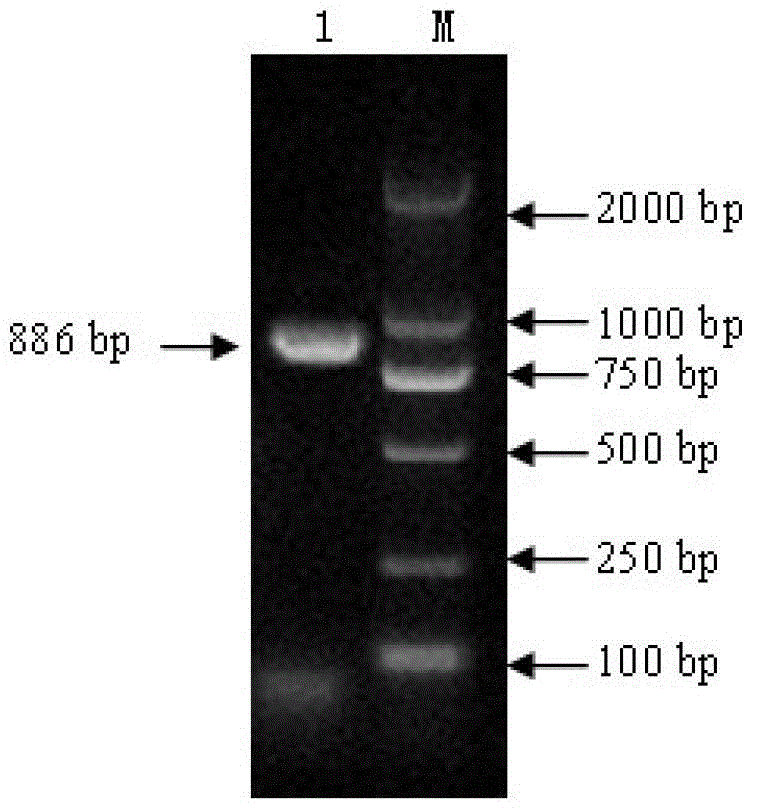
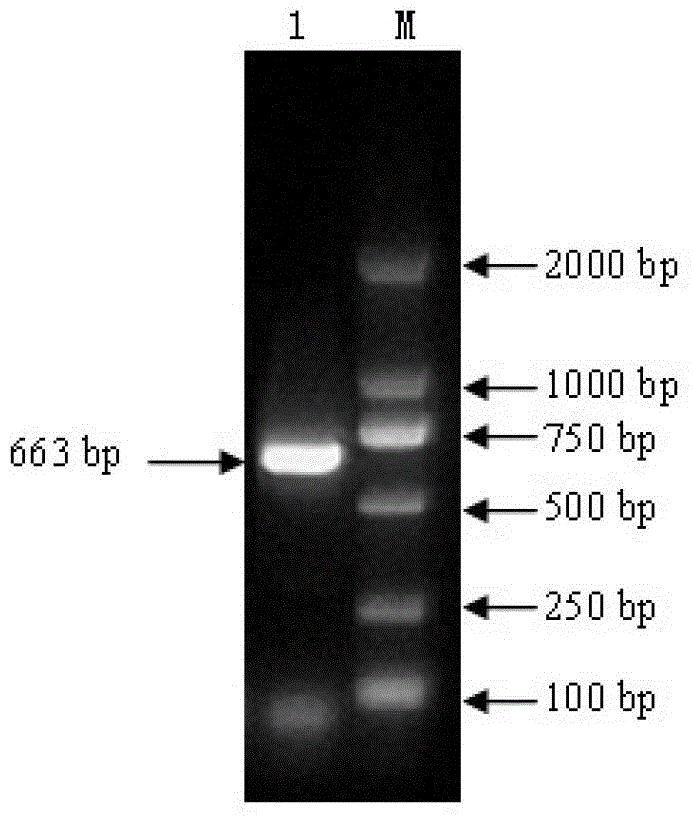
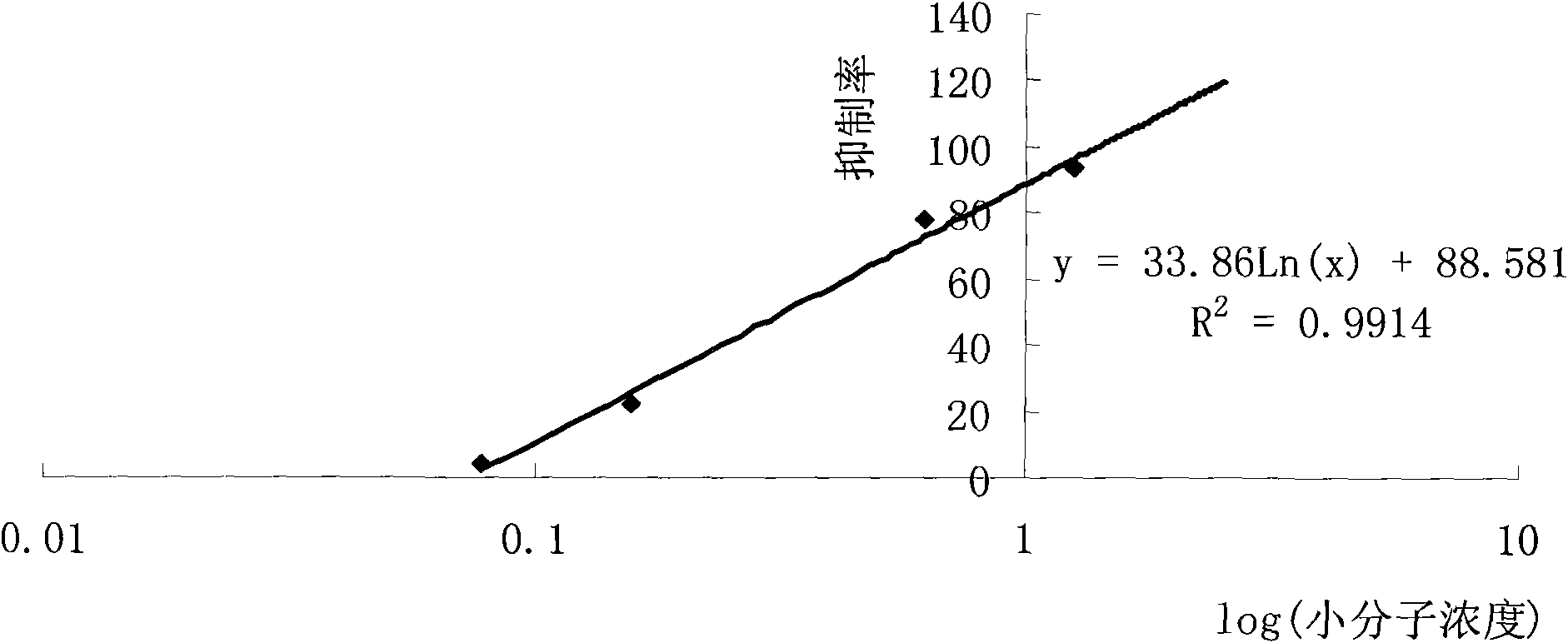
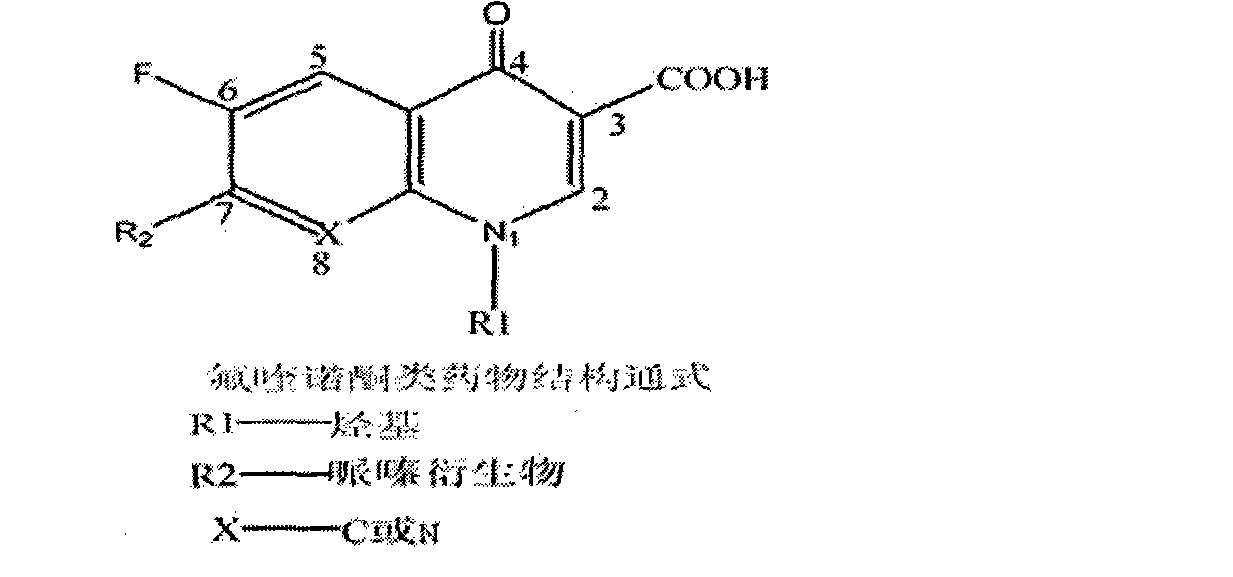
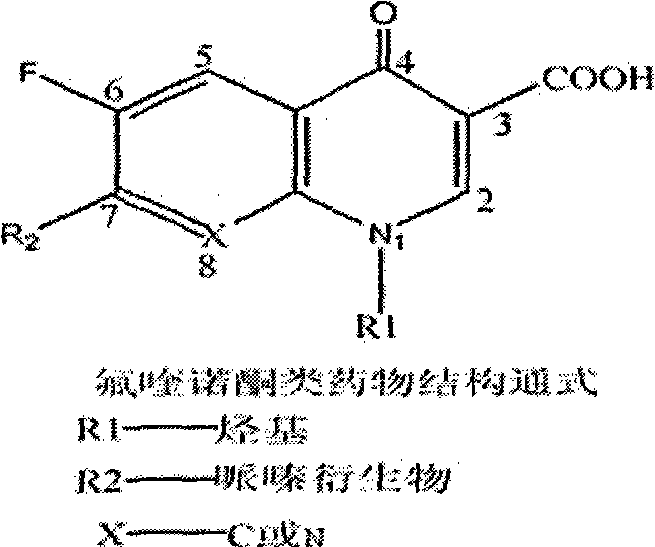
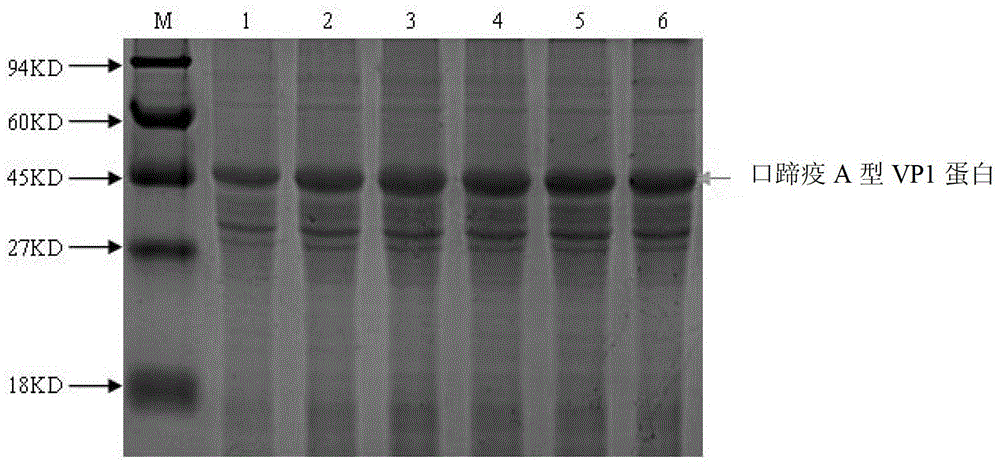
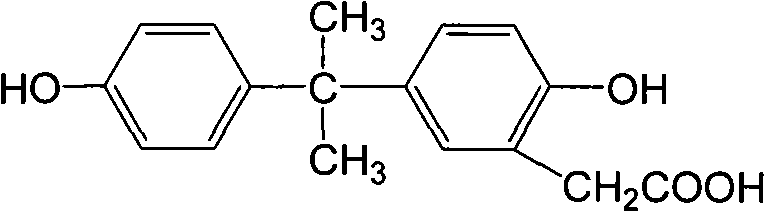
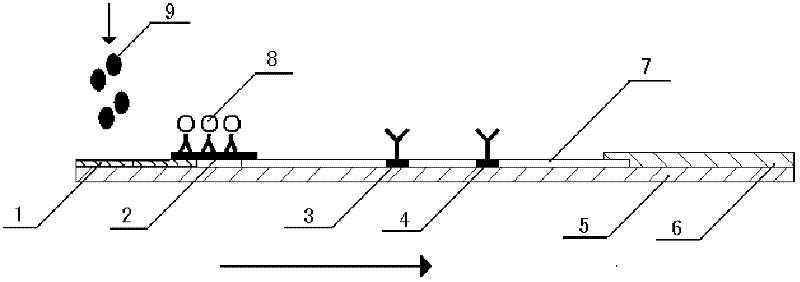
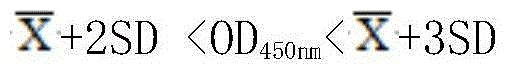Patents
Literature
204 results about "Hybridoma technology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hybridoma technology is a method for producing large numbers of identical antibodies (also called monoclonal antibodies). This process starts by injecting a mouse (or other mammal) with an antigen that provokes an immune response. A type of white blood cell, the B cell, produces antibodies that bind to the injected antigen. These antibody producing B-cells are then harvested from the mouse and, in turn, fused with immortal B cell cancer cells, a myeloma, to produce a hybrid cell line called a hybridoma, which has both the antibody-producing ability of the B-cell and the longevity and reproductivity of the myeloma. The hybridomas can be grown in culture, each culture starting with one viable hybridoma cell, producing cultures each of which consists of genetically identical hybridomas which produce one antibody per culture (monoclonal) rather than mixtures of different antibodies (polyclonal). The myeloma cell line that is used in this process is selected for its ability to grow in tissue culture and for an absence of antibody synthesis. In contrast to polyclonal antibodies, which are mixtures of many different antibody molecules, the monoclonal antibodies produced by each hybridoma line are all chemically identical.
