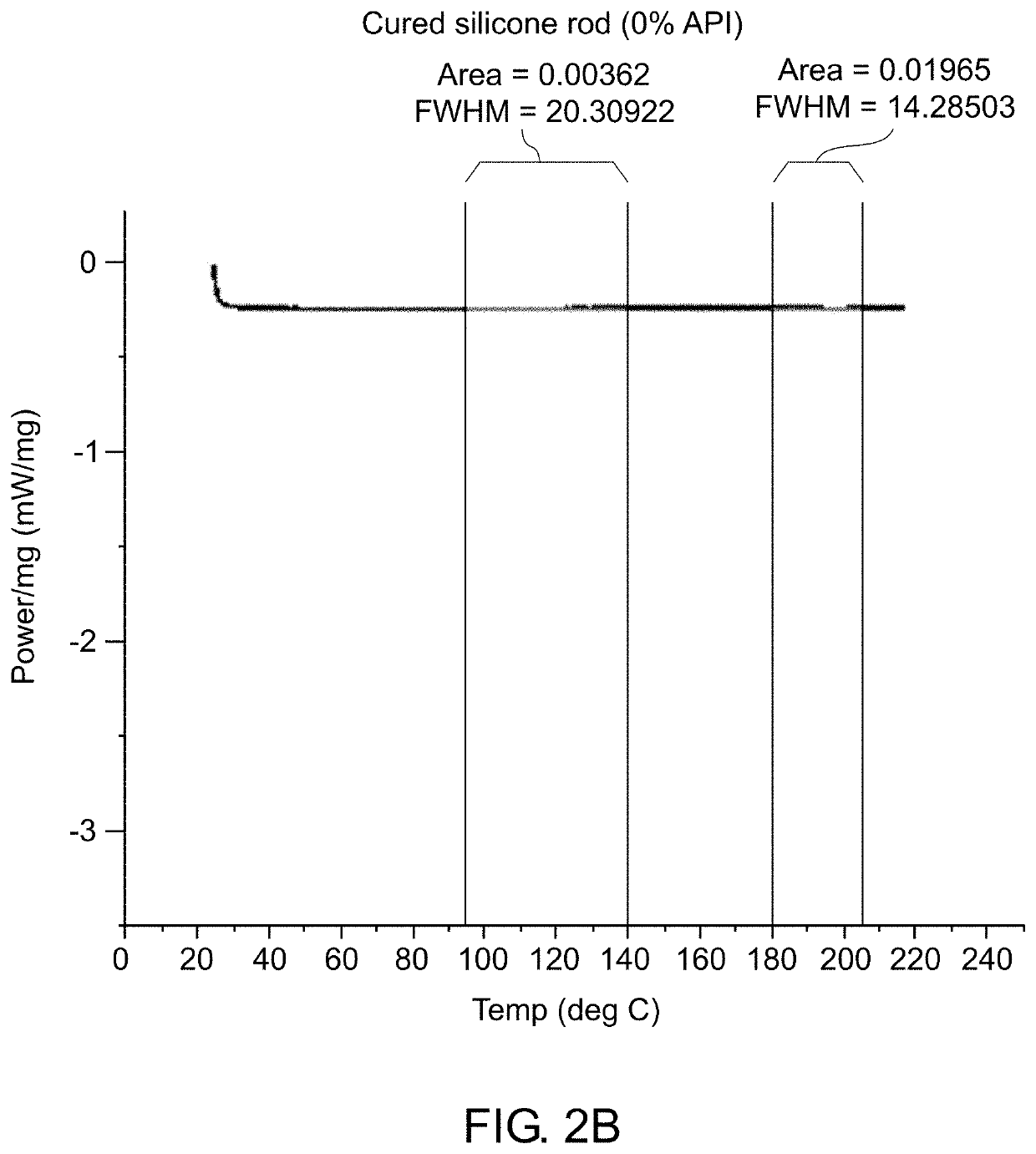
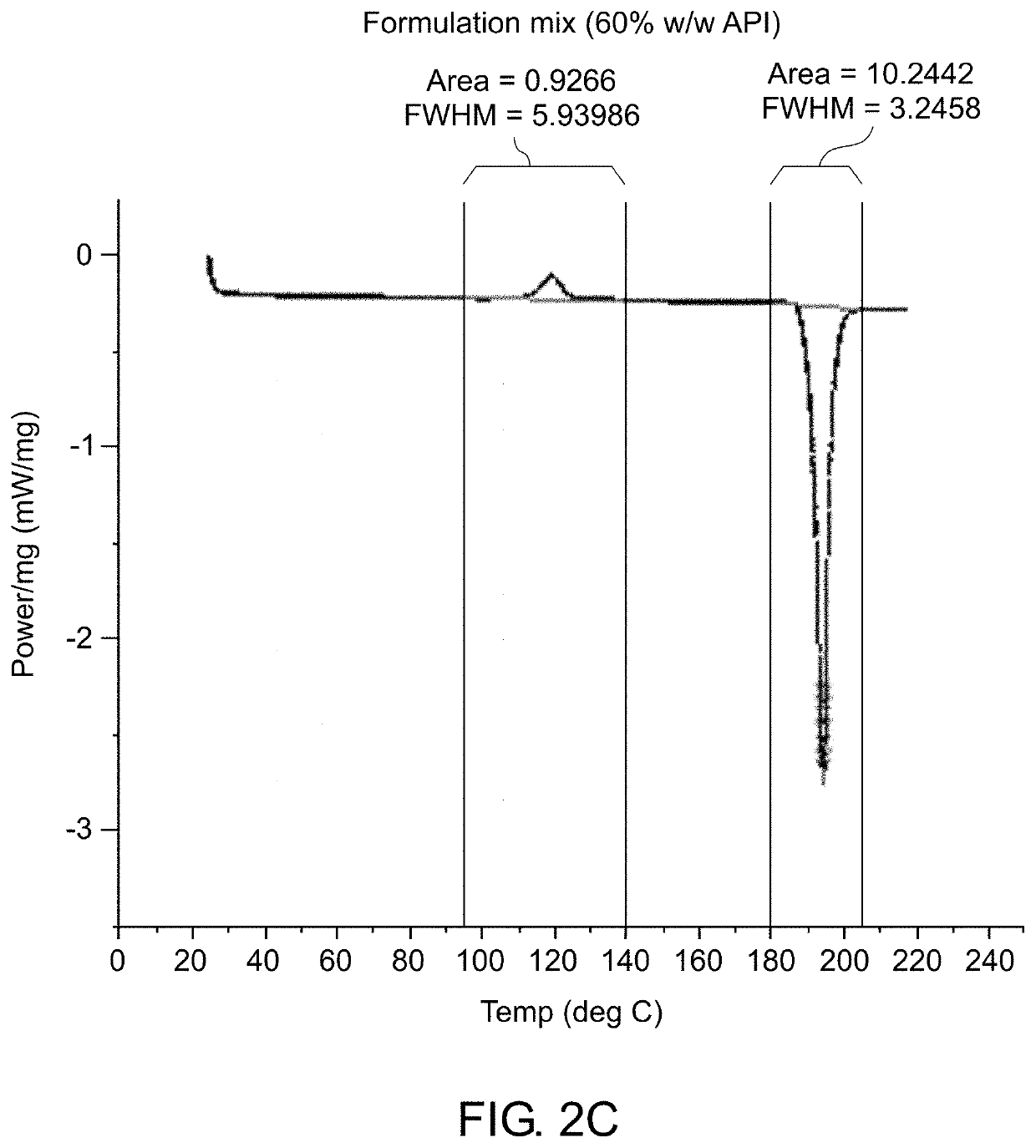
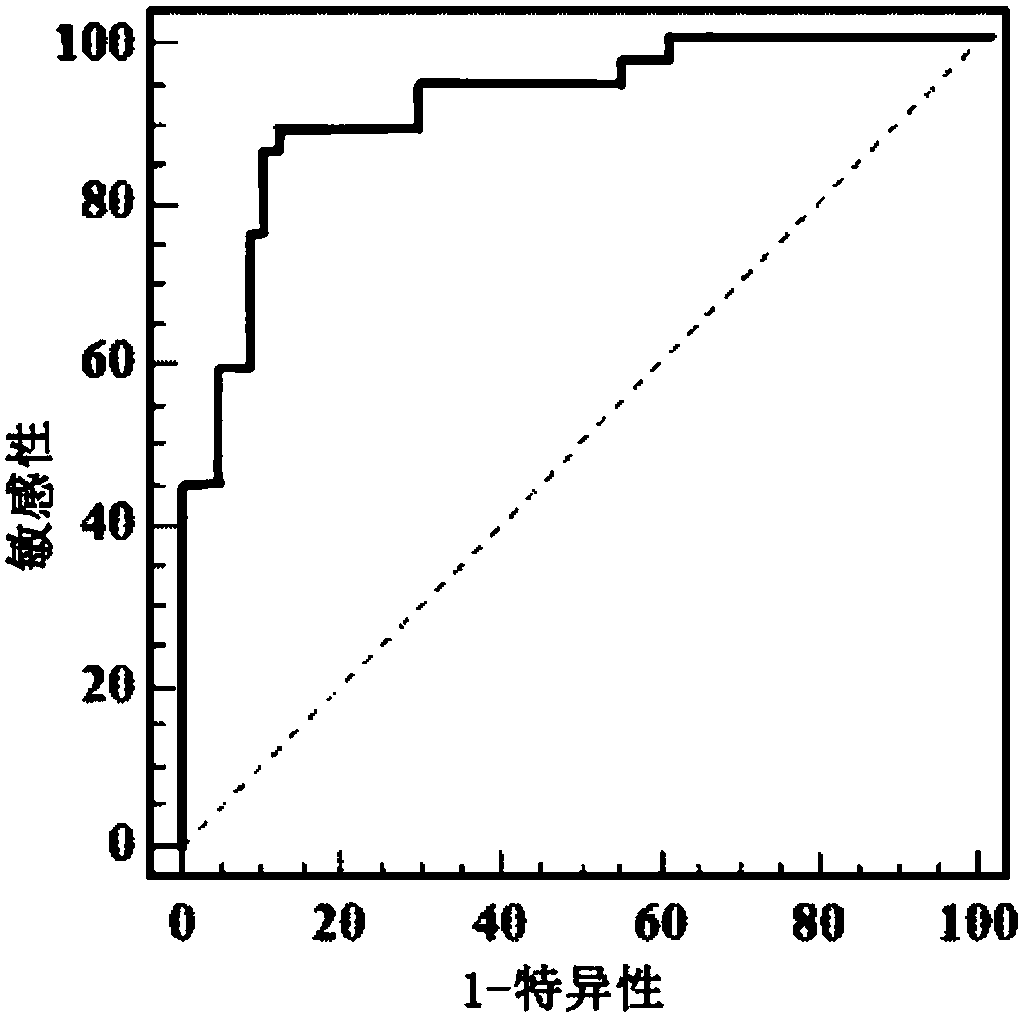
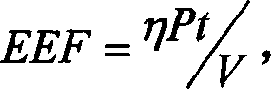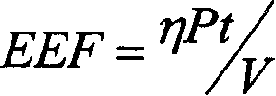Patents
Literature
56 results about "Pre-Therapy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Occurring before therapy.
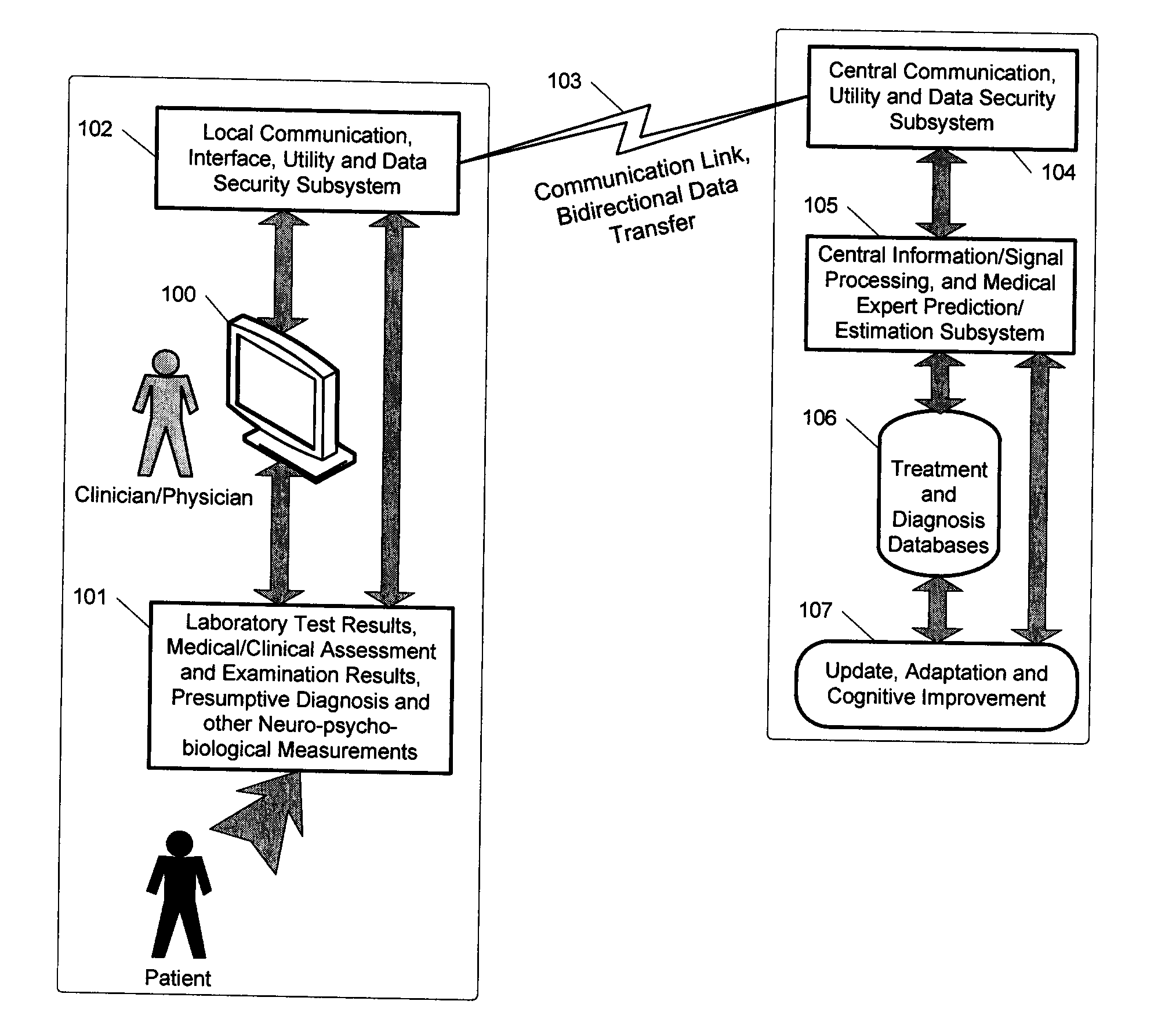
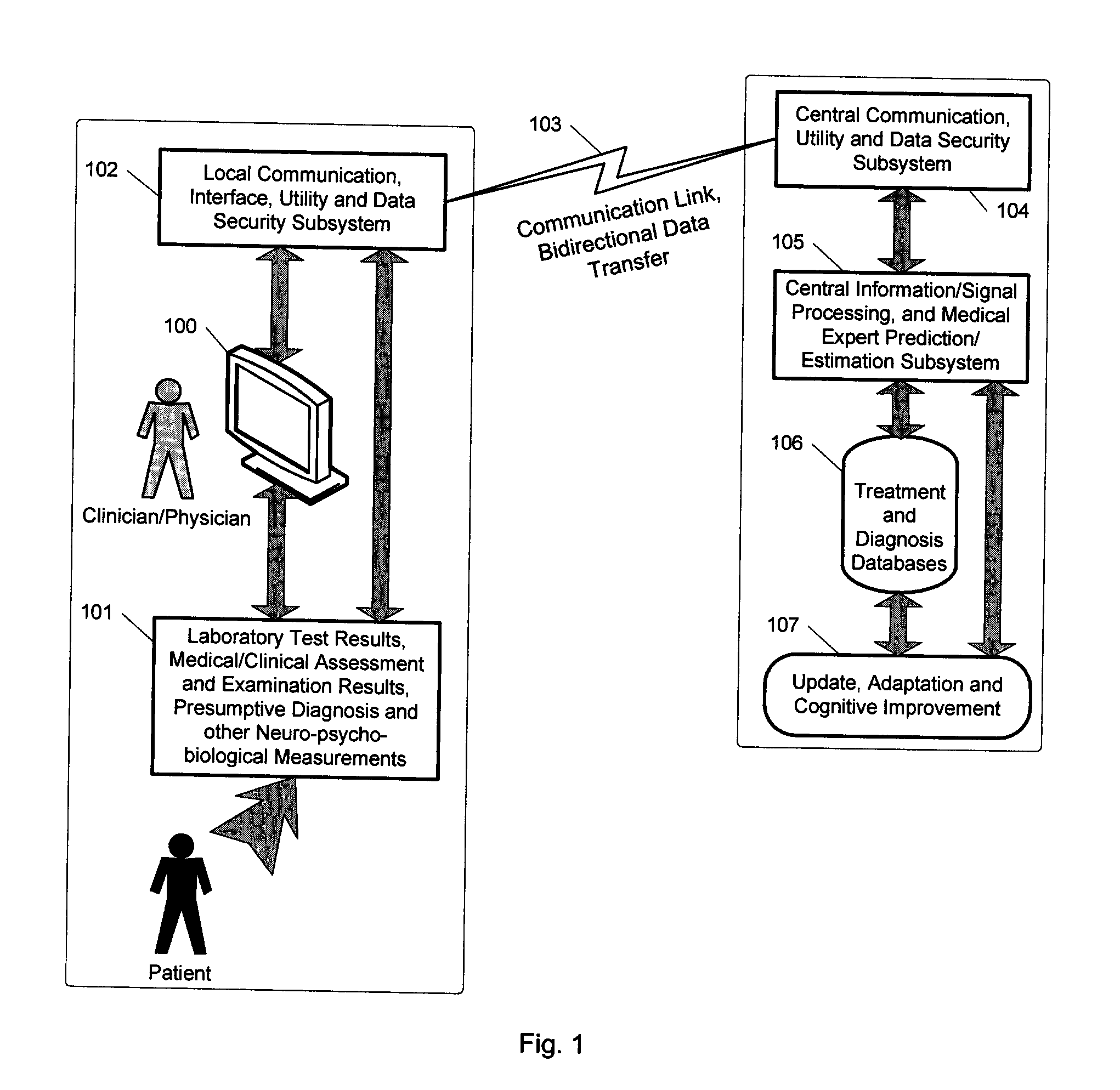
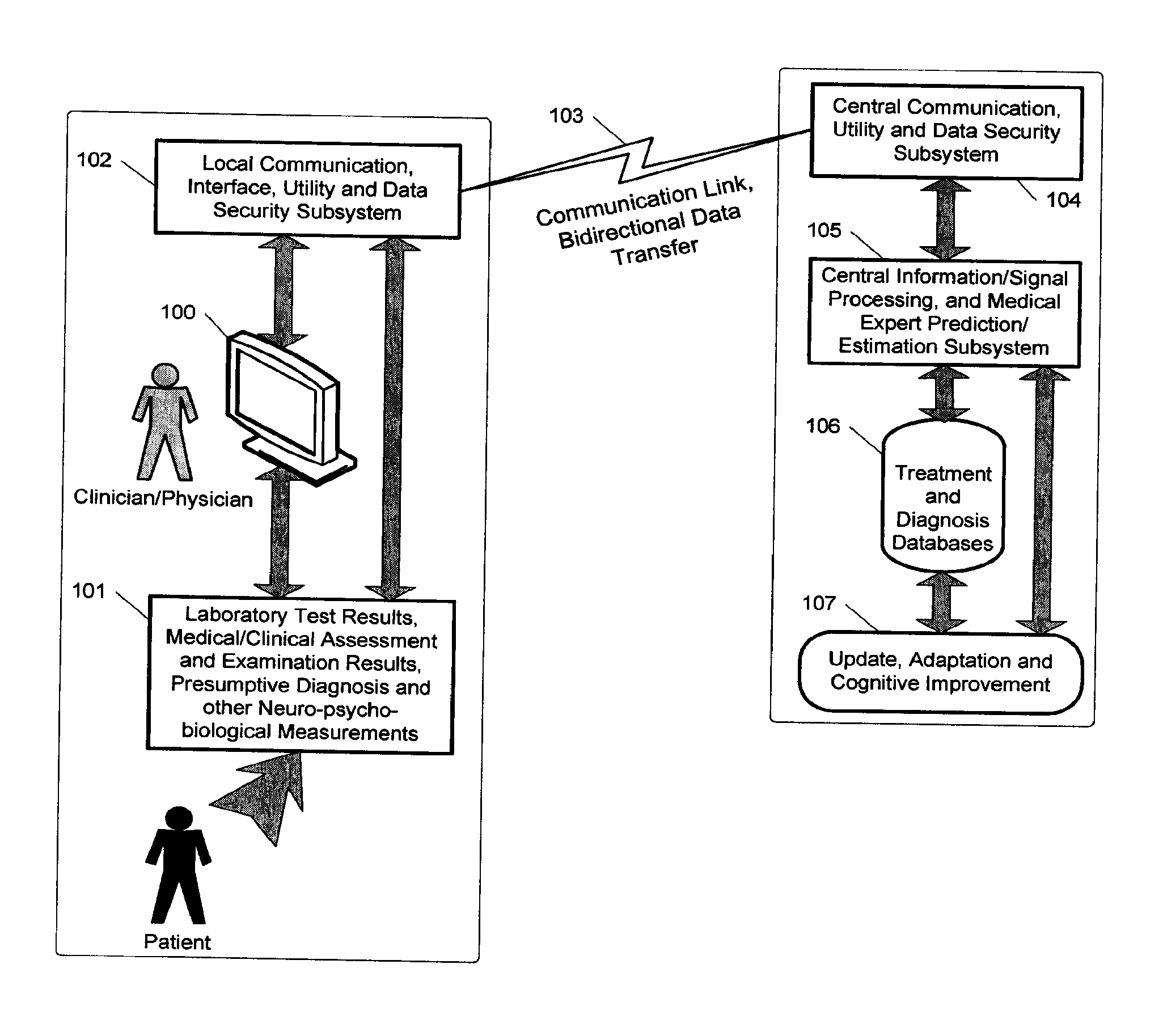
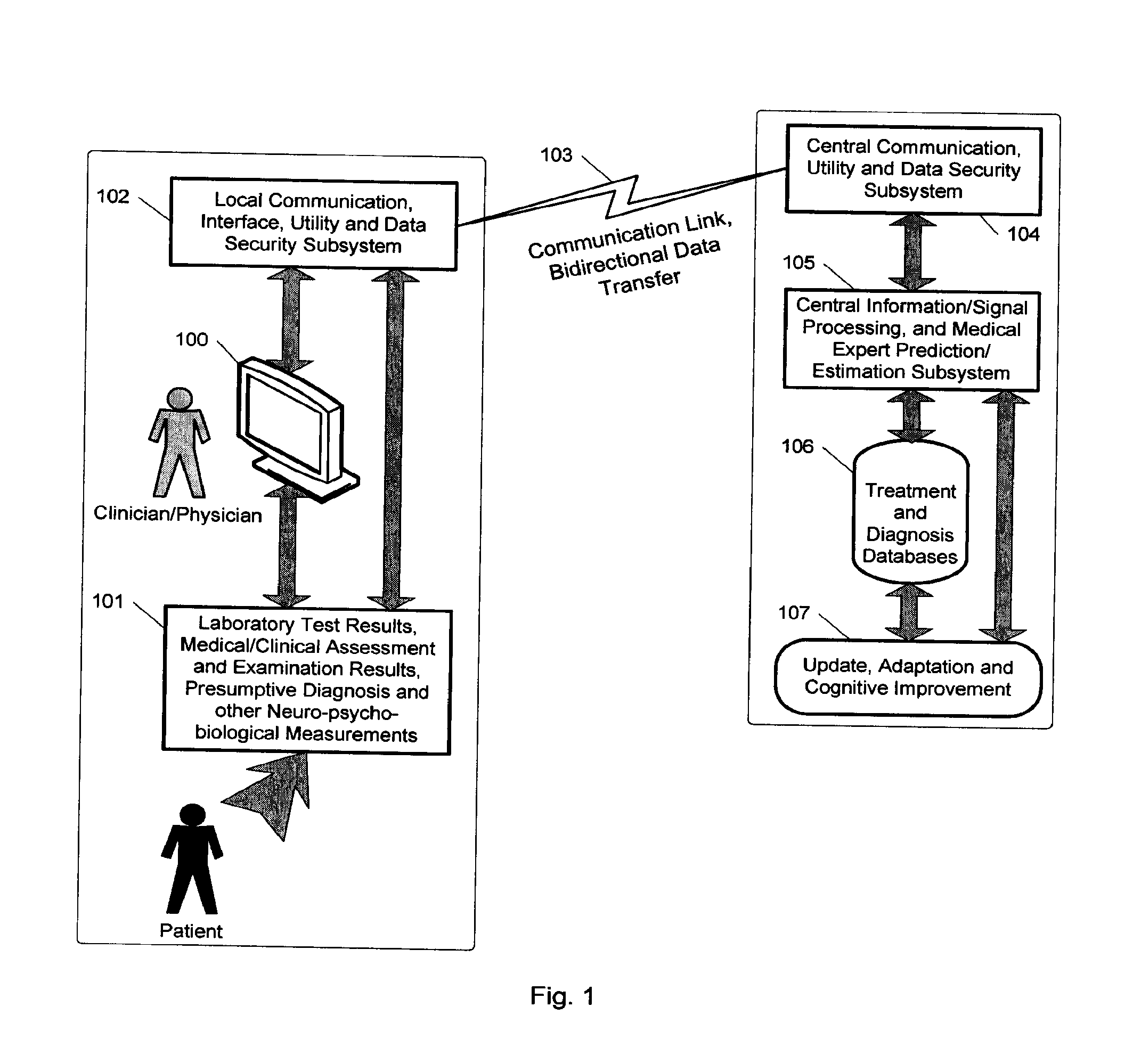
Expert system for determining patient treatment response
ActiveUS20110119212A1Error minimizationMinimize complexityElectroencephalographyMedical data miningDiseaseInformation processing
A medical digital expert system to predict a patient's response to a variety of treatments (using pre-treatment information) is described. The system utilizes data fusion, advanced signal / information processing and machine learning / inference methodologies and technologies to integrate and explore diverse sets of attributes, parameters and information that are available to select the optimal treatment choice for an individual or for a subset of individuals suffering from any illness or disease including psychiatric, mental or neurological disorders and illnesses. The methodology and system can also be used to determine or confirm medical diagnosis, estimate the level, index, severity or critical medical parameters of the illness or condition, or provide a list of likely diagnoses for an individual suffering / experiencing any illness, disorder or condition.
