A Path Planning Method Based on Nondisplay Topological Vector Map
A technology of vector map and path planning, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, road network navigators, navigation, etc., and can solve problems such as application difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The technical solutions of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
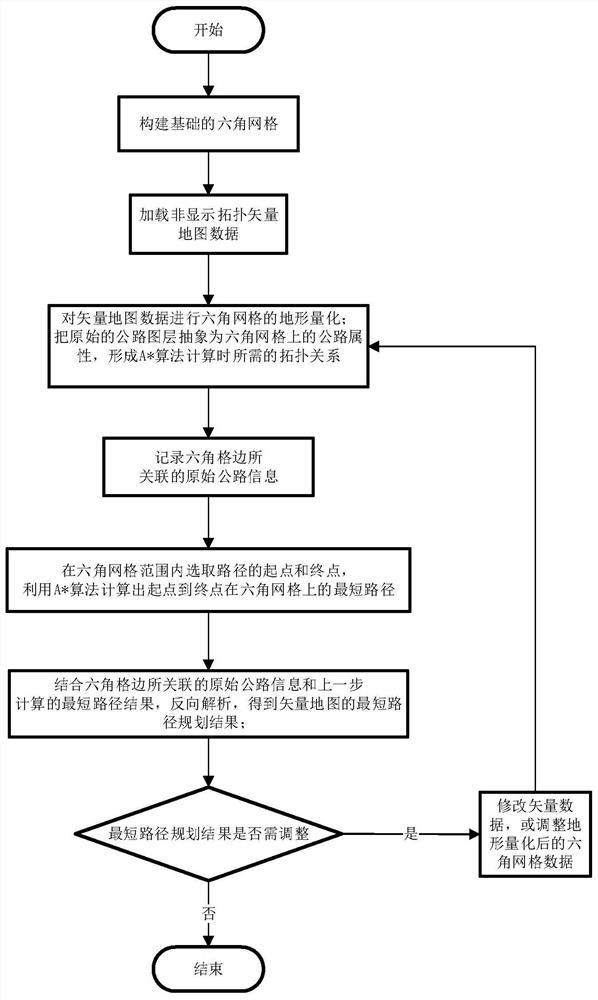
[0045] See figure 1 , which shows a flow chart of a method for path planning based on a non-display topology vector map according to the present invention, the method includes the following steps:
[0046] Step 1: Build the base hex grid:
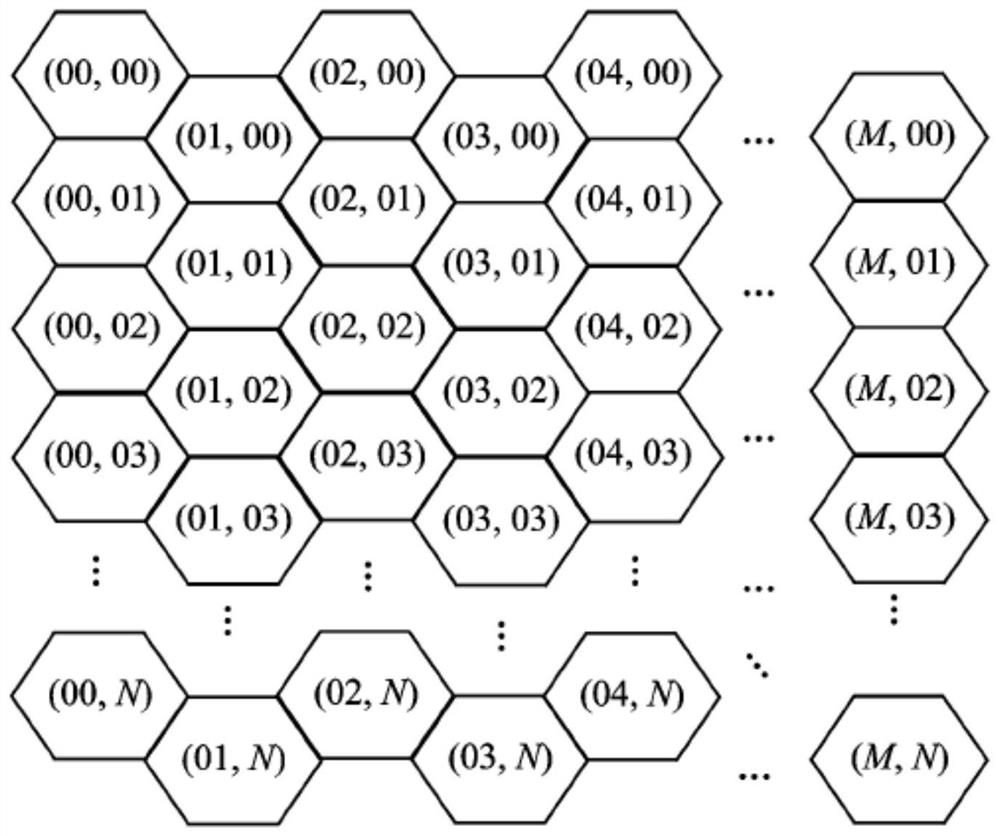
