Reciprocating side drive magnetic motor
A reciprocating, engine technology, applied in the direction of electromechanical devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of air leakage, high manufacturing accuracy, damage to the cylinder block, etc., and achieve the effect of simplifying the transmission structure and reducing the requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
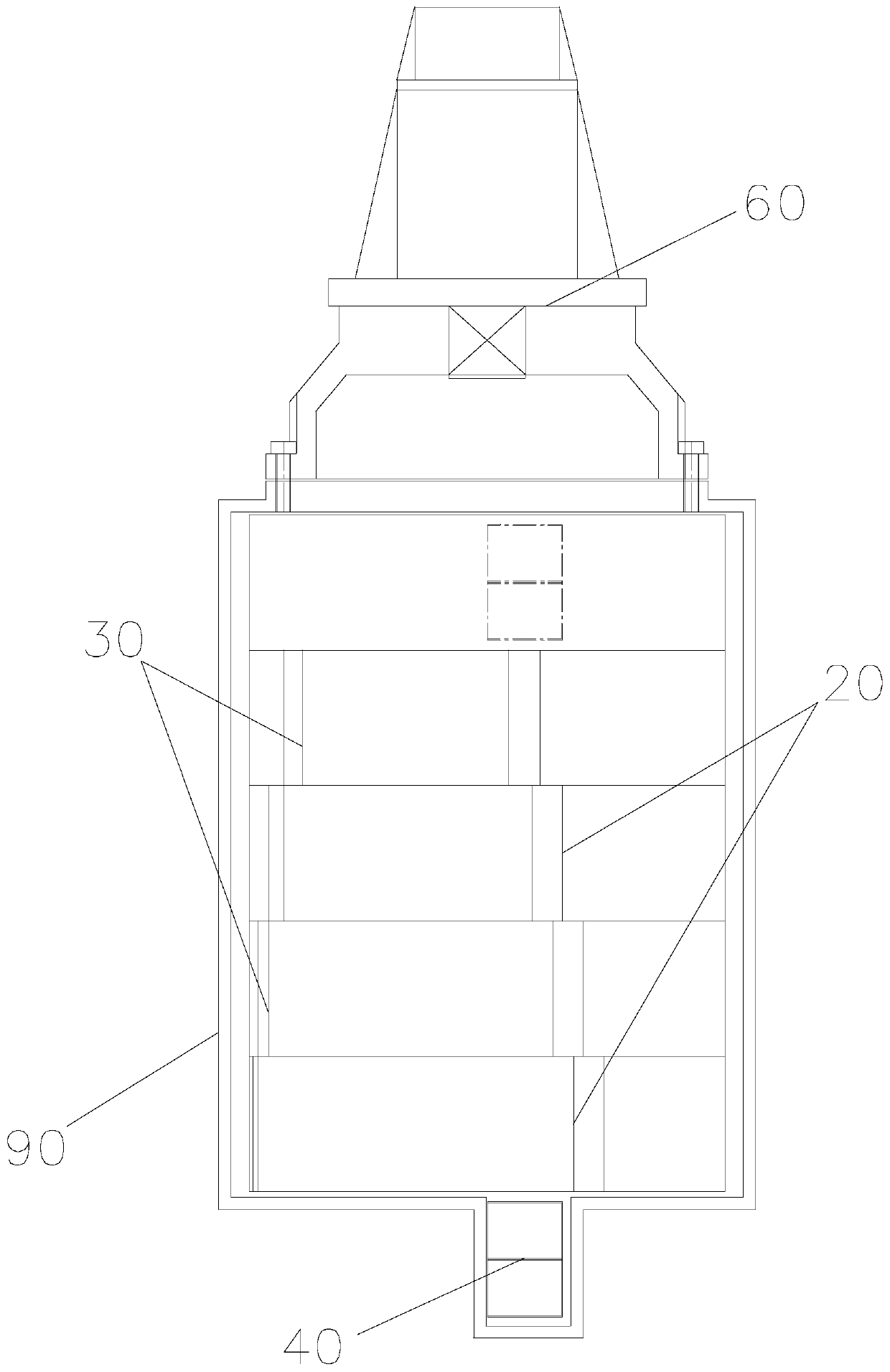
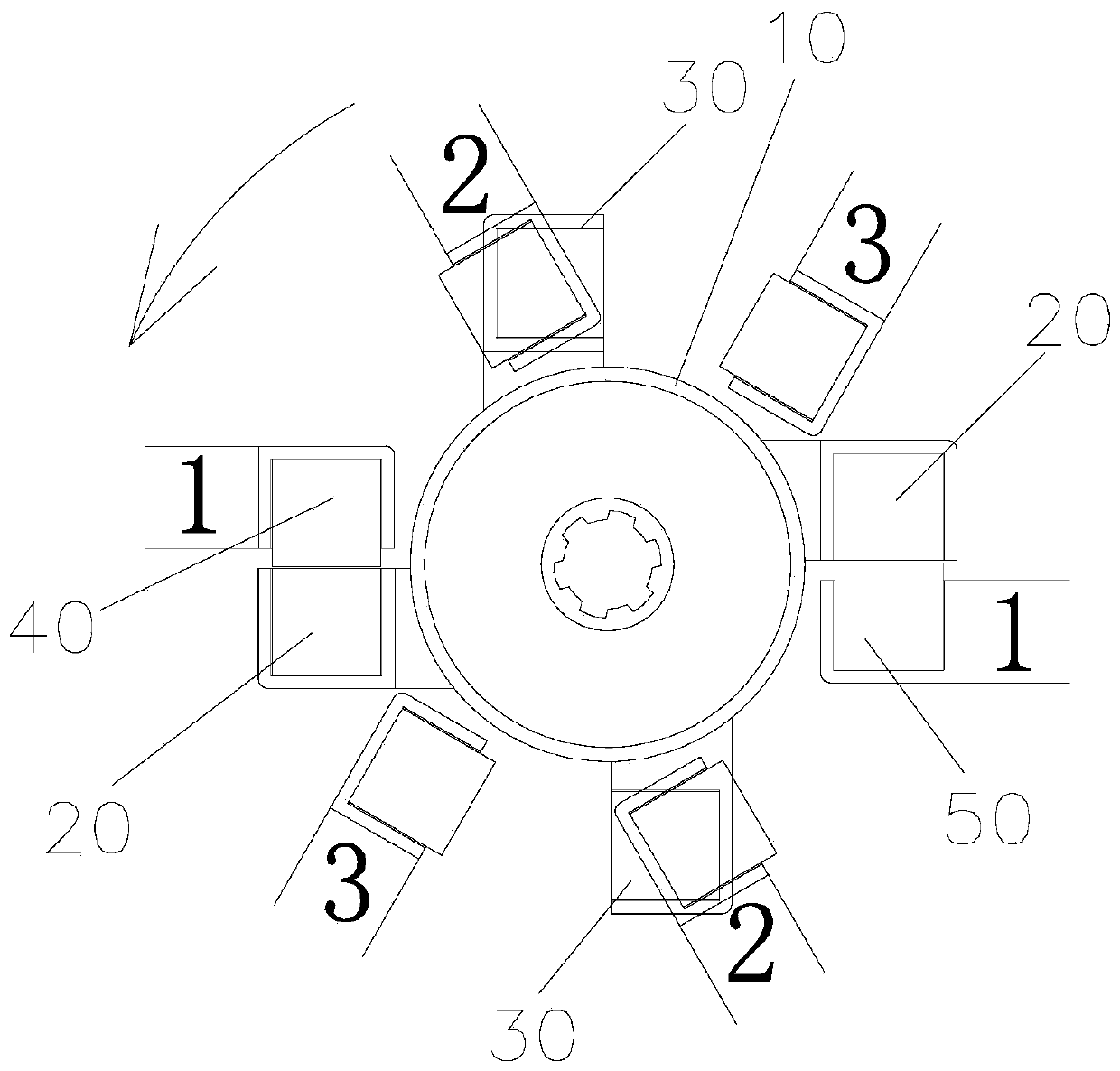
[0036] Such as figure 1 and figure 2As shown, the present embodiment provides a reciprocating edge-driven magnetic motor, which includes a housing and a rotating main shaft 10 with an inner radius r connected to the housing through bearings, and also includes two first internal magnets mounted on the side of the rotating main shaft 10 at equal angles. Bar 20, two second inner magnetic strips 30 installed at equal angles on the side of the rotating main shaft 10, three outer magnetic blocks 40, and a first driving part for driving the corresponding outer magnetic blocks 40 to reciprocate along the axis of the rotating main shaft 10; The upper surface of the first inner magnetic strip 20 and the upper surface of the second inner magnetic strip 30 are gradually rising step surfaces, the left end of the first inner magnetic strip 20 upper surface is lower than the right end, the second inner magnetic strip 30 upper surface The left end is higher than the right end, and the first...