Owner:DIGITAL MEDICAL EXPERTS
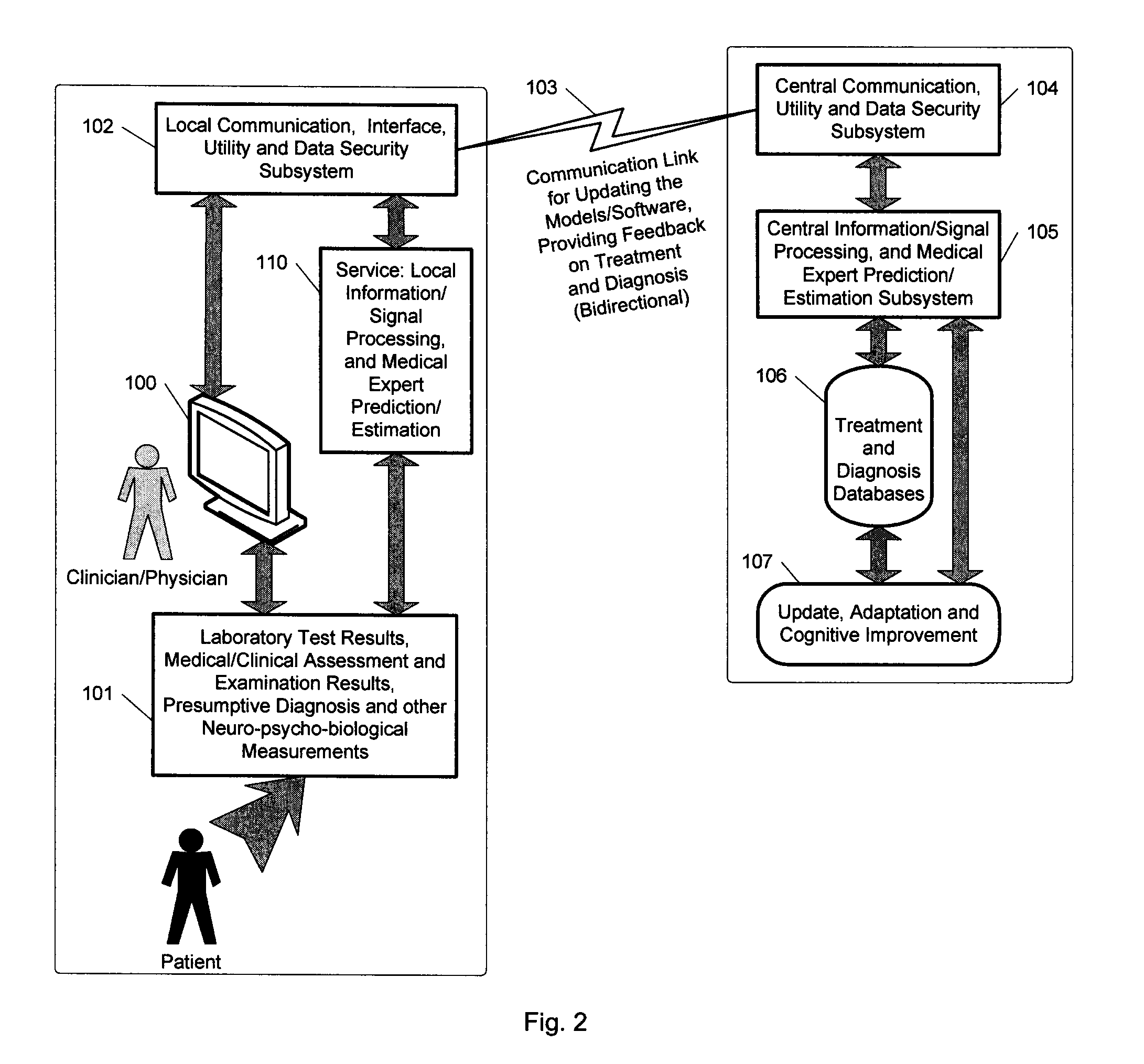
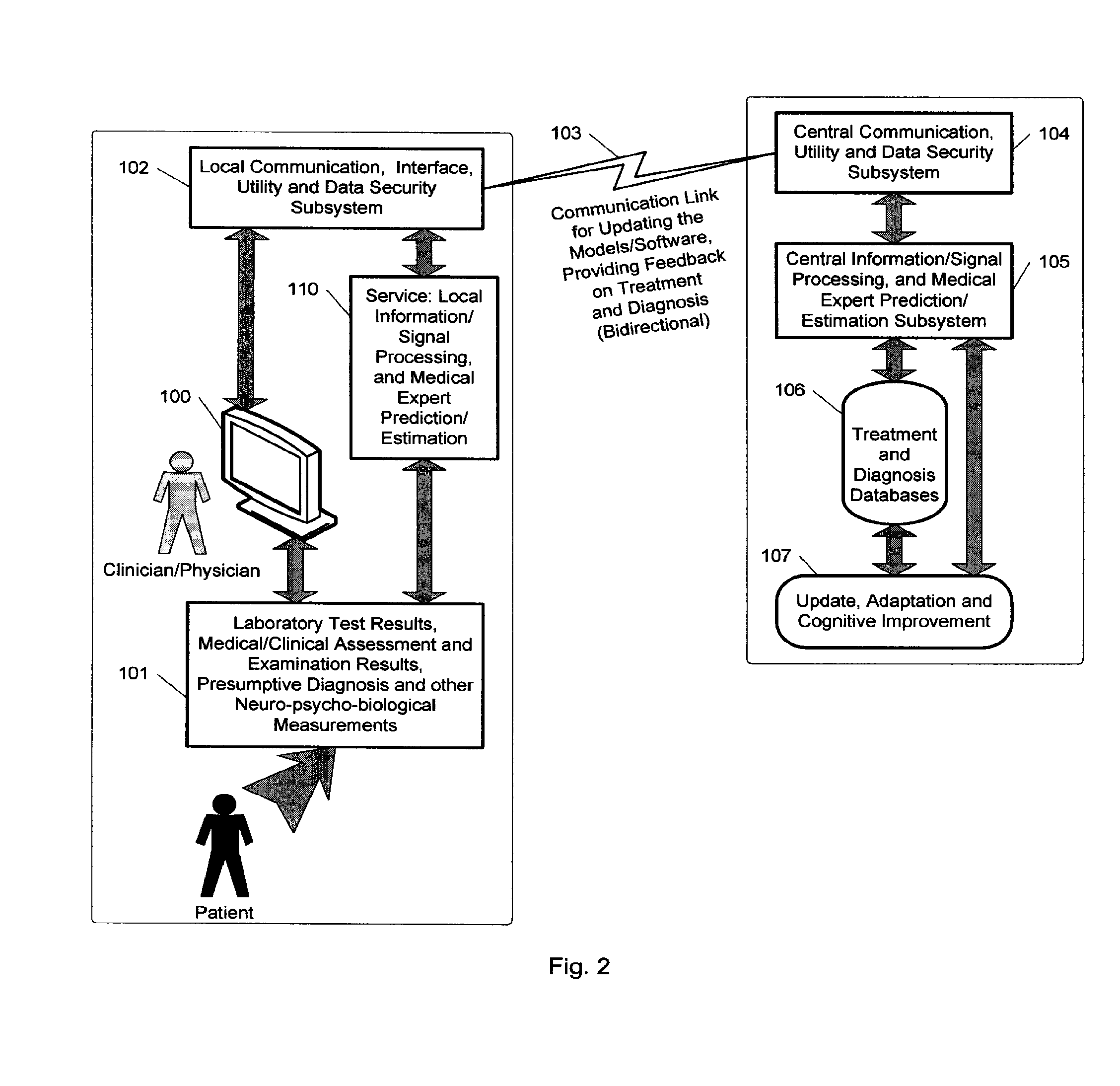
Expert system for determining patient treatment response
ActiveUS20140279746A1Improve performanceMinimize complexityMedical data miningHealth-index calculationDiseaseInformation processing
A medical digital expert system to predict a patient's response to a variety of treatments (using pre-treatment information) is described. The system utilizes data fusion, advanced signal / information processing and machine learning / inference methodologies and technologies to integrate and explore diverse sets of attributes, parameters and information that are available to select the optimal treatment choice for an individual or for a subset of individuals suffering from any illness or disease including psychiatric, mental or neurological disorders and illnesses. The methodology and system can also be used to determine or confirm medical diagnosis, estimate the level, index, severity or critical medical parameters of the illness or condition, or provide a list of likely diagnoses for an individual suffering / experiencing any illness, disorder or condition.