Preparation method of anti-fluoroquinolone rabbit monoclonal antibody and application thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of anti-fluoroquinolone rabbit monoclonal antibodies and application thereof. Six fluoroquinolone medicaments are chosen in the invention and coupled with Bovine serum albumin (BSA) to synthesize immunoantigens respectively. The above six immunoantigens are injected subcutaneously in the backs of immune rabbits after being mixed together. The anti-fluoroquinolone rabbit monoclonal antibodies are obtained by hybridoma technique. Rabbit monoclonal antibodies, which are superior to rat monoclonal antibodies, are prepared in the invention. More antigenic determinants are identified when rabbits are chosen as the experimental animal instead of rats. In addition, more integrated experiments can be carried out in rabbit spleens, since the spleens of rabbits are larger than that of rats. The invention provides the possibility of high throughput screening for fusion cells. The anti-fluoroquinolone antibodies of wide-adaptability in the invention has good detection effect on fluoroquinolones, such as enrofloxacin, ofloxacin, Difloxacin, Pefloxacin, Fleroxacin, Danofloxacin, etc., thus making it applicable to fluoroquinolone residue detection on food, forage and environmental samples.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Competitive ELISA method based on foot-and-mouth disease A type VP1 protein and its monoclonal antibody
InactiveCN103554234AHigh purityImprove production efficiencySsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenDisease
The invention relates to a competitive ELISA method based on a foot-and-mouth disease A type VP1 protein and its monoclonal antibody, also relates to a preparation method of the foot-and-mouth disease A type VP1 protein, and a preparation method of the monoclonal antibody of the foot-and-mouth disease A type VP1 protein, and belongs to the technical field of animal immunological detection. In the invention, a primer pair C1 and C2 and a primer pair E1 and E2 are amplified to obtain a gene sequence of the foot-and-mouth disease A type VP1 protein, the foot-and-mouth disease A type VP1 protein is obtained by constructing an expression plasmid, introducing the expression plasmid into a prokaryotic expression host and carrying out inducible purification, the foot-and-mouth disease A type VP1 protein monoclonal antibody is obtained by treating the foot-and-mouth disease A type VP1 protein as an antigen through a hybridomas technology, and the competitive ELISA method used for detecting a foot-and-mouth disease A type antibody is established based on the foot-and-mouth disease A type VP1 protein and its monoclonal antibody. The detection method has a strong specificity and a good stability, and can be used for detecting a foot-and-mouth disease A type serum antibody. By comparing a result obtained through the detection method with a liquid phase blocking ELISA kit, the coincidence rate is 95.8%.
Owner:广西壮族自治区动物疫病预防控制中心
Hybridoma cell line of monoclonal antibody against African swine fever virus and secreted monoclonal antibody thereof
InactiveCN101831407AHigh utility valueMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulins against virusesBALB/cPurification methods
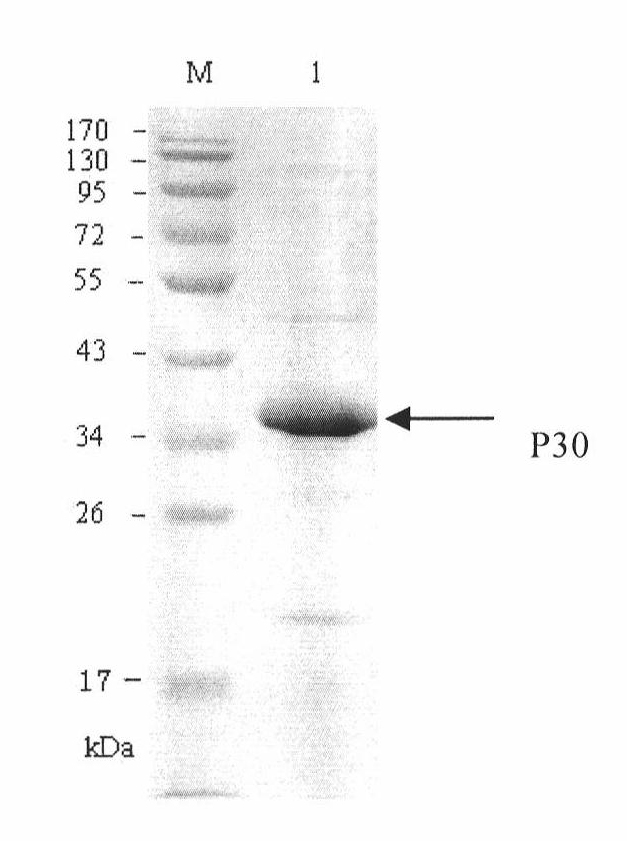
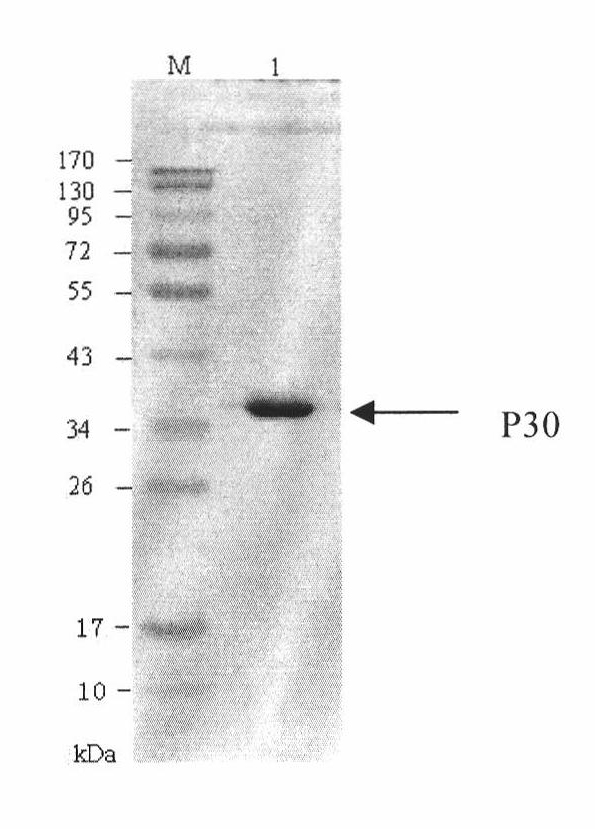
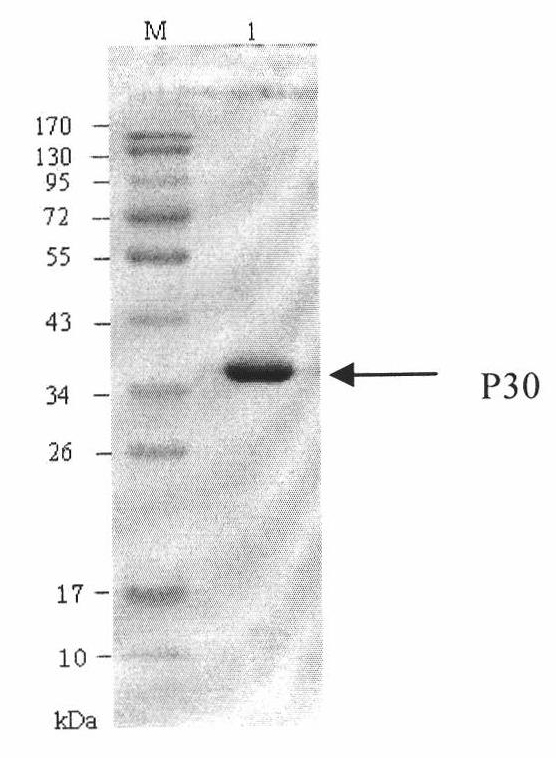
The invention discloses a hybridoma cell line of a monoclonal antibody against African swine fever virus and the secreted monoclonal antibody thereof. The preparation method of the invention comprises the following steps: preparing a recombined P30 soluble antigen by prokaryotic expression; immunizing a BALB / c mouse; and finally fusing, screening and cloning by a hybridoma technology to obtain the hybridoma cell line which can stably secrete the monoclonal antibody against African swine fever virus P30 protein. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the monoclonal antibody with the cell line, an antibody purification method and a labeling method for horseradish peroxidase of the antibody. The monoclonal antibody can be used in detecting the African swine fever viral antibody in pig serum.
