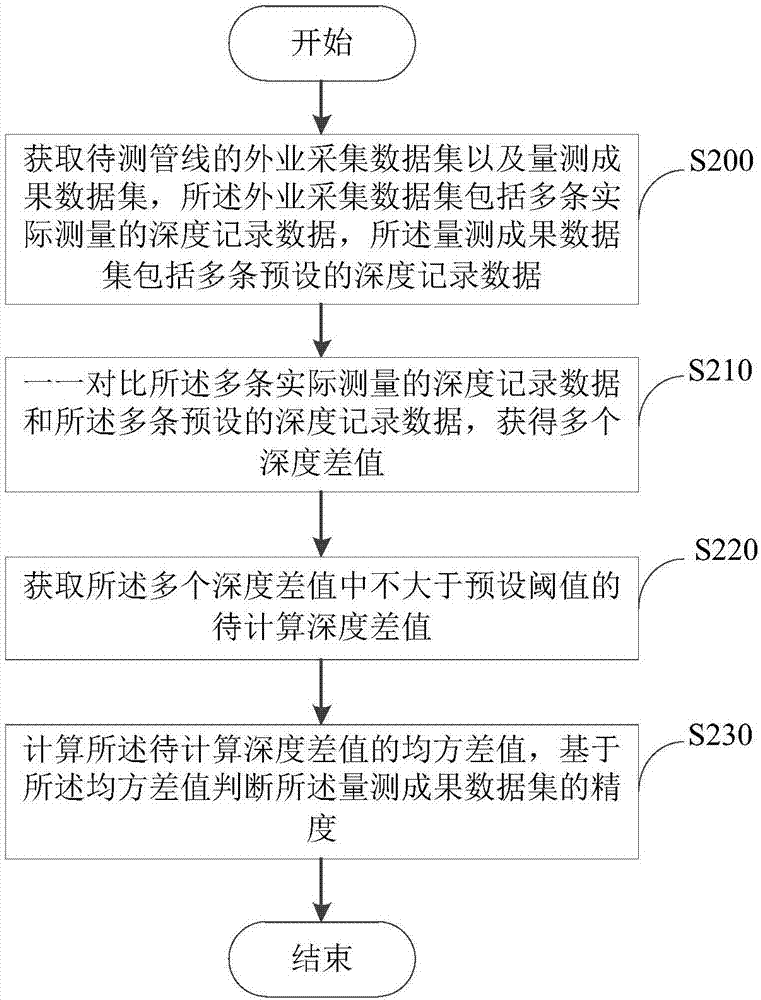
Method and device for detecting buried depth accuracy of pipeline
An embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for detecting buried depth accuracy of a pipeline, and relates to the technical field of data processing. The method includes: acquiring a field operation acquisition data set and a measurement result data set of the pipeline to be measured, wherein the field operation acquisition data set includes a plurality of actually measured depth record data, and the measurement result data set includes a plurality of preset depth record data; comparing the actually measured depth record data and the preset depth record data one by one to obtain a plurality of depth difference values; acquiring a plurality of to-be-calculated depth difference values that are not larger than a preset threshold; calculating a mean square difference of the to-be-calculated depth difference values, and judging the accuracy of the measurement result data set based on the mean square difference value. Thus the accuracy of the statistical result data of the pipeline depth is achieved to support the inspection on mathematical accuracy of the pipeline data.
Owner:SICHUAN SURVEYING & MAPPING PROD QUALITY SUPERVISION & INSPECTION STATION OF THE MINIST OF NATURAL RESOURCES SICHUAN SURVEYING & MAPPING PROD QUALITY SUPERVISION & INSPECTION STATION
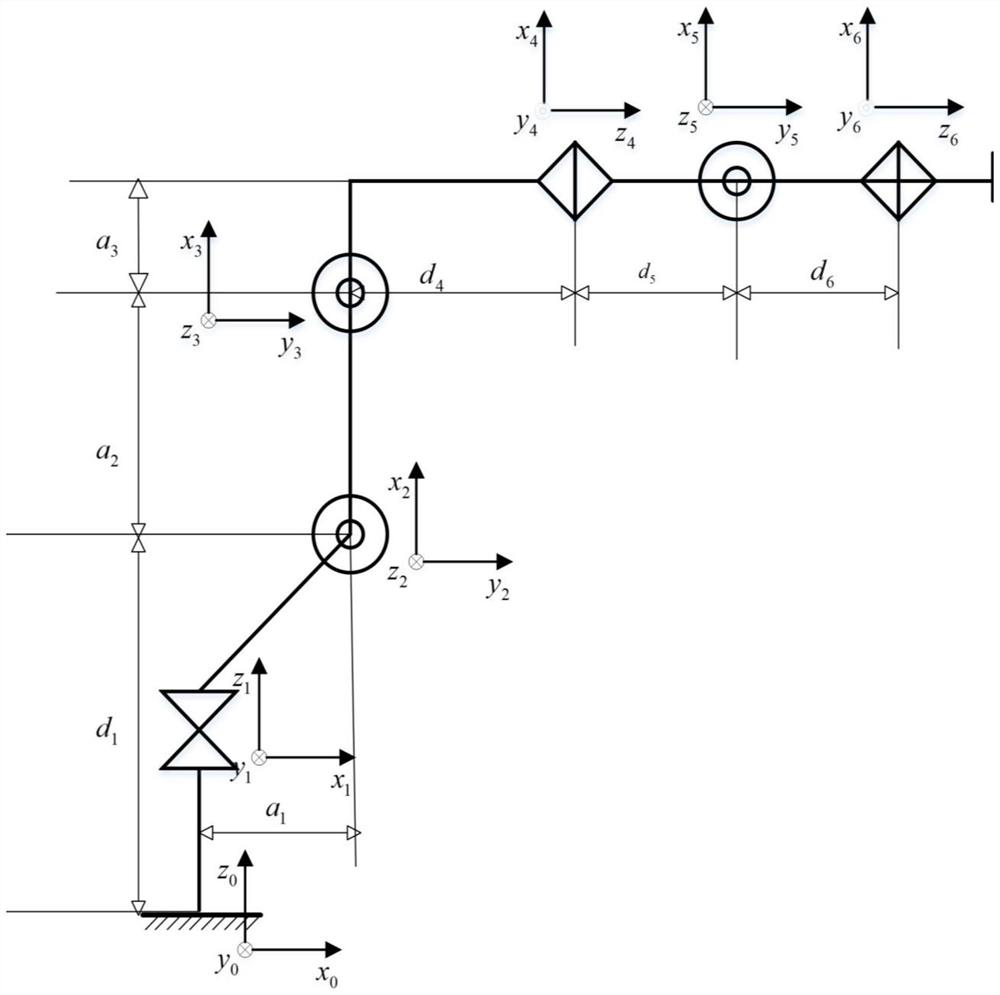
