Method of selecting for antibodies
A technology of antibodies and antibody mimics, applied in chemical instruments and methods, anti-animal/human immunoglobulins, library screening, etc., can solve problems such as inability to obtain antibodies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0137] Example 1: Illustration of Self-Labeling by Cells Expressing Anti-EpCAM Antibodies
[0138] Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) was chosen as a suitable target polypeptide (bait antigen). EpCAM is a glycosylated 30- to 40-kDa type I membrane protein that contains three potential N-linked glycosylation sites.
[0139] HEK293 cells were transfected with the EpCAM expression construct (HEK293 cells are usually EpCAM negative) together with a secreted HA-tagged anti-EpCAM single chain antibody expression construct. After a 24 hour incubation period, cells were stained with a fluorescently labeled anti-HA-tag antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry to determine which cells had self-labeled their membrane EpCAM with the encoded anti-EpCAM antibody.
[0140] result in figure 1 shown in . Cells expressing both the 'bait' antigen (EpCAM) and the scFv were highly fluorescent, whereas all other cells (expressing EpCAM only or scFv only) were not. This shows that scFv-sec...
Embodiment 2
[0141] Example 2: Optimizing stringency to prevent labeling of non-relevant cells
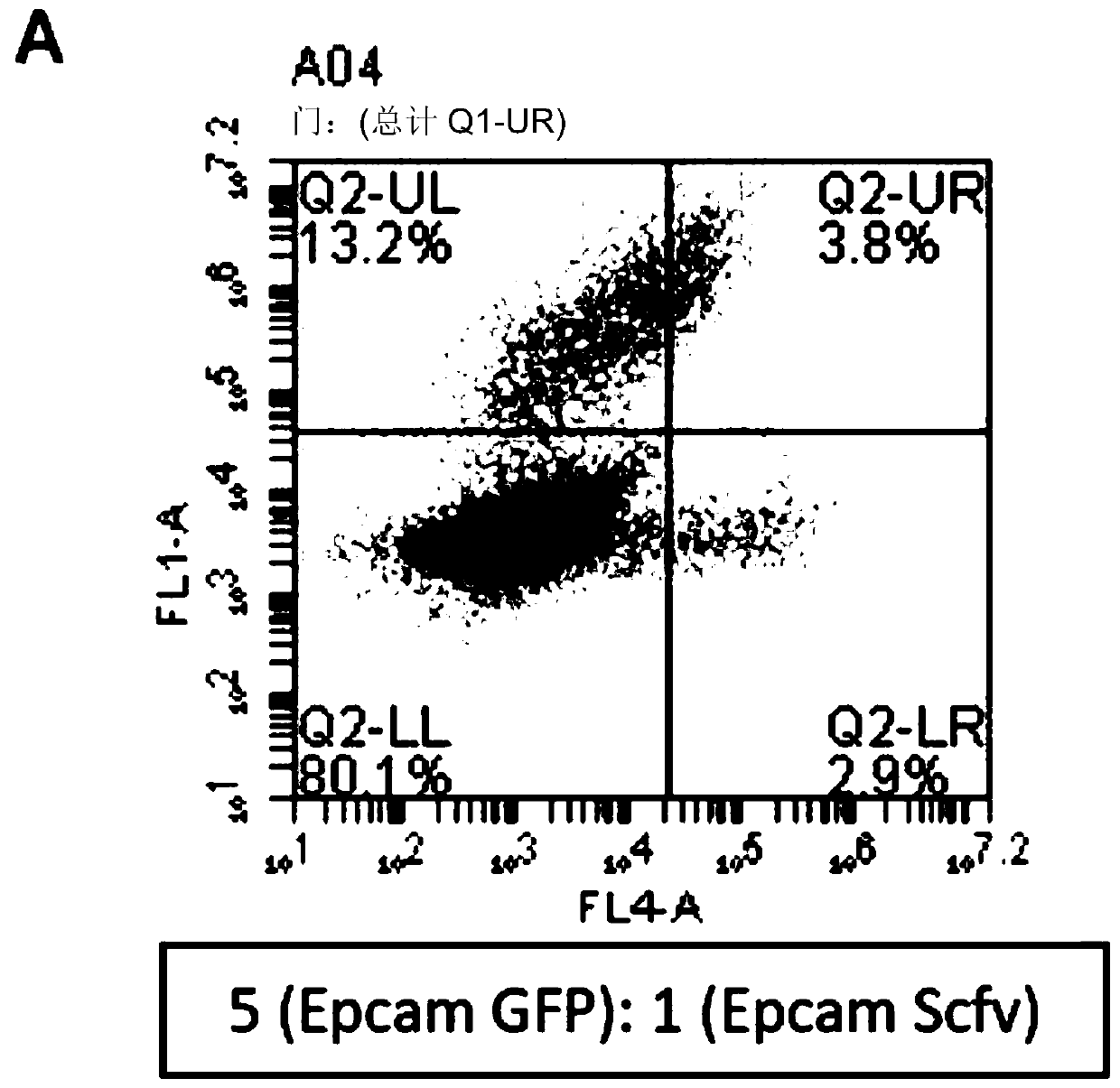
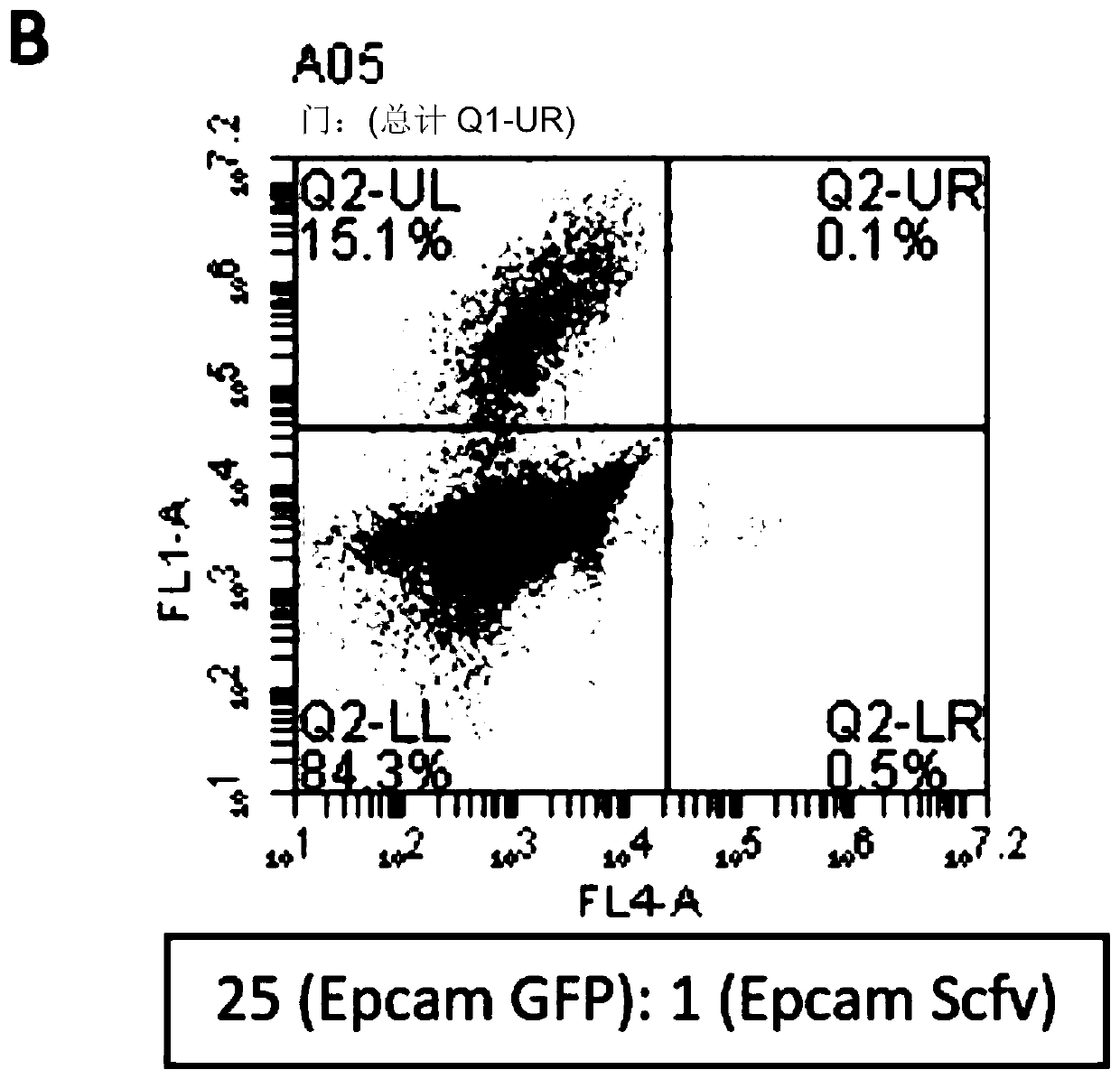