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
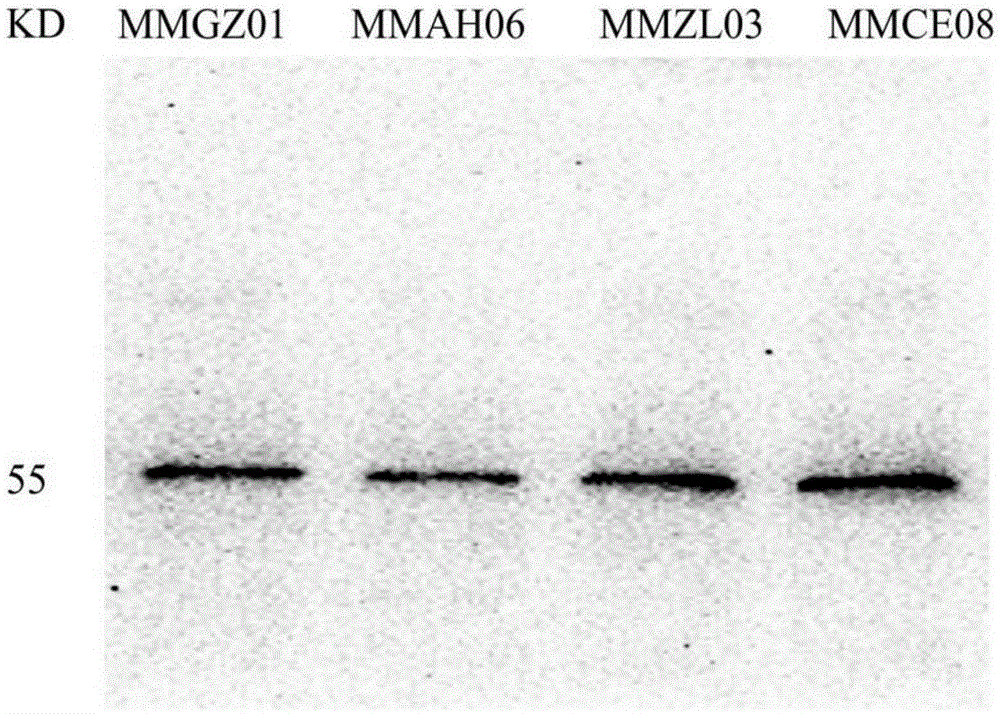
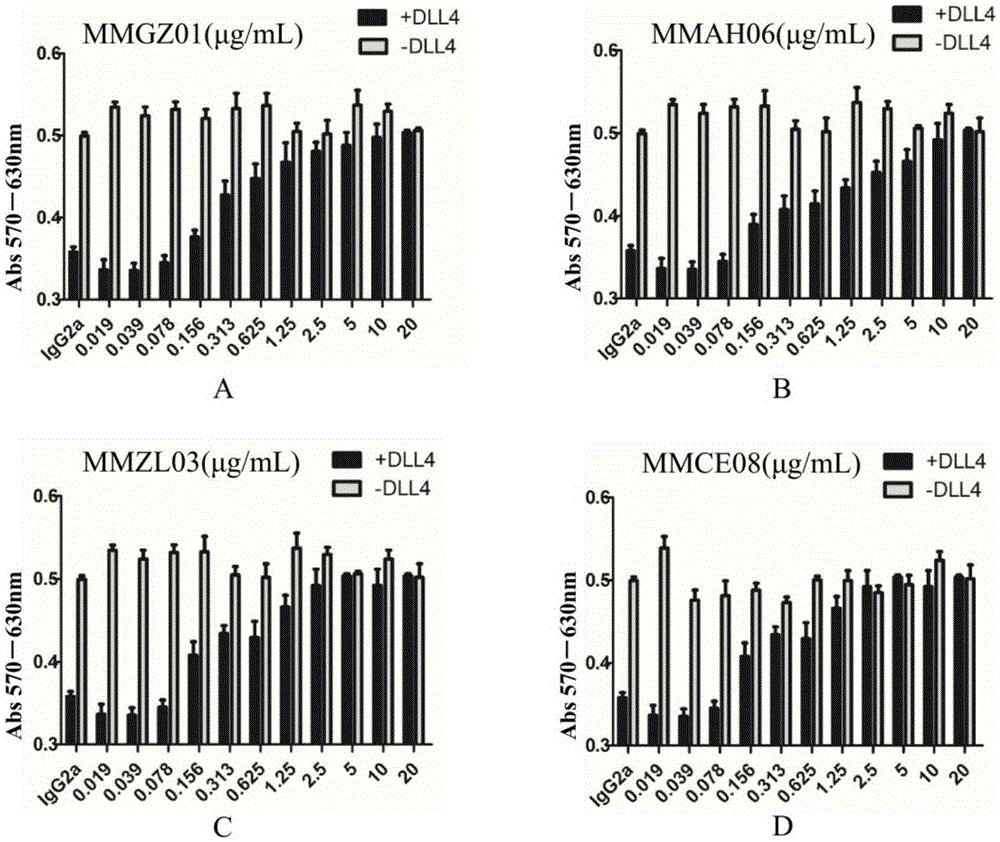
Anti-human Delta like 4 monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN105384818AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsBALB/cAntigen
By use of hybridoma technology, recombinant human Delta like 4 (rhDll4) is used as an antigen for immunizing a BALB / c mice to obtain a high affinity and biological activity anti-human Delta like 4 monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody is characterized in that: the monoclonal antibody can be combined with rhDll4 specifically, and can block human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) proliferation suppression of the rhDll4. Specifically, screening, a preparation method, and nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the heavy chain variable region and the light chain variable region of the anti-human Delta like 4 monoclonal antibody are disclosed, and the nucleotide and amino acid sequences comprise nucleotide and amino acid sequences corresponding to complementarity determining regions CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
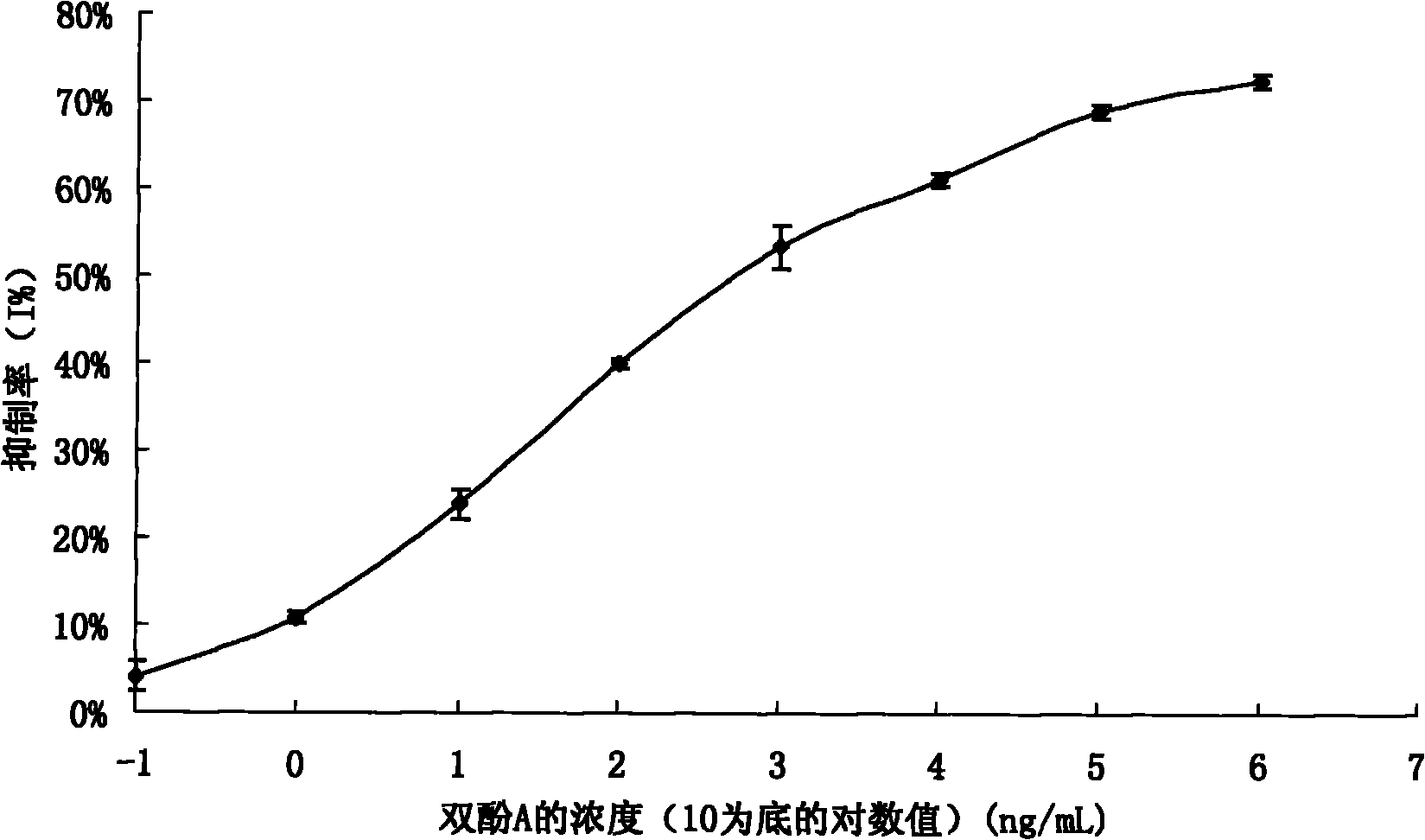
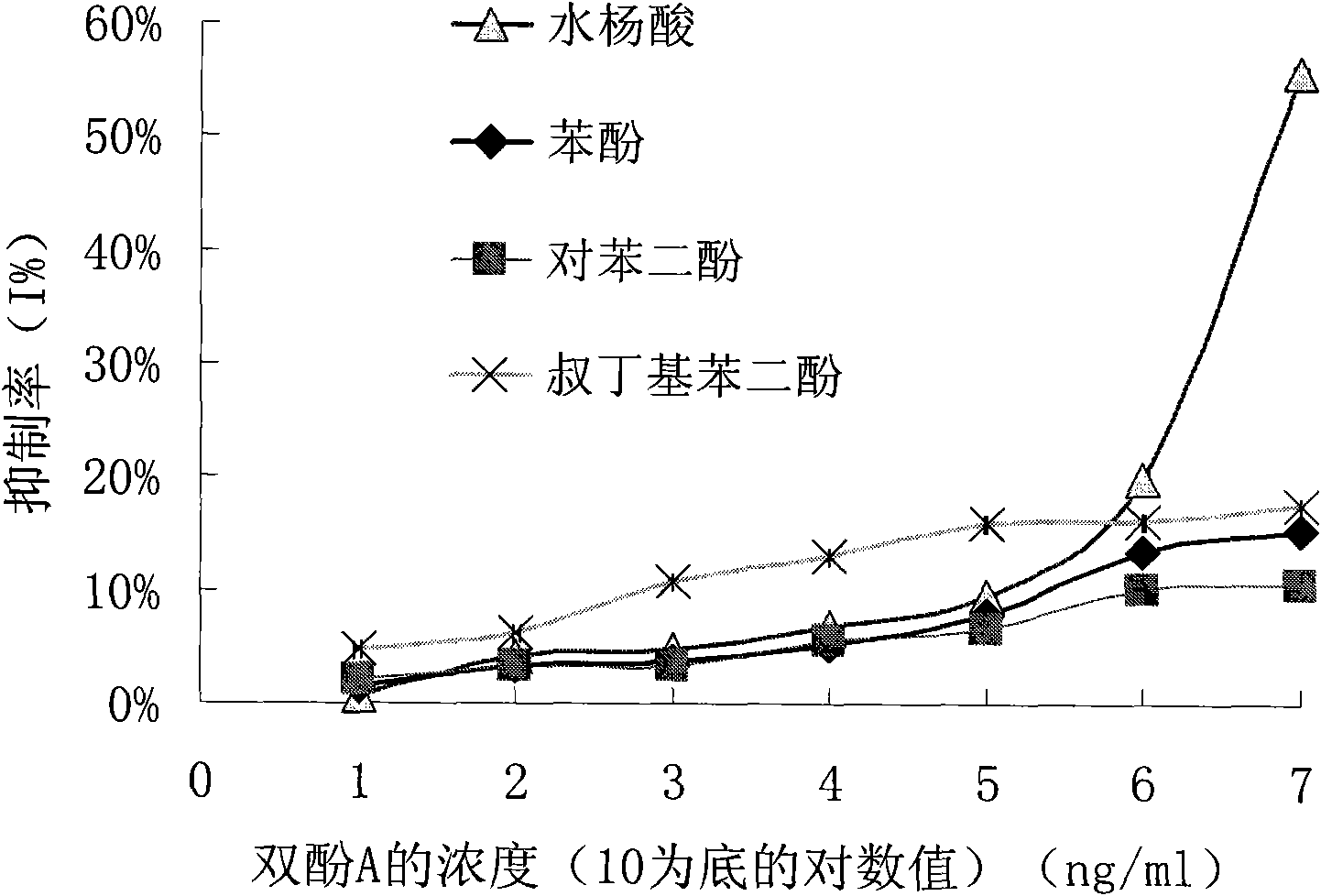
Preparation method of anti-bisphenol A monoclonal antibody
InactiveCN101863981AEffective monitoringRapid Field MonitoringSerum albuminTissue culturePolyethylene glycolCarrier protein
The invention discloses a preparation method of an anti-bisphenol A monoclonal antibody. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: combining bisphenol A and a macromolecule carrier protein to prepare an artificial immunity antigen and a coating antigen; preparing splenocyte suspension from a bisphenol A artificial immunity antigen immunity mouse; fusing the mouse splenocyte and mouse myeloma cells SP2 / 0 in the presence of polyethylene glycol; detecting by hybridoma technology and subcloning for many times to obtain positive hybridoma cells which can stably secrete bisphenol A antibody, wherein the secreted antibody belongs to the IgG1 subclass; and establishing a bisphenol A indirect competition ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) test by utilizing the monoclonal antibody secreted by cell lines with high antibodytiter, wherein the minimum limit of detection can reach 0.324ng / mL. The antibody has no cross reaction with compounds with benzene ring structures, such as benzene, phenol, tert-butylphenol, p-hydroxylphengl, o-hydroxybenzoic acid and the like, has strong specificity and can be used for immunity detection of bisphenol A.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Anti-porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus monoclonal antibody and application
ActiveCN101979512AImmunoglobulins against virusesMicroorganism based processesBALB/cBiological property
The invention discloses an anti-porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus monoclonal antibody and application. The invention provides an anti-porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain 3C3 with collection number of CGMCC No. 4109. The invention also provides the anti-porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus monoclonal antibody generated by the anti-porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain 3C3 with collection number of CGMCC No. 4109. An experiment of the invention proves that: a purified PRRSV JXA1 strain is used for immunizing BALB / c mice, one hybridoma cell strain which can stably secrete PRRSV monoclonal antibodies is screened by utilizing the hybridoma technology and the biological characteristic identification is performed on the hybridoma cell strain so as to lay the foundation for further establishing a specific, sensitive and rapid PRRSV detection method.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL DISEASE CONTROL CENT
Single-chain antibody against fenitrothion and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102229672AStrong specificityHigh affinityMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulinsEscherichia coliSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention relates to a single-chain antibody against fenitrothion and a preparation method thereof. A ribosome display library of a whole set of single-chain antibody genes against the fenitrothion is constructed by using a ribosome display technology and rounding a hybrid tumor technology, and three single-chain antibody genes with high affinity and high specificity for the fenitrothion are screened from the library. After the single-chain antibody genes are connected with vectors PPOW3.0 and then subjected to soluble expression in escherichia coli, three soluble proteins with molecular weights of about 30KDa are obtained; and by enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA) and Biacore analysis, the three antibody proteins have high affinity and high specificity for the fenitrothion, so excellent single-chain antibody genes and antibody proteins are provided for establishing ELISA and immune sensors. The invention has significance for realizing quick, simple, convenient and accurate detection of organic phosphorus pesticide residue, and provides a new direction.