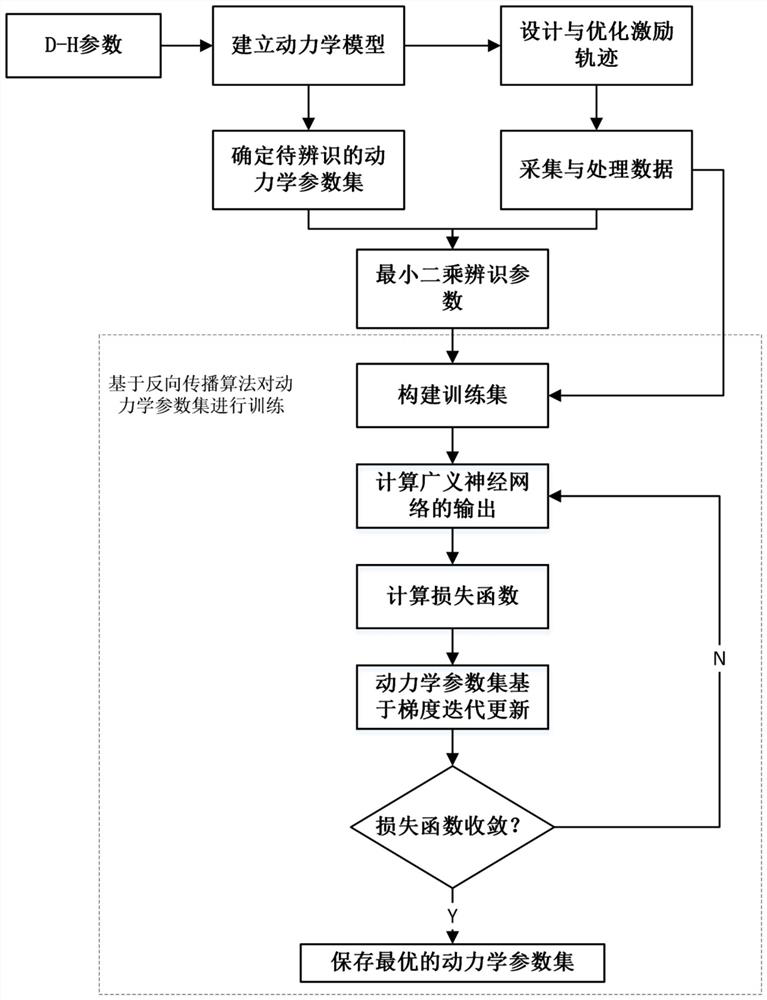
Identification method for kinetic parameters of robot
PendingCN114169230AOvercoming Susceptibility to NoiseOvercoming noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationMean squareAlgorithm
The invention discloses an identification method for kinetic parameters of a robot. The identification method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting joint motion data when multiple groups of robots execute an excitation track as a training set; s2, calculating a corresponding theoretical joint torque under the training set data according to the established kinetic model, calculating a mean square error between the theoretical joint torque and the collected measurement joint torque, and defining the mean square error as a loss function; s3, in each round of training, calculating the gradient of the loss function about the kinetic parameters based on a back propagation algorithm; and S4, performing iterative training on the kinetic parameters along the negative gradient direction of the loss function, gradually reducing the loss function along with training, and when the loss function is converged to a minimum value, storing the corresponding kinetic parameters at the moment as an identification result to complete parameter identification. According to the method, the parameter identification precision is improved, and the problems that the