Owner:DIGITAL MEDICAL EXPERTS
System and method for ablating a tissue site by electroporation with real-time monitoring of treatment progress
InactiveUS20190175248A1Reduce deliveryRaise the possibilitySurgical needlesComputer-aided planning/modellingTreatments proceduresExAblate
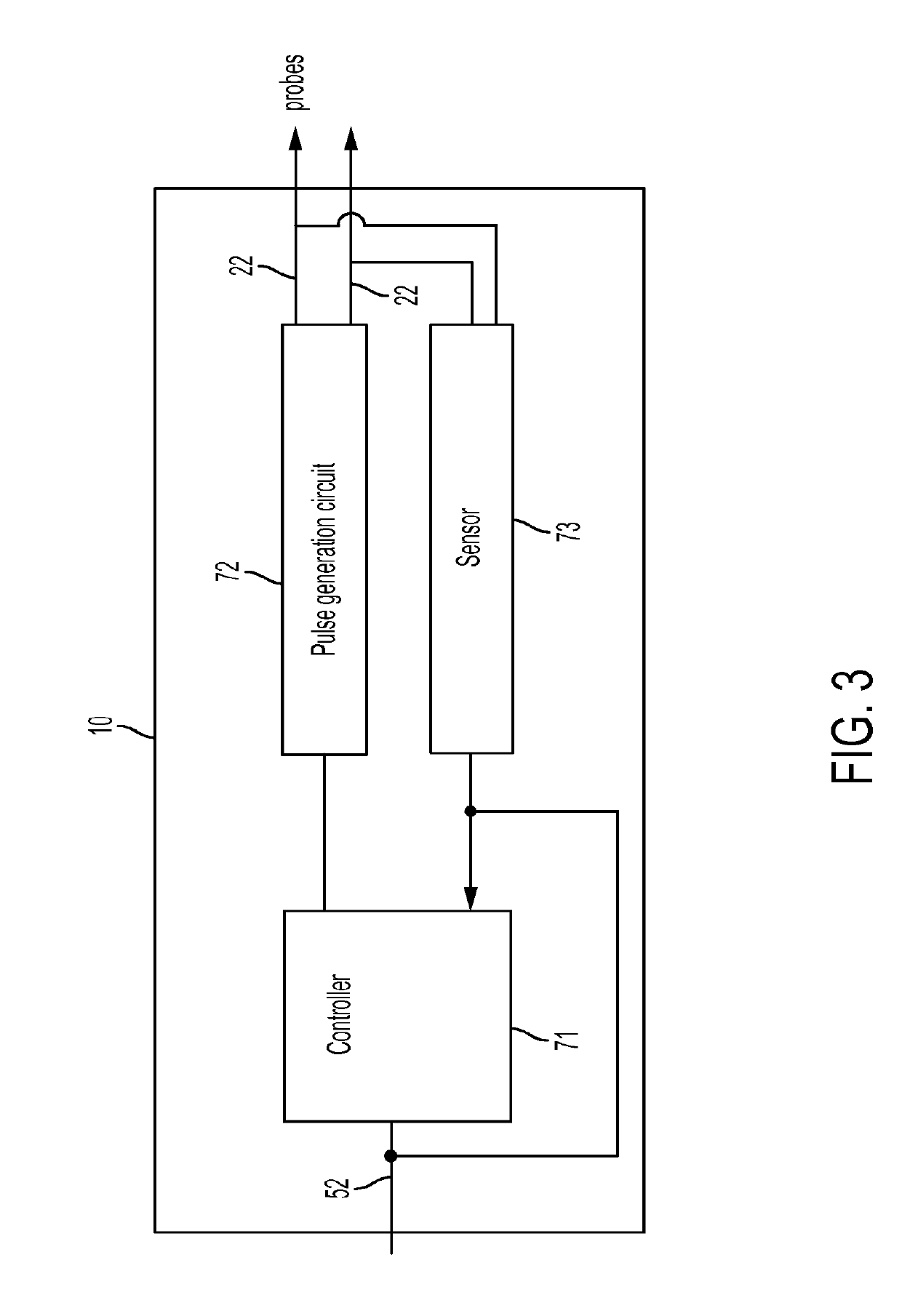
A medical system for ablating a tissue site with real-time monitoring during an electroporation treatment procedure. A pulse generator generates a pre-treatment (PT) test signal prior to the treatment procedure and intra-treatment (IT) test signals during the treatment procedure. A treatment control module determines impedance values from the PT test signal and IT test signals and determines a progress of electroporation and an end point of treatment in real-time based on the determined impedance values while the treatment progresses.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
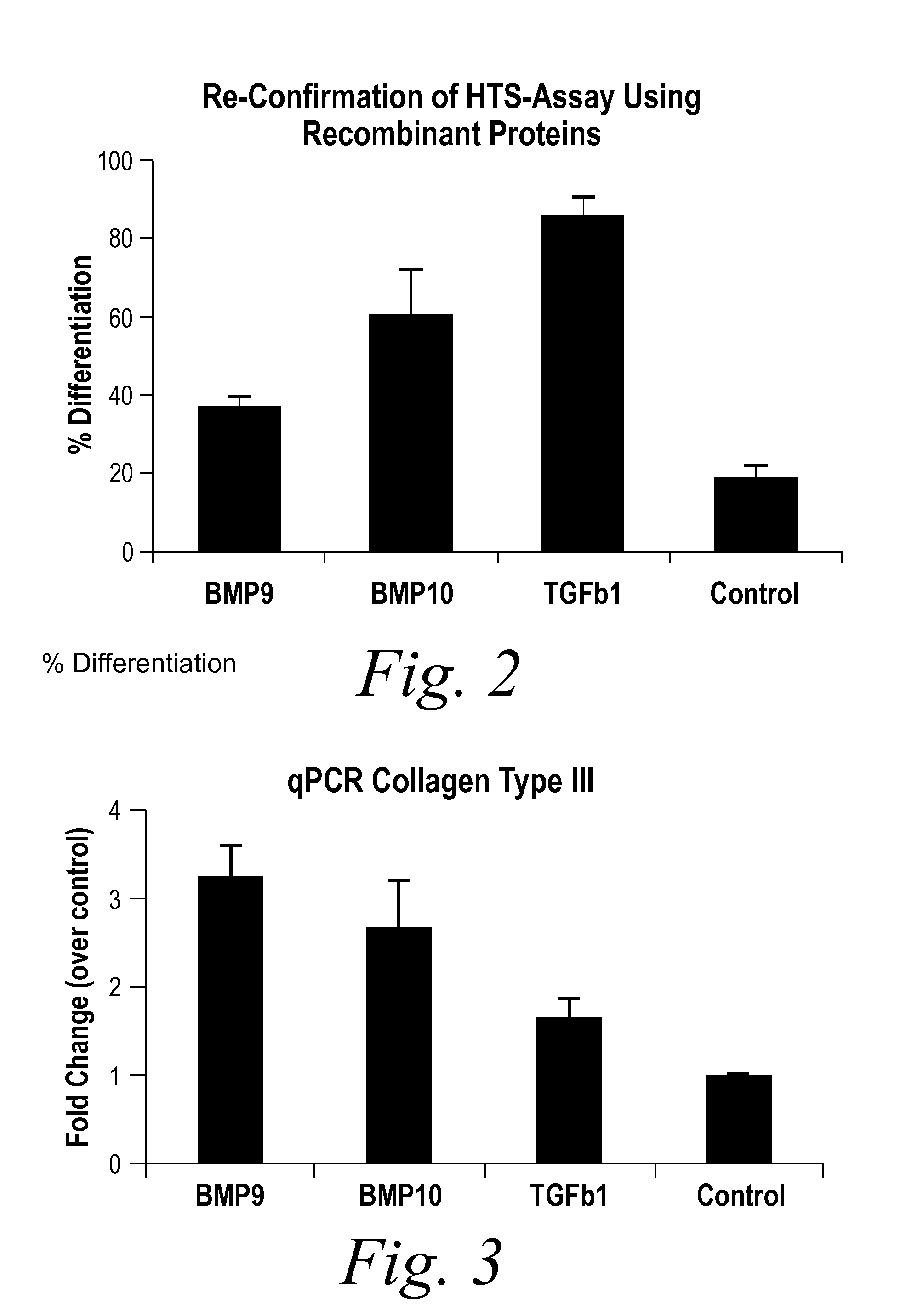
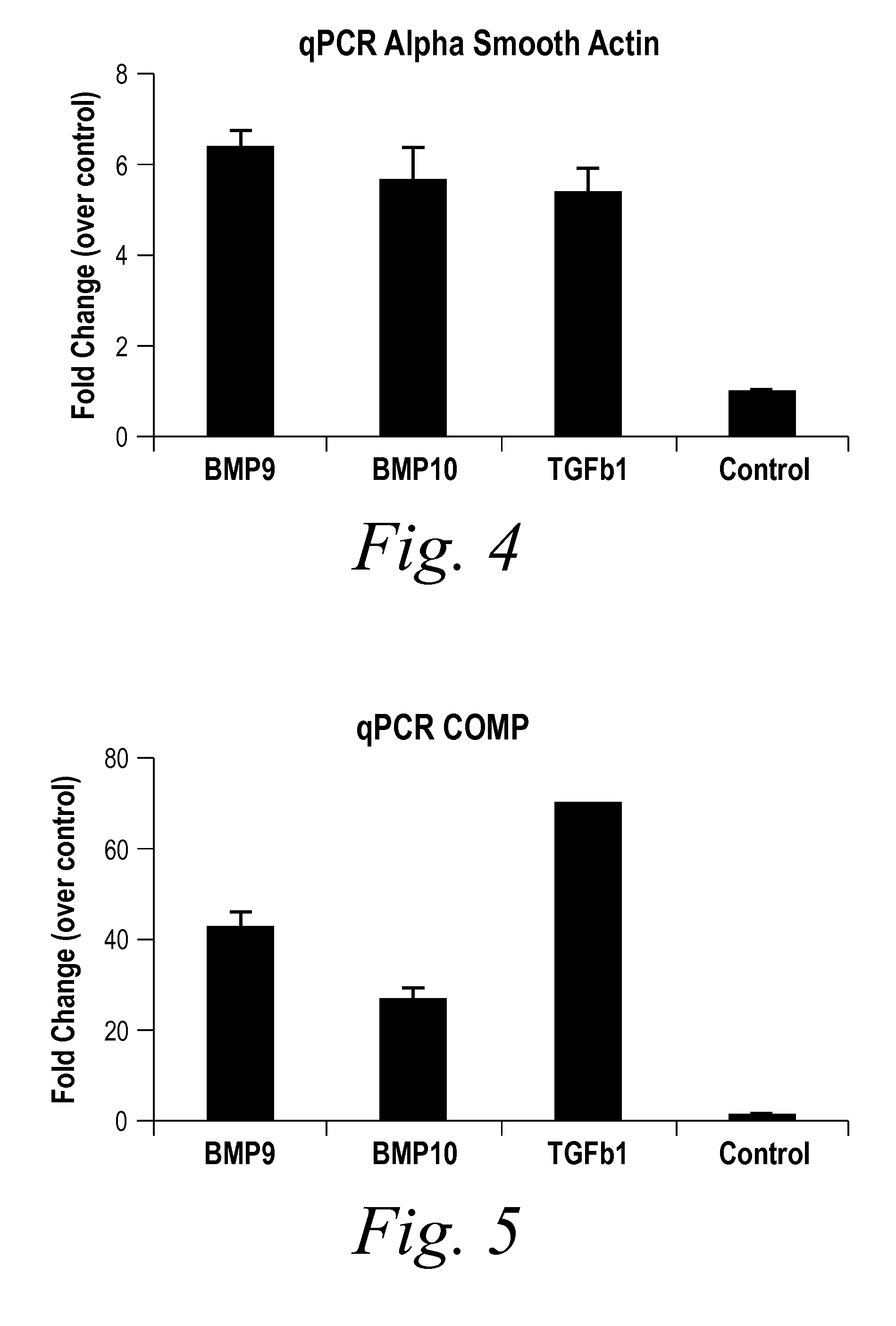
Diagnostic BioMarkers for Fibrotic Disorders
InactiveUS20130209490A1Easy to detectOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFiberFibrosis
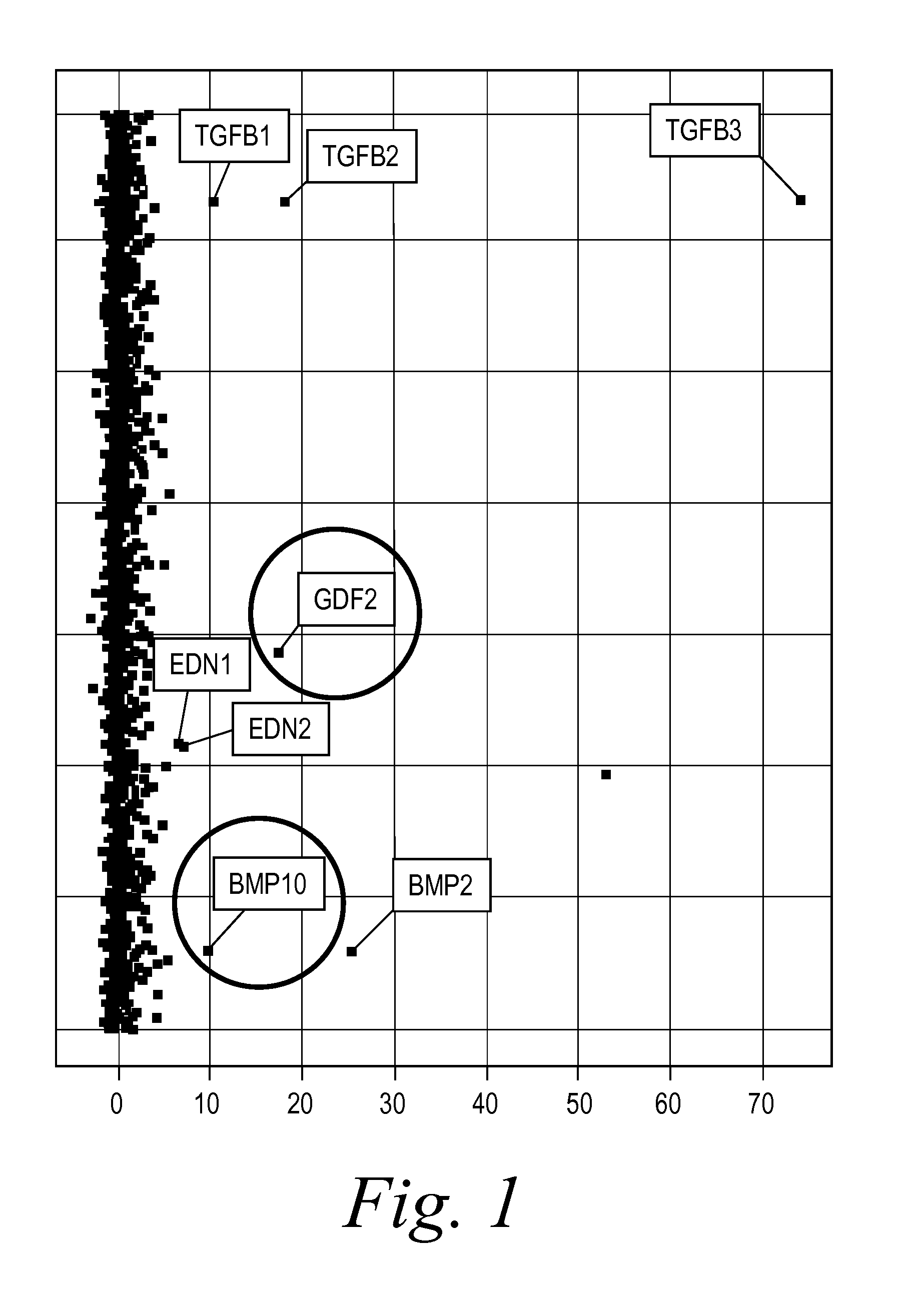
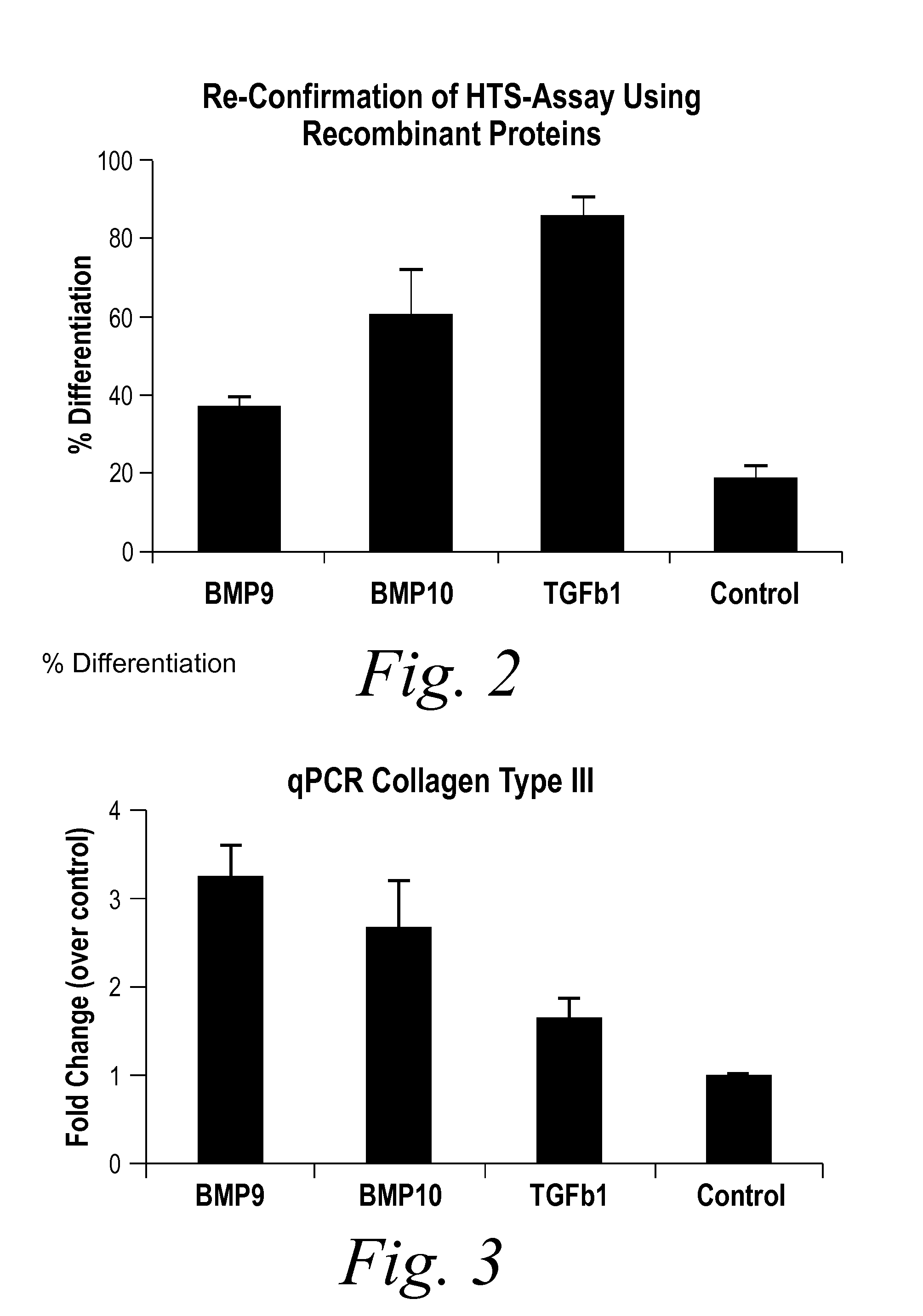
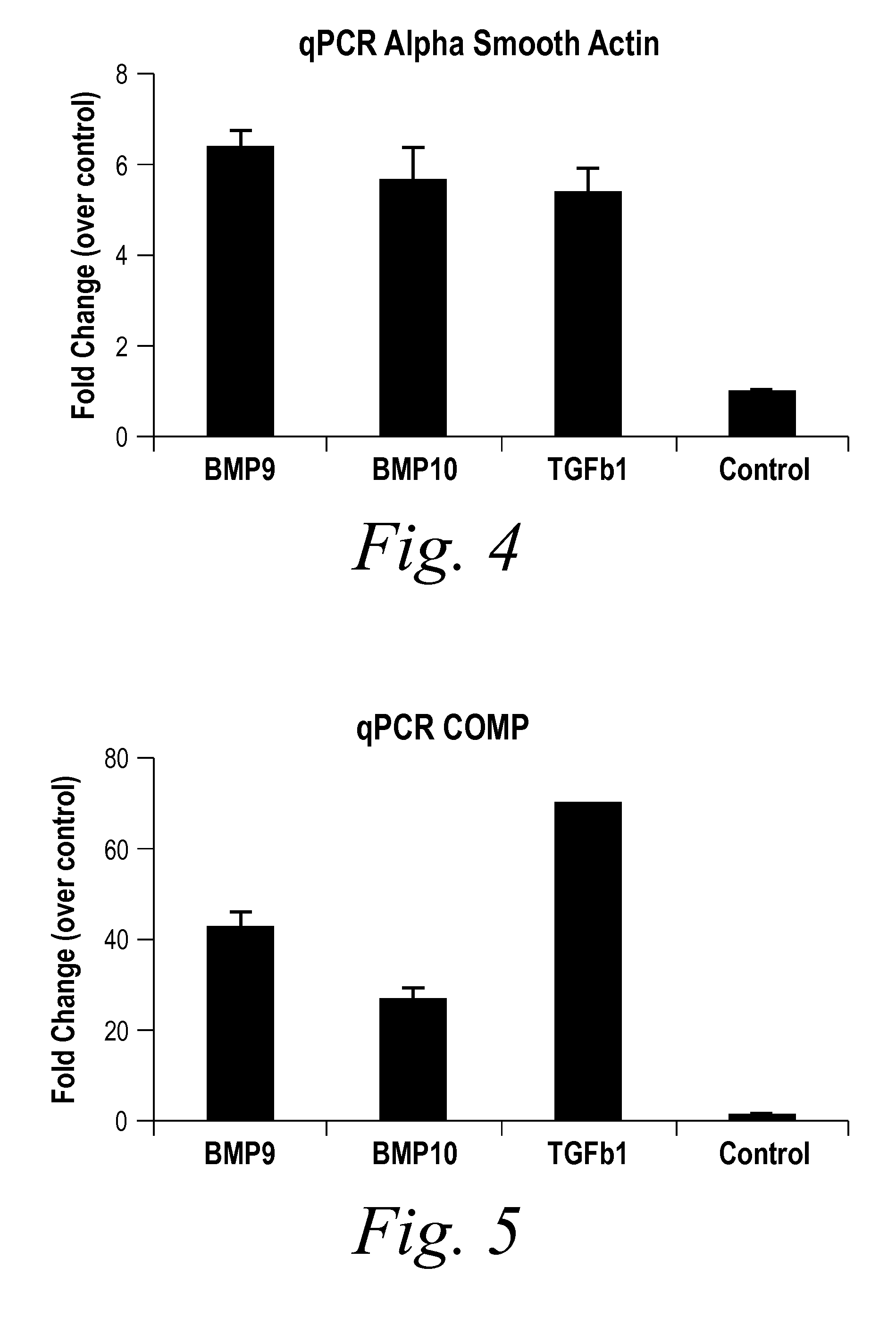
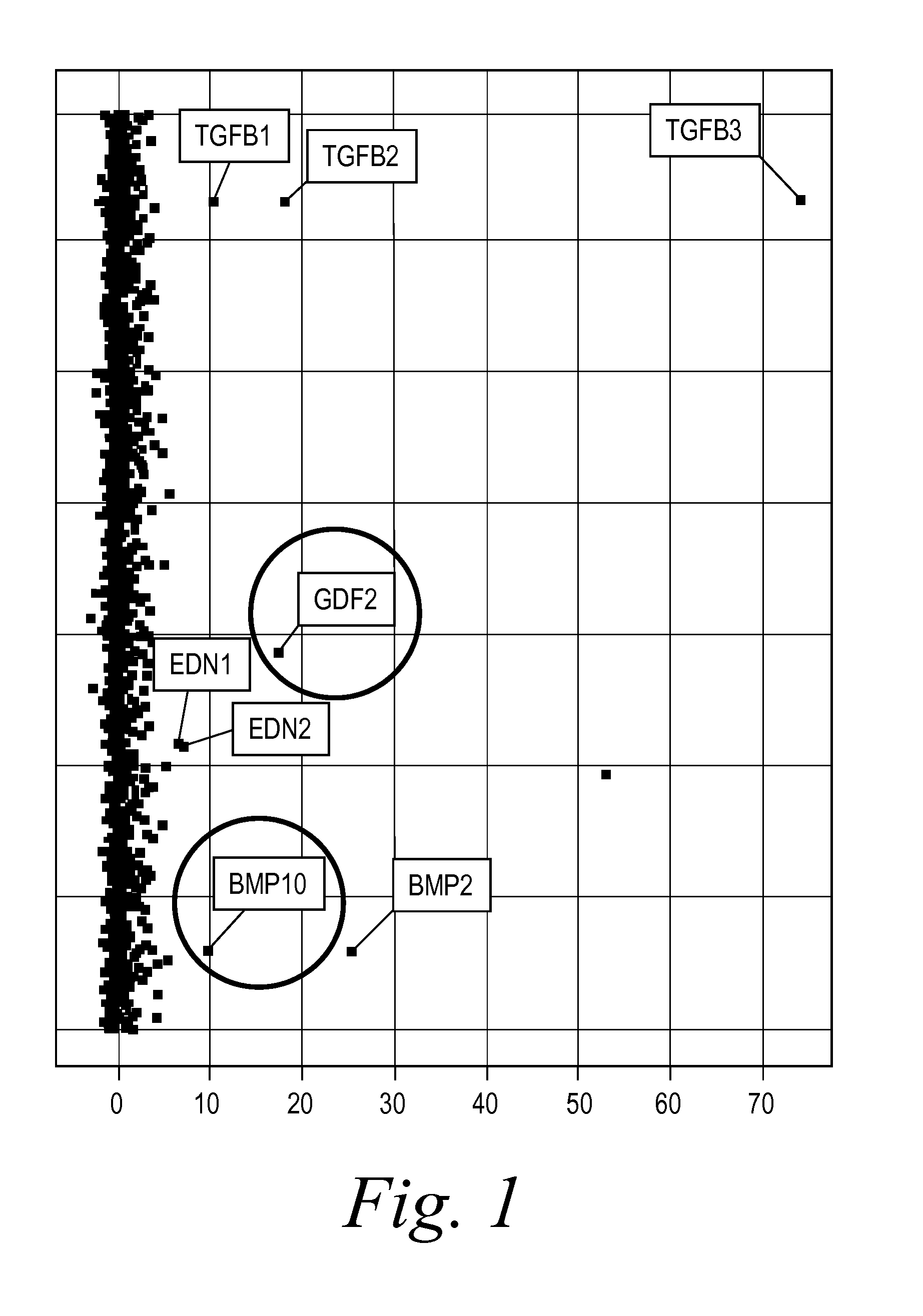
The present invention provides novel methods of inhibiting fibrosis, as well as methods of treating or inhibiting fibrotic disorders, using BMP9 and / or BMP10 antagonists. The present invention also provides methods of assessing whether a subject has or is at risk of developing a fibrotic disorder by detecting levels of BMP9 and / or BMP10. Further provided are methods of assessing the efficacy of a treatment regimen for treating a fibrotic disorder by detecting and comparing pre-treatment levels of BMP9 and BMP10 with post-treatment levels of BMP9 and BMP10.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Enhancement agent for high intensity focused ultrasound treatment and method for screening the same
InactiveUS20090117052A1Increase energy depositionImprove efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCosmetic preparationsHepatic tumorMedicine
The present invention discloses an enhancement agent for high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) treatment, which is administered to a patient before HIFU treatment and can reduce the level of EEF at the target location to be treated with HIFU. EEF is presented by the expression: EEF=ηPt / V (unit: J / mm3), and refers to the HIFU energy needed to effectively treat a tumor per unit volume of the tumor, wherein, η=0.7; P refers to the total acoustic power of HIFU source (unit: W); t refers to the total time of HIFU treatment (unit: s); V refers to the volume of HIFU-induced lesions (unit: mm3). If the amount of EEF at the target location before administration of the enhancement agent is defined as EEF(base) and the amount of EEF at the target location after administration of the enhancement agent is defined as EEF(measurement), the ratio between EEF(base) and EEF(measurement) is more than 1, preferably more than 2, and more preferably over 4. The use of the enhancement agent for HIFU treatment of the present invention makes it possible to treat deep-seated tumors. In addition, patients with hepatic tumors can be effectively treated without removal of ribs. Accordingly, the present invention discloses methods for increasing acoustic energy deposition at target location during HIFU treatment and screening the enhancement agents for HIFU treatment.