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Preparation method of heavy metallic lead resistant monoclonal antibody
InactiveCN101041696AEfficient synthesisPromote rapid developmentImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTissue cultureAntigenDiethylenetriamine
The invention discloses a making method of heavy-metal lead monoclonal antibody in the biological technical domain, which is characterized by the following: coupling lead ion and carrier protein through p-aminobenzene-diethylenetriamine pentoacetic acid as bifunctional metal chelant; obtaining full antigen; crossing splenocyte and Sp2 / 0 marrow tumour cell to make crossed tumour cell; sieving; obtaining stable strong secretory specificity anti-lead monoclonal monomer to inhibit Pb-DTPA.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of heavy metal mercury monoclonal antibody
InactiveCN101139398AFast pushStrong antigenicityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingBALB/cSpleen cell
The present invention relates to a preparation method of heavy metal mercury monoclonal antibody, which belongs to the field of biotechnology. The present invention is particularly used in the preparation of specificity-recognition heavy metal mercury monoclonal antibody and in the fast mercury high-sensitivity measurement remained in the agricultural production and the agricultural production environment. The heavy metal mercury ion and the carrier albumen are coupled into full antigens through bifunctional metal chelate 1-(4-separate-cyano phenyl)-EDTA; the full antigens are used on Balb / C mouse and the spleen cells and the Sp2 / 0 myeloma cells are used to prepare hybridoma cells through the hybridoma technology. And monoclonal antibody which can stably excrete anti-Hg-EDTA is generated. The preparation technology in the present invention is easy and practical: the whole preparation process of the antigen requires no special instrument. The present invention is suitable for factory-scale production.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Humanized monoclonal antibody targeting Claudin18.2 as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112940124AStrong specificityThe preparation method is simple and easyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseHybridoma technology
The invention relates to a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting Claudin18.2 as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the present invention, the Claudin18.2 humanized monoclonal antibody obtained through the cell fusion and the hybridoma technology can be highly specifically combined with CHO-Claudin18.2 cells, but is almost not combined with CHO-Claudin18.1 cells, the preparation method of the Claudin18.2 humanized monoclonal antibody of the present invention has simple steps, and the obtained Claudin18.2 humanized monoclonal antibody has good ADCC and CDC activity on the expression of Claudin18.2 positive tumor cells. The humanized monoclonal antibody of Claudin18.2 disclosed by the invention is high in specificity and small in side effect, and has a very good prospect in application to treatment and / or prevention or diagnosis of Claudin18.2-related diseases such as tumors.
Owner:NANJING KAEDI BIOTHERAPEUTICS LTD
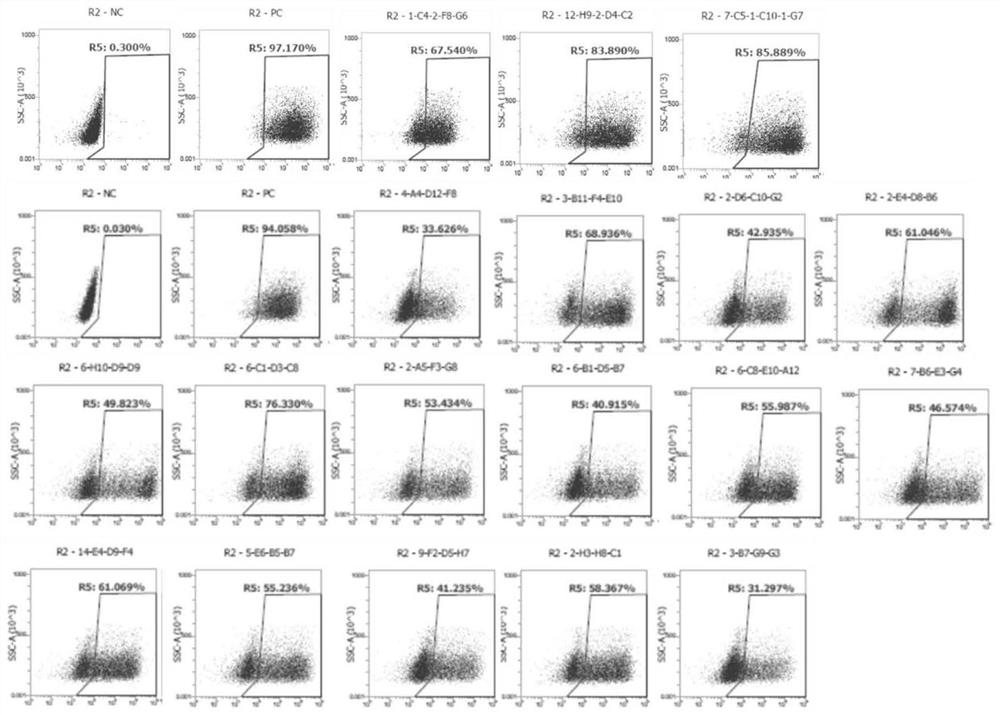
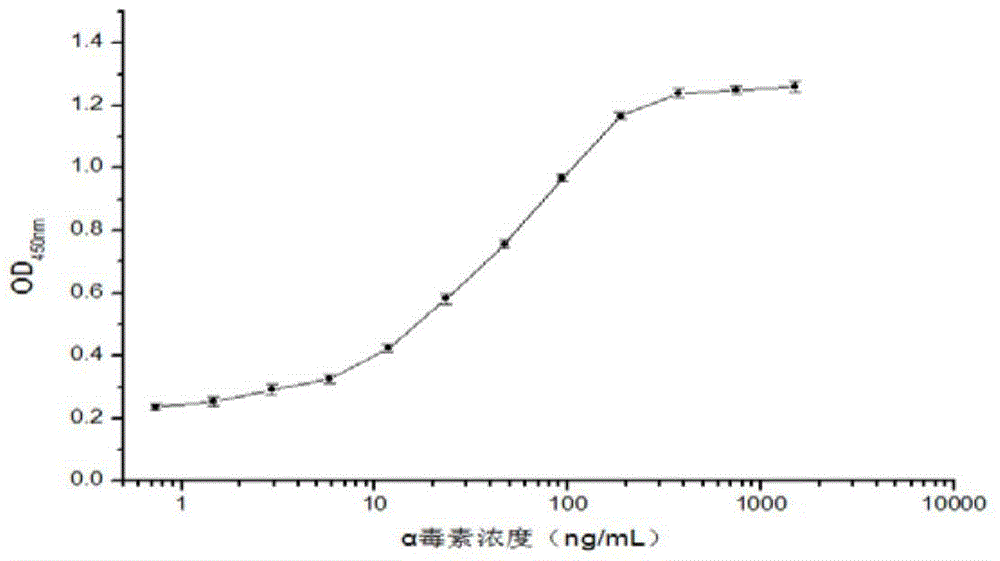
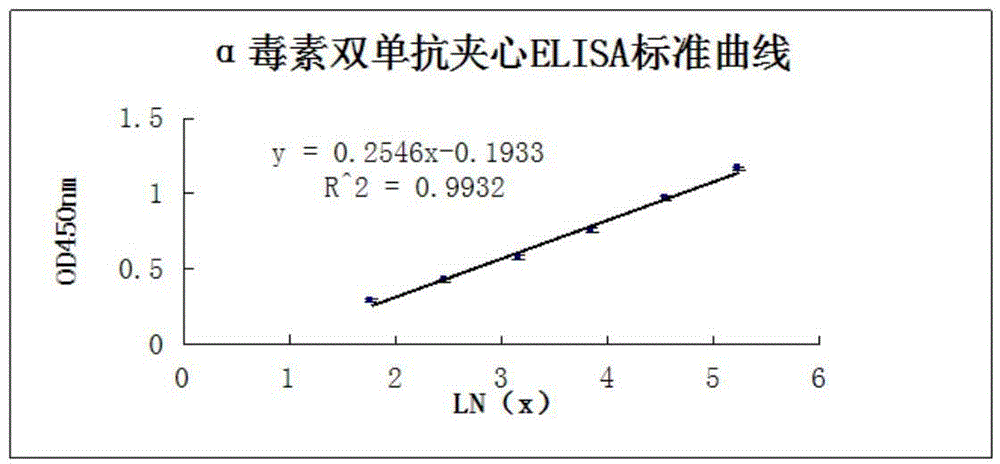
Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin double-antibody sandwich ELIS quantitative determination method
ActiveCN103941004AStrong specificityStrong responsivenessMaterial analysisAlpha-toxinClostridium perfringens toxoid
