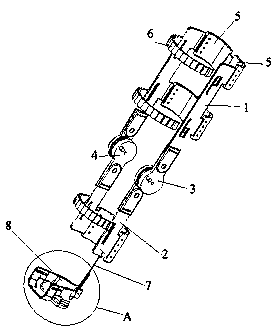
Driven type lower limb motion force assisting exoskeleton device
A passive, exoskeleton technology, applied in manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the tension spring force of the steel wire rope, breaking the wire rope, increasing exercise load and discomfort, and achieving the effect of avoiding friction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
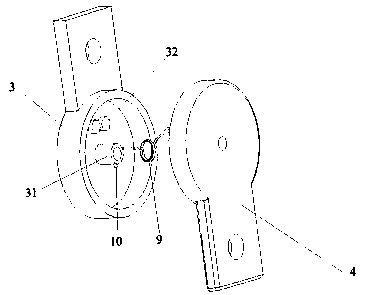
[0052] as attached image 3 And attached Figure 4 As shown, in this embodiment, there is one torsion spring 9, and the torsion spring 9 is sleeved on the first protrusion 31, and one end of the torsion spring 9 is fixed on the thigh connecting plate 3 as a fixed end, and the other end of the torsion spring 9 As a movable end, a first limit protrusion 11 is provided on the shank connection plate 4, and the movable end of the torsion spring 9 is aligned with the first limit protrusion when the relative rotation angle of the thigh connection plate 3 and the shank connection plate 4 reaches a set value. From 11 to offset.
[0053] In this way, the torsion spring 9 is sleeved on the first protrusion 31, and one end of the torsion spring 9 is fixed on the thigh connection plate 3. When the human leg is bent, the first protrusion 31 on the thigh connection plate 3 drives the torsion spring 9 rotates around the shank connection plate 4, when the relative rotation angle of the thigh...
Embodiment 2
[0067] The difference between embodiment two and embodiment one is:
[0068] as attached Figure 5 And attached Figure 6 As shown, in the present embodiment, there is one torsion spring 9, and the torsion spring 9 is sleeved on the second protrusion 41, and one end of the torsion spring 9 is fixed on the shank connecting plate 4 as a fixed end, and the other end of the torsion spring 9 As a movable end, a second position-limiting protrusion 12 is provided on the thigh connection plate 3, and the movable end of the torsion spring 9 is aligned with the second position-limiting protrusion when the relative rotation angle of the thigh connection plate 3 and the shank connection plate 4 reaches a set value. From 12 to offset.
[0069] In this way, the torsion spring 9 is sleeved on the second protrusion 41, and one end of the torsion spring 9 is fixed on the shank connection plate 4. When the human leg is bent, the second protrusion 41 on the shank connection plate 4 drives the ...
Embodiment 3
[0075] The difference between embodiment three and embodiment one is:
[0076] as attached Figure 7 And attached Figure 8 As shown, in this embodiment, there are two torsion springs 9, and the two torsion springs 9 are respectively sleeved on the first protrusion 31 and the second protrusion 41, and the lower leg connection plate 4 is provided with a first stop protrusion. 11, the thigh connection plate 3 is provided with a second limit protrusion 12, and one end of the torsion spring 9 sleeved on the first protrusion 31 is fixed on the thigh connection plate 3 as a fixed end, and is sleeved on the first protrusion 31. The other end of the torsion spring 9 on the lifter 31 is used as a movable end when the relative rotation angle of the thigh connection plate 3 and the shank connection plate 4 reaches a set value, and the first stop protrusion 11 is offset;
[0077] One end of the torsion spring 9 sleeved on the second protrusion 41 is fixed on the shank connection plate 4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com