Owner:CHONGQING HAIFU MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
A formulation for improving seizure control
PendingUS20220133652A1Improving seizure controlSeizure control has improvedNervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsGeneral anaesthesiaEpileptic encephalopathy
Described herein is a method of improving seizure control in a patient experiencing uncontrolled seizures persisting 10 minutes or more, comprising administering fenfluramine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, base, acid or amine thereof, at a dose of from 0.2 to 1.2 m / kg / day for a period of about 12 hours to about 7 days to a patient having been put into a therapeutic, medically-induced coma via a general anesthetic; and after about 12 hours to about 7 days, weaning the patient from the general anesthetic and assessing whether the seizure control has improved as compared to a pre-treatment time point. The patient experiencing seizures may have epilepsy or epileptic encephalopathy that has led to established status epilepticus (SE), refractory status epilepticus (RSE) or super-refractory status epilepticus (SRSE).
Owner:ZOGENIX INT
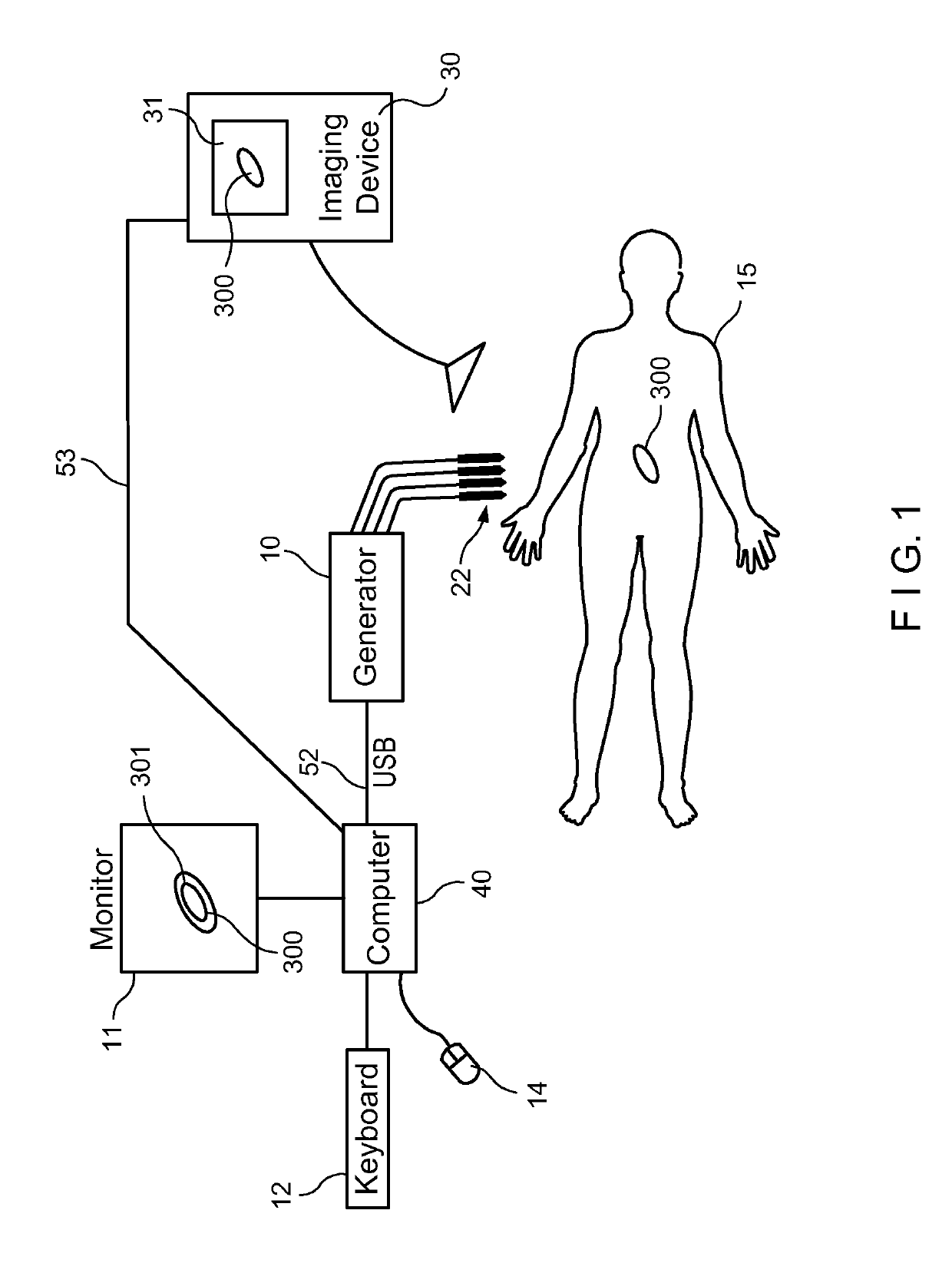
Radio-frequency electrical membrane breakdown for the treatment of high risk and recurrent prostate cancer, unresectable pancreatic cancer, tumors of the breast, melanoma or other skin malignancies, sarcoma, soft tissue tumors, ductal carcinoma, neoplasia, and intra and extra luminal abnormal tissue
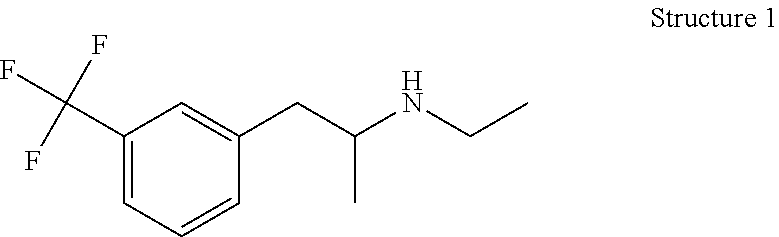
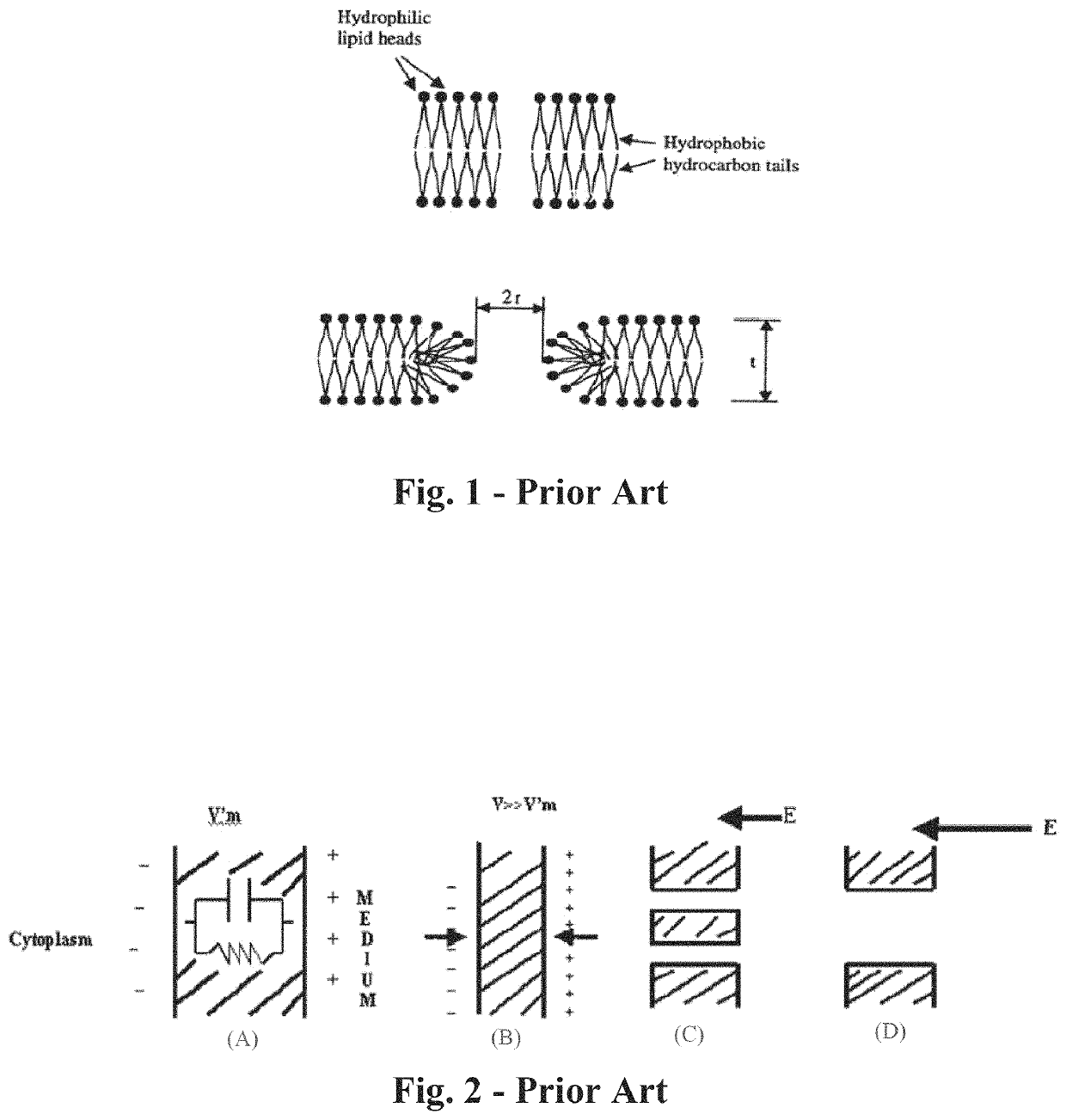
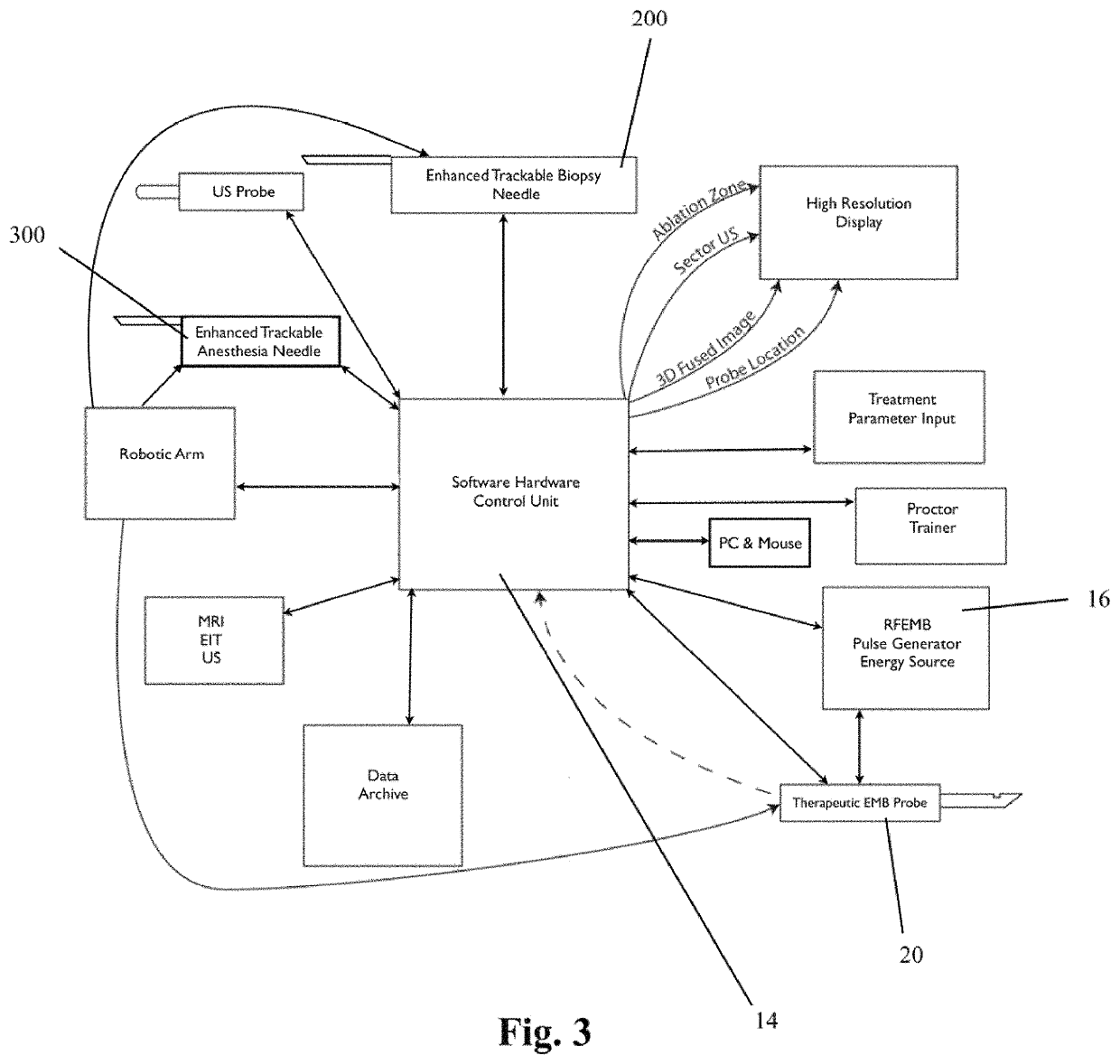
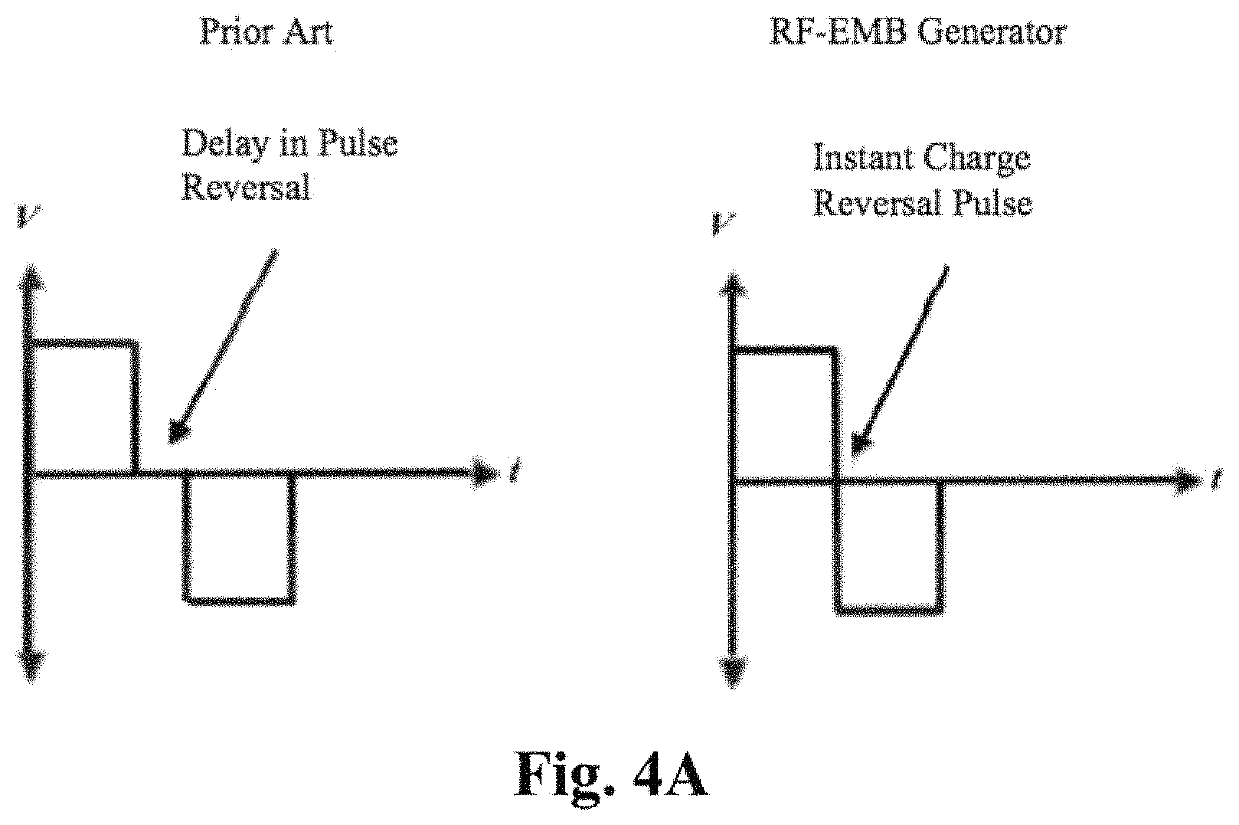
ActiveUS11141216B2Safe and effectiveSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsCellular componentAnesthesia needle
An imaging, guidance, planning and treatment system integrated into a single unit or assembly of components, and a method for using same, that can be safely and effectively deployed to treat prostate cancer in all medical settings, including in a physician's office or in an outpatient setting. The system utilizes the novel process of Radio-Frequency Electrical Membrane Breakdown (“EMB” or “RFEMB”) to destroy the cellular membranes of unwanted or cancerous tissue without denaturing the intra-cellular contents of the cells comprising the tissue, thereby exposing tumor antigens and other intra-cellular components which can have an immunologic effect on local or distant cancerous tissue, with or without the addition of immunologic adjutant drugs. The system preferably comprises at least one EMB treatment probe 20, at least one trackable biopsy needle 200, at least one trackable anesthesia needle 300, and at least one controller unit for at least partially automating the treatment process.
Owner:IMMUNSYS INC
In-situ bladder cancer animal model and identification method
InactiveCN104173115AFacilitate experimental researchImprove accuracyVeterinary instrumentsIn vivo experimentPre-Therapy
The invention relates to an in-situ bladder cancer animal model. An establishment method of the animal model comprises the step of perfusing 20mg / mL carcinogen MNU solution in a bladder of an SD rat to cause the bladder cancer, wherein 0.1mL of carcinogen MNU solution is perfused per time per week, and six times in total. The in-situ bladder cancer animal model has the advantages that the novel establishment method is provided for the in-situ bladder cancer animal model; a novel method for establishing the model of detecting the bladder cancer through a living body is provided, so that a tumour model not beneficial to further in vivo experiment can be removed, and meanwhile, the effect of pretherapy and post-treatment of the bladder caner animal model can be evaluated by utilizing CT (Computed Tomography) scanning; the method for diagnosing the in-situ bladder cancer of the rat through CT scanning is more sensitive, higher in accuracy, and more direct and convenient, and can provide convenience for further experiment research of the animal model.