least square method is susceptible to noise interference and can only identify linear system parameters are solved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Image retrieval method based on decomposable word pack model
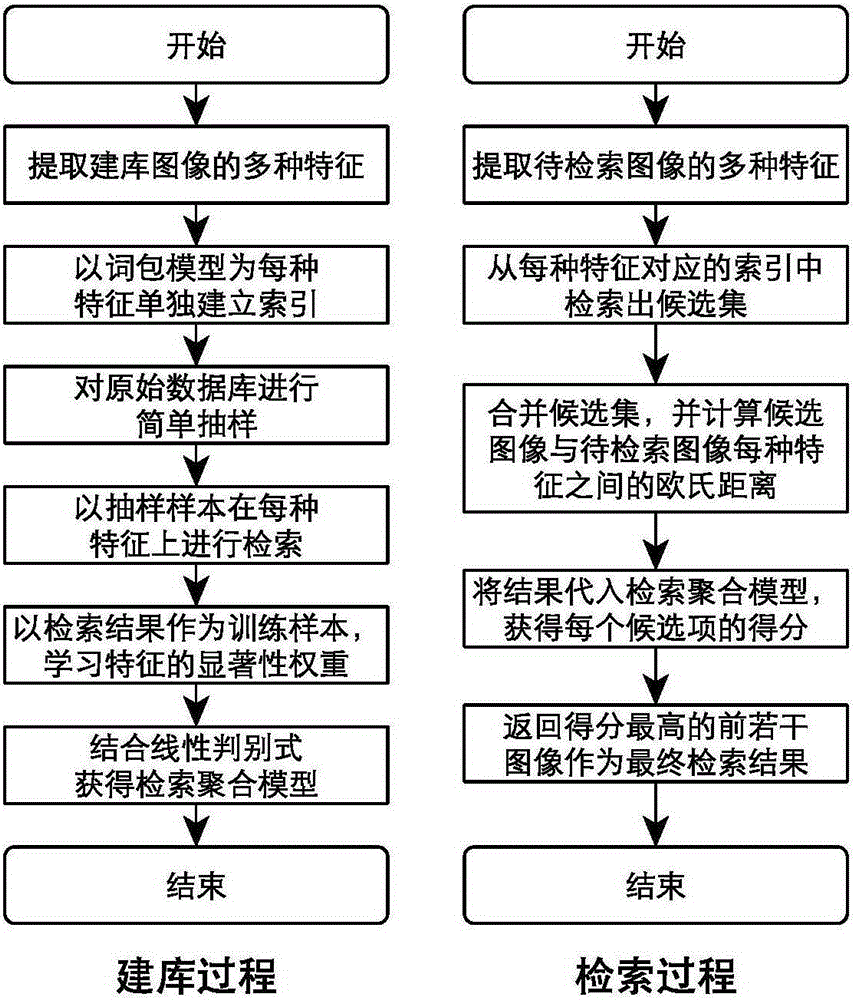
ActiveCN106611016AImprove retrieval accuracySpecial data processing applicationsImage extractionImage retrieval
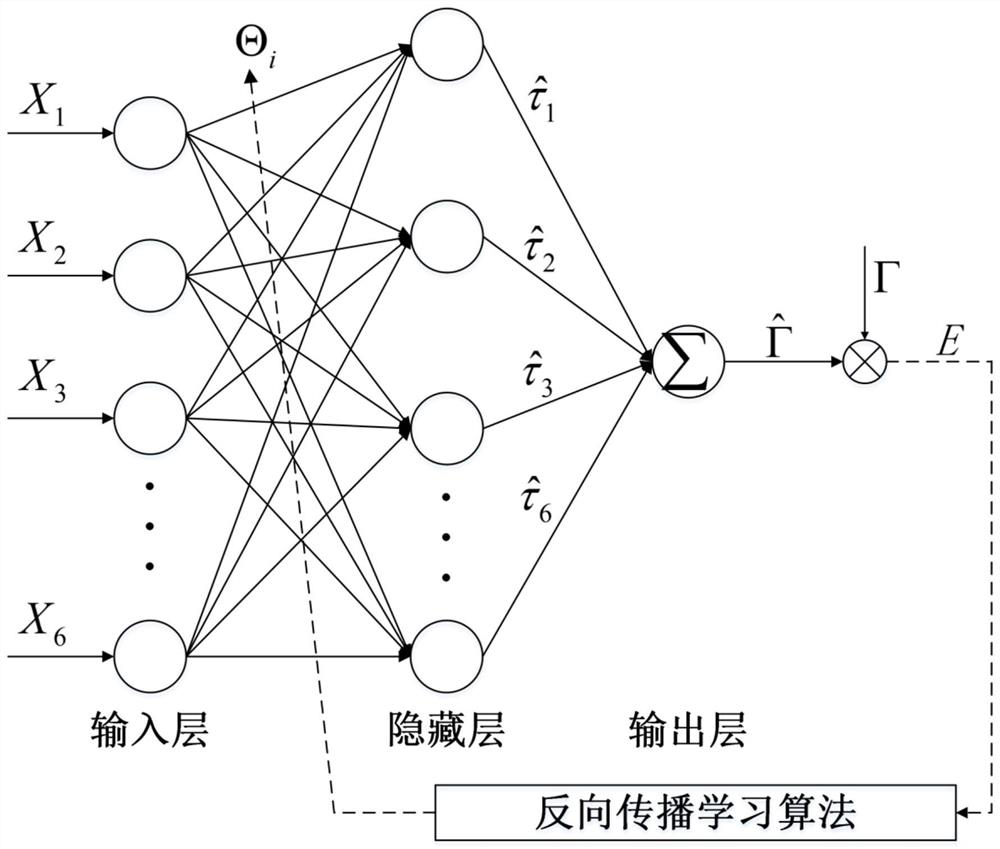
The invention provides an image retrieval method based on a decomposable word pack model. The method comprises the following four portions: first, extracting a plurality of features of an image, and separately establishing an index for each feature; second, in view of the indexes in the features, organizing each feature data via the word pack model, clustering the feature data, and using a clustering center as an entry in the word pack model; third, establishing a linear judgment function for the retrieval of the plurality of features, learning significant weights of the features by the least-mean-square-error criterion in a pre-retrieval process, and using the significant weights as coefficients in the linear judgment function; and fourth, independently providing a candidate set of each feature in a retrieval process. The final retrieval results of the plurality of features are clustered by the linear judgment function by using the significant weights of the features. By adoption of the method, high retrieval accuracy can be obtained, and the method is suitable for actual large-scale image retrieval applications.