The invention relates to a clostridium perfringens alpha toxin double-antibody sandwich ELIS quantitative determination method. According to the clostridium perfringens alpha toxin double-antibody sandwich ELIS quantitative determination method, alpha toxin protein obtained via prokaryotic expression is taken as an immunogen; monoclonal antibodies obtained via hybridoma technique are taken as detection antibodies and capture antibodies; reaction conditions are optimized via experiments; alpha toxin protein samples with a series of concentration are used for construction of a standard curve; the double-antibody sandwich ELIS method is established; and indexes of the double-antibody sandwich ELIS are verified. The clostridium perfringens alpha toxin double-antibody sandwich ELIS quantitative determination method specifically comprises following steps: (1) prokaryotic expression of alpha toxin; (2) preparation of anti-alpha toxin monoclonal antibodies; (3) establishment of the double-antibody sandwich ELIS method; (4) establishment of the standard curve; and (5) performance evaluation on the double-antibody sandwich ELIS method. The clostridium perfringens alpha toxin double-antibody sandwich ELIS quantitative determination method is excellent in specificity, and high in sensitivity and stability, is fast and convenient, and can be used for effective quantitative determination of alpha toxin in A-E type clostridium perfringens cultural supernatants; and the high-efficient detection method is provided for alpha toxin determination.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting cow milk beta-lactoglobulin and sensitizing residues thereof based on colloidal gold probes
ActiveCN106248956AHigh sensitivityShort reaction timeBiological material analysisBiological testingElisa methodSpecific antibody
The invention discloses a method for detecting cow milk beta-lactoglobulin and sensitizing residues thereof based on colloidal gold probes. Beta-lactoglobulin IgE epitope monoclonal antibodies are prepared through a hybridoma technology, with beta-lactoglobulin as the antigen, corresponding polyclonal antibodies are prepared through a conventional technology, and then specific antibodies are prepared through affinity purification; the monoclonal antibodies are covalently immobilized to an ELISA plate to serve as capture antibodies, and a sandwich ELISA method is established with the colloidal gold probes labeled with the biotinylation beta-lactoglobulin polyclonal antibodies as detection antibodies; the light absorption value is detected through an ELIASA, and the allergen beta-lactoglobulin and sensitizing residues thereof in foods are quantitatively detected by establishing a standard curve. The method has the advantages of being easy to implement, high in sensitivity, good in specificity, short in detection time and the like, provides an effective means for rapidly analyzing and detecting related allergens and sensitizing residues thereof in various foods with high sensitivity and high throughout and has good application and popularization prospects.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
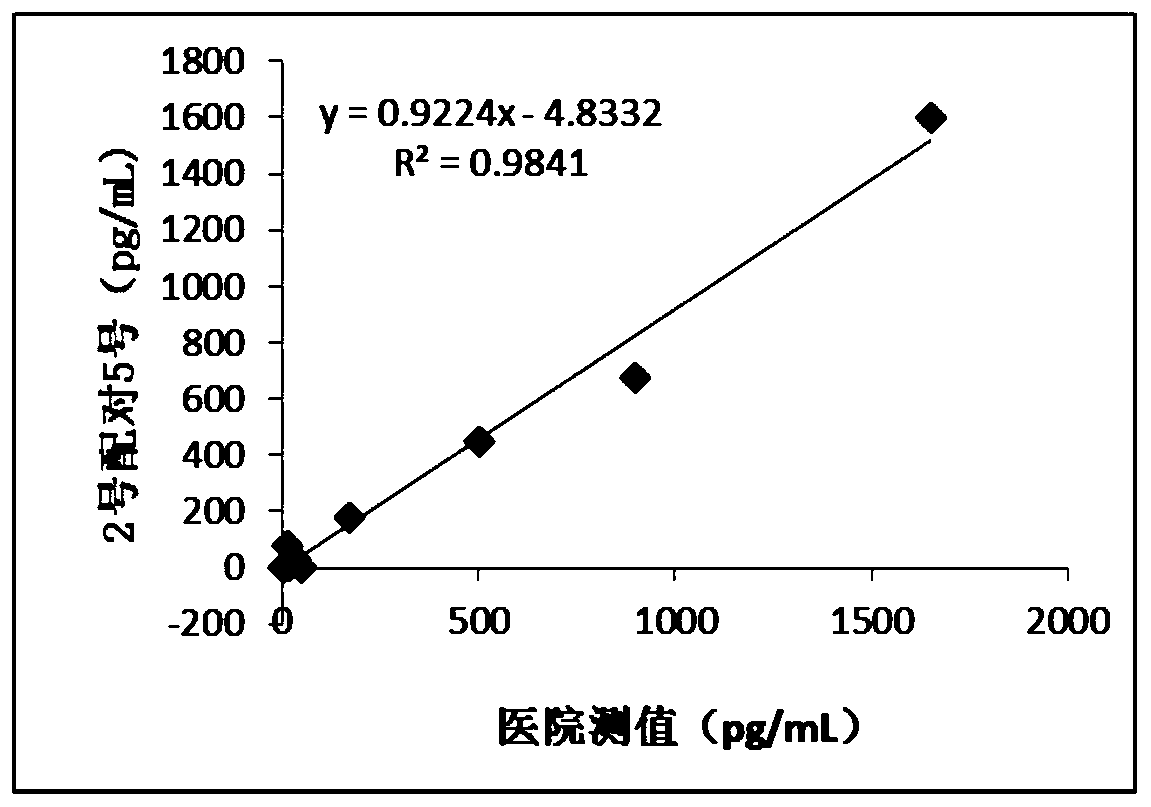
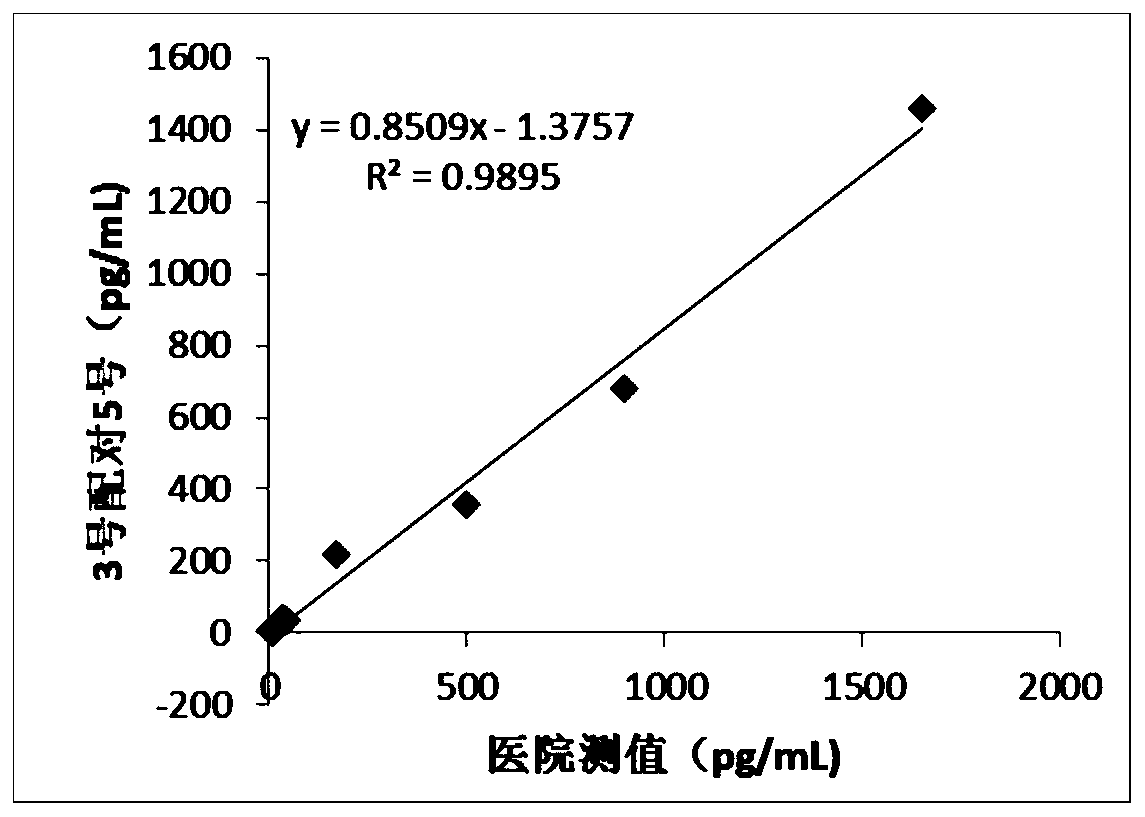
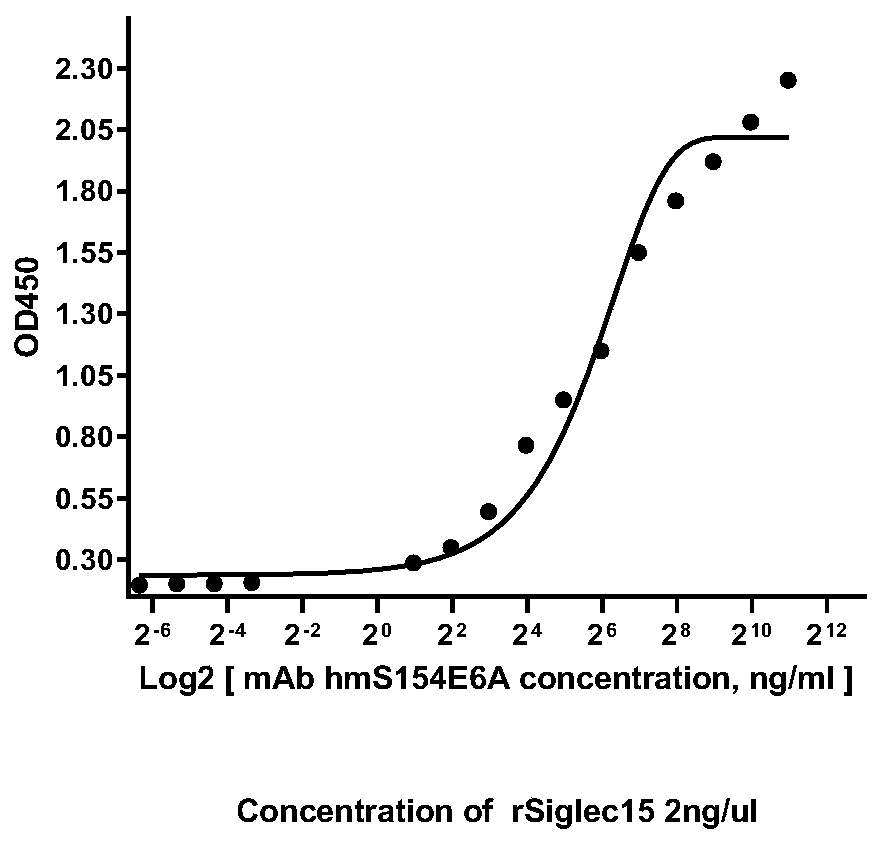
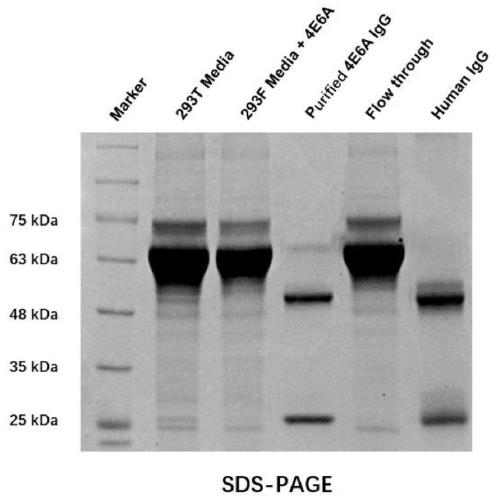
Siglec-15 monoclonal antibody and applications thereof
ActiveCN112159475ADeregulation of the immune systemBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenDisease
The invention relates to a Siglec-15 monoclonal antibody and applications thereof. Through a cell fusion and hybridoma technology, the obtained human Siglec-15 monoclonal antibody can highly and specifically bind to the cells expressing human Siglec-15 antigen; the monoclonal antibody targeting human Siglec-15 is simple in preparation method; and the obtained anti-human Siglec-15 monoclonal antibody can well detect Siglec-15 protein expressed on tumor cells. The monoclonal antibody targeting the Siglec-15 is high in antibody specificity and has good application prospects on treating and / or preventing or diagnosing diseases, such as tumor, related to the Siglec-15.
Owner:NANJING KAEDI BIOTHERAPEUTICS LTD
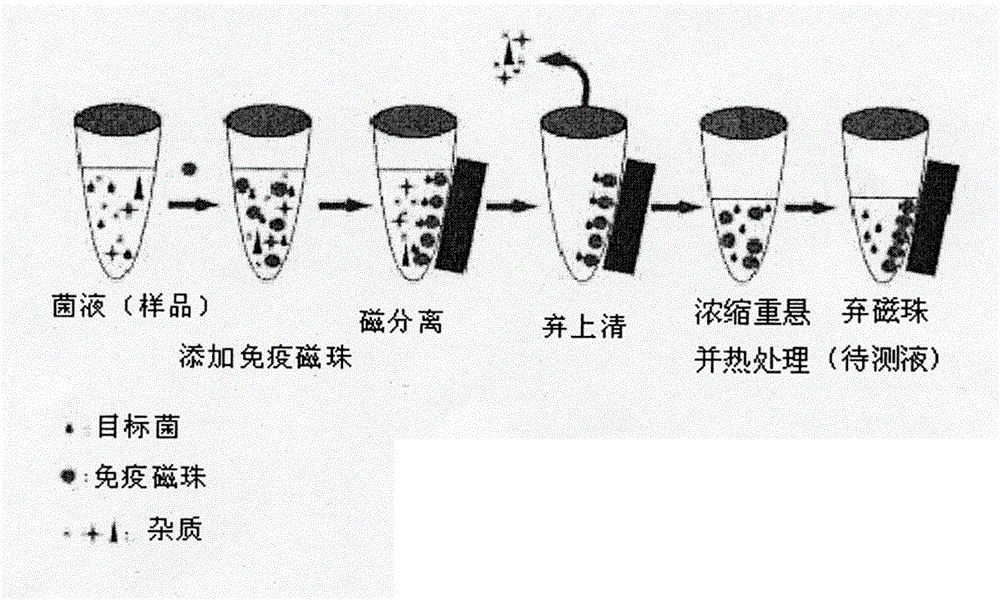
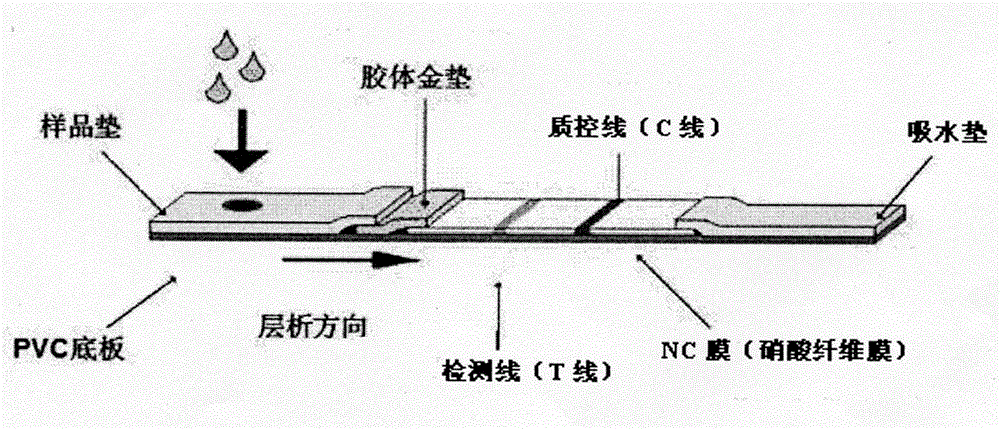
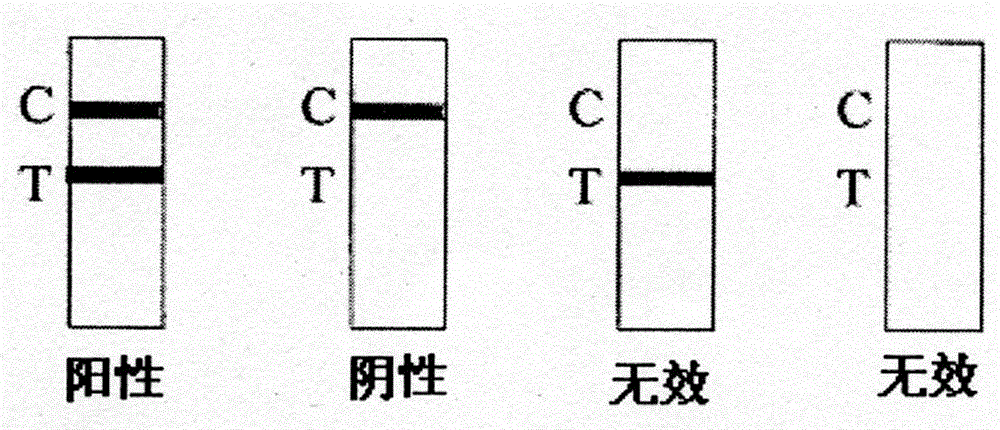
Magnetic immunochromatography for quickly detecting L. monocytogenes and preparation of test strip for detection
InactiveCN102393462AMeet qualitative testing needsTo achieve the purpose of quantitative detectionMaterial analysisMagnetic beadControl line