[0142] Two populations of EpCAM-expressing cells were prepared. Some expressed anti-EpCAM antibodies while others expressed green fluorescent protein (GFP). Cells were mixed at different ratios (where antibody-expressing cells were always the fewest) and incubated for different times to visualize immobilized and surface-bound antibody by staining in the red channel. A small number of antibody-expressing cells were always self-labeled first, resulting in cells in the lower right quadrant of the flow cytometry plot (cells were red rather than green, indicating that antibody-producing cells were labeled before non-relevant cells).
[0143] The results are shown in FIG. 2 . Even at a dilution of 1:125, a significant number of cells appeared in the lower right quadrant, representing cells expressing antibodies that bind cell surface antigens.
Embodiment 3
[0144] Example 3: Generation of DRD1 Antibody
[0145] In this example, the target polypeptide (bait) is DRD1; it is expressed in CHO cells (see image 3 ). Target polypeptide (bait) constructs and antibody libraries were cloned into CHO cells using retroviral transfer vectors.
[0146] Target polypeptide (bait) cell lines were generated by integrating the gene for the target polypeptide (bait) along with a selectable marker into the host cell (CHO) genome using a retroviral system (see Figure 4 ). The target polypeptide construct also contains the gene for the Tet repressor protein (TetR). Expression of the target polypeptide (bait) is driven by a doxycycline-inducible promoter.
[0147] CHO cells were infected with a library of retroviral particles encoding a cDNA-based library of human scFv sequences encoding human-like scFv sequences. For scFv libraries, retroviral transfer vectors were modified to contain constitutive promoters (SFFV) and flanking regions of scFv an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com