[0047] Define a hexagonal grid numbering scheme, such as figure 2 As shown, the abscissa M and the ordinate N represent the column index and row index in the hexagonal grid, respectively;
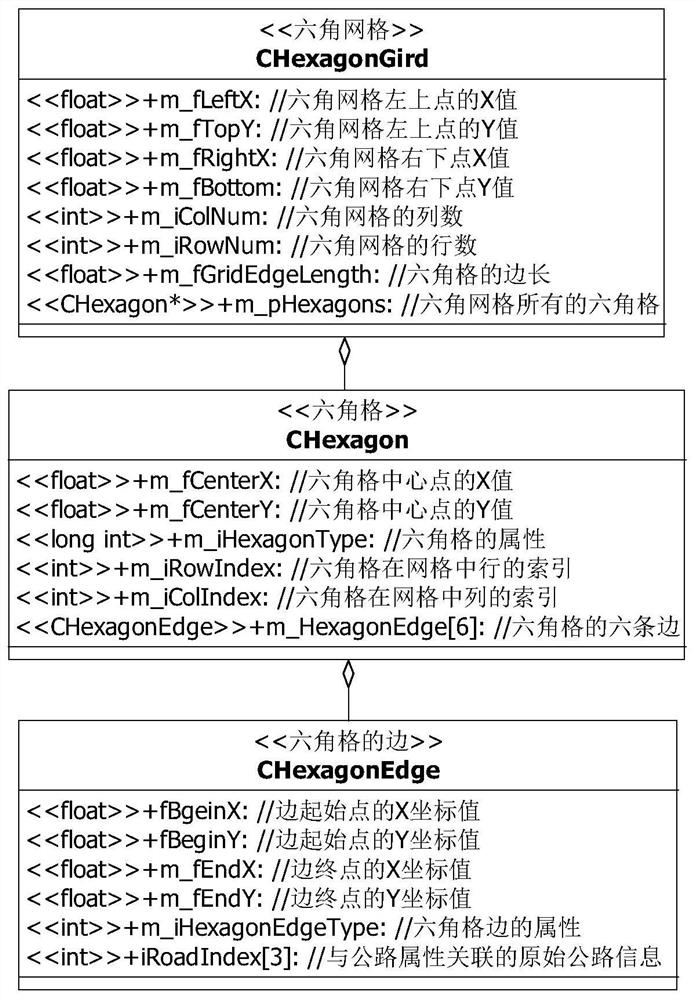
[0048] According to actual data, such as: path planning range, original vector road layer data (such as Image 6 shown), the speed of the vehicle on different terrains and roads of different grades, set the size of the hexagonal grid, and establish the hexagonal grid model (such as Figure 7 shown), and build a data structure, wherein the unit of the hexagonal grid is an adjacent spliced hexagonal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com