Edible and biodegradable utensils
A technology of utensils and peanut powder, which is applied in the field of edible and biodegradable utensils, and can solve the problems of non-degradable compostable utensils and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0662] Example 1: Water Test
[0663] The materials used to make the utensils of the present invention are more heat resistant than other "pure" bio-based utensils (eg, PLA-based and CPLA-based utensils). Purely bio-based utensils will become soft and lose their function in liquids of about 60 degrees Celsius to about 70 degrees Celsius. Two water trials were performed: "W1" using a spoon and fork, and "W2" using a spoon and fork.
[0664] In W1, the tested compositions were high gluten wheat flour (~26%), (whole grain) corn flour (~20%), rice flour (~13%), soybean flour (~6%) and water / milk / Soy milk (~34%).
[0665] In W1, the spoon / fork (utensil) was placed in a cup of boiling water and allowed to cool; total time of utensil in water was 45 minutes. After 30 minutes, the utensils were not deformed and the tines (or piercing parts) of the utensils did not soften until 45 minutes.
[0666] In W2, the tested compositions were high gluten wheat flour (~26%), (whole grain) c...
example 2
[0670] Example 2: Curves of a test harness
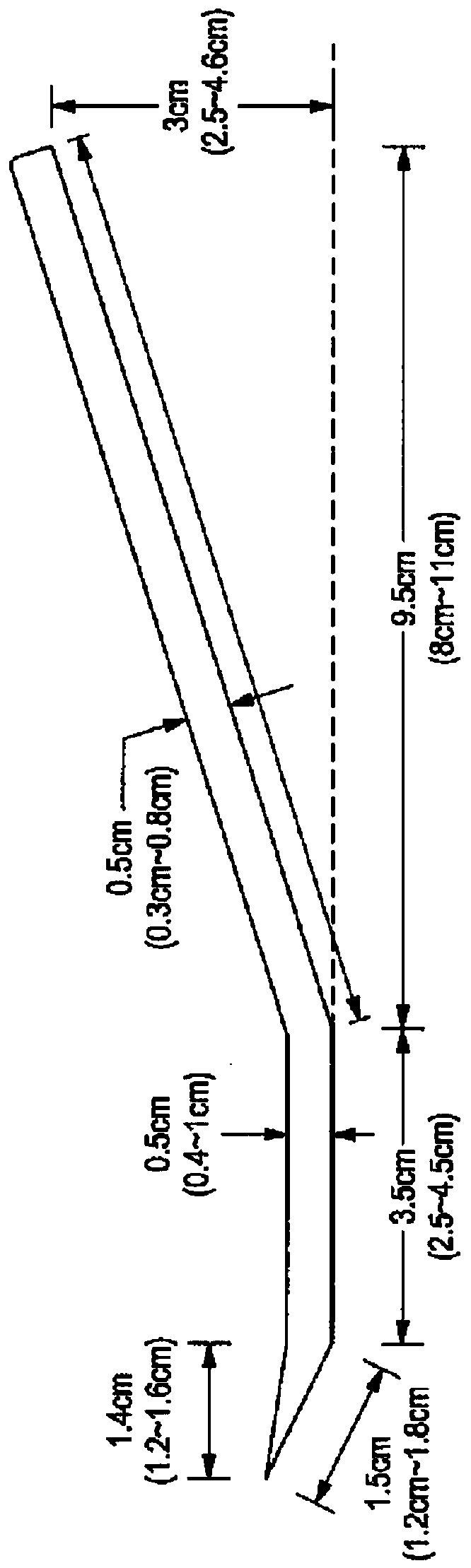
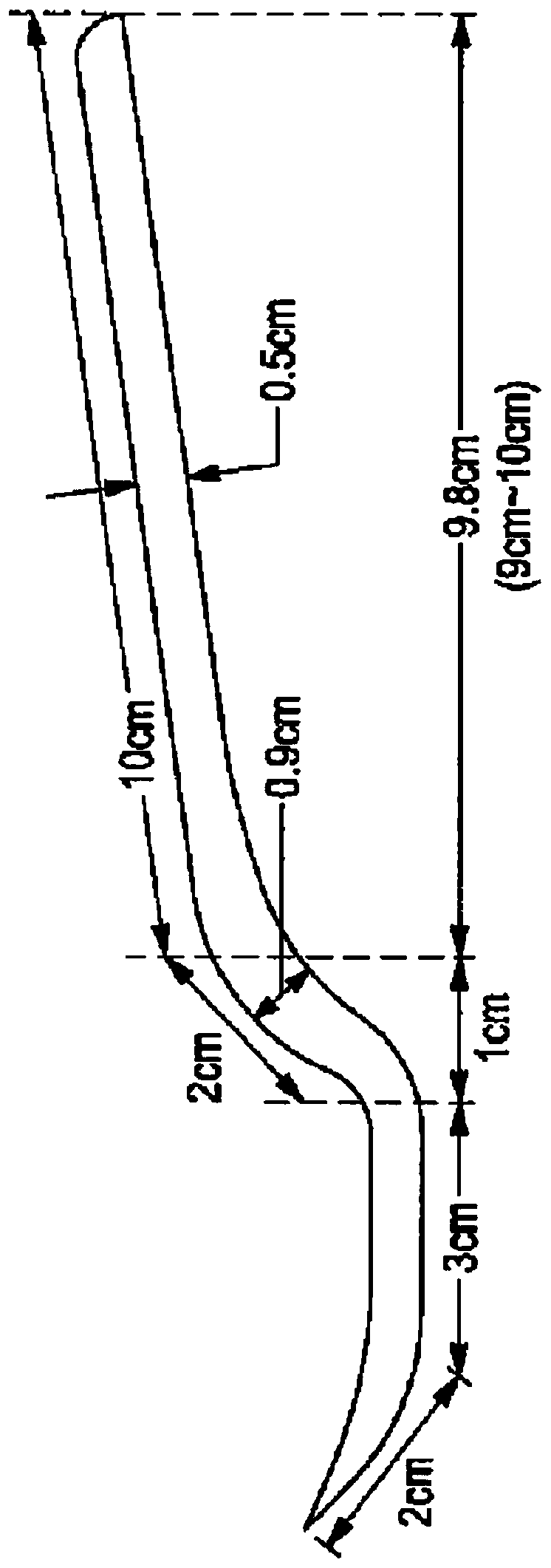
