Time-division double-time-slot scheduling method for large-span space-based data link
A scheduling method and time-division duplex technology, applied in duplex signal operations, digital transmission systems, radio transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of large distance changes between nodes, increased access difficulty, and large propagation delay, etc. Achieve the effect of shortening idle time, improving network capacity, and improving channel utilization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
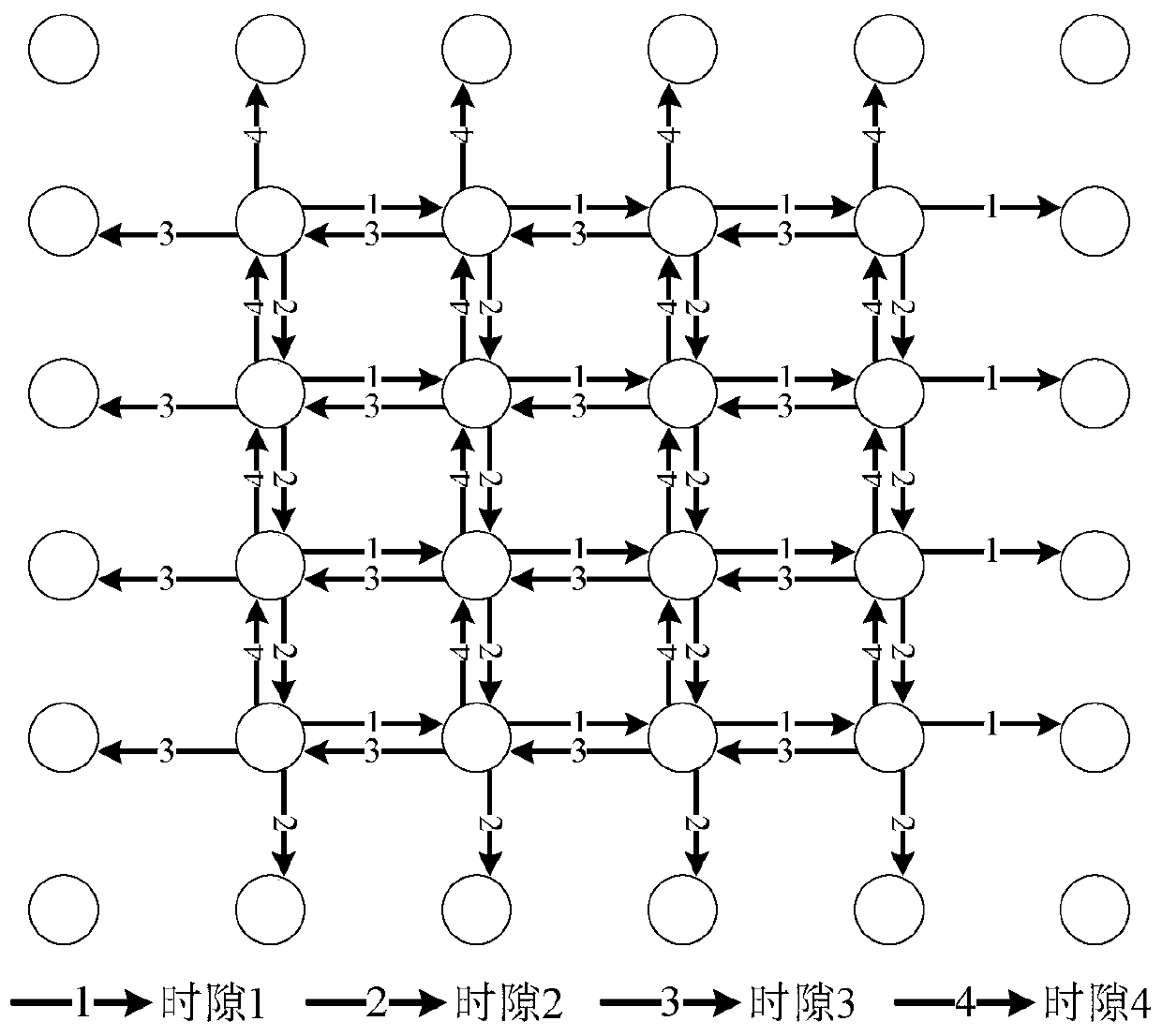
[0031] refer to figure 2 . The antennas of each node start from the right in a clockwise direction, and the right, rear, left, and front antenna switching sequences occupy a time slot and send signals in turn. Lines with the same serial number represent links that can multiplex the same time slot for communication. right way. Since satellite nodes are far away from each other, generally the effective communication distance of each satellite is one hop, so the interference to satellite nodes beyond one hop can be ignored; and the satellite is equipped with a directional antenna, so in practice, Each satellite can only communicate with its 4 neighbor satellites in front, back, left and right. At this time, using the spatial multiplexing of the directional narrow beam antenna, nodes in other directions can use different areas to transmit data packets at the same time without interfering with each other, so the number of time slots can be greatly saved. Therefore, in an option...