The invention discloses a magnetic immunochromatography for quickly detecting L. monocytogenes. The method comprises the following steps of: screening a specific reaction rat monoclonal antibody of the obtained L. monocytogenes by using a hybridoma technique, using the specific reaction rat monoclonal antibody as a magnetic bead labeled antibody, and coupling the monoclonal antibody to the surface of a magnetic nanomaterial in a chemical bonding mode to obtain an immunomagnetic bead; constructing a magnetic immunochromatographic test strip by using a sample pad, a magnetic bead labeled conjugate pad, a chromatographic film pre-coated with a detection line T for rabbit antiserum and a control line C for goat anti-mouse (IgG) for the L. monocytogenes, and an absorbent pad; and during detection, judging macroscopic color development belts formed in the detection line T area and the control line C area according to the color of the magnetic nanomaterial on the surface of the immunomagnetic bead, or putting the used test strip on a magnetic signal detector, detecting the detection line T area and the control line C area formed after immunochromatography to obtain quantitative reaction data, so that the L. monocytogenes are quickly qualitatively or quantitatively detected.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Preparing method of heavy metal cadmium monoclonal antibody
InactiveCN101016337AStrong antigenicitySolve technical difficultiesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMaterial analysisAntigenAcetic acid
The invention discloses a making method of heavy-metal cadmium monoclonal antibody in the biological technical domain, which is characterized by the following: detecting residual cadmium in the agricultural product sensitively and rapidly; coupling cadmium ion and carrier protein through 1-(4-isothiocyanic phenyl)-ethanediamine tetraacetate difunctional metal chelant to form complete antigen; obtaining stable Cd-EDTA monoclonal antibody.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Monoclonal antibody for detecting imidacloprid pesticide residue
InactiveCN101880325AHigh analytical capacityLarge analysis capacitySerum albuminMicroorganism based processesBALB/cPesticide residue
The invention relates to an imidacloprid pesticide against monoclonal antibody and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: immunizing a BALB / c mouse by using a coupling substance of immune hapten 1-[6-(2-carboxyethylsulfenyl-3-pyridine) methyl]-N-nitro-2-imidazoline imine and bovine serum albumin, preparing hybrid tumor cells from spleen cells and myeloma cells Sp2 / 0 of the immunized mouse by the hybrid tumor technology, and obtaining hybrid tumor strains 2F11 / A9 capable of stably secreting the imidacloprid pesticide against monoclonal antibody. By effectiveness verification, the antibody can be used for sensitive and quick detection of imidacloprid residues in agricultural production environments and agricultural products. The preparation technique for the imidacloprid pesticide against monoclonal antibody is simple and feasible, does not need special instruments and equipment in the whole preparation process of the antibody, and is easy for scale production in factories.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Hybridoma cell strain 6F9, antibody and application of hybridoma cell strain 6F9
ActiveCN110699327AStrong specificityHigh affinityBiological material analysisMicroorganism based processesAntigenAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly discloses a hybridoma cell strain 6F9, an anti-human CD70 monoclonal antibody generated by the hybridoma cell strain 6F9 and an application of the hybridoma cell strain 6F9. The the hybridoma cell strain 6F9 uses a biologically-active human CD70 recombinant protein as an antigen, and obtains a specific monoclonal antibody capable of binding human CD70 with high affinity at the cell level through hybridoma technology screening. The antibody has potential value in tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BLUE SHIELD PHARM CO LTD
Colon bacillus outer membrane protein monoclonal antibody and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102584992AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENBALB/c
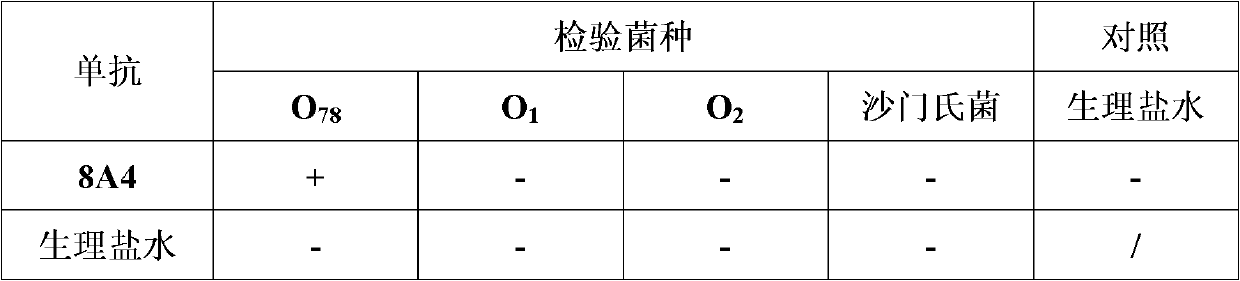
The invention belongs to the technical field of veterinary biology, and particularly relates to a colon bacillus outer membrane protein monoclonal antibody and a preparation method and an application thereof. The antibody is prepared by taking cloned, expressed and purified taking avian pathogenic escherichia coli 78 (APECO78) outer membrane protein as an antigen immune BALB / c mouse with a hybrid tumor technology. The antibody has high specificity and high sensitivity, and an experimental basis is laid for future rapid and specific detection of colon bacillus infection with an immunology method. Meanwhile, as proved by an experiment, the monoclonal antibody disclosed by the invention has high neutralizing activity and protecting efficiency on colon bacillus infection of the same type, and can be used for preventing colibacillosis.