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Detecting method of self-adaptive frequency tracking current
InactiveCN102193016AAccurate trackingReal-time detectionCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage-current phase anglePower flowAlgorithm
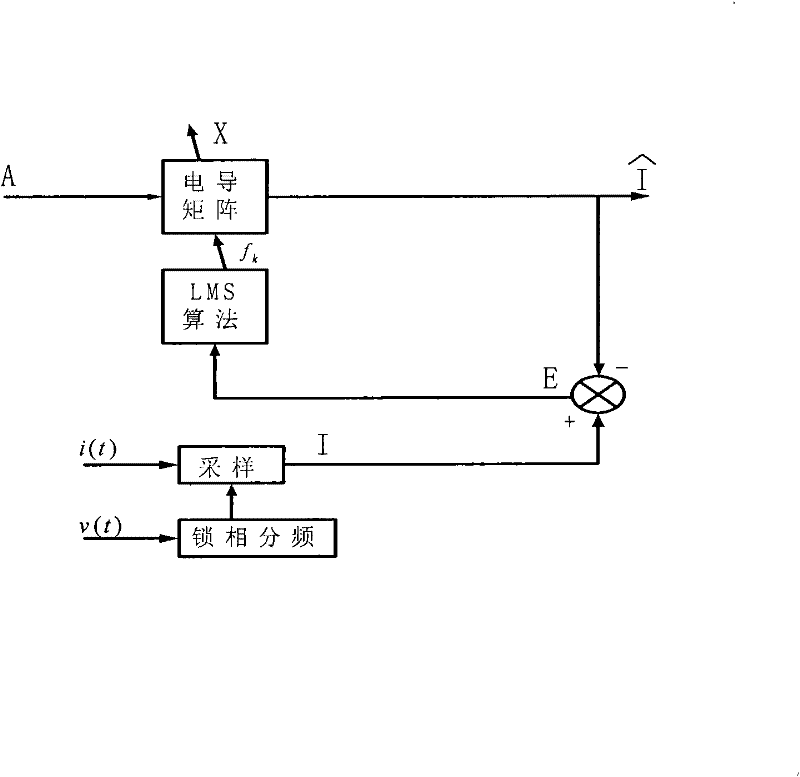
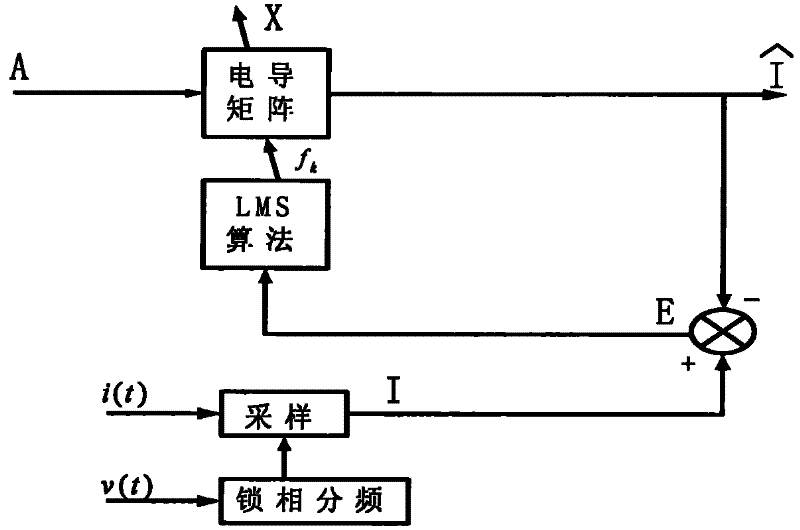
The invention discloses a frequency dividing detecting method of a self-adaptive frequency tracking current based on improved extended Prony's spectral estimation. The method comprises the steps of enabling a load current to approach a group of sampling data sequences {in} with equally spaced distance by using N index combinations with amplitudes Bk, phases theta k and frequencies fk according to an extended Prony's spectral estimation method; optimizing the frequency fk of an electric conductance matrix in the extended Prony's spectral estimation on line by using an LMS algorithm in a self-adaptive adjusting algorithm; and figuring out an optimal solution xk under the condition to obtain amplitudes and phases of a fundamental wave and each-order harmonic wave so that a mean square difference Epsilon (n) of an error between an output and a self-adaptive adjusting result is expected to be minimum. By using the detecting method disclosed