Embodiment 2
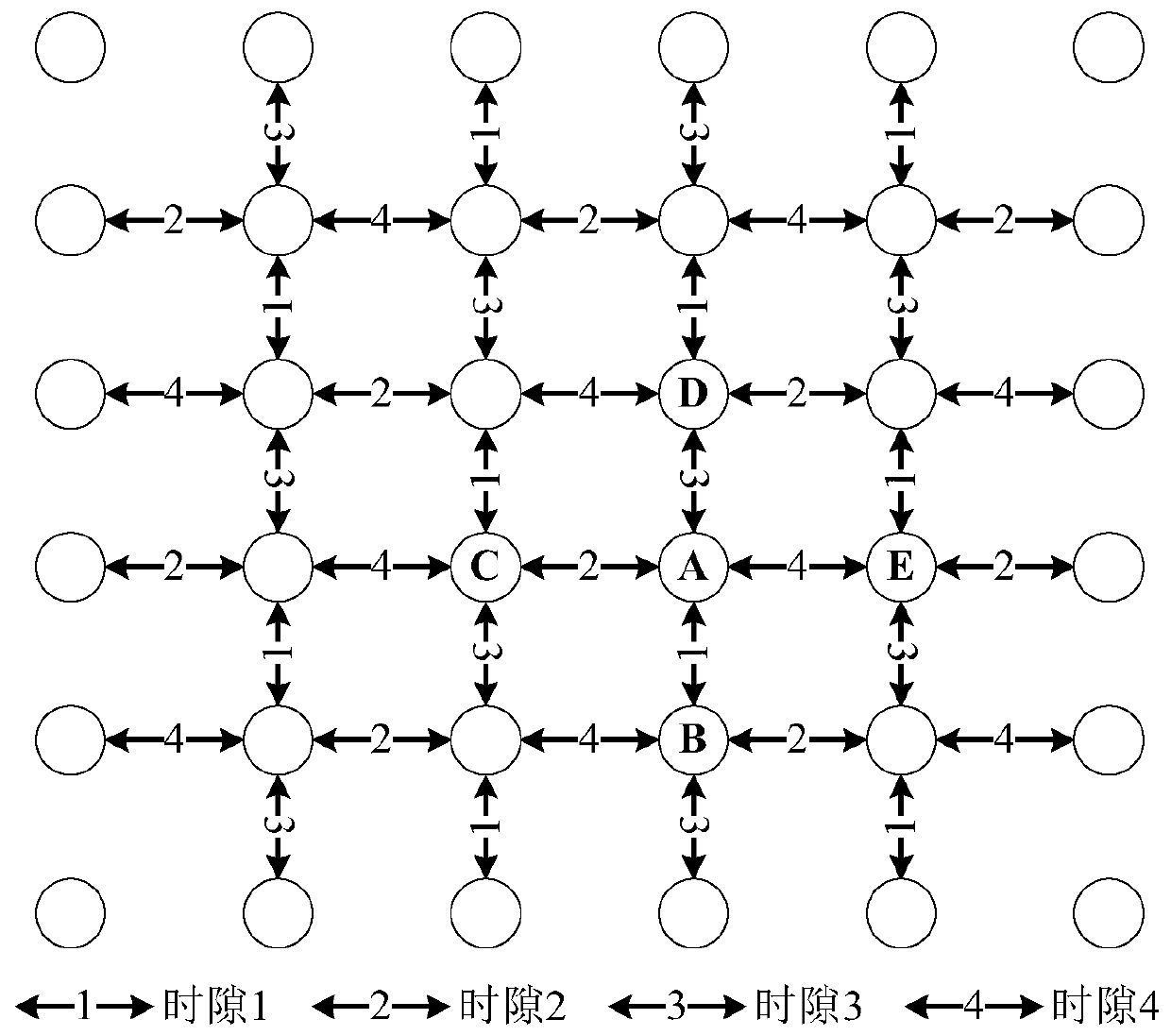
[0033] refer to image 3 . Satellites are used to communicate with front and back satellites on the same orbit, and adjacent satellites on adjacent orbits. Each satellite node can only communicate with its front, back, left, and right four one-hop neighbor satellite nodes B, C, D, and E; B, C, D, and E are one-hop neighbor nodes that node A can communicate with, node B is behind node A, node C is on the left of node A, node D is in front of node A, node E is on the right of node A Square, the nodes in odd columns and rows and the nodes in even columns and rows behind, left, front and right each take a time slot to send signals in turn; the nodes in odd columns and rows and the nodes in even columns and odd rows The front, right, rear, and left antenna switching sequences of the nodes each occupy a time slot to send signals in turn; lines with the same serial number represent link pairs that can multiplex the same time slot for communication. Simultaneously transmit data pack...