Owner:XIN HUA HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Use of genomic signatures to predict responsiveness of patients with prostate cancer to post-operative radiation therapy
Methods, compositions, and kits for identifying individuals who will be responsive to post-operative radiation therapy for treatment of prostate cancer are disclosed. In particular, the invention relates to a genomic signature based on expression levels of DNA Damage Repair genes that can be used to identify individuals likely to benefit from post-operative radiation therapy after a prostatectomy.
Owner:DECIPHER BIOSCI INC +1
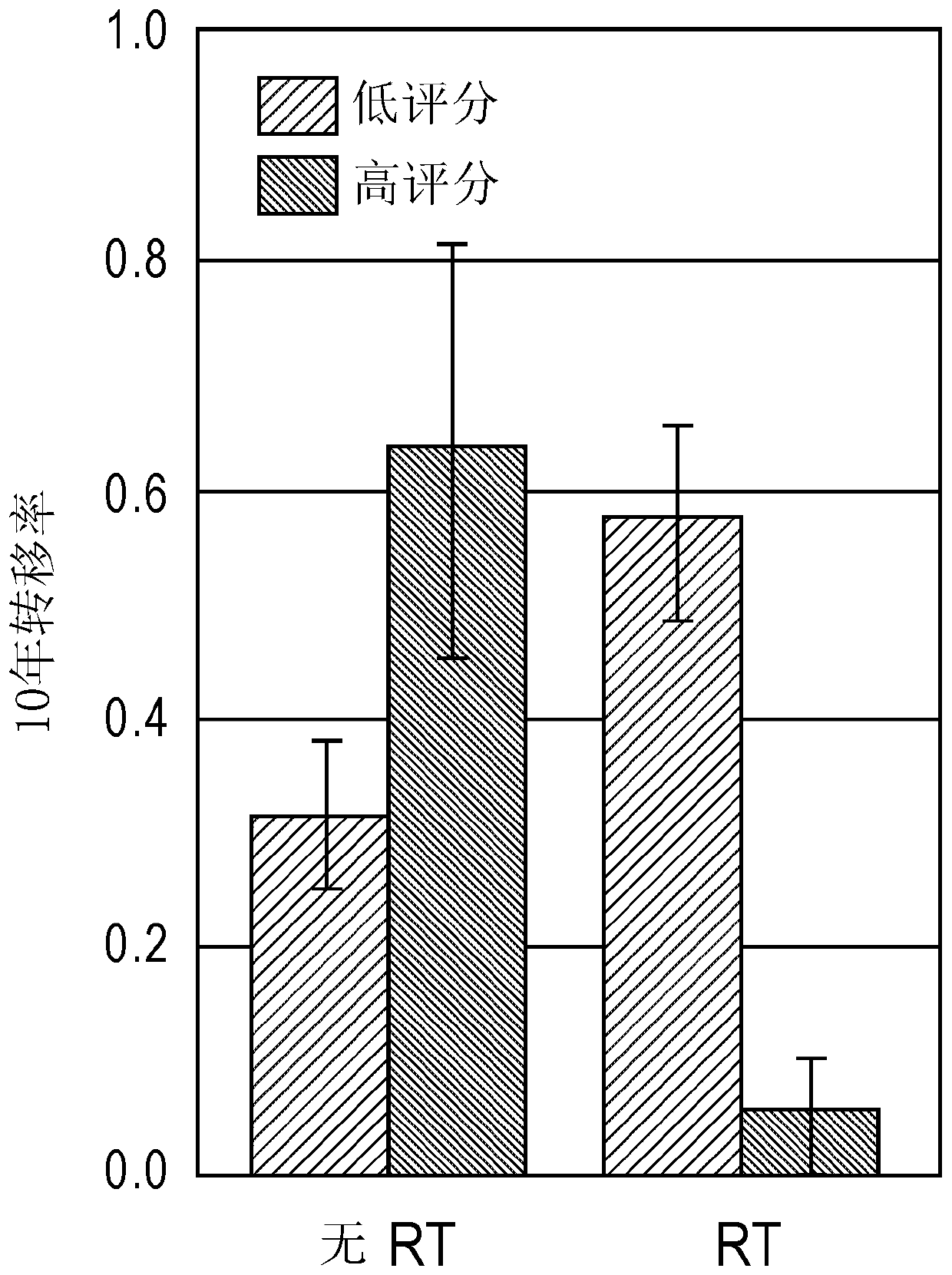
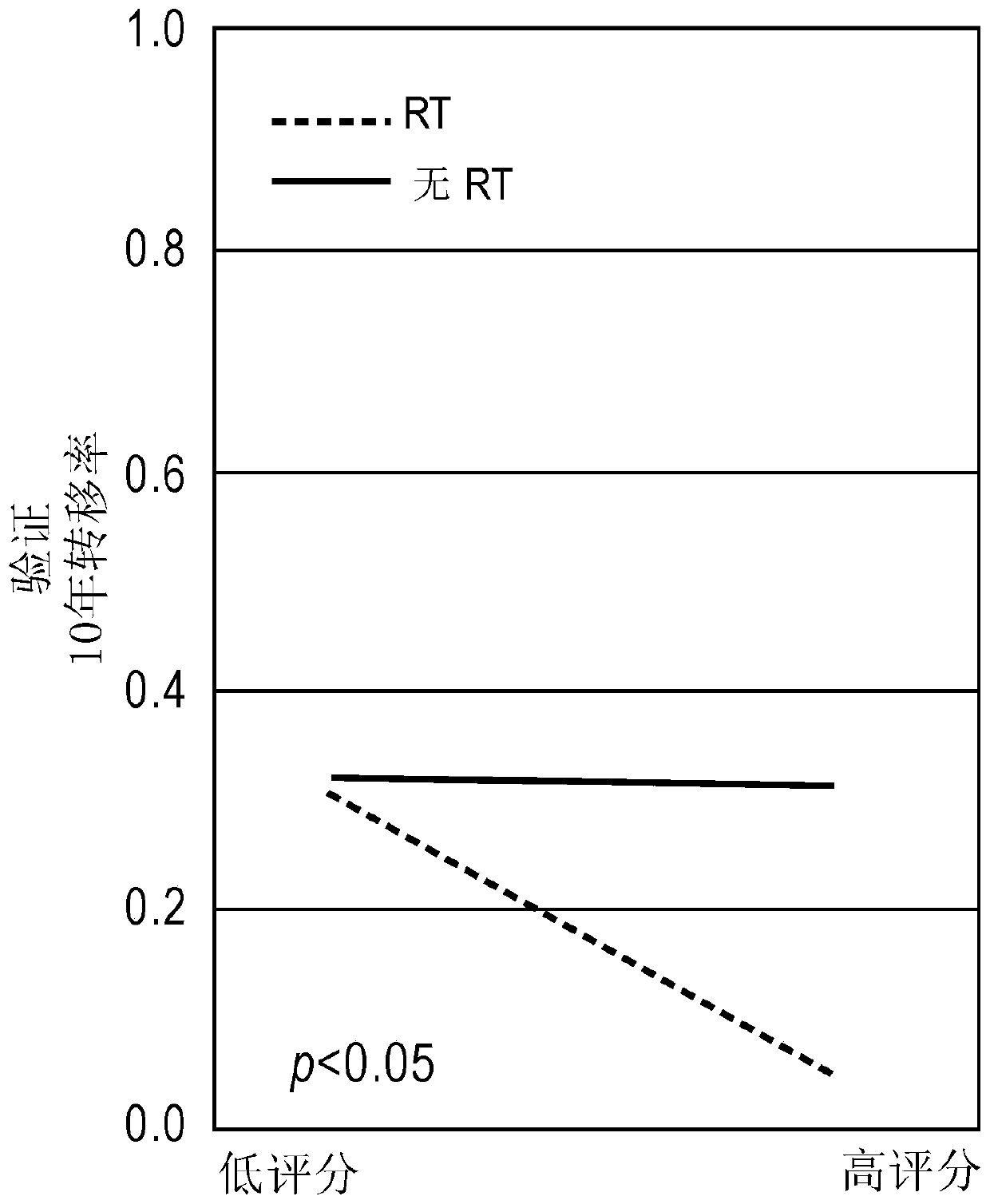
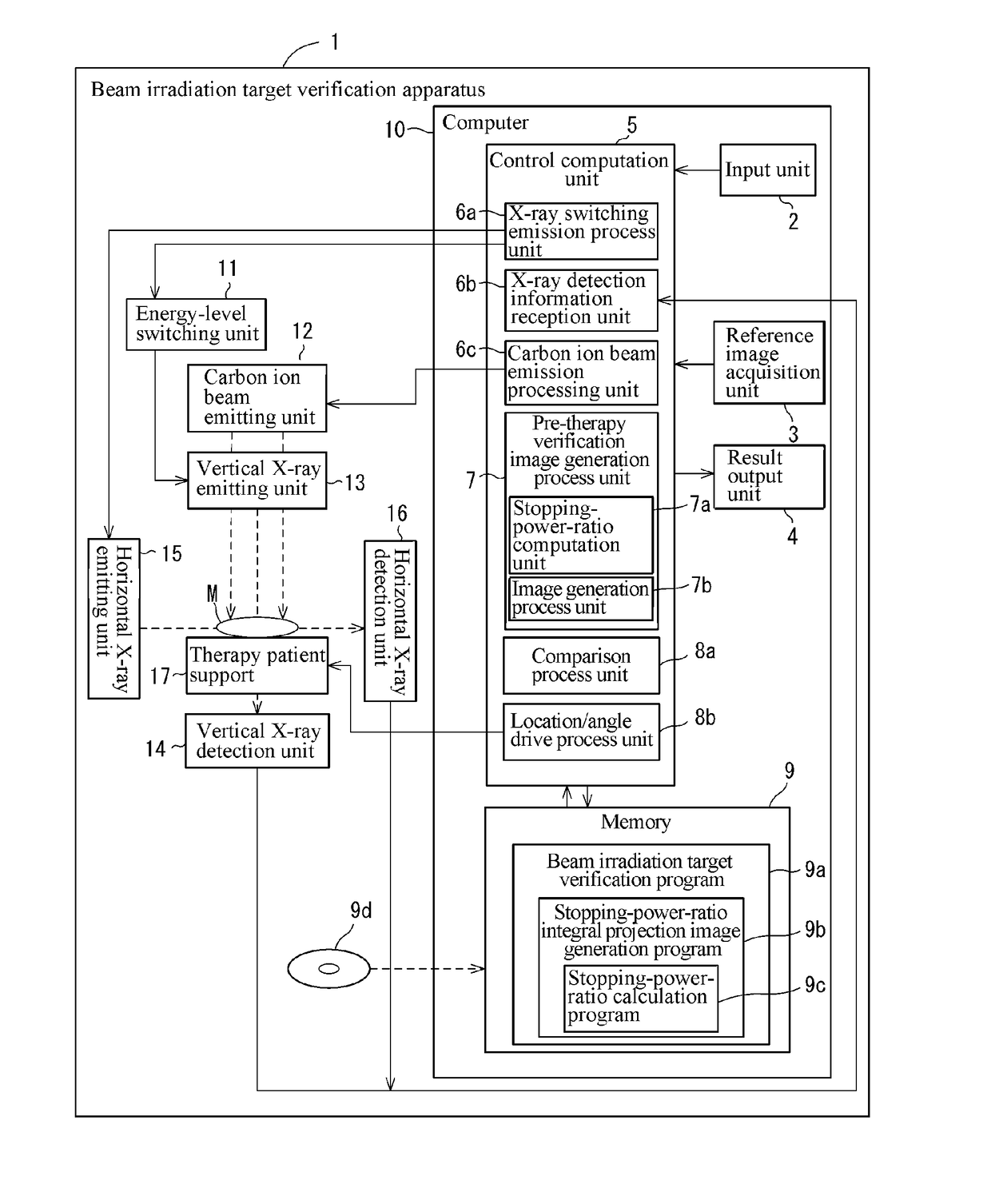
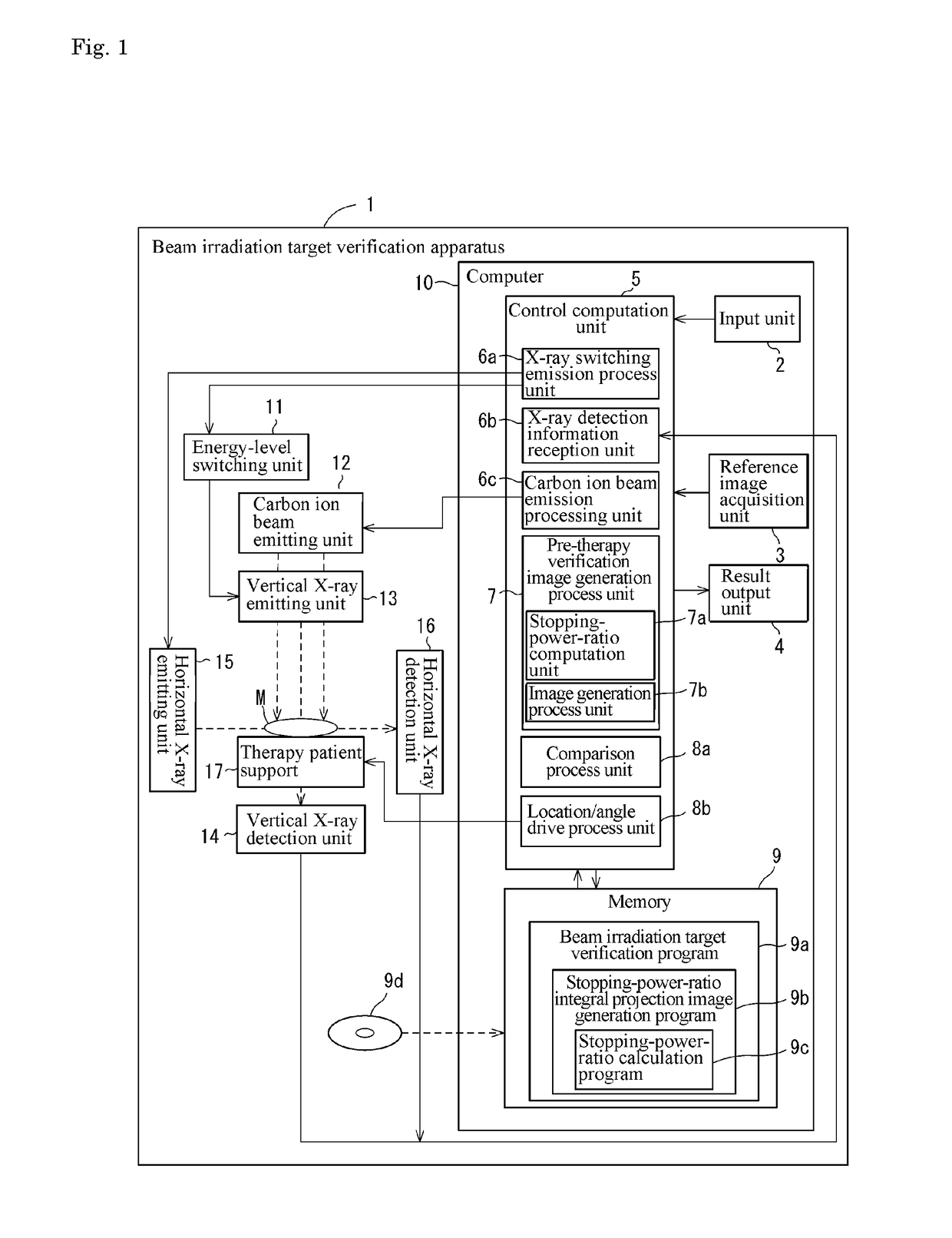
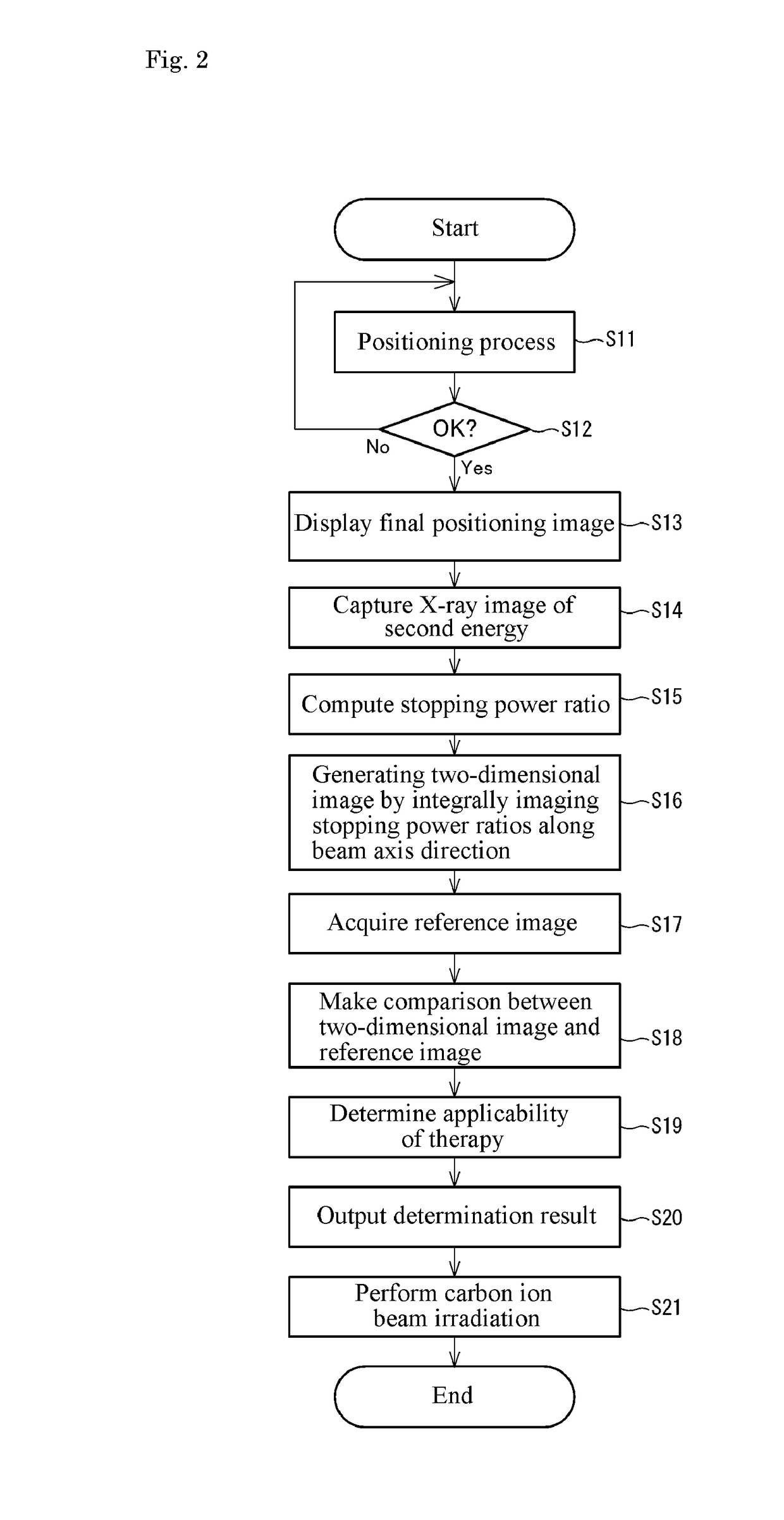
Beam irradiation target confirmation device
ActiveUS20170113065A1Lower levelEasy to measureHealth-index calculationComputerised tomographsReference imageLight beam
A beam irradiation target verification apparatus (1) includes an X-ray switching emission process unit (6a) that causes a vertical X-ray emitting unit (13) to emit at least two types of X-rays using an energy-level switching unit (11), a vertical X-ray detection unit (14) that detects an X-ray emitted from the vertical X-ray emitting unit (13), a pre-therapy verification image generation process unit (7) that generates pre-therapy verification images (20B) and (20C) based on detection information on at least two types of X-rays obtained by the vertical X-ray detection unit (14), a reference image acquisition unit (3) that acquires a reference image (20A) obtained at a therapy planning stage, a comparison process unit (8a) that makes comparisons between the pre-therapy verification images (20B) and (20C) and the reference image (20A), and a result output unit (4) that outputs a comparison result obtained by the comparison process unit (8a). Thus, there is provided a beam irradiation target verification apparatus for therapeutic purposes capable of measuring internal conditions of a therapy patient and determining necessity of changing a therapy plan, easily and at a relatively low exposure level.