by the invention, components to be detected can be fast and accurately figured out under the conditions of frequency variation and fundamental current mutation; moreover, the detecting method can also be applied to fast detection of single-order harmonic waves; small error and strong real-time property are obtained and actual application requirements are satisfied.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
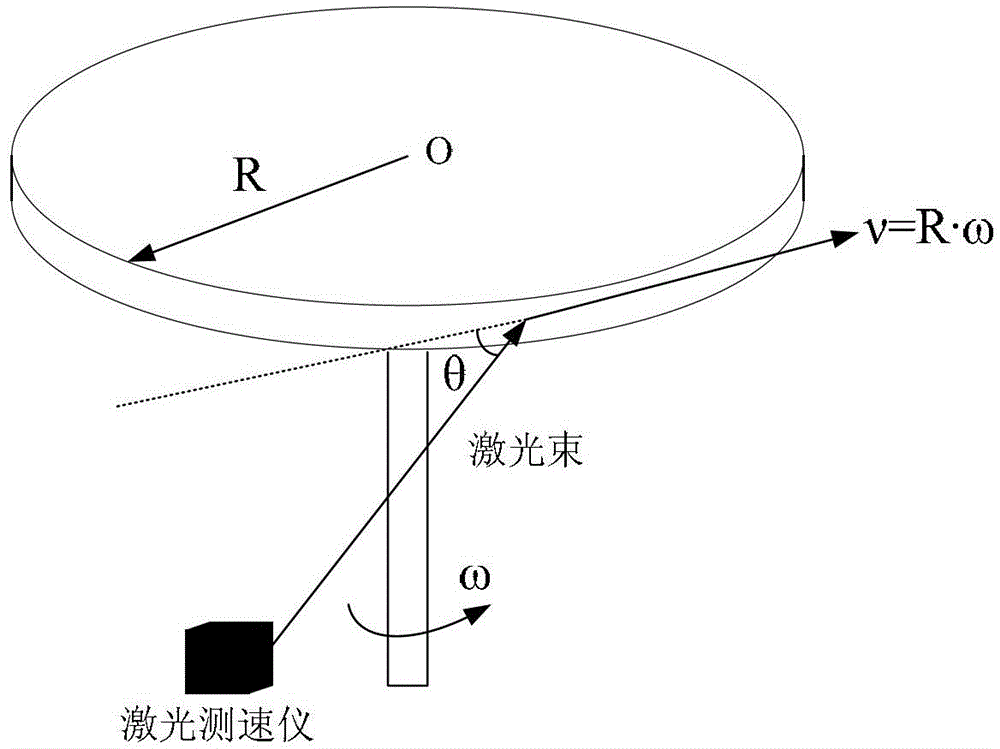
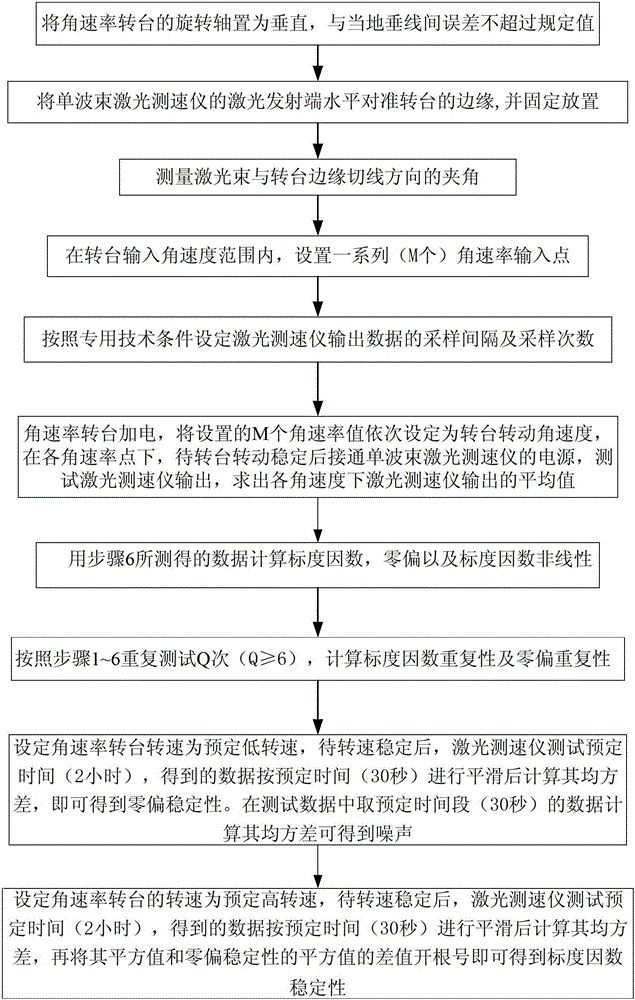
Accuracy testing and calculating method of single-beam laser speedometer for combined navigation
The invention relates to an accuracy testing and calculating method of a single-beam laser speedometer for combined navigation. The method comprises the following ten steps of: 1) setting the rotating shaft position of a turntable; 2) horizontally aligning the laser transmitting end of the speedometer to the edge of the turntable; 3) measuring an included angle between a laser beam and the tangential direction of the edge of the turntable; 4) setting an angular rate input point within an input angular speed range; 5) setting the output data sampling interval and times of the speedometer according to a standard; 6) testing and calculating an output average value under the condition of the input angular speed; 7) calculating a scale factor, zero bias and scale factor nonlinearity by using the data obtained in the