Owner:兆丰华生物科技(南京)有限公司 +1
Rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes through combined nanometer immunomagnetic bead technology-colloidal gold chromatography
The invention provides a method for rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes through combined nanometer immunomagnetic bead technology-colloidal gold chromatography. The method comprises the following steps: labeling a monoclonal antibody 1B12 by using a streptavidin-biotin mediated and coupled nanometer magnetic bead so as to prepare an immunomagnetic bead wherein the monoclonal antibody 1B12 has an accession number of CGMCC No. 10312 and is prepared and screened by using hybridoma technique; labeling another matching monoclonal antibody 3B10 with an accession number of CGMCC No. 10311 by using colloidal gold so as to obtain a labeled antibody, respectively using polyvalent antiserum and goat anti-mouse IgG as a detection line T and a quality control line C and constructing a colloidal gold immunochromatographic test strip from a conjugation pad of the colloidal gold-labeled antibody, a chromatographic membrane of the detection line T and the quality control line C and a water absorption pad; and in detection of a sample, subjecting the immunomagnetic bead and bacteria in the sample to specific capture and enrichment, then pouring an enrichment liquid onto a sample pad of the test strip and judging and reading chromogenic strips visible to naked eyes formed at the detection line T and the quality control line C according to the color of colloidal gold so as to realize rapid semi-quantitative detection of Listeria monocytogenes.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Mold toxin penicillic acid monoclone antibody and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101429250ANo cross reaction rateHigh sensitivityTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsElisa kitCulture expansion
The invention provides a mycotoxin penicillic acid monoclonal antibody and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of coupling penicillic acid to carrier protein respectively so as to obtain complete antigen, immunizing a mouse with the complete antigen, adopting a hybridoma technique and obtaining the monoclonal antibody by cell fusion, screening, cloning, culture expansion and an animal in vivo induction ascites method. The obtained antibody has the titer of 1:2.05x10<5>, is of an IgG1 type, has no cross reaction rate with aflatoxin B1, zearalenone, T-2 toxin and Fumonisins, has the affinity constant of 1.54x10<8> L / mol, and can be used for developing ELISA kits for detecting the penicillic acid.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +1
Anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN112979802AImprove bindingEnsuring biological activity in vivoNervous disorderAntipyreticImmunologic disordersAutoimmune condition
The invention provides an anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody and application thereof. By taking recombinant human IL-33 as an immunogen, a murine anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody is prepared through a hybridoma technique; binding activity analysis is carried out on the murine antibody, blocking activity analysis is carried out on binding of IL-33 and ST2, sequencing is carried out, a human-mouse chimeric anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody is constructed, and kinetic parameters of the chimeric antibody are detected. On the basis of performance analysis of the murine antibody and the chimeric antibody, a humanized anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody is constructed by adopting a CDRs transplantation technology and a complementary determining region (CDR) mutation design, kinetic parameters and affinity of the humanized antibody are detected, and IL33-induced cytokine release is blocked. The anti-human IL-33 monoclonal antibody has relatively high affinity to IL-33, can effectively block binding of IL-33 and a receptor ST2 thereof, inhibits immune response related to an IL-33 / ST2 pathway, and has a good application prospect in treatment of asthma, inflammatory diseases, diabetes and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:MABWELL (SHANGHAI) BIOSCIENCE CO LTD
Antigen, antibody and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit of amantadine
ActiveCN108152499ARetain chemical structureGood potencyColor/spectral properties measurementsTissue sampleCarrier protein
The invention discloses an antigen, an antibody and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit of amantadine. Firstly, an amantadine hapten is prepared, wherein the molecular structural formulaof the amantadine hapten is as shown in formula (I) (The formula is shown in the description.); then, the amantadine hapten is coupled with carrier protein to obtain an artificial antigen; and then, amonoclonal antibody of amantadine is obtained through a hybridoma technique, thereby establishing a competitive ELISA method and kit according to the monoclonal antibody of amantadine. The ELISA kitof amantadine, disclosed by the invention, can be used for detecting the content of amantadine in an animal tissue sample, the detection limit is 0.10mu g / kg, IC50 is 0.79mu g / L, and the linear detection range is 0-16.2mu g / L; and the method is simple, convenient and quick, is low in cost, high in sensitivity and highstrong in specificity, and is suitable for on-site quick detection.
Owner:广东标允生物科技有限公司 +1
Expression of cymbidium mosaic virus coat protein gene and preparation method for antibody of cymbidium mosaic virus coat protein gene
InactiveCN101748136AIncrease contentHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesBALB/cDisease
The invention discloses an expression of cymbidium mosaic virus (Cymbidium Mosaic Virus, CymMV) coat protein gene and a preparation method for antibody of cymbidium mosaic virus coat protein gene. A prokaryotic expression system is used for expressing the coat protein of the cymbidium mosaic virus, and the cymbidium mosaic virus coat protein gene immune rabbit, the BALB / C mouse are used for preparing the polyclonal anti-serum; and the hybridoma technique is used for preparing the monoclonal antibody, and the prepared antibody is used for establishing the immune capture RT-PCR and ELISA method for detecting the high specificity, sensitivity and accuracy of CymMV. The invention provides technical support for the diagnosis of the virus, disease-resistance breeding and cultivation of virus-free seedlings. The expression of cymbidium mosaic virus coat protein gene and the preparation method for its antibody provided by the invention provides material base and technical support for rapid detection and diagnosis of the cymbidium mosaic virus, typing and the study on molecular biology, and lays the foundations for prevention and treatment of cymbidium mosaic virus disease.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Heavy metal copper monoclonal antibody and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101560257AStrong antigenicitySolve technical difficultiesTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsBALB/cCarrier protein
The invention relates to a preparation method of a heavy metal copper monoclonal antibody, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The preparation method is specially used for the preparation of the specifically recognized heavy metal copper monoclonal antibody and the high-sensitivity rapid detection of copper residue in agriculture products and agriculture production environment. Heavy metal copper ions are coupled with a carrier protein by a bifunctional metal chelating agent 1-(4- isothiocyanatobenzo)-ethylenediamine tetracetic acid to form a complete antigen, the complete antigen is used for immunizing a Balb / C mouse, spleen cells and Sp2 / 0 myeloma cells are used for preparing hybridoma cells by the hybridoma technology, so as to obtain the monoclonal antibody with steady secretion of anti-Cu-EDTA. The preparation technology of the antibody is simple and feasible, and the whole preparation process of the antigen does not need any special instrument or equipment, thereby having easy factory-scale production.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
CIAPIN1 monoclone antibody for multidrug resistant differential diagnosis of stomach cancer and method for preparing the same
InactiveCN101492506AImprove the detection rateBacteriaImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBALB/cStomach cancer
