A method, system and sampling device for automatic detection of zero-crossing point of fundamental wave voltage
A technology of zero-crossing voltage and fundamental wave voltage, which is applied in measuring devices, measuring current/voltage, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve problems such as complex circuits and poor anti-interference, and achieve low hardware cost, high precision, and improved accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
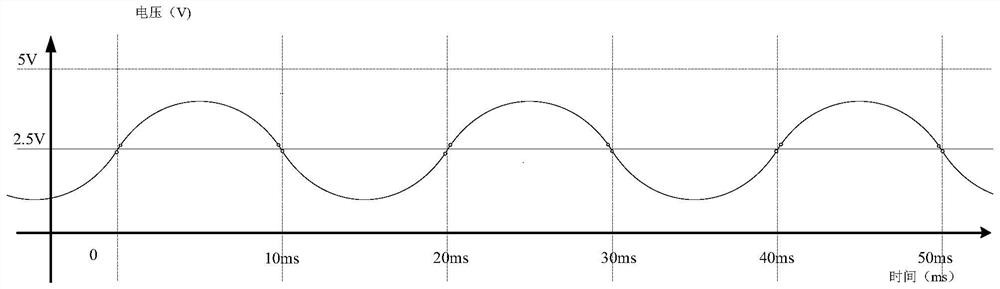
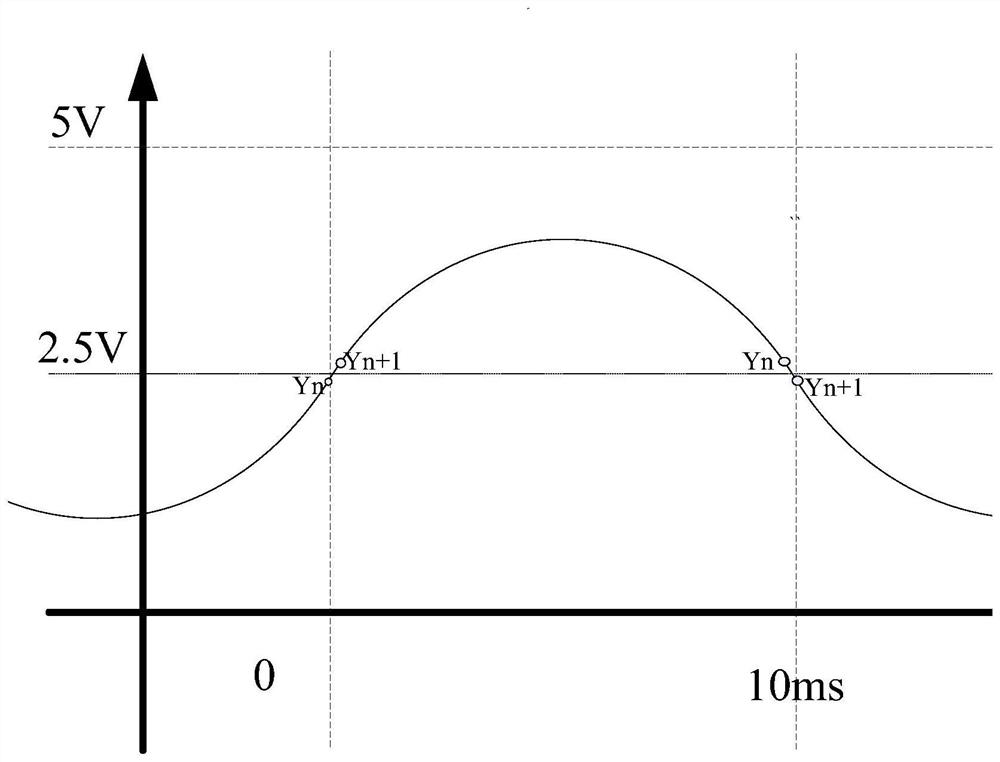
[0120] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 It is a standard 50Hz voltage sampling waveform diagram, and there are front and rear sampling points at the zero crossing point of the waveform. Such as figure 2 Shown is an enlarged view of the front and rear sampling points at the zero crossing point of the waveform, and the sampling numbers are Xn, Xn+1;
[0121] Embodiment 1 is used to calculate the zero-crossing point under the following conditions: the fundamental wave voltage sine wave zero-crossing point; after the fundamental wave voltage sine wave superimposes the notch wave, its positive zero-crossing point and reverse zero-crossing point quantity in the sampling period are the same as the fundamental wave sine wave The same; after the fundamental sine wave is superimposed with harmonics, the number of positive zero-crossing points and reverse zero-crossing points in the sampling period is the same as that of the fundamental sine wave.
[0122] Step 1: Based on Figure 9 It can ...
Embodiment 2
[0147] Embodiment 2 is the same as step 1-step 5 of embodiment 1, and step 6 is changed.
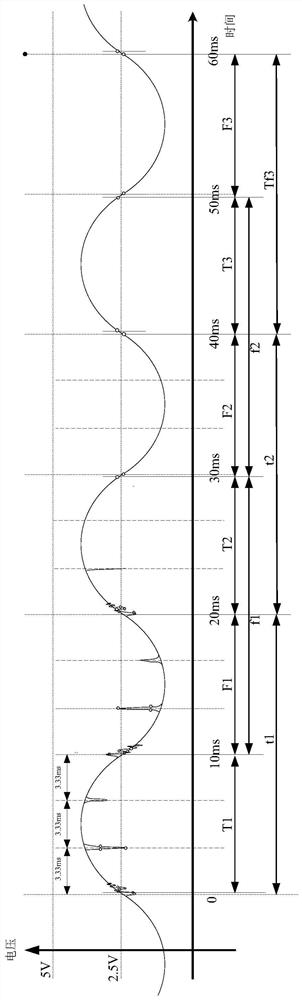
[0148] Such as image 3 The waveform diagram of the three cycles after superimposing the notch wave for the 50Hz fundamental voltage sine wave.
[0149] t1~t3: From the zero point of the positive half cycle of the previous fundamental voltage sine wave or notch wave zero point at the zero point of the positive half cycle of the fundamental voltage sine wave to the next zero point of the positive half cycle of the fundamental voltage sine wave or the fundamental voltage sine wave The time period of the notch zero crossing at the positive half cycle zero crossing.
[0150] f1~f3: From the zero point of the negative half cycle of the previous fundamental voltage sine wave or the notch zero point at the zero point of the negative half cycle of the fundamental voltage sine wave to the next zero point of the negative half cycle of the fundamental voltage sine wave or the fundamental voltage s...
Embodiment 3
[0168] Such as Figure 7 It is the three-period waveform diagram after the 50Hz fundamental voltage sine wave superimposes harmonics, and the zero-crossing sampling point is marked.
[0169] When the 50Hz fundamental voltage sine wave is superimposed with harmonics, the number of forward voltage zero-crossing point arrays and reverse voltage zero-crossing point arrays within the sampling period is the same as that of the fundamental voltage sine wave using the method in Embodiment 1 for calculation.
[0170] This embodiment is used to calculate the case where the number of forward voltage zero-crossing point arrays and reverse voltage zero-crossing point arrays within the sampling period after the 50Hz fundamental voltage sine wave is superimposed with harmonics is greater than that of the fundamental voltage sine wave.
[0171] t1~t3: the time period from the harmonic zero-crossing point at the zero-crossing point of the positive half cycle of the previous 50Hz fundamental wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com