previous step; 8) repetitively testing according to the step 1 to the step 6 to calculate scale and zero bias repeatability; 9) setting the rotating speed of the turntable to a low rotating speed, and testing and calculating mean-square deviation of data after the data is smoothed according to preset time to obtain zero bias stability and noise; and 10) setting the rotating speed of the turntable to a high rotating speed, testing and calculating mean-square deviation of data after the data is smoothed according to preset time to obtain an initial value of scale factor stability, and finally taking a square root of a difference value between the squared value of the initial value of scale factor stability and the squared value of the zero bias stability to obtain the scale factor stability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Secondary voltage control method and device for controlling reactive power of generator to be uniform
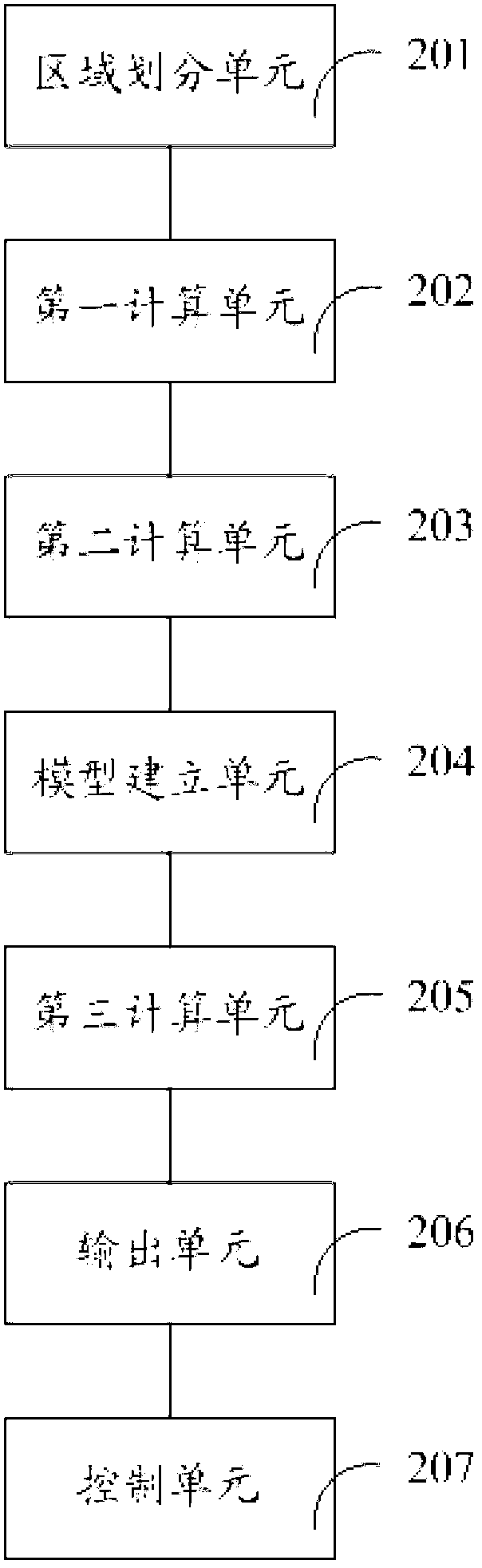
ActiveCN102709920AUniform reactive outputStable supportReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationElectric generator controlMean squarePower flow
The invention discloses a secondary voltage control method for controlling reactive power of a generator to be uniform. The secondary voltage control method the steps of dividing the grid needing to be controlled into M control areas; according to the whole network