Owner:NAT INST FOR QUANTUM & RADIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Diagnostic methods and compositions for cancer immunotherapy
PendingCN113260633AOrganic active ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiendomysial antibodiesAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention provides diagnostic methods, therapeutic methods, and compositions for the treatment of cancer. The compositions and methods described herein can be used, for example, to determine the propensity of a patient to benefit from treatment with a PD-L1 axis binding antagonist and to treat such patients accordingly. Using the compositions and methods of the disclosure, a patient, such as a human cancer patient, may be determined to be likely to benefit from treatment with a PD-L1 axis binding antagonist if the patient exhibits an elevated pre-treatment expression level of one or more of CST7, NKG7, GZMH, MT-ND4, HLA-H, CCL5, CD8A, CMC1, CD8B, HCST, MT-CYB, MT-ND4L, KLRG1, MT-CO2, MT-ATP6, PLEK, CTSW, HLA-C, LYAR, LITAF, GZMB, KLRD1, FGFBP2, KLRC4-KLRK1, KLRK1, B2M, GZMA, ID2, CX3CR1, PRSS23, GNLY, PRF1, and PATL2. Exemplary PD-L1 axis binding antagonists that may be used in conjunction with the compositions and methods of the disclosure are PD-L1 binding antagonists, such as anti-PD-L1 antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof, including atezolizumab, as well as PD-1 binding antagonists, such as anti-PD-1 antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
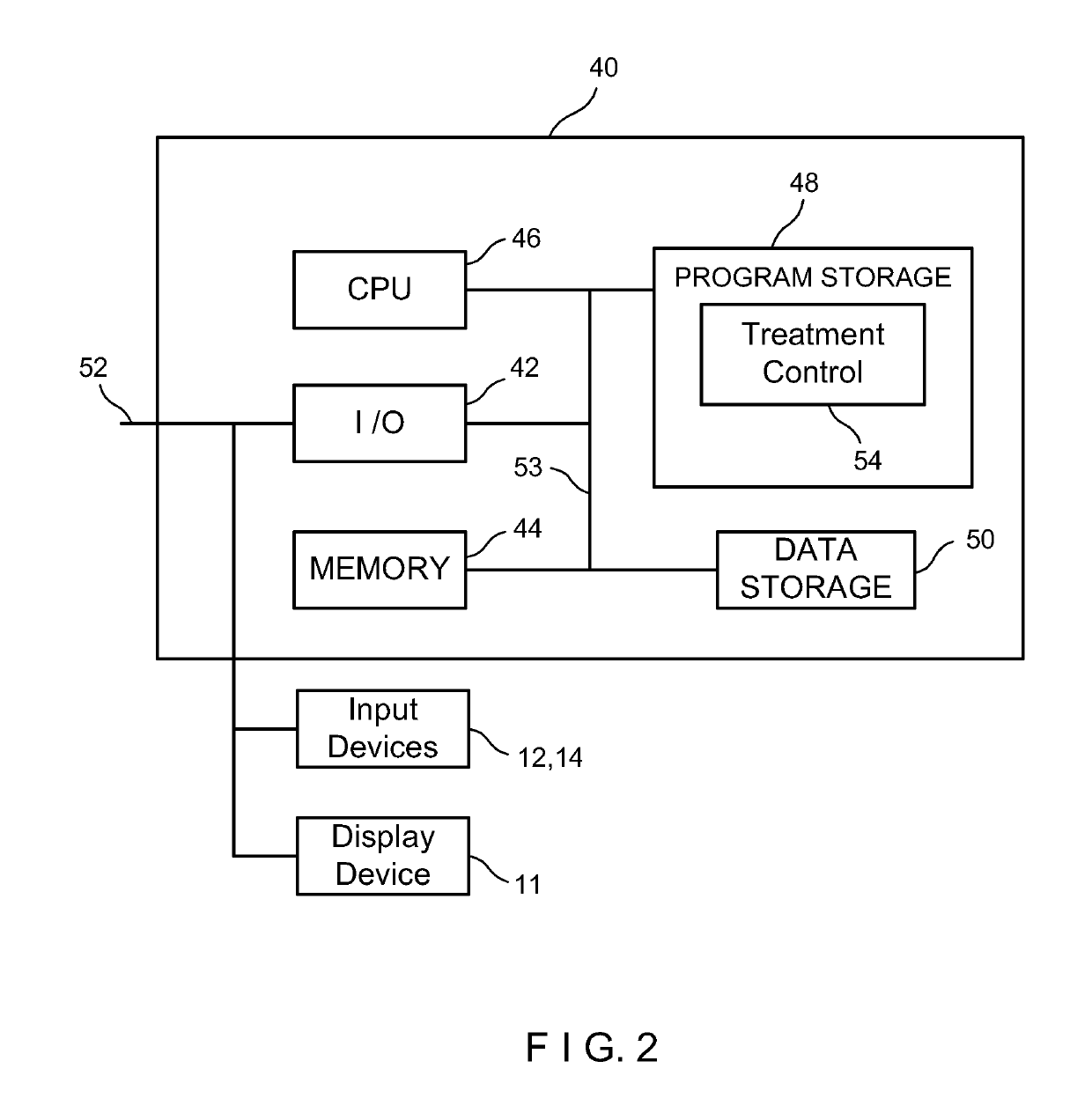
Apparatus, method, computer-readable medium, and use for therapy planning in treatment of a patient
InactiveUS8315810B2Lower Level RequirementsGood effectPhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPlatelet
An apparatus, method, system, computer-readable medium and use for individual patient therapy planning of diseases such as cancer for different therapy modalities, such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy is provided. A new aspect of the invention is that the degree of bone marrow depression of the patient is related to the count of immature blood platelets, which are measured before each treatment. Some embodiments of the invention provide an advantage allowing reducing the level of uncertainty in the prediction of the risk of bone marrow depression, and thus enabling to safely improve the therapy effect by an increase of the radiation dosage and / or chemical dosage to the individual patient while the risk for bone marrow depression is minimized.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Biomarker assay for use in monitoring autism
The present invention relates to protein kinase A (PKA) for use in diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (ASD) phenotype 1 in an ASD patient wherein PKA levels are measured in a sample of the patient and wherein ASD phenotype 1 is diagnosed if the measured levels are lower than PKA levels in an age and sex-matched control sample. Additionally, the present invention relates to PKA for use in monitoring variation in ASD severity in an ASD patient, wherein PKA levels are measured in a sample of the patient and an increase in ASD severity is characterized by a decrease of PKA levels compared to PKA levels measured in previous samples of the patient. The present invention also relates to PKA for use in monitoring efficacy of an ASD treatment in an ASD phenotype 1 patient, wherein PKA levels are measured in a sample of the patient and wherein a positive response to the ASD treatment is characterized by an increase of PKA levels in comparison to baseline PKA levels of the patient prior to treatment. Furthermore, the present invention is directed to methods of diagnosing ASD phenotype 1 as well as kits comprising means to measure PKA levels.
Owner:STALICLA SA
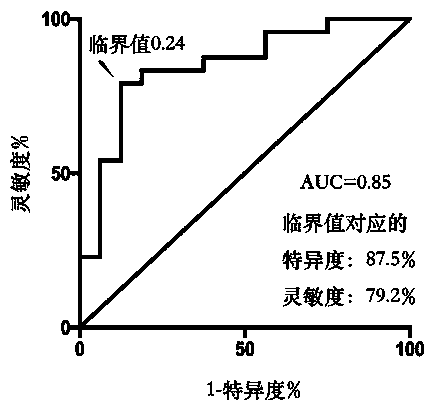
Method for predicting platinum chemosensitivity of ovarian cancer patient by combining serum glycosylation modification with CA125
Glycosylation modification in serum of an ovarian cancer patient before treatment is detected, and the sensitivity of the ovarian cancer patient to platinum chemotherapeutic drugs is subjected to prognosis evaluation by combining alpha 2, 3 sialic acid N-sugar chains with CA125. A detection object of the kit is serum of an ovarian cancer patient before treatment; the method comprises the followingsteps: detecting serum glycosylation modification by using an analytical instrument, calculating the relative expression quantity of alpha 2, 3 sialic acid type N-sugar chains, and performing binarylogistic regression analysis in combination with the content of CA125 in serum of a patient by using SPSS software to obtain a prediction probability; taking 0.24 as a critical value, if the prediction probability is greater than 0.24, determining that the patient is a drug-resistant patient, and if the prediction probability is less than 0.24, determining that the patient is a sensitive patient.The method has the advantages that the chemotherapy effect of the medicine on the patient is predicted by utilizing the proper marker, a treatment scheme more suitable for the patient is selected, andthe survival rate of the ovarian cancer patient is further improved.
Owner:THE OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
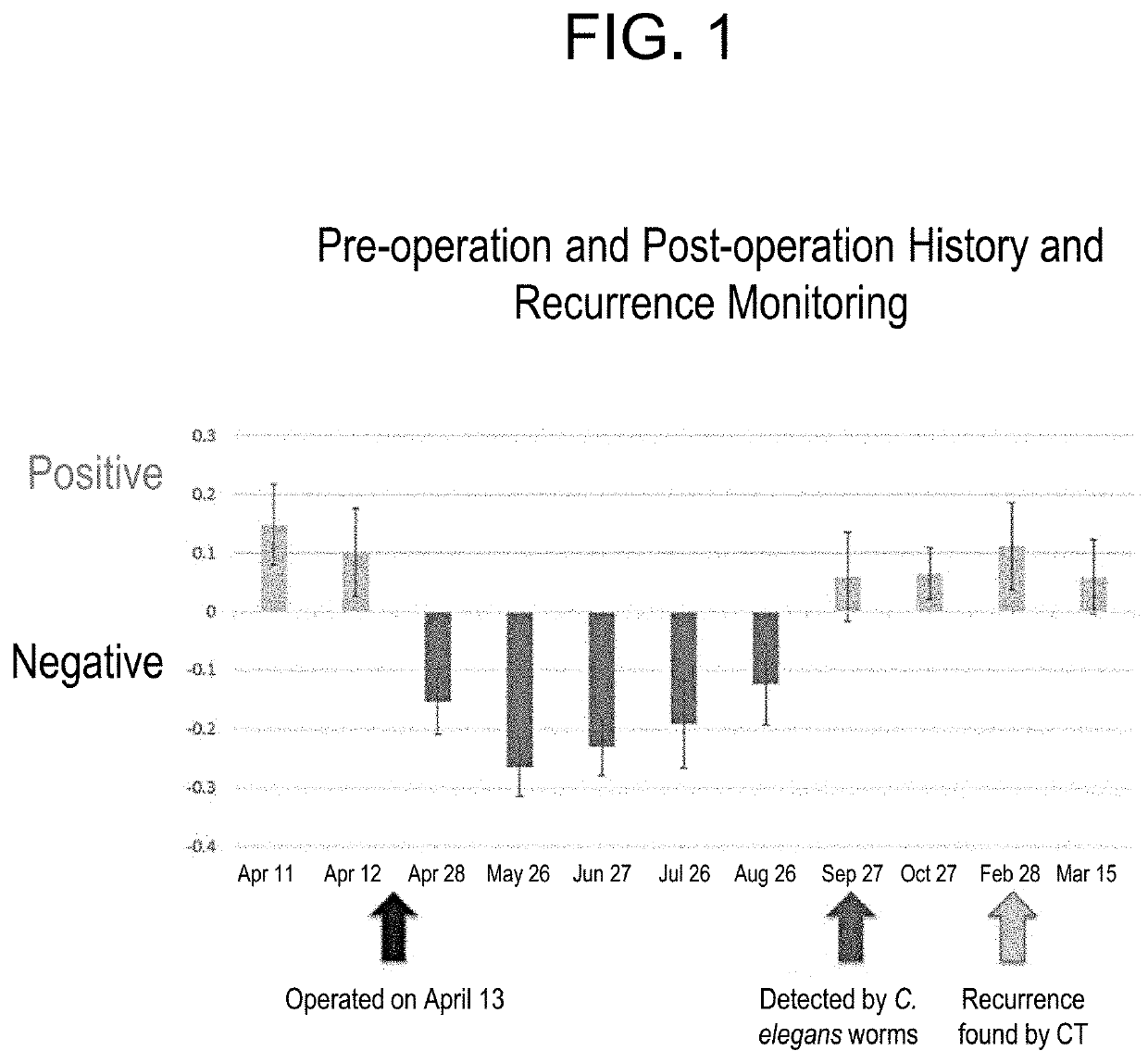
Method for predicting therapeutic effect and/or recurrence monitoring in cancer patients
PendingUS20200400653A1Guaranteed predictive effectDisease diagnosisBiological testingAfter treatmentACTH measurement
The present invention provides a method for predicting a therapeutic effect and / or monitoring recurrence in a cancer patient. Disclosed is a method for detecting a therapeutic effect of cancer treatment in a cancer patient, comprising: measuring nematode tactic behavior to each of pre-treatment urine and in-treatment or post-treatment urine from the cancer patient; and comparing a result of measuring the tactic behavior to the pre-treatment urine and a result of measuring the tactic behavior to the in-treatment or post-treatment urine, wherein when attraction is weakened or avoidance is strengthened after the treatment, it is determined that the therapeutic effect is detected.
Owner:HIROTSU BIO SCI INC +1
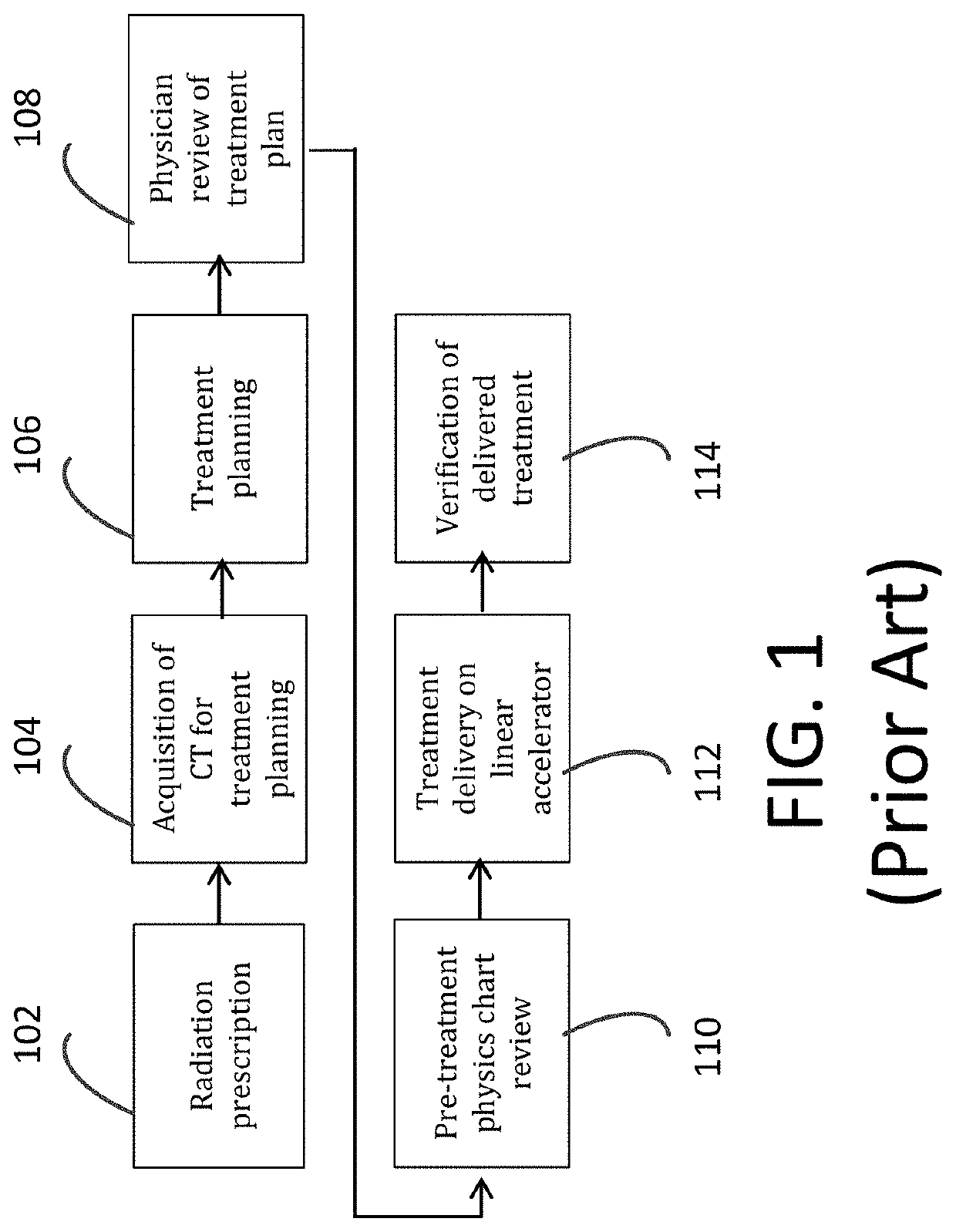
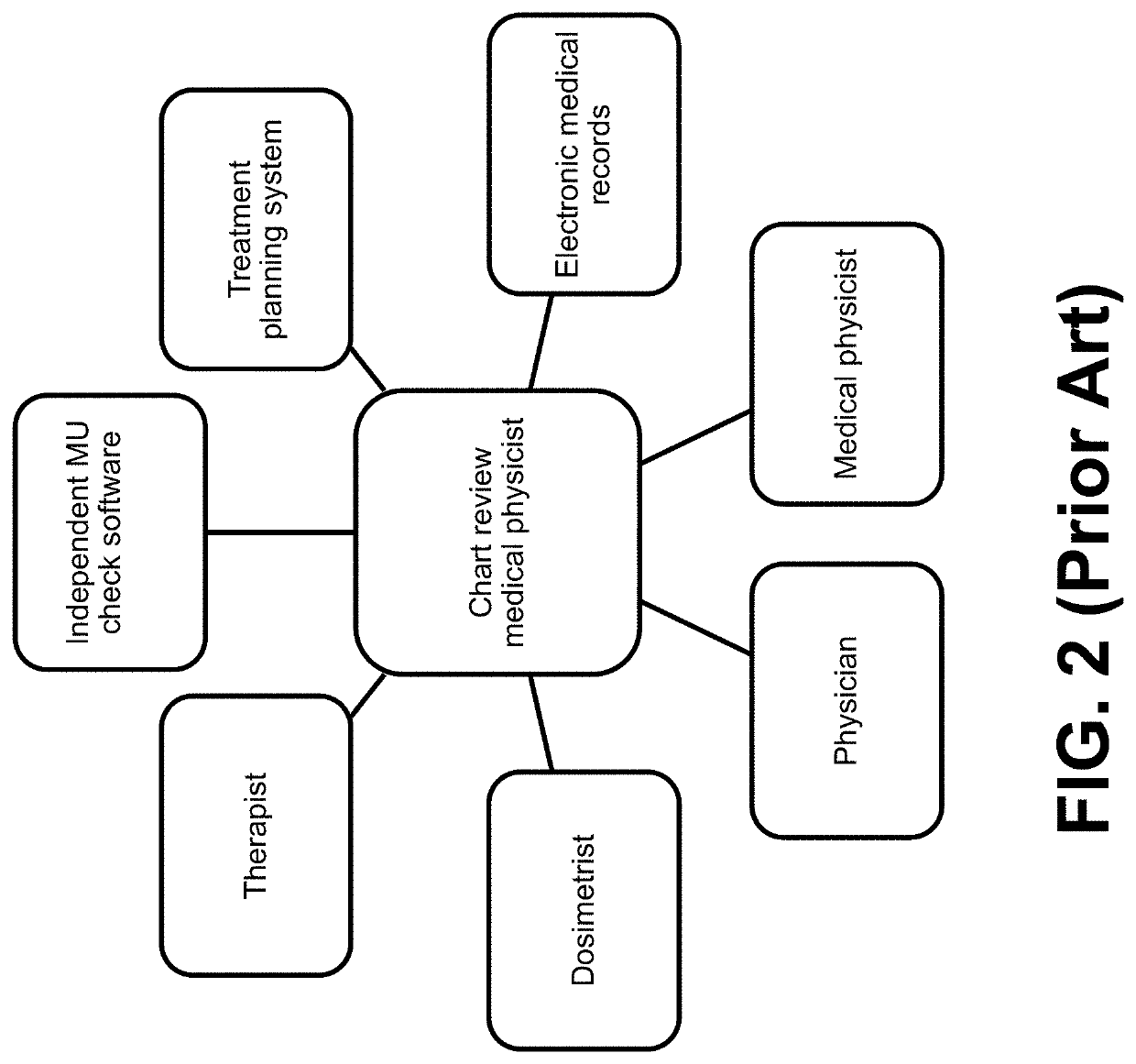
Computer-implemented method of evaluating a protocol for radiation therapy including a pre-treatment physics chart review (TPCR)
A computer-implemented method evaluates a protocol for radiation therapy for a target volume of a patient. The method uses a computer system executing software instructions establishing computer processes. The computer processes receiving and storing data defining the protocol and characterizing the target volume. The computer processes parse the data to extract parameters characterizing the protocol. The computer processes apply the extracted parameters and the target volume to a model that represents relationships among sub-processes and variables pertinent to execution of the protocol in a patient. The computer processes obtain from the model an evaluation of the protocol and providing the evaluation as an output.