[0671] For example Figure 1A , Figure 1C , Figure 4 , Figure 5 and Figure 7 As shown, the implements of the present invention include curves having angles of about 18 degrees to about 22 degrees, about 19 degrees to about 21 degrees, or about 20 degrees + / - 5 degrees. This curve is important in maintaining the form, strength and usefulness of the implement.
[0672] Tested the integrity of the "curve" of several spoons and forks. Spoons and forks made from a high-gluten composition and spoons and forks from a low-gluten composition were manufactured and tested. Additionally, spoons and forks made from gluten-free compositions were manufactured but not tested.
[0673] Place each spoon or fork in a glass of water of about 70°C to about 100°C. Put the spoon (or fork) in the liquid for about 5 minutes, then take it out, use it for solid food, then put the spoon (or fork) back in the liquid after it has cooled, and leave it...
example 3
[0674] Example 3: Compressive force
[0675] Compression test:
[0676] Equipment: AILIYIQI ATH-500 Spring Tensile and Compression Testing Machine
[0677] Maximum force: 500N
[0678] Maximum compression area: 18cm 2 (diameter 48mm)
[0679] Compositions used for compression testing: high gluten wheat flour (~26%), (whole grain) corn flour (~20%), rice flour (~13%), soybean flour (~6%) and water / milk / soymilk ( ~34%).