Embodiment 2
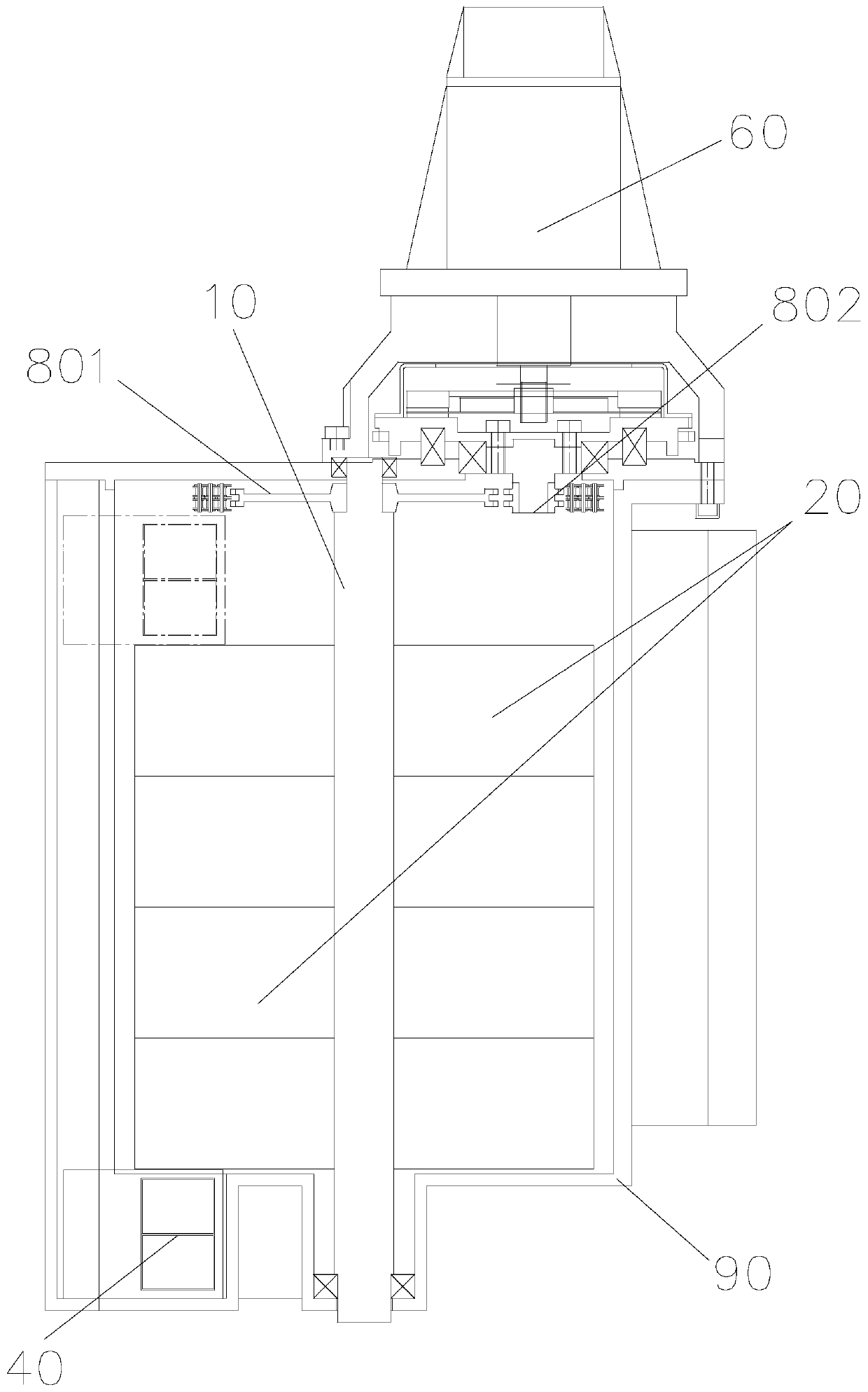
[0045] Such as Figure 13 and Figure 14 As shown, the structure of the reciprocating edge-driven magnetic motor of this embodiment is similar to that of Embodiment 1, the only difference being that the upper surface of the first inner magnetic strip 20 and the upper surface of the second inner magnetic strip 30 in this embodiment are gradually raised During the movement of the outer magnetic block 40, the rotating main shaft 10 rotates continuously and stably. When the repulsive force is constant, the rotation angle of the rotating main shaft 10 is constant for the unit distance of the outer magnetic block 40 movement. The first driving part includes a rotary servo motor mounted on the casing, a first driving sprocket 701 coaxially mounted on the output shaft of the rotary servo motor, a first driven sprocket 702 rotatably mounted on the casing, and used to realize the first driving sprocket. The first transmission chain 703 of sprocket wheel 701 and first driven sprocket 70...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Such as Figure 15 As shown, the structure of Embodiment 3 is similar to that of Embodiment 1, except that the angle between the lower surfaces of two adjacent outer magnetic blocks 40 is 30°, and each outer magnetic block 40 is located on the left side of the end surface of the rotating spindle 10 .
[0048] Embodiment 1 Compared with Embodiment 3, Embodiment 1 moves each outer magnetic block 40 once to drive the rotating spindle 10 to rotate 30°, compensating the angle between adjacent outer magnetic blocks 40 and the adjacent corresponding inner magnetic strips The angle difference between the included angles makes the adjacent outer magnetic blocks 40 align with the corresponding inner magnetic strips at the other end of the rotating main shaft 10 to realize continuous driving, and the outer magnetic blocks 40 are alternately distributed at the two ends of the rotating main shaft 10 , and the angle between them is relatively large, which is convenient for the full u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com