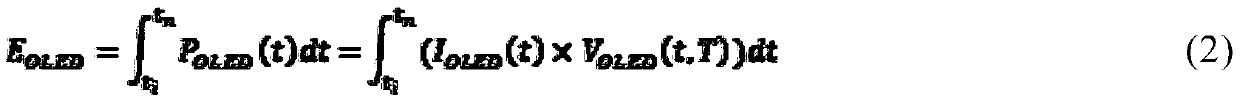Compensation systems and methods for display OLED degradation
A technology of emissive display and memory, applied in the field of image correction, which can solve the problems of uneven brightness, chemical properties and performance, brightness difference, aging, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
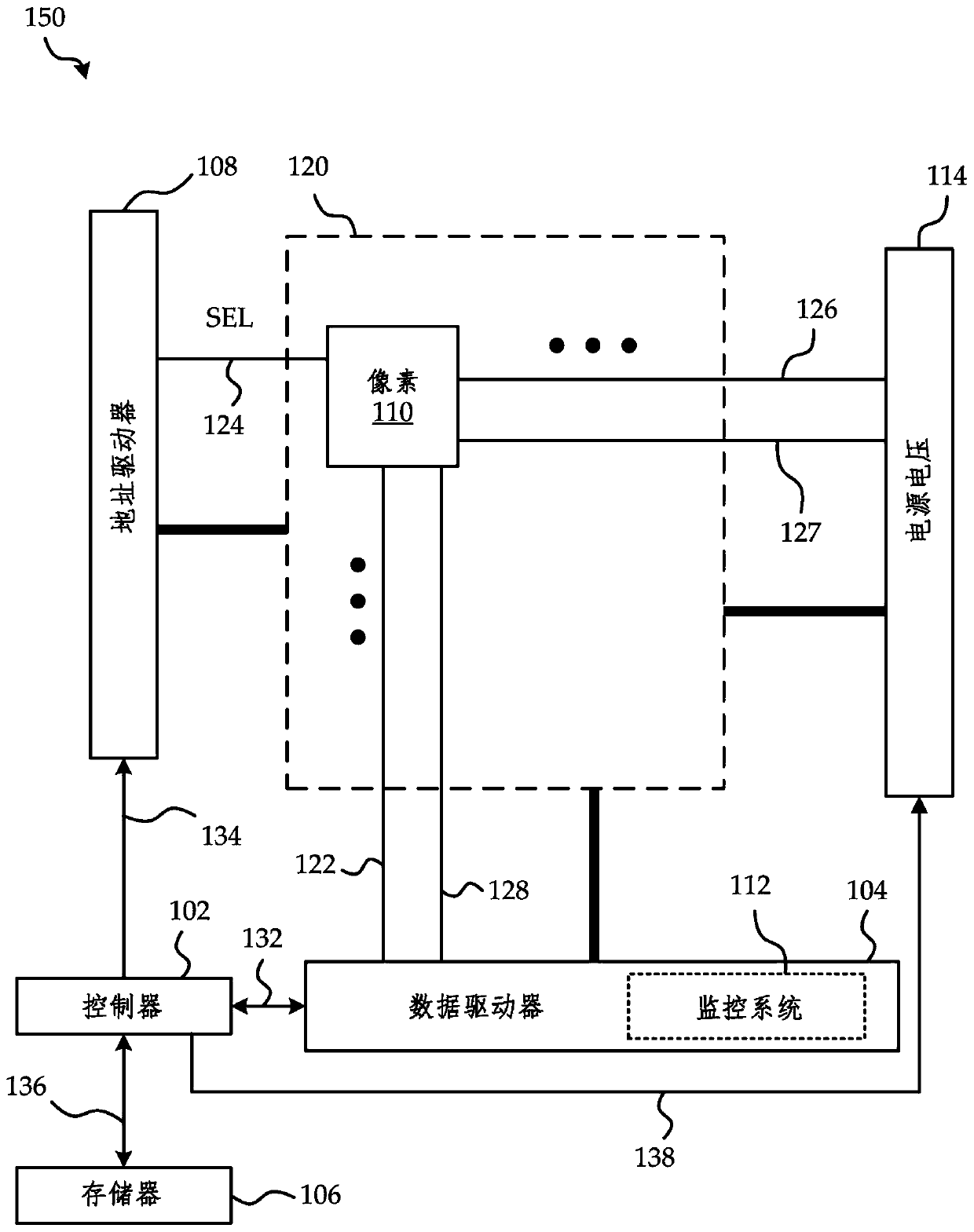
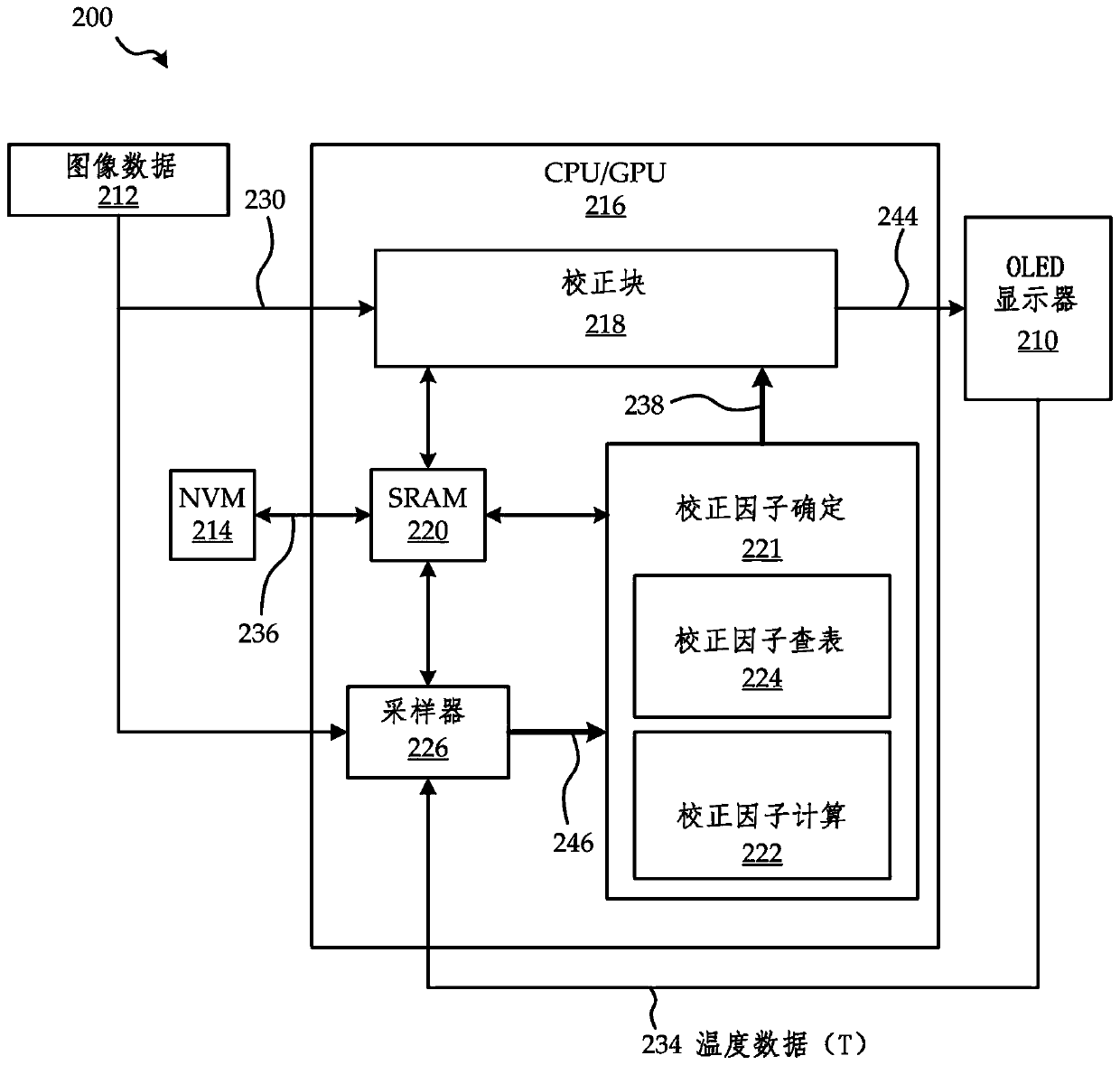
[0024] To facilitate image correction, methods such as In-Pixel Compensation (IPC) or electrical measurements or a combination of IPC compensation and electrical measurements may also be used to obtain correction data for a particular display after singulation. The correction data is then stored on non-volatile memory (NVM) chips inside the display system and final product as initial correction data for subsequent processing and updating when further degradation occurs.
[0025] Although the embodiments described herein are in the context of AMOLED displays, it should be understood that the degradation correction systems and methods described herein are applicable to any other display that includes pixels that experience degradation similar to OLEDs described below.
[0026] It should be understood that the embodiments described herein relate to systems and methods of image correction and degradation compensation, and do not limit the operation of the display technologies under...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com