[0680] method:
[0681] 1. Plug in and open
[0682] 2. Set to record maximum force
[0683] 3. Place the stressed area of the utensil (fork or spoon) on the fixed plate
[0684] 4. Pull down the measuring handle so that the moving plate compresses the forks
[0685] 5. Read data and clean up debris
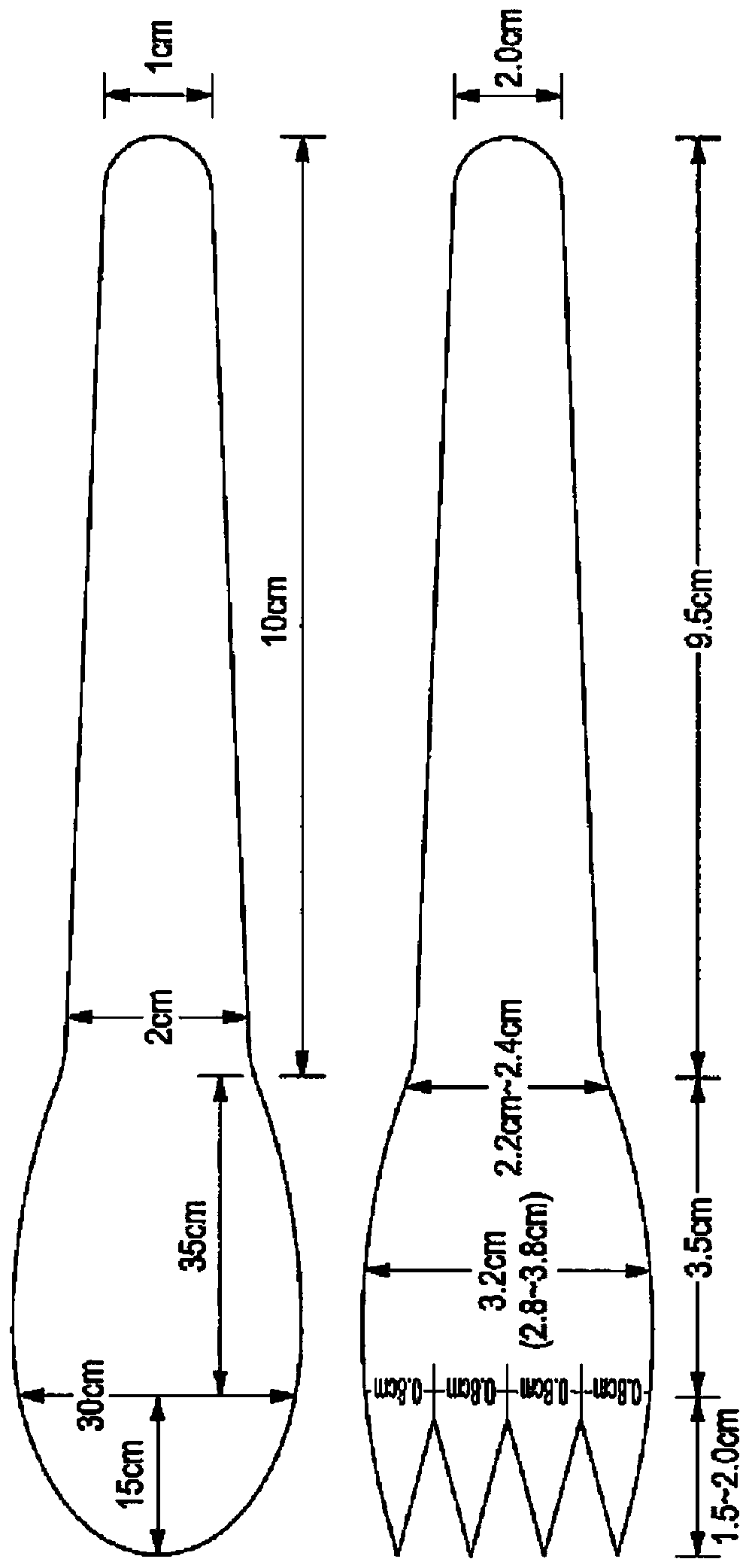
[0686] Figure 8 Three different locations on the fork that were tested are shown. The top circle has a break force of 284-308N, the middle circle has a break force of 255-351N, and the bottom circle has a break force of 230-328N.
[0687] Figure ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compression force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compression force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compression force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com