MMC capacitor voltage-sharing strategy with low switching frequency and complexity
A switching frequency, capacitor voltage equalization technology, applied in the power field, can solve the problems of high switching loss of the converter valve, difficult to meet engineering requirements, difficult to dissipate heat of switching devices, etc. high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
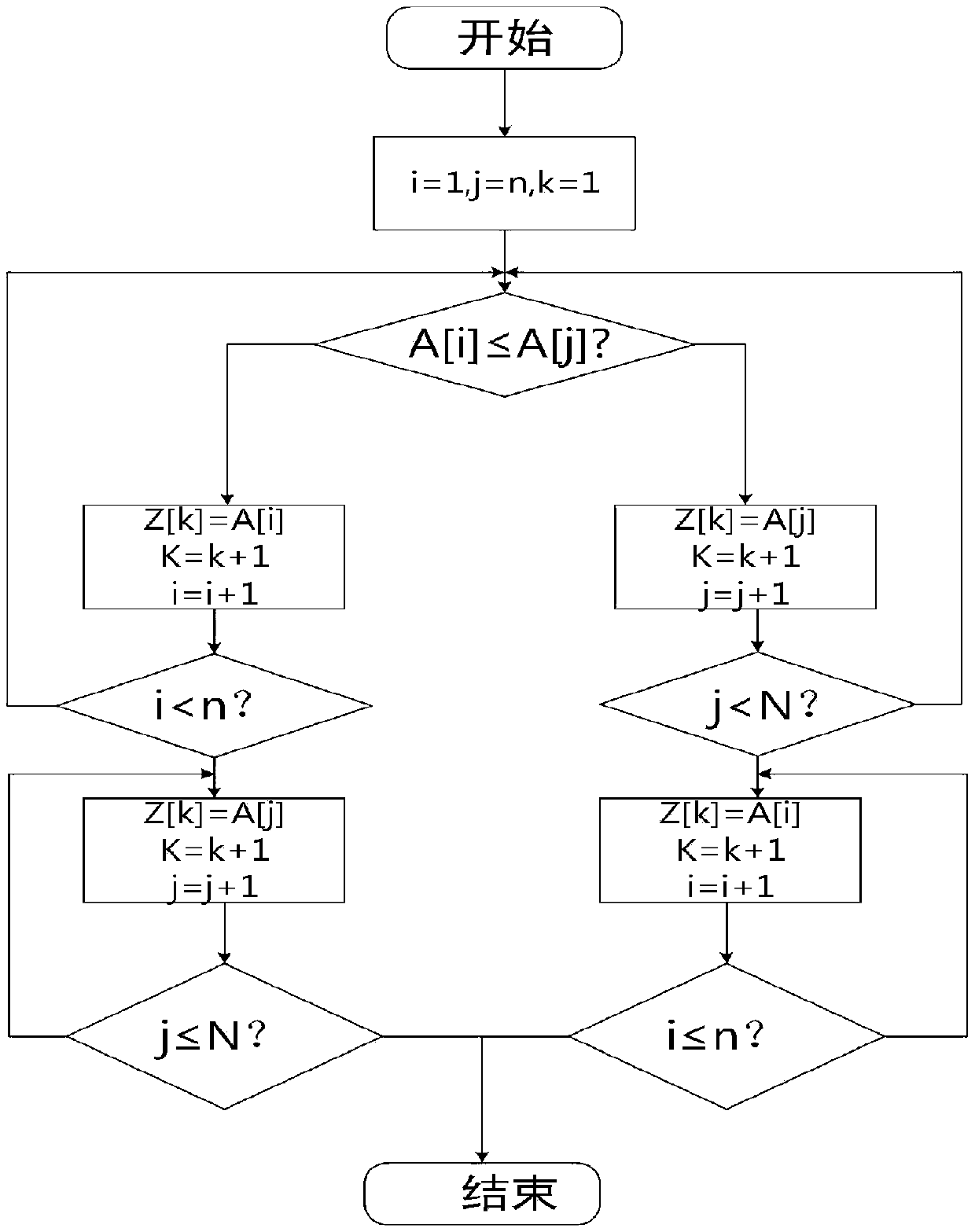
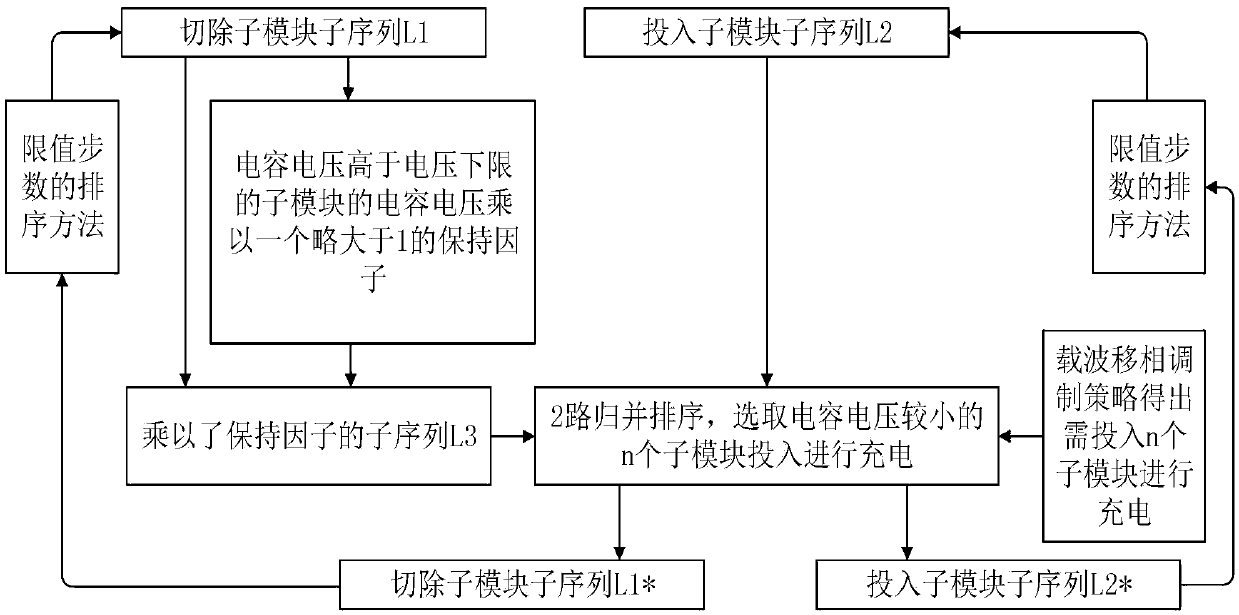
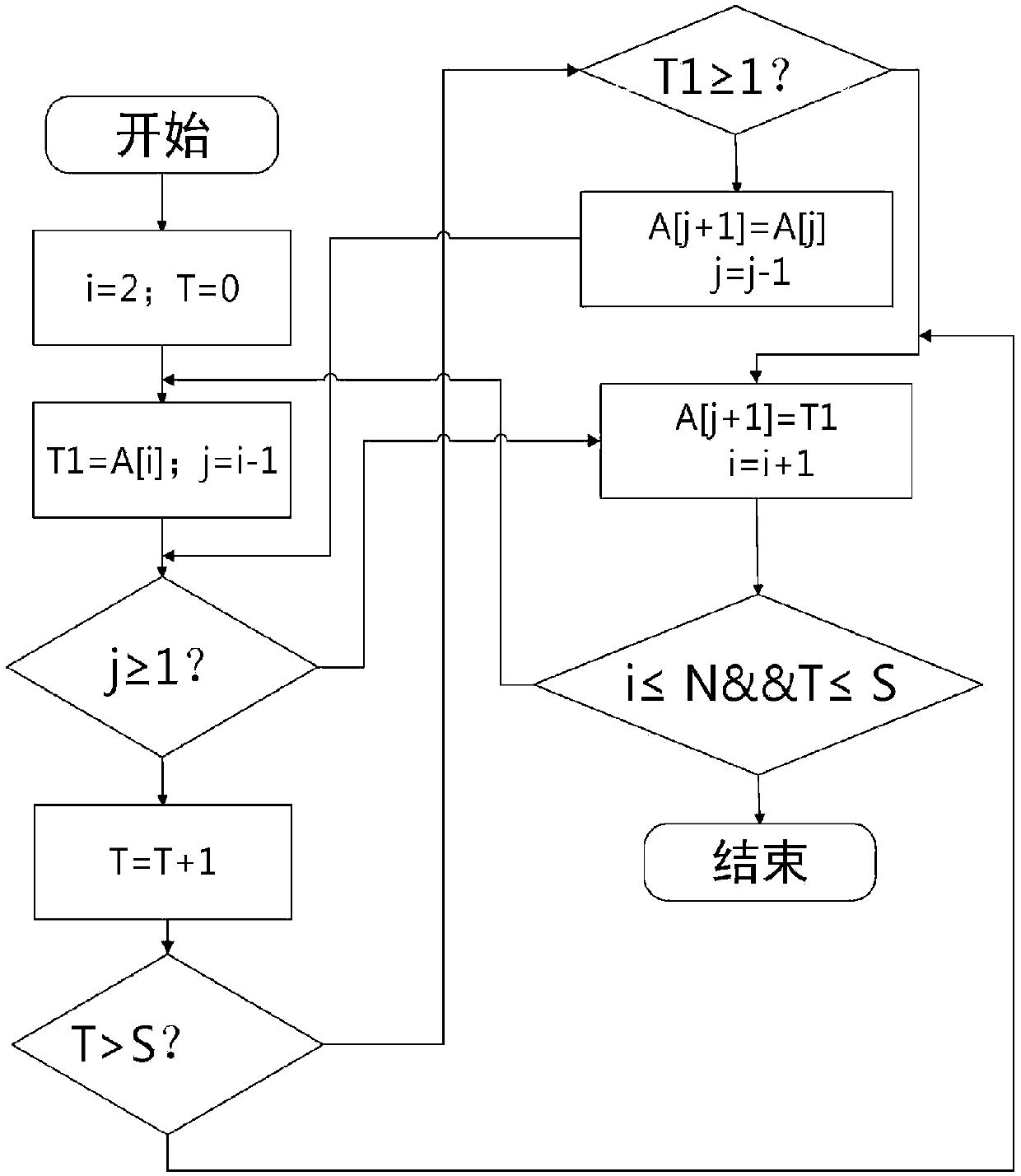
[0021] In order to facilitate a better understanding of the content of the solution of the present invention, the solution of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific examples. figure 1 It is the flow chart of the MMC capacitor voltage equalization strategy provided by the present invention (putting into charging), and the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0022] Step S1: Quickly monitor the capacitor voltage value of each sub-module in the bridge arm, compare it with the initially set upper and lower limits of the sub-module voltage, and calculate the maximum difference ΔU between the sub-module capacitor voltages Cmax For determining the number of steps S in step S3;
[0023] Step S2: Determine the number of sub-modules to be put in and out, monitor the current direction of each bridge arm, and determine the charging and discharging of the sub-modules in the bridge arm;
[0024] Step S3: Considering that in one cycle, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com