Embodiment 3
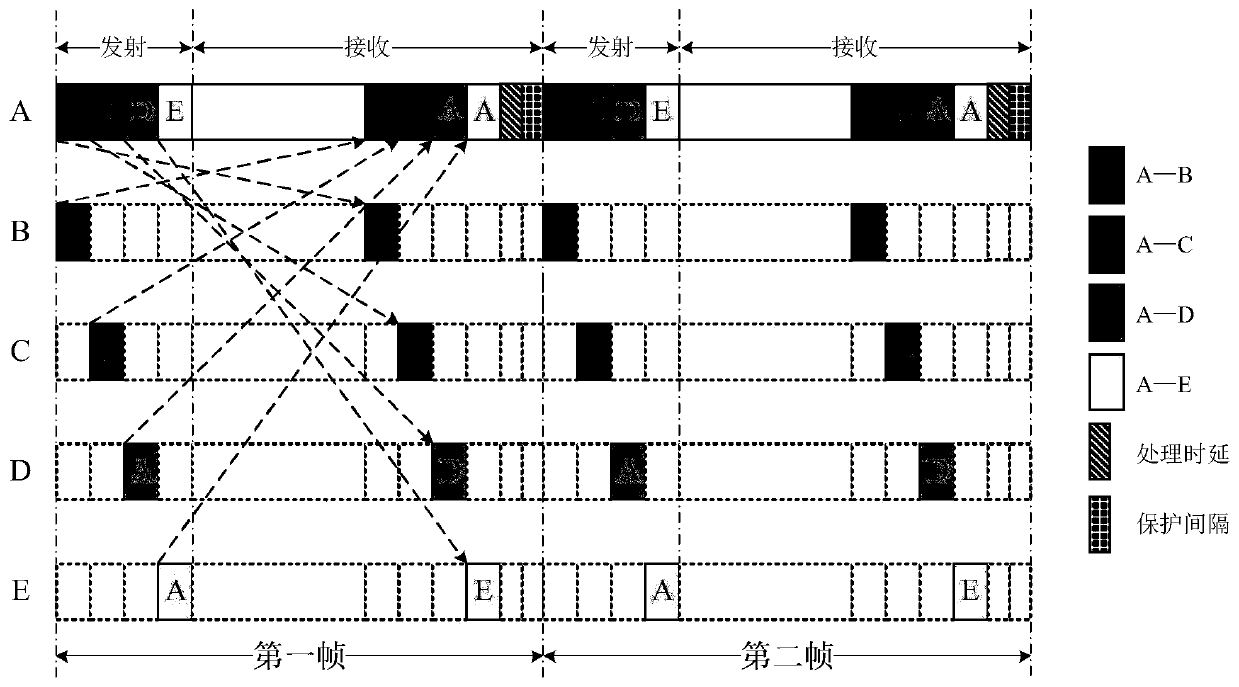
[0036] refer to Figure 4 . The sending time is longer than the propagation time delay, and the node antennas of the two communicating parties divide a time slot into two parts, the sending state and the receiving state, which are separated before and after and have the same length. Node A is in the sending state in the first half and in the receiving state in the second half; Node B is correspondingly in the receiving state in the first half, and in the sending state in the second half; the completion of node A’s transmission is delayed to node B’s reception after a propagation time delay, and node B’s transmission is delayed to node A’s reception after a propagation time delay.
[0037] refer to Figure 5 . In the satellite scenario, the propagation delay is relatively large. Generally, the sending time is shorter than the propagation delay. The node antennas of the two communication parties still divide a time slot into two parts, the sending state and the receiving state...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com