The invention relates to a mouse anti-human CIAPIN1 monoclonal antibody for confirming multi-drug resistant gastric cancer, and a preparation method thereof. The invention is characterized in that the monoclonal antibody is obtained by adopting the hybrid tumor technology; the heavy chain is 1gG1; the light chain is k; the molecular weight is 39KD; and the affinity is 3.6x10. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) synthesizing primers; (2) synthesizing single-chain DNA by carrying out reverse transcription on SGC-7901 / VCR general RNA of a human gastric-cancer multi-drug resistant cell; (3) expanding human CIAPIN1 gene cDNA by using the primers F and R and by adopting a PCR method; (4) constructing CIAPIN1 gene induction expression plasmids pET28-CIAPIN1 and pGEX-CIAPIN1; (5) constructing engineering bacteria B21-CIAPIN1 and DE3-CIAPIN1; (6) using the engineering bacteria B21-CIAPIN1 and DE3-CIAPIN1 to carry out prokaryotic expression and purification on CIAPIN1 protein; (7) using CIAPIN1 protein to immunize a 4-week-old Balb / C mouse so that mouse anti-human CIAPIN1 antibody is generated; and (8) using the serum of the immunized mouse to prepare the mouse anti-human CIAPIN1 monoclonal antibody. The invention can better identify multi-drug resistant gastric cancer and non-multi-drug resistant gastric cancer of clinical gastric cancer patients, and predict clinical prognosis of the gastric cancer patients.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
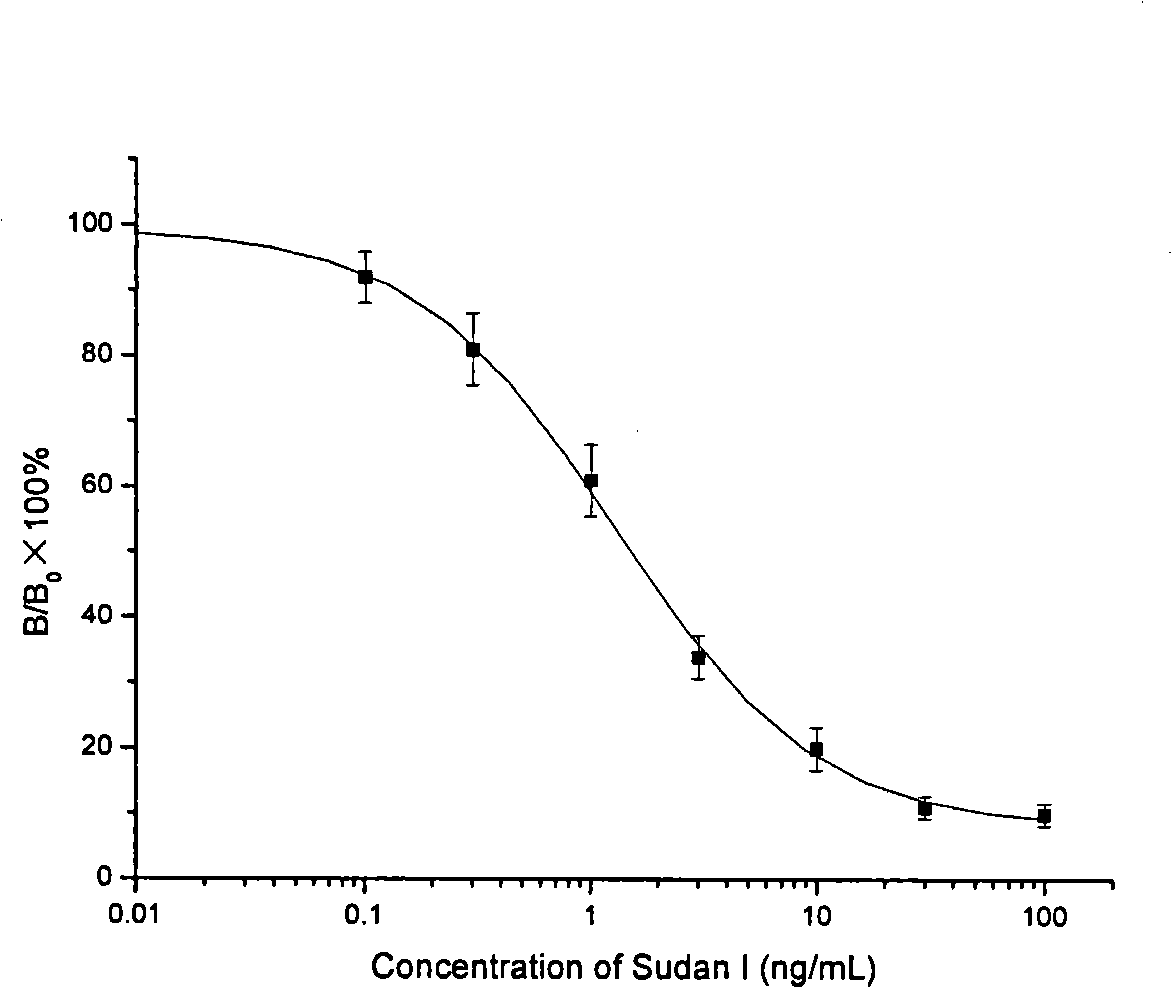
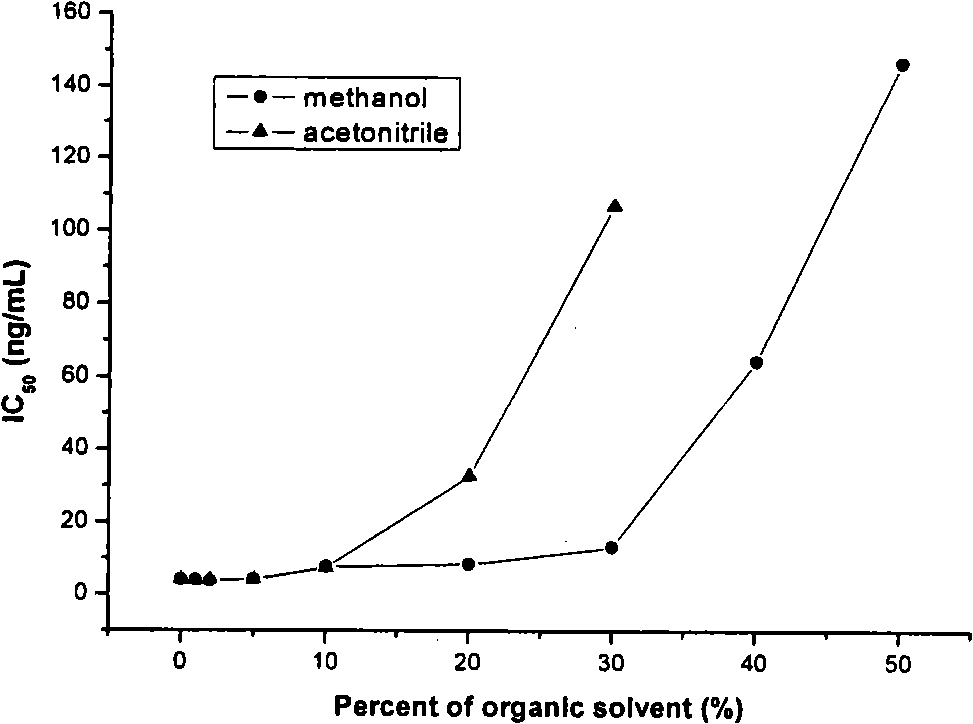
ELISA adsorption analysis method for detecting monoclonal antibodies of sudan red NO.1 in foodstuff
InactiveCN101358978AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMaterial analysisRelative standard deviationMethanol
The present invention discloses a monoclonal antibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent analysis method (ELISA) which is used for determining the content of the Sudan dye 1. The method is characterized in that the modified compound which is used for synthesizing the Sudan dye 1 is coupled with protein to prepare immunogen and coating antigen. The anti-Sudan dye 1 monoclonal antibody is prepared with the hybridoma technology which comprises immunization, fusion, screening and other steps. The antibody is used for immunoassay of the Sudan dye, and the concentration range of the standard curve is 0.1 to 100 ng / mL; the concentration of the IC50 is 1.1 to 2.0ng / mL; the rate of the cross reaction between the antibody and the Sudan dye 2 to 4 is 0.95 to 33.9 percent; the antibody can hardly perform the cross reaction with the other 6 kinds of addable pigments of the food; therefore, the established ELISA not only has high sensitivity but also has high specificity. The 6 kinds of food sold in the market are extracted by methanol after being labeled; the extracted solution can be determined by the ELISA after being appropriately diluted; the recovery of standard addition of the Sudan dye 1 is 88.2 to 110.5 percent; and the relative standard deviation is 1.5 to 17.4 percent. The HPLC and the ELISA are used for analyzing the labeled sample, and the two methods have good relativity (r is equal to 0.9840, and n is equal to 9).
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
IL-6 reorganization monoclonal antibody and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110655576ASolve the problem of low fusion efficiencySolve instability, there is a risk of antibody gene lossBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsTotal rnaPlasma cell
The invention provides a preparation method of an IL-6 reorganization monoclonal antibody. The preparation method comprises the following steps of performing immunization on a mouse with IL-6, after immunization, taking the spleen of the mouse, and preparing an unicellular suspension; screening memory B cells and pulp cells with a flow cytometry instrument; respectively culturing the obtained cells, adding the obtained culture supernatant in a culture device coated with the IL-6, continuing performing culturing, detecting cell strains secreting a specific antibody, and screening the antibody which can specially recognize antigen protein, and performing cloning; extracting total RNA on the obtained cells strains, performing reverse transcription to obtain cDNA, amplifying the variable regions of a heavy chain and a light chain of the antibody, and performing separate connection to a carrier; and then performing cell transfection, and producing the IL-6 reorganization monoclonal antibody. Through screening once, a large quantity of antibody sequences can be obtained, the gene information of the antibodies can be obtained, and the problems that cells in a hybridoma technique is low infusion rate and the antibody gene is lost, are solved.
Owner:CUSABIO TECH LLC
human-mouse chimeric Siglec-15-resistant neutralizing full-molecule IgG and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111378043AMaintain recognition specificityHigh activityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsChimeric antibodyGenetic engineering
The invention discloses human-mouse chimeric Siglec-15-resistant neutralizing full-molecule IgG and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biological pharmacy. Miceimmune to Siglec-15-specific peptide are adopted, a mouse-derived Siglec-15-resistant monoclonal antibody is prepared through a hybridoma technology, and the recombinant human-mouse chimeric Siglec-15-resistant full-molecule IgG is prepared by using a genetic engineering technology and an antibody engineering technology. Specific amino acid segments in the extracellular region of Siglec-15 can berecognized effectively through the chimeric antibody, and combination of Siglec-15 protein with Sialyl-Tn protein is inhibited. The invention discloses the human-mouse chimeric Siglec-15-resistant full-molecule IgG, the human-mouse chimeric Siglec-15-resistant full-molecule IgG includes a light chain variable region and a heavy chain variable region, wherein the amino acid sequence of the light chain variable region is shown in SEQ ID NO. 5, and the amino acid sequence of the heavy chain variable region is shown in SEQ ID NO. 6 or a conservative variant which is obtained through conservative mutation of the amino acid sequence by using addition, deletion, substitution and modification of one or more amino acids. The invention also discloses a DNA molecule, expression vector, host cells andapplication of the full-molecule IgG antibody.
Owner:SHENZHEN INNOVATION CENT OF SMALL MOLECULE DRUG DISCOVERY CO LTD
Immune detection method for residual aryl-N-methyl carbamate pesticide
InactiveCN101314618AImprove practicalityLarge analysis capacityImmunoglobulinsMaterial analysisBALB/cMethyl carbamate
The invention relates to a method for detecting the residual immunity of an aryl-N-methylcarbamates pesticide, and belongs to the biotechnology field. The method includes the steps as follows: a carrier protein is coupled with a general hapten (HA) of the aryl-N-methylcarbamates pesticide to obtain a complete antigen; by applying the hybridoma technique, the antigen immunized Balb / C mice are screened by adopting the ELISA method and subcloned by adopting the limiting dilution method to obtain the hybridoma cell strains capable of stably secreting the aryl-N-methylcarbamates pesticide; and monoclonal antibodies are prepared. Based on the monoclonal antibodies, four ELISA detection methods for detecting the residual immunity of the aryl-N-methylcarbamates pesticide are established. The method has high specificity, sensitivity and stability, and provides a quick, sensitive and specific technology for trace-detecting the aryl-N-methylcarbamates pesticides.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Anti-human marrow mesenchymal stem cell monoclonal antibody ZUE12 and use
The present invention provides a kind of anti-human marrow mesenchymal stem cell monoclonal antibody ZUE12. By using human marrow mesenchymal stem cell as antigen and applying hybrid tumor technology, the present invention prepares monoclonal antibody resisting human mesenchymal stem cell a establishes method of detecting mesenchymal stem cell with the monoclonal antibody as probe and through flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescent staining and imunoblotting. The present invention provides effective means for the research of mesenchymal stem cell specificity and platform for further description of the biological characteristic of mesenchymal stem cell, and may be applied in various detection technology and clinical research.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com