Use of genomic signatures to predict responsiveness of patients with prostate cancer to post-operative radiation therapy
A technology for radiation therapy, prostate cancer, applied in the direction of genomics, measurement devices, biological tests, etc., can solve problems such as different responses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0250] Example 1: Development of a Gene Signature to Predict Postoperative Radiation Therapy Response in Prostate Cancer Patients.
[0251] DNA damage repair (DDR) genes and pathways are significantly associated with increased risk of metastatic progression (Evans et al., Patient-Level DNA Damage and Repair Pathway Profiles and Prognosis After Prostateectomy for High-Risk Prostate, JAMA Oncol. 2016 Jan 7:1-10 ). To assess the use of DDR genes in radiation response signatures in prostate cancer patients before prostatectomy. A compilation of 1,800 genes from Gene Ontology (GO) and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)—which are associated with DNA damage and radiation responses and the human exome array platform—was collected to identify the most likely predictors of response to radiation therapy (RT) subset of responsive genes.
[0252] To develop a postoperative radiation therapy response signature, patients treated and untreated with RT within one year were matched 1:1 in the ...
Embodiment 2
[0257] Example 2: PORTOS predicts response to radiation therapy in prostate cancer patients.
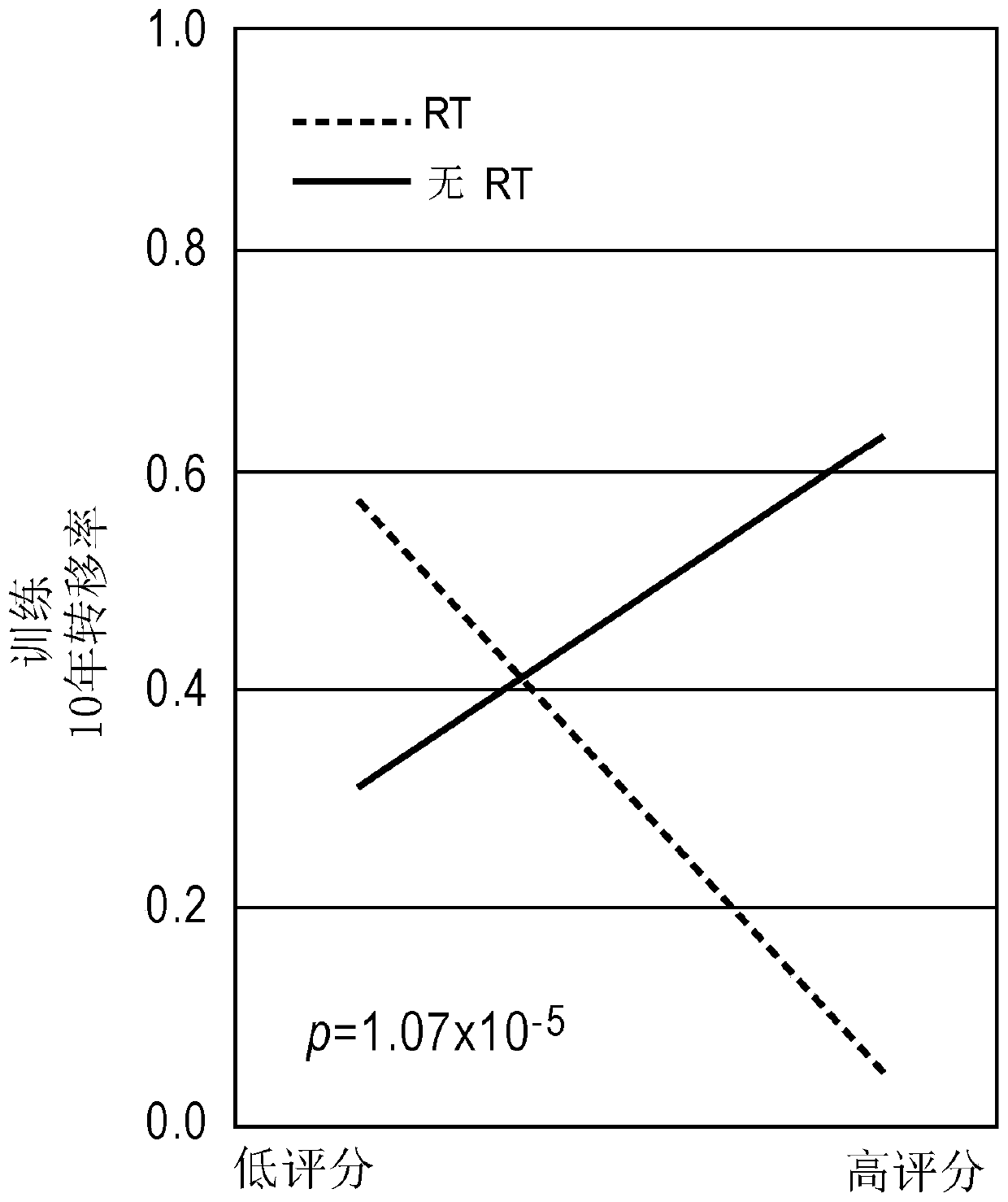
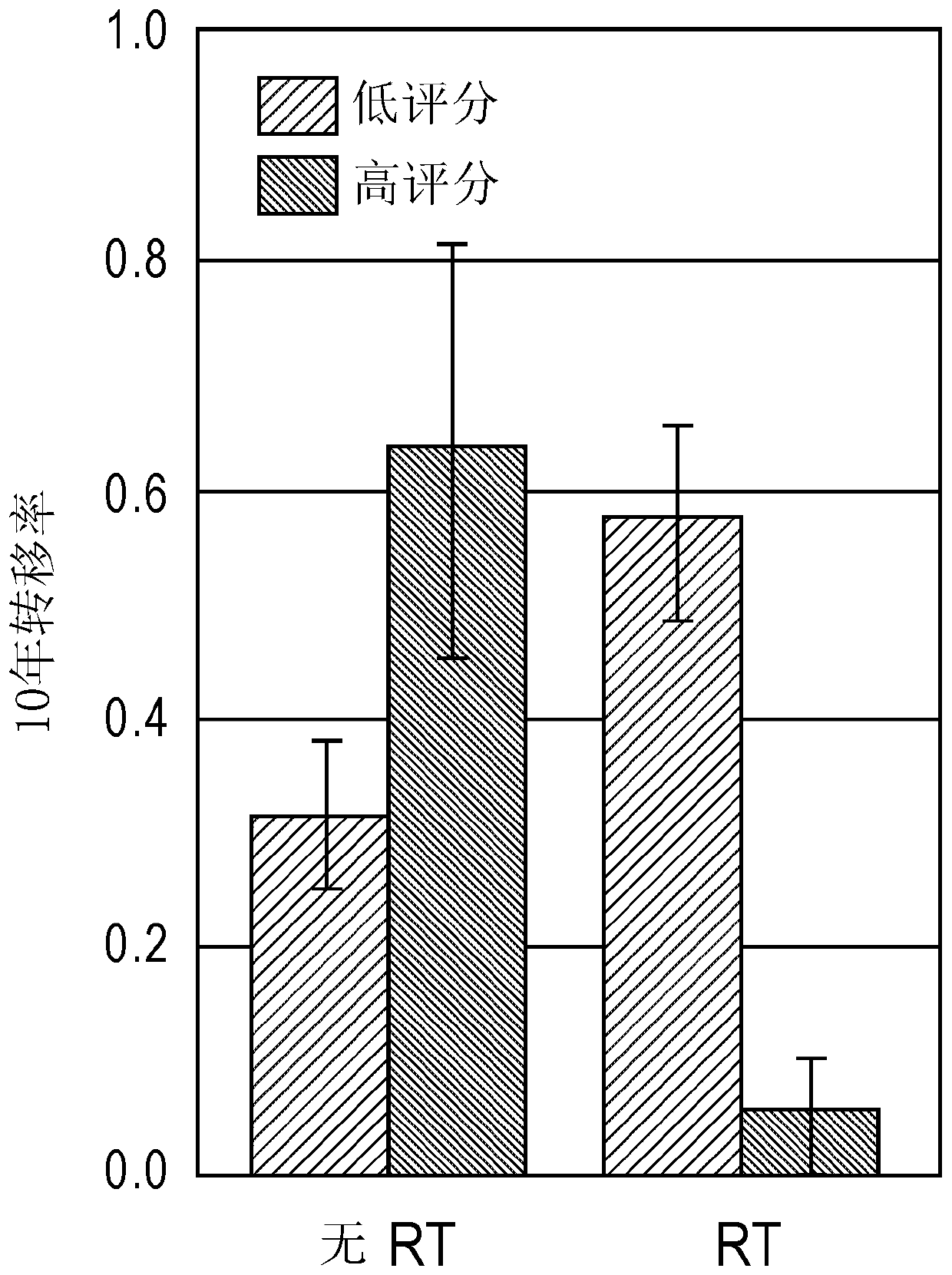
[0258] In the matched training cohort, PORTOS was able to predict response to radiotherapy (RT), as evidenced by a significant interaction term (p Figure 1A ). Among patients with high scores (PORTOS>0), treated patients had better outcomes than untreated patients, with a 10-year metastatic rate of 5% in RT-treated patients and 63% in untreated patients (p Figure 1B with 2A ), while among patients with low scores (PORTOS Figure 1B with 2B ). These results indicate that PORTOS of the present invention can be used to predict the benefit of postoperative RT in patients with prostate cancer. These results also indicate that the methods of the present invention are useful in the treatment of prostate cancer. These results further demonstrate that the methods of the present invention can be used to predict response to postoperative radiation therapy and treat prostate cancer in subjec...