Owner:MUNBODH RESHMA
Assistant for high-intensity focusing ultrasonic therapy and its screening method
The invention discloses an adjuvant for high-intensity focusing and ultrasonic (HIFU) treatment, which can be used for lowering the EEF of the HIFU therapeutic target region for the patients, the adjuvant makes it possible to carry out HIFU treatment during deep layer tumor treatment without the requirement of ablation of the patients' rib. The invention also provides a method for increasing target region energy deposition and screening HIFU adjuvant in HIFU treatment.
Owner:CHONGQING HAIFU (HIFU) TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
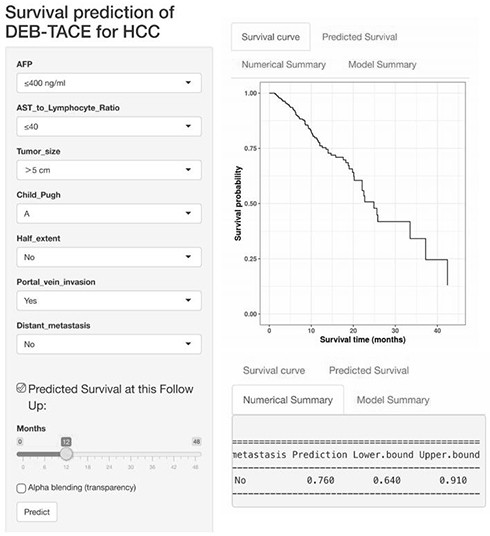
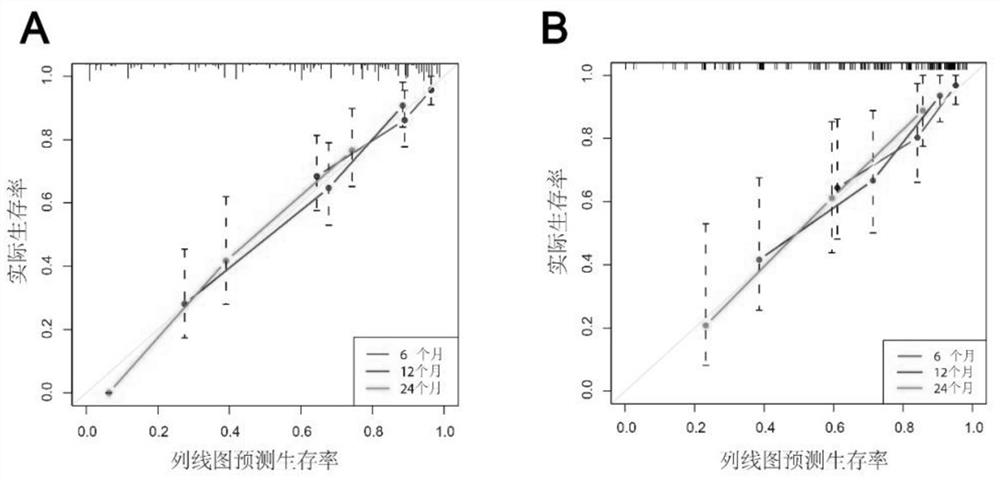
Kit for predicting prognosis of drug-loaded microsphere chemoembolization treatment of liver cancer
ActiveCN113138259AGood predictive abilityImprove consistencyTesting medicinal preparationsEmbolization TherapyVena porta
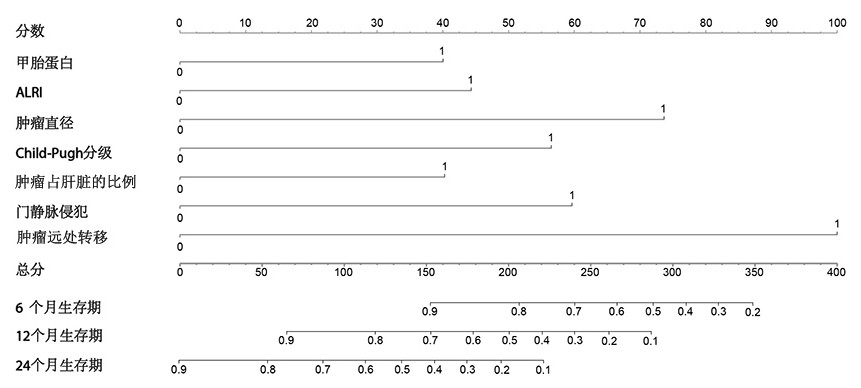
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical biology, and particularly discloses a kit for predicting prognosis of drug-loaded microsphere chemoembolization treatment of liver cancer, and the kit comprises reagents and / or instruments for detecting the alpha fetoprotein expression quantity, ALRI, the tumor diameter, Child-Pugh grading, proportion of tumor in liver, a portal vein invasion state and a tumor remote metastasis state. The kit disclosed by the invention can be used for predicting the lifetime of the liver cancer patient after DEB-TACE treatment according to clinical indexes of the liver cancer patient before DEB-TACE treatment and evaluating DEB-TACE treatment prognosis of the liver cancer patient, so that an interventional doctor can screen patient crowds suitable for DEB-TACE treatment before an operation; and clinical doctors can accurately evaluate the prognosis of the patient conveniently, and an individualized follow-up visit scheme can be made according to the expected lifetime.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Apparatus, method, computer-readable medium, and use for therapy planning in treatment of a patient
InactiveUS20090292481A1Lower Level RequirementsGood effectPhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTreatment effect
An apparatus, method, system, computer-readable medium and use for individual patient therapy planning of diseases such as cancer for different therapy modalities, such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy is provided. A new aspect of the invention is that the degree of bone marrow depression of the patient is related to the count of immature blood platelets, which are measured before each treatment. Some embodiments of the invention provide an advantage allowing reducing the level of uncertainty in the prediction of the risk of bone marrow depression, and thus enabling to safely improve the therapy effect by an increase of the radiation dosage and / or chemical dosage to the individual patient while the risk for bone marrow depression is minimized.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Implantable drug delivery devices for localized drug delivery
ActiveUS11338119B2Reduce and eliminate toxicityIncrease concentrationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedical devicesDiseaseActive agent
Provided herein are drug implants comprising a therapeutically active agent for the treatment of disease in a subject. In some cases, the drug implant may comprise a polymer matrix and a therapeutically active agent disposed therein. Additionally provided are methods for manufacturing the drug implants and methods of treating diseases with the implants. In some cases, the drug implant may comprise bicalutamide, e.g., for use in the treatment of prostate cancer.
Owner:ALESSA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Tumor immune cell therapy platform
PendingCN111297896AStandardize the treatment processTumor Treatment GuidelinesMammal material medical ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAfter treatmentTumor therapy
The invention discloses a tumor immune cell therapy platform. Tumor immune cell therapy can be standardized through the following steps: one, the establishing of immune function test items; two, the establishing of test specification technologies; three, the training of medical staff and laboratory staff; four, the establishing of a standardized management system; five, the controlling of quality;and six, the establishing of a clinical grade CAR-T cell preparation technology platform; through the building of the platform, tumor treatment can be more standardized, and the probability of errorduring treatment can be reduced; and the monitoring before and after treatment can be performed on the immune cells and cytokines of patients, and therefore, the platform has important clinical significance in preventing CRS.
Owner:王宝中
United gene marker for prostatic cancer treatment evaluation and detection kit thereof
InactiveCN108486249ADrug resistance assessmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDocetaxelPre-Therapy
The invention provides a molecular marker combination for pre-evaluating drug resistance in a prostatic cancer chemotherapy process. The molecular marker is formed by two prostatic cancer sensitive genes (a P53 gene and a GSTP1 gene) and a miRNA (a miRNA-155), and can be applied for evaluating the chemotherapy drug resistance. In addition, the invention further provides a primer group and a kit for the evaluation; and the invention further provides application of the above primer group and kit in a united discriminant equation of molecular marker expression quantity. Through evaluating the relative expression quantity of the gene, the drug resistance existing in the combined prostatic cancer treatment of docetaxel and prednisone can be evaluated better.
Owner:毛强平
Precision medical methods for cancer immunotherapy
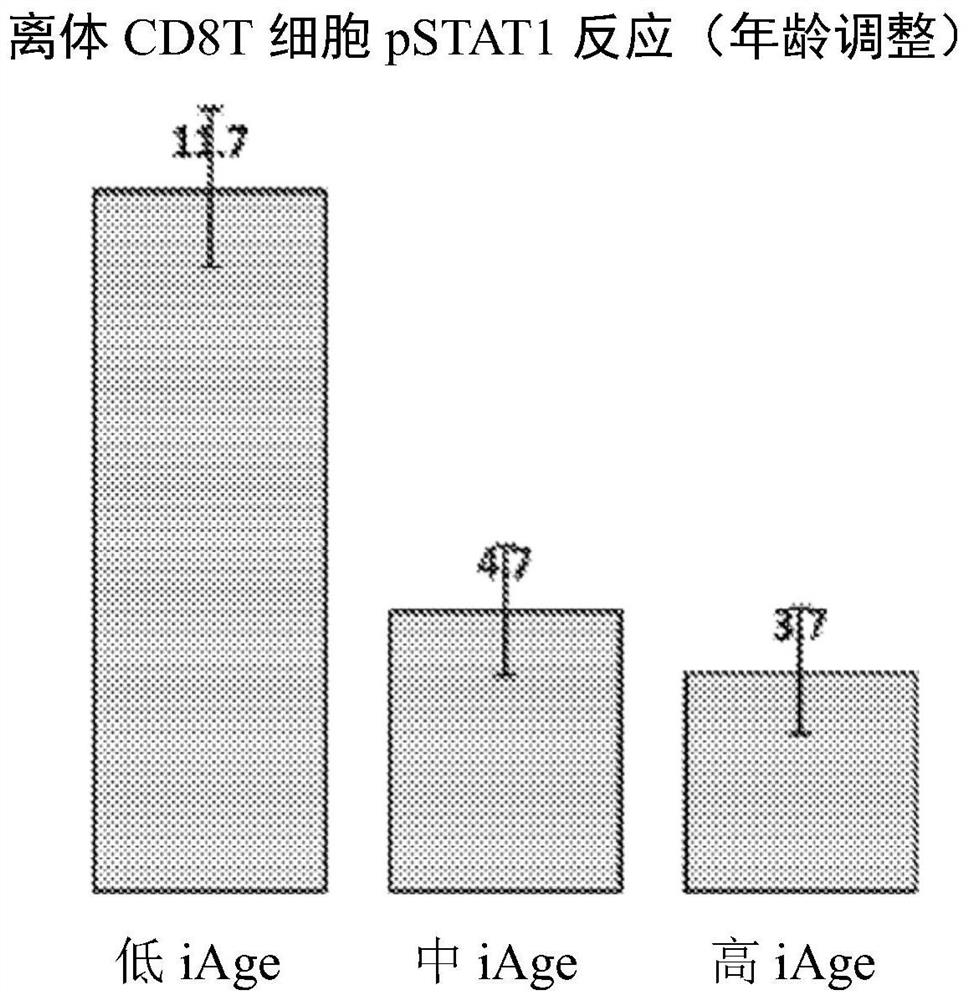
Cancer immunotherapy has obtained a huge clinical success, and even the most difficult-to-treat cancer also has a relatively long lifetime. However, this effect is observed only in a small number of persons and no biomarkers of this reaction. The methods described herein use two independent systemic chronic inflammation metrics (inflammation age-iAge-and cytokine response score-CRS) to stratify cancer patients into responders and non-responders to cancer immunotherapy, thereby improving the outcome of cancer immunotherapy. The iAge personalized immunoproteomic markers / features create an individualized initial therapy to reduce the iAge and convert unresponsive patients to reactants prior to treatment. By treating a patient to reduce its iAge and improve its CRS, unresponsive persons can be converted into reactants.
Owner:艾迪菲斯健康有限公司
Detection method for colorectal cancer polygene ctDNA
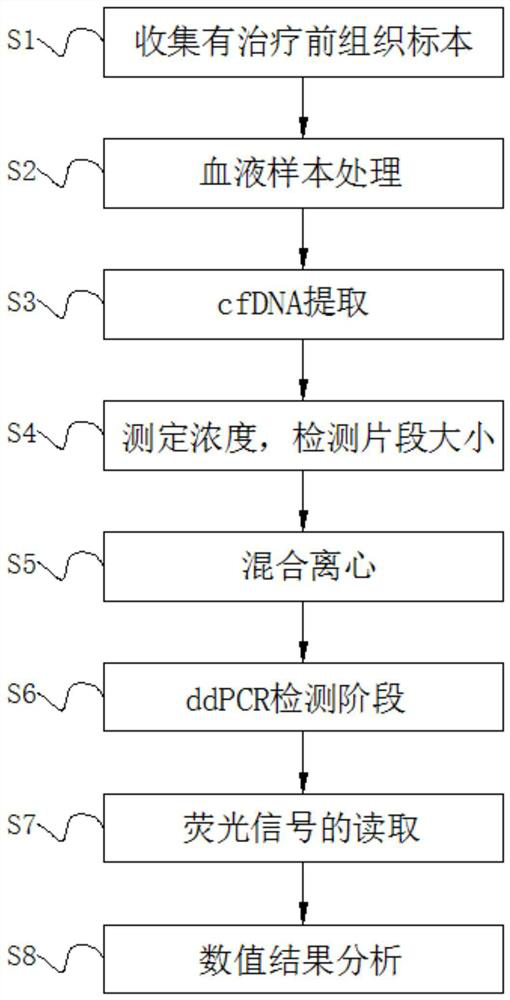
PendingCN113684264AHigh sensitivityLess traumaticMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesTumour tissue
The invention discloses a detection method for colorectal cancer polygene ctDNA, which specifically comprises the following steps: S1, collecting a pre-treatment tissue specimen; S2, treating a blood sample; S3, performing cfDNA extraction; S4, measuring the concentration and detecting the size of a fragment; S5, performing mixing and centrifuging; S6, performing a ddPCR detection stage; S7, reading a fluorescence signal; and S8, analyzing a numerical result. The invention relates to the technical field of molecular diagnosis gene detection. According to the detection method for the colorectal cancer polygene ctDNA, ddPCR amplification is performed on cfDNA through a specific detection primer and a probe of a reference gene beta-Actin; an amplification product is detected; finally, fluorescence signal data is analyzed; fluorescence information of KRAS, NRAS, PIK3CA and BRAF genes and the reference gene beta-Actin is obtained; plasma ctDNA possibly replaces tumour tissue biopsy; and as a molecular marker for auxiliary diagnosis of colorectal cancer, change of RAS (KRAS, NRAS), BRAF and PIK3CA gene mutation states in ctDNA of a patient before and during cetuximab treatment is dynamically monitored.