power flow equation, obtaining reactive coordination factors of the controlled generator in each control area; according to the reactive coordination factors of the controlled generator in each control area, computing mean square difference value of the reactive coordination factors of the controlled generator in each control area; according to the mean square deviation, building a secondary voltage control model of each control area; solving the secondary voltage control model of each control area to obtain reactive regulating quantity of the controlled generator in the corresponding area; outputting the controlled reactive regulating quantity of the controlled generator in each area; and performing secondary voltage control. The invention also provides a secondary voltage control device for controlling the reactive power of the generator to be uniform, more uniform of the reactive power of the generator in the area is realized, and dynamic reactive support capability and voltage stable margin of the system are improved.
Owner:POWER DISPATCHING CONTROL CENT OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Rock foundation pit blasting parameter dynamic regulation and control method
PendingCN110826714AConstruction safetyData processing applicationsGenetic algorithmsPopulation sampleDifference of Gaussians
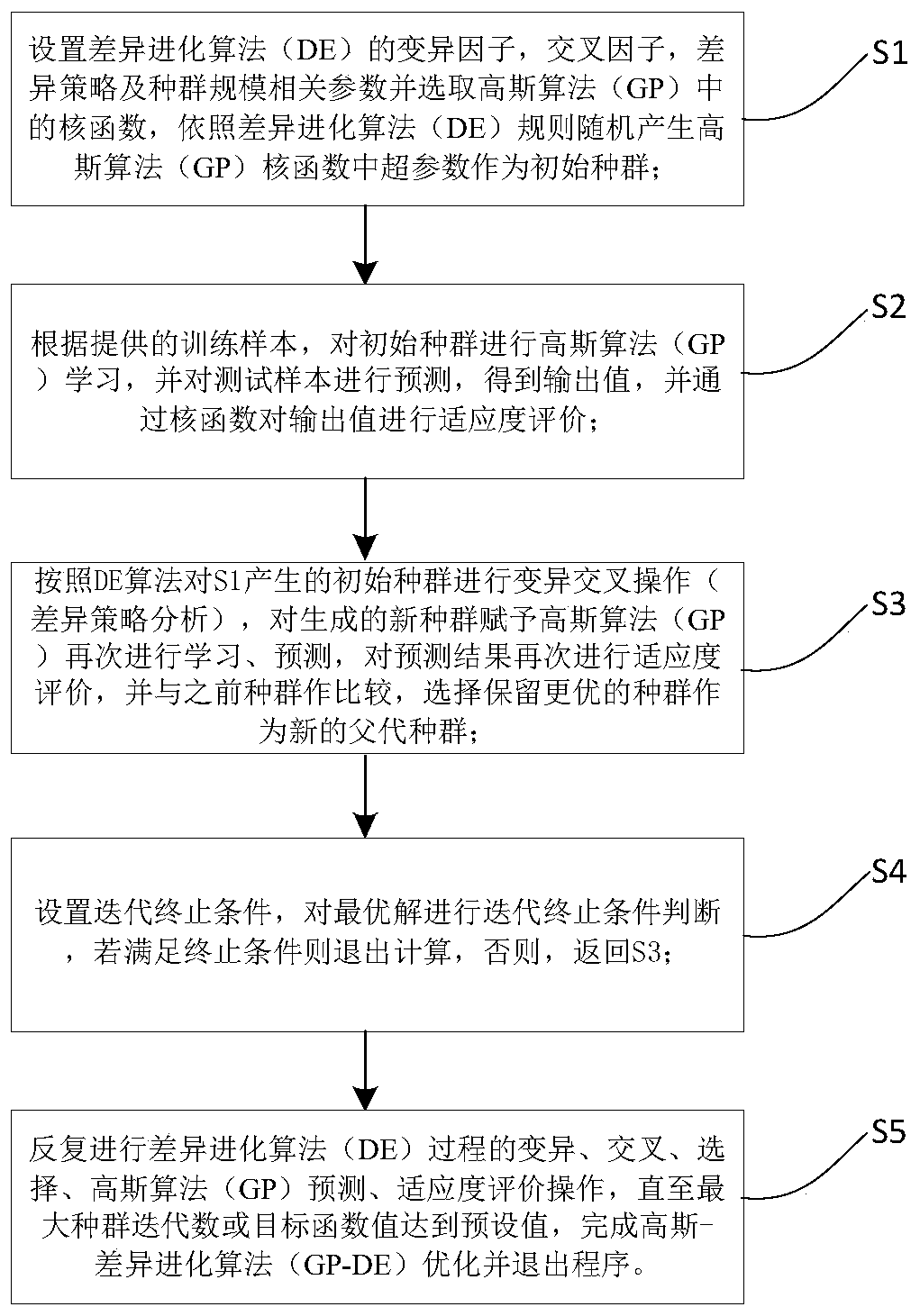
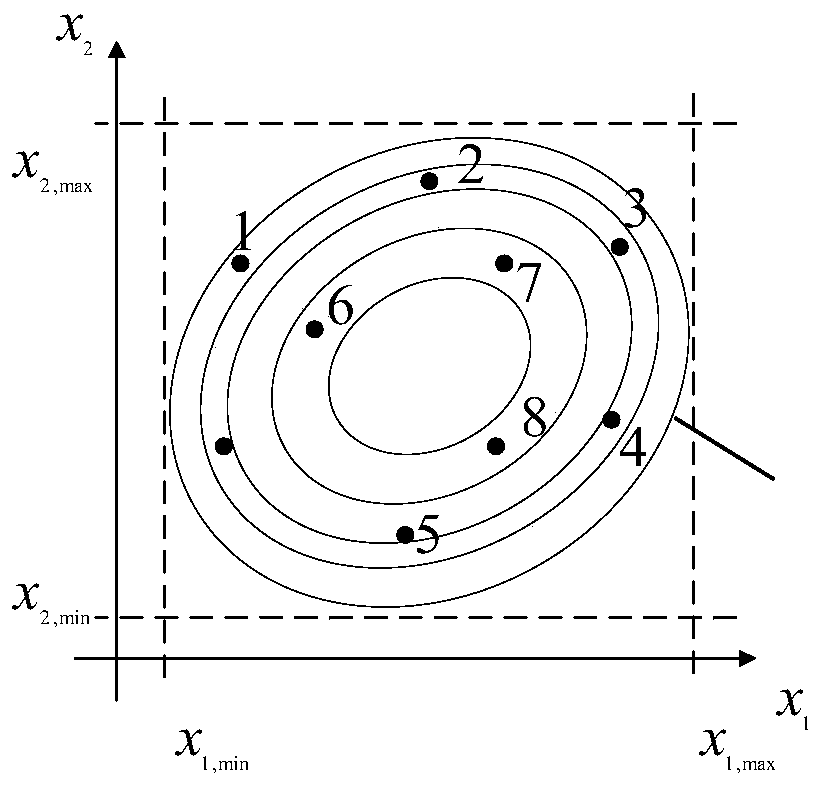
The invention discloses a rock foundation pit blasting parameter dynamic regulation and control method. The method comprises steps of establishing a nonlinear mapping relationship between an input vector and an output vector by using a GP machine learning method; taking the optimal hyper-parameter in the GP as a population sample in the DE algorithm, searching each optimal hyper-parameter of the GP through variation, intersection and selection in the DE process by means of the optimization capability of DE, optimizing the GP model, and improving the prediction capability of the GP model, thereby predicting an output value closer to an optimal solution. Furthermore, the optimal output value of the prediction result of the GP model and the mean square error between the output value and the control value are used as the fitness function of DE, and the prediction capability of the GP model is improved by optimizing the sample population and gradually approaching the optimal solution, so that the target vector closer to the optimal solution is predicted. According to the method, a Gaussian-differential evolution algorithm (GP-DE) blasting intelligent optimization algorithm is introducedon the basis of blasting monitoring data analysis to quickly and effectively optimize the blasting parameters, so that the construction process is ensured to be carried out safely.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com