Embodiment 3
[0259] Example 3: PORTOS predicts response to radiation therapy in independent validation of the model
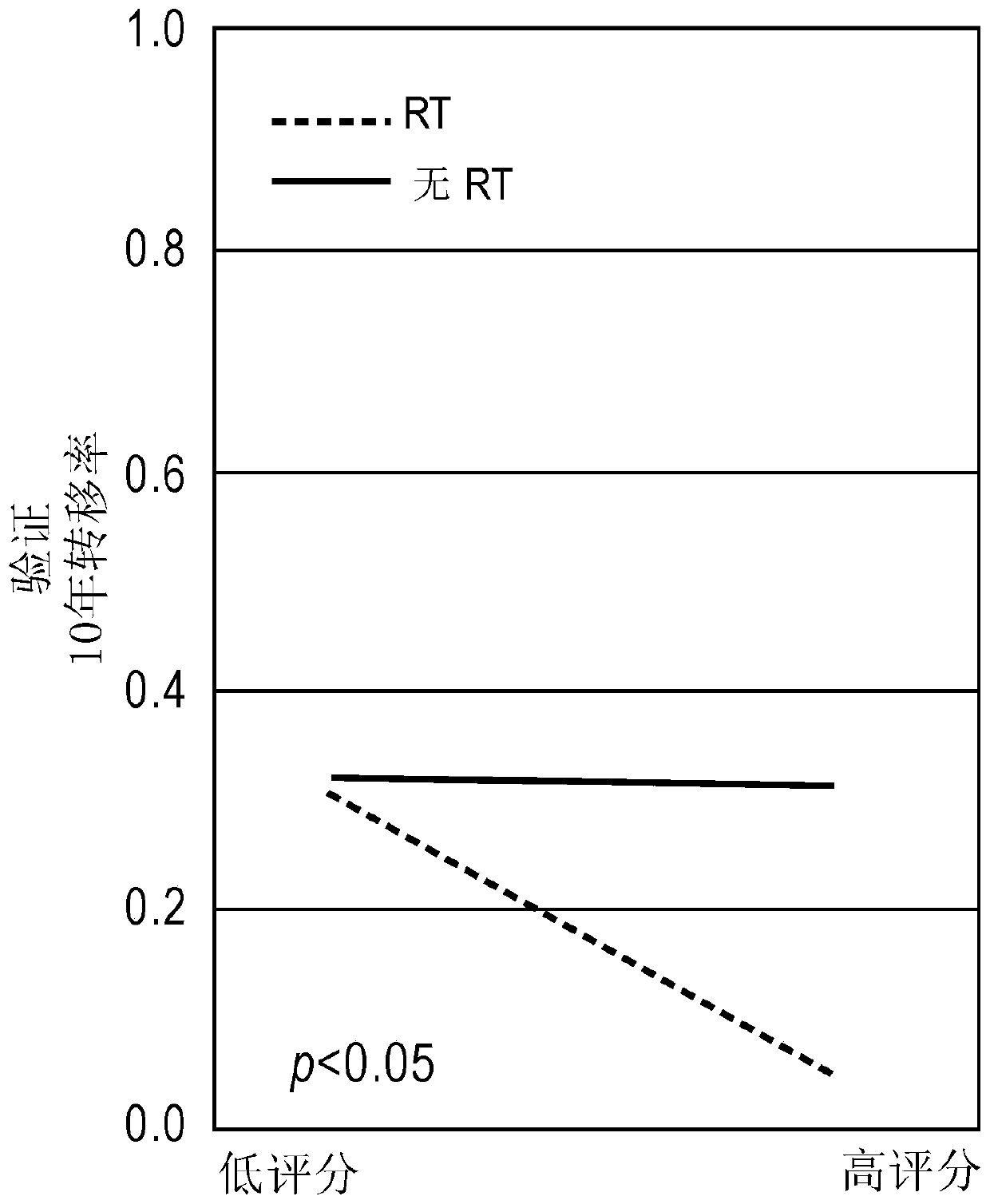
[0260] To validate the model independently, matched treated and untreated radiotherapy (RT) patient cohorts were designed using pooled cohorts from four clinical sites (MCII, THU, TJU, and DVA). These results were confirmed in independently matched validation cohorts with significant interaction terms (p Figure 1C ). Within the high PORTOS group, RT-treated patients had better outcomes than untreated patients (p=0.01, HR=0.19 [0.048-0.78], Figure 2C ), with a 10-year metastatic rate of 4% in RT-treated patients and 31% in untreated patients ( Figure 1D ). In the low PORTOS group, untreated patients had similar outcomes to treated patients (p=0.77, HR=0.92 [0.56-1.5], Figure 2D ), where the 10-year metastatic rate was 31% in RT-treated patients and 32% in untreated patients ( Figure 1D ).
[0261] These results provide further evidence that patients with high scores...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com