Owner:浙江天远生物科技有限公司
Polymolecular marker and device for clinically evaluating sensitivity of ulcerative colitis patient to golimumab
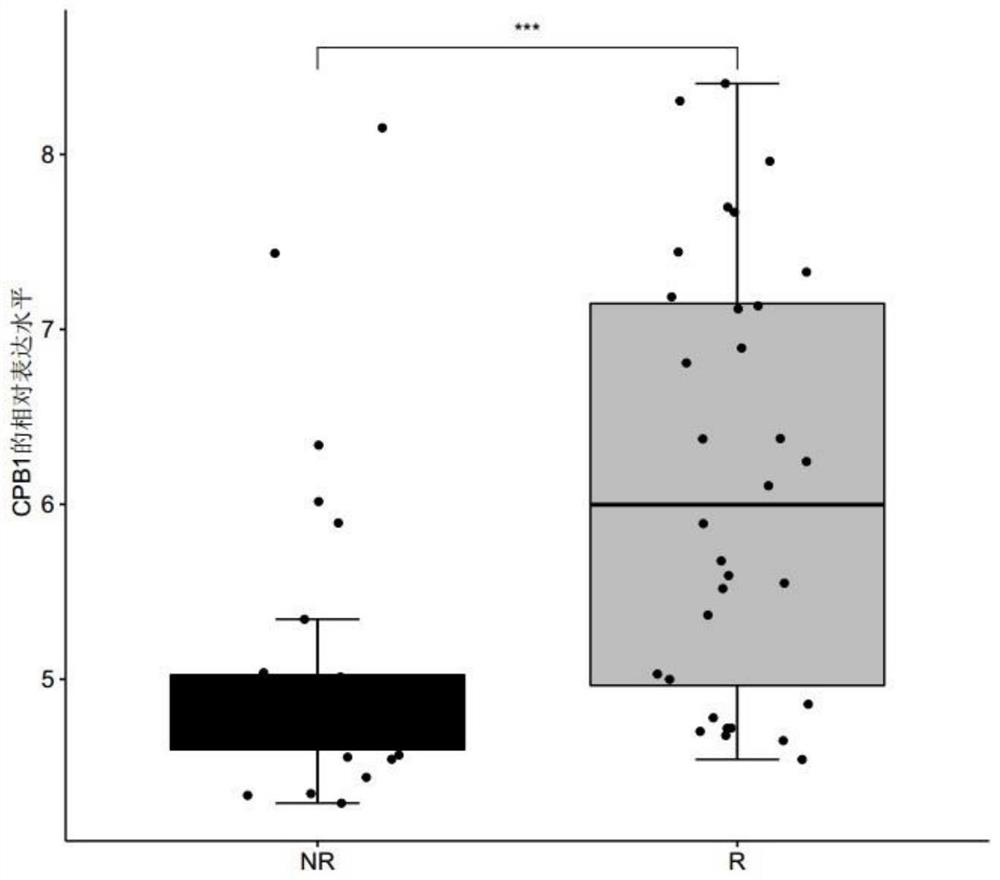
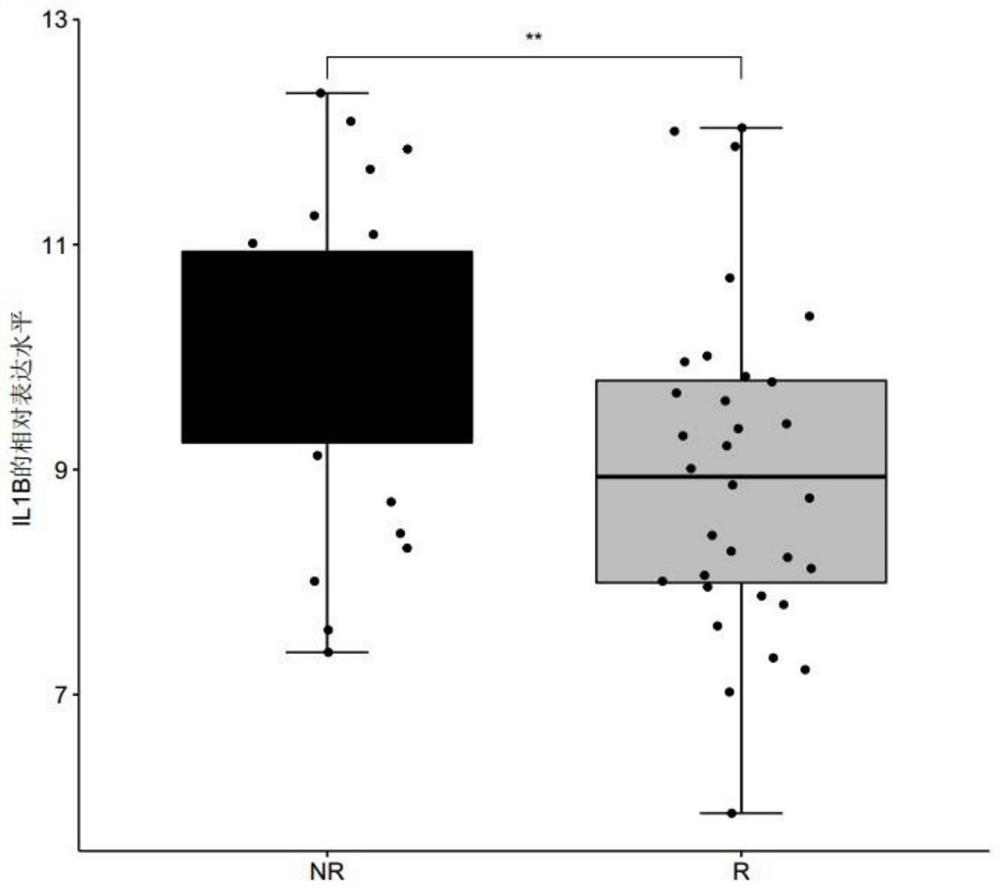
InactiveCN113999903AShort detection cycleImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAfter treatmentUlcerative colitis
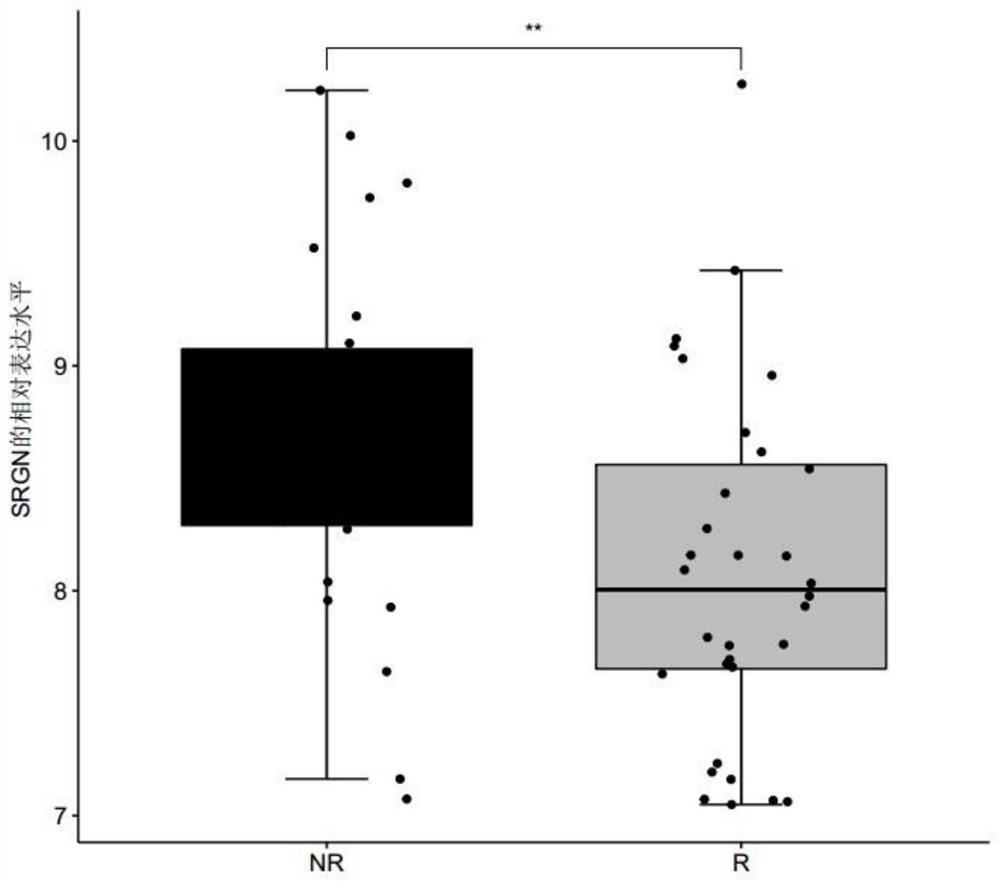
The invention discloses a polymolecular marker and a device for clinically evaluating the sensitivity of ulcerative colitis patients to golimumab, wherein the polymolecular marker comprises CPB1, IL1B and / or SRGN, and the accuracy of predicting the sensitivity of the ulcerative colitis patients to the golimumab is high; and the polymolecular marker can be used for monitoring the sensitivity of the ulcerative colitis patients to golimumab in real time before and after treatment, so that clinical doctors can conveniently adopt personalized treatment schemes in time, and blind medication is avoided.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Methods and compositions for identifying whether a subject suffering from a cancer will achieve a response with an immune-checkpoint inhibitor
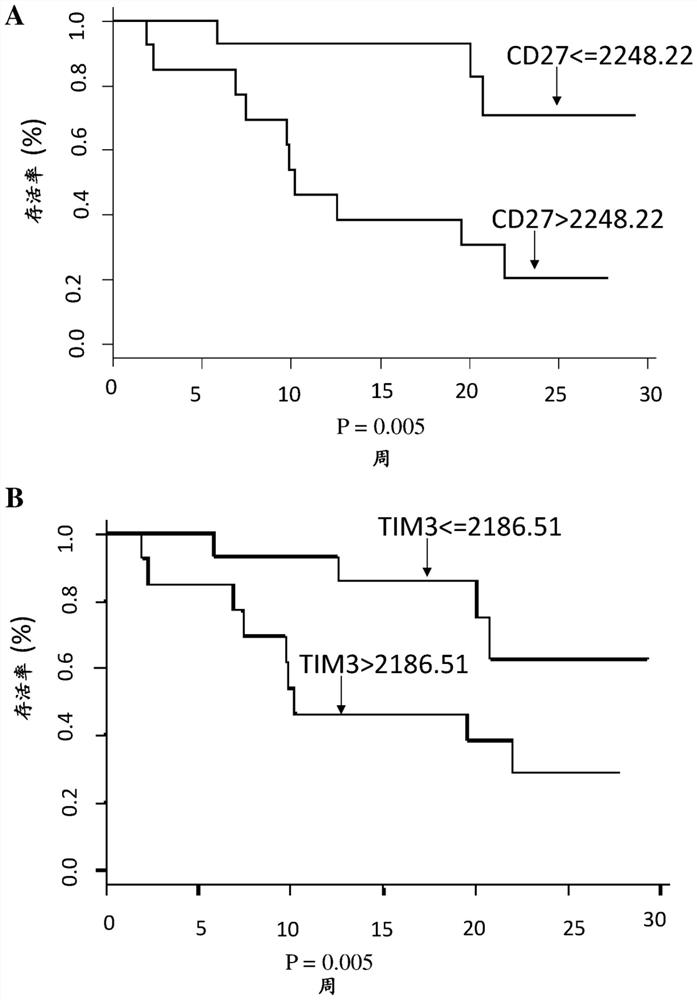
The present invention relates to use of soluble CD27 as a biomarker to predict the reponse to an immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. Inventors have worked with two cohorts of patients and have identified a soluble marker, CD27, present in the plasma of patients with renal cell cancer whose pre-treatment concentrations predict the response to anti-PD-1 / PD- L1. This marker appears more as a predictive marker of response to anti-PD1 / PD-L1 treatment, than as a prognostic marker. Indeed, it is not associated with better survival in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer treated with an antiangiogenic agent. This marker is not correlated with conventional clinical markers of severity that classify patients with metastatic renal cancer.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Use of human MIR135a-3p in preparation of preparations for diagnosing and treating prostate cancer
InactiveCN106367415AEasy to operateEasy to get materialsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHigh risk populationsProstate cancer
The invention belongs to the biotechnical field, and concretely relates to a new prostate cancer molecule marker microRNA 135a-3p (MIR135a-3p) and a use thereof in the preparation of preparations for diagnosing and treating the prostate cancer. The use comprises the following steps: screening prostate cancer high-risk populations, diagnosing the prostate cancer, designing prostate cancer drug target, monitoring the prostate cancer treatment condition, and carrying out prognosis detection on the prostate cancer. A method using the molecule marker and a diagnostic kit containing the molecule marker to diagnose the prostate cancer has the characteristics of simplicity in operation, convenience in material drawing, good safety, no wounds, high specificity, high sensitivity, and easiness in massive screening.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
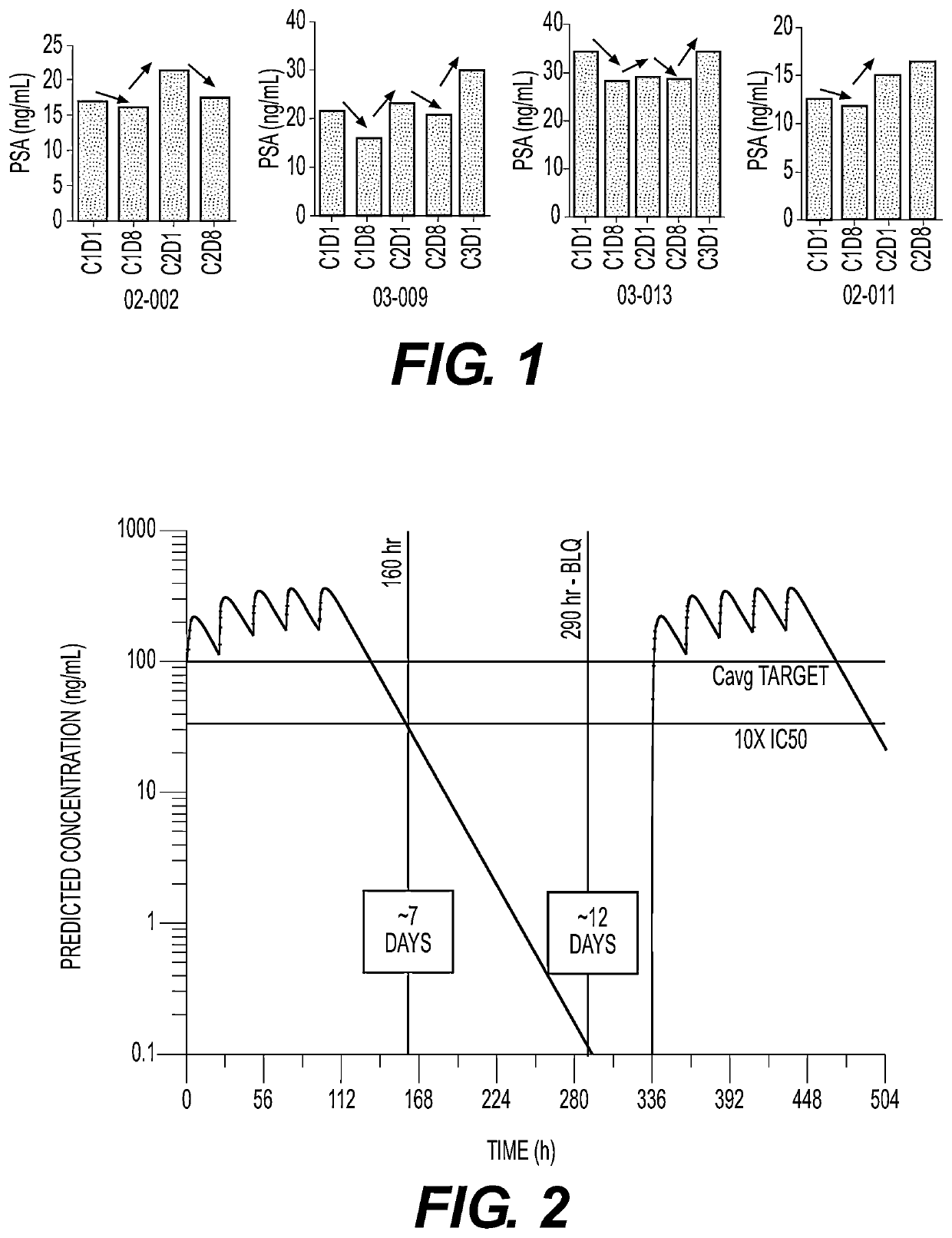
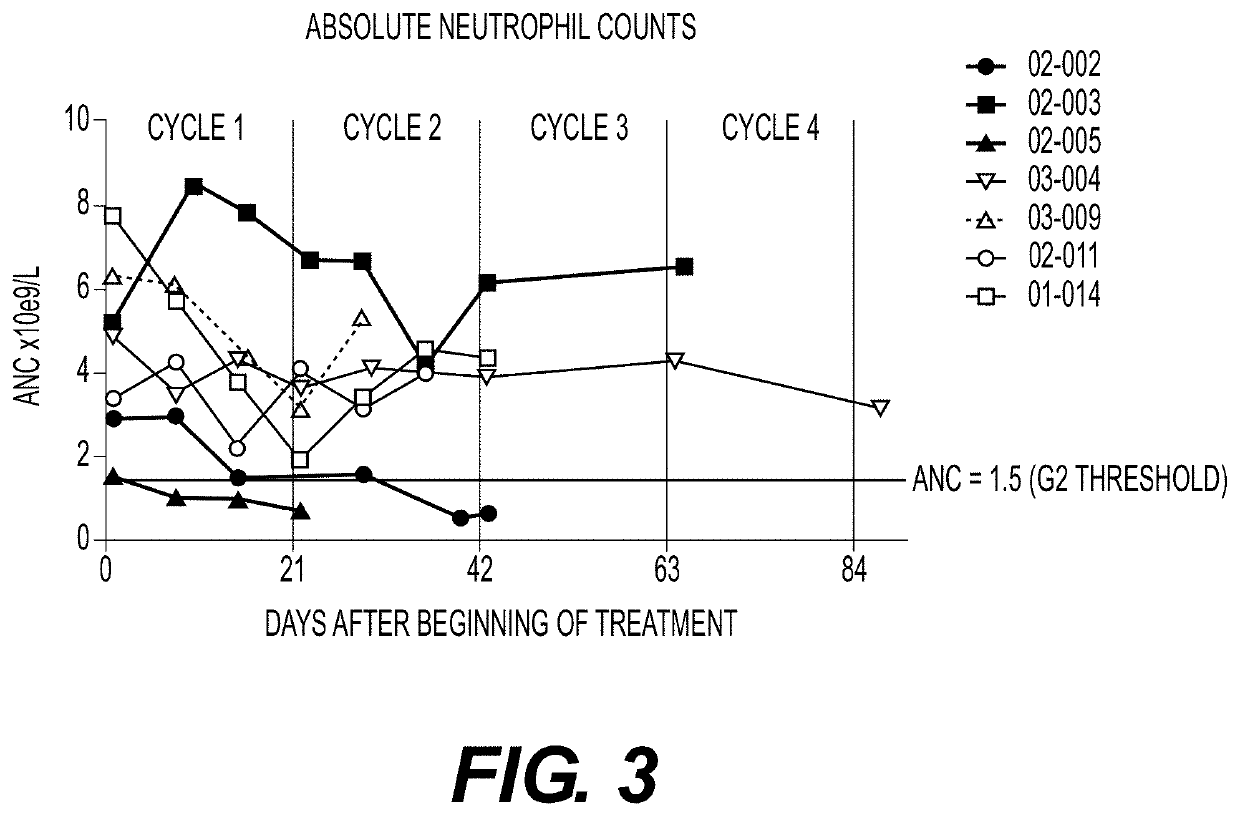
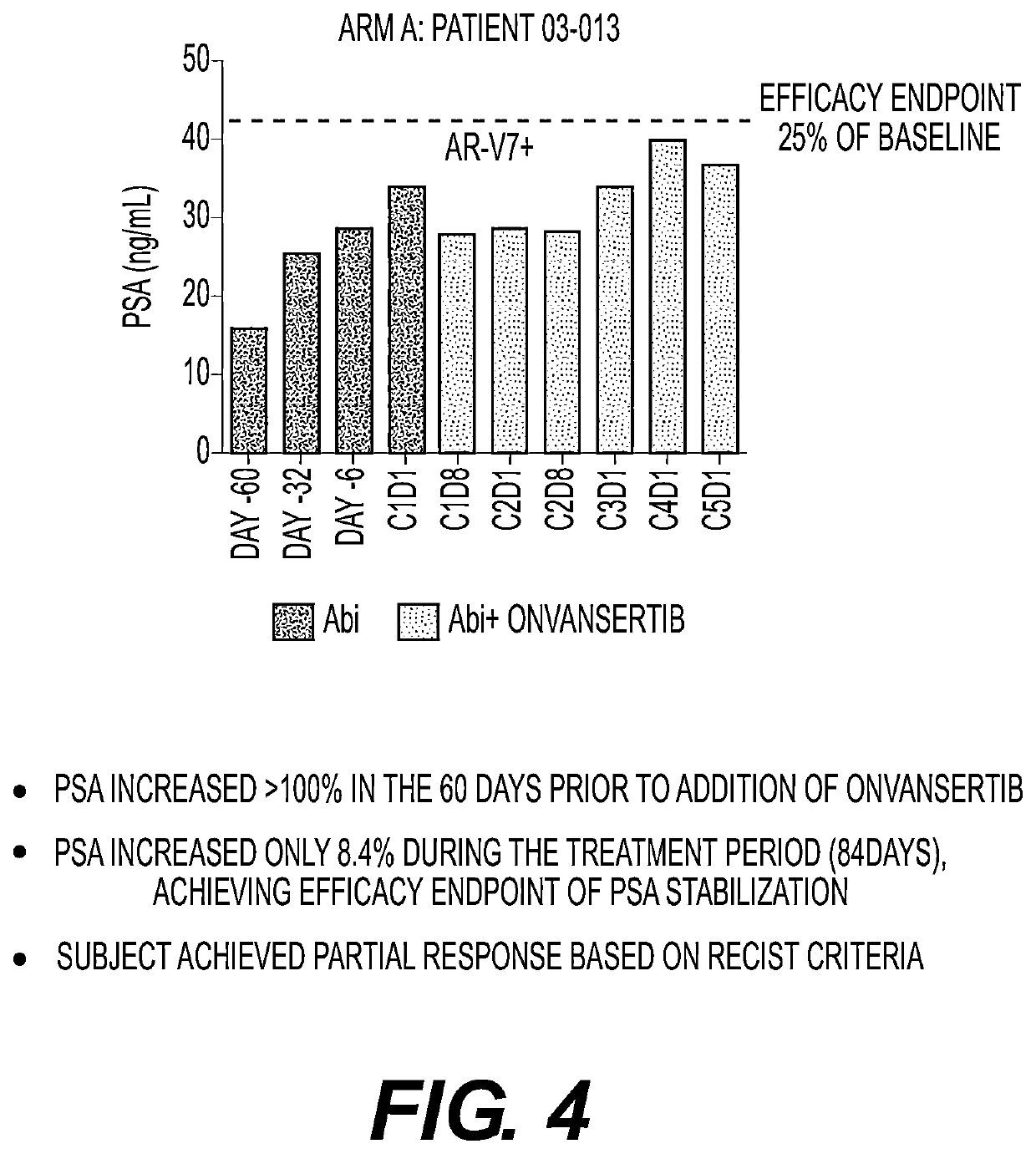
Plk1 inhibitors and psa levels in prostate cancer
Provided is a method comprising recommending treatment of a prostate cancer patient with a polo-like kinase-1 (PLK1) inhibitor if the patient has rising prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels.Also provided is a method comprisingmeasuring prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels in at least two samples from a prostate cancer patient, the samples obtained from the patient at different times; andrecommending treatment of the patient with a PLK1 inhibitor if the PSA levels in the samples increase over time, ornot recommending treatment of the patient with a PLK1 inhibitor if the PSA levels in the samples do not increase over time.Additionally provided is a method comprising recommending treatment of a PLK1 inhibitor to a patient having a prostate cancer that has an altered androgen receptor that does not require ligand for activation.
Owner:CARDIFF ONCOLOGY INC
Implantable Drug Delivery Devices for Localized Drug Delivery
ActiveUS20210290920A1Reduce and eliminate toxicityIncrease concentrationPowder deliverySurgical needlesDiseaseActive agent
Provided herein are drug implants comprising a therapeutically active agent for the treatment of disease in a subject. In some cases, the drug implant may comprise a polymer matrix and a therapeutically active agent disposed therein. Additionally provided are methods for manufacturing the drug implants and methods of treating diseases with the implants. In some cases, the drug implant may comprise bicalutamide, e.g., for use in the treatment of prostate cancer.
Owner:ALESSA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Diagnostic BioMarkers for Fibrotic Disorders
The present invention provides novel methods of inhibiting fibrosis, as well as methods of treating or inhibiting fibrotic disorders, using BMP9 and / or BMP10 antagonists. The present invention also provides methods of assessing whether a subject has or is at risk of developing a fibrotic disorder by detecting levels of BMP9 and / or BMP10. Further provided are methods of assessing the efficacy of a treatment regimen for treating a fibrotic disorder by detecting and comparing pre-treatment levels of BMP9 and BMP10 with post-treatment levels